Steganalysis of Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech with Unknown Embedding Rates Using Multi-Scale Transformer and Multi-Task Learning Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Integrating multi-task learning: Differing from the existing methods [24,25], our method utilizes the multi-task learning mechanism to enhance the detection performance by combining classification and regression, where classification distinguishes between cover and steganographic samples, and regression estimates the embedding rate. This joint learning framework improves feature extraction by capturing both discrete and continuous variations in embedding rates, enabling the model to learn more informative representations. The regression task provides additional supervision, reinforcing the classification process and improving the model’s ability to detect steganographic samples with varying embedding rates.
- Proposing a multi-scale transformer framework: Unlike the existing steganalysis methods [24,25] that focus on the handcrafted features, our method proposes the multi-scale transformer-based framework, which can capture hierarchical dependencies within speech frames while preserving both local and global contextual information.
2. Related Work
3. Problem Statement
4. Proposed Method
4.1. Input Module
4.2. Codeword Embedding Module
4.3. Multi-Scale Transformer Module
4.3.1. Subframe-Level Transformer
4.3.2. Pairwise Subframe-Level Transformer
4.3.3. Frame-Level Transformer
4.4. Multi-Task Learning Mechanism
4.4.1. Classification Task
4.4.2. Regression Task
4.4.3. Joint Loss Function
5. Experimental Result and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Setup and Metrics
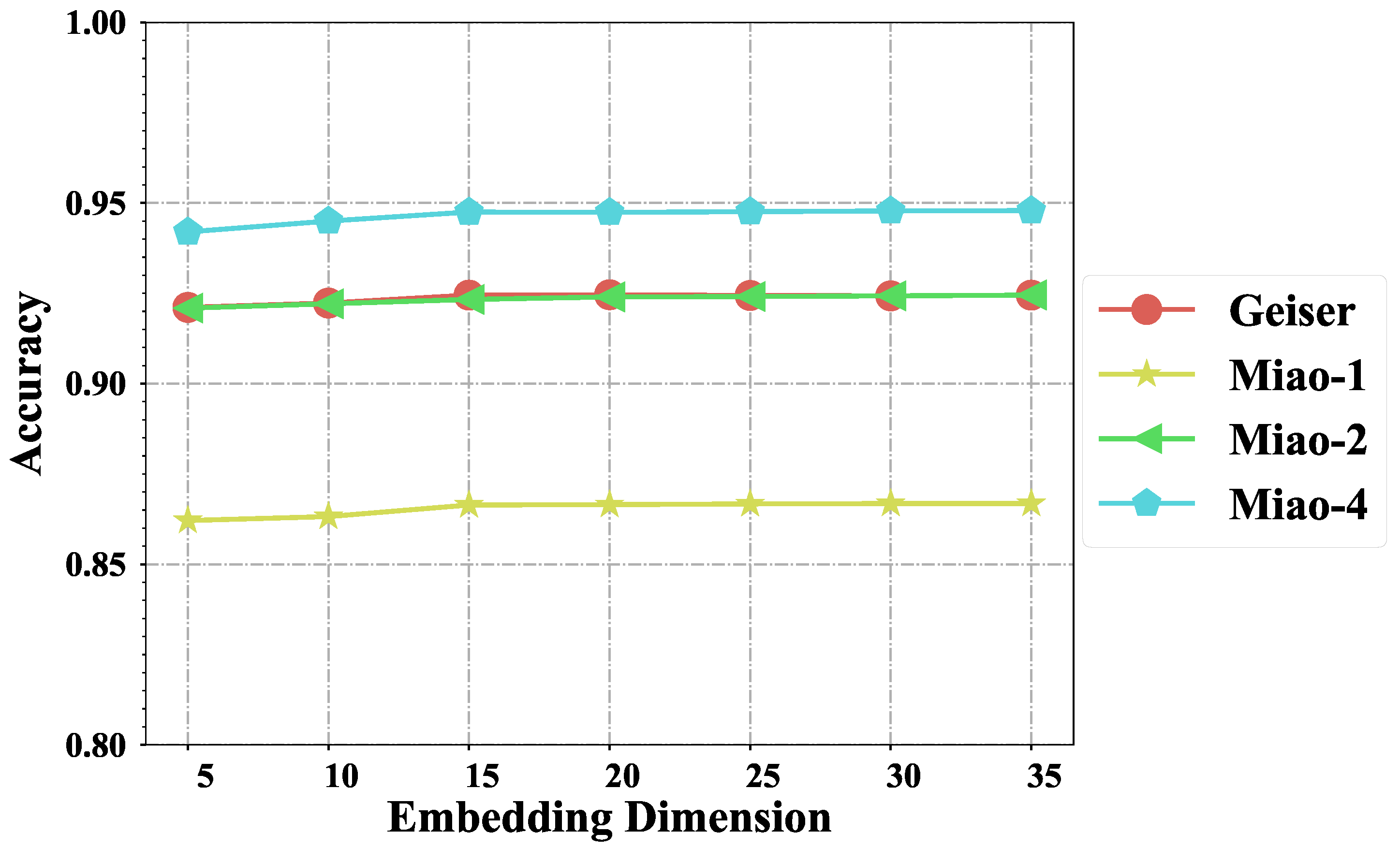
5.2. Effect of Embedding Dimension
5.3. Influence of the Transformer Layer
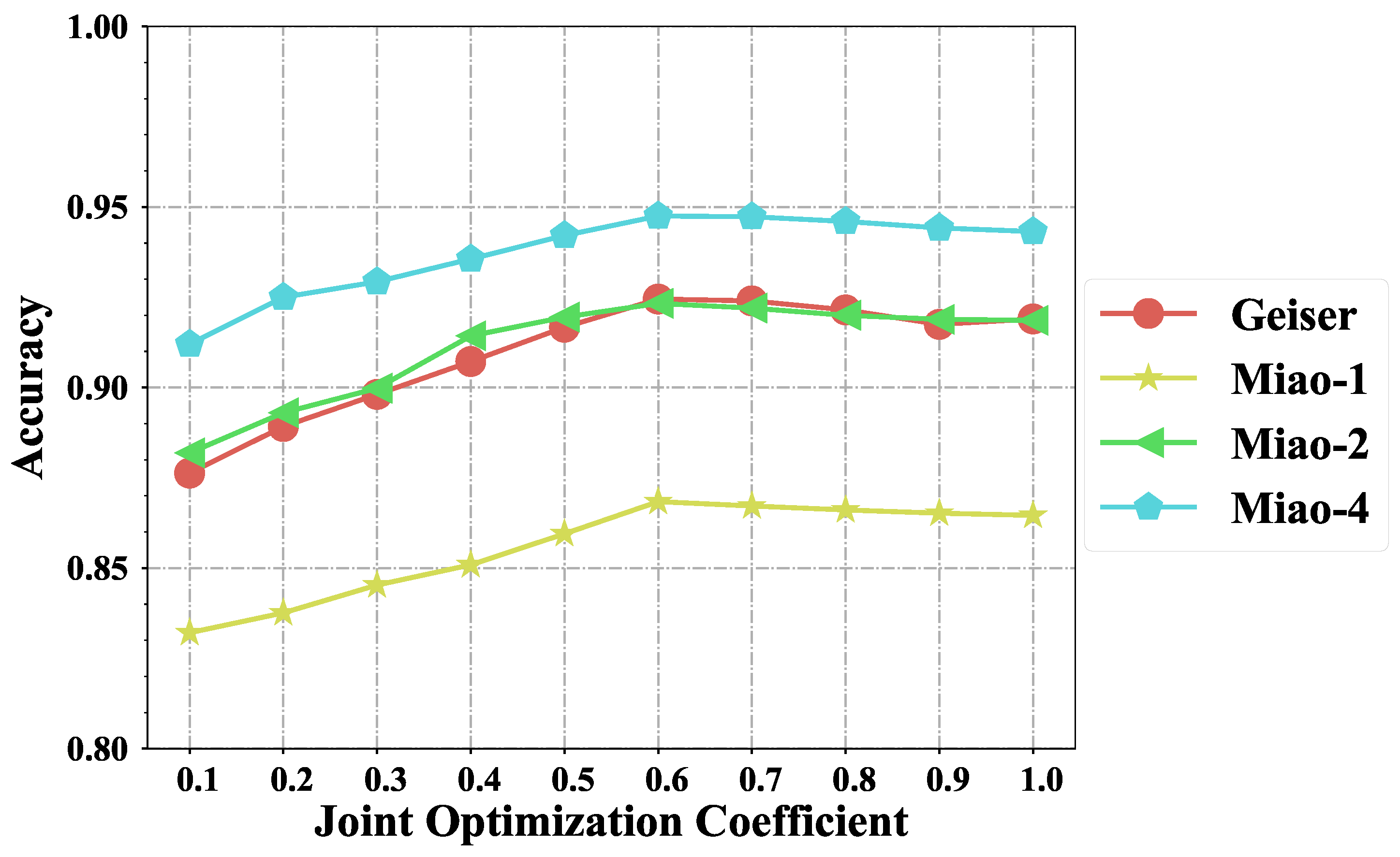
5.4. Effect of Joint Optimization Coefficient
5.5. Analysis of the Regression Task
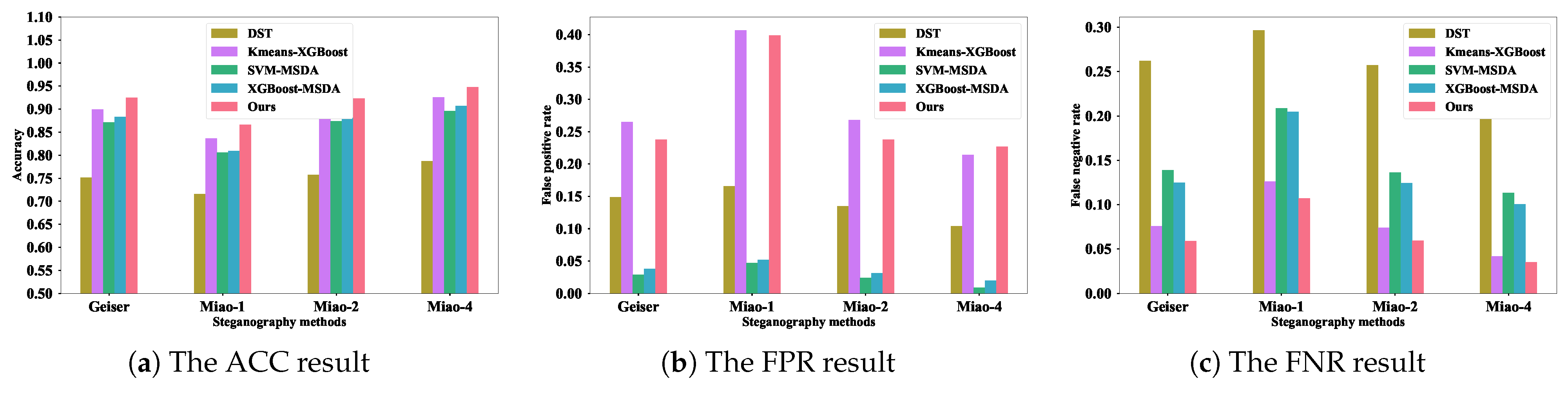
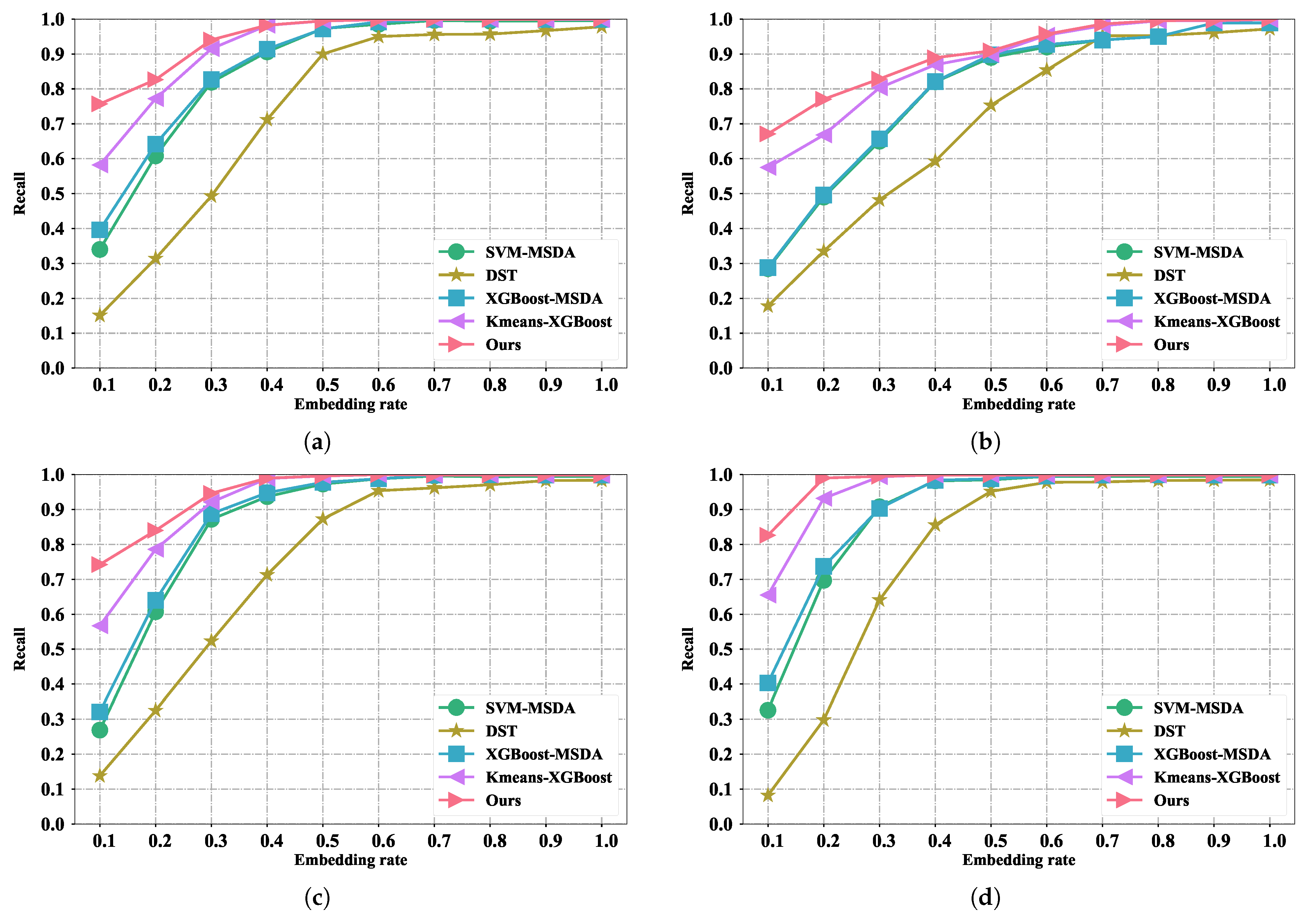
5.6. Performance Comparison with the Existing Methods
