On the Non-Local Surface Plasmons’ Contribution to the Casimir Force between Graphene Sheets
Abstract
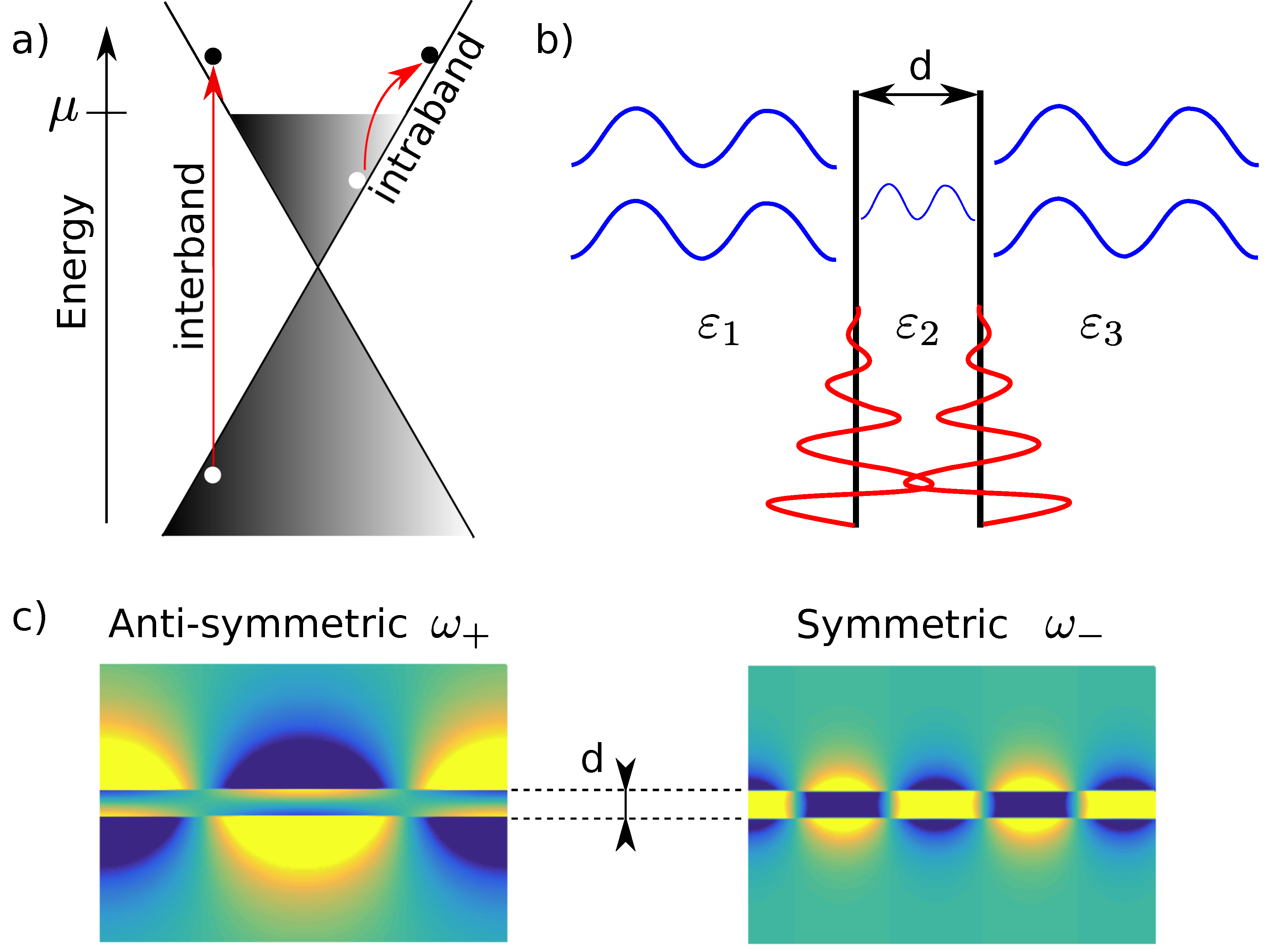
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework and Results
2.1. Graphene Response
2.2. Lifshitz Formalism
2.3. Intrinsic Graphene
3. Discussion
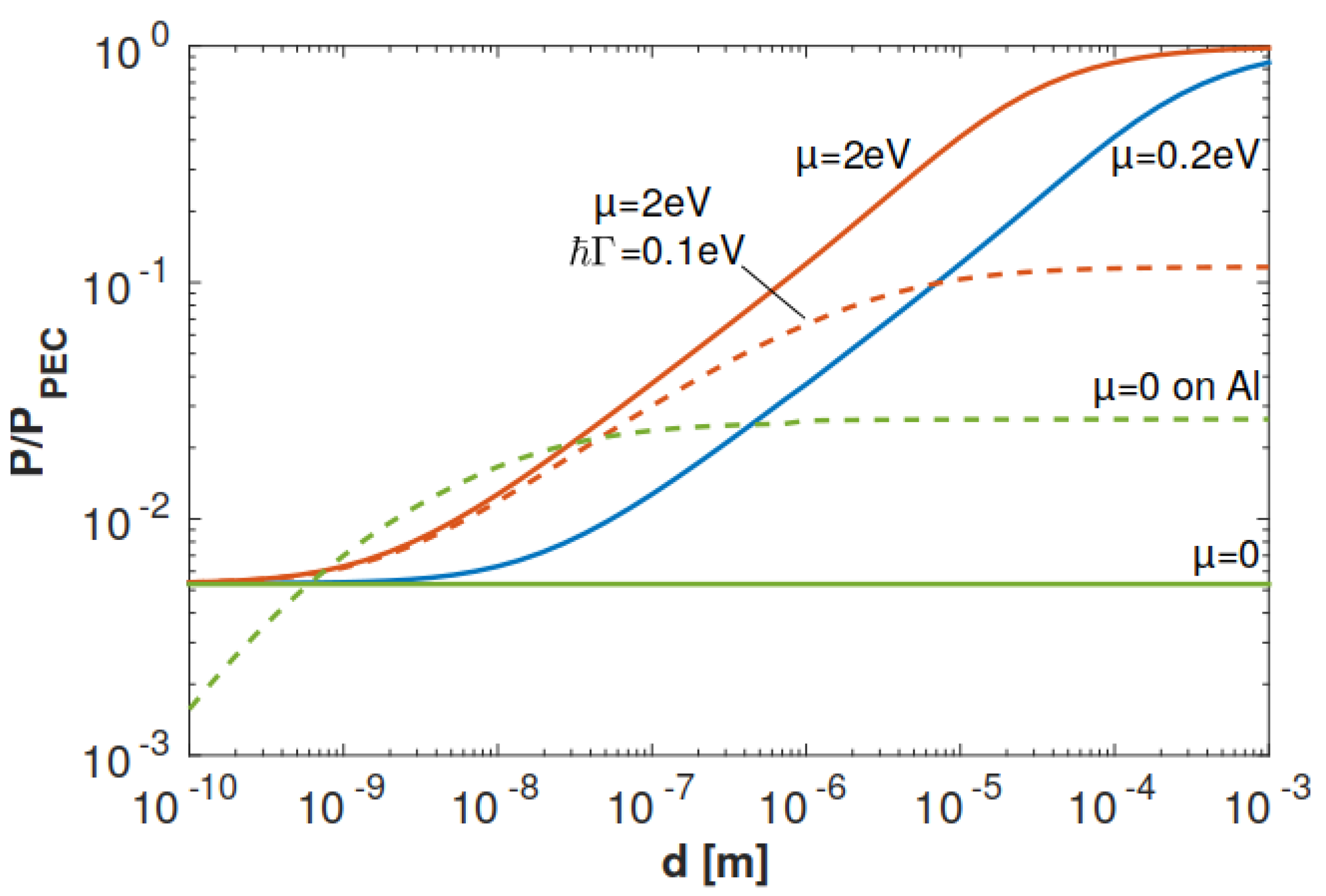
3.1. Effects of Doping and Loss
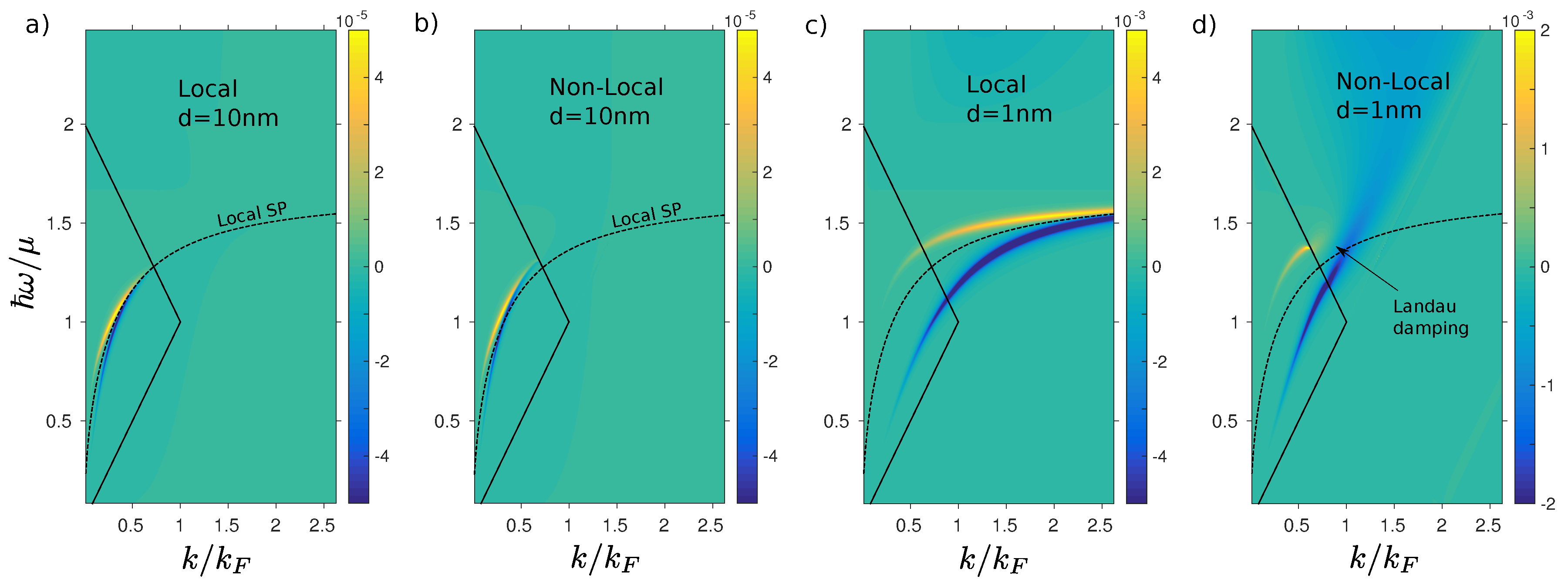
3.2. Non-Local Plasmons
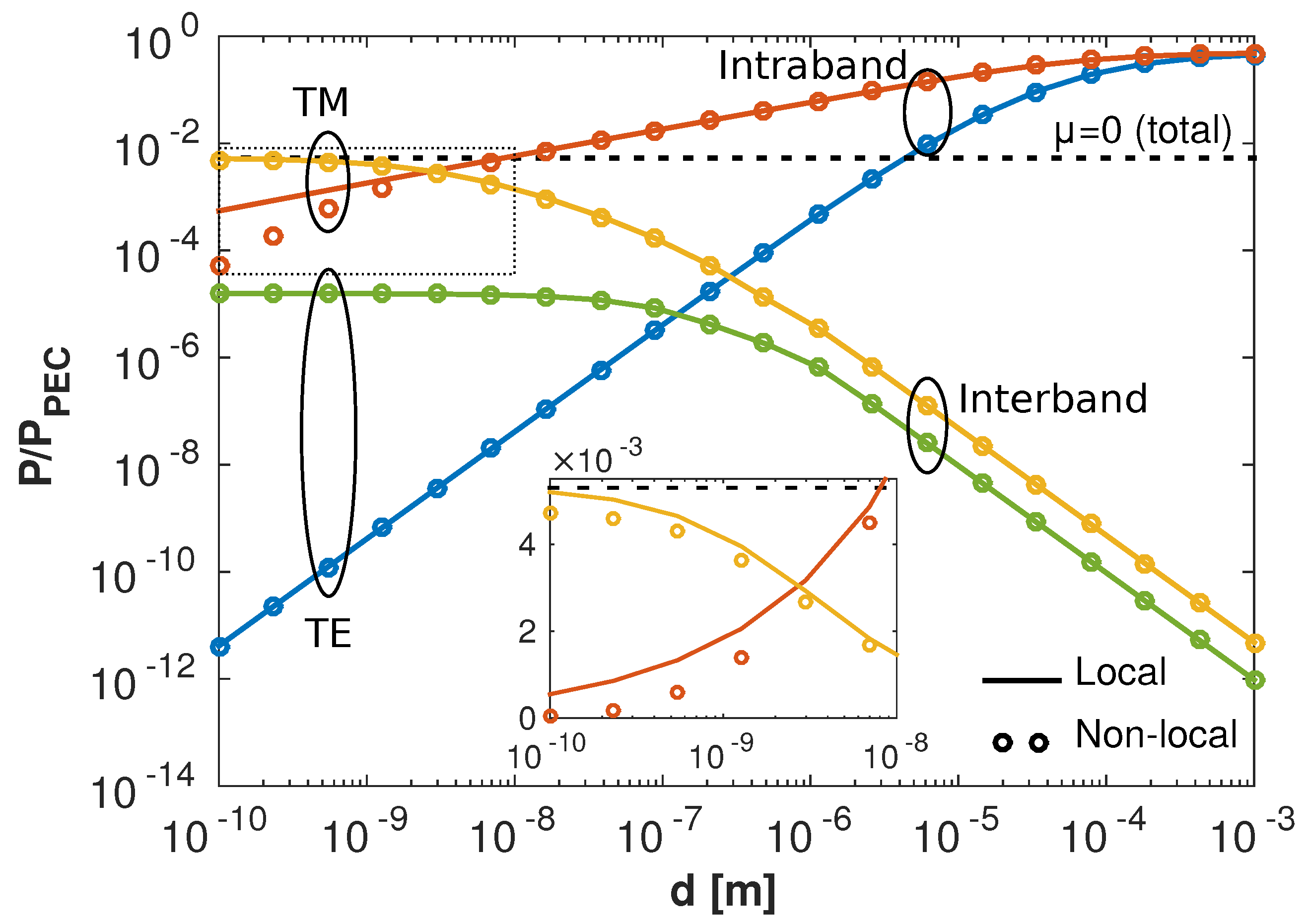
3.3. Contributions to the Forces
3.4. Dirac Cone Approximation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milonni, P.; Shih, M. Casimir forces. Contemp. Phys. 1992, 33, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoreaux, S. The Casimir force: Background, experiments, and applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 201–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, F.; Munday, J.N.; Iannuzzi, D.; Chan, H.B. Casimir forces and quantum electrodynamical torques: Physics and nanomechanics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2007, 13, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellieu, L.; Deparis, O.; Muller, J.; Sarrazin, M. Quantum Vacuum Photon Modes and Superhydrophobicity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 024501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardar, M.; Golestanian, R. The “friction” of vacuum, and other fluctuation-induced forces. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 71, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.; McCauley, A.P.; Rodriguez, A.W.; Reid, M.T.H.; Johnson, S.G. Casimir Repulsion between Metallic Objects in Vacuum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 090403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkel, C.; Joulain, K.; Mulet, J.P.; Greffet, J.J. Coupled surface polaritons and the Casimir force. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 69, 023808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozhenko, I.; Lambrecht, A. Repulsive Casimir forces and the role of surface modes. