Innovative Vibrating Hydraulic Dredge for Striped Venus (Chamelea gallina) Fishing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1.
- The envisaged outcomes of this newer gear are as follows:
- 2.
- increase the selectivity towards clam juveniles;
- 3.
- minimize the amount of discard taken on board;
- 4.
- reduce the bycatch of vagile fauna;
- 5.
- improve the clams’ commercial quality;
- 6.
- monitor in real time the functioning and effectiveness of the adopted modifications.
2. Materials and Methods
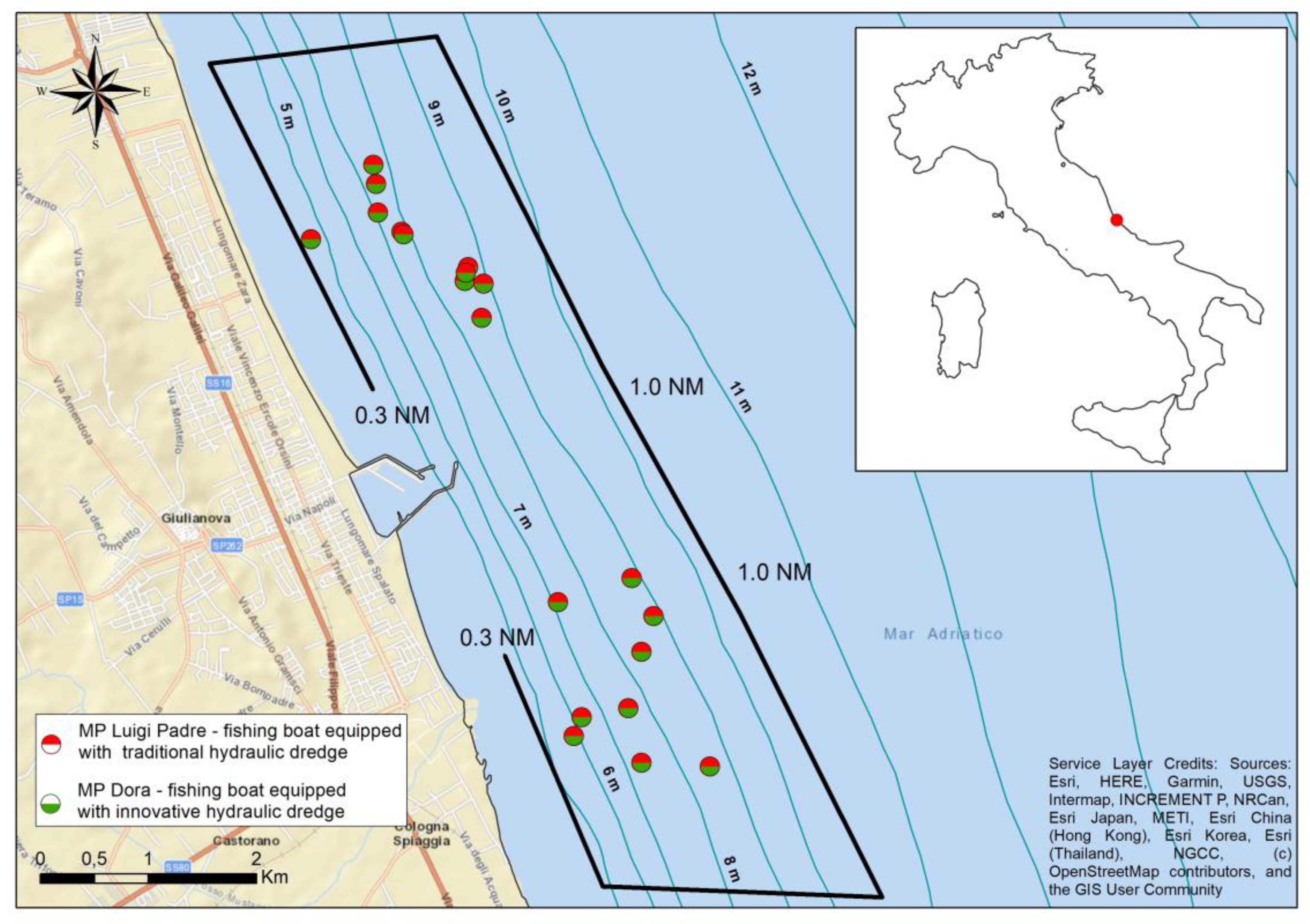
2.1. Experimental Design
- the MP Luigi Padre (registration 8PC 601, overall length 14.90 m, gross tonnage 14 GT, engine power 150 HP), mounting a traditional hydraulic dredge (mouth width, 3 m; total weight, 600 kg; fixed bottom panel, with horizontal rods; space between the rods, 12.5 mm; hydraulic power, 1.8 bar);
- the MP Dora (registration 7PC 366, overall length 15.95 m, gross tonnage 16 GT, engine power 150 HP), equipped with an innovative gear whose construction characteristics are shown below (mouth width, 3 m; vibrating part of the bottom panel, with horizontal rods; space between the rods, 12.5 mm; hydraulic power, 1.8 bar).
