Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Small-scale V2I safety applications are feasible, though there is nuance in their implementation.
- Using high-resolution video data streams for these applications is, most likely, unfeasible. Instead, using object data streams will maximise system feasibility.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- Costs associated with the deployment and maintenance of the computational resources that are necessary for sensor processing need to be reduced.
- The use of mmWave connectivity is, most likely, necessary for the use of video data streams.
Abstract
Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X) communications is a technology that enables intelligent vehicles to exchange information and thus coordinate with other vehicles, road users, and infrastructure. However, despite advancements in cellular technology for V2X applications, significant challenges remain regarding the ability of the system to meet stringent Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements when deployed at scale. Thus, smaller-scale V2X use case deployments may embody a necessary stepping stone to address these challenges. This work assesses network architectures for an Intelligent Perception System (IPS) blind road junction or blind corner scenarios. Measurements were collected using a private 5G NR network with Sub-6GHz and mmWave connectivity, evaluating the feasibility and trade-offs of IPS network configurations. The results demonstrate the feasibility of the IPS as a V2X application, with implementation considerations based on deployment and maintenance costs. If computation resources are co-located with the sensors, sufficient performance is achieved. However, if the computational burden is instead placed upon the intelligent vehicle, it is questionable as to whether an IPS is achievable or not. Much depends on image quality, latency, and system performance requirements.
Keywords:
V2X; V2X communications; Vehicle-to-Everything; ITS; cellular; C-V2X; 5G NR; latency; V2I; network planning 1. Introduction
In recent years, the concept of intelligent vehicles and the field of Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) have reached a point where they are both technically and commercially feasible. This is underscored by the ongoing research and commercial ventures by major automotive companies such as General Motors’s Cruise [1], Alphabet’s Waymo [2], Tesla [3], and Uber [4]. These advancements have sparked interest and research within the industry on the notion of the “connected” intelligent vehicle which represents a natural progression of existing endeavours to integrate advanced sensing and computational capabilities into vehicles. Consequently, these endeavours have led to the generation and processing of substantial volumes of data within new intelligent vehicles, data that could potentially be shared with other relevant parties, including nearby vehicles or traffic management authorities. The significance of this progression is accentuated by the efforts of wireless communications standard-setting bodies like the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) [5,6] for cellular networks, and the IEEE [7] for Wi-Fi.
Thus, in a broad sense, Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications describe a framework that enables a connected intelligent vehicle (CIV) to exchange information with fellow road users and stakeholders in automotive environments. As such, the primary objective of V2X communications systems is to enhance road safety and optimise traffic flow by enabling effective communication and coordination among stakeholders within a road traffic ecosystem. Incorporating V2X communications introduces a diverse array of potential scenarios and applications, encompassing safety and traffic efficiency and extending to infotainment and eCommerce uses [8,9]. Consequently, these potential applications involve a considerable number and variety of stakeholders, necessitating a robust, secure, and reliable wireless communication technology as the underlying foundation.
Cellular communications, fostered by the efforts of 3GPP [10], has long been under consideration as a prospective technology for V2X communications [11]. Within the domain of V2X communications, cellular communications are commonly denoted as C-V2X. The extensive global deployment of cellular base stations establishes a strong foundation for C-V2X to cater to a diverse range of users, including vehicles, trains, cyclists, pedestrians, and stationary infrastructure, thus resulting in the inclination towards leveraging cellular as a viable V2X access technology. The 3GPP has formulated multiple specifications for C-V2X, where the initial specification emerged as a part of 3GPP Release 14 [12] in 2017, often referred to as LTE-V2X due to its basis in the 4th generation of cellular, 4G LTE. Subsequently, another specification was introduced with the advent of the fifth generation of cellular technology (5G NR) in 3GPP Release 15 [13] in 2019, commonly recognised as NR-V2X.
