Development of a Novel IoT-Based Hierarchical Control System for Enhancing Inertia in DC Microgrids
Highlights
- A hierarchical control strategy combining decentralized SG-emulating converters and centralized IoT-based coordination is proposed.
- The method significantly improves inertial response and voltage stability in DC multi-microgrid (DCMMG).
- The proposed approach enables effective real-time cooperation between distributed energy storage units, enhancing system reliability.
- It facilitates greater integration of renewable energy sources into DC microgrids by addressing the low.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Real-time monitoring of multiple DC microgrids (MGs) through IoT technology.
- Development of a hierarchical control structure that combines decentralized and centralized control methods. The decentralized control managing local battery operations to improve inertia through individual responses to system dynamics, while centralized control, based on IoT coordinates and optimizes battery collaboration to ensure overall system balance and stability.
- Detailed explanation of secondary control strategies employed to facilitate collaborative operation between batteries, accompanied by an analysis of the effectiveness of these strategies in achieving system balance.
- Verification of the control method’s effectiveness through the development of a DC microgrid model, followed by an analysis of the system’s performance under various operating conditions. The results demonstrated the proposed control method’s effectiveness in enhancing overall system performance.
2. System Description
- The First Layer
- The second layer
- The third layer
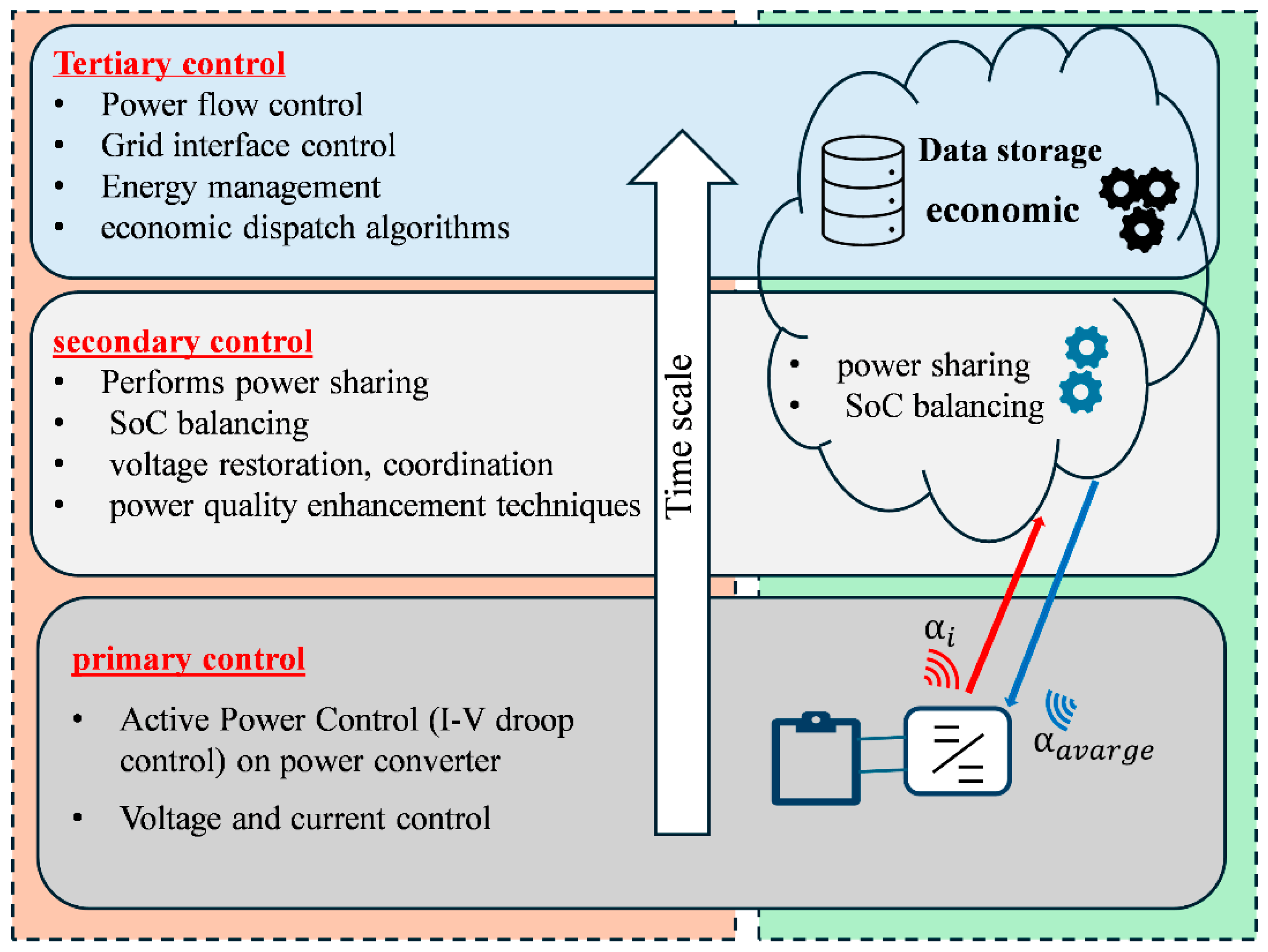
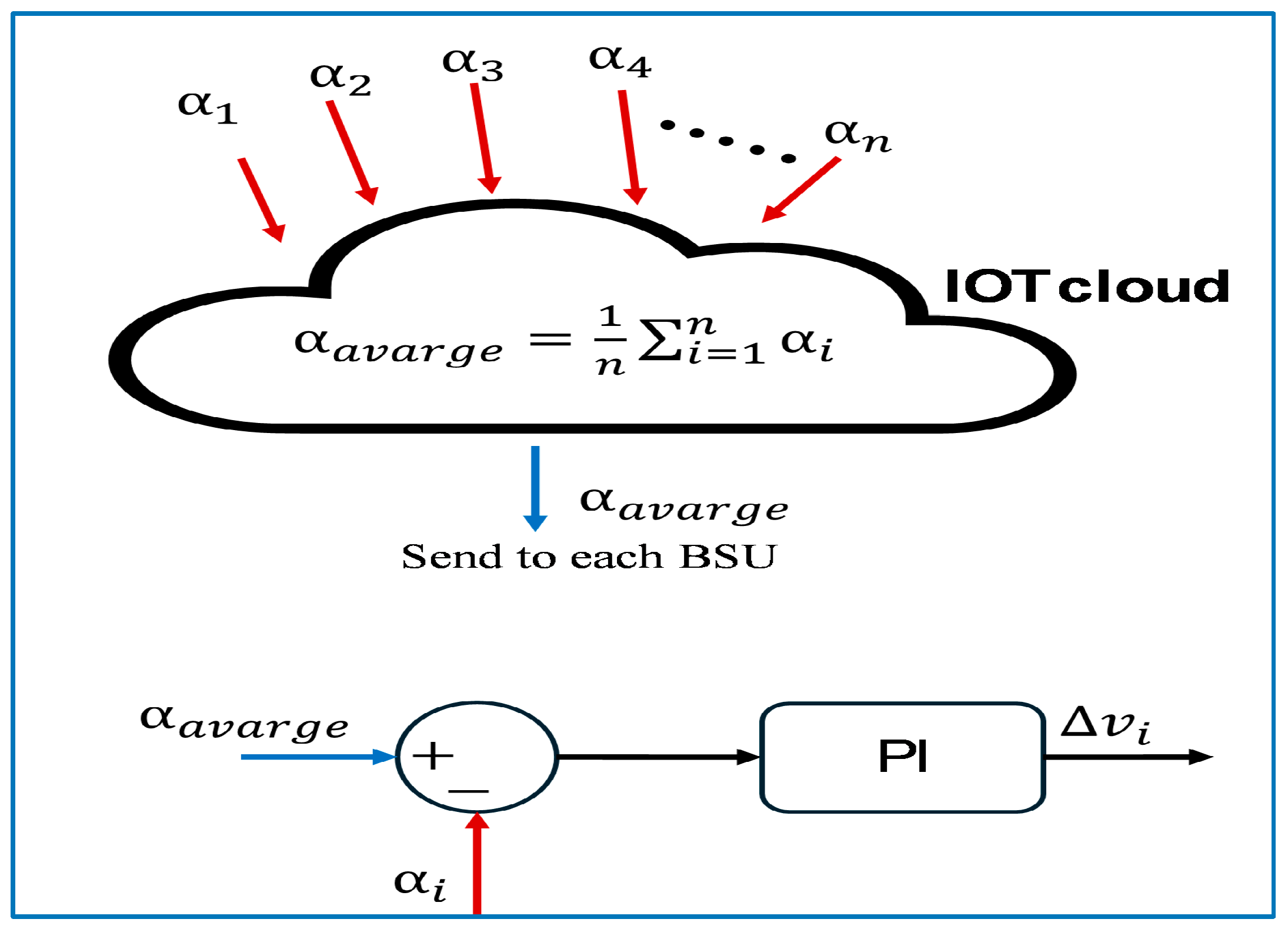