5.7. Ablation Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, X.; Tan, Y.; Qin, J.; Tan, Y. Advancements and challenges in coverless image steganography: A survey. Signal Process. 2024, 228, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiadi, D.R.I.M.; Ghosal, S.K.; Sahu, A.K. AI-Powered Steganography: Advances in Image, Linguistic, and 3D Mesh Data Hiding—A Survey. J. Future Artif. Intell. Technol. 2025, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, M.; Shao, T.; Rose, K.; Yin, P.; Mccarthy, S. StegaNeRV: Video Steganography using Implicit Neural Representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 888–898. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Qin, J.; Xiang, X.; Tan, Y. Robust coverless video steganography based on pose estimation and object tracking. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 87, 103912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wen, J.; Peng, W. Generative text steganography with large language model. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 10345–10353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wei, P.; Fu, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, W. Imperceptible Text Steganography based on Group Chat. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Niagra Falls, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Ni, J.; Hu, X.; Li, B. Efficient Audio Steganography Using Generalized Audio Intrinsic Energy With Micro-Amplitude Modification Suppression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 6559–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, P.; Yan, D.; Ying, K.; Wang, R.; Dong, L. Audio steganography cover enhancement via reinforcement learning. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheddar, H.; Hemis, M.; Himeur, Y.; Megías, D.; Amira, A. Deep learning for steganalysis of diverse data types: A review of methods, taxonomy, challenges and future directions. Neurocomputing 2024, 581, 127528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Sun, S.; Weng, S.; Yu, L.; He, J. A two-stream-network based steganalysis network: TSNet. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samukic, A. UMTS/IMT-2000 Standardisation: 3 GPP Third Generation Partnership Project: Development of Standards for the New Millennium. In Wireless Multimedia Network Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 75–93. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, S.; Bai, S. Steganography integration into a low-bit rate speech codec. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Tang, G.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Z.; Shen, L. A triple-layer steganography scheme for low bit-rate speech streams. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2015, 74, 11763–11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Steganography in vector quantization process of linear predictive coding for low-bit-rate speech codec. Multimed. Syst. 2017, 23, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Steganography integrated into linear predictive coding for low bit-rate speech codec. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 2837–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tao, H.; Xiao, B.; Chang, C. Steganography in low bit-rate speech streams based on quantization index modulation controlled by keys. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, B.; Vary, P. High rate data hiding in ACELP speech codecs. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 4005–4008. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Al-Hawbani, A. A new scheme for covert communication via 3G encoded speech. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2012, 38, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Huang, L.; Shen, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, Z. Steganalysis of compressed speech based on Markov and entropy. In Proceedings of the Digital-Forensics and Watermarking: 12th International Workshop, IWDW 2013, Auckland, New Zealand, 1–4 October 2013; Revised Selected Papers 12. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Cai, T.; Tang, M.; Wang, L. AMR steganalysis based on the probability of same pulse position. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Wu, Y.; Chang, C.C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J. Steganalysis of adaptive multi-rate speech using statistical characteristics of pulse pairs. Signal Process. 2017, 134, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, Y. Steganalysis of AMR speech based on multiple classifiers combination. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 140957–140968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tian, H.