A Preliminary Hazard Assessment of Kolumbo Volcano (Santorini, Greece)
Abstract
1. Introduction
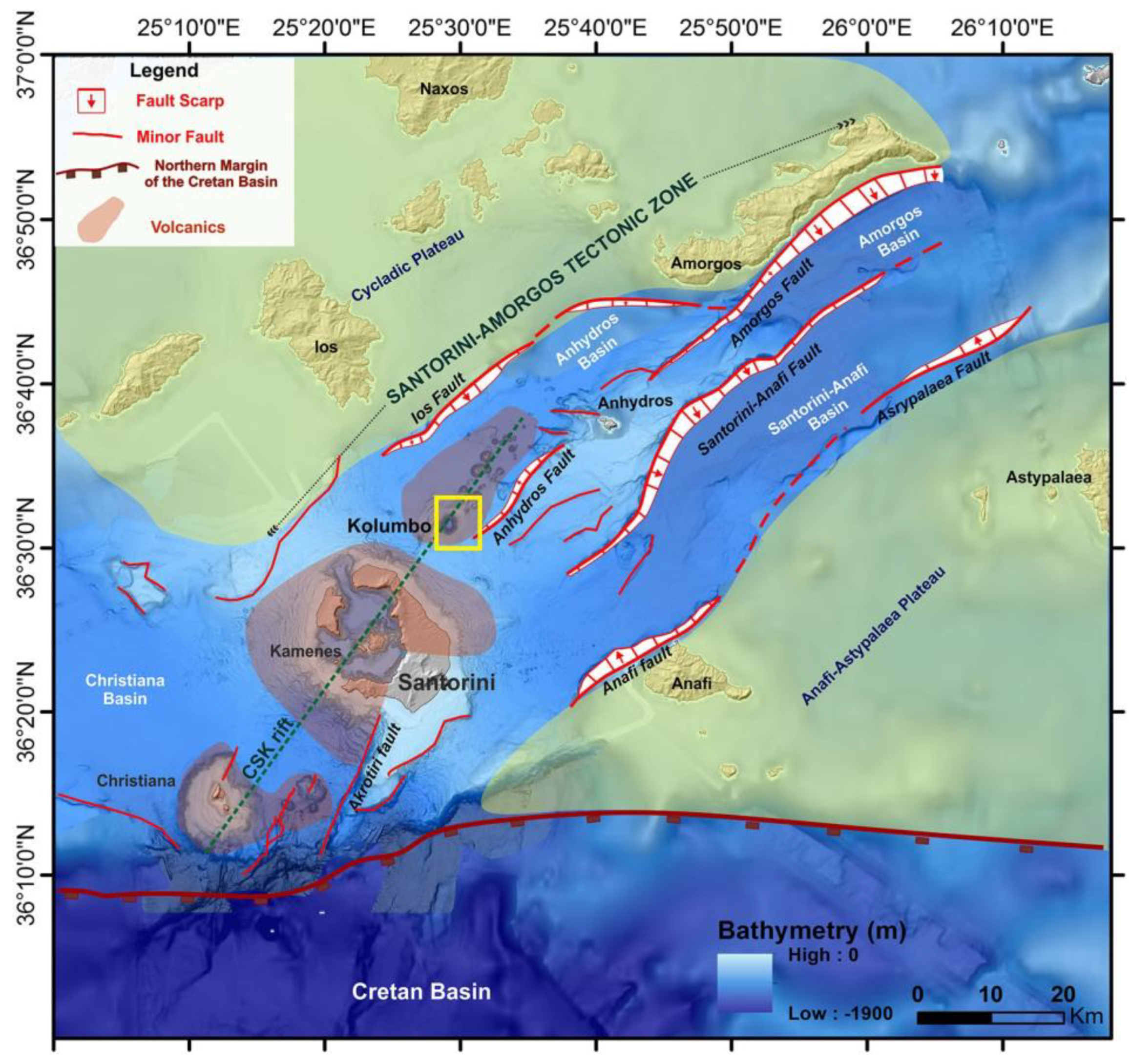
1.1. Geological Setting
1.2. The 1650 CE Eruption
2. Materials and Methods
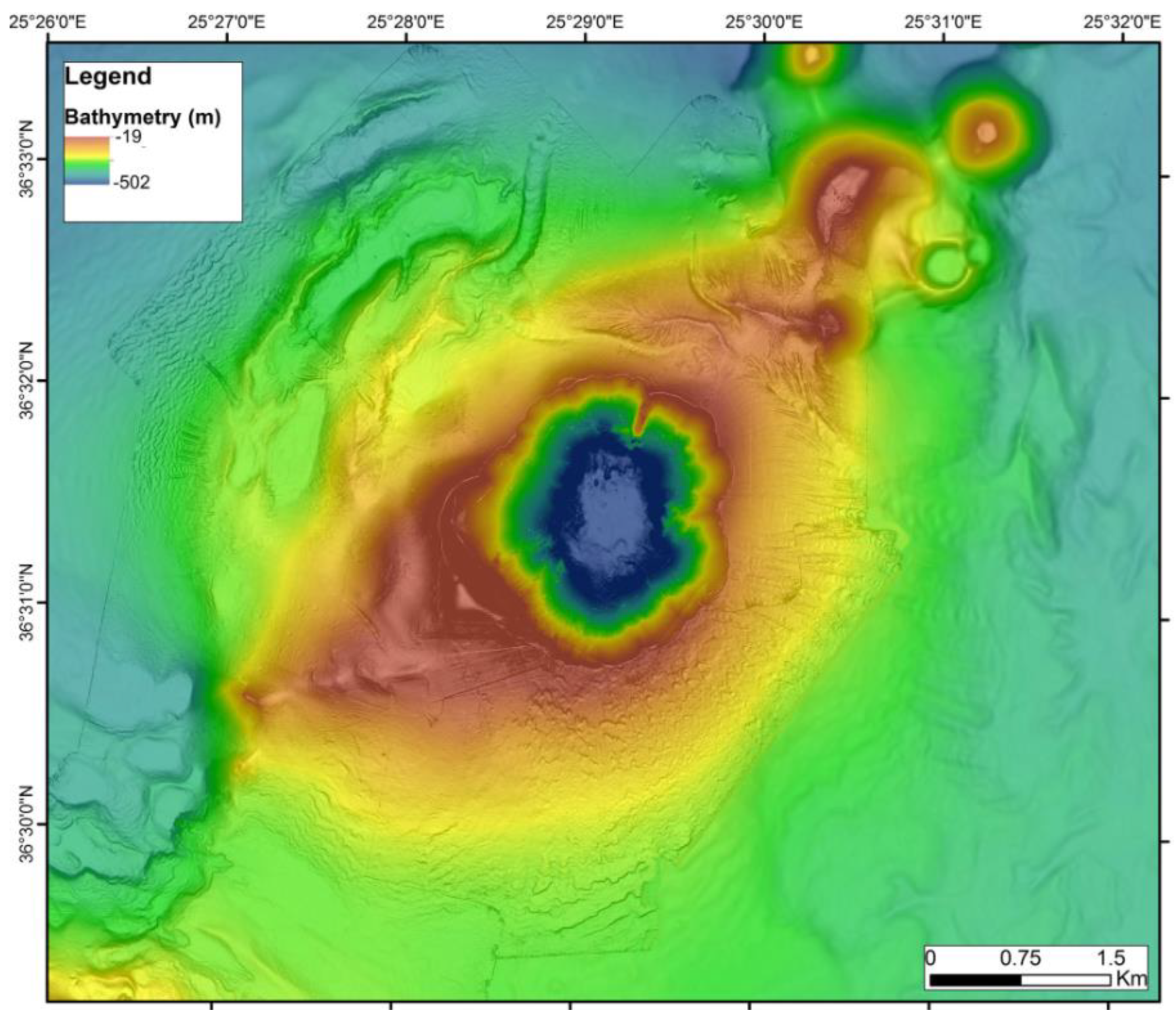
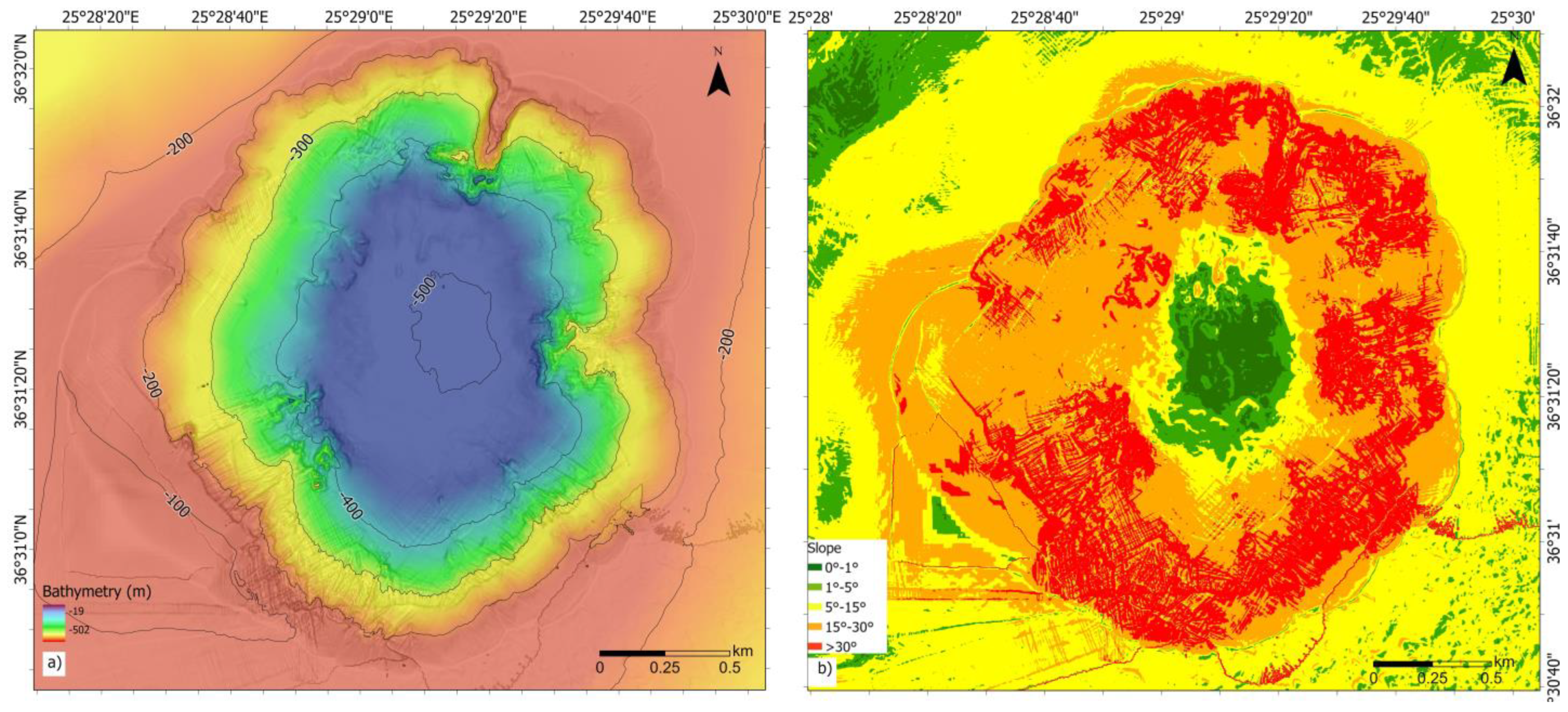
2.1. Seafloor Analysis
- 0°–1°: flat to gentle slopes, characterised by terrain with minimal elevation changes, where there may be instability [39];
- 1°–5°: gentle slopes;
- 5°–15°: moderately steep slopes that can affect stability;
- 15°–30°: steep slopes that are more prone to erosion and landslides, especially in areas with loose or unconsolidated materials;