3. Proposed Hierarchical Control Strategy for DC Microgrids Based on IOT
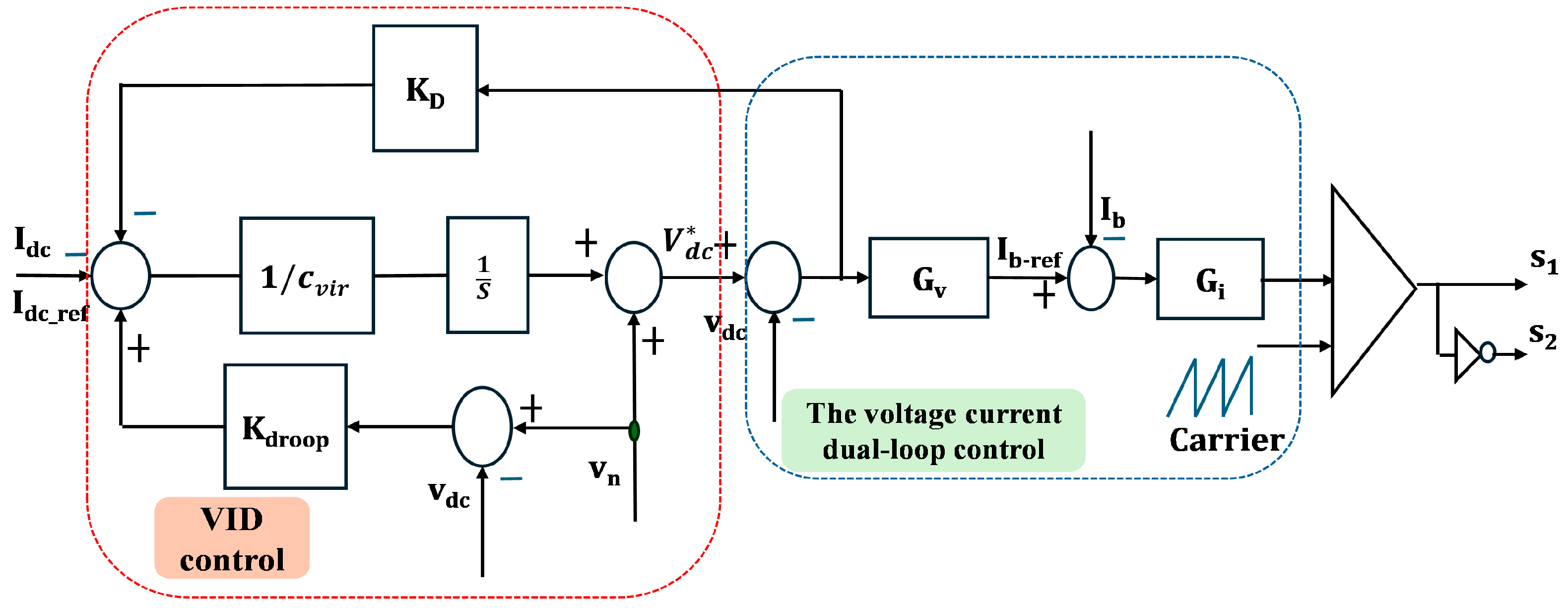
3.1. Primary Control
3.2. Secondary Control
3.3. Tertiary Control
3.4. Proposed Control Strategy for Multi-DC Microgrids
4. The Concept of Virtual Inertia in DCMGs
4.1. The Methods of VIC in DC Microgrids
- Augmented Inertia Control (AIC) [14]: the core idea behind this method is to replace the fixed droop factor with one that is a function of the rate of change in voltage. When a voltage change occurs, the droop factor decreases, causing the current to increase rapidly. This helps to mitigate voltage fluctuations. AIC is simple to implement, but can introduce high-frequency disturbances, potentially leading to stability issues.
- Virtual DC Machine Control (VDCM) [28]: This approach controls power converters to simulate the dynamic response of a DC machine, including its inertia and damping characteristics. While VDCM offers theoretically better performance and is more suitable for DC systems, its modeling and control design still require further simplification to improve practical implementation.
- Analogous Virtual Synchronous Generator Control (AVSG) [30]: In this method, power converters are regulated to match the dynamic characteristics of VSG, including its inertia and damping effects. This control strategy adjusts the converters’ output in response to load variations, emulating the behavior of traditional synchronous machines. Currently, the AVSG method is more advanced in terms of technical implementation and holds significant potential for large-scale applications. Due to its practicality and effectiveness in ensuring system stability, the VSG approach is preferred. In this paper, AVSG will be considered as the method to improve the inertia of the system.