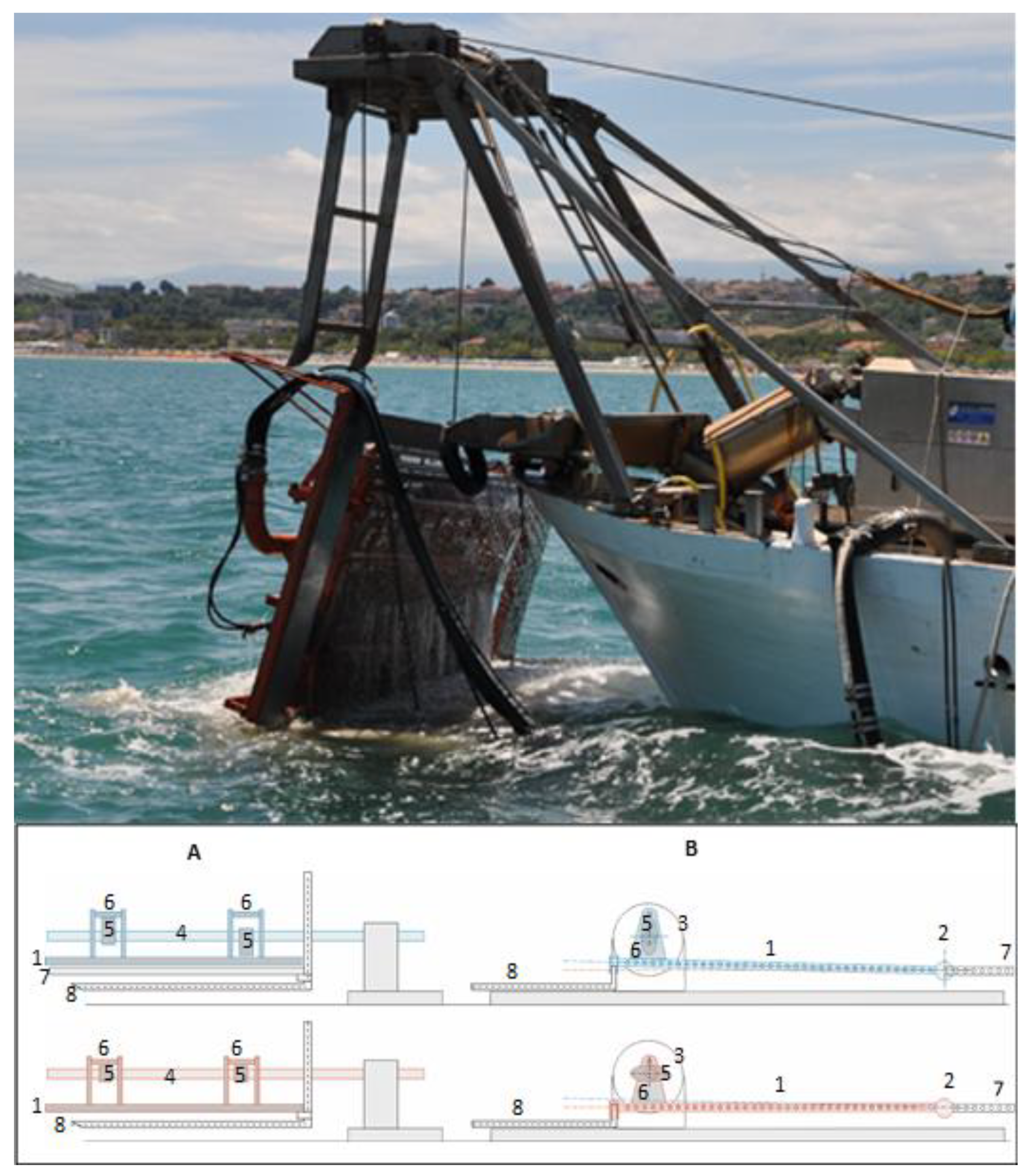
2.2. The Innovative Hydraulic Dredge
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Catches
3.1.1. Validation of the Innovative System
3.1.2. Entire Take, Undersize Capture and Commercial Catch
3.1.3. Biometric Analyses
3.2. Discard
3.3. Vagile Fauna
3.4. Videos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scarcella, G.; Mosteiro Cabanelas, A.; Research for PECH Committee. The Clam Fisheries Sector in the EU: The Adriatic Sea Case. European Parliament, D.G. Internal Policies, 2016. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2016/573412/IPOL_STU(2016)573412_EN.pdf (accessed on 16 November 2021).
