Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: The Characterization and Testing of Pt-Co/SiO2 Catalysts Prepared with Alternative Cobalt Precursors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. BET Surface Area and Porosity Measurements
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction
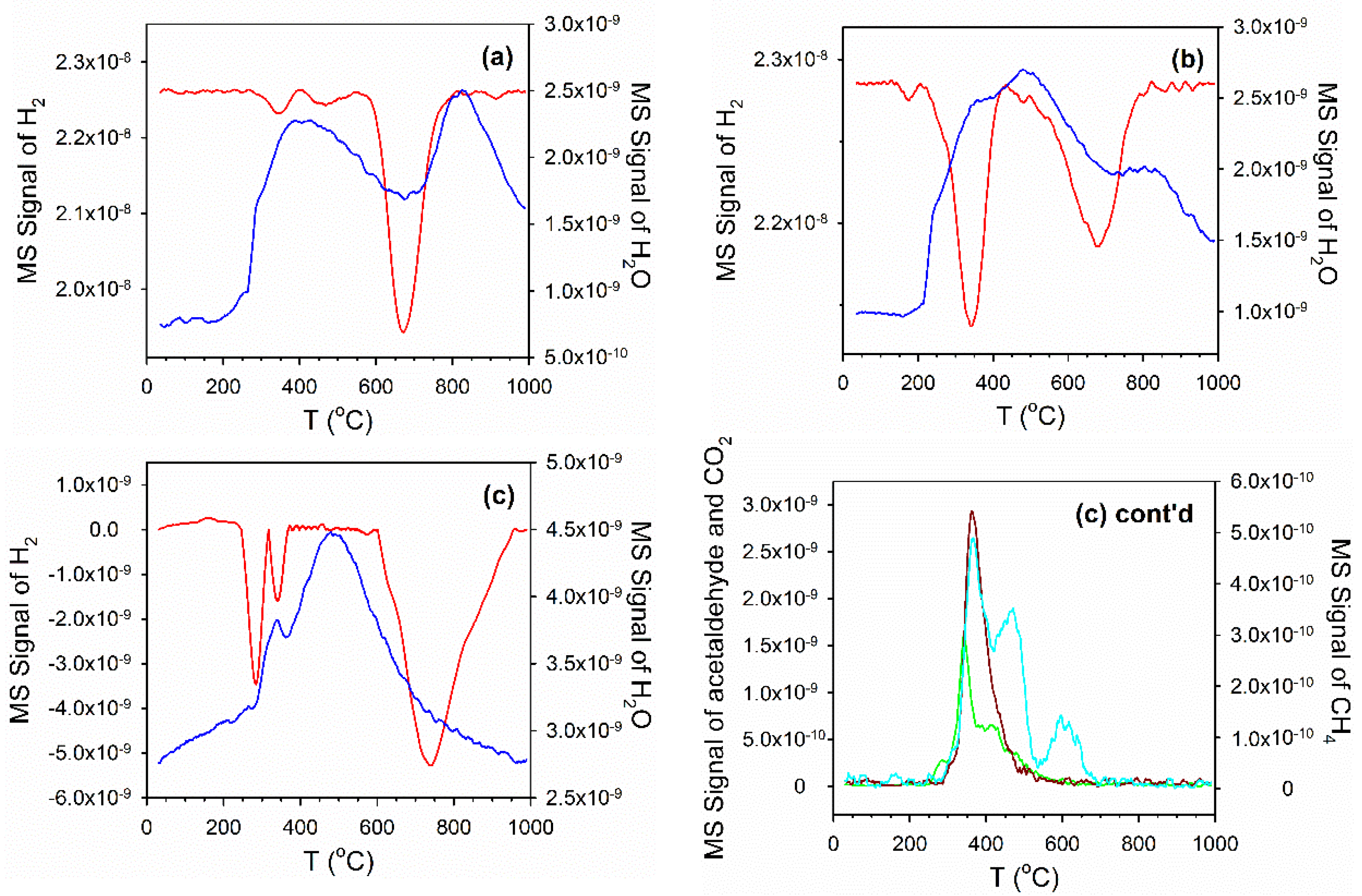
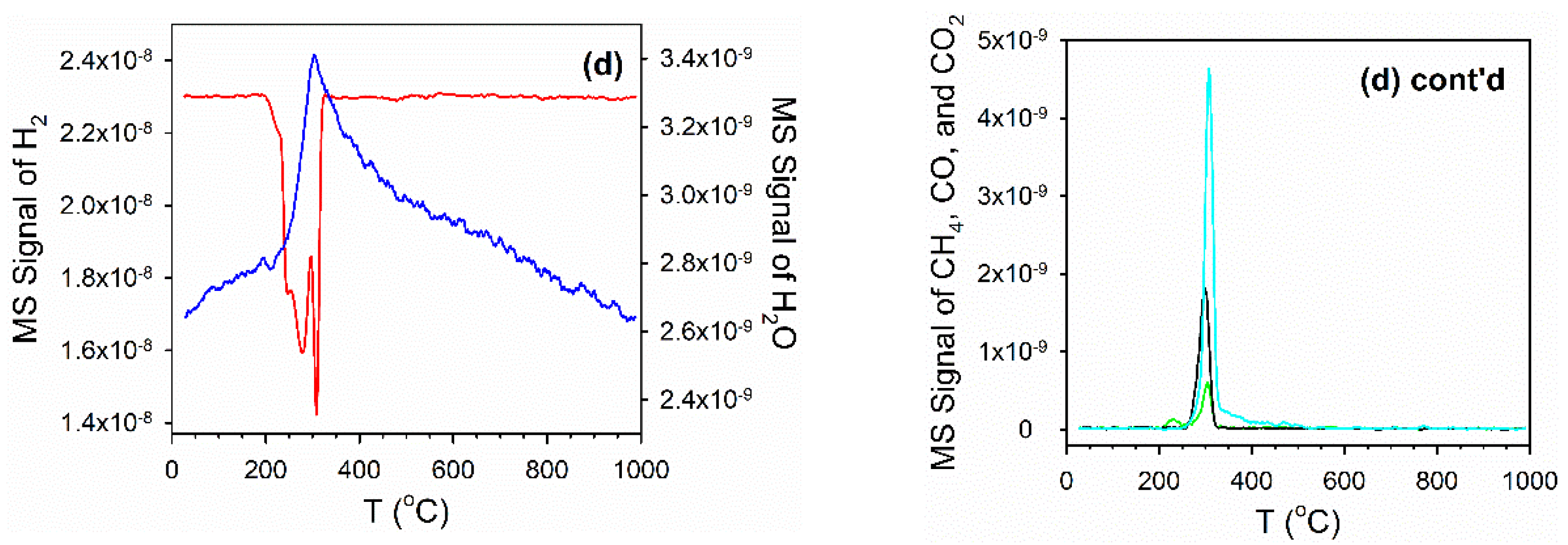
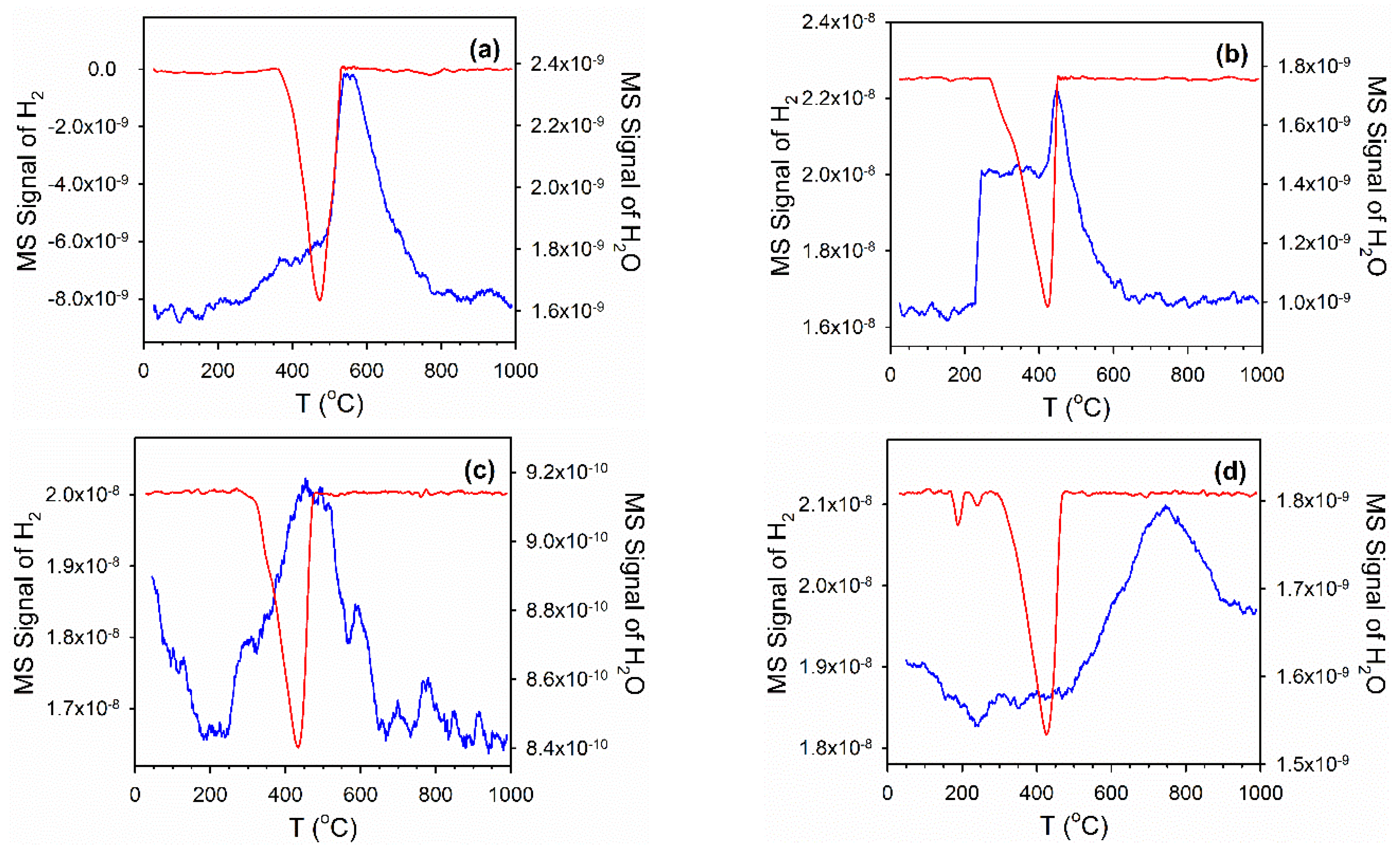
2.4. Temperature-Programmed Reduction (TPR) and TPR-MS
2.5. Hydrogen Chemisorption and Percentage Reduction by Pulse Reoxidation
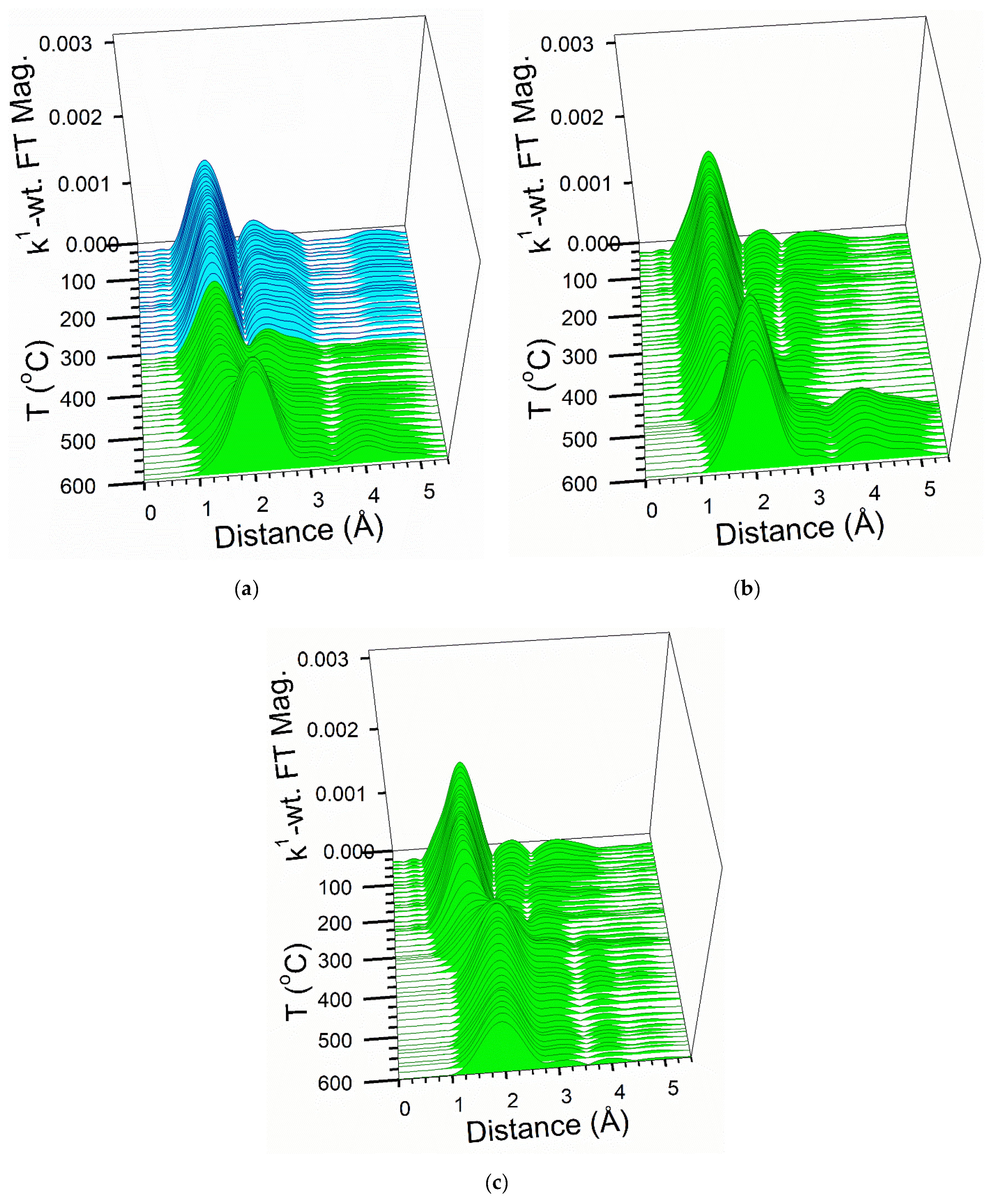
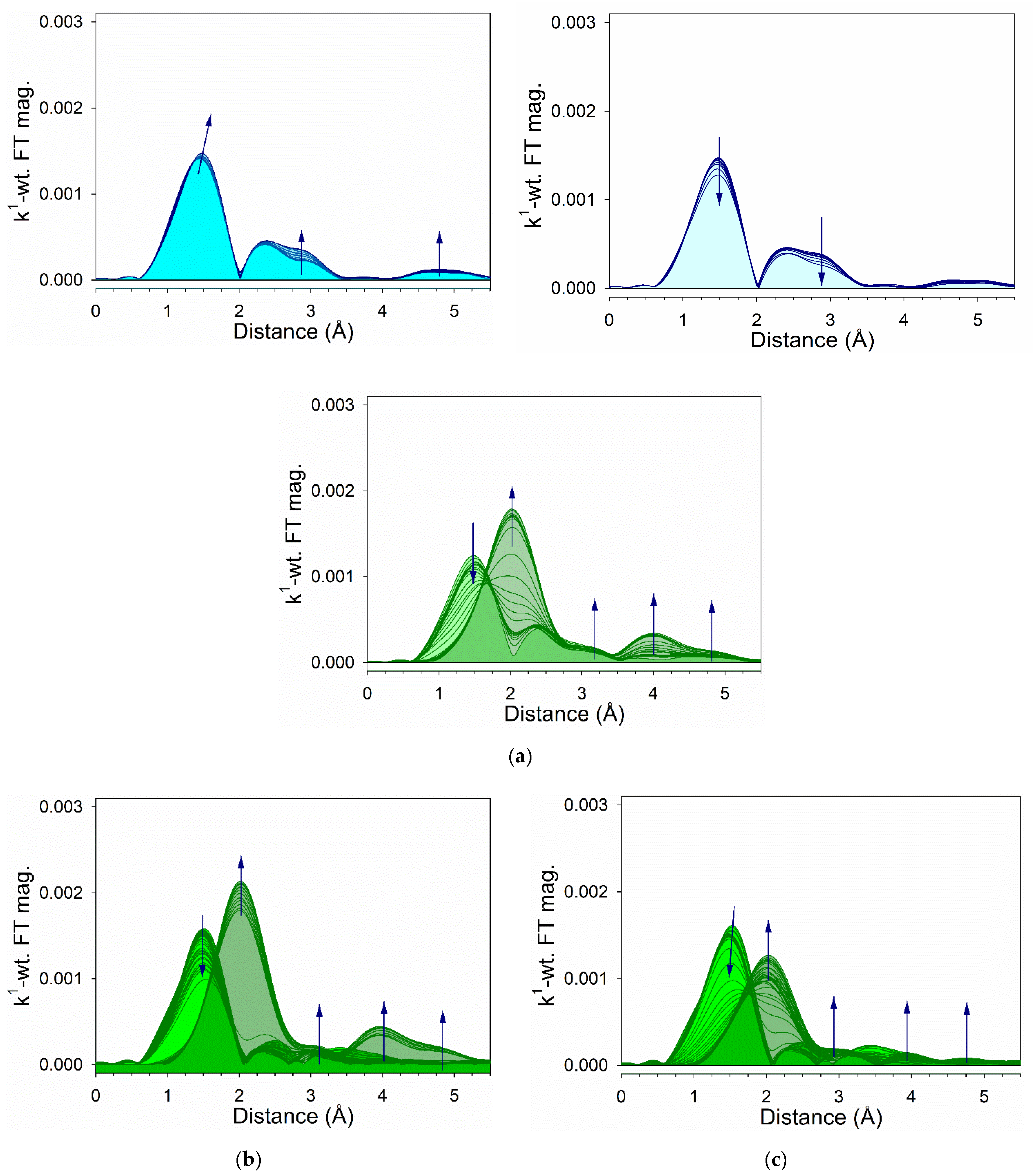
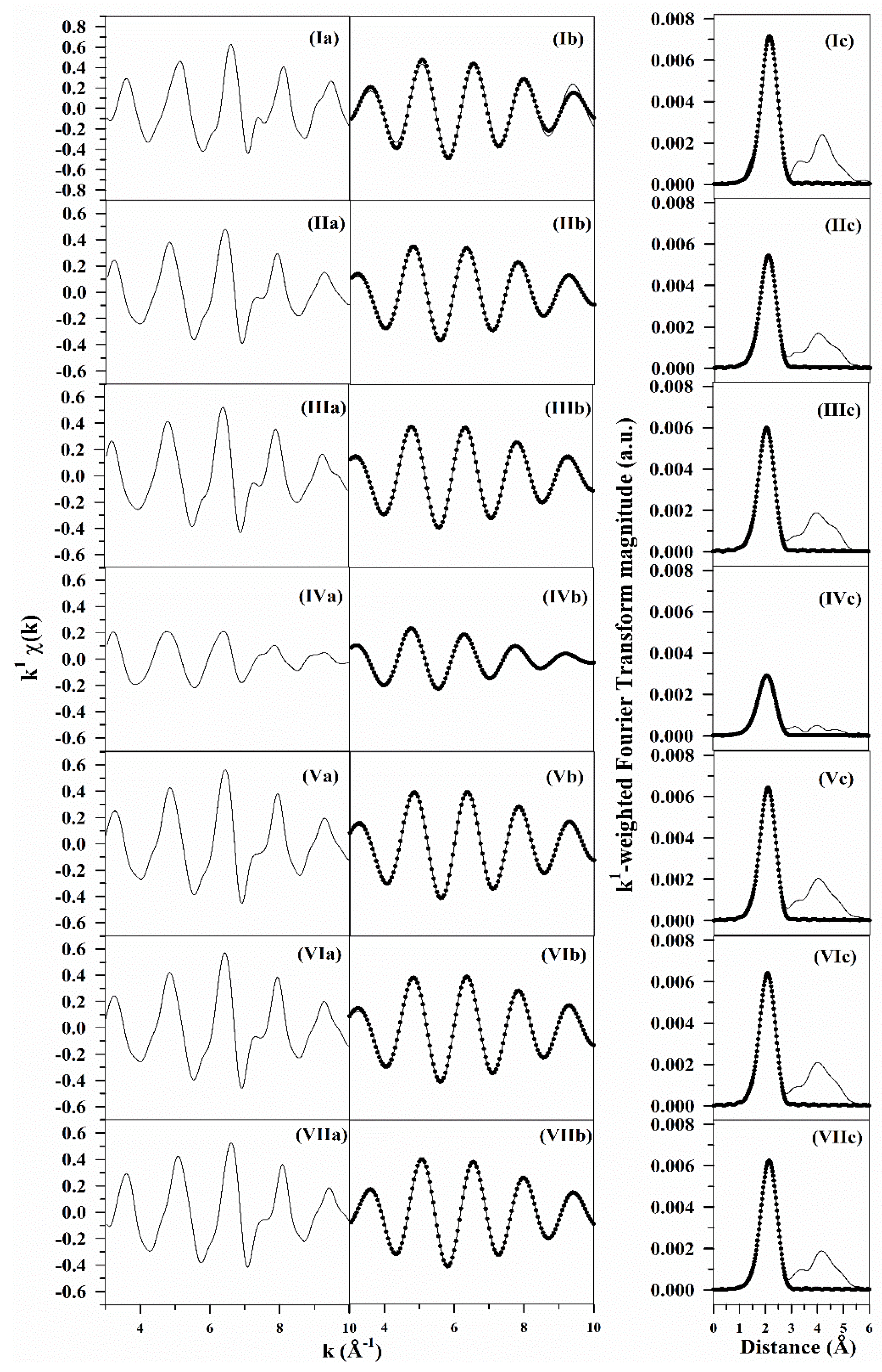
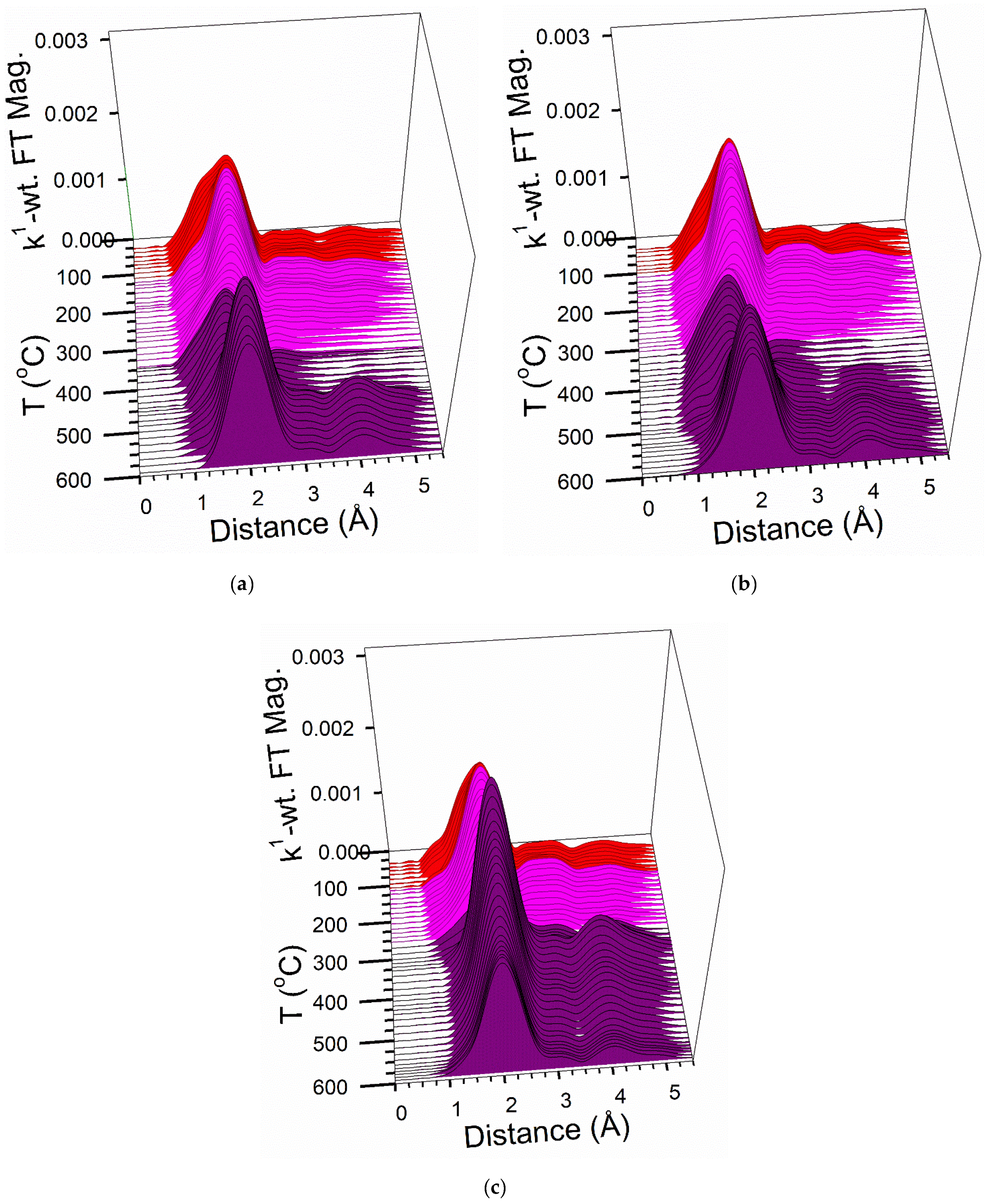
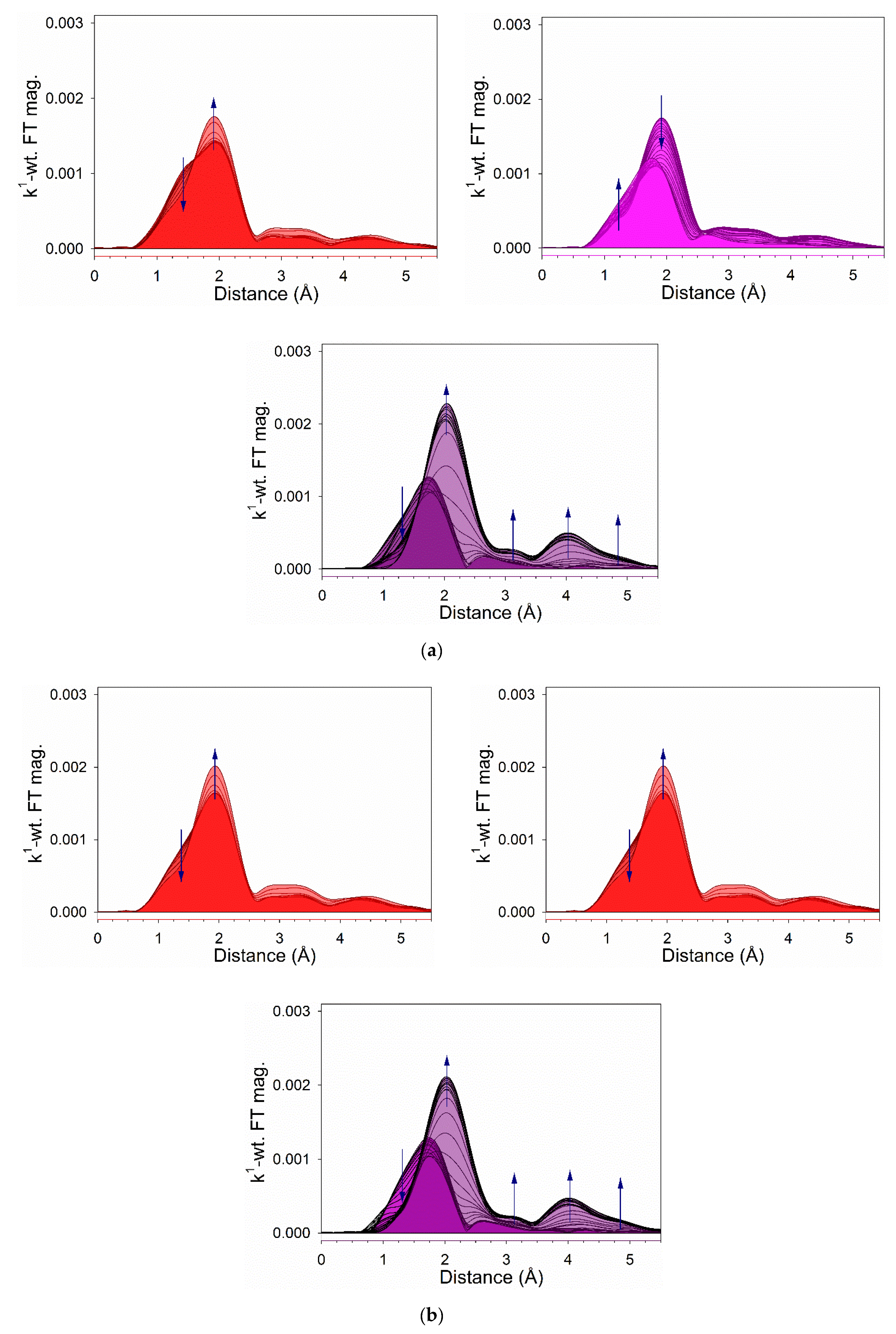
2.6. TPR-EXAFS/TPR-XANES Spectroscopies
2.7. Catalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Structural Properties
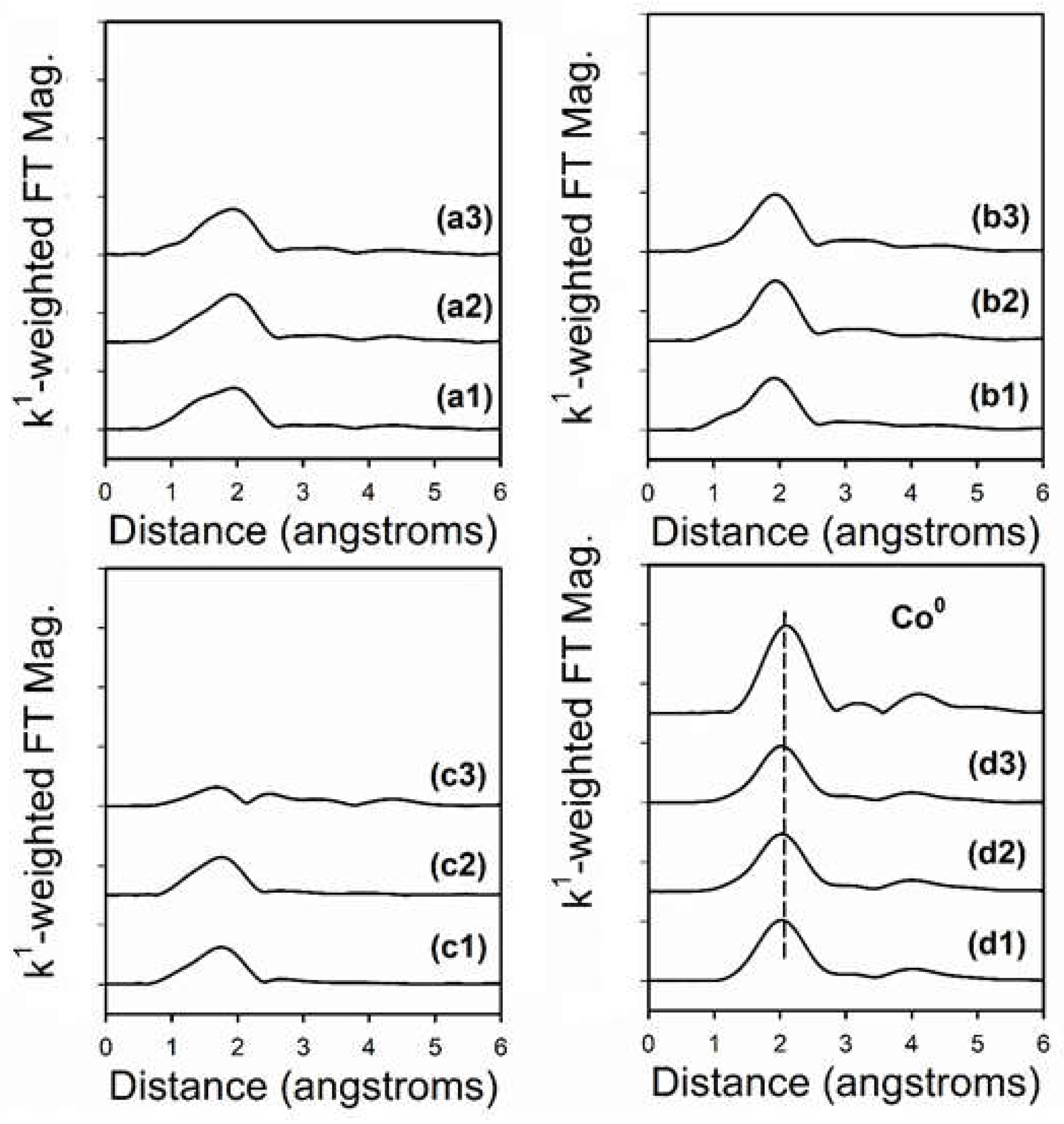
3.2. Cobalt Reducibility and Particle Size
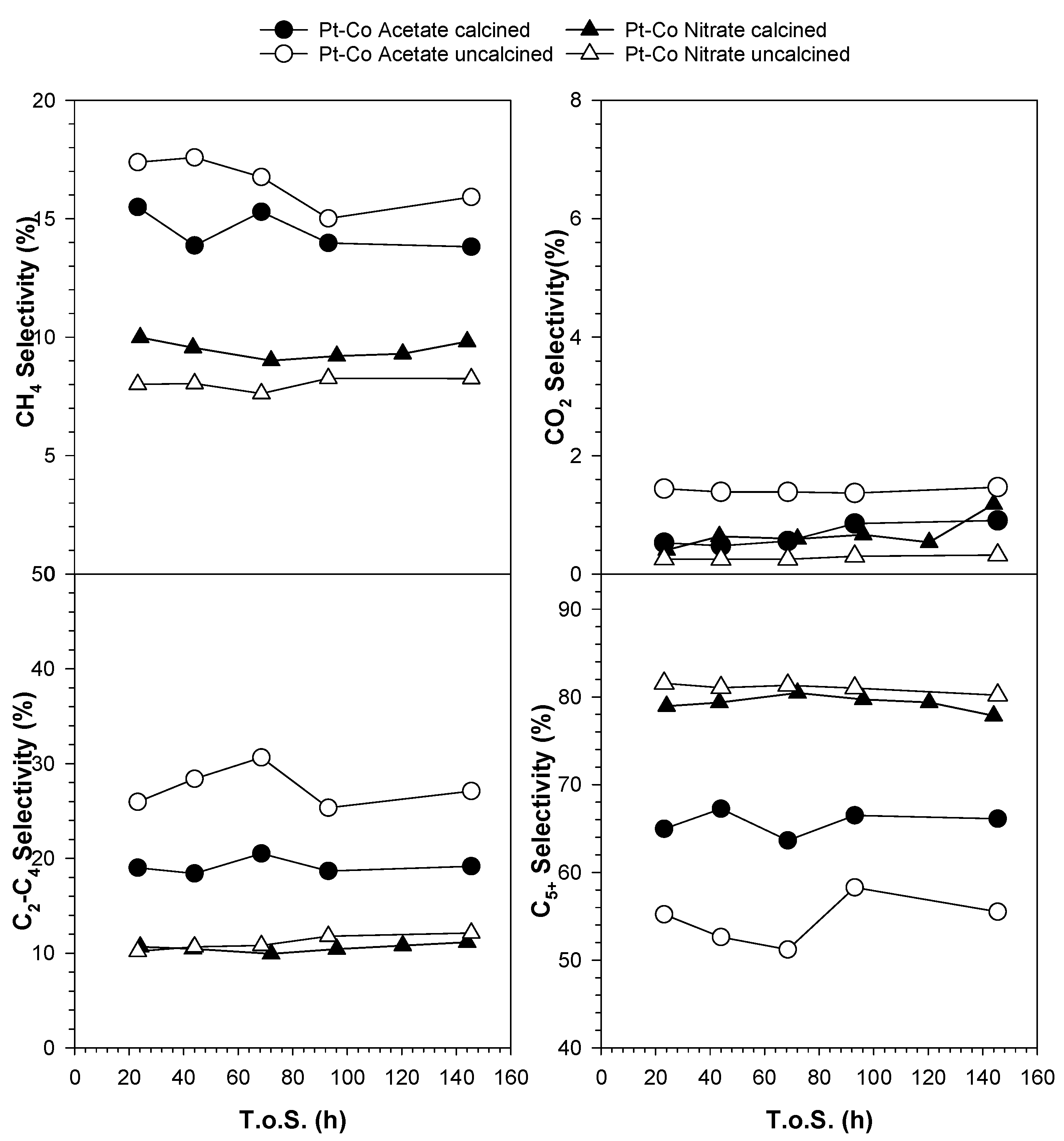
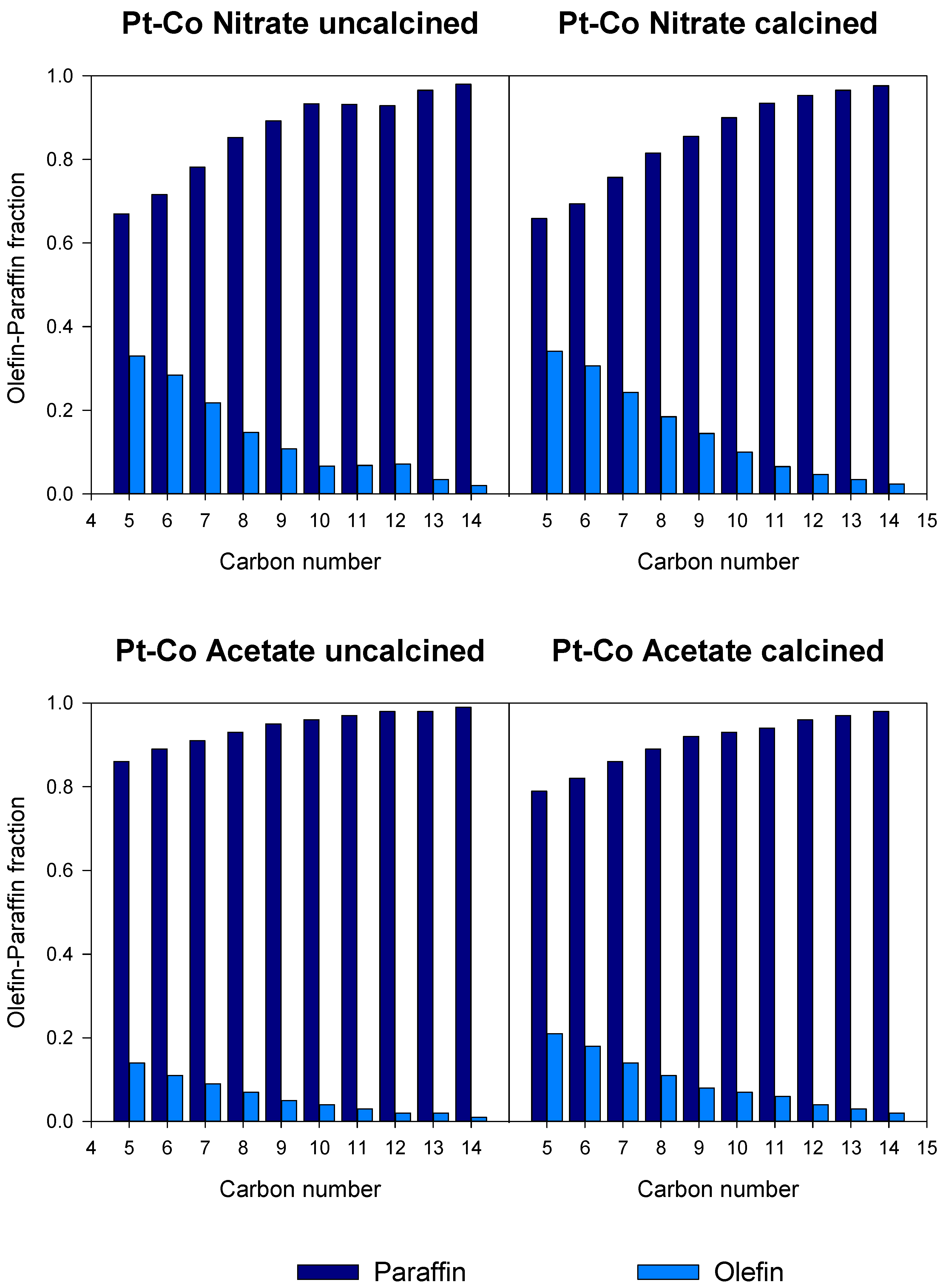
3.3. Catalytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaub, G.; Rohde, M.; Subiranas, A.M. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. In Development and Perspectives, Proceedings of the DGMK/SCI-Conference “Synthesis Gas Chemistry”, Dresden, Germany, 4–6 October 2006; Ernst, S., Jess, A., Nees, F., Perego, C., Rupp, M., Santacesaria, E., Eds.; German Society for Petroleum and Coal Science and Technology: Hamburg, Germany, 2006; pp. 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, R.L.; Visagie, J.L.; van Berge, P.J.; Bolder, F.H. Catalysts. U.S. Patent 5,733,839, 31 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesia, E. Design, synthesis, and use of cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 161, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Racoillet, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Support, loading, and promoter effects on the reducibility of cobalt catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 233, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Chen, Y.-W. Influence of metal loading on the reducibility and hydro-genation activity of cobalt/alumina catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1991, 77, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.; Khodakov, A.Y. Promotion of cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts with noble metals: A review. