Image Prompt Adapter-Based Stable Diffusion for Enhanced Multi-Class Weed Generation and Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
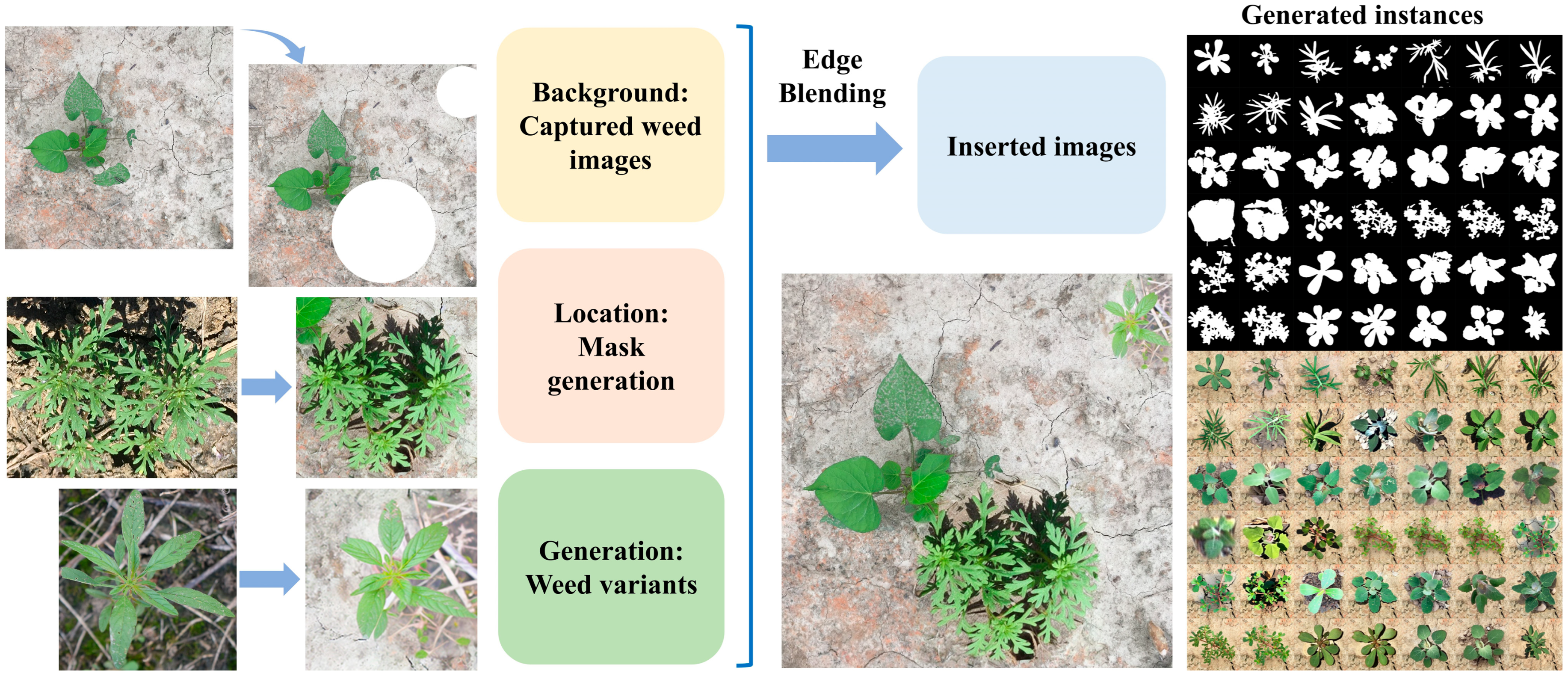
2.1. Dataset Curation
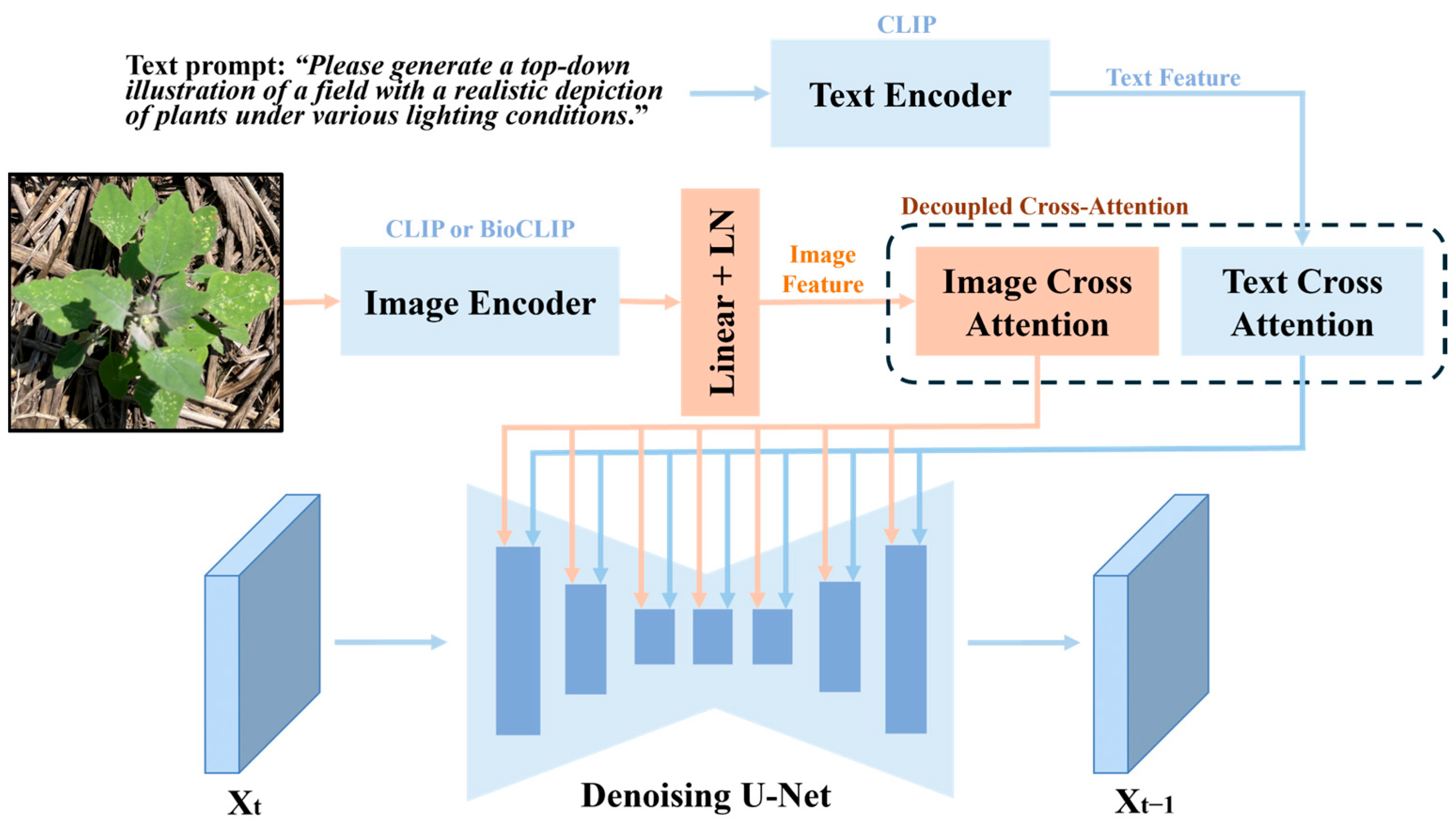
2.2. IP-Adapter-Based Stable Diffusion for Weed Generation
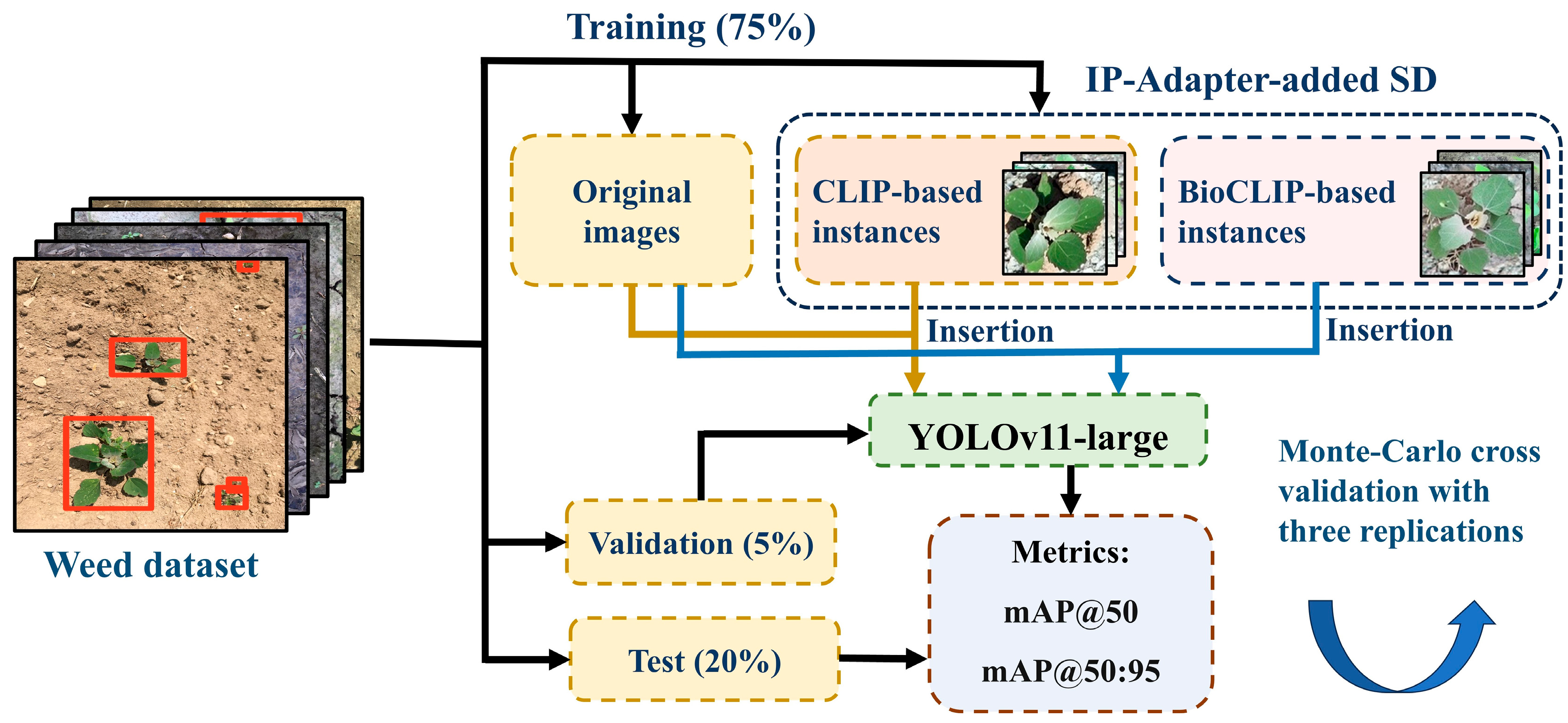
2.3. YOLOv11 for Weed Detection
2.4. Performance Metrics
3. Results
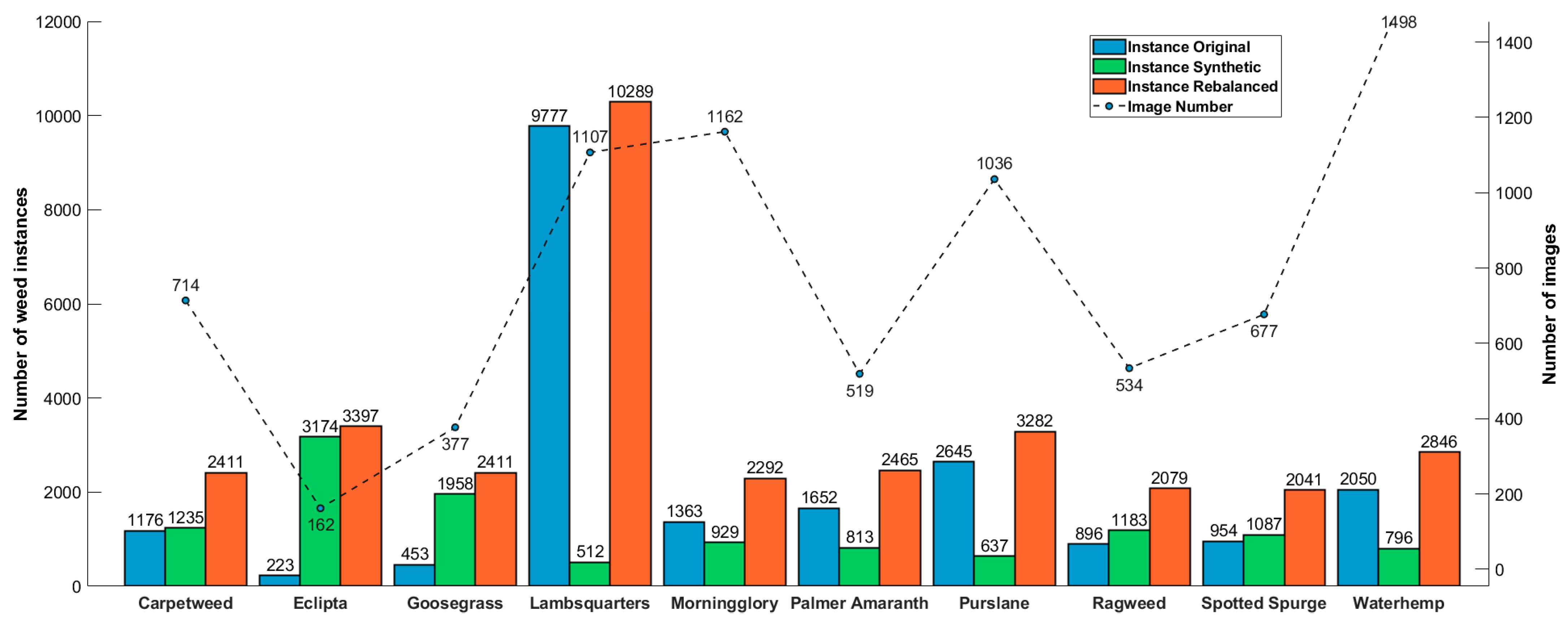
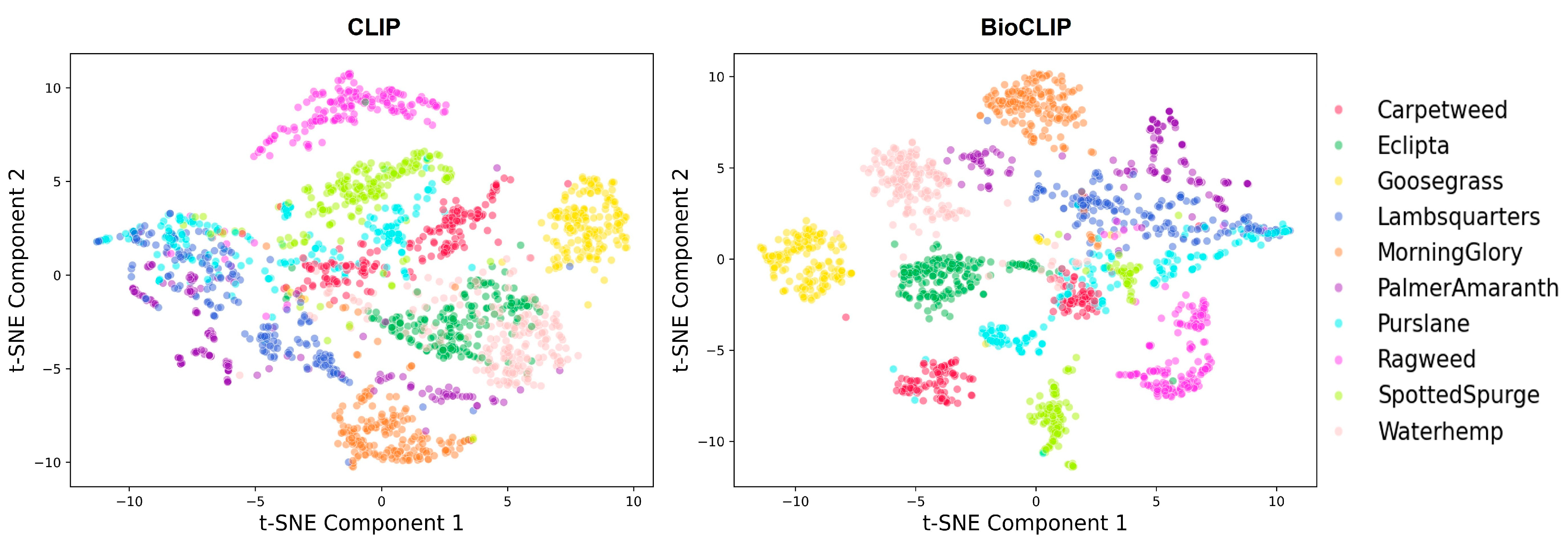
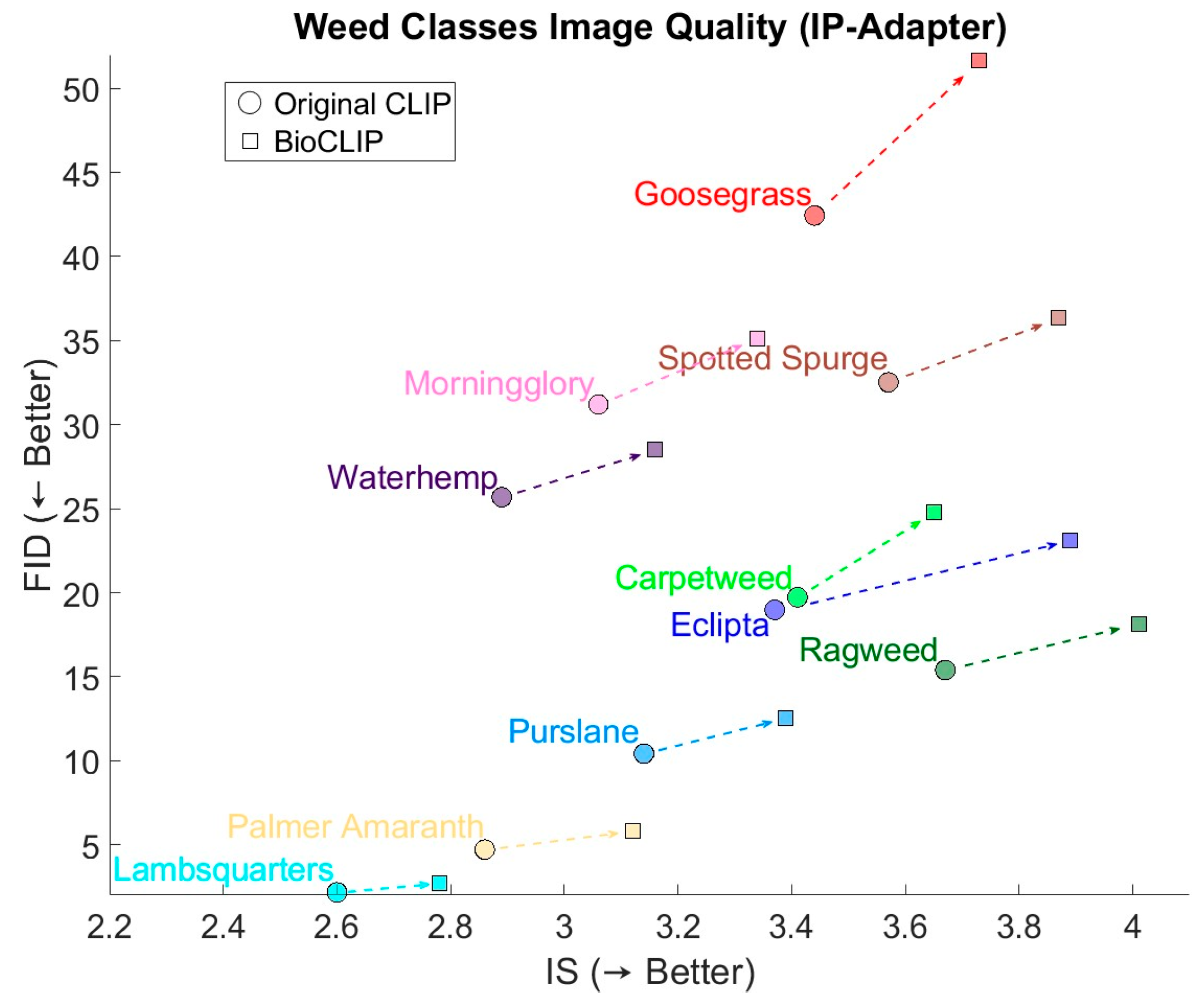
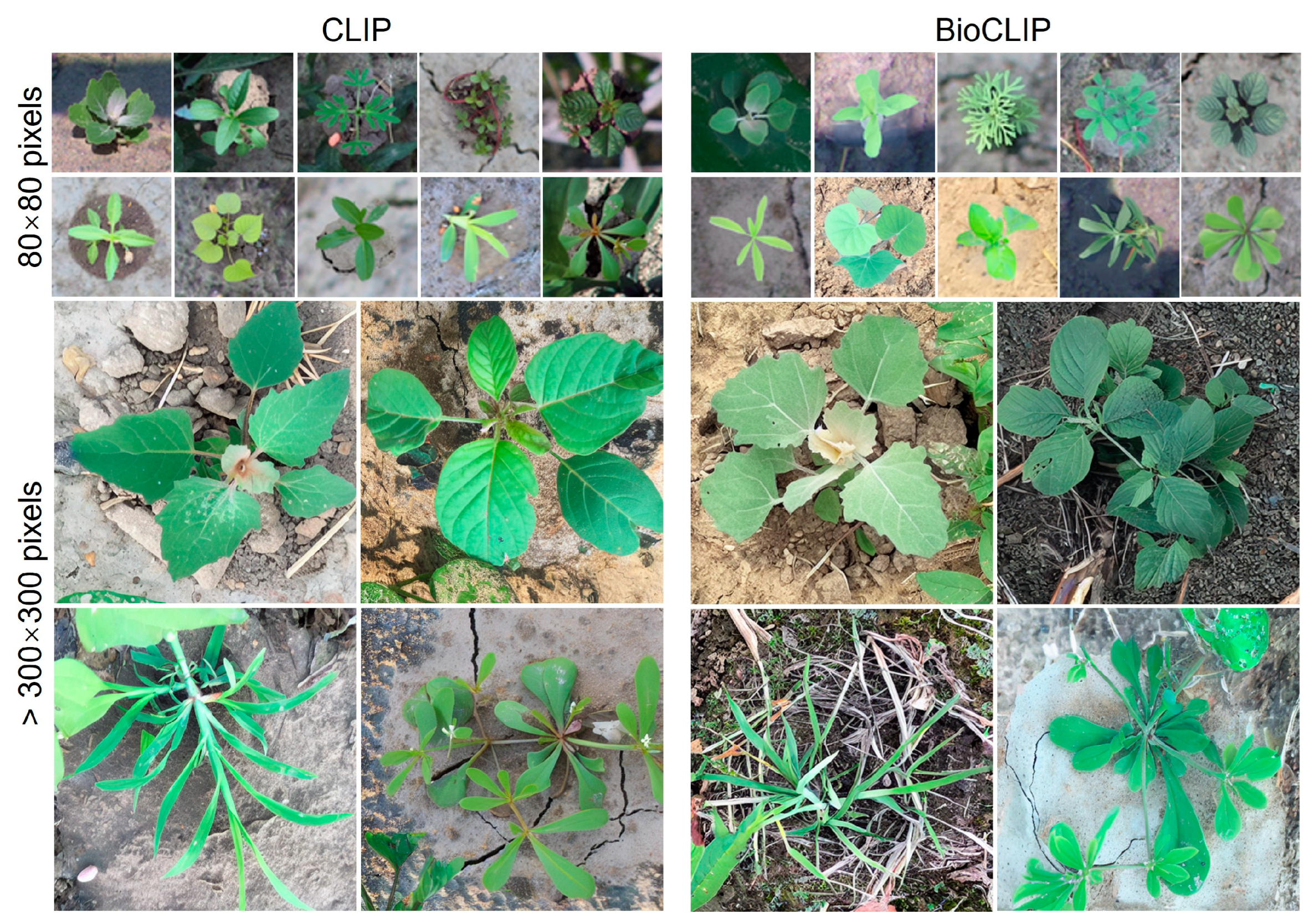
3.1. General Overall
3.2. Quality of Generated Weeds
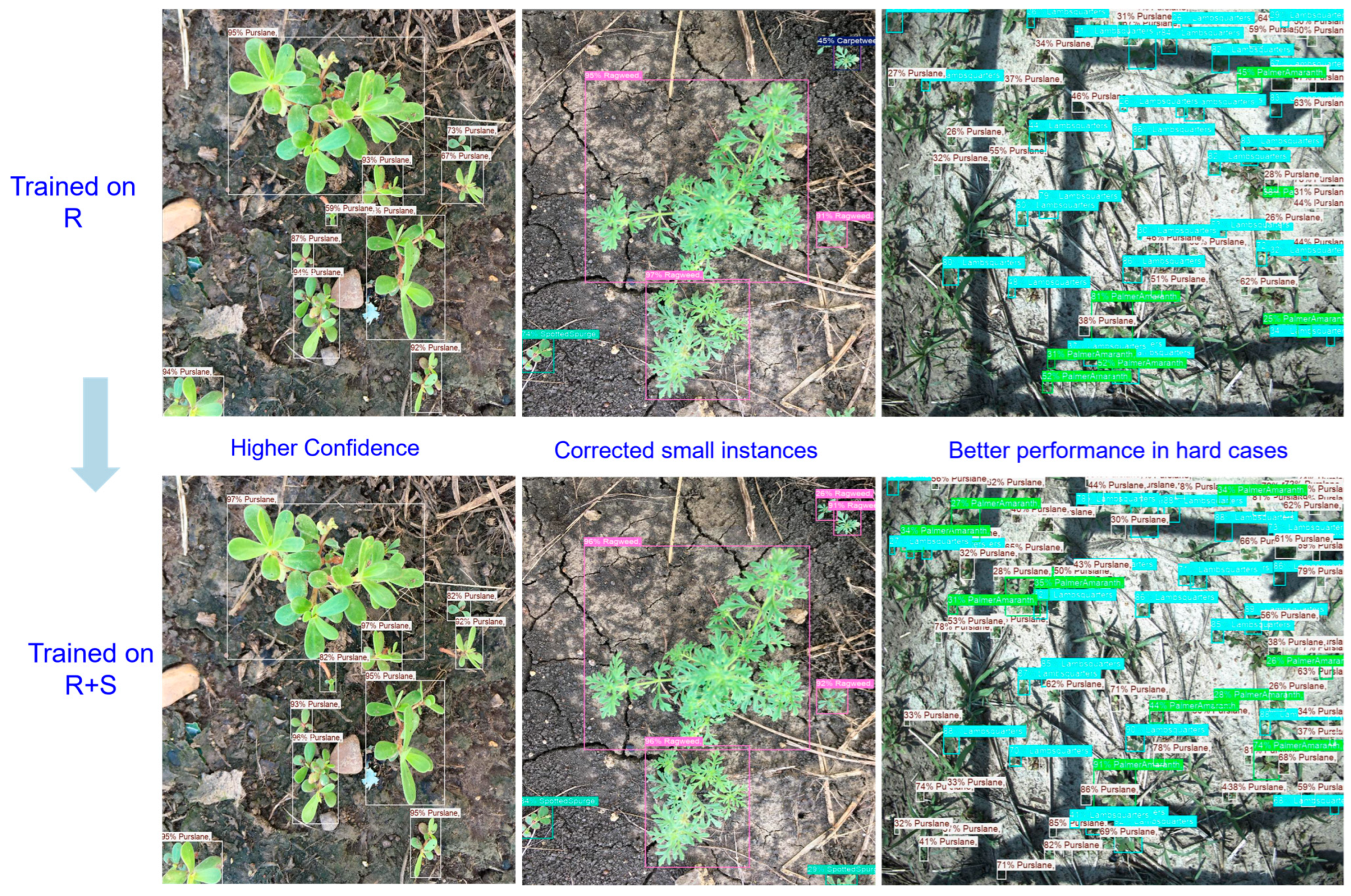
3.3. Weed Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oerke, E.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.S. Grand challenges in weed management. Front. Agron. 2020, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Crimaldi, M.; Cirillo, V.; Sarghini, F.; Maggio, A. Drone and sensor technology for sustainable weed management: A review. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Lach, L.; Zuniga, R.; Morrison, D. Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. BioScience 2000, 50, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Perspectives on transgenic, herbicide-resistant crops in the United States almost 20 years after introduction. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Délye, C.; Jasieniuk, M.; Le Corre, V. Deciphering the evolution of herbicide resistance in weeds. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. 