Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films with 80% Average Transmittance and 32 Ohms per Square Sheet Resistance: A Genuine Alternative to Commercial High-Performance Indium Tin Oxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Substrate Preparation
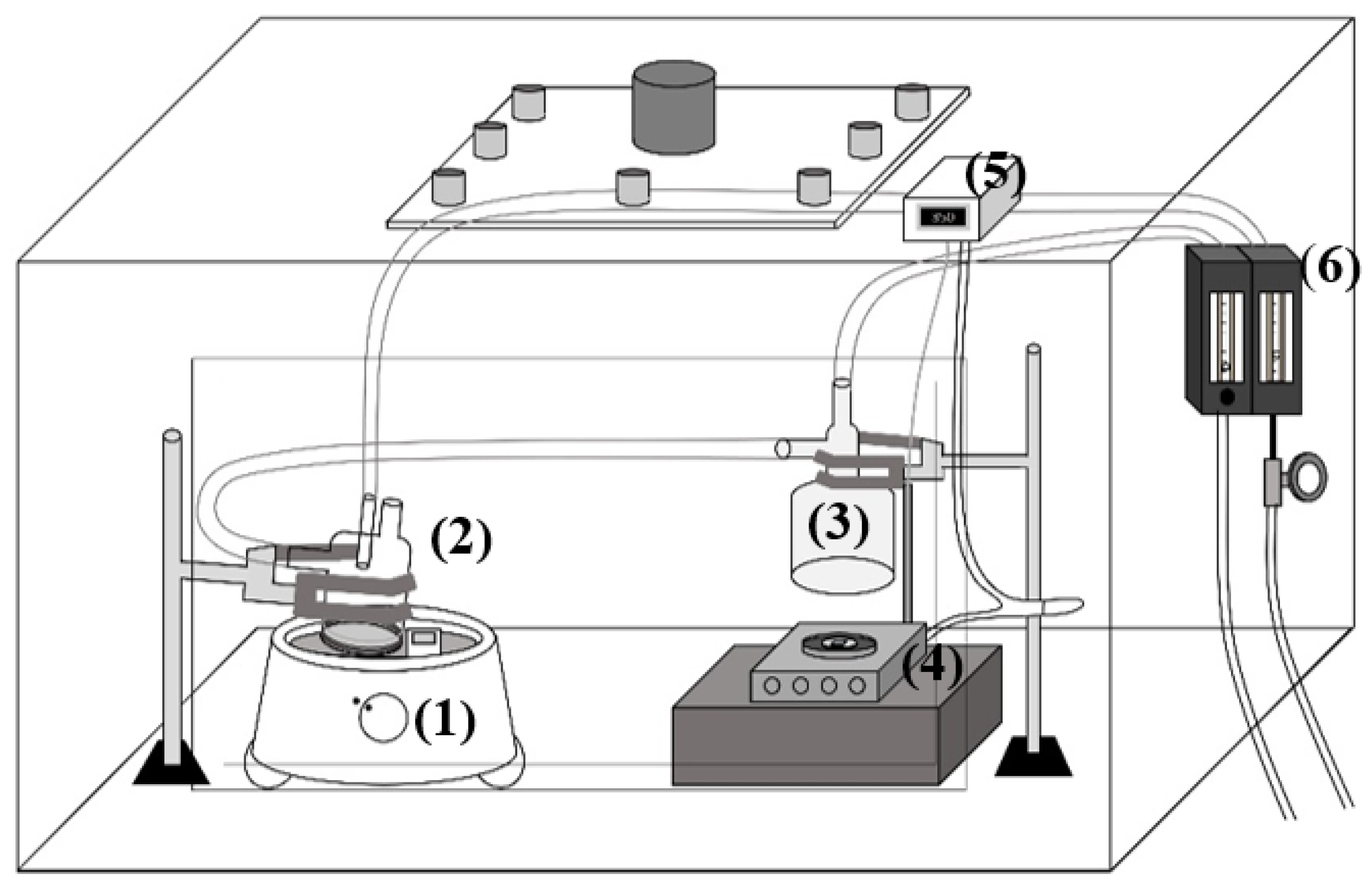
2.2. Spray Pyrolysis Deposition Process
2.3. Characterization Instruments
3. Results
3.1. Optical Characterization
3.2. Deposition Thicknesses
3.3. Electrical Characterization
3.4. Nanostructural Characterization
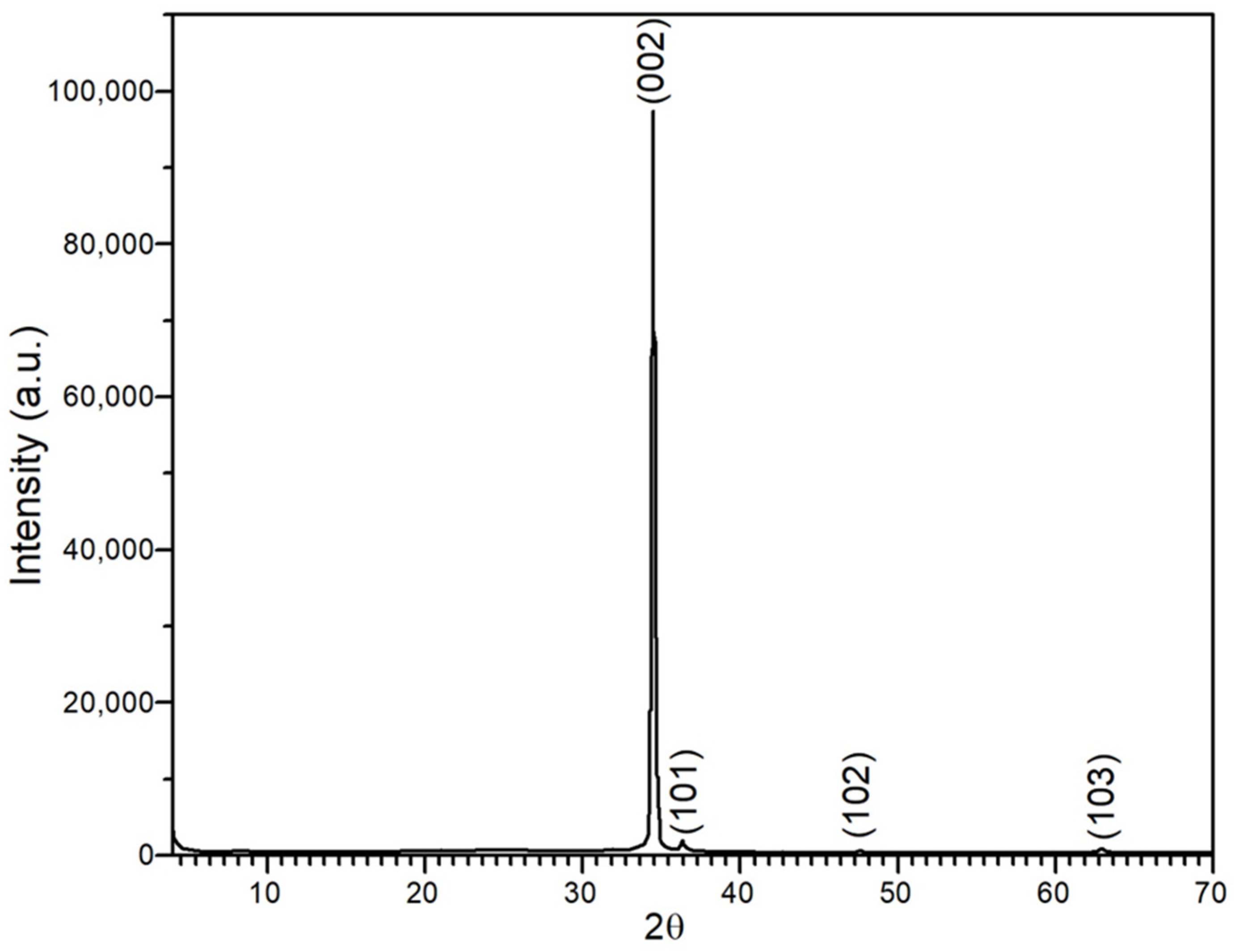
3.4.1. X-ray Diffraction Characterization
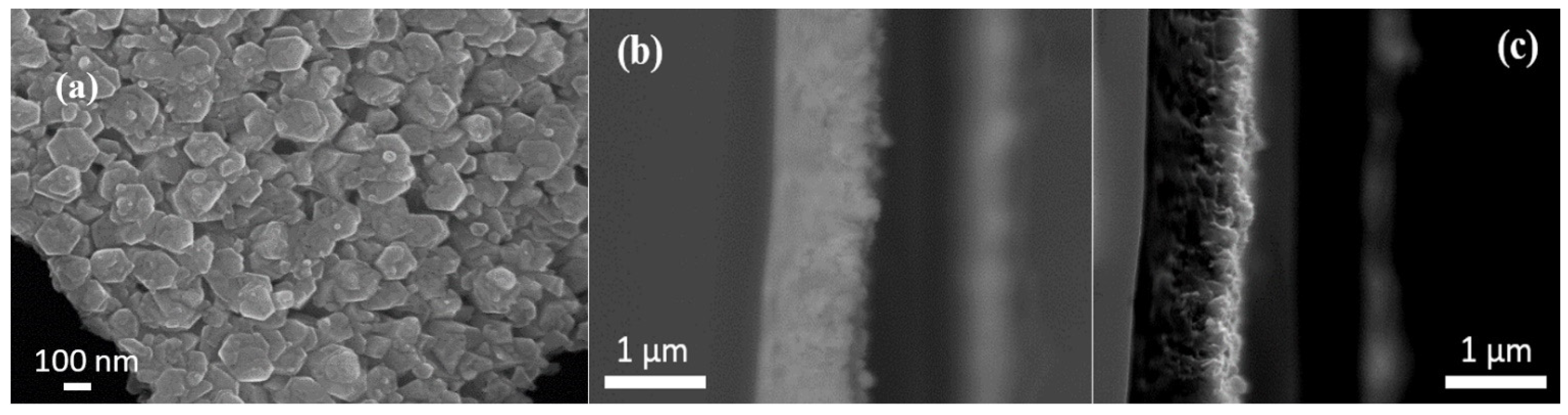
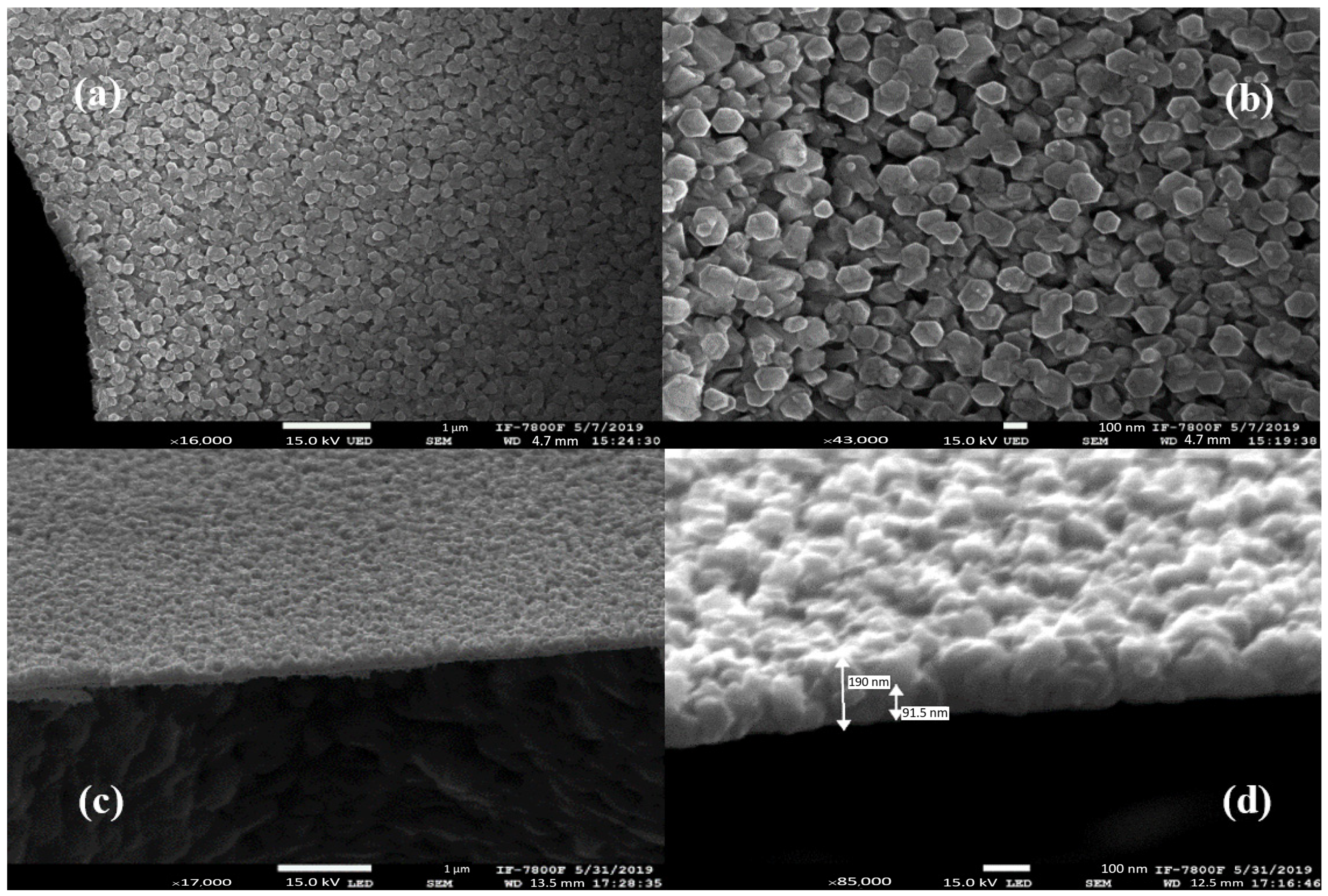
3.4.2. SEM Characterization
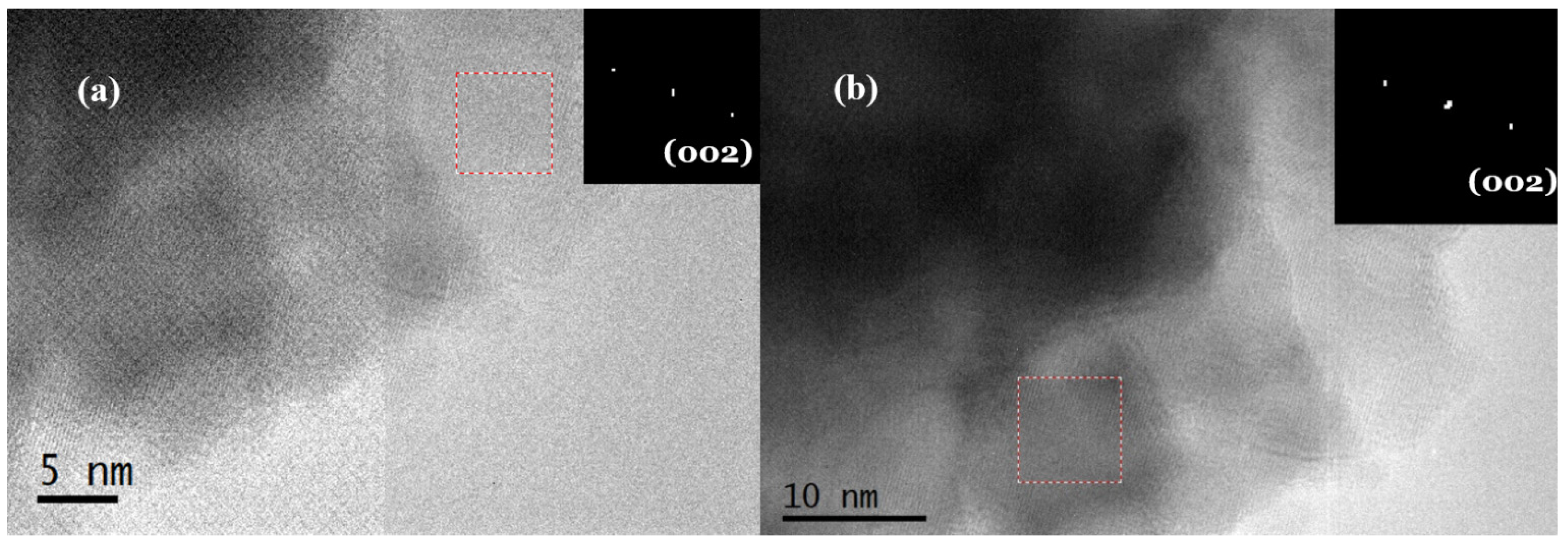
3.4.3. TEM Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguilar del Valle, M.d.P.; Garrido, L.F.; Alonso-Huitrón, J.C.; Terrones Pacheco, L.; Cruz-Manjarrez, H.; Reyes-Gasga, J.; Pérez-Martínez, A.L.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A. Design, growth, and characterization of crystalline copper oxide p-type transparent semiconductive thin films with figures of merit suitable for their incorporation into translucent devices. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nateq, M.H.; Ceccato, R. Enhanced sol–gel route to obtain a highly transparent and conductive aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin film. Materials 2019, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo-Cortez, K.; Islas, S.R.; Serrano-Lázaro, A.; Ortiz, A.; García-Sánchez, M.F.; Alonso, J.C.; Martínez, A.; Ramos, C.; Dutt, A.; Santana, G. A novel soft deposition methodology for textured ZnO:Al thin films as efficient transparent conductive oxide layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 9, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani Meymian, M.-R.; Mousavi, M.-A.; Rabbani, M.; Fallah, M. Effects of thallium–aluminum-codoped zinc oxide thin film as a new transparent conducting oxide. Phys. Stat. Solidi 2021, 218, 2000619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rosas, A.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Alonso-Huitrón, J. Enhanced electroluminescence from silicon quantum dots embedded in silicon nitride thin films coupled with gold nanoparticles in light emitting devices. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtaran, S. Al doped ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis technique: Influence of different annealing time. Opt. Mater. 2021, 114, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, G.; Kabiraj, D.; Basak, D. High conductivity along with high visible light transparency in Al implanted sol-gel ZnO thin film with an elevated figure of merit value as a transparent conducting layer. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Dong, J. Investigation on transparent, conductive ZnO:Al films deposited by atomic layer deposition process. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmedov, A.K.; Murliev, E.K.; Asvarov, A.S.; Muslimov, A.E.; Kanevsky, V.M. Transparent conductive indium zinc oxide films: Temperature and oxygen dependences of the electrical and optical properties. Coatings 2022, 12, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.-C.; Koo, H.-S.; Chen, D.-X.; Chen, C.-M. Fabricating high-conduction and high-transparency tungsten-doped zinc oxide films by pulse laser deposition technique. Crystals 2022, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, N.; Yang, P. Influence of annealing temperature on optical properties of sandwiched ZnO/Metal/ZnO transparent conductive thin films. Micromachines 2022, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdyb, A.; Krawczak, E.; Gułkowski, S. The influence of annealing on the properties of ZnO:Al layers obtained by RF magnetron sputtering. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2018, 26, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Gilmore, C.M.; Piqué, A.; Horwitz, J.S.; Mattoussi, H.; Murata, H.; Kafafi, Z.H.; Chrisey, D.B. Electrical, optical, and structural properties of indium–tin–oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 6451–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, W.; Yao, T.; Guan, M.; Gan, Z.; Chu, J.; Gai, L. Excellent properties of Ga-doped ZnO film as an alternative transparent electrode for thin-film solar cells. Int. J. Appl. Glas. Sci. 2022, 14, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, B.; Swami, S.K.; Dutta, V. Fabrication of highly conducting ZnO/Ag/ZnO and AZO/Ag/AZO transparent conducting oxide layers using RF magnetron sputtering at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 129, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.J.; Ramírez, E.B.; Juárez, B.; González, J.; García-León, J.M.; Escobar-Alarcón, L.; Alonso, J.C. Low