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. Rev. l’IFP 2009, 64, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vada, S.; Hoff, A.; Adnanes, E.; Schanke, D.; Holmen, A. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on supported cobalt catalysts promoted by platinum and rhenium. Top. Catal. 1995, 2, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.M.; Poudyal, S.; Miller, J.T.; Bartholomew, C.H.; Hecker, W.C. Reducibility of alumina-supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts: Effects of noble metal type, distribution, retention, chemical state, bonding, and influence on cobalt crystallite size. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 449, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Chaney, J.A.; Patterson, P.M.; Das, T.K.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Study of the promotion of Re on the reduction property of Co/Al2O3 catalysts by in situ EXAFS/XANES of Co K and Re LIII edges and XPS. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 264, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronning, M.; Nicholson, D.G.; Holmen, A. In situ EXAFS study of the bimetallic inter-action in a rhenium-promoted alumina-supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2001, 72, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guczi, L.; Bazin, D.; Kovacs, I.; Borko, L.; Schay, Z.; Lynch, J.; Parent, P.; Lafon, C.; Stefler, G.; Koppany, Z.; et al. Structure of Pt-Co/Al2O3 and Pt-Co/NaY bimetallic catalysts: Characterization by in situ EXAFS, TPR, XPS and by activity in CO Hydrogenation. Top. Catal. 2002, 20, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Chaney, J.A.; Patterson, P.M.; Das, T.K.; Maillot, J.C.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Study of the promotion of Pt on the reduction property of Co/Al2O3 catalysts by in situ EXAFS of Co K and Pt LIII edges and XPS. J. Synch. Rad. 2004, 11, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesia, E.; Soled, S.L.; Fiato, R.A.; Via, G.H. Bimetallic synergy in cobalt-ruthenium Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts. J. Catal. 1993, 143, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.M.; Shannon, M.D.; Casci, J.L. Imaging promoter atoms in cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts using SuperSTEM microscopy. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2006, 172, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Jacobs, G.; Qian, D.; Ji, Y.; Klettlinger, J.L.S.; Hopps, S.D.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Synergistic effect of hybrid Pt-Cd additives on a 15%Co/Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 600, 117610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steen, E.; Claeys, M.; Dry, M.E.; van de Loosdrecht, J.; Viljoen, E.L.; Visagie, J.L. Stability of nanocrystals: Thermodynamic analysis of oxidation and re-reduction of cobalt in water/hydrogen mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3575–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loegdberg, S.; Boutonnet, M.; Walmsley, J.C.; Jaras, S.; Holmen, A.; Blekkan, E.A. Effect of water on the space-time yield of different supported cobalt catalysts during Fiscer-Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 393, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Patterson, P.M.; Li, J.; Sanchez, L.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: XAFS studies of the effect of water on a Pt-promoted Co/Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 247, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, N.A.; Gloriot, V.; Smiley, D.D.; Jacobs, G.; Pendyala, V.R.R.; Graham, U.M.; Ma, W.; Gnanamani, M.K.; Shafer, W.D.; Maclennan, A.; et al. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Comparisons of Al2O3 and TiO2 supported Co catalysts prepared by aqueous impregnation and CVD methods. In Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis, Catalysts and Catalysis: Advances and Applications; Davis, B.H., Occelli, M.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2016; pp. 85–106, Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Jermwongratanachai, T.; Jacobs, G.; Shafer, W.D.; Ma, W.; Pendyala, V.R.R.; Davis, B.H.; Kitiyanan, B.; Khalid, S.; Cronauer, D.C.; Kropf, A.J.; et al. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Oxidation of a fraction of cobalt crystallites in research catalysts at the onset of FT at partial pressures mimicking 50% CO conversion. Top. Catal. 2014, 57, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Xia, G.