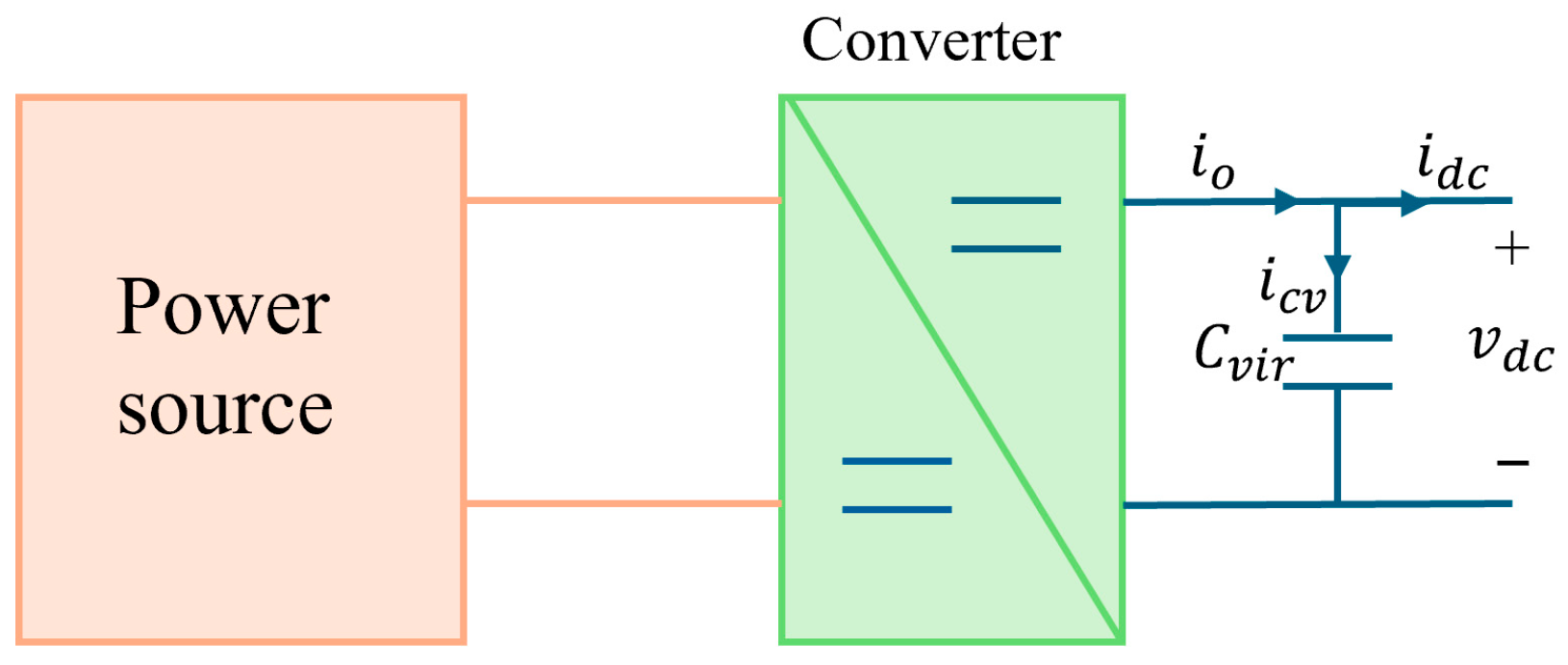
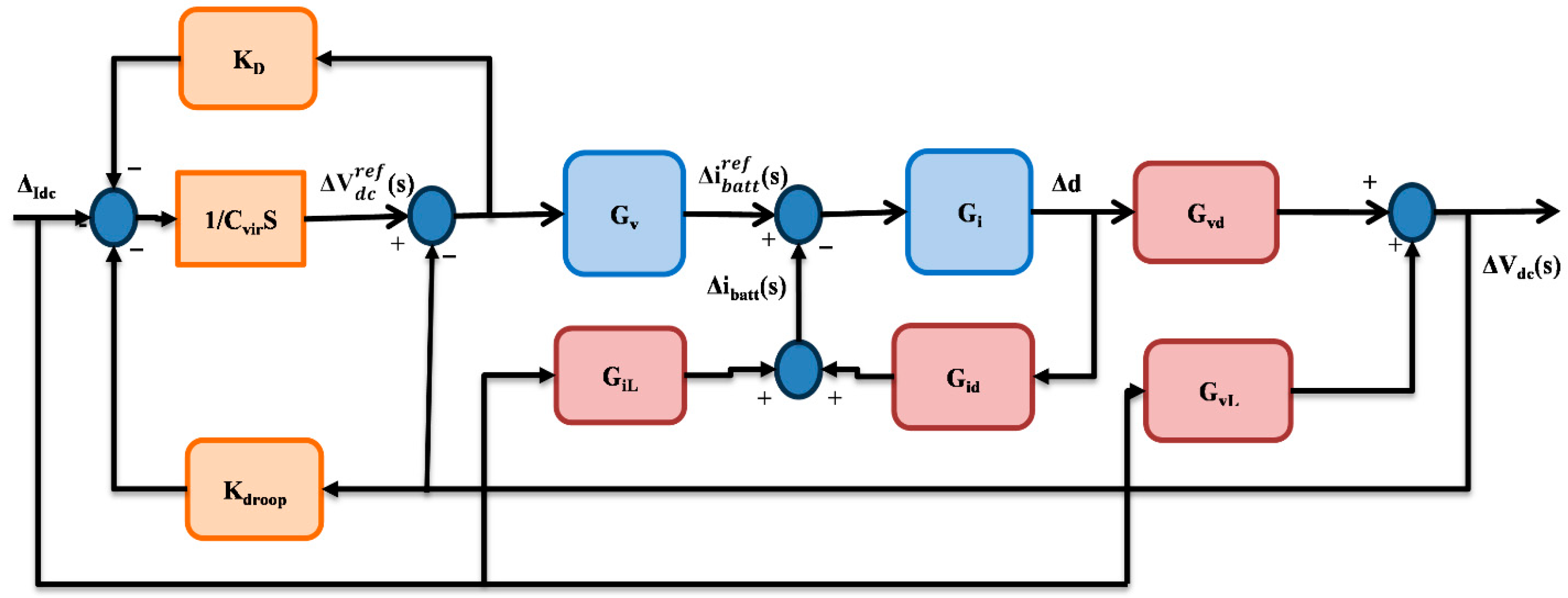
4.2. The Concept of AVSG in DC Microgrids
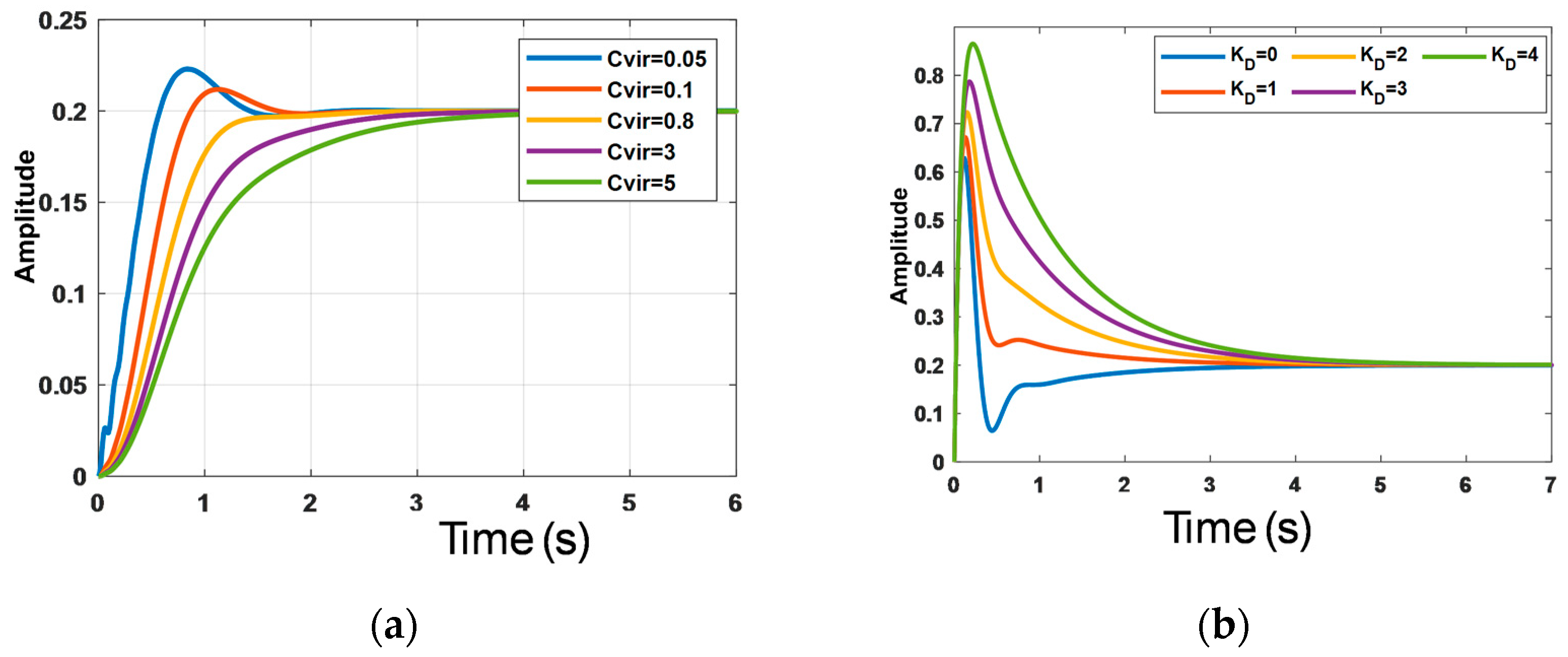
4.3. Determination of the Values of Cvir and kdamp
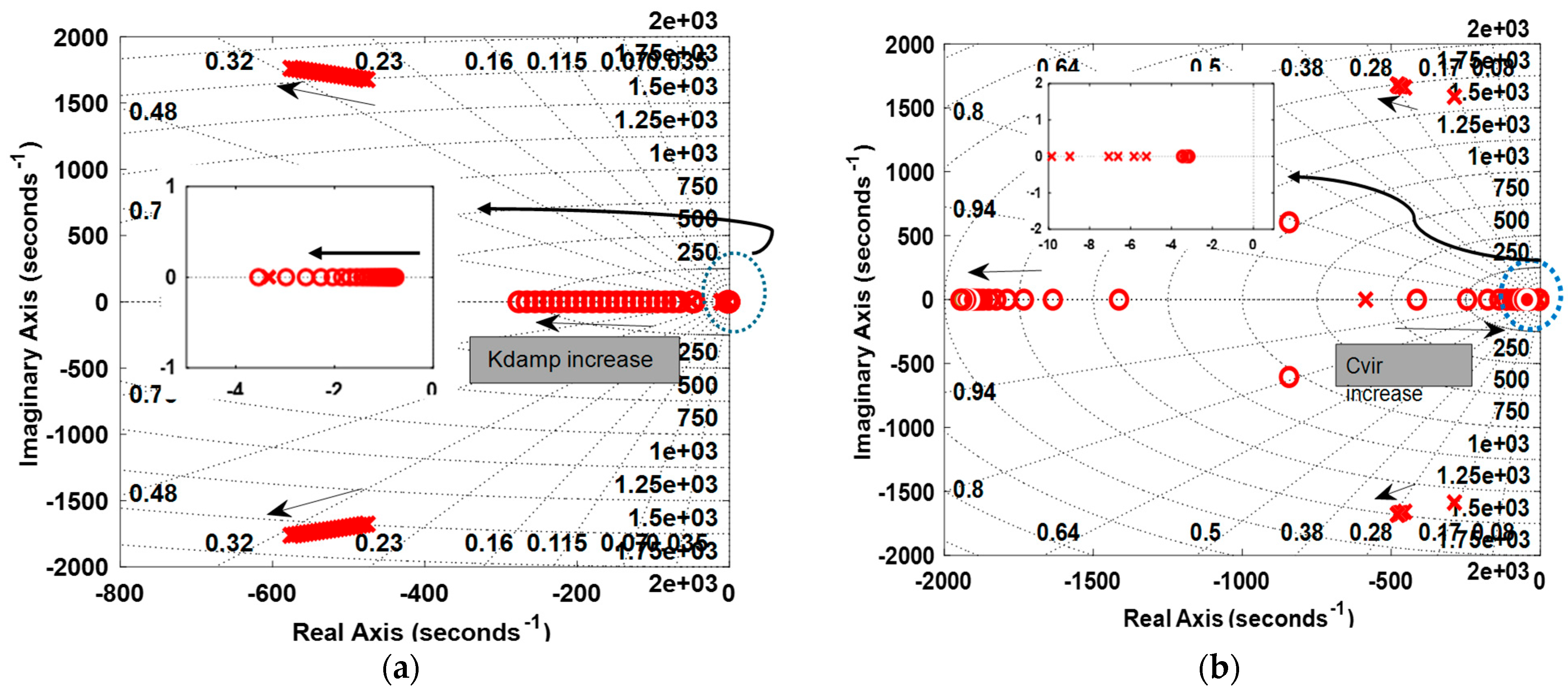
4.4. Stability Analysis
4.5. Case Study to Show the Effect of VIC on the System Response
5. Secondary Control for Interconnected DC MGs
5.1. Mathematical Model of the Proposed Coordinated Control of ESUs
- Scalability: The system is suitable for a wide range of applications, from small residential microgrids to large-scale utility systems.
- Adaptability: It accommodates varying ESU capacities and configurations without requiring significant modifications to the system design.
- Robustness: It maintains overall system performance even in case of faults or disconnections of individual ESUs.
- Accuracy: The power-sharing algorithm ensures equitable energy contributions from each ESU.
- Efficiency: By optimizing energy storage utilization, the system enhances overall energy efficiency and reduces operational costs.