2025. Available online: www.weedscience.org (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Heap, I.; Duke, S.O. Overview of glyphosate-resistant weeds worldwide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.H.; Charudattan, R.; Duke, S.O.; Fennimore, S.A.; Marrone, P.; Slaughter, D.C.; Swanton, C.; Zollinger, R. Weed management in 2050: Perspectives on the future of weed science. Weed Sci. 2018, 66, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhards, R.; Andujar Sanchez, D.; Hamouz, P.; Peteinatos, G.G.; Christensen, S.; Fernandez-Quintanilla, C. Advances in site-specific weed management in agriculture—A review. Weed Res. 2022, 62, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Sunil, G.C.; Zhang, Y.; Koparan, C.; Sun, X. Development and evaluation of a machine vision and deep learning-based smart sprayer system for site-specific weed management in row crops: An edge computing approach. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Lu, Y.; Brainard, D. Improvements and evaluation of a smart sprayer prototype for weed control in vegetable crops. In 2025 ASABE Annual International Meeting Paper No. 2500549; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machleb, J.; Peteinatos, G.G.; Kollenda, B.L.; Andújar, D.; Gerhards, R. Sensor-based mechanical weed control: Present state and prospects. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 176, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Qu, M.; Wang, G.; Ma, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Qi, J.; Gao, X.; Li, H.; Jia, H. Crop detection technologies, mechanical weeding executive parts and working performance of intelligent mechanical