Influence of Paddle Parameters on Particle Conveying and Mixing in an Organic Fertilizer Continuous Conveying Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
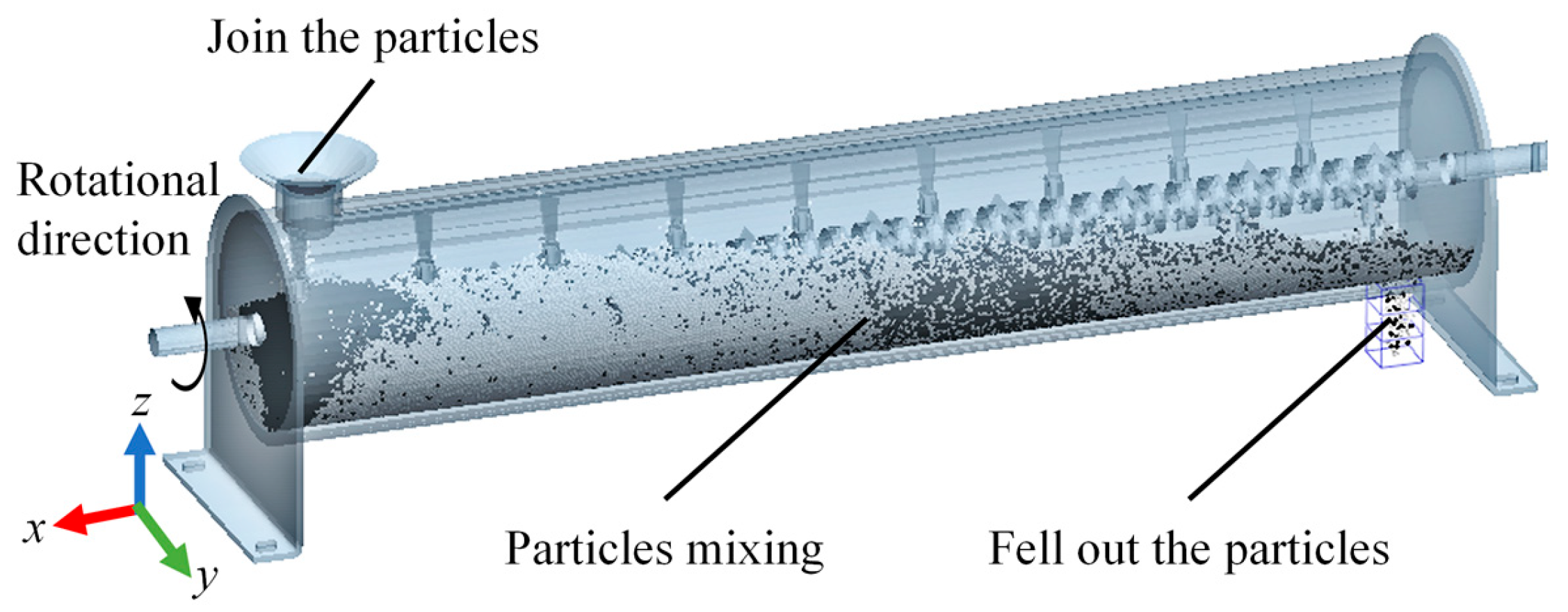
2. Working Principle and Structural Design
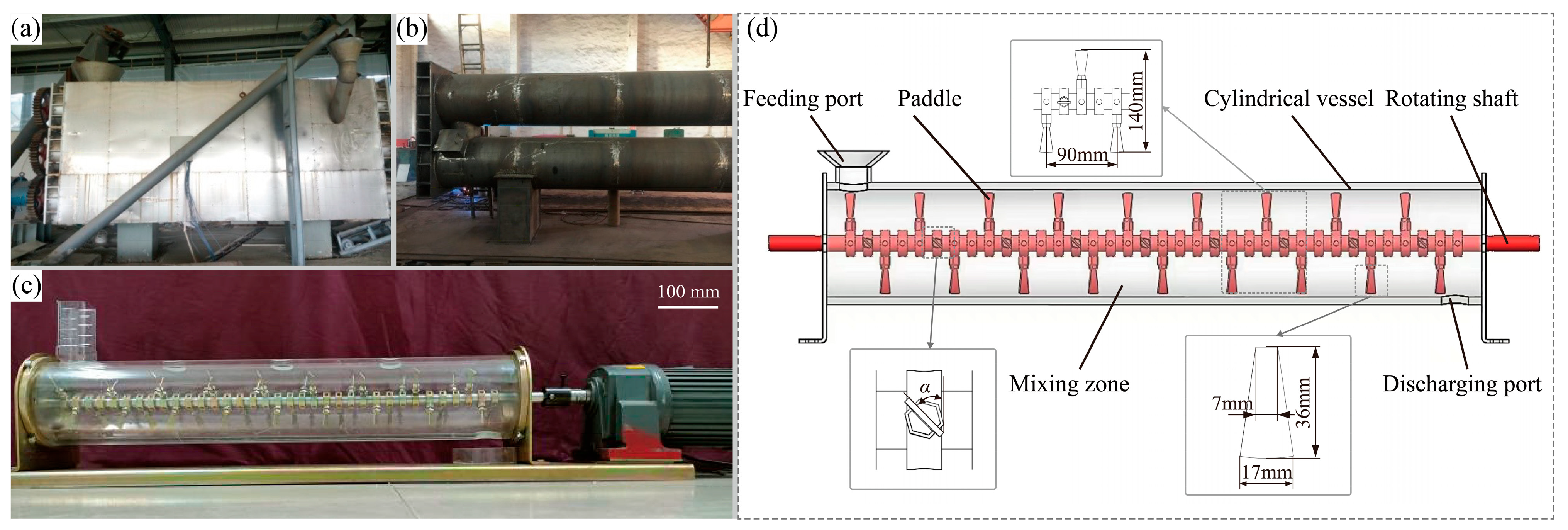
2.1. Geometry and Paddle Structure
2.2. Discrete Element Method (DEM) Model and Parameters
2.3. DEM
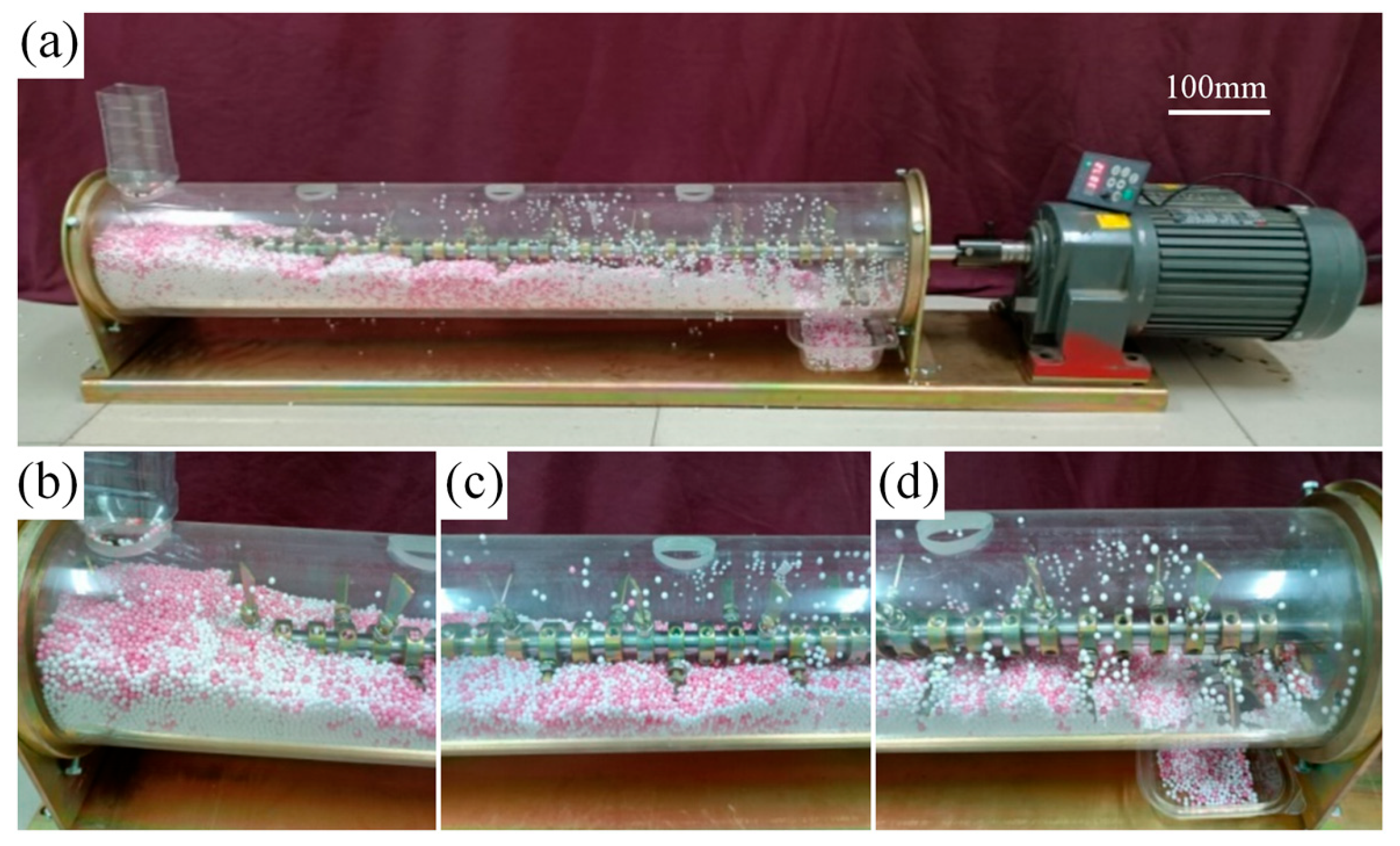
2.4. Validation of the DEM Model
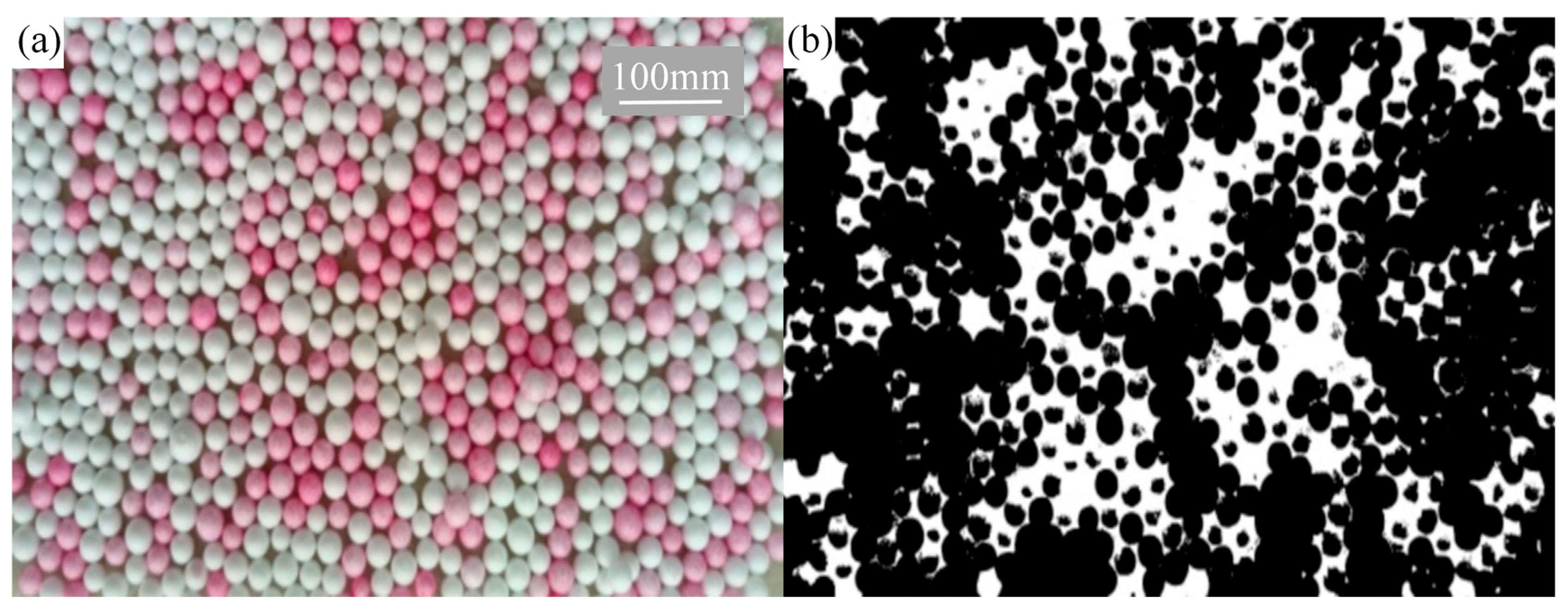
2.5. Expression Method of Mixing Uniformity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DEM Model Verification
3.2. Mixing Performance
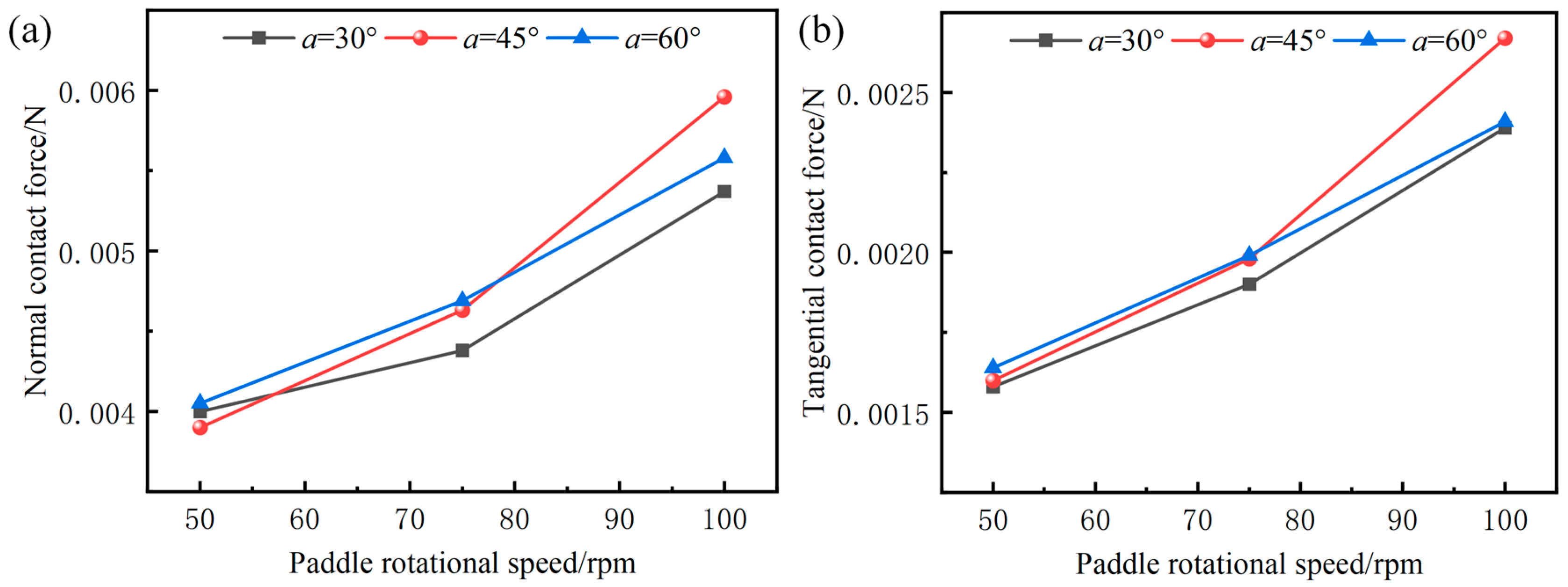
3.3. Average Contact Forces
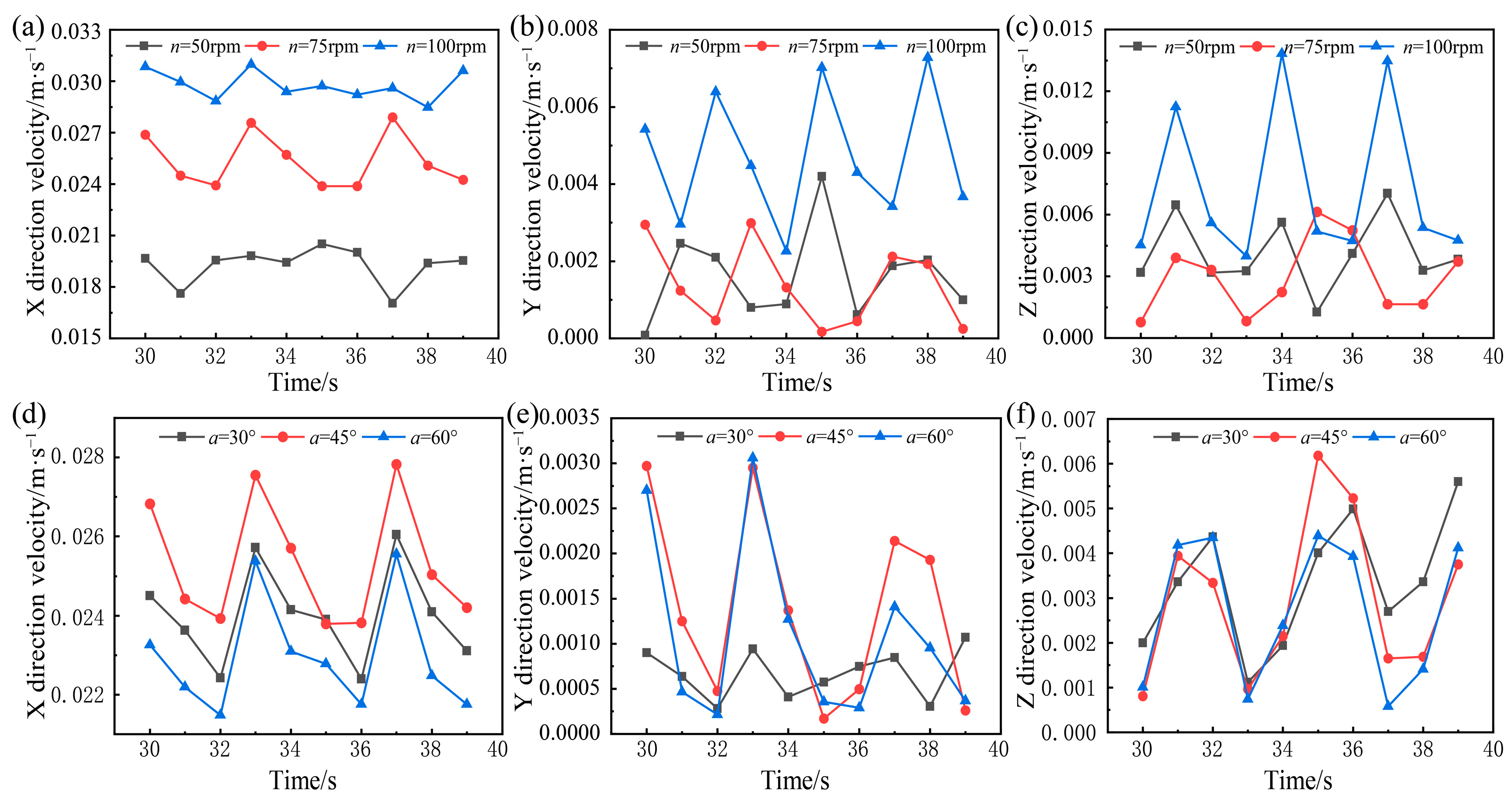
3.4. Particle Velocity
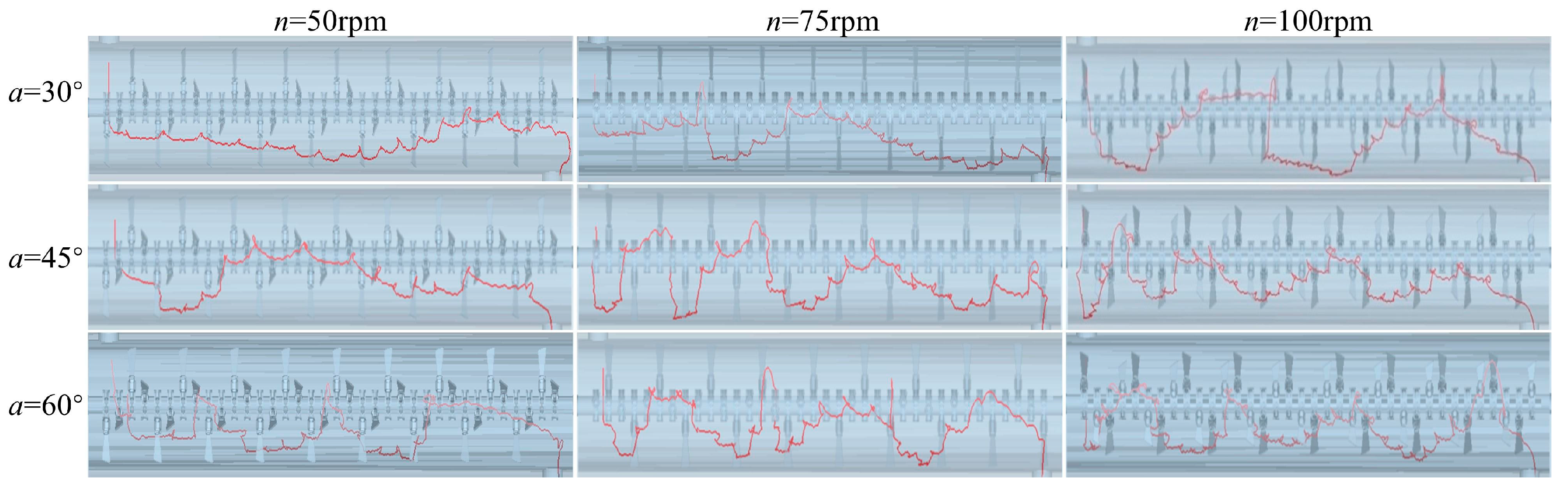
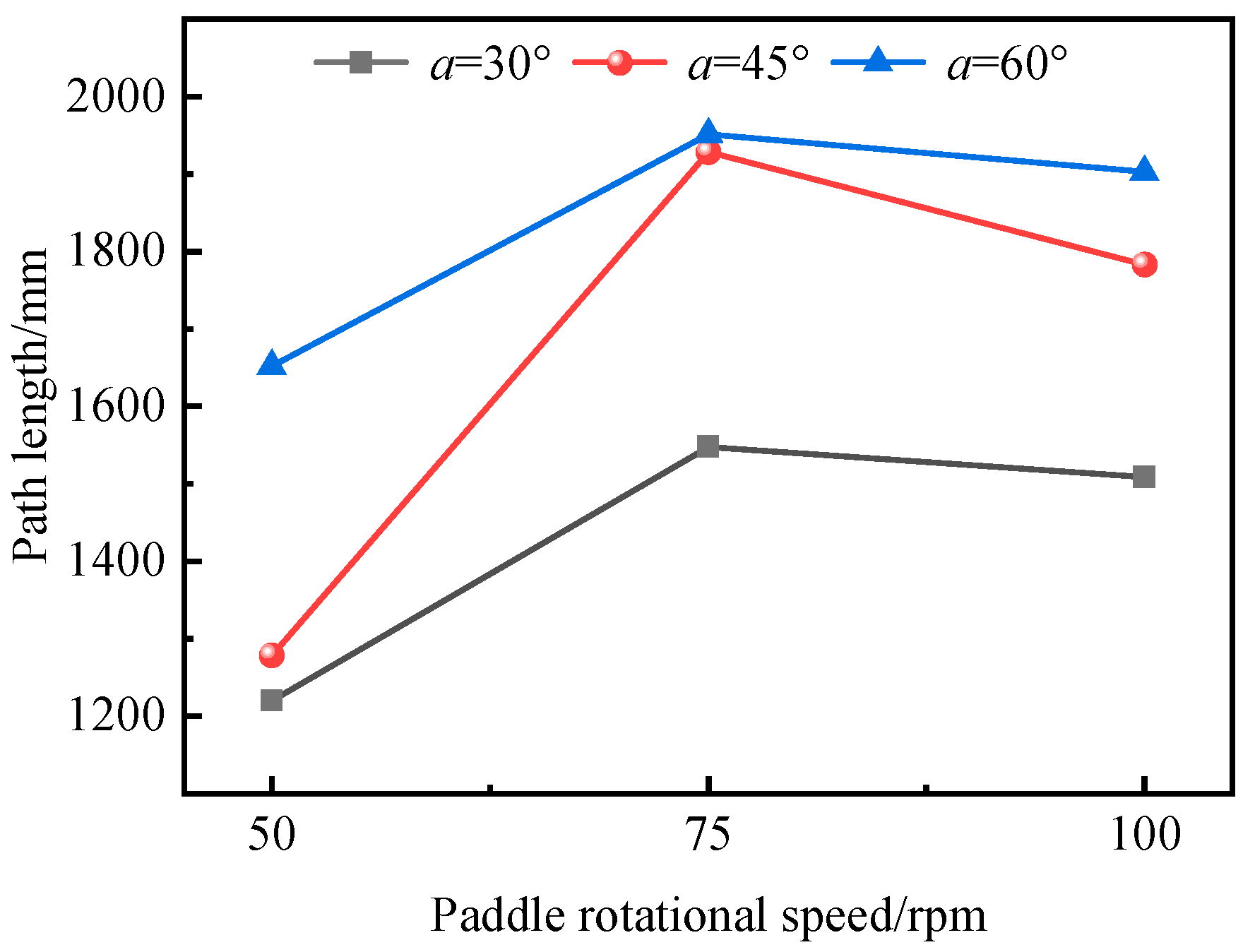
3.5. Particle Trajectory
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makan, A.; Fadili, A. Sustainability assessment of large-scale composting technologies using PROMETHEE method. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Aborisade, M.A.; Liu, S.; Lu, S.; Oba, B.T.; Xu, X.; Cheng, X.; He, M.; Song, Y.; Ding, H. The history and prediction of composting technology: A patent mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, N.; Lin, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Ding, G.; Xu, T.; Li, J. Recycling of nutrients from organic waste by advanced compost technology—A case study. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, X. Composting process and odor emission varied in windrow and trough composting system under different air humidity conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.H.; Bai, Z.H.; Chadwick, D.; Misselbrook, T.; Ma, L. The progress of composting technologies from static heap to intelligent reactor: Benefits and limitations. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Bai, Z.H.; Ma, L. Advanced composting technologies promotes environmental benefits and eco-efficiency: A life cycle assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Wu, Y.Q. Hyperthermophilic Composting Technology for Organic Solid Waste Treatment: Recent Research Advances and Trends. Processes 2021, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosou, F.; Kekes, T.; Boukouvalas, C. Life Cycle Assessment of the Canned Fruits Industry: Sustainability through Waste Valorization and Implementation of Innovative Techniques. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullakasim, W.; Khongman, K.; Sukcharoenvipharat, W.; Usaborisut, P. Development and Performance Testing of a Combined Cultivating Implement and Organic Fertilizer Applicator for Sugarcane Ratooning. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, K.L.; Zhang, L.F. Design and Testing of a Small-Scale Composting Facility for Sheep Manure Utilizing Aeration and Thermal Treatment. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, X. Concurrent aerobic methane oxidation and biodegradation of waste in shallow layer of landfill during aeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finore, I.; Feola, A.; Russo, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Di Donato, P.; Nicolaus, B.; Poli, A.; Romano, I. Thermophilic bacteria and their thermozymes in composting processes: A review. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Sui, B.; Meng, H.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Kuang, C. Design and performance test of aerobic fermentation rotary reactor pilot plant for biogas residue. Trans. CSAE 2018, 34, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, T.; Li, N.; Qi, Y.; Si, F.; Yang, B. Effect of Induced Mixing on Bacterial Community Structure and Metabolic Activity in Reservoir. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 2624–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Wang, B.; Tang, C.-J.; Chen, G.-H.; Wu, D. Elucidating the effect of mixing technologies on dynamics of microbial communities and their correlations with granular sludge properties in a high-rate sulfidogenic anaerobic bioreactor for saline wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minglani, D.; Sharma, A.; Pandey, H.; Dayal, R.; Joshi, J.B.; Subramaniam, S. A review of granular flow in screw feeders and conveyors. Powder Technol. 2020, 366, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadidi, B.; Ebrahimi, M.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Lohi, A. Mixing performance analysis of non-cohesive particles in a double paddle blender using DEM and experiments. Powder Technol. 2022, 397, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Yaraghi, A.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Lohi, A. The effect of impeller configurations on particle mixing in an agitated paddle mixer. Powder Technol. 2018, 332, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezo, M.; Pezo, L.; Jovanovic, A.P.; Terzic, A.; Andric, L.; Loncar, B.; Kojic, P. Discrete element model of particle transport and premixing action in modified screw conveyors. Powder Technol. 2018, 336, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezo, L.; Jovanovic, A.; Pezo, M.; Colovic, R.; Loncar, B. Modified screw conveyor-mixers—Discrete element modeling approach. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaraghi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Lohi, A. Mixing assessment of non-cohesive particles in a paddle mixer through experiments and discrete element method (DEM). Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Yaraghi, A.; Jadidi, B.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Lohi, A. Assessment of bi-disperse solid particles mixing in a horizontal paddle mixer through experiments and DEM. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, C.; Zhang, X. Design and experiment of solid organic fertilizer crushing and striping machines. Trans. CSAE 2023, 39, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Jiménez del Val, I.; Glassey, J.; Kavousi, F. Integration Approaches to Model Bioreactor Hydrodynamics and Cellular Kinetics for Advancing Bioprocess Optimisation. J. Bioeng. 