Improved Collision Avoidance Algorithm of Autonomous Rice Transplanter Based on Virtual Goal Point
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modification of Artificial Potential Field Method
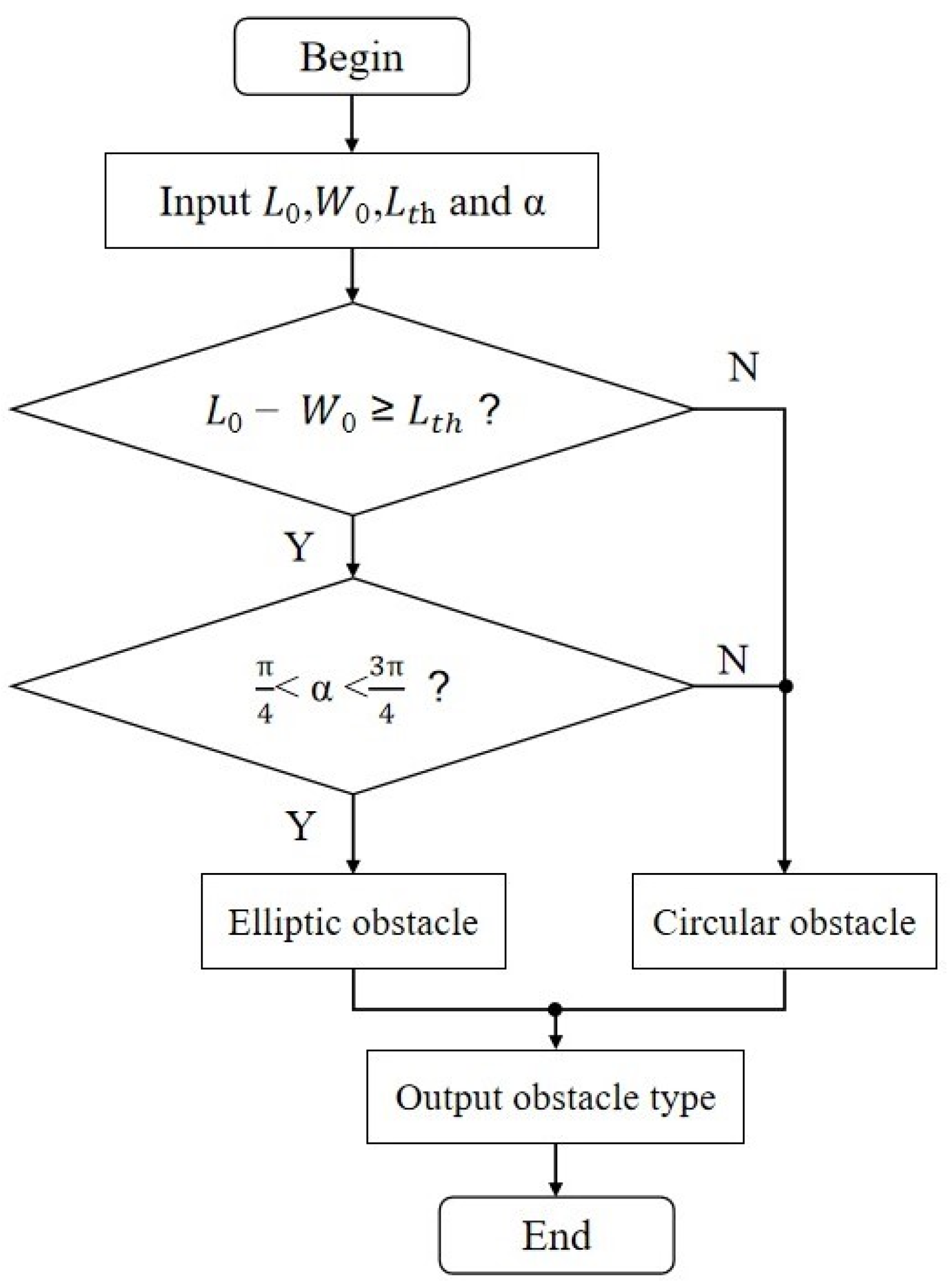
2.1.1. Modification of Repulsive Force Field of Obstacles
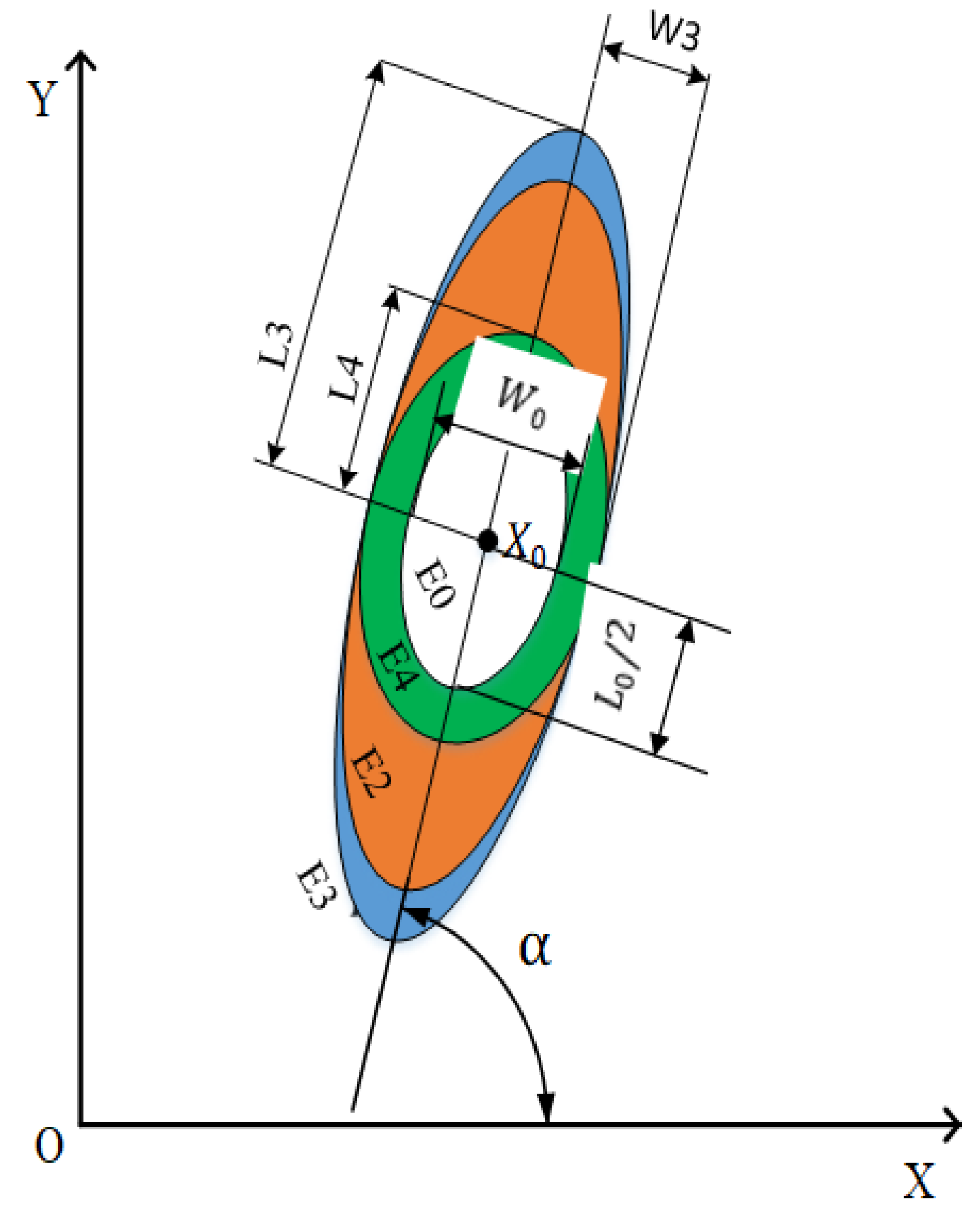
2.1.2. Development of Elliptic Repulsive Force Field
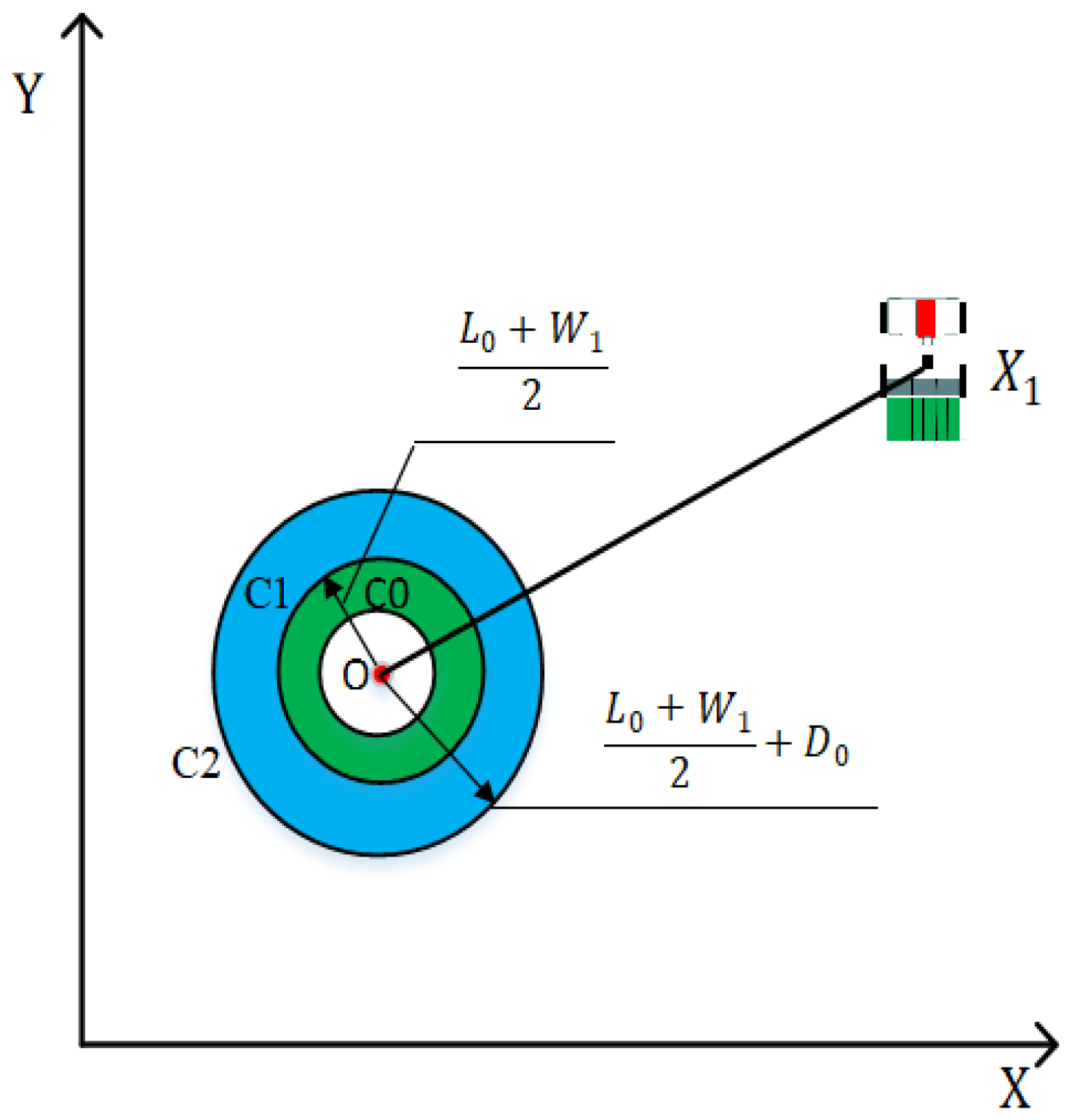
2.1.3. Development of Repulsive Force Field of a Circular Obstacle
2.1.4. Development of Repulsive Force Field of a Circular Obstacle
2.1.5. Calculation of Resultant Force of Improved Artificial Potential Field
2.2. Determination of Virtual Goal Point
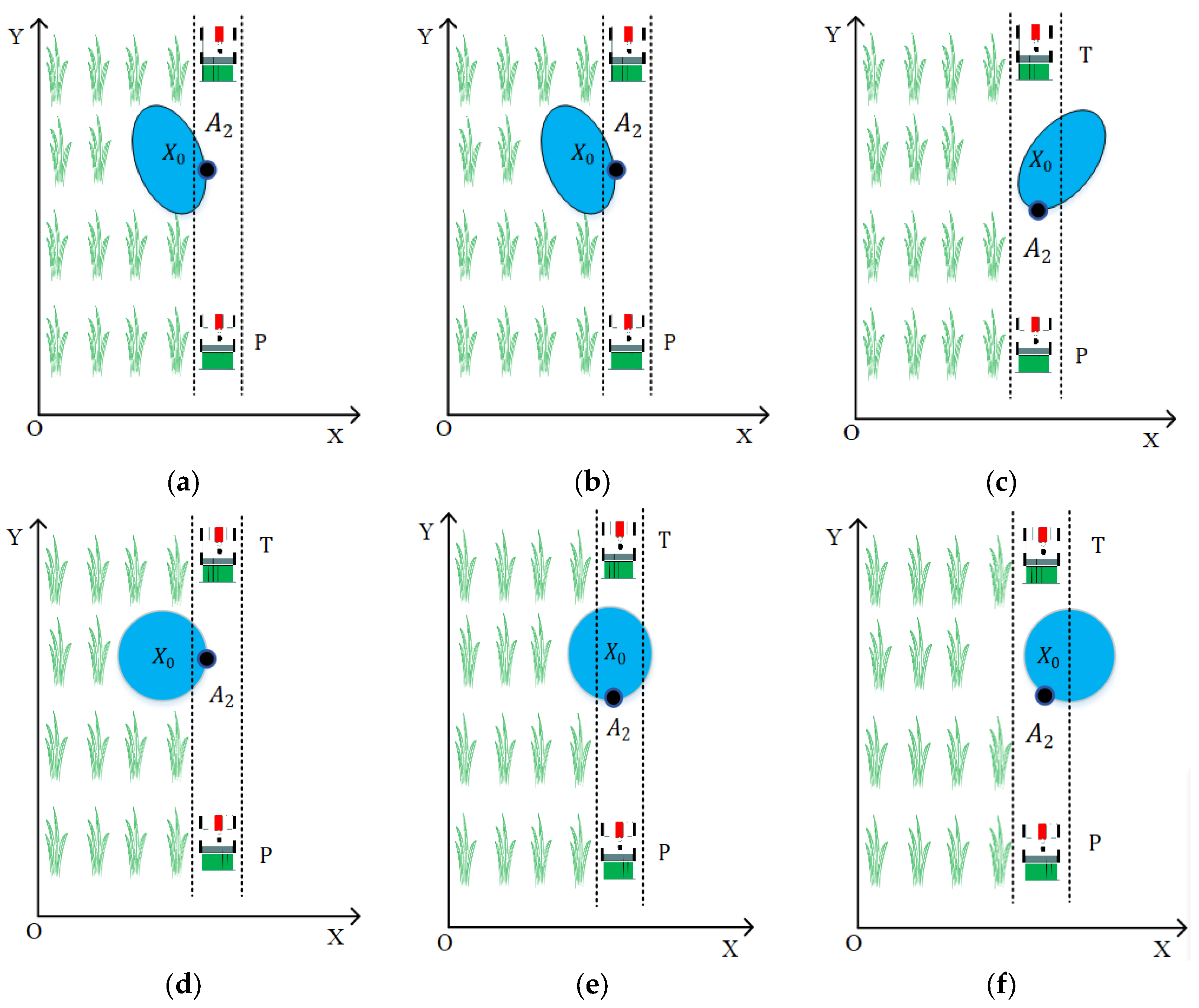
2.2.1. Analysis of Obstacle Avoidance Scene for Agriculture Machines
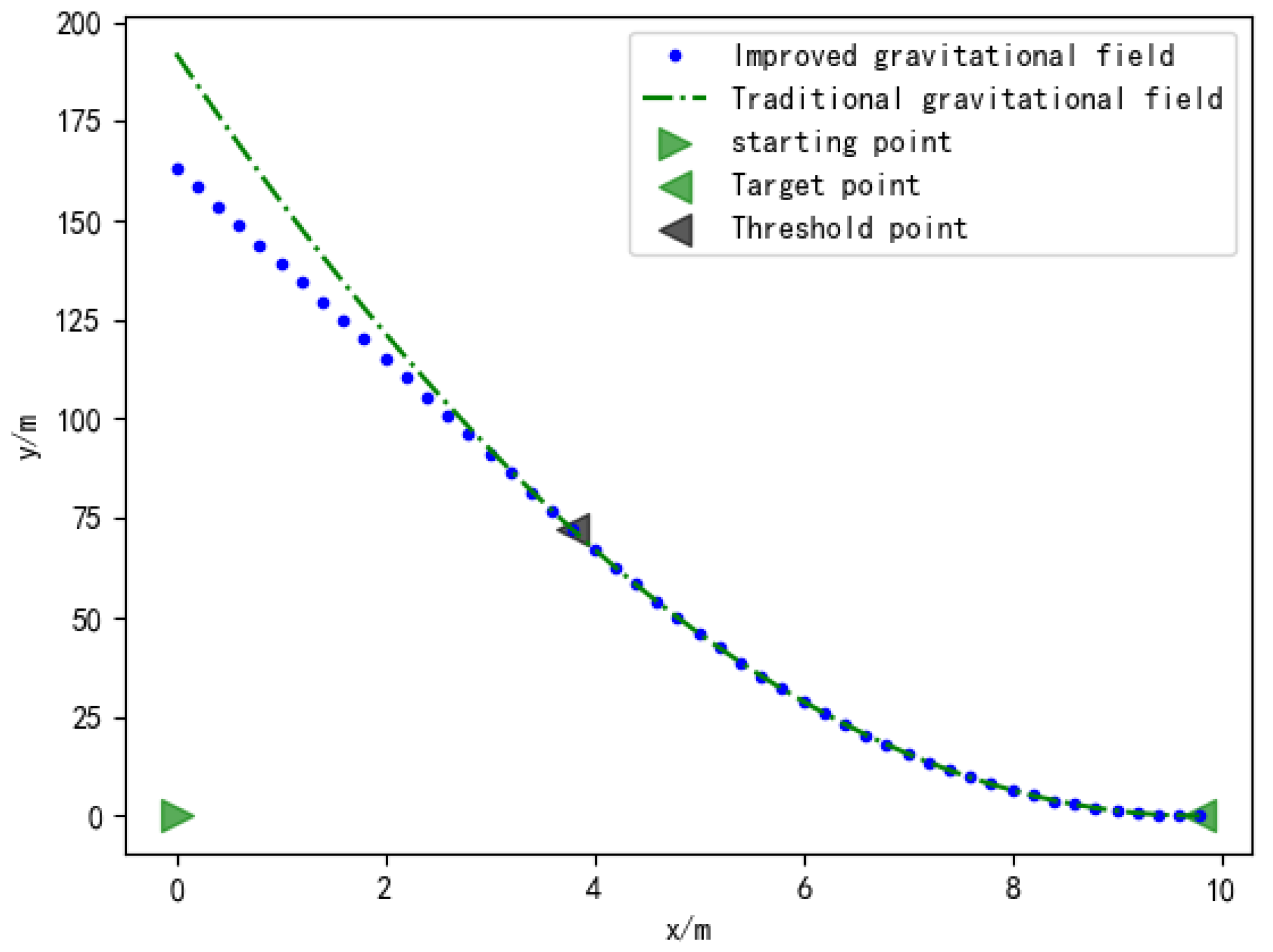
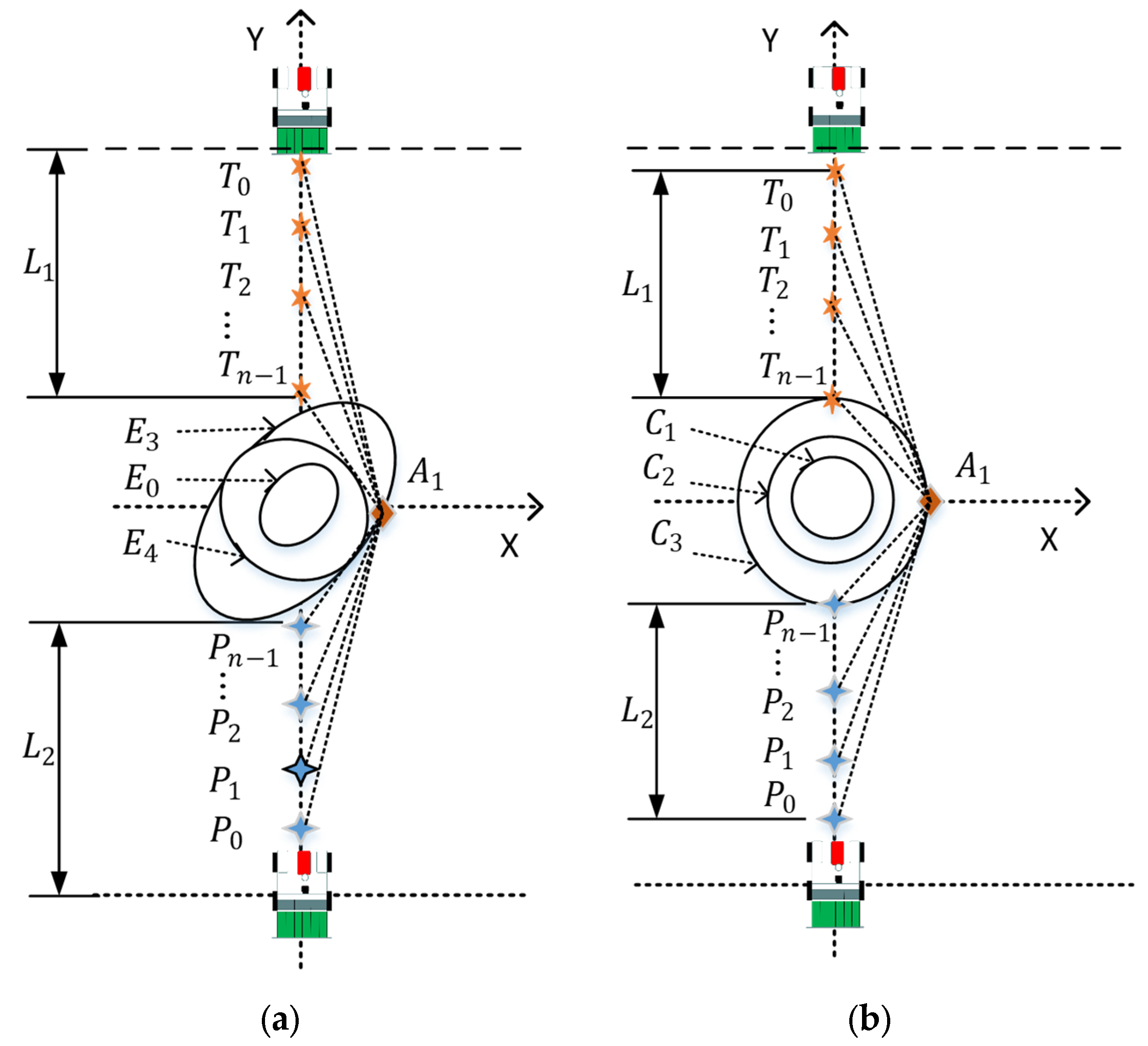
2.2.2. Setting and Adjusting Strategies of Virtual Target Points
- (1)
- Initial selection for start points
- (2)
- Determination of start point and virtual goal point
- (3)
- Switch between the virtual target point and the actual target point
2.3. Path Smoothing
2.4. Simulation Parameters
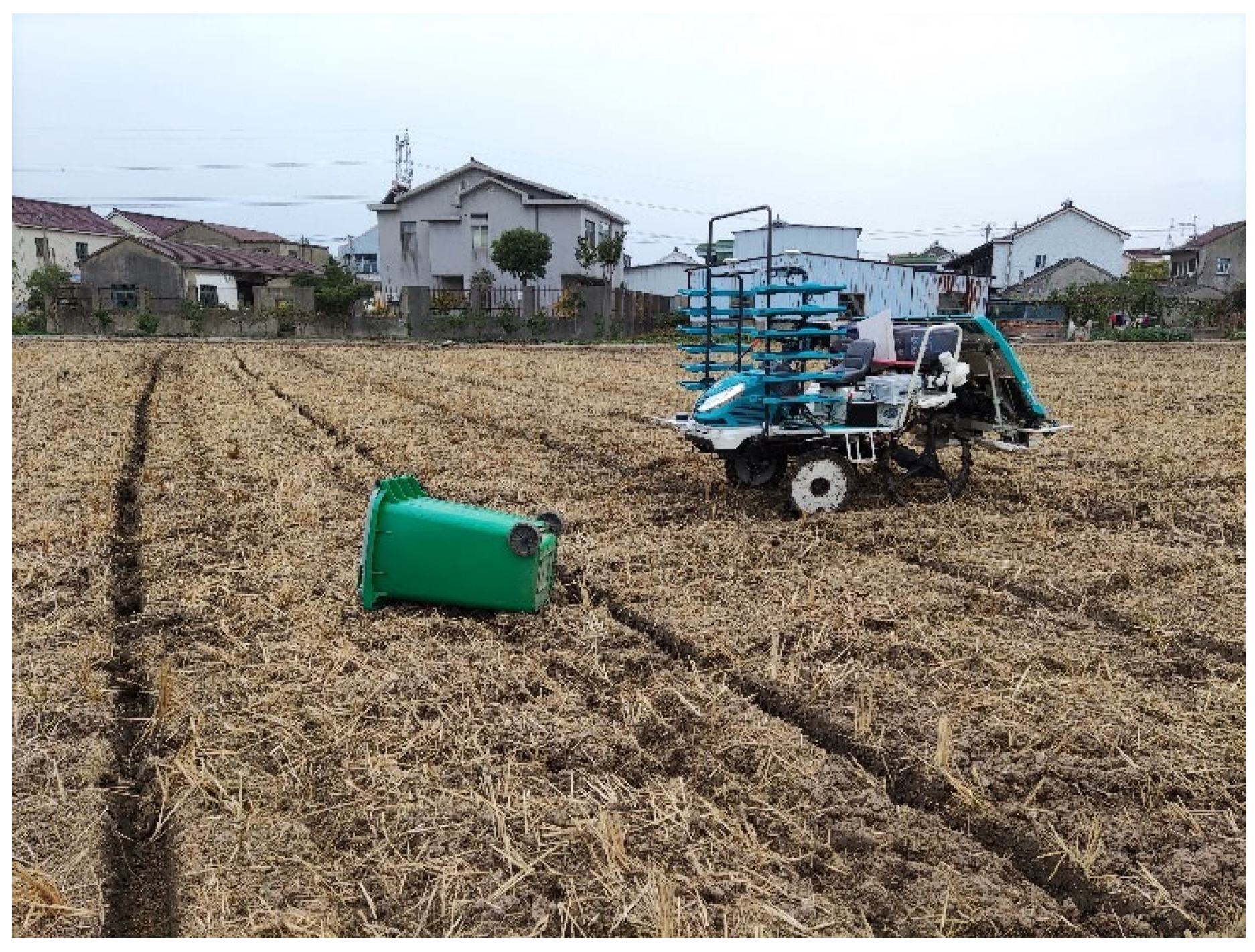
2.5. Test Platform
3. Algorithm Design and Path Evaluation
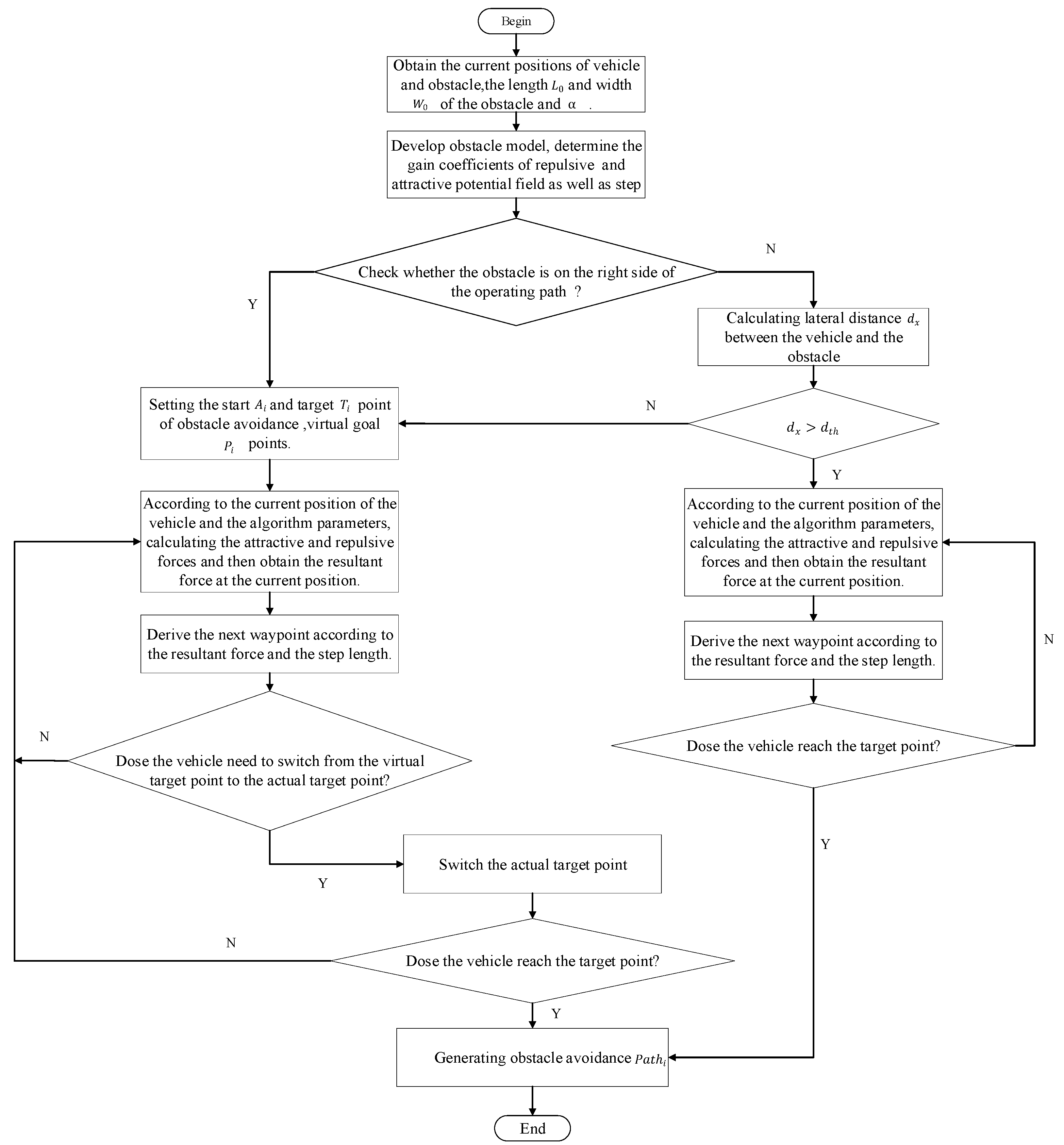