- >30°: very steep slopes that are highly susceptible to instability and failure.
2.2. Hazard Zonation
3. Results
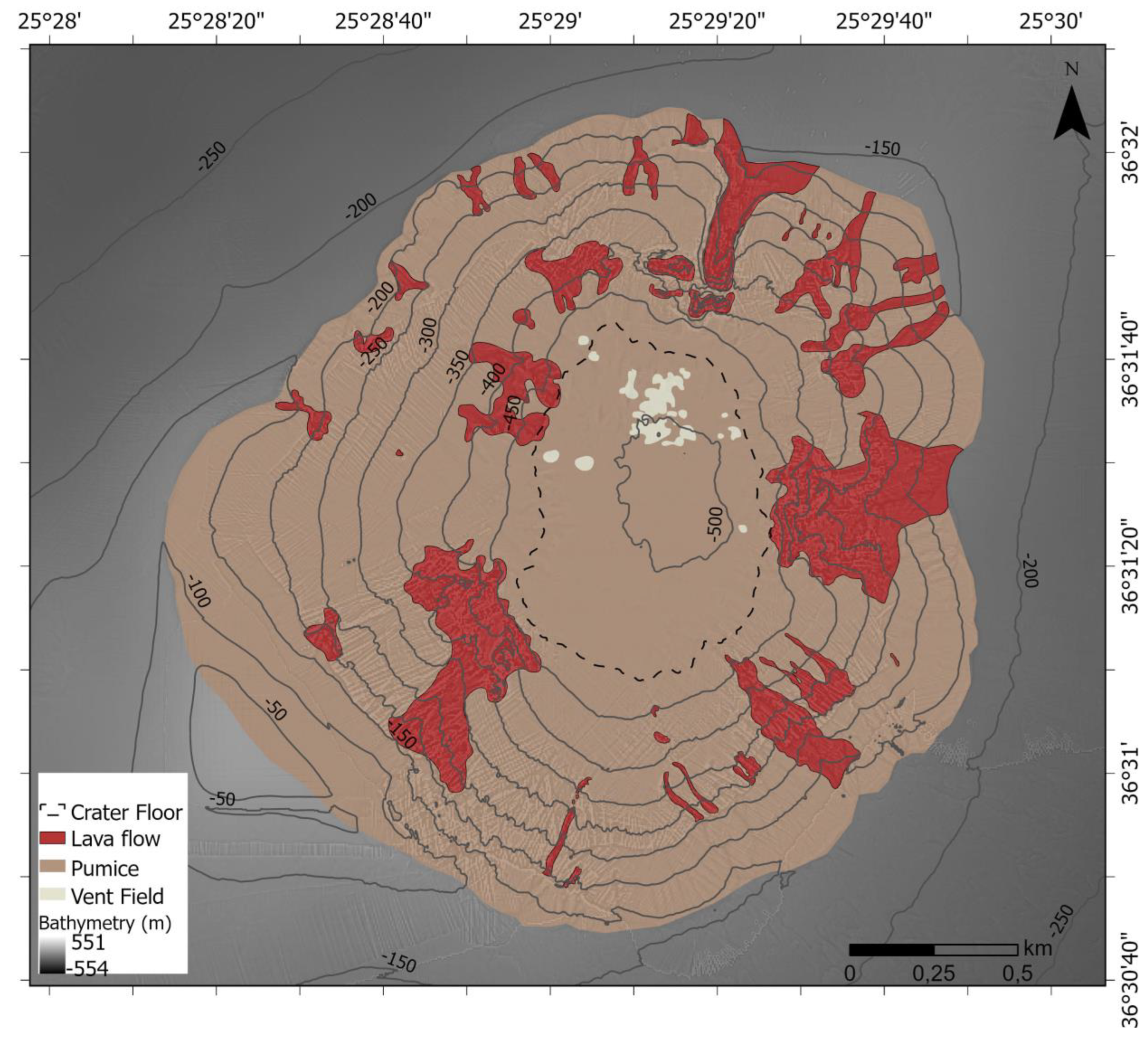
3.1. Seafloor Analysis
3.2. Hazard Zonation
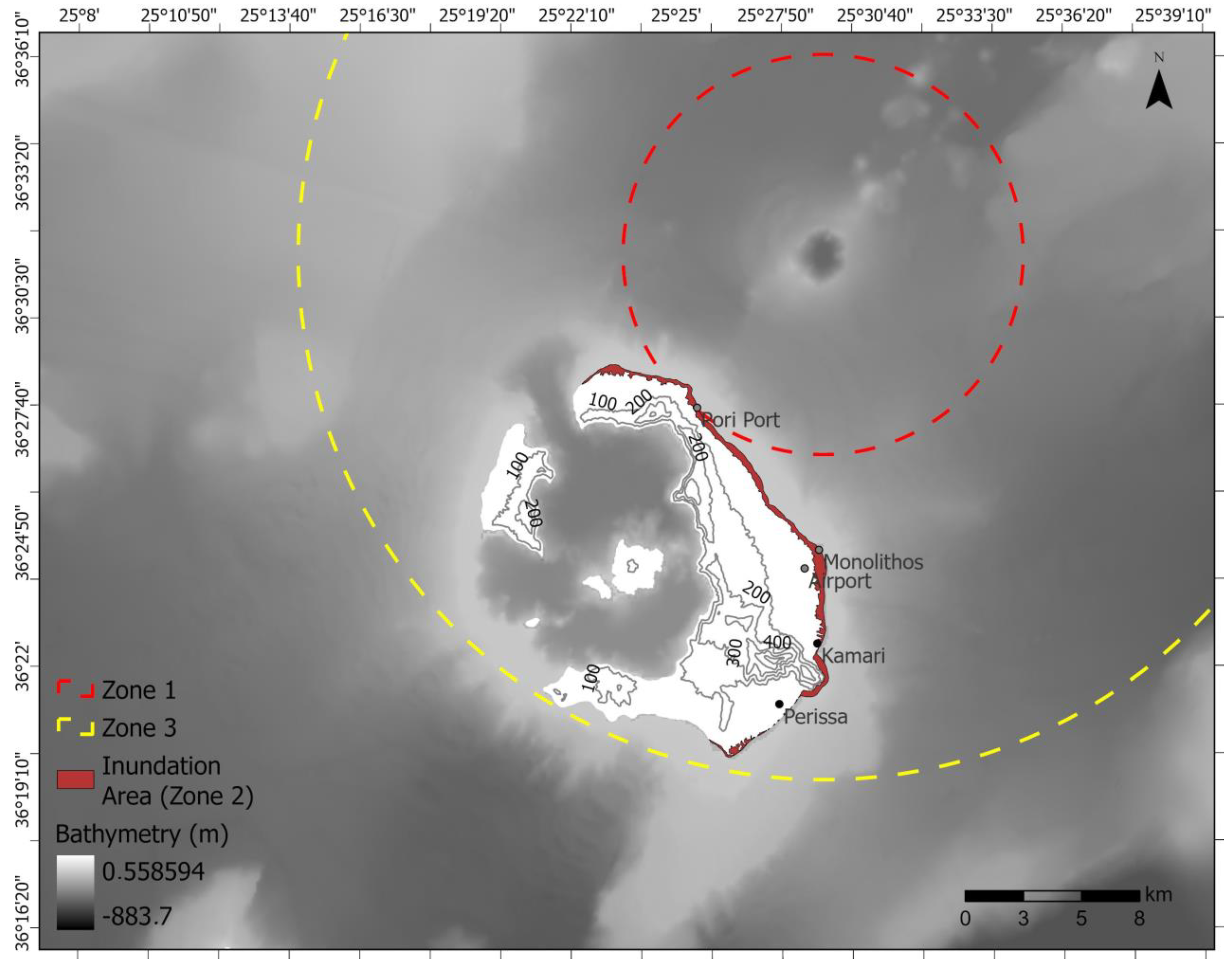
- Zone 1 (up to 7 km off Kolumbo’s crater), exclusion zone: This zone includes the offshore area around Kolumbo and reaches up to Santorini’s coastline. The zone was drawn based on its nearness to the crater and on the historical accounts of casualties offshore due to asphyxiation. In this zone, access must be strictly prohibited due to the danger of asphyxiation caused by toxic gas