temperature-pyrosol-deposition of aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films for transparent conducting contacts. Thin Solid Films 2016, 605, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouf, S.; Beniaiche, A.; Kardarian, K.; Mendes, M.J.; Sanchez-Sobrado, O.; Águas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Low-temperature spray-coating of high-performing ZnO:Al films for transparent electronics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolys. 2017, 127, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mallick, A.; Dou, B.; van Hest, M.F.A.M.; Garner, S.M.; Basak, D. A novel blanket annealing process to achieve highly transparent and conducting Al doped ZnO thin films: Its mechanism and application in perovskite solar cells. Sol. Energy 2018, 174, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koralli, P.; Fiat Varol, S.; Mousdis, G.; Mouzakis, D.E.; Merdan, Z.; Kompitsas, M. Comparative studies of undoped/Al-doped/In-doped ZnO transparent conducting oxide thin films in optoelectronic applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, D.R.; Lin, S.-Y.; Huang, J.-L. Improved properties of Al-doped ZnO film by electron beam evaporation technique. Microelectron. J. 2007, 38, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.M.; Abd El-Raheem, M.M.; Megahed, N.M.; Mohamed, H.A. Optimization of the optical and electrical properties of electron beam evaporated aluminum-doped zinc oxide films for opto-electronic applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizarro, M. High photocatalytic activity of ZnO and ZnO:Al nanostructured films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 97, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, R.; Maldonado, A.; Vega-Pérez, J.; Acosta, D.; De La Luz Olvera, M. Indium doped ainc oxide thin films deposited by ultrasonic chemical spray technique, starting from zinc acetylacetonate and indium chloride. Materials 2014, 7, 5038–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, T.; Aegerter, M. Optical, electrical and structural properties of sol gel ZnO:Al coatings. Thin Solid Films 1999, 351, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Al-Hartomy, O.A.; El Okr, M.; Nawar, A.M.; El-Gazzar, S.; El-Tantawy, F.; Yakuphanoglu, F. Semiconducting properties of Al doped ZnO thin films. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 131, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozati, S.M.; Akesteh, S. Characterization of ZnO:Al thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Charact. 2007, 58, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, D.; Nirmal Peiris, T. Overview on transparent conducting oxides and state of the art of low-cost doped ZnO systems. Sci. Forec. J. Mater. Chem. Engin. 2018, 1, 1004. Available online: https://scienceforecastoa.com/Articles/SJMCE-V1-E1-1004.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Aguilar-Del-Valle, M.d.P.; Cruz-Manjarrez, H.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A. Simple fabrication and characterization of an aluminum nanoparticle monolayer with well-defined plasmonic resonances in the far ultraviolet. Metals 2018, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Moreno-Rios, M.; García-García, R.; Pérez-Martínez, A.L.; Reyes-Gasga, J. Role of the substrate on the growth of silicon quantum dots embedded in silicon nitride thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 208, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Arenas, J.; Pérez-Martínez, A.L.; Alonso, J.C. Role of ammonia in depositing silicon nanoparticles by remote plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Mater. Lett. 2014, 125, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rosas, A.L.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.A.; Alonso-Huitrón, J.C. Photoluminescence enhancement from silicon quantum dots located in the vicinity of a monolayer of gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 92923–92931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiour, A.; Benhaya, A.; Bentrcia, T. Impact of deposition methods and doping on structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO-Al thin films. Optik 2019, 186, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manifacier, J.C.; Gasiot, J.; Fillard, J.P. A simple method for the determination of the optical constants n, k and the thickness of a weakly absorbing thin film. J. Phys. E 1976, 9, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Contreras, I.R.; Muñoz-Rosas, A.L.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A. Resolution improvement in Haacke’s figure of merit for transparent conductive films. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lin, S.; Huang, S.; Shrestha, S.; Conibeer, G. Can Tauc plot extrapolation be used for direct-band-gap semiconductor nanocrystals? J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgonos, A.; Mason, T.O.