weeding: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1361002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseen, M.U.; Long, J.M. Laser weeding technology in cropping systems: A comprehensive review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lati, R.N.; Siemens, M.C.; Rachuy, J.S.; Fennimore, S.A. Intrarow weed removal in broccoli and transplanted lettuce with an intelligent cultivator. Weed Technol. 2016, 30, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, D.G.; Kamath, R.; Balachandra, M. Deep learning techniques for weed detection in agricultural environments: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 113193–113214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Young, S. A survey of public datasets for computer vision tasks in precision agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J. Weed database development: An updated survey of public weed datasets and cross-season weed detection adaptation. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, D.; Olaniyi, E.; Huang, Y. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) for image augmentation in agriculture: A systematic review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, G.; Singh, A. Generative AI in vision: A survey on models, metrics and applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Hong, S.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cui, B.; Yang, M.H. Diffusion models: A comprehensive survey of methods and applications. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, M. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with clip latents. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, F.A.; Hondru, V.; Ionescu, R.T.; Shah, M. Diffusion models in vision: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10850–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S. Low-Rank Adaptation for Fast Text-To-Image Diffusion Fine-Tuning, version 0.0.1; [Computer software]; 2023. GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/cloneofsimo/lora (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Ruiz, N.; Li, Y.; Jampani, V.; Pritch, Y.; Rubinstein, M.; Aberman, K. Dreambooth: Fine tuning text-to-image diffusion models for subject-driven generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22500–22510. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Rao, A.; Agrawala, M. Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3836–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, C.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Z.; Shan, Y. T2i-adapter: Learning adapters to dig out more controllable ability for text-to-image diffusion models. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2024, 38, 4296–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Yang, W. IP-Adapter: Text compatible image prompt adapter for text-to-image diffusion models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.06721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; Volume 139, pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, H.; Gómez, A.; Altares-López, S.; Ribeiro, A.; Andújar, D. Analysis of stable diffusion-derived fake weeds performance for training convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 214, 108324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Lu, Y. Weed image augmentation by ControlNet-added stable diffusion for multi-class weed detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. 