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 80, 042510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.W.; Capasso, F.; Johnson, S.G. The Casimir effect in microstructured geometries. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.W.; Hui, P.C.; Woolf, D.P.; Johnson, S.G.; Lončar, M.; Capasso, F. Classical and fluctuation- induced electromagnetic interactions in micron-scale systems: Designer bonding, antibonding, and Casimir forces. Ann. Phys. (Berl.) 2015, 527, 45–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, R.; Villarreal, C.; Mochán, W.L. Exact surface impedance formulation of the Casimir force: Application to spatially dispersive metals. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 68, 052103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, R.; Svetovoy, V.B. Correction to the Casimir force due to the anomalous skin effect. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 69, 062102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernelius, B.E. Effects of spatial dispersion on electromagnetic surface modes and on modes associated with a gap between two half spaces. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 235114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernelius, B.E. Retarded interactions in graphene systems. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 195427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, R.; Pendry, J.B. van der Waals interactions at the nanoscale: The effects of nonlocality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18422–18427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosdoff, D.; Phan, A.; Woods, L.; Bondarev, I.; Dobson, J. Effects of spatial dispersion on the Casimir force between graphene sheets. Eur. Phys. J. B 2012, 85, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-González, P.; Nikitin, A.Y.; Golmar, F.; Centeno, A.; Pesquera, A.; Vélez, S.; Chen, J.; Navickaite, G.; Koppens, F.; Zurutuza, A.; et al. Controlling