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Jin, C.; Yan, Z.; Li, M.; Hu, Z.; Nie, H.; Li, D. Thermodynamics of oxidation of an alumina-supported cobalt catalyst by water in F-T synthesis. Catal. Today 2016, 264, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambal, A.S.; Kugler, E.L.; Gardner, T.H.; Dadyburjor, D.B. Effect of Surface Modification by Chelating Agents on Fischer−Tropsch Performance of Co/SiO2 Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 16675–16688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronauer, D.C.; Elam, J.W.; Kropf, A.J.; Marshall, C.L.; Gao, P.; Hopps, S.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Preconditioning effects upon Co-containing promoted and unpromoted catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.W.; Kim, S.-M.; Kang, S.-H.; Chary, K.V.R.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Jun, K.-W. Effect of support and cobalt precursors on the activity of Co/AlPO4 catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 311, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpranot, J.; Kaewkun, S.; Praserthdam, P.; Goodwin, J.G. Effect of cobalt precursors on the dispersion of cobalt on MCM-41. Catal. Lett. 2003, 91, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Tsubaki, N.; Fujimoto, K. The reaction performances and characterization of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis Co/SiO2 catalysts prepared from mixed cobalt salts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 202, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, N.; Sun, S.; Fujimoto, K. Different Functions of the Noble Metals Added to Cobalt Catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. J. Catal. 2001, 199, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardon, J.-S.; Lermontov, A.S.; Gengembre, L.; Chernavskii, P.A.; Griboval-Constant, A.; Khodakov, A.Y. Effect of cobalt precursor and pretreatment conditions on the structure and catalytic performance of cobalt silica-supported Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 2005, 230, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of water on the deactivation of Pt promoted Co/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 228, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.H.; Iglesia, E. Technology Development for Iron and Cobalt Fischer-Tropsch Catalysts; National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL): Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell, F.A.; Jackson, S.D. The genesis of supported cobalt catalysts. Appl. Petrochem. Res. 2017, 7, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, M.; Mehrbod, M.; Dawson, C.; Davis, B.H.; Lietti, L.; Cronauer, D.C.; Kropf, A.J.; Marshall, C.L.; Jacobs, G. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Foregoing calcination and utilizing reduction promoters leads to improved conversion and selectivity with Co/silica. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 559, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrbod, M.; Martinelli, M.; Castro, J.D.; Alhraki, N.; Cronauer, D.C.; Kropf, A.J.; Marshall, C.L.; Jacobs, G. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Direct cobalt nitrate reduction of promoted Co/Al2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2021, 369, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrbod, M.; Martinelli, M.; Martino, A.G.; Cronauer, D.C.; Kropf, A.J.; Marshall, C.L.; Jacobs, G. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Direct cobalt nitrate reduction of promoted Co/TiO2 catalysts. Fuel 2019, 245, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millipore-Sigma, Chemical Supplier. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/united-states.html (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- The MAK-Collection Part. I: MAK Value Documentations; DFG, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Volume 23, ISBN 978-3-527-31595-6.
- Krumm, S. The Erlangen geological and mineralogical software collection. Comput. Geosci. 1999, 25, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, M. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Chem. Engin. News Arch. 2001, 79, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, T. WinXAS: A Program for X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Data Analysis under MS-Windows. J. Synchrot. Radiat. 1998, 5, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Ji, Y.; Davis, B.H.; Cronauer, D.C.; Kropf, A.J.; Marshall, C.L. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Temperature programmed EXAFS/XANES investigation of the influence of support type, cobalt loading, and noble metal promoter addition to the reduction behavior of cobalt oxide particles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 333, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B. ATOMS: Crystallography for the X-ray absorption spectroscopist. J. Synchrot. Radiat 2001, 8, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newville, M.; Ravel, B.; Haskel, D.; Rehr, J.J.; Stern, E.A.; Yacoby, Y. Analysis