- Froglia, C. Clam fisheries with hydraulic dredges in the Adriatic sea. In Marine Invertebrate Fisheries: Their Assessment and Management; Caddy, J.F., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989; pp. 507–521. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regolamento (CE) n. 1967/2006 del Consiglio del 21 Dicembre 2006 Relativo alle Misure di Gestione per lo Sfruttamento Sostenibile delle Risorse della Pesca nel Mar Mediterraneo e Recante Modifica del Regolamento (CEE) n. 2847/93 e che Abroga il Regolamento (CE) n. 1626/94. Gazzetta Ufficiale Unione Europea del 08.02.2007, L 36; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regolamento (UE) n. 1380/2013 del Parlamento Europeo e del Consiglio dell’11 Dicembre 2013 Relativo alla Politica Comune della Pesca, che Modifica i Regolamenti (CE) n. 1954/2003 e (CE) n. 1224/2009 del Consiglio e che Abroga i Regolamenti (CE) n. 2371/2002 e (CE) n. 639/2004 del Consiglio, Nonché la Decisione 2004/585/CE del Consiglio. Gazzetta Ufficiale Unione Europea del 28.12.2013, L 354; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- MiPAAF. Piano di Gestione Nazionale Rigetti per la Risorsa Vongola (Chamelea Gallina) (art. 15 EU Reg. 1380/2013); MiPAAF: Roma, Italy, 2019; 97p. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, A.; Brčić, J.; Herrmann, B.; Lucchetti, A.; Virgili, M. Assessment of size selectivity in hydraulic clam dredge fisheries. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, M.; Tarulli, E.; Palladino, S. Classificazione e descrizione degli attrezzi da pesca in uso nelle marinerie italiane con particolare riferimento al loro impatto ambientale. Quad. Ric. Mar. ICRAM 2002, 3, 1–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ponti, M.; Fava, F. Aspetti ecologici e ambientali legati alla pesca delle vongole. In Le Vongole dell’Alto Adriatico tra Ambiente e Mercato; Trevisan, G., Ed.; Franco Angeli: Milano, Italy, 2011; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- MiPAAF. Piano di Gestione Nazionale per Draghe Idrauliche (art. 19 del Regolamento CE n. 967/2006); MiPAAF: Roma, Italy, 2014; 176p. [Google Scholar]
- MiPAAF. Decreto 1 Dicembre 1998, n. 515, Regolamento Recante Disciplina Dell’Attività dei Consorzi di Gestione dei Molluschi Bivalvi. Gazzetta Ufficiale Serie Generale n. 73 of 29.03.1999; MiPAAF: Roma, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fridman, A.L. Theory and Design of Commercial Fishing Gear (Translated from Russian); National Technical Information Service, US Department Commerce: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1973; p. 489.