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, C.C. Steganalysis of adaptive multi-rate speech based on extreme gradient boosting. Electronics 2020, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y. Detecting steganography of adaptive multirate speech with unknown embedding rate. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2017, 2017, 5418978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tian, H.; Mazurczyk, W.; Chang, C.C.; Quan, H.; Chen, Y. Steganalysis of adaptive multi-rate speech with unknown embedding rates using clustering and ensemble learning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 111, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. An overview of multi-task learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. A survey on multi-task learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 34, 5586–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nie, F.; Huang, H.; Risacher, S.; Ding, C.; Saykin, A.J.; Shen, L. Sparse multi-task regression and feature selection to identify brain imaging predictors for memory performance. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Xiao, A.; Wu, E.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Transformer in transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 15908–15919. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Video swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3202–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Huang, Y.; Tang, S. An approach to information hiding in low bit-rate speech stream. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM 2008—2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.; Liu, K.; He, S.; Zhao, J. How to generate a good word embedding. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Shen, Y. On the dimensionality of word embedding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 895–906. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. RNN-SM: Fast steganalysis of VoIP streams using recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1854–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Hyper-Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| The embedding dimension | 20 |
| The number of attention heads in the transformer layer | 5 |
| The number of transformer layers | 2 |
| The dropout rate in the transformer layer | 0.2 |
| Hidden size in transformer | 20 |
| Dropout rate | 0.3 |
| Steganography Method | Average MSE Value |
|---|---|
| Geiser’s method [17] | 0.0206 |
| Miao’s () method [18] | 0.0341 |
| Miao’s () method [18] | 0.0224 |
| Miao’s () method [18] | 0.0101 |
| Index | Network Description | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | without the subframe-level transformer | 0.9201 |
| #2 | without the pairwise subframe-level transformer | 0.9186 |
| #3 | without the frame-level transformer | 0.9172 |
| #4 | without the regression task | 0.9190 |
| #5 | the whole proposed method | 0.9245 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Abdullah, A.; Samian, N.; Roslan, N.A. Steganalysis of Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech with Unknown Embedding Rates Using Multi-Scale Transformer and Multi-Task Learning Mechanism. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2025, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp5020029
Sun C, Abdullah A, Samian N, Roslan NA. Steganalysis of Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech with Unknown Embedding Rates Using Multi-Scale Transformer and Multi-Task Learning Mechanism. Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy. 2025; 5(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp5020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Congcong, Azizol Abdullah, Normalia Samian, and Nuur Alifah Roslan. 2025. "Steganalysis of Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech with Unknown Embedding Rates Using Multi-Scale Transformer and Multi-Task Learning Mechanism" Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy 5, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp5020029
APA StyleSun, C., Abdullah, A., Samian, N., & Roslan, N. A. (2025). Steganalysis of Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech with Unknown Embedding Rates Using Multi-Scale Transformer and Multi-Task Learning Mechanism. Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy, 5(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp5020029