of multiple-scattering XAFS data using theoretical standards. Physical B 1995, 208–209, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Halawy, S.; Ebrahim, M. The non-isothermal decomposition of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate: A kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Therm. Anal. Calor. 1994, 41, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, J.C.; Gnanamani, M.K.; Jacobs, G.; Ma, W.; Ji, Y.; Khalid, S.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Synthesis, characterization, and reaction testing investigation of cobalt carbide. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
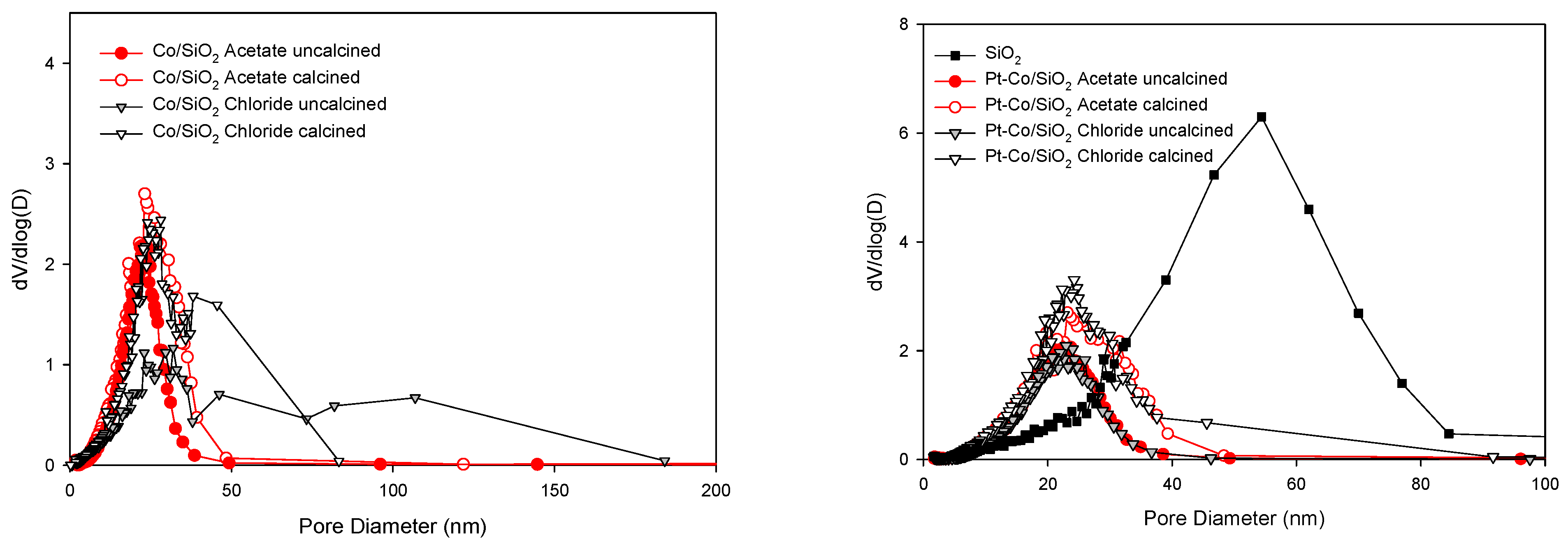
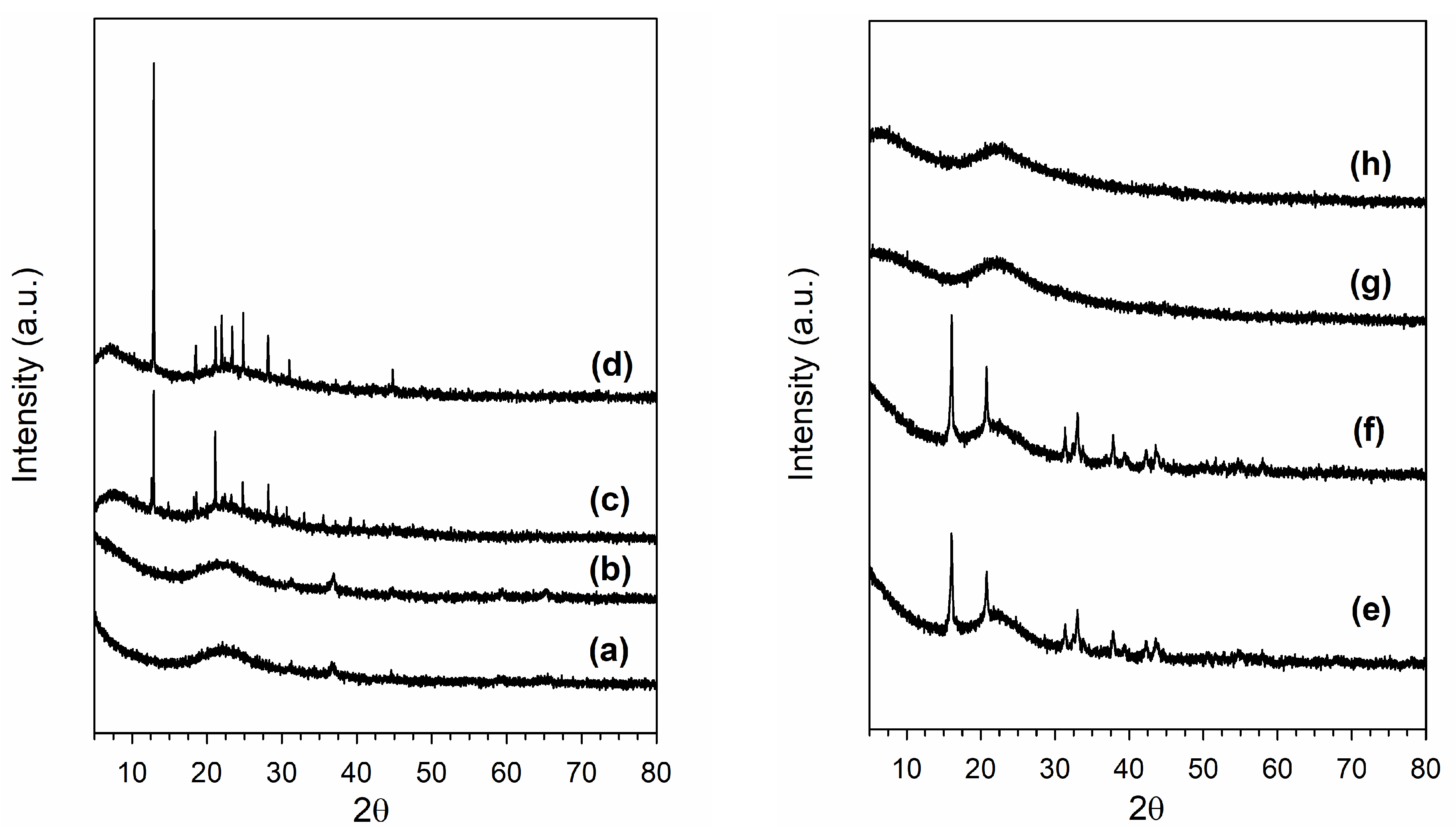
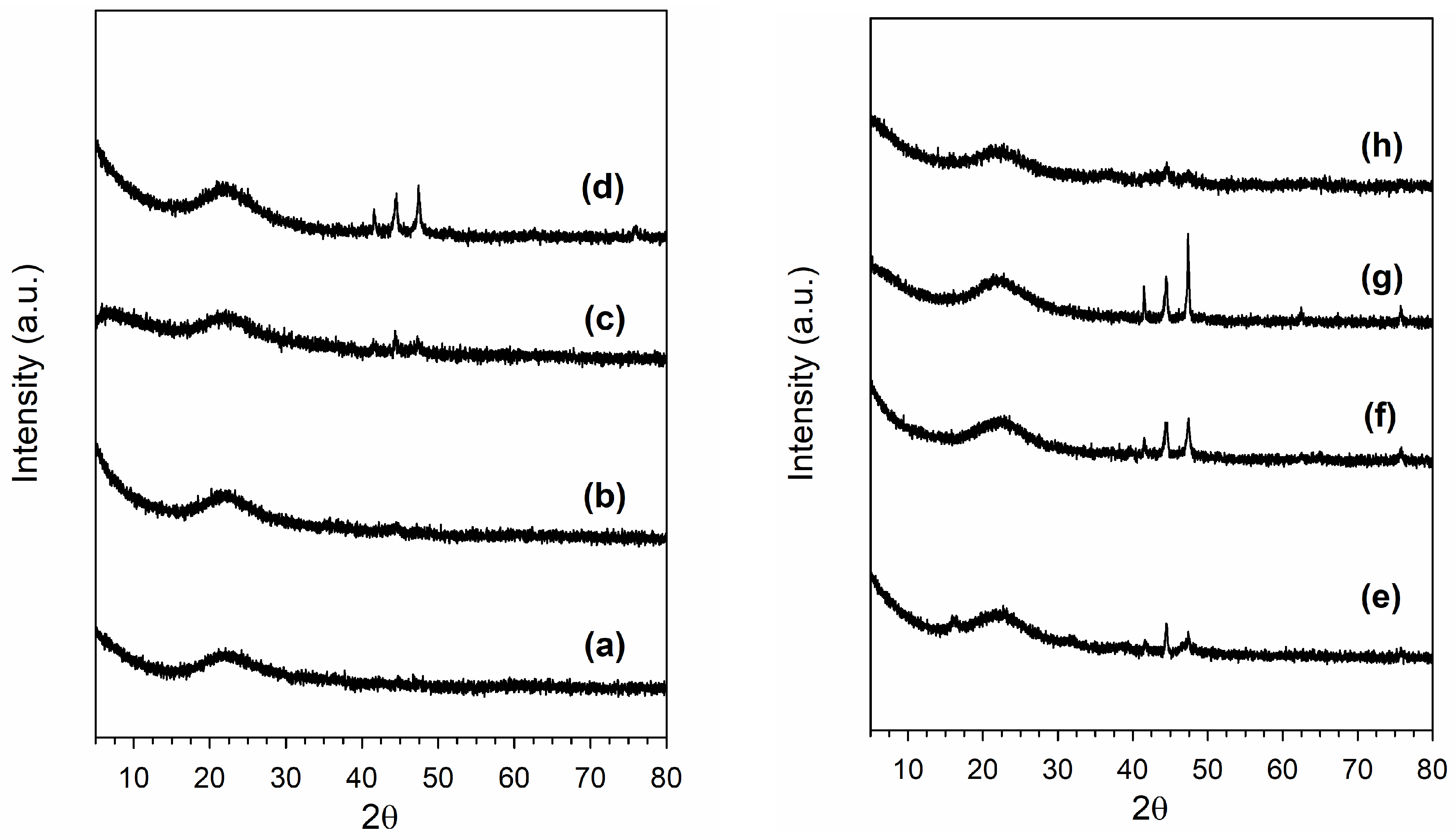
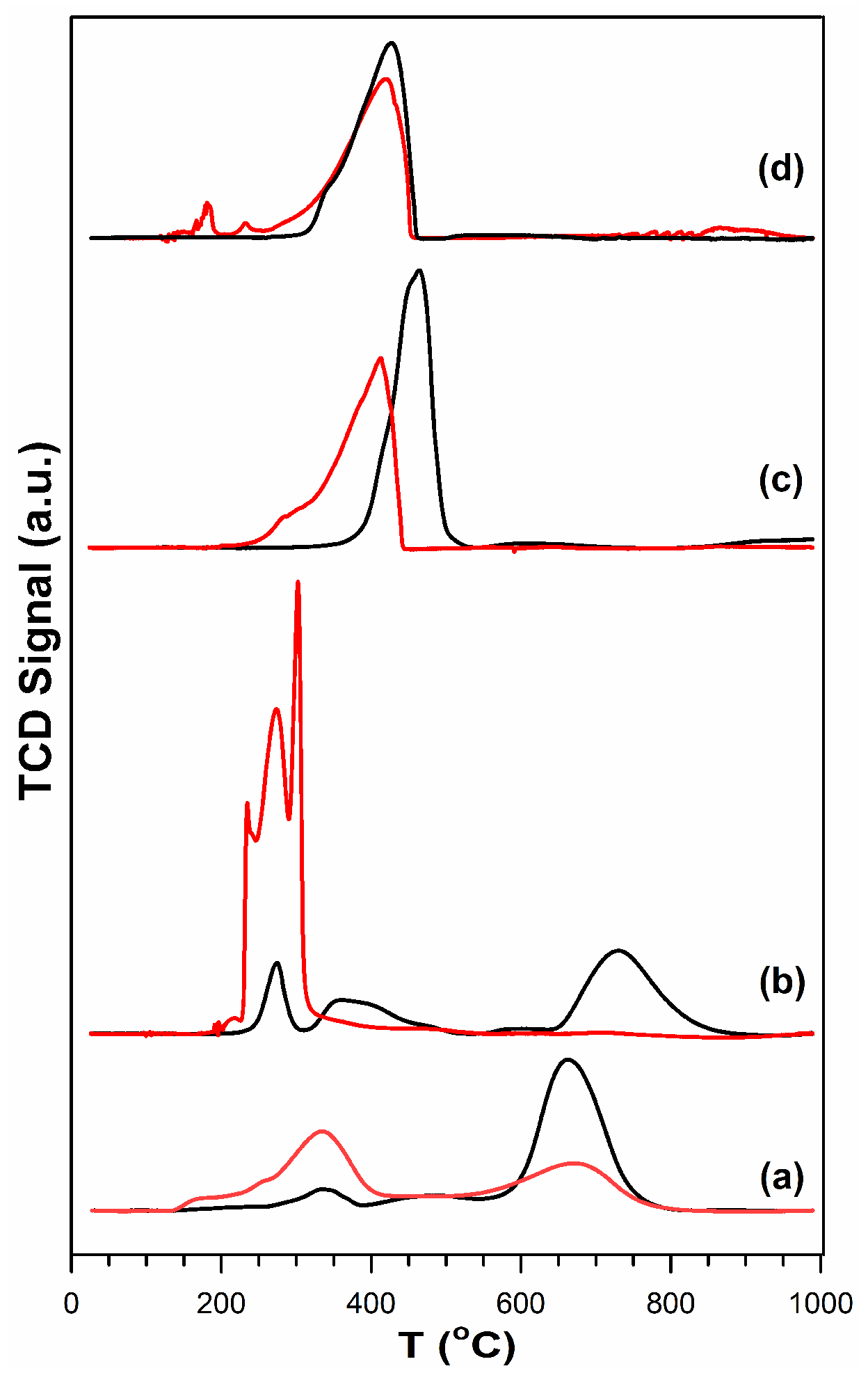









| Sample | Thermal Treatment | As (BET) (m2/g) | Vp (BJH Ads) (cm3/g) | Average Dp (BJH Ads) (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Air-calcined | 349 | 2.64 | 35.1 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | Uncalcined | 160 | 0.64 | 16.2 |
| Reduced | 256 | 1.01 | 16.4 | |
| Air-calcined | 244 | 1.09 | 19.3 | |
| Air-calcined/reduced | 247 | 1.10 | 19.2 | |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | Uncalcined | 148 | 0.59 | 16.2 |
| Reduced | 273 | 1.15 | 17.8 | |
| Air-calcined | 242 | 1.05 | 18.5 | |
| Air-calcined/reduced | 248 | 1.08 | 18.8 | |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | Uncalcined | 207 | 0.91 | 21.1 |
| Reduced | 287 | 1.43 | 22.2 | |
| Air-calcined | 250 | 1.28 | 22.6 | |
| Air-calcined/reduced | 285 | 1.57 | 24.3 | |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | Uncalcined | 192 | 0.87 | 19.6 |
| Reduced | 265 | 1.07 | 17.6 | |
| Air-calcined | 257 | 1.12 | 19.2 | |
| Air-calcined/reduced | 284 | 1.29 | 19.7 |
| Sample Description | Calcination | N Co-Co Metal | R Co-Co (Å) Metal | e0 (eV) | σ2 (Å2) | r-Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co0 foil | - | 12 ** | 2.489 (0.010) | 6.34 (1.28) | 0.00804 (0.00062) | 0.019 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | Yes | 9.0 (0.42) | 2.491 (0.0036) | −3.54 (0.470) | 0.00736 (0.00052) | 0.0018 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | No | 9.3 (0.44) | 2.487 (0.0037) | −4.15 (0.486) | 0.00674 (0.00052) | 0.0018 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | No | 8.6 (0.82) | 2.514 (0.0083) | −3.20 (0.916) | 0.0135 (0.00125) | 0.0066 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | Yes | 9.3 (0.42) | 2.488 (0.0035) | −2.41 (0.461) | 0.00611 (0.00049) | 0.0017 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | No | 9.0 (0.41) | 2.487 (0.0035) | −2.93 (0.467) | 0.00580 (0.00049) | 0.0018 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | No | 9.6 (0.37) | 2.489 (0.0029) | 6.23 (0.368) | 0.00707 (0.00043) | 0.0012 |
| Catalyst | Calcined? | H2 Desorbed per g cat (μmol/gcat) | Uncorr. % Disp. | Uncorr. Average Cluster Diam. (nm) | % Red. | Corr. % Disp. | Corr. AverageCluster Diam. (nm) | Average Est’d Domain Diam. from XRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | Yes | 16.3 | 1.56 | 66.4 | 18.1 | 8.6 | 12.0 | 17.8 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | No | 4.4 | 0.57 | 180.9 | 9.1 | 6.3 | 16.6 | 21.6 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | Yes | 49.5 | 4.74 | 21.9 | 35.9 | 13.2 | 7.8 | 7.2 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt acetate | No | 21.4 | 2.80 | 37.1 | 52.1 | 5.5 | 19.5 | 19.2 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | Yes | ** | - | - | 18.6 | - | - | 31.7 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | No | ** | - | - | 56.0 | - | - | 33.1 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | Yes | 3.3 | 0.31 | 334 | 54.6 | 0.6 | 182.2 | 24.0 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from cobalt chloride | No | 6.2 | 0.79 | 153 | 57.7 | 1.3 | 85.8 | 30.2 |
| Catalyst | Calcined? | Co0 HCP (100) Position (2θ in °) | Co0 (100) Average Crystallite Domain Diameter (nm) | * Co0 HCP (002) Position (2θ in °) | Co0 (002) Average Crystallite Domain Diameter (nm) | Co0 HCP (101) Position (2θ in °) | Co0 (101) Average Crystallite Domain Diameter (nm) | Average Crystallite Diameter from the 3 Peaks (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Acetate | Yes | - | - | 44.71 | 17.8 | - | - | - |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Acetate | Yes | - | - | 44.65 | 7.2 | - | - | - |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Acetate | No | 41.62 | 18.7 | 44.32 | 19.4 | 47.31 | 26.8 | 21.6 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 Cobalt Acetate | No | 41.58 | 22.1 | 44.47 | 14.7 | 47.43 | 20.8 | 19.2 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Chloride | Yes | 41.62 | 33.0 | 44.48 | 29.5 | 47.51 | 32.7 | 31.7 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Chloride | Yes | 41.54 | 31.9 | 44.52 | 19.9 | 47.41 | 20.3 | 24.0 |