- Notti, E.; Lucchetti, A.; Sala, A. Gli strumenti di cattura in uso: Aspetti relativi alla selettività ed al risparmio energetico. In Atti Convegno “Il Mare Adriatico e le sue Risorse”; Marini, A., Bombace, G., Iacobone, G., Eds.; Carlo Saladino Editore: Palermo, Italy, 2017; pp. 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Froglia, C. Il contributo della ricerca scientifica alla gestione della pesca dei molluschi bivalvi con draghe idrauliche. Biol. Mar. Medit. 2000, 7, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, A.; Lucchetti, A.; Affronte, M. Effects of turtle excluder devices on bycatch and discards reduction in the demersal fisheries of Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Living Res. 2011, 24, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaspar, M.B.; Chícharo, L.M. Modifying dredges to reduce bycatch and impacts on the benthos. In By Catch Reduction in the World’s Fisheries; Kennely, S.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2007; pp. 95–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi, J. Impact des techniques de pêche sur l’environnement en Méditerranée. Etudes Rev. GFCM 2008, 84, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Dalgıç, G.; Ceylan, Y. Seasonal discards and by-catch of striped venus clam (Chamelea gallina) (Mollusca, Bivalves) fishery in the Black Sea. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 12, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Bianchini, M.L.; Ceccarelli, P.; Orecchia, P.; Rambaldi, E.; Volterra, L. Indagine sui molluschi bivalvi di interesse commerciale (telline, cannolicchi e vongole) delle coste della Toscana, del Lazio e della Campania: 1985 1987. Quad. Ist. Idrobiol. Acquacolt. G. Brunelli 1987, 7, 7–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, F.; Rambaldi, E.; Brinati, C. Catture accessorie e rigetti nella pesca di Ensis siliqua minor (L.) con turbosoffiante. Quad. Ist. Idrobiol. Acquacolt. G. Brunelli 1996, 15, 41–157. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccarella, R. Studio dell’efficienza delle draghe turbosoffianti e loro effetto sulle comunità bentoniche. Boll. Malacol. 1994, 30, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaldi, E.; Bianchini, M.L.; Priore, G.; Prioli, G.; Mietti, N.; Pagliani, T. Preliminary appraisal of an innovative hydraulic dredge with vibrating and sorting bottom on clam beds (Chamelea gallina). Hydrobiology 2001, 465, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaldi, E.; Priore, G.; Prioli, G.; Mietti, N.; Pagliani, T.; Bianchini, M.L. Valutazioni preliminari di una draga idraulica per bivalvi con fondo vibrante e vagliatore. Biol. Mar. Medit. 2000, 7, 917–921. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, M.L. Uno strumento di supporto decisionale per i finanziamenti sui fondi europei: Il caso dell’innovazione per la riduzione dell’impatto ambientale nella pesca. CURSA (pas) Saggi 2019, 10, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mascilongo, G.; Costa, C.; Pochi, D.; Fanigliulo, R.; Costa, C.; Bianchini, M.L.; Di Mattia, G.; Corsi, V.; Di Giacinto, F.; Di Renzo, L.; et al. Sperimentazione di attrezzature innovative per incrementare la selettività e ridurre l’impatto ambientale della pesca delle vongole (Chamelea gallina): Avvio del progetto europeo di innovazione. In Proceedings of the VIII Convegno Nazionale SIRAM, La Spezia, Italy, 8–9 November 2019; pp. 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 22nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 1–718. [Google Scholar]