Numerous works have studied the efficacy of both LTE-V2X and NR-V2X for various V2X communications use cases and applications. In general, studies have shown that C-V2X can uphold QoS metrics [14,15,16,17] to support more basic V2X communications use cases outlined by the 3GPP [8,18], such as traffic information, traffic flow management, infotainment and eCommerce services. Certain works specifically address the teleoperation type use case [14,16,19], often within the context of commercial cellular networks. The consensus among these investigations is that achieving an advanced use case like teleoperation is viable under ideal circumstances; however, challenges relating to cell coverage, handover performance, and congestion management pose significant obstacles, reducing feasibility considerably.
These findings from studies in commercial cellular networks are further reinforced by those completed with private cellular networks. Several works demonstrate that in controlled scenarios LTE-V2X could uphold QoS metrics for advanced V2X use cases [20,21]. Recent works studying NR-V2X and its enhancements [22,23,24,25], also within private cellular networks, have shown very promising performance for the technology’s capacity as a candidate wireless access technology for V2X communications. While C-V2X has significant potential as a V2X communications candidate, it is clear from previous studies that it is not yet ready to be deployed at scale for advanced use cases, such as teleoperation, due to the challenges associated with reliability in terms of upholding QoS metrics.
Given these challenges associated with deployment at scale, it is reasonable to initially begin with developing V2X communications, both in technology and commerce, with smaller-scale implementations that have the most significant potential impact. Implementations of this calibre can benefit from a more predictable wireless channel and can be deployed in locations with existing infrastructure. As such, if conducted correctly, smaller-scale implementations can be used to focus on considerations for developing sufficient QoS for V2X communications applications and use cases at a larger scale. One such application that fits these criteria is that of the blind road junction or blind corner, wherein the view of significant portions of a junction or road is occluded by static obstructions. In automotive environments, these blind road junctions and blind corners represent a cohort of particularly hazardous scenarios that an intelligent vehicle must contend with. Convex mirrors [26] are often placed at these locations (see Figure 1) to allow drivers to see around the occlusions that render the junctions and corners blind. However, given the difficulty of detecting objects in the convex mirror itself [27,28], the safety of these locations can likely be improved by the introduction of fixed sensors with V2I communications capabilities [29], also known as a Fixed Sensor Node (FSN), shown in Figure 2.
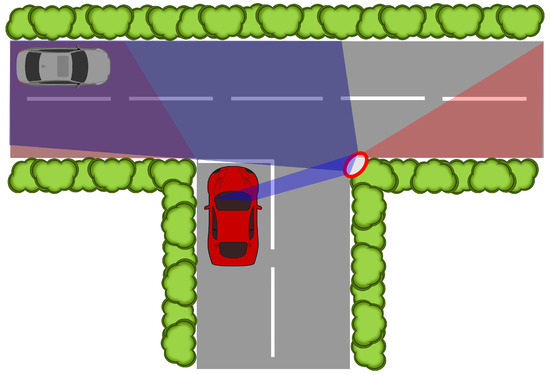
Figure 1.
Blind T-junction scenario with occlusions caused by foliage near the roadside. The occluded vehicle on the major road is revealed for the ego vehicle (red vehicle) by the convex mirror (red ellipse).
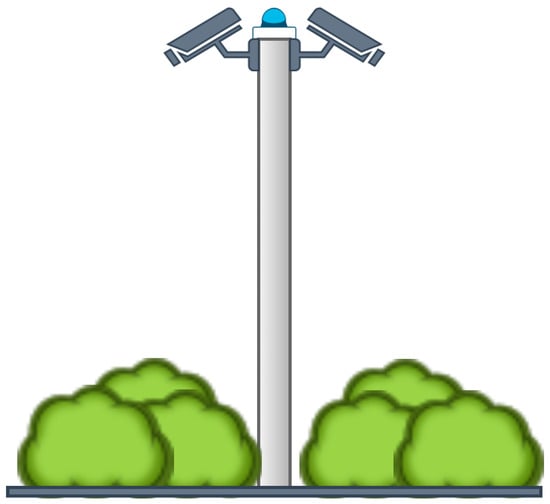
Figure 2.
Example of an FSN, with several sensors mounted at a high vantage to appropriately observe a blind junction scenario.