| 12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Chloride | No | 41.50 | 45.6 | 44.49 | 21.4 | 47.38 | 32.3 | 33.1 |
| 0.5% Pt-12% Co/SiO2 from Cobalt Chloride | No | 41.76 | 26.8 | 44.47 | 28.3 | 47.43 | 35.6 | 30.2 |
| Catalyst | CO Conversion [%] | Selectivity [%] | α for C10-C17 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2-C4 | C5+ | CO2 | |||
| Co/SiO2 Nitrate calcined | 48.2 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 81.4 | 1.1 | - |
| Pt-Co/SiO2 Nitrate uncalcined | 48.9 | 8.0 | 10.2 | 81.5 | 0.3 | 0.792 |
| Pt-Co/SiO2 Nitrate calcined | 45.4 | 8.5 | 10.1 | 80.5 | 0.9 | 0.789 |
| Pt-Co/SiO2 Acetate uncalcined | 45.1 | 13.5 | 25.2 | 58.7 | 2.5 | 0.693 |
| Pt-Co/SiO2 Acetate calcined | 47.1 | 12.6 | 19.6 | 65.9 | 1.9 | 0.766 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehrbod, M.; Martinelli, M.; Watson, C.D.; Cronauer, D.C.; Kropf, A.J.; Jacobs, G. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: The Characterization and Testing of Pt-Co/SiO2 Catalysts Prepared with Alternative Cobalt Precursors. Reactions 2021, 2, 129-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions2020011
Mehrbod M, Martinelli M, Watson CD, Cronauer DC, Kropf AJ, Jacobs G. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: The Characterization and Testing of Pt-Co/SiO2 Catalysts Prepared with Alternative Cobalt Precursors. Reactions. 2021; 2(2):129-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions2020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehrbod, Mohammad, Michela Martinelli, Caleb D. Watson, Donald C. Cronauer, A. Jeremy Kropf, and Gary Jacobs. 2021. "Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: The Characterization and Testing of Pt-Co/SiO2 Catalysts Prepared with Alternative Cobalt Precursors" Reactions 2, no. 2: 129-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions2020011
APA StyleMehrbod, M., Martinelli, M., Watson, C. D., Cronauer, D. C., Kropf, A. J., & Jacobs, G. (2021). Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: The Characterization and Testing of Pt-Co/SiO2 Catalysts Prepared with Alternative Cobalt Precursors. Reactions, 2(2), 129-160. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions2020011