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Direct optical band gap measurement in polycrystalline semiconductors: A critical look at the Tauc method. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 240, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergen, Ö.B.; Arda, E. Determination of optical band gap energies of CS/MWCNT bio-nanocomposites by Tauc and ASF Methods. Synth. Met. 2020, 269, 116539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, A.R. Revisiting the optical bandgap of semiconductors and the proposal of a unified methodology to its determination. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacaksiz, E.; Aksu, S.; Yilmaz, S.; Parlak, M.; Altunbaş, M. Structural, optical and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO microrods prepared by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 4076–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Yuldashev, S.; Nguyen, H.D.; Jeon, H.C.; Kang, T.W. Fabrication of aluminium doped zinc oxide (AZO) transparent conductive oxide by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, S56–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Cameron, D.C. Optical and electrical properties of transparent conductive ITO thin films deposited by sol-gel process. Thin Solid Films 2000, 377–378, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamar, E.; Rami, M.; Messaoudi, C.; Sayah, D.; Ennaoui, A. Structural, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1999, 56, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snure, M.; Tiwari, A. Structural, electrical, and optical characterizations of epitaxial Zn1−xGaxO films grown on sapphire (0001) substrate. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 124912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna Reddy, K.T.; Miles, R.W. Growth and characterization of sprayed ZnO:Ga thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1998, 17, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.; Mao, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J. Fabrication of AZO and FAZO films using low-cost spin-coating method. Opt. Mater. 