graphene plasmons with resonant metal antennas and spatial conductivity patterns. Science 2014, 344, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescato, Y.; Giannini, V.; Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Maier, S.A. Graphene Sandwiches as a Platform for Broadband Molecular Spectroscopy. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, A.M.A.; Francescato, Y.; Roschuk, T.; Shautsova, V.; Chen, Y.; Sidiropoulos, T.T.P.H.; Hong, M.; Giannini, V.; Maier, S.A.S.; Cohen, L.L.F.; et al. Plasmon-induced optical anisotropy in hybrid graphene-metal nanoparticle systems. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Xiao, X.; Caldwell, J.D.J.; Zhang, C.; Maier, S.A.S.; Li, X.; Giannini, V. Graphene Plasmon Cavities Made with Silicon Carbide. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3640–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundeberg, M.B.; Gao, Y.; Asgari, R.; Tan, C.; Van Duppen, B.; Autore, M.; Alonso-González, P.; Woessner, A.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Tuning quantum nonlocal effects in graphene plasmonics. Science 2017, 357, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Caldwell, J.D.J.; Maier, S.A.S.; Giannini, V. Theoretical analysis of graphene plasmon cavities. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiffi, E.; Pendry, J.; Arroyo-Huidobro, P. Singular graphene metasurfaces. EPJ Appl. Metamater. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppens, F.H.L.; Chang, D.E.; García de Abajo, F.J. Graphene Plasmonics: A Platform for Strong Light-Matter Interactions. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3370–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Girit, C.; Zettl, A.; Crommie, M.; Shen, Y.R. Gate-variable optical transitions in graphene. Science 2008, 320, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyatkovskiy, P.K. Dynamical polarization, screening, and plasmons in gapped graphene. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 025506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermin, N.D. Lindhard Dielectric Function in the Relaxation-Time Approximation. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 1, 2362–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, E.M. The theory of molecular attractive forces between solids. Sov. Phys. JETP 1956, 2, 73–83. Available online: http://www.jetp.ac.ru/cgi-bin/e/index/e/2/1/p73?a=list; Reprinted in Perspectives in Theoretical Physics: The Collected Papers of E.M. Lifshitz; Pitaevskii, L.P., Ed.; Pergamon Press Plc: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 329–350. [CrossRef]
- Dzyaloshinskii, I.E.; Lifshitz, E.M.; Pitaevskii, L.P. Van der Waals forces in liquid films. Sov. Phys. JETP 1960, 10, 161–170. Available online: http://www.jetp.ac.ru/cgi-bin/e/index/e/10/1/p161?a=list; Reprinted in Perspectives in Theoretical Physics: The Collected Papers of E.M. Lifshitz; Pitaevskii, L.P., Ed.; Pergamon Press Plc: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 425–442. [CrossRef]
- Dzyaloshinskii, I.E.; Lifshitz, E.M.; Pitaevskii, L.P. General Theory of Van der Waals’ Forces. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1961, 4, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchitskaya, G.L.; Mohideen, U.; Mostepanenko, V.M. The Casimir force between real materials: Experiment and theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1827–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosdoff, D.; Woods, L.M. Casimir forces and graphene sheets. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 155459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchitskaya, G.L.; Mostepanenko, V.M.; Sernelius, B.E. Two approaches for describing the Casimir interaction in graphene: Density-density correlation function versus polarization tensor. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 125407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Neto, A.H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.R.