3.1. Design of Obstacle Avoidance Algorithm
3.2. Evaluation Rule for the Obstacle Avoidance Path
3.2.1. Estimation of the Path Curvature
3.2.2. Evaluation of the Path Length
3.2.3. Evaluation of the Path Length
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation and Analysis
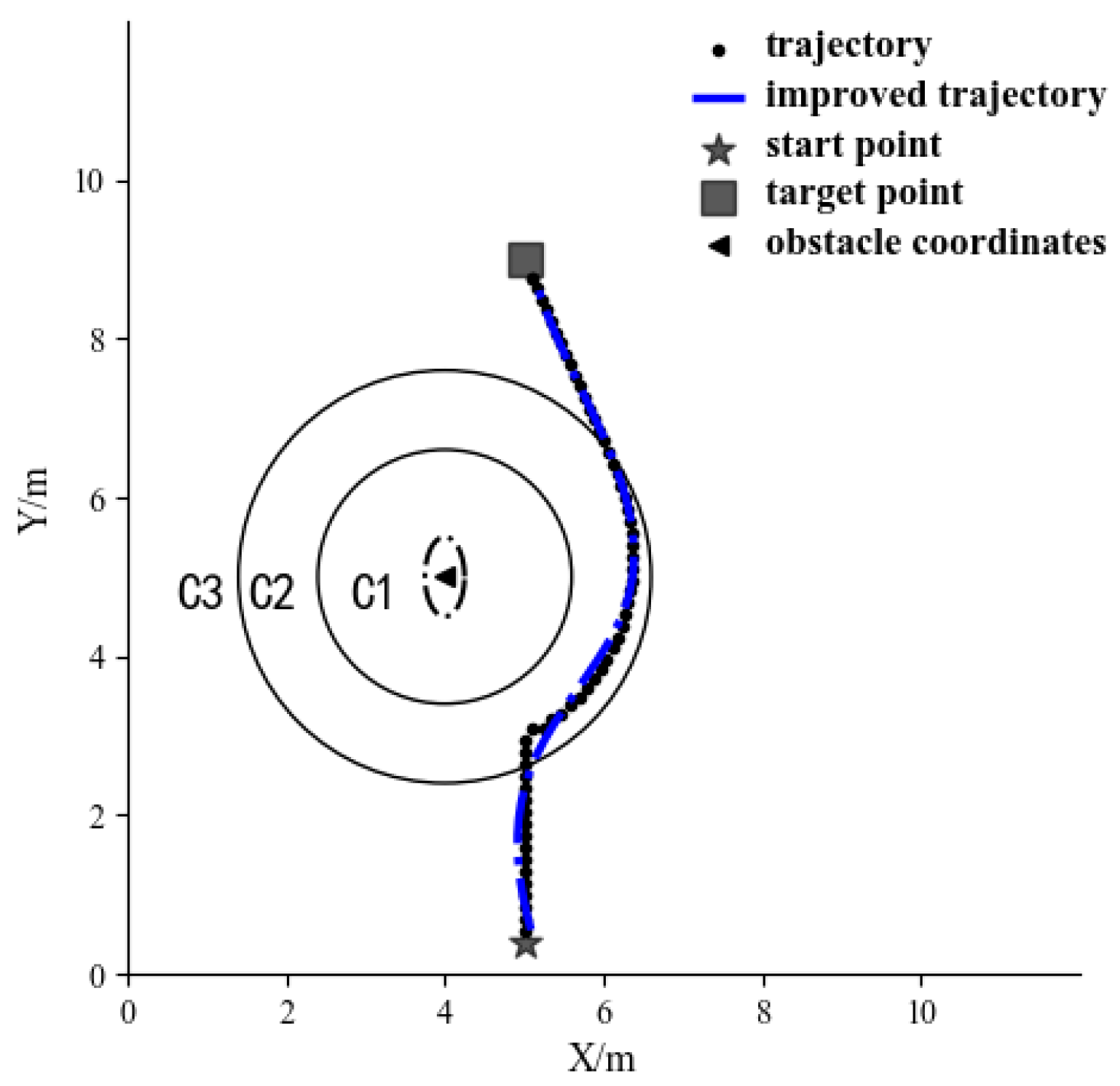
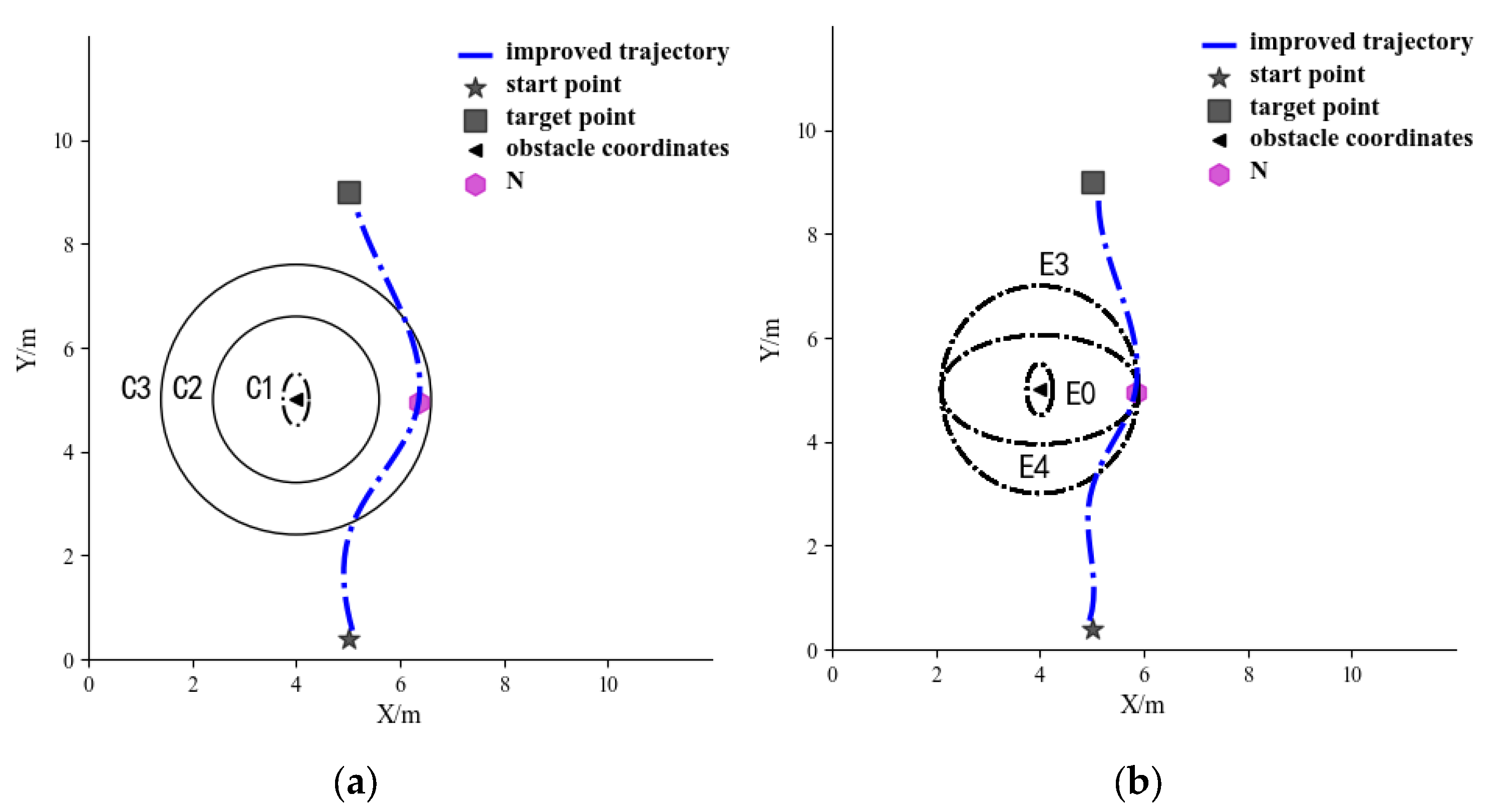
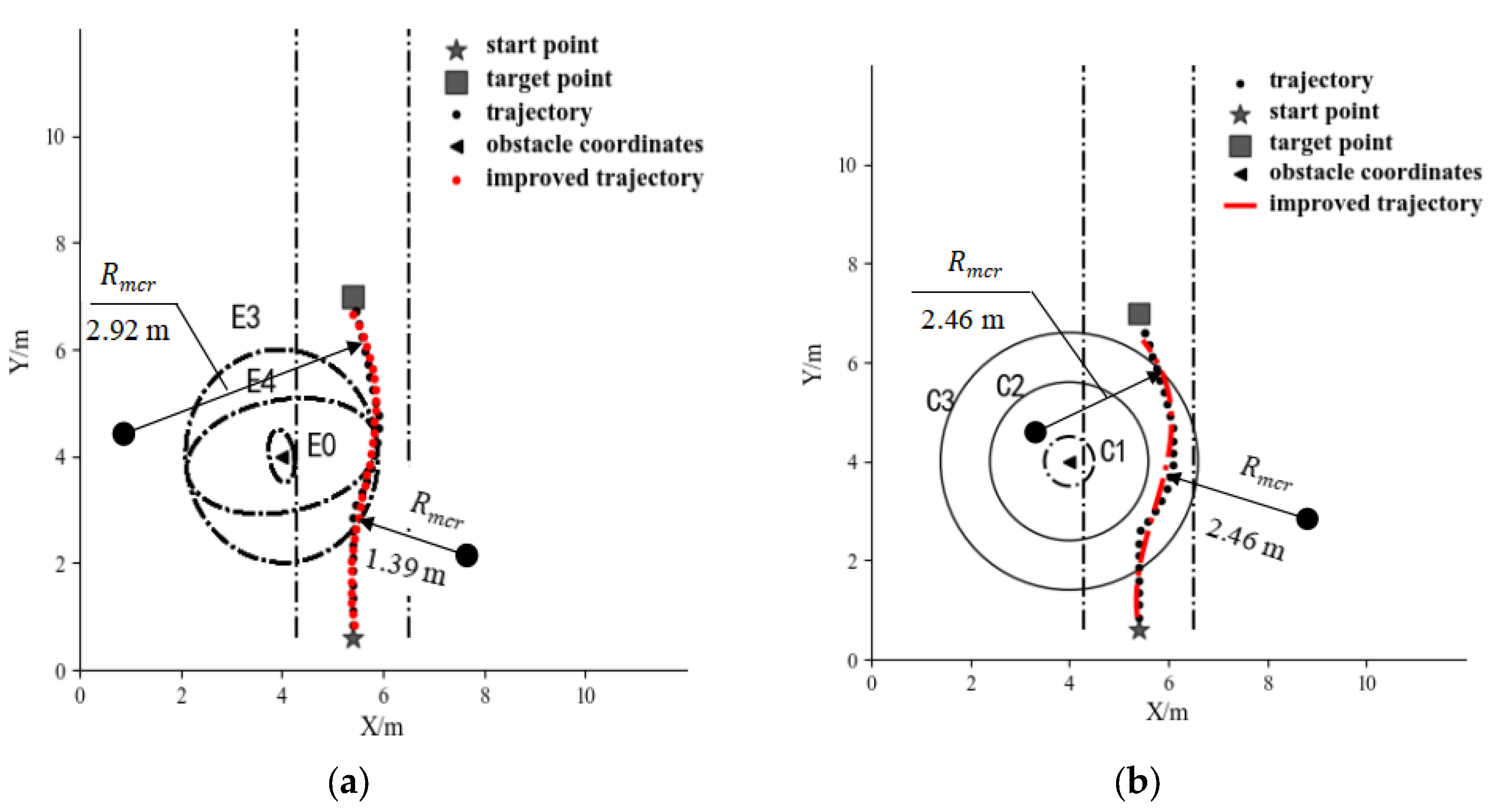
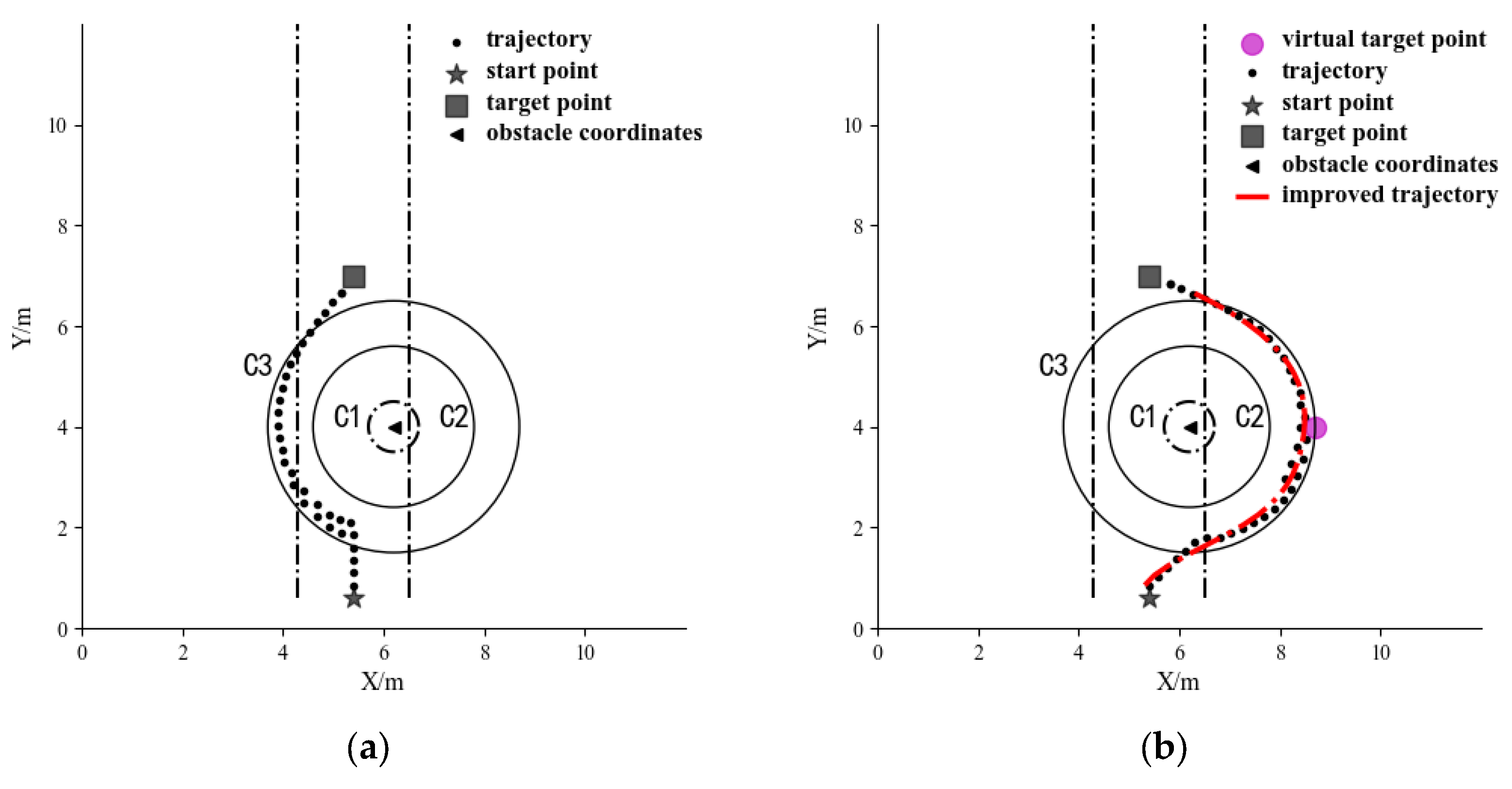
4.1.1. Comparison of Obstacle Avoidance Path under the Action of the Elliptic and Circular Repulsive Force Fields
4.1.2. Comparison of Obstacle Avoidance Effect for the Case of an Obstacle Located on the Left of the Operating Path
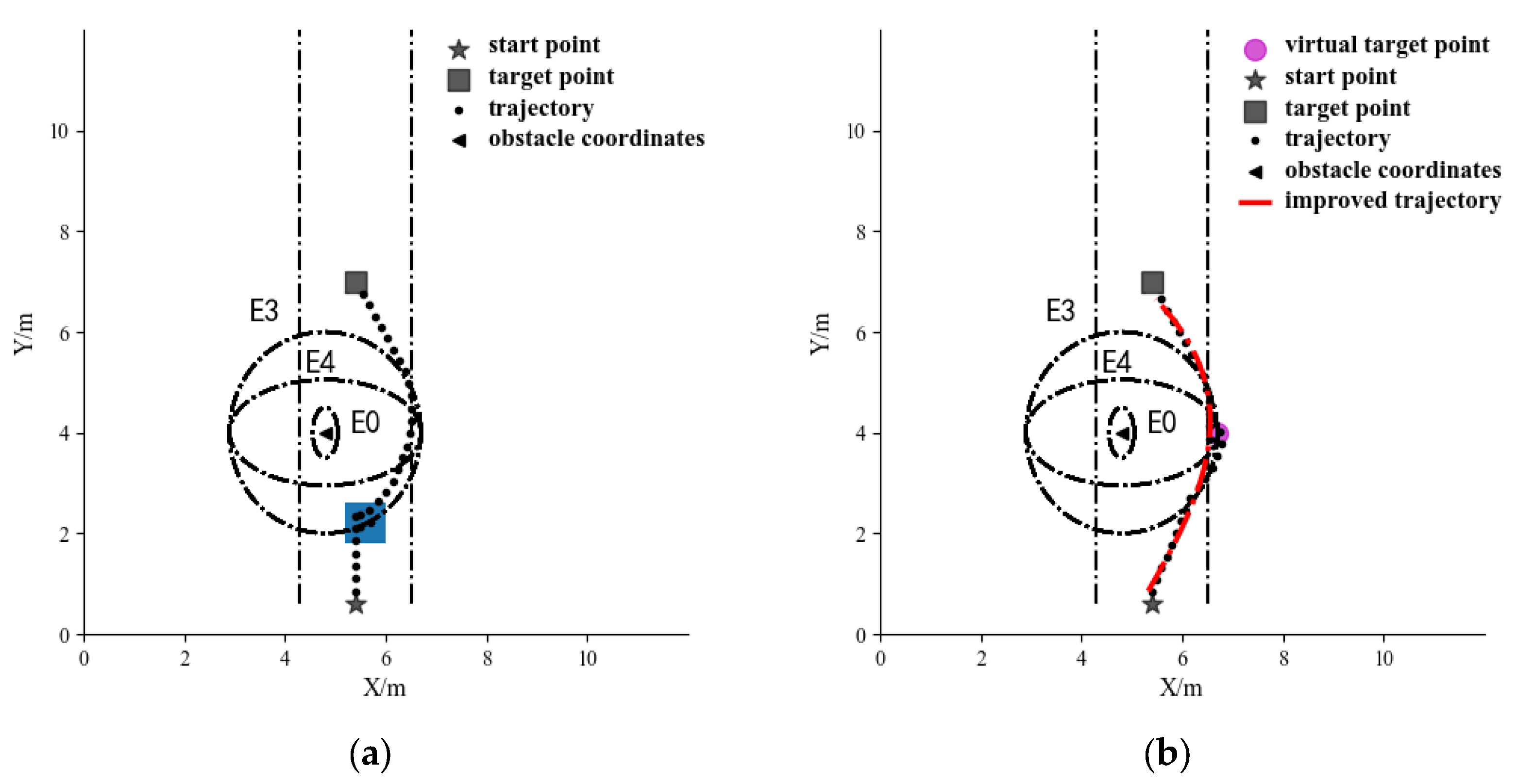
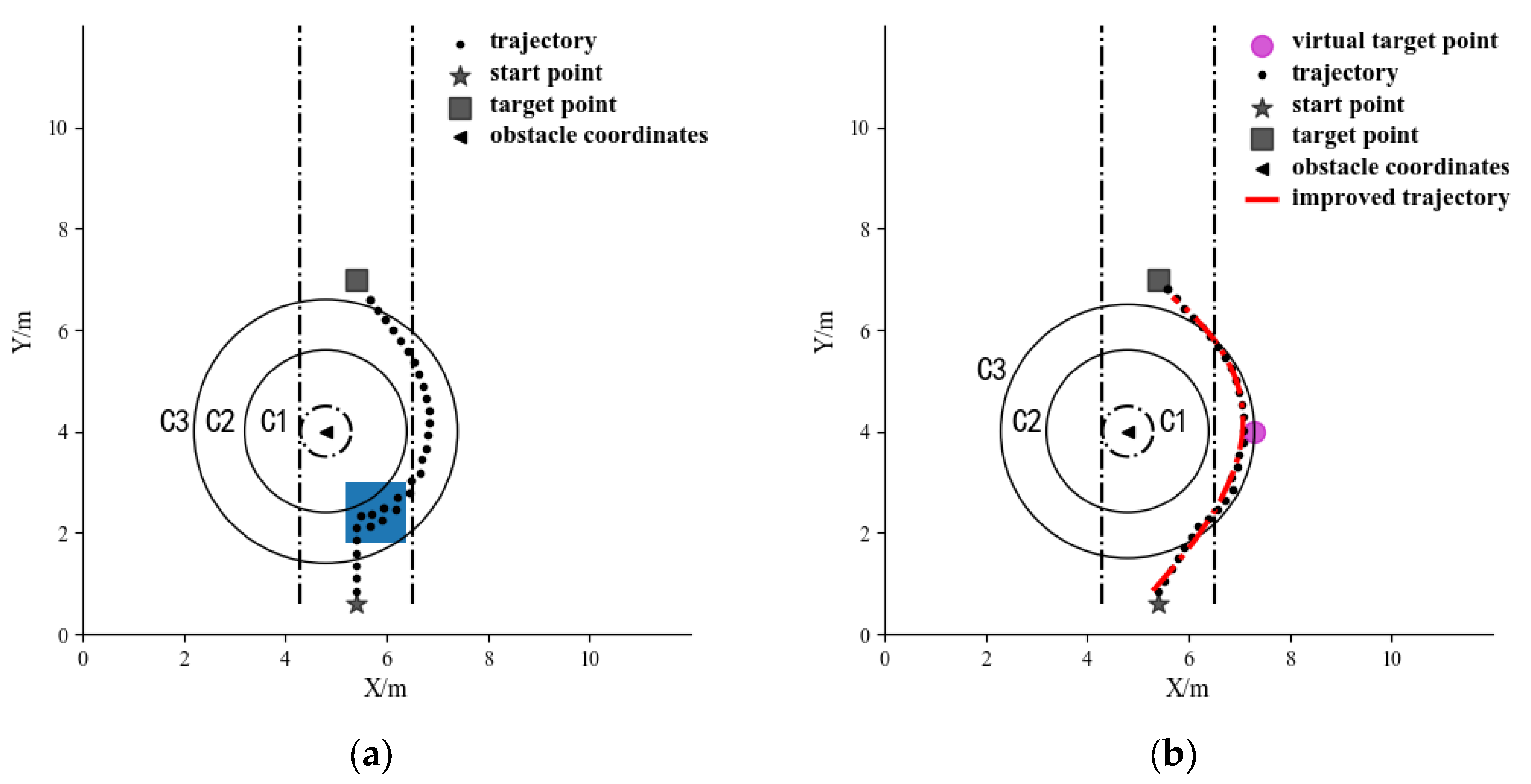
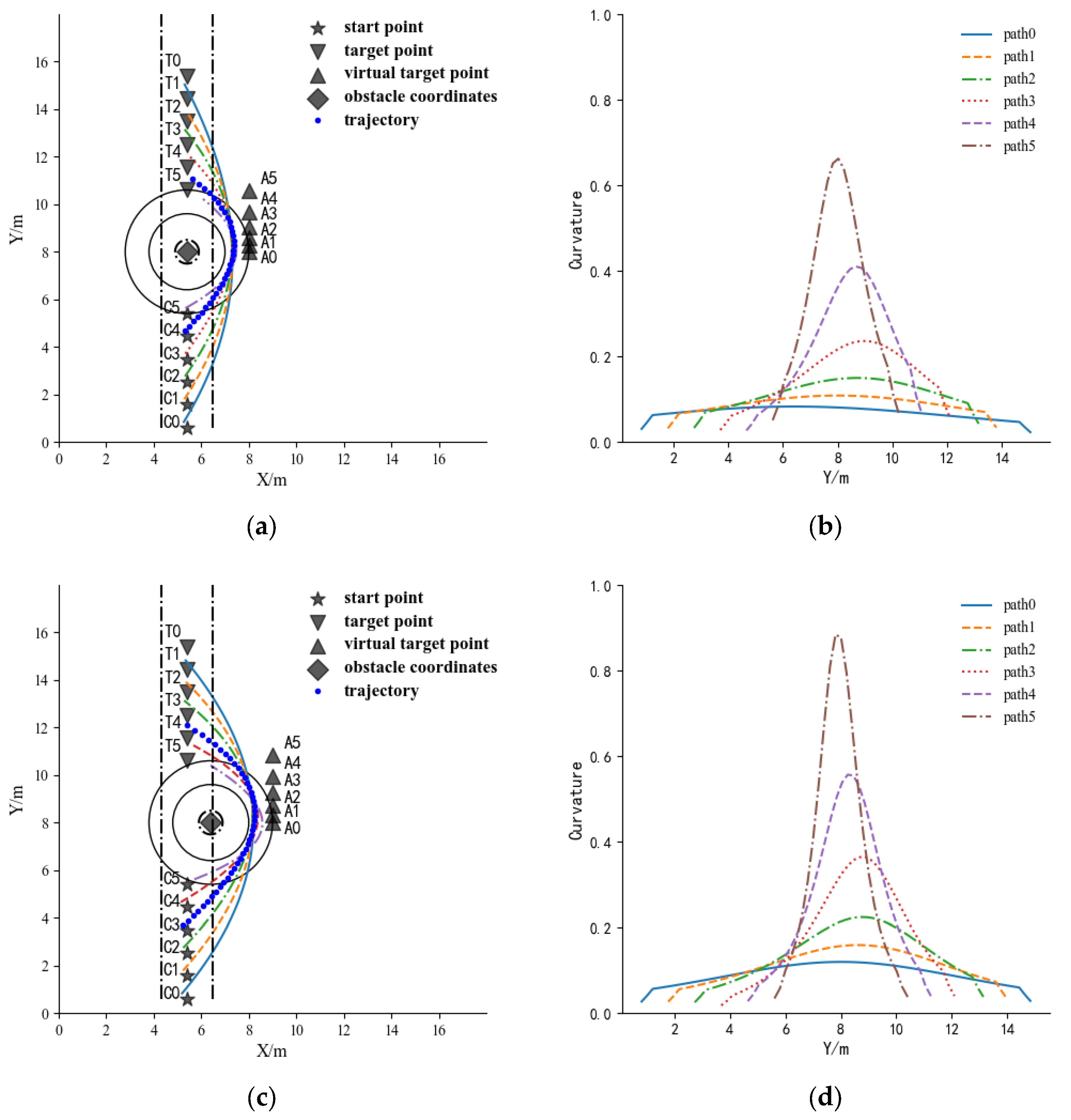
4.1.3. Comparison of Obstacle Avoidance Effect for the Case of an Obstacle Located in the Operating Path
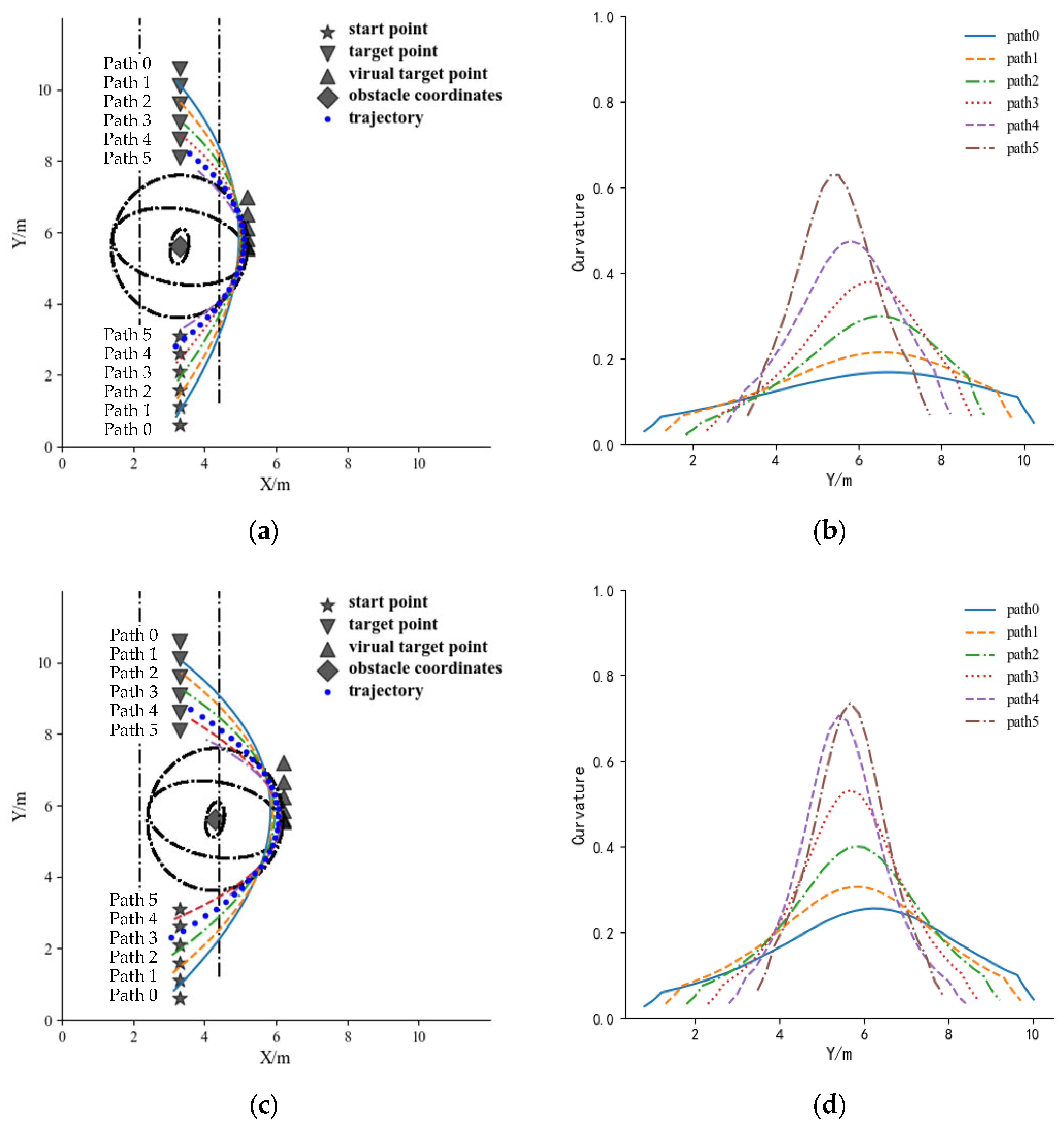
4.1.4. Comparison of Obstacle Avoidance Effect for the Case of an Obstacle Located on the Right of the Operating Path
4.2. Evaluation and Selection of Optimal Path
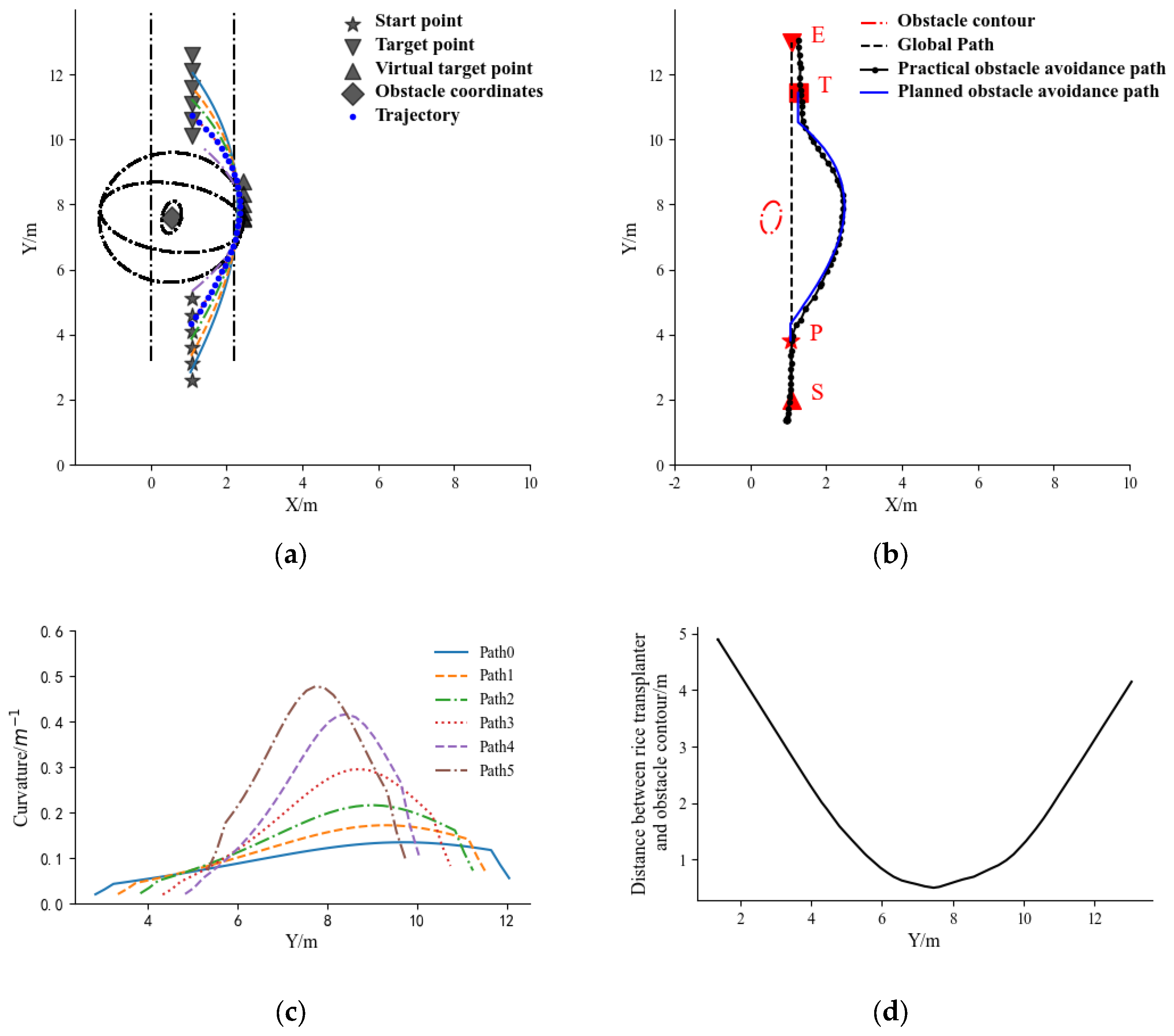
5. Field Experiments
5.1. Field Experiments
5.2. Field Experiments for the Obstacle Located on the Left Operating Path
5.3. Field Experiments for the Obstacle Located in the Operating Path