- Bortz, J.; Lienert, G.; Boehnke, K. Verteilungsfreie Methoden in der Biostatistik (3. Auflage); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–952. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, R.; Revill, A. A simple statistical method for catch comparison studies. Fish. Res. 2009, 95, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehtari, A.; Gelman, A.; Gabry, J. Practical Bayesian model evaluation using leave-one-out cross-validation and WAIC. Stat. Comput. 2017, 27, 1413–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vehtari, A.; Simpson, D.; Gelman, A.; Yao, Y.; Gabry, J. Pareto Smoothed Importance Sampling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1507.02646v7, preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Carlin, J. Beyond power calculations: Assessing Type S (sign) and Type M (magnitude) errors. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 9, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizzi, F.; Caccia, M.G.; Simoncini, G.A.; Mancuso, A.; Reggi, M.; Fermani, S.; Brizi, L.; Fantazzini, P.; Stagioni, M.; Falini, G.; et al. Shell properties of commercial clam Chamelea gallina are influenced by temperature and solar radiation along a wide latitudinal gradient. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruschke, J.K. Doing Bayesian Data Analysis: A Tutorial with R, Jags, and Stan, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dalgıc, G.; Okumuş, I.; Karayucel, S. The effect of fishing on growth of the clam Chamelea gallina (Bivalvia: Veneridae) from the Turkish Black Sea coast. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 2010, 90, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschino, V.; Deppieri, M.; Marin, M.G. Evaluation of shell damage to the clam Chamelea gallina captured by hydraulic dredging in the Northern Adriatic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morello, E.B.; Froglia, C.; Atkinson, R.J.A.; Moore, P.G. Hydraulic dredge discards of the clam (Chamelea gallina) fishery in the western Adriatic Sea. Italy Fish. Res. 2005, 76, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.R.; Mullen, C.; Brand, A.R. Predator and scavenger aggregation to discarded by catch from dredge fisheries: Importance of damage level. J. Sea Res. 2004, 51, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, J.; García, T.; Gallardo Roldâan, H.; Leòn, E.; Lozano, M.; Baro, J.; Rueda, J.L. Discard analysis and damage assessment in the wedge clam mechanized dredging fisheries of the northern Alboran Sea (W Mediterranean Sea). Fish. Res. 2017, 187, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.J. The Effects of Fishing on Marine Ecosystems and Communities; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1990; p. 274. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.J.; Harding, M.J.C. Physical disturbance and marine benthic communities: The effects of mechanical harvesting of cockles on non target benthic infauna. J. Appl. Ecol. 1997, 34, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranovi, F.; Giovanardi, O. The impact of hydraulic dredging for short necked clams, Tapes spp., on an infaunal community in the lagoon of Venice. Sci. Mar. 1994, 58, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Tuck, I.D.; Bailey, N.; Harding, M.; Sangster, G.; Howell, T.; Graham, N.; Breen, M. The impact of water jet dredging for razor clams, Ensis spp., in a shallow sandy subtidal environment. J. Sea Res. 2000, 43, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P.K.; Thrush, S.F.; Agardy, M.T.; Hofman, R.J. Environmental effects of marine fishing. Aquat. Cons. Mar. Freshwat. Ecosyst. 1995, 5, 205–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzievangelou, D.; Aguzzi, J.; Ogston, A.; Suárez, A.; Thomsen, L. Visual monitoring of key deep-sea megafauna with an Internet Operated crawler as a tool for ecological status assessment. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 184, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine microbenthic communities. Mar. Biol. 1986, 92, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, F.; Gaspar, M.B.; Santos, M.N.; Monteiro, C.C. A comparison of bycatch and discard mortality in three types of dredge used in the Portuguese Spisula solida (solid surf clam) fishery. Aquat. Living Res. 2009, 22, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercaldo Allen, R.; Goldberg, R.; Clark, P.; Kuropat, C.; Meseck, S.L.; Rose, J. Benthic ecology of northern quahog beds with different hydraulic dredging histories in Long Island sound. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 32, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çolakoğlu, S. Bycatch and discards from two types of bivalve dredges targeting Donax trunculus and Chamelea gallina used in the southern coast of the Marmara Sea, Turkey. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochi, D.; Fanigliulo, R.; Bisaglia, C.; Cutini, M.; Grilli, R.; Fornaciari, L.; Betto, M.; Pari, L.; Gallucci, F.; Capuzzi, L.; et al. Test rig and method for comparative evaluation of conventional and bio-based hydraulic fluids and lubricants for agricultural transmissions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fishing Vessel | Bottom Panel | # of Hauls | Mean Weight (kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Take | StD | Undersize | StD | Commercial | StD | |||
| Luigi Padre | Fixed | 40 | 128 | ±63 | 52 | ±35 | 75 | ±33 |
| Dora | vibrating | 40 | 110 | ±67 | 17 | ±24 | 93 | ±60 |
| Fishing Vessel | Bottom Panel | # of Hauls | Size (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | ≥25 | ||||
| Luigi Padre | fixed | 13 | 103 | 33 | 28 | 35 | 191 | |
| Dora | vibrating | 13 | 25 | 29 | 31 | 62 | 243 | |
| Fishing Vessel | Bottom Panel | # Biometries | Mean (mm) | StD | Mode (mm) | Median (mm) | Min-Max (mm) | |
| Luigi Padre | fixed | 390 | 24.1 | 3.52 | 20 | 24 | 10–35 | |
| Dora | vibrating | 390 | 25.6 | 2.89 | 24 | 25 | 18–37 | |
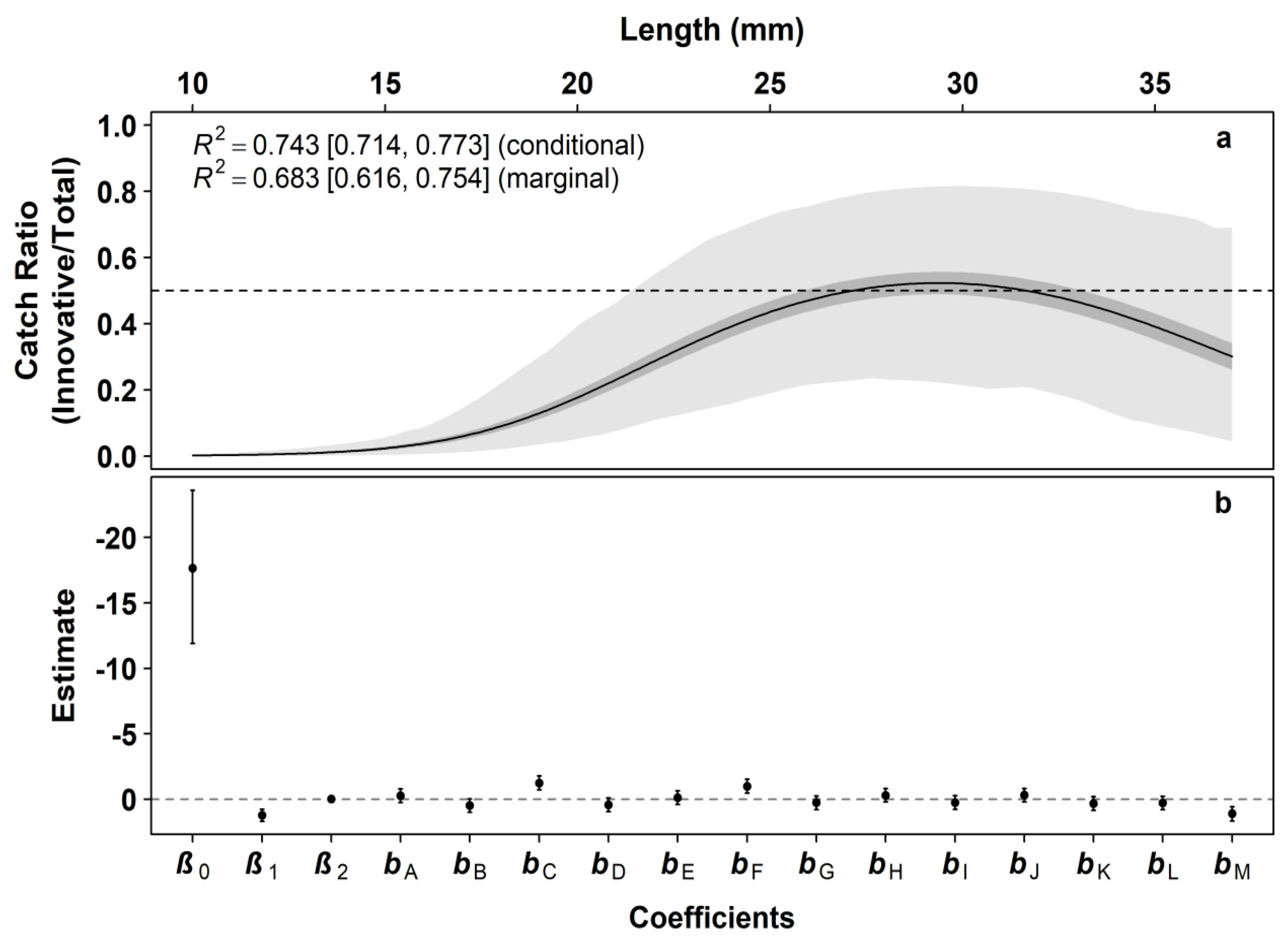
| Model | ELPD | ELPD SE | ELPD Diff | ELPD Diff SE | LOOIC | LOOIC SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic | −229.645 | 10.946 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 459.289 | 21.892 |
| Quadratic | −235.182 | 11.205 | −5.537 | 3.755 | 470.364 | 22.410 |