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernelius, B.E. Casimir interactions in graphene systems. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 95, 57003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mak, K.F.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T.F. Seeing Many-Body Effects in Single- and Few-Layer Graphene: Observation of Two-Dimensional Saddle-Point Excitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 046401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intravaia, F.; Lambrecht, A. Surface Plasmon Modes and the Casimir Energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 110404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, V.; Zhang, Y.; Forcales, M.; Rivas, J.G. Long-range surface polaritons in ultra-thin films of silicon. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 19674–19685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, T.; Schliemann, J.; Peres, N.M.R. Dynamical polarizability of graphene beyond the Dirac cone approximation. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 085409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francescato, Y.; Pocock, S.R.; Giannini, V. On the Non-Local Surface Plasmons’ Contribution to the Casimir Force between Graphene Sheets. Physics 2020, 2, 22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2010003
Francescato Y, Pocock SR, Giannini V. On the Non-Local Surface Plasmons’ Contribution to the Casimir Force between Graphene Sheets. Physics. 2020; 2(1):22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancescato, Yan, Simon R. Pocock, and Vincenzo Giannini. 2020. "On the Non-Local Surface Plasmons’ Contribution to the Casimir Force between Graphene Sheets" Physics 2, no. 1: 22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2010003
APA StyleFrancescato, Y., Pocock, S. R., & Giannini, V. (2020). On the Non-Local Surface Plasmons’ Contribution to the Casimir Force between Graphene Sheets. Physics, 2(1), 22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics2010003