emissions, and the proximity to Kolumbo’s crater poses an imminent threat due to pyroclastic flows, ashfall, and potential tsunami generation.
- Zone 2, inundation area (8 km off Kolumbo’s crater) high-risk zone: In this zone, which encompasses the coast of Santorini, ashfall and tsunami generation pose significant threats to life. The zone was drawn based on the historical record and the tsunami model by Karstens et al. [13]. It is important to note that the model is based on numerical simulations and was not optimised for inundation; therefore, the acreage of the land is estimated and open to debate. The area should be evacuated to prevent a repetition of the 1650 casualties both inland and offshore, as it contains the most heavily impacted areas of Pori port, Kamari, Monolithos, and Perissa, where water reached up to 2 km2 inland. Additionally, this zone is extremely close to the only airport on the island, and its location could be compromised due to this proximity in a future eruption, creating problems with transport and isolating the island.
- Zone 3 (22 km off Kolumbo), moderate-risk zone: In this zone, the area is less likely to be affected by a tsunami; however, toxic gas emissions and ashfall still pose a significant hazard that can cause severe health issues as well as destruction of cultivated land and property. According to Fouqué [12], in 1650 CE, the toxic gas emissions reached the shores of Turkey. Considering that the prevailing wind conditions in Santorini indicates that the prevailing wind directions at Thira are the north and northwest (Figure S1) [46], the zone was drawn to include the whole island since, in the case of an eruption scenario similar to the 1650 CE eruption, the winds would carry the toxic gas and ashfall across the island. The use of protective masks, eye protection goggles, and burn-resistant clothes would be necessary to avoid health-associated risks.