2022, 126, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, H.; Turkoglu, F.; Kurt, M.; Yaman, M.D.; Akca, F.G.; Aygun, G.; Ozyuzer, L. Improvement of optical and electrical properties of ITO thin films by electro-annealing. Vacuum 2015, 120, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, N.; Wibowo, A.; Kubicek, B.; Kautek, W.; Ligorio, G.; List-Kratochvil, E.; Dimopoulos, T. Rapid processing of In-doped ZnO by spray pyrolysis from environment-friendly precursor solutions. Coatings 2019, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova-Malinovska, D.; Tzenov, N.; Tzolov, M.; Vassilev, L. Optical and electrical properties of R.F. magnetron sputtered ZnO:Al thin films. Mater. Sci. Engin. B 1998, 52, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, G.S.; Xu, H.R.; Jiang, X.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yan, D.L.; Yuan, L.; Yu, A.B. Preparation of indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film with (400) preferred orientation by sol–gel spin coating method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8047–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, A.H.; Shah, M.A.; Asokan, K. Structural, optical and electrical properties of ITO thin Films. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, W.; Abou-Helal, M.; Barth, S.; Beil, D.; Höche, T.; Afify, H.; Demian, S. Transparent semiconducting ZnO:Al thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 1999, 2, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizarro, M.; Sánchez-Arzate, A.; Garduño-Wilches, I.; Alonso, J.C.; Ortiz, A. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO and ZnO:Al by spray pyrolysis with high photocatalytic properties. Catal. Today 2011, 166, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozati, S.M. Effect of film thickness on the physical properties of ZnO:Al thin films deposited using a spray pyrolysis technique. Can. J. Phys. 2008, 86, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
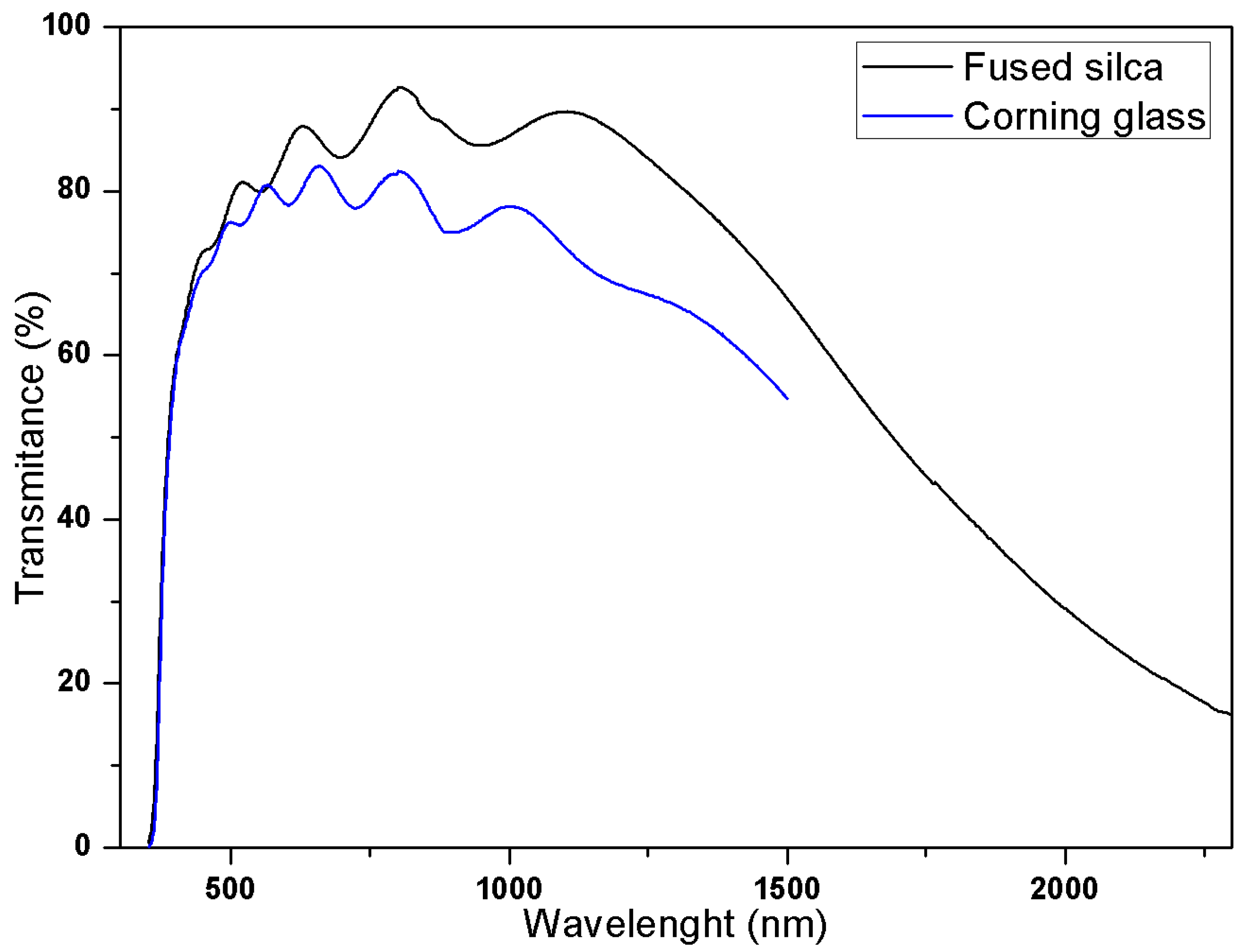
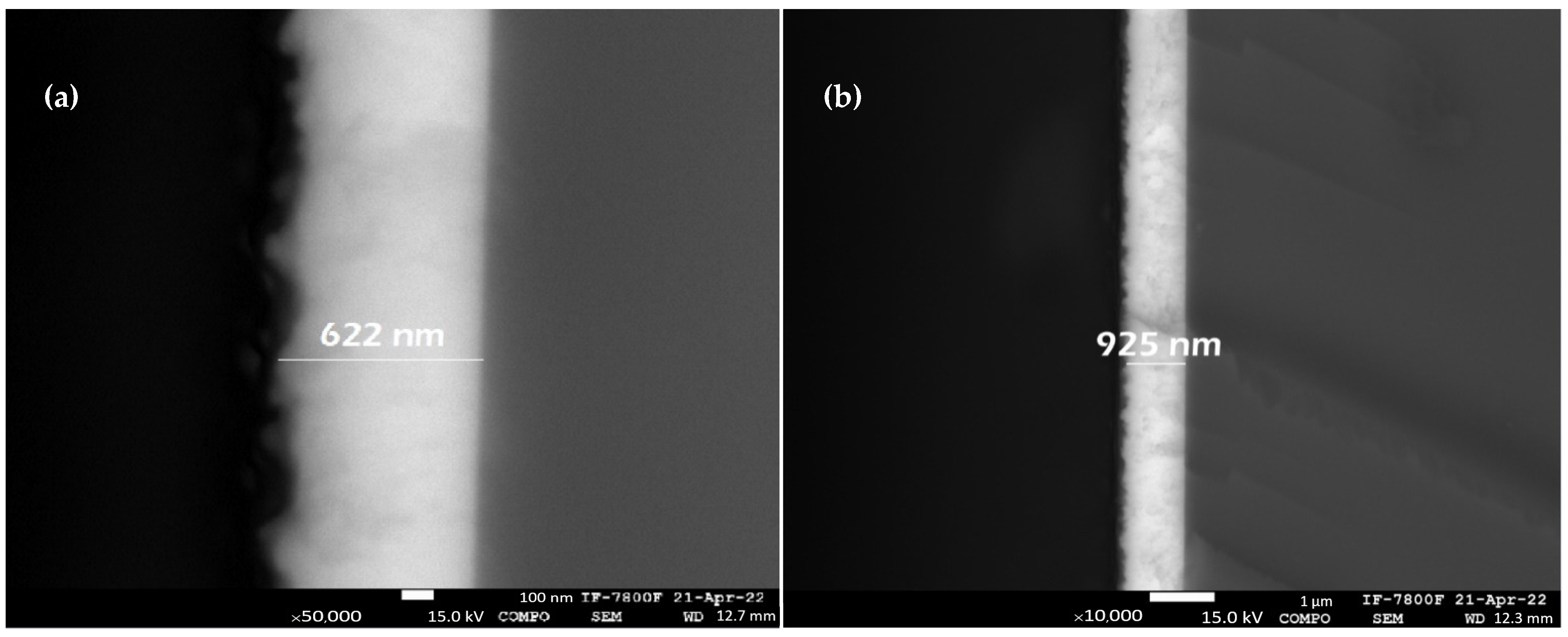

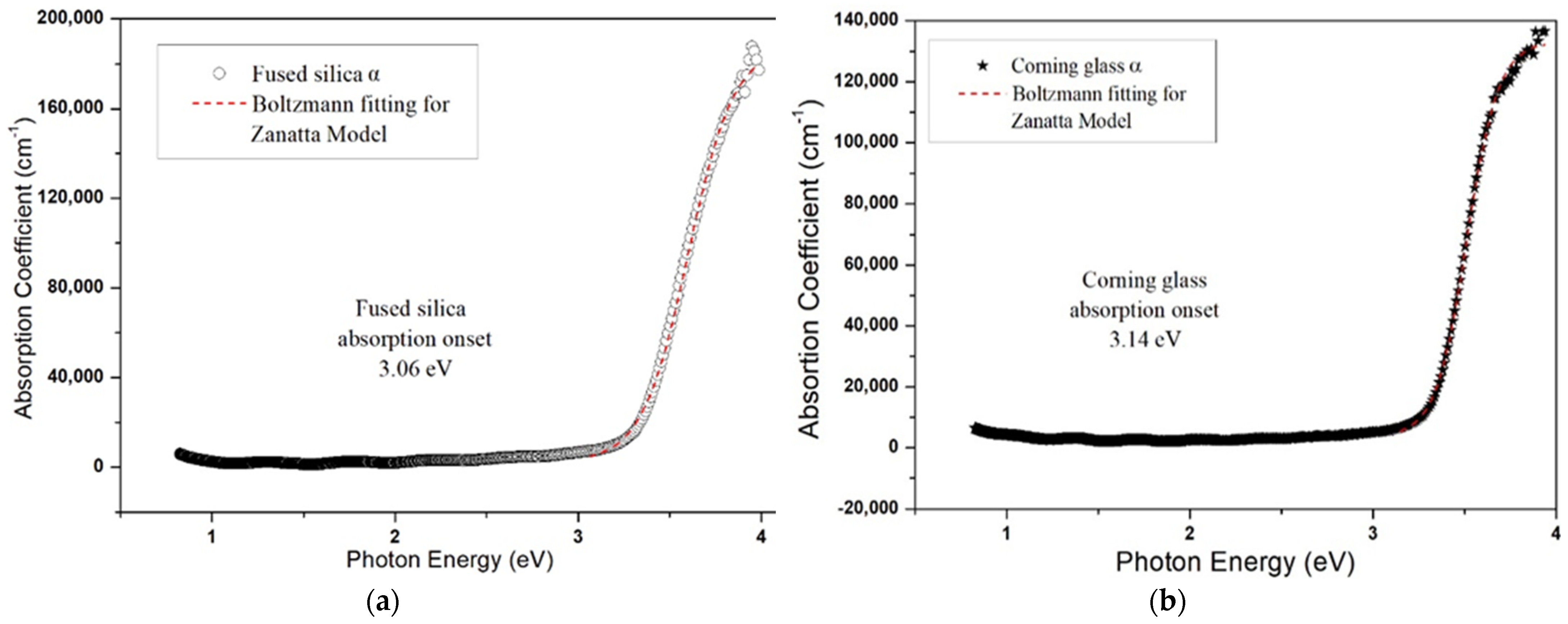
| Sample | Average Transmittance (%) | Sheet Resistance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | 75.7 | 19.0 | 56.4 | 59.2 | 65.4 |
| Fused Silica | 80.2 | 31.9 | 57.0 | 60.1 | 67.4 |
| Material | Deposition Technique | Sheet Resistance | Average Transmittance (%) | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO:Al-Tl | 1 at% of Tl to aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) | Sol-gel-spin coating | 1920 | 2.83 | 85 | 76.6 | 77.9 | 80.7 | [4] |