5.2. Discussion of Control Objectives Achievement
5.3. Determination of the Range for λ
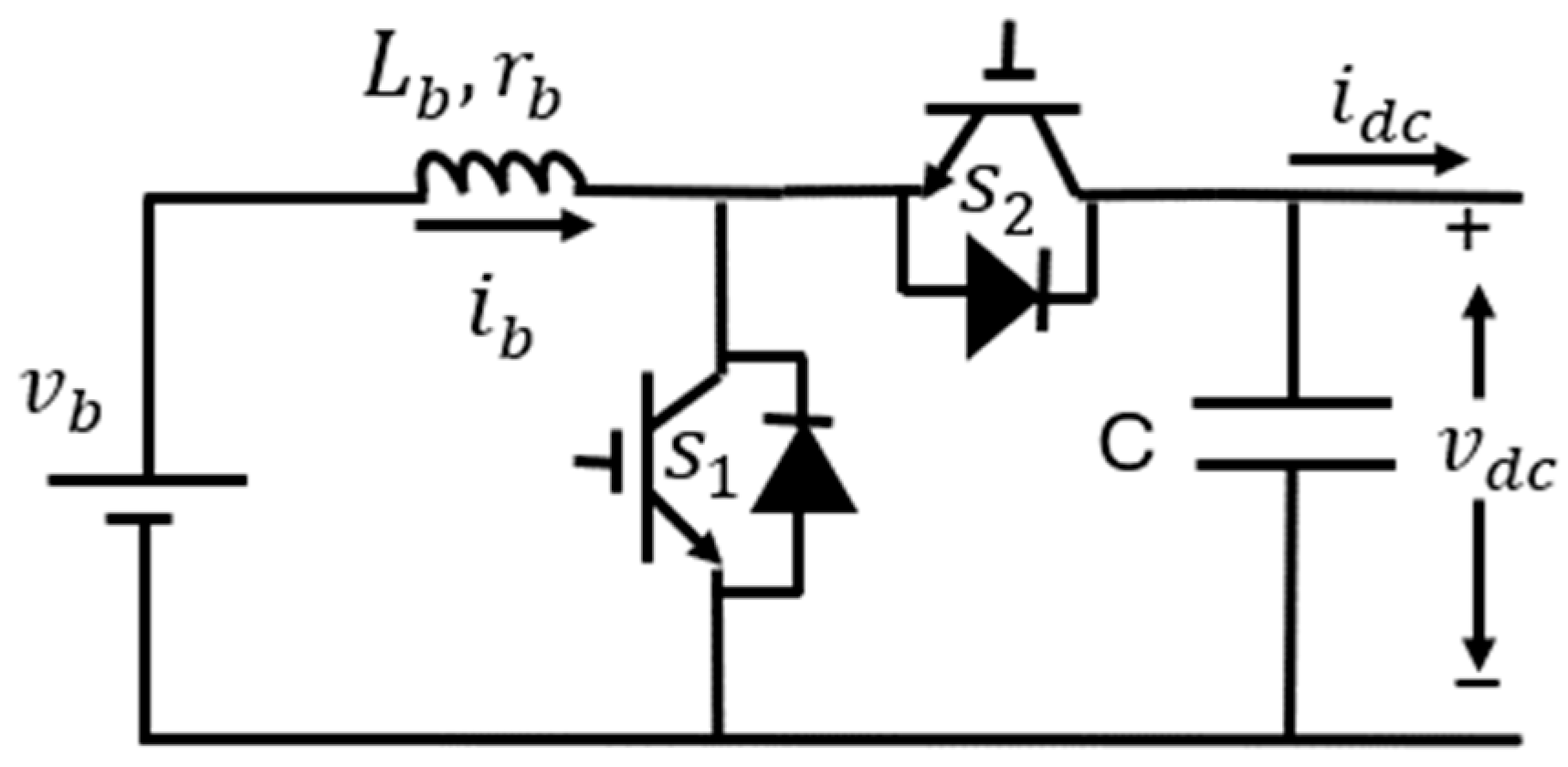
5.4. Complete Control Block Diagram of ESU
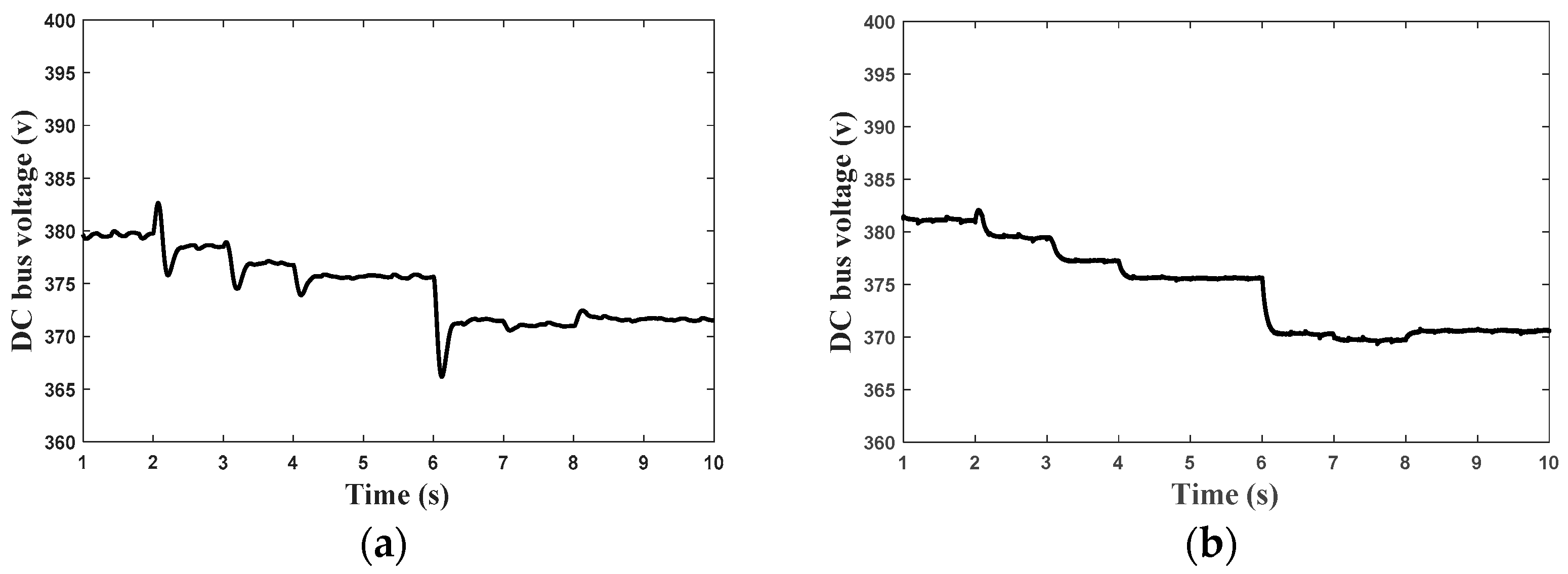
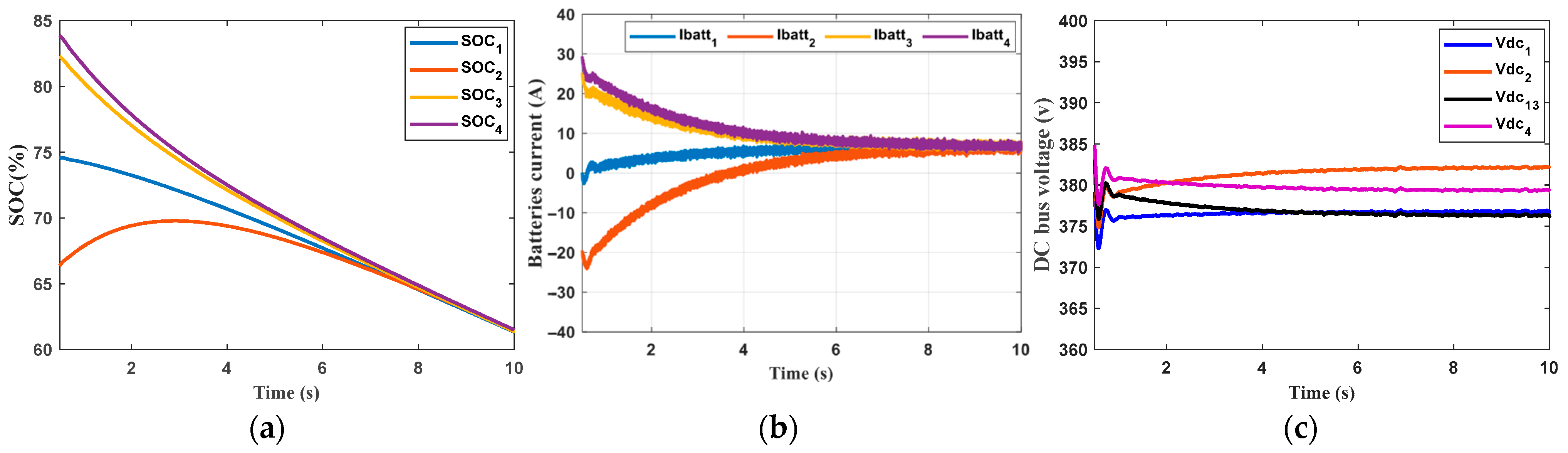
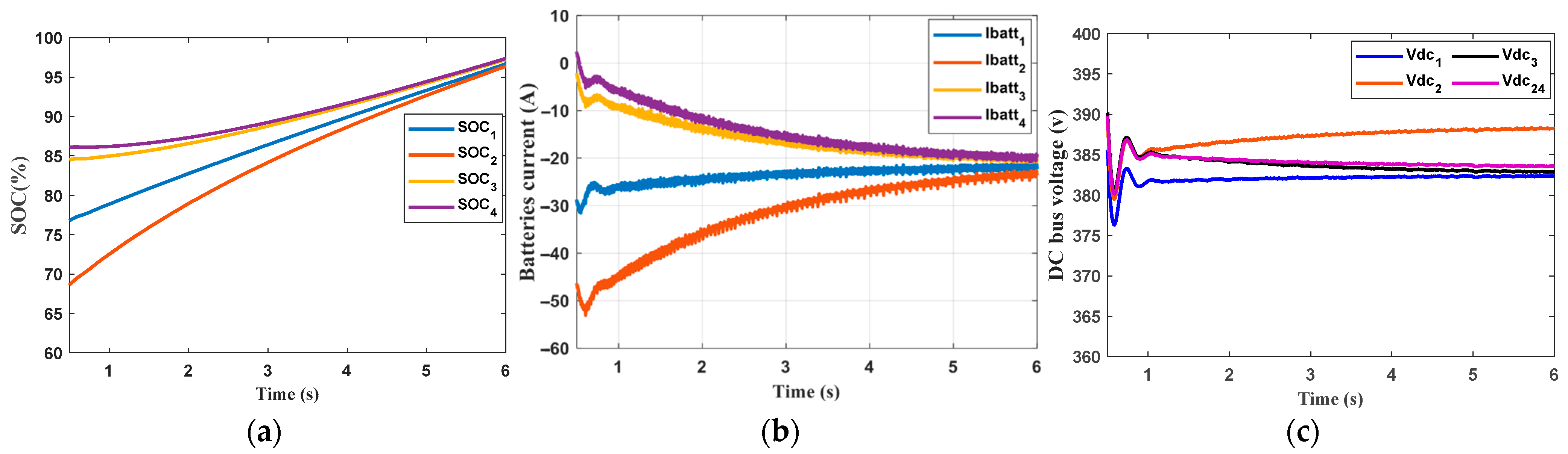
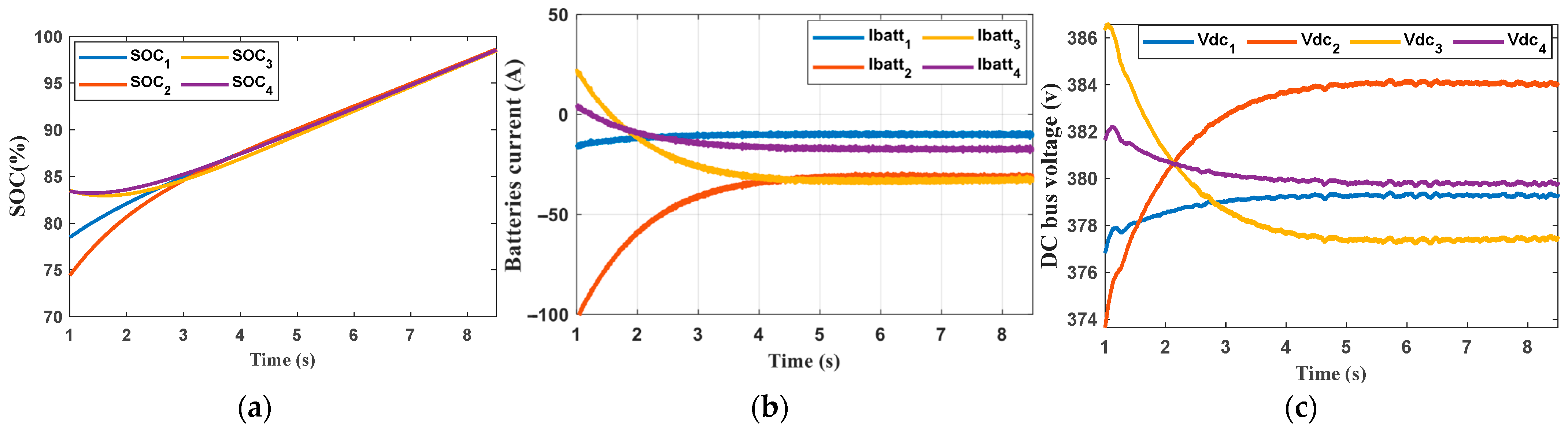
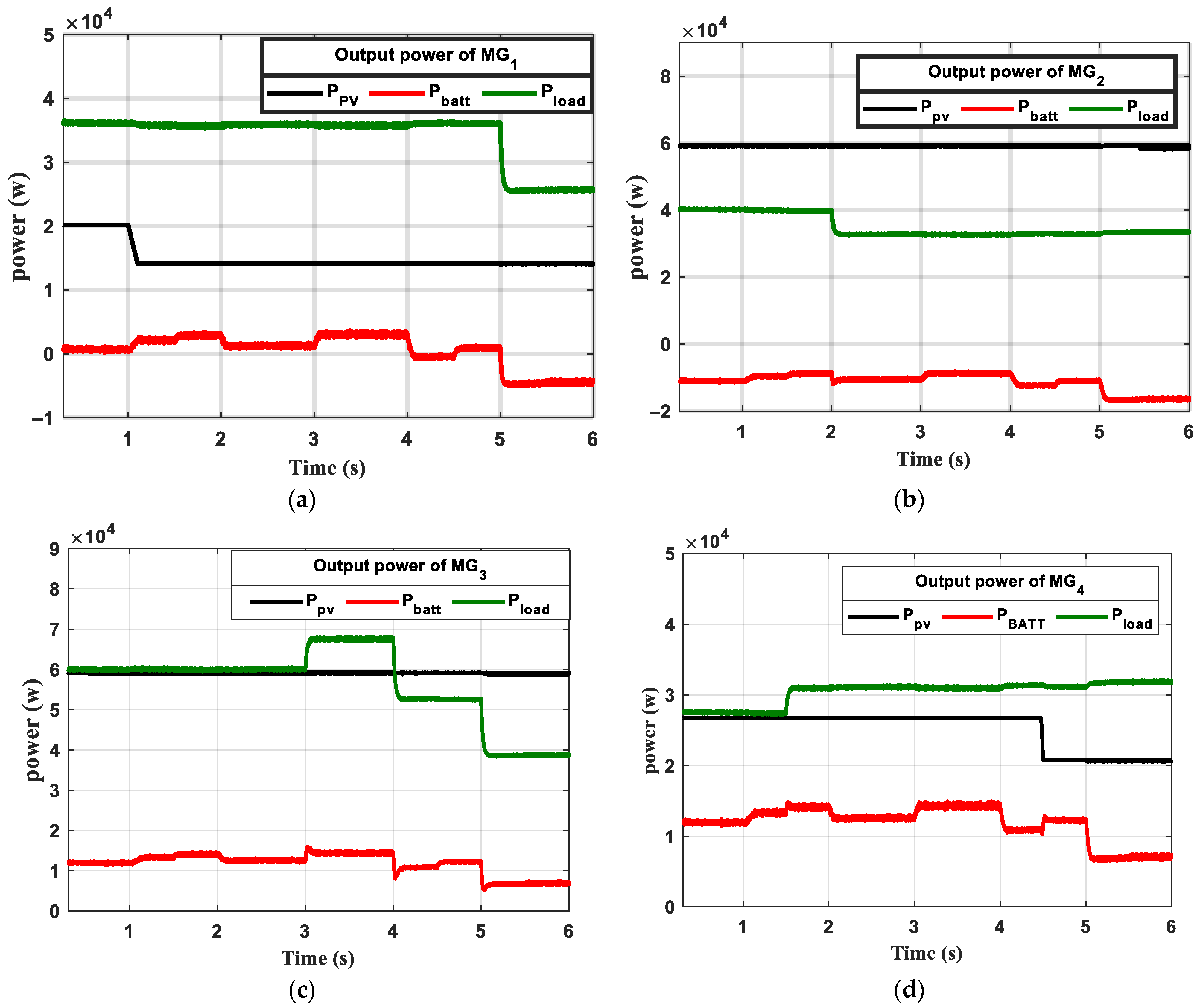
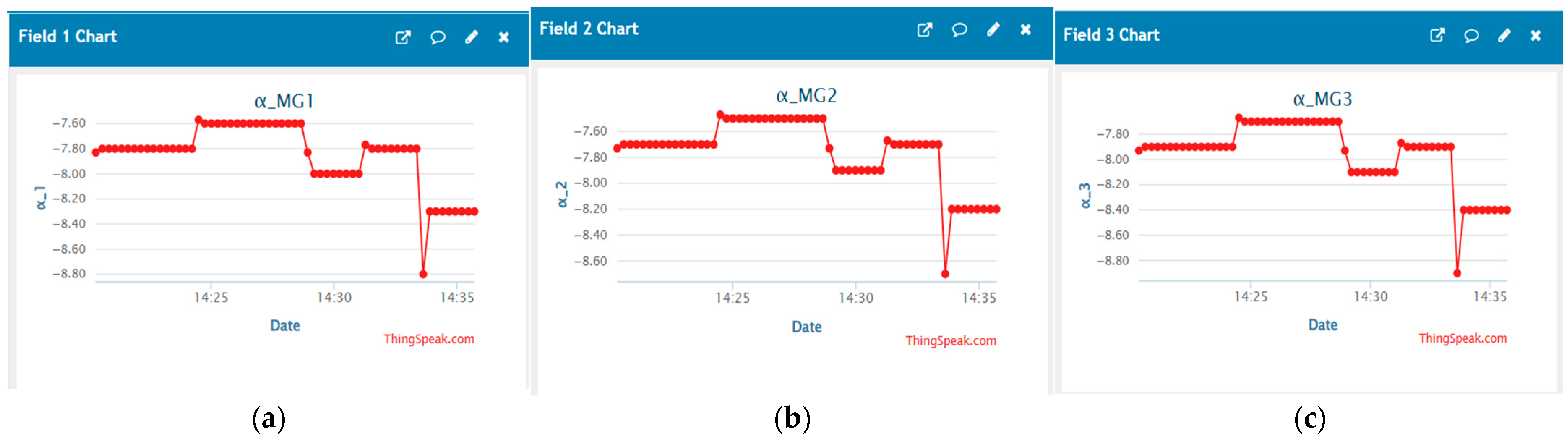
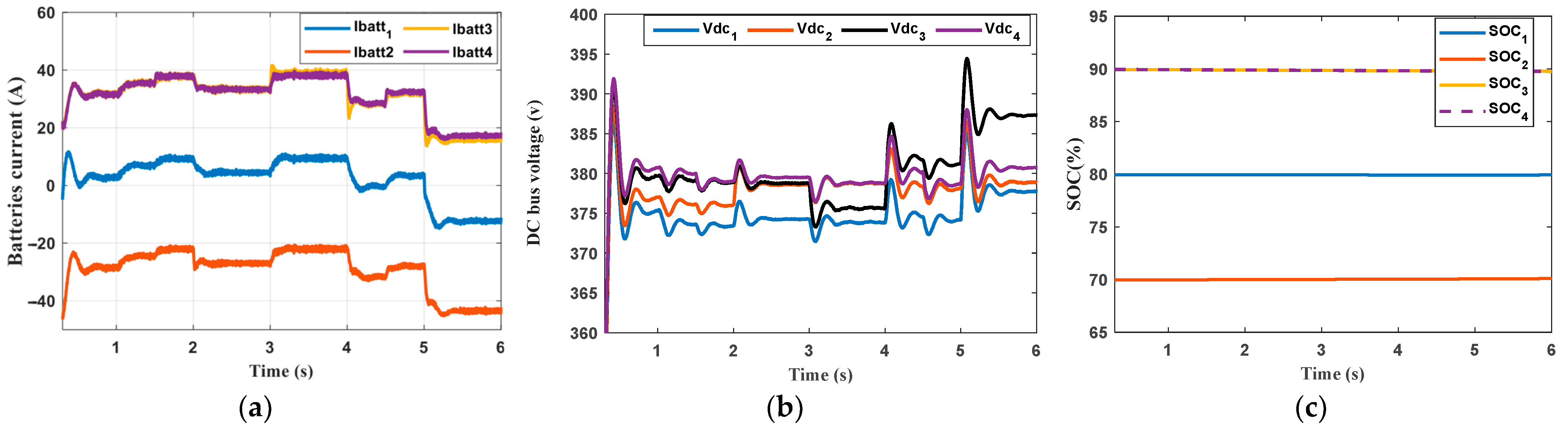
6. Results and Discission
- The first scenario
- The second scenario
- Comparison with the pervious control scheme
7. Conclusions
- Secondary Control: The secondary control successfully enabled cooperation between ESUs, which was evident during both charging and discharging, regardless of whether the ESUs had the same or different capacities.
- Primary Control: The primary control significantly improved the dynamic response of the system during load changes and varying irradiance conditions.
- Effect of Parameters: The effects of the parameters Cvir and kdamp were studied. It was observed that increasing the value of Cvir improved voltage regulation, although the system required more time to stabilize. For the parameter kdamp, a slower system response was observed, along with an increase in overshoot.
- Impact of λ: The parameter λ was also examined, and higher values of λ resulted in quicker balancing between ESUs, although this negatively impacted the output current of the converters.