3.3. Proposed Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fontaine, F.R.; Roult, G.; Michon, L.; Barruol, G.; Muro, A.D. The 2007 Eruptions and Caldera Collapse of the Piton de La Fournaise Volcano (La Réunion Island) from Tilt Analysis at a Single Very Broadband Seismic Station. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2803–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNISDR (United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction). Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030; UNISDR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, F.; De Coster, B.; Juvin, N.; Flohic, F.; Gaillard, J.-C.; Texier, P.; Morin, J.; Sartohadi, J. People’s Behaviour in the Face of Volcanic Hazards: Perspectives from Javanese Communities, Indonesia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 172, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, F.; Hreinsdóttir, S.; Hooper, A.; Árnadóttir, T.; Pedersen, R.; Roberts, M.J.; Óskarsson, N.; Auriac, A.; Decriem, J.; Einarsson, P.; et al. Intrusion Triggering of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull Explosive Eruption. Nature 2010, 468, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlodversdottir, H.; Petursdottir, G.; Carlsen, H.K.; Gislason, T.; Hauksdottir, A. Long-Term Health Effects of the Eyjafjallajökull Volcanic Eruption: A Prospective Cohort Study in 2010 and 2013. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laeger, K.; Petrelli, M.; Andronico, D.; Misiti, V.; Scarlato, P.; Cimarelli, C.; Taddeucci, J.; Del Bello, E.; Perugini, D. High-Resolution Geochemistry of Volcanic Ash Highlights Complex Magma Dynamics during the Eyjafjallajökull 2010 Eruption. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, K.; Geshi, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Oikawa, T. Special Issue “The Phreatic Eruption of Mt. Ontake Volcano in 2014”. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, M.A.; Yeo, I.A.; Watson, S.; Wysoczanski, R.; Seabrook, S.; Mackay, K.; Hunt, J.E.; Lane, E.; Talling, P.J.; Pope, E.; et al. Fast and Destructive Density Currents Created by Ocean-Entering Volcanic Eruptions. Science 2023, 381, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Government of Greece 2021. Available online: www.statistics.gr (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Dominey-Howes, D.; Minos-Minopoulos, D. Perceptions of Hazard and Risk on Santorini. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 137, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.L.; Caracausi, A.; Chavagnac, V.; Nomikou, P.; Polymenakou, P.N.; Mandalakis, M.; Kotoulas, G.; Magoulas, A.; Castillo, A.; Lampridou, D. Kolumbo Submarine Volcano (Greece): An Active Window into the Aegean Subduction System. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouqué, F. Santorin et ses Éruptions; Masson & Cie: Paris, France, 1879. [Google Scholar]
- Karstens, J.; Crutchley, G.J.; Hansteen, T.H.; Preine, J.; Carey, S.; Elger, J.; Kühn, M.; Nomikou, P.; Schmid, F.; Dalla Valle, G.; et al. Cascading Events during the 1650 Tsunamigenic Eruption of Kolumbo Volcano. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D. Active Tectonics of the Mediterranean Region. Geophys. J. Int. 1972, 30, 109–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, X.L.; Angelier, J. The Hellenic Arc and Trench System: A Key to the Neotectonic Evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean Area. Tectonophysics 1979, 60, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druitt, T.H.; Edwards, L.; Mellors, R.M.; Pyle, D.M.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Lanphere, M.; Davies, M.; Barreirio, B. Santorini Volcano: Geological Society [London] Memoir; The Geological Society: London, UK, 1999; Volume 19, 165p. [Google Scholar]
- Nomikou, P.; Hübscher, C.; Carey, S. The Christiana–Santorini–Kolumbo Volcanic Field. Elements 2019, 15, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preine, J.; Karstens, J.; Hübscher, C.; Nomikou, P.; Schmid, F.; Crutchley, G.J.; Druitt, T.H.; Papanikolaou, D. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of the Christiana-Santorini-Kolumbo Volcanic Field, Aegean Sea. Geology 2022, 50, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomikou, P.; Hübscher, C.; Ruhnau, M.; Bejelou, K. Tectono-Stratigraphic Evolution through Successive Extensional Events of the Anydros Basin, Hosting Kolumbo Volcanic Field at the Aegean Sea, Greece. Tectonophysics 2016, 671, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.J.; MacGillivray, J.A.; Synolakis, C.E.; Benjamini, C.; Keller, J.; Kisch, H.J.; Klügel, A.; Van Der Plicht, J. Geoarchaeological Tsunami Deposits at Palaikastro (Crete) and the Late Minoan IA Eruption of Santorini. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomikou, P.; Polymenakou, P.N.; Rizzo, A.L.; Petersen, S.; Hannington, M.; Kilias, S.P.; Papanikolaou, D.; Escartin, J.; Karantzalos, K.; Mertzimekis, T.J.; et al. SANTORY: SANTORini’s Seafloor Volcanic ObservatorY. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 796376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, D.J.W.; Pe-Piper, G.; Perissoratis, C.; Anastasakis, G. Distribution and Chronology of Submarine Volcanic Rocks around Santorini and Their Relationship to Faulting. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2007, 291, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübscher, C.; Ruhnau, M.; Nomikou, P. Volcano-Tectonic Evolution of the Polygenetic Kolumbo Submarine Volcano/Santorini (Aegean Sea). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 291, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomikou, P.; Carey, S.; Papanikolaou, D.; Croff Bell, K.; Sakellariou, D.; Alexandri, M.; Bejelou, K. Submarine Volcanoes of the Kolumbo Volcanic Zone NE of Santorini Caldera, Greece. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 90–91, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstens, J.; Preine, J.; Crutchley, G.J.; Kutterolf, S.; Van Der Bilt, W.G.M.; Hooft, E.E.E.; Druitt, T.H.; Schmid, F.; Cederstrøm, J.M.; Hübscher, C.; et al. Revised Minoan Eruption Volume as Benchmark for Large Volcanic Eruptions. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaver, M.; Carey, S.; Nomikou, P.; Smet, I.; Godelitsas, A.; Vroon, P. A Distinct Source and Differentiation History for Kolumbo Submarine Volcano, Santorini Volcanic Field, Aegean Arc. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 3254–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilias, S.P.; Nomikou, P.; Papanikolaou, D.; Polymenakou, P.N.; Godelitsas, A.; Argyraki, A.; Carey, S.; Gamaletsos, P.; Mertzimekis, T.J.; Stathopoulou, E.; et al. New Insights into Hydrothermal Vent Processes in the Unique Shallow-Submarine Arc-Volcano, Kolumbo (Santorini), Greece. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polymenakou, P.N.; Nomikou, P.; Hannington, M.; Petersen, S.; Kilias, S.P.; Anastasiou, T.I.; Papadimitriou, V.; Zaka, E.; Kristoffersen, J.B.; Lampridou, D.; et al. Taxonomic Diversity of Microbial Communities in Sub-Seafloor Hydrothermal Sediments of the Active Santorini-Kolumbo Volcanic Field. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1188544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, S.N.; Bell, K.L.C.; Rosi, M.; Marani, M.; Nomikou, P.; Walker, S.L.; Faure, K.; Kelly, J. Submarine Volcanoes of the Aeolian Arc, Tyrrhenian Sea. In New Frontiers in Ocean Exploration: The E/V Nautilus and NOAA Ship Okeanos Explorer 2011 Field Season; Bell, K.L.C., Elliott, K., Martinez, C., Fuller, S.A., Eds.; Oceanography: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, L.; Simkin, T.; Kimberly, P. Volcanoes of the World, 3rd ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Druitt, T.H.; Kutterolf, S.; Ronge, T.A.; The Expedition 398 Scientists. Expedition 398 Preliminary Report: Hellenic Arc Volcanic Field; International Ocean Discovery Program: College Station, TX, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, E.E.E.; Nomikou, P.; Toomey, D.R.; Lampridou, D.; Getz, C.; Christopoulou, M.-E.; O’Hara, D.; Arnoux, G.M.; Bodmer, M.; Gray, M.; et al. Backarc Tectonism, Volcanism, and Mass Wasting Shape Seafloor Morphology in the Santorini-Christiana-Amorgos Region of the Hellenic Volcanic Arc. Tectonophysics 2017, 712–713, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannington, M.D. (Ed.) RV POSEIDON Fahrtbericht/Cruise Report POS510—ANYDROS: Rifting and Hydrothermal Activity in the Cyclades Back-arc Basin, Catania (Italy)—Heraklion (Greece); GEOMAR Report, N. Ser. 043; GEOMAR Helmholtz-Zentrum für Ozeanforschung: Kiel, Germany, 2018; 56 + Appendix pp. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A.; Peralta-Reyes, M. Geomorphological Mapping Global Trends and Applications. Geographies 2023, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.T.; Macmillan-Lawler, M.; Rupp, J.; Baker, E.K. Geomorphology of the Oceans. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.; Jakobsson, M.; Allen, G.; Dorschel, B.; Falconer, R.; Ferrini, V.; Lamarche, G.; Snaith, H.; Weatherall, P. The Nippon Foundation—GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project: The Quest to See the World’s Oceans Completely Mapped by 2030. Geosciences 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.; Lamarche, G.; Le Gonidec, Y.; Lucieer, V.; Weber, T.; Heffron, E. Semi-automated benthic habitat mapping using MBES and AUV data: A case study from the Bounty Trough, New Zealand. Geosciences 2020, 10, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Micallef, A.; Krastel, S.; Savini, A. (Eds.) Submarine Geomorphology; Springer Geology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennelly, P.J. Terrain Maps Displaying Hill-Shading with Curvature. Geomorphology 2008, 102, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; et al. Submarine Landslides. In Marine Geo-Hazards in China; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 179–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Encyclopedia of Volcanoes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Chrapkiewicz, K.; Paulatto, M.; Heath, B.A.; Hooft, E.E.E.; Nomikou, P.; Papazachos, C.B.; Schmid, F.; Toomey, D.R.; Warner, M.R.; Morgan, J.V. Magma Chamber Detected Beneath an Arc Volcano With Full-Waveform Inversion of Active-Source Seismic Data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst 2022, 23, e2022GC010475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchi, W.; Woo, G. Probabilistic Eruption Forecasting and the Call for an Evacuation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 2007GL031922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchi, W.; Bebbington, M.S. Probabilistic Eruption Forecasting at Short and Long Time Scales. Bull. Volcanol. 