2024, 11, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.C.; Xu, L.M.; Ma, S.; Niu, C.; Yan, C.G.; Zhao, S.J. The effect of paddle configurations on particle mixing in a soil-fertilizer continuous mixing device. Powder Technol. 2021, 391, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Z.; Chu, X.H.; Liu, Q.P. Effect of blade geometry on the powder spreading process in additive manufacturing. Particuology 2024, 94, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.S. DEM study of the effect of impeller design on mixing performance in a U-shape ribbon mixer. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Tong, Z.; Yang, D.; Hou, C. Design and performance experiment of multi-segment type auger in process of organic fertilizer production. Trans. CSAE 2018, 34, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Song, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, F.; Ma, H.; Ma, M. Simulative Calibration on Contact Parameters of Discrete Elements for Covering Soil on Whole Plastic Film Mulching on Double Ridges. Trans. CSAM 2019, 50, 49–56, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.P.; Gan, J.Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yu, A.B. Discrete particle simulation for mixing of granular materials in ribbon mixers: A scale-up study. Powder Technol. 2022, 400, 117222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Paddle Setting | Rotational Speed n/rpm | Paddle Angle α/° |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 30 |
| 2 | 50 | 45 |
| 3 | 50 | 60 |
| 4 | 75 | 30 |
| 5 | 75 | 45 |
| 6 | 75 | 60 |
| 7 | 100 | 30 |
| 8 | 100 | 45 |
| 9 | 100 | 60 |
| Input Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/mm | 3 |
| Particle density/(kg·m−3) | 1100 |
| Particle Poisson’s ratio | 0.4 |
| Particle shear modulus/Pa | 1.09 × 106 |
| Equipment material density/(kg·m−3) | 7 850 |
| Poisson ratio of equipment material | 0.3 |
| Shear modulus of equipment/Pa | 1.01 × 1010 |
| Coefficient of restitution between particles | 0.2 |
| Coefficient of static friction between particles | 0.4 |
| Coefficient of rolling friction between particles | 0.3 |
| Coefficient of restitution between particles and equipment | 0.3 |
| Coefficient of static friction between particles and equipment | 0.5 |
| Coefficient of rolling friction between particles and equipment | 0.4 |
| Time step/s | 4.77 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Zhao, R.; Pei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, P. Influence of Paddle Parameters on Particle Conveying and Mixing in an Organic Fertilizer Continuous Conveying Device. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7060184
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Tong Z, Zhao R, Pei Y, Chen Y, Zhou P. Influence of Paddle Parameters on Particle Conveying and Mixing in an Organic Fertilizer Continuous Conveying Device. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(6):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7060184
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiuli, Yinzhi Zhang, Zhenwei Tong, Renzhong Zhao, Yikun Pei, Yong Chen, and Peilin Zhou. 2025. "Influence of Paddle Parameters on Particle Conveying and Mixing in an Organic Fertilizer Continuous Conveying Device" AgriEngineering 7, no. 6: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7060184
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhang, Y., Tong, Z., Zhao, R., Pei, Y., Chen, Y., & Zhou, P. (2025). Influence of Paddle Parameters on Particle Conveying and Mixing in an Organic Fertilizer Continuous Conveying Device. AgriEngineering, 7(6), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7060184