- IoT integration: IoT-based centralized coordination of ESUs improved inertia and enhanced DCMMG system stability through real-time data exchange, monitoring and decision-making.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Y.; Ning, X.; Yang, P.; Xu, L. Review of power sharing, voltage restoration and stabilization techniques in hierarchical controlled DC microgrids. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 149202–149223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.; Huang, Q.; Zalhaf, A.S.; Bamisile, O.; Li, J.; Mansour, D.E.A.; Lin, X.; Yehia, D.M. Energy Management in Residential Microgrid Based on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring and Internet of Things. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 1907–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.N.; Jamian, J.J.; Rasid, M.M. Optimal multi-objective sizing of renewable energy sources and battery energy storage systems for formation of a multi-microgrid system considering diverse load patterns. Energy 2024, 304, 131921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomizu, Y.; Yehia, D.M.; Iioka, D.; Matsumura, T. Formulated representation for upper limitation of deliverable power in low-voltage DC distribution system. IEEJ Trans. Power Energy 2011, 131, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modu, B.; Abdullah, M.P.; Sanusi, M.A.; Hamza, M.F. DC-based microgrid: Topologies, control schemes, and implementations. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 70, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Shafiullah, M.; Ahmed, C.B.; Alowaifeer, M. A Review of Microgrid Energy Management and Control Strategies. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 21729–21757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, E.K.; Yehia, D.M.; Azmy, A.M. Adaptive droop control for balancing SOC of distributed batteries in DC microgrids. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 4667–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, W.; He, G. An Adaptive Virtual Inertial Control Strategy for DC Distribution Networks. Energies 2024, 17, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. A comparative study on damping methods of virtual synchronous generator control. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, EPE 2019 ECCE Europe, Genova, Italy, 3–5 September 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, G.V.; Periasamy, S.; Lu, D.D.C. Capacitor Current Control Based Virtual Inertia Control of Autonomous DC Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 6908–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Konstantinou, G.; Pou, J.; Zou, G.; Zhang, X. Multi-Objective Controller Design for Grid-Following Converters with Easy Transfer Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 6566–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Xue, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F.; Chen, H. Flexible Droop Coefficient-Based Inertia and Voltage Cascade Control for Isolated PV-Battery DC Microgrid. Energies 2022, 15, 9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Dragicevic, T.; Blaabjerg, F. A New Perspective for Relating Virtual Inertia with Wideband Oscillation of Voltage in Low-Inertia DC Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 7029–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Mishra, J.P.; Roy, B.K. Virtual DC machine: An inertia emulation and control technique for a bidirectional DC-DC converter in a DC microgrid. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhong, Q.C. Small-Signal Modeling and Parameters Design for Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Meng, F.; Xie, Z.; Yue, Y. An Inertia and Damping Control Method of DC-DC Converter in DC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, D.M.; Numair, M.; Mansour, D.A. Novel IoT-Based Droop Control for Battery SoC Balancing among Multiple Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2024, 15, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, E.W.; Mansour, D.A.; Abd el-Ghany, H.A.; Dawoud, S.M.; Azmy, A.M. A novel IoT-based adaptive protection scheme for active DC distribution systems incorporating networked microgrids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 238, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, K.; Xing, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, J. A simplified consensus-based distributed secondary control for battery energy storage systems in DC microgrids. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 155, 109627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Iyer, V.M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Zou, K. New Mesh Configurations with Decentralized Droop Control Method for DC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wei, M.; Luo, D.; Yang, L. Energy balancing strategy for the multi-storage islanded DC microgrid based on hierarchical cooperative control. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 12, 1390621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Al-Ismail, F.S.; Shafiullah, M.; Hossain, M.I.; Shahriar, M.S.; Mostafa, S.G.; Abido, M.A. A New Voltage Compensation and State of Charge-Assisted Power Sharing Strategy for DC Microgrids. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 15971–15983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, F.; You, S. Distributed Unified Controller Design for Parallel Battery Storage System in DC Shipboard Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, M.; Liu, J.; Jamborsalamati, P.; Rafi, F.H.M.; Rahman, S.; Hossain, J.; Stegen, S.; Lu, J. Internet of Things Platform for Energy Management in Multi-Microgrid System to Improve Neutral Current Compensation. Energies 2018, 11, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheba, M.A.; Mansour, D.A.; Abbasy, N.H. A new low-cost and low-power industrial internet of things infrastructure for effective integration of distributed and isolated systems with smart grids. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 4554–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangam, S.V.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Jambotkar, A.P.C.K. Smart Grid Communication Protocols. Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev. 2019, 3, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Zou, J.; Chung, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Voropai, N.; Xu, D. Multi-microgrid Energy Management Systems: Architecture, Communication, and Scheduling Strategies. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, N.; DIng, K.; Du, L.; Zhang, H. An SOC-Based Virtual DC Machine Control for Distributed Storage Systems in DC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinipour, A.; Hojabri, H. Virtual inertia control of PV systems for dynamic performance and damping enhancement of DC microgrids with constant power loads. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Luo, A.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Dong, Y.; Guerrero, J.M. A Virtual Inertia Control Strategy for DC Microgrids Analogized with Virtual Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6005–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| MG1 | MG2 | MG3 | MG4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV array | 20 kW at 25 °C and 1000 W/m2 | 60 kW at 25 °C and 1000 W/m2 | 60 kW at 25 °C and 1000 W/m2 | 30 kW at 25 °C and 1000 W/m2 |
| PV converter | = 0.2 mH, = 0.002 Ω, = 0.003 mF | = 0.5 mH, = 0.005 Ω, = 0.003 mF | = 0.5 mH, = 0.005 Ω, = 0.003 mF | = 0.25 mH, = 0.0025 Ω, = 0.003 mF |
| Battery unit | 110 V, capacity = 100 Ah | |||
| Battery converter | P = 30 kW, = 0.373 mH, = 0.005 Ω, C = 0.002 F | |||
| Voltage control of B-DC | Kp = 3, Ki = 100 | |||
| Current control of B-DC | Kp = 0.005, Ki = 0.1 | |||
| Cvir = 0.5, kdamp = 0.5, Rd = 0.2 | ||||
| Scheme | Improved Transient Response | Effective Power Sharing | Maintain SOC Balance | Applicable for Any Network Configuration | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | YES | YES | NO | NO | Less |
| [17] | NO | YES | YES | YES | Less |
| [19] | NO | YES | YES | YES | Moderate |
| [20] | NO | YES | YES | NO | Complex |
| [23] | NO | YES | YES | YES | Complex |
| [28] | YES | YES | YES | NO | Complex |
| Proposed | YES | YES | YES | YES | Less |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belal, E.K.; Yehia, D.M.; Azmy, A.M.; Ali, G.E.M.; Lin, X.; EL Gebaly, A.E. Development of a Novel IoT-Based Hierarchical Control System for Enhancing Inertia in DC Microgrids. Smart Cities 2025, 8, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050166
Belal EK, Yehia DM, Azmy AM, Ali GEM, Lin X, EL Gebaly AE. Development of a Novel IoT-Based Hierarchical Control System for Enhancing Inertia in DC Microgrids. Smart Cities. 2025; 8(5):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050166
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelal, Eman K., Doaa M. Yehia, Ahmed M. Azmy, Gamal E. M. Ali, Xiangning Lin, and Ahmed E. EL Gebaly. 2025. "Development of a Novel IoT-Based Hierarchical Control System for Enhancing Inertia in DC Microgrids" Smart Cities 8, no. 5: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050166
APA StyleBelal, E. K., Yehia, D. M., Azmy, A. M., Ali, G. E. M., Lin, X., & EL Gebaly, A. E. (2025). Development of a Novel IoT-Based Hierarchical Control System for Enhancing Inertia in DC Microgrids. Smart Cities, 8(5), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050166