2012, 74, 1777–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantner, K.; Carey, S.; Nomikou, P. Integrated Volcanologic and Petrologic Analysis of the 1650AD Eruption of Kolumbo Submarine Volcano, Greece. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2014, 269, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsigera, A.; Nomikou, P.; Team, S. Addressing the Hazard Risks of Kolumbo Submarine Volcano (Santorini, Greece). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Humanitarian Krisis Management 2023, International Hellenic University, Thessaloniki, Greece, 14–16 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Iowa Environmental Mesonet. Iowa State University. 2024. Available online: http://mesonet.agron.iastate.edu/ (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Horwell, C.J.; Baxter, P.J. The Respiratory Health Hazards of Volcanic Ash: A Review for Volcanic Risk Mitigation. Bull. Volcanol. 2006, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, R. Monitoring and Mitigation of Volcano Hazards; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilloy, A.; Malamud, B.D.; Winter, H.; Joly-Laugel, A. A Review of Quantification Methodologies for Multi-Hazard Interrelationships. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 196, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, M.T. Hazards from Lahars and Jökulhlaups. In The Encyclopedia of Volcanoes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, G.N. A Short Meteorological Overview of the Eyjafjallajökull Eruption 14 April–23 May 2010. Weather 2010, 65, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BNPB-National Disaster Management Agency, Tsunami Selat Sunda. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/indonesia/indonesia-sunda-straights-tsunami-emergency-plan-action-mdrid014 (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- The World Bank and the Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery. The January 15, 2022 Hunga Ton-ga-HungaHa’apai Eruption and Tsunami, Tonga: Global Rapid Post Disaster Damage Estimation (Grade) Report; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/TheWorldBank: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://shorturl.at/tBJY3 (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Escartin, J.; Barreyre, T.; Cannat, M.; Garcia, R.; Gracias, N.; Deschamps, A.; Salocchi, A.; Sarradin, P.-M.; Ballu, V. Hydrothermal Activity along the Slow-Spreading Lucky Strike Ridge Segment (Mid-Atlantic Ridge): Distribution, Heatflux, and Geological Controls. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 431, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.S.; Delaney, J.R.; Juniper, S.K. Establishing a New Era of Submarine Volcanic Observatories: Cabling Axial Seamount and the Endeavour Segment of the Juan de Fuca Ridge. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 426–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillet, N.; Jorry, S.; Crawford, W.C.; Deplus, C.; Thinon, I.; Jacques, E.; Saurel, J.M.; Lemoine, A.; Paquet, F.; Satriano, C.; et al. Birth of a Large Volcanic Edifice Offshore Mayotte via Lithosphere-Scale Dyke Intrusion. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooner, S.L.; Chadwick, W.W. Inflation-Predictable Behavior and Co-Eruption Deformation at Axial Seamount. Science 2016, 354, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, W.W.; Wilcock, W.S.D.; Nooner, S.L.; Beeson, J.W.; Sawyer, A.M.; Lau, T.-K. Geodetic Monitoring at Axial Seamount Since Its 2015 Eruption Reveals a Waning Magma Supply and Tightly Linked Rates of Deformation and Seismicity. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2022, 23, e2021GC010153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Slope Works, ArcGIS Pro Documentation. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/tool-reference/3d-analyst/how-slope-works.htm (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Slope (Spatial Analyst), ArcGIS Pro Documentation. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/tool-reference/spatial-analyst/slope.htm (accessed on 24 July 2024).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsigera, A.; Nomikou, P.; Pavlopoulos, K. A Preliminary Hazard Assessment of Kolumbo Volcano (Santorini, Greece). GeoHazards 2024, 5, 816-832. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5030041
Katsigera A, Nomikou P, Pavlopoulos K. A Preliminary Hazard Assessment of Kolumbo Volcano (Santorini, Greece). GeoHazards. 2024; 5(3):816-832. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsigera, Anna, Paraskevi Nomikou, and Kosmas Pavlopoulos. 2024. "A Preliminary Hazard Assessment of Kolumbo Volcano (Santorini, Greece)" GeoHazards 5, no. 3: 816-832. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5030041
APA StyleKatsigera, A., Nomikou, P., & Pavlopoulos, K. (2024). A Preliminary Hazard Assessment of Kolumbo Volcano (Santorini, Greece). GeoHazards, 5(3), 816-832. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards5030041