| Linear | −242.174 | 11.805 | −12.529 | 5.733 | 484.347 | 23.610 |
| Coefficient | Estimate | Standard Error (SE) | 05% CI | 95% CI | MCSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0 | −17.664 | 3.594 | −23.601 | −11.889 | 0.06559 |
| β1 | 1.219 | 0.285 | 0.767 | 1.685 | 0.00511 |
| β2 | −0.021 | 0.006 | −0.030 | −0.012 | 0.00010 |
| bA | −0.267 | 0.304 | −0.793 | 0.248 | 0.00741 |
| bB | 0.484 | 0.307 | −0.011 | 1.006 | 0.00745 |
| bC | −1.242 | 0.329 | −1.792 | −0.714 | 0.00715 |
| bD | 0.430 | 0.312 | −0.101 | 0.958 | 0.00749 |
| bE | −0.121 | 0.307 | −0.643 | 0.397 | 0.00718 |
| bF | −0.991 | 0.315 | −1.525 | −0.454 | 0.00725 |
| bG | 0.258 | 0.313 | −0.231 | 0.797 | 0.00734 |
| bH | −0.297 | 0.300 | −0.804 | 0.209 | 0.00721 |
| bI | 0.256 | 0.306 | −0.258 | 0.784 | 0.00715 |
| bJ | −0.310 | 0.306 | −0.816 | 0.196 | 0.00713 |
| bK | 0.329 | 0.320 | −0.190 | 0.849 | 0.00737 |
| bL | 0.288 | 0.307 | −0.207 | 0.794 | 0.00723 |
| bM | 1.094 | 0.322 | 0.575 | 1.671 | 0.00746 |
| Group | Common Name | Species | Occurrences | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Vibrating | |||
| n.a. | ---- | undetermined | 6 | 5 |
| cephalopods | cuttlefish | Sepia officinalis | 4 | |
| Selachians | skate | Raja sp. | 2 | |
| bony fishes | Dover sole | Solea vulgaris | 13 | 5 |
| bony fishes | tub gurnard | Chelidonichthys lucerna | 2 | |
| bony fishes | greater weever | Trachinus draco | (1) | |
| bony fishes | spotted flounder | Citharus linguatula | 1 | |
| bony fishes | generic bony fish | ? | (2) | 1 |
| TOTAL | 27 | 12 | ||
| Parameter | Variation % | Fixed | Vibrating |
|---|---|---|---|
| entire take | 86 | + | − |
| undersized capture | 32 | − − − | + + + |
| commercial catch | 124 | − − | + + |
| biometry | n.a. | − − | + + |
| discard collection | 76 | − | + |
| presence of vagile fauna | 44 | − − − | + + + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mascilongo, G.; Costa, C.; Chatzievangelou, D.; Pochi, D.; Fanigliulo, R.; Di Giacinto, F.; Di Renzo, L.; Giansante, C.; Ferri, N.; D'Alterio, N.; et al. Innovative Vibrating Hydraulic Dredge for Striped Venus (Chamelea gallina) Fishing. AgriEngineering 2022, 4, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4010001
Mascilongo G, Costa C, Chatzievangelou D, Pochi D, Fanigliulo R, Di Giacinto F, Di Renzo L, Giansante C, Ferri N, D'Alterio N, et al. Innovative Vibrating Hydraulic Dredge for Striped Venus (Chamelea gallina) Fishing. AgriEngineering. 2022; 4(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMascilongo, Giuseppina, Corrado Costa, Damianos Chatzievangelou, Daniele Pochi, Roberto Fanigliulo, Federica Di Giacinto, Ludovica Di Renzo, Carla Giansante, Nicola Ferri, Nicola D'Alterio, and et al. 2022. "Innovative Vibrating Hydraulic Dredge for Striped Venus (Chamelea gallina) Fishing" AgriEngineering 4, no. 1: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4010001
APA StyleMascilongo, G., Costa, C., Chatzievangelou, D., Pochi, D., Fanigliulo, R., Di Giacinto, F., Di Renzo, L., Giansante, C., Ferri, N., D'Alterio, N., Costa, C., & Bianchini, M. L. (2022). Innovative Vibrating Hydraulic Dredge for Striped Venus (Chamelea gallina) Fishing. AgriEngineering, 4(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4010001