| ITO | - | Sol-gel | 250 | 1.50 | 80 | 76.8 | 77.3 | 78.4 | [41] |
| ZnO:Al | Annealed at 550 °C with Zn film | DC magnetron sputtering | 350 | 8.80 | 90 | 72.4 | 75.1 | 80.7 | [18] |
| ITO | - | Spray pyrolysis | 500 | 5.00 | 85 | 72.4 | 74.3 | 78.4 | [42] |
| ZnO:Ga | Prepared on float glass at 400 °C | Magnetron sputtering | 825 | 5.50 | 85 | 71.8 | 73.9 | 78.2 | [14] |
| Zn1−xGaxO | 1% of Ga | Pulsed laser deposition | 200 | 7.20 | 87 | 71.4 | 73.8 | 78.8 | [43] |
| ZnO:Ga | - | Magnetron sputtering | 300 | 7.33 | 85 | 69.6 | 72.0 | 76.9 | [44] |
| ZnO:Al/Ag/ZnO:Al | - | Magnetron sputtering | 70 | 5.30 | 80 | 67.7 | 69.6 | 73.6 | [15] |
| ZnO:Al | Prepared on float glass at 400 °C | Magnetron sputtering | 825 | 10.80 | 83 | 65.7 | 68.4 | 74.0 | [14] |
| ZnO/Ag/ZnO | - | Magnetron sputtering | 70 | 5.40 | 78 | 65.9 | 67.8 | 71.7 | [15] |
| ZnO:Al | - | Magnetron sputtering | 2210 | 24.00 | 88 | 64.0 | 67.5 | 75.1 | [12] |
| ZnO:Al | Films prepared at 450 °C | Spin-coating | 547 | 60.70 | 93 | 61.6 | 65.9 | 75.6 | [45] |
| ZnO:In | - | Radio frequency magnetron sputtering | 380 | 8.95 | 77 | 61.8 | 64.1 | 69.0 | [9] |
| ITO | - | Electro annealing | 256 | 15.00 | 79 | 60.3 | 63.0 | 69.0 | [46] |
| ZnO:In | - | Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis | 1800 | 21.20 | 80 | 58.9 | 62.0 | 68.7 | [47] |
| ZnO:Al | - | Magnetron sputtering | 400 | 45.00 | 85 | 58.1 | 61.9 | 70.3 | [48] |
| ZnO:Al-F | Films prepared at 450 °C | Spin-coating | 620 | 91.30 | 89 | 56.4 | 60.9 | 70.7 | [45] |
| ZnO:Al | Films prepared below 390 °C and without subsequent annealing | Low-cost, own-designed ultrasonic spray pyrolysis | 642 | 31.00 | 80 | 56.7 | 60.1 | 67.4 | This work |
| ZnO/Metal/ZnO | 50 nm ZnO/Ti/Cu/Ti/50 nm ZnO | Magnetron sputtering | 70 | 6.60 | 65 | 53.8 | 55.5 | 59.1 | [11] |
| ITO | - | Sol-gel-spin coating | 180 | 230.00 | 85 | 49.3 | 54.0 | 64.8 | [49] |
| ZnO:Al | - | Sol-gel-spin coating | 350 | 156.00 | 82 | 49.5 | 53.8 | 63.7 | [7] |
| ZnO/Metal/ZnO | 50 nm ZnO/Cu/50 nm ZnO | Magnetron sputtering | 60 | 10.10 | 60 | 47.6 | 49.5 | 53.4 | [11] |
| ZnO:W | 1.0 wt% tungsten | Pulsed laser deposition | 86 | 229.00 | 75 | 43.6 | 47.7 | 57.2 | [10] |
| ZnO:In | 450 °C and a ratio of [In]/[In+Zn] = 3.0 at% | Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis | 1000 | 34.20 | 60 | 42.1 | 44.7 | 50.3 | [23] |