3SeasonWeedDet10: A three-season, 10-class dataset for benchmarking AI models for robust weed detection [Data set]. Zenodo 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. CottonWeedDet12: A 12-class weed dataset of cotton production systems for benchmarking AI models for weed detection [Data set]. Zenodo 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.; Chen, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z. YOLOWeeds: A novel benchmark of YOLO object detectors for multi-class weed detection in cotton production systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.; Wu, J.; Thompson, M.J.; Campolongo, E.G.; Song, C.H.; Carlyn, D.E.; Dong, L.; Dahdul, W.M.; Stewart, C.; Berger-Wolf, T.; et al. Bioclip: A vision foundation model for the tree of life. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 19412–19424. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLO by Ultralytics, Version 11.0.0; [Computer Software]; 2024. GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved techniques for training GANs. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Dowson, D.C.; Landau, B. The Fréchet distance between multivariate normal distributions. J. Multivar. Anal. 1982, 12, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Roweis, S. Stochastic neighbor embedding. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 December 2002; pp. 857–864. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasumana, S.; Ramalingam, S.; Veit, A.; Glasner, D.; Chakrabarti, A.; Kumar, S. Rethinking fid: Towards a better evaluation metric for image generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 9307–9315. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, R.; Park, J.; Shechtman, E.; Paris, S.; Park, T. Scaling up gans for text-to-image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 10124–10134. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.; Gokaslan, A.; Kuleshov, V.; Tompkin, J. The gan is dead; long live the gan! a modern gan baseline. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 44177–44215. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Raj, B.; Liu, Z.; Barsoum, E. Softvq-vae: Efficient 1-dimensional continuous tokenizer. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–12 June 2025; pp. 28358–28370. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, T.; KS, U.R.; Naik, S.M.; Panja, M.; Manvitha, B. Ten years of generative adversarial nets (GANs): A survey of the state-of-the-art. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2024, 5, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Z.; Peng, X. Artificial-intelligence-generated content with diffusion models: A literature review. Mathematics 2024, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. Computer Vision—ECCV 2014. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatriain, X. Prompt design and engineering: Introduction and advanced methods. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.14423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Feng, Q.; Chen, H.; Dai, Q.; Hu, H.; Xu, H.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.G. A survey on video diffusion models. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 57, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatkal, N.R.; Nalawade, S.M.; Shelke, M.S.; Sahni, R.K.; Walunj, A.A.; Kadam, P.B.; Ali, M. Review of cutting-edge weed management strategy in agricultural systems. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2025, 18, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FarmWise. Titan: AI-Powered Mechanical Weeding Robot. 2021. Available online: https://farmwise.io/ (accessed on 14 November 2025).
- Patel, D.; Gandhi, M.; Shankaranarayanan, H.; Darji, A.D. Design of an autonomous agriculture robot for real-time weed detection using CNN. In Advances in VLSI and Embedded Systems; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Darji, A.D., Joshi, D., Joshi, A., Sheriff, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Weed Classes | R Only | R+CP (0.5) | R+CP (1.0) | R+S (CLIP) | R+S (BioCLIP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carpetweed | 80.83% | 81.77% | 81.67% | 82.17% | 81.83% |
| Eclipta | 92.63% | 92.67% | 90.13% | 93.87% | 92.77% |
| Goosegrass | 91.20% | 91.80% | 91.10% | 92.63% | 91.10% |
| Lambsquarters | 77.37% | 77.97% | 78.27% | 78.93% | 79.00% |
| Morningglory | 92.67% | 93.23% | 93.60% | 94.27% | 94.07% |
| Palmer Amaranth | 89.17% | 89.10% | 89.37% | 89.70% | 89.30% |
| Purslane | 75.7% | 76.17% | 76.87% | 77.30% | 77.47% |
| Ragweed | 86.27% | 87.03% | 87.6% | 88.13% | 88.13% |
| Spotted Spurge | 87.63% | 88.73% | 89.1% | 88.70% | 89.37% |
| Waterhemp | 94.30% | 94.63% | 94.80% | 94.77% | 94.27% |
| Total | 86.77% | 87.30% | 87.27% | 88.03% | 87.90% |