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; He, Y.Q. Research progress on navigation path planning of agricultural machinery. Nongye Jixie Xuebao Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Song, J.Y. Real-time motion planning for mobile robots by means of artificial potential field method in unknown environment. Ind. Robot 2010, 37, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Zhao, T.T.; Li, W.J. Mobile robot path planning based on improved artificial potential field method. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference of Intelligent Robotic and Control Engineering, IRCE 2018, Lanzhou, China, 24–27 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zavlangas, P.G.; Tzafestas, S.G. Motion control for mobile robot obstacle avoidance and navigation: A fuzzy logic-based approach. Syst. Anal. Modell. Simul. 2003, 43, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, B.; Vesal, M.A.; Amani, H. Obstacle avoidance for an autonomous vehicle using force field method. Int. J. Automot. Eng. 2017, 7, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Molinos, E.J.; Llamazares, A.; Ocana, M. Dynamic window-based approaches for avoiding obstacles in moving. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 118, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y. Research on static path planning method of small obstacles for automatic navigation of agricultural machinery. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguinaga, I.; Borro, D.; Matey, L. Parallel RRT-based path planning for selective disassembly planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 36, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.M.; Zou, X.J.; Jia, C.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; Zeng, Z.Q. RRT-based path planning for an intelligent litchi-picking manipulator. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lida, M.; Suyama, T.; Suguri, M.; Masuda, R. Implementation of deep-learning algorithm for obstacle detection and collision avoidance for robotic harvester. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 174, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Li, M.L. Rapid path planning algorithm for mobile robot in dynamic environment. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henten, V.E.J.; Hemming, J.; Tuijl, V.B.A.J.; Kornet, J.G.; Meuleman, J.; Bontsema, J. An autonomous robot for harvesting cucumbers in greenhouses. Auton. Robot. 2002, 13, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Henten, E.J.; Hemming, J.; Van Tuijl, B.A.J.; Kornet, J.G.; Bontsema, J. Collision-free motion planning for a cucumber picking robot. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 86, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Luo, Y.G.; Li, K.Q. Adaptive coordinated collision avoidance control of autonomous ground vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2018, 232, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.; Zhu, L.X.; Li, J.H.; Zou, X.J.; Tang, Y.C. Collision-free path planning for a guava-harvesting robot based on recurrent deep reinforcement learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 188, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, M.; Mercorelli, P. FFTSMC with Optimal Reference Trajectory Generated by MPC in Robust Robotino Motion Planning with Saturating Inputs. In Proceedings of the 2021 American Control Conference (ACC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 25 May 2021; pp. 1470–1477. [Google Scholar]
- De Simone, M.C.; Rivera, Z.B.; Guida, D. Obstacle avoidance system for unmanned ground vehicles by using ultrasonic sensors. Machines 2018, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfeir, J.; Saad, M.; Saliah-Hassane, H. An improved artificial potential field approach to real-time mobile robot path planning in an unknown environment. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–18 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Daily, R.; Bevly, D.M. Harmonic potential field path planning for high-speed vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–13 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, S.M.H.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.Z. Obstacle avoidance of mobile robots using modified artificial potential field algorithm. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Kaizu, Y.; Igarashi, S.; Imou, K. The development of autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance for a robotic mower using machine vision technique. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.J.; Zhao, N.; Zhou, L.; Wang, M.C.; Yang, L.L.; Fang, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.F. Vision-based moving obstacle detection and tracking in paddy field using improved Yolov3 and deep SORT. Sensors 2020, 20, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.Z.; Li, S.C.; Ji, Y.H.; Cao, R.Y.; Zhang, M. Dynamic obstacle detection based on panoramic vision in the moving state of agricultural machineries. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 184, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.L.; Qu, C.X.; Du, S.F.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yin, P.; Zhao, N.; Qu, S.G. Research on obstacle avoidance algorithm for unmanned ground vehicle based on multi-sensor information fusion. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 1022–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.T.; Chi, R.J.; Xiong, Z.X.; Ma, Y.Q.; Ban, C.; Zhu, X.L. Obstacle winding strategy of rice transplanter based on artificial potential field method after optimization. Nongye Jixie Xuebao Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53 (Suppl. S1), 20–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Howie, C.; Kevin, L.; Seth, H.; George, K.; Wolfram, B.; Lydia, K.; Sebastian, T. Principles of Robot Motion: Theory, Algorithms, and Implementations; MIT Press (MIT Series on Intelligent Robotics and Autonomous Agents): Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Shang, Z.J.; Li, R.F.; Cui, B.B. Adaptive sliding mode path tracking control of unmanned rice transplanter. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| m | ||
| 3.0 | / | |
| 2.0 | / | |
| 2.0 | / | |
| 0.25 | m | |
| 1.0 | m | |
| 0.3 | m | |
| Coordinate of starting point | (5.4,0.6) | m |
| Coordinate of goal point | (5.4,7.0) | m |
| 3.14 | m | |
| 2.20 | m | |
| 1.0 | m | |
| (Elliptic obstacle) | 0.5 | m |
| (Circular obstacle) | 0.8 | m |
| 45 | ° | |
| 1.05 | m |
| Path Number | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curvature index | 1.00 | 0.926 | 0.836 | 0.690 | 0.429 | 0.0 |