| ITO | - | Thermal evaporation | 150 | 166.00 | 60 | 36.0 | 39.2 | 46.5 | [50] |
| ZnO:Al | FAr 5 sccm and 45 W | DC magnetron sputtering | 51 | 6.86 × 103 | 75 | 31.0 | 35.9 | 48.2 | [3] |
| ZnO:Al | Thin films containing 2 at% Al | Sol–gel | 106 | 3.84 × 104 | 79 | 27.5 | 32.8 | 46.7 | [2] |
| ZnO:Al | - | Sol-gel-spin coating | 244 | 2.35 × 106 | 85 | 19.6 | 25.0 | 40.8 | [19] |
| ZnO:Al | 3% | Atomic layer deposition | 18 | 5.56 × 105 | 75 | 20.0 | 24.9 | 38.7 | [8] |
| ZnO:In | - | Sol-gel-spin coating | 245 | 3.51 × 106 | 85 | 18.8 | 24.2 | 40.0 | [19] |
| ZnO:Al | 3 h annealing (400 °C) | Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis | 94 | 1.48 × 106 | 50 | 12.1 | 15.3 | 24.6 | [6] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cisneros-Contreras, I.R.; López-Ganem, G.; Sánchez-Dena, O.; Wong, Y.H.; Pérez-Martínez, A.L.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A. Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films with 80% Average Transmittance and 32 Ohms per Square Sheet Resistance: A Genuine Alternative to Commercial High-Performance Indium Tin Oxide. Physics 2023, 5, 45-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5010004
Cisneros-Contreras IR, López-Ganem G, Sánchez-Dena O, Wong YH, Pérez-Martínez AL, Rodríguez-Gómez A. Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films with 80% Average Transmittance and 32 Ohms per Square Sheet Resistance: A Genuine Alternative to Commercial High-Performance Indium Tin Oxide. Physics. 2023; 5(1):45-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleCisneros-Contreras, Ivan Ricardo, Geraldine López-Ganem, Oswaldo Sánchez-Dena, Yew Hoong Wong, Ana Laura Pérez-Martínez, and Arturo Rodríguez-Gómez. 2023. "Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films with 80% Average Transmittance and 32 Ohms per Square Sheet Resistance: A Genuine Alternative to Commercial High-Performance Indium Tin Oxide" Physics 5, no. 1: 45-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5010004
APA StyleCisneros-Contreras, I. R., López-Ganem, G., Sánchez-Dena, O., Wong, Y. H., Pérez-Martínez, A. L., & Rodríguez-Gómez, A. (2023). Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films with 80% Average Transmittance and 32 Ohms per Square Sheet Resistance: A Genuine Alternative to Commercial High-Performance Indium Tin Oxide. Physics, 5(1), 45-58. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5010004