| Weed Classes | R Only | R+CP (0.5) | R+CP (1.0) | R+S (CLIP) | R+S (BioCLIP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carpetweed | 90.60% | 91.30% | 91.53% | 91.80% | 91.30% |
| Eclipta | 96.17% | 95.77% | 94.43% | 96.4% | 96.27% |
| Goosegrass | 95.37% | 95.77% | 95.8% | 96.4% | 95.77% |
| Lambsquarters | 93.57% | 93.83% | 93.97% | 94.2% | 94.23% |
| Morningglory | 97.90% | 98.00% | 97.93% | 97.97% | 98.03% |
| Palmer Amaranth | 96.97% | 97.07% | 97.23% | 97.27% | 96.87% |
| Purslane | 89.63% | 90.30% | 89.73% | 90.33% | 90.53% |
| Ragweed | 94.57% | 95.07% | 95.23% | 95.70% | 95.60% |
| Spotted Spurge | 95.33% | 95.7% | 95.47% | 95.23% | 95.60% |
| Waterhemp | 97.63% | 97.70% | 97.73% | 97.80% | 97.37% |
| Total | 94.80% | 95.10% | 94.90% | 95.30% | 95.17% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, B.; Lu, Y. Image Prompt Adapter-Based Stable Diffusion for Enhanced Multi-Class Weed Generation and Detection. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7110389
Deng B, Lu Y. Image Prompt Adapter-Based Stable Diffusion for Enhanced Multi-Class Weed Generation and Detection. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(11):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7110389
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Boyang, and Yuzhen Lu. 2025. "Image Prompt Adapter-Based Stable Diffusion for Enhanced Multi-Class Weed Generation and Detection" AgriEngineering 7, no. 11: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7110389
APA StyleDeng, B., & Lu, Y. (2025). Image Prompt Adapter-Based Stable Diffusion for Enhanced Multi-Class Weed Generation and Detection. AgriEngineering, 7(11), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7110389