| Length index | 0.0 | 0.241 | 0.406 | 0.618 | 0.820 | 1.00 |
| value | 0.40 | 0.515 | 0.578 | 0.646 | 0.663 | 0.60 |
| Path Number | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curvature index | 1.00 | 0.926 | 0.816 | 0.646 | 0.376 | 0.0 |
| Length index | 0.0 | 0.200 | 0.394 | 0.597 | 0.759 | 1.00 |
| value | 0.40 | 0.490 | 0.564 | 0.616 | 0.605 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Ge, D. Improved Collision Avoidance Algorithm of Autonomous Rice Transplanter Based on Virtual Goal Point. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 698-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6010041
Li J, Zhang M, Li M, Ge D. Improved Collision Avoidance Algorithm of Autonomous Rice Transplanter Based on Virtual Goal Point. AgriEngineering. 2024; 6(1):698-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinyang, Miao Zhang, Meiqing Li, and Deqiang Ge. 2024. "Improved Collision Avoidance Algorithm of Autonomous Rice Transplanter Based on Virtual Goal Point" AgriEngineering 6, no. 1: 698-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6010041
APA StyleLi, J., Zhang, M., Li, M., & Ge, D. (2024). Improved Collision Avoidance Algorithm of Autonomous Rice Transplanter Based on Virtual Goal Point. AgriEngineering, 6(1), 698-723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6010041