Hazardous automotive scenarios such as occluded or blind road junctions have been considered by the research community for many years [30]. However, most of the research focuses on the motion planning aspect of navigating these scenarios. Some studies exclusively rely on the intelligent vehicle’s own capabilities to safely navigate the hazardous scenario [31]. Sama et al. [32] present a reinforcement learning algorithm trained on human data to determine how the intelligent vehicle should behave, whereas Solomitckii et al. [33] propose the use of mmWave radar with reflectors installed at the junction to allow the intelligent vehicle to see around corners. Other works take into consideration the use of external sensors via V2I communications to inform the motion planning of the intelligent vehicle [34,35]. Fewer works address the communications perspective of this occluded use case. Notably, Jaktheerangkoon et al. [36] demonstrate using DSRC that direct V2V communications are likely not a feasible option given Line-of-Sight (LOS) constraints. Buchholz et al. [37] and Annu et al. [38] develop and demonstrate V2I use cases using Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) [39] technology, demonstrating its efficacy over cloud computing.
The aim of this work is to investigate the wireless access challenges of a blind road junction V2I use case, specifically regarding the degree to which the trade-offs between network performance and implementation cost affect the feasibility of the V2I system. In particular, this work intends to study only the technical feasibility of the V2I system. Legal, standardisation, or insurance implications surrounding the security, privacy, and risk factors of this concept are not within the scope of this work. Additionally, the experimental methodology and data analysis techniques can be replicated using off-the-shelf equipment and therefore can be easily re-implemented, repeated, and augmented.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows; an overview of the chosen small-scale V2I use case is presented in Section 2. The experimental methodology used to conduct this study is outlined in Section 3. Section 4 presents the results of the measurement study and discusses the findings for each of the network architectures. Section 5 discusses the limitations of this study and future work. Finally, Section 6 concludes this paper.
2. Intelligent Perception System (IPS) Overview
The following section presents an overview of the system architecture necessary to enable the blind road junction V2I use case.
As previously mentioned, the safety of blind road junctions can likely be improved by the introduction of so-called FSNs. An FSN is a system, mounted at an appropriate vantage point, composed of one or more sensing modalities, e.g., RGB cameras, LiDAR, radar, and thermal cameras, that allow an object detection algorithm to perceive regions of interest. As such, one or more FSNs combined with V2X communications capabilities can be referred to as an Intelligent Perception System (IPS), illustrated in Figure 3. At these blind or occluded locations, one or more FSNs can be installed in positions where sensors can perceive the region of interest and any roads that may connect to it to form an IPS. Using sensor fusion technology [40], information about the region(s) of interest can collected into some form of Local Dynamic Map (LDM) [41] and transmitted to nearby CIVs in a publisher-subscriber groupcast type information dissemination model.
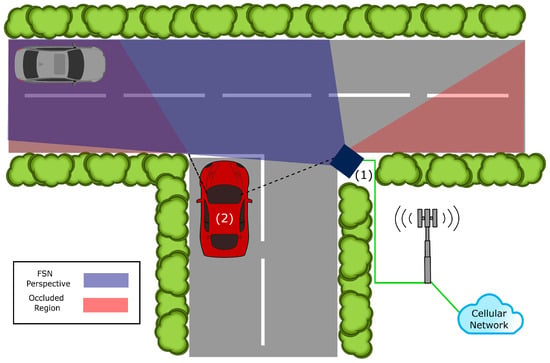
Figure 3.
The Intelligent Perception System (IPS) with a CIV, in red, approaching a blind T-junction that is served by a Fixed Sensor Node (FSN), in navy, with an appropriate vantage of the occluded region. Two configurations: (1) FSN computing, (2) car computing.
A key concern for the implementation of an IPS is the most appropriate location of the computation. Processing of the various sensing modalities by the object detection algorithm and the sensor fusion technologies at the FSN(s) requires a significant degree of computational power. Thus, it would be reasonable to suggest that the computation should be deployed where the data are being generated, i.e., co-located with the FSN(s). However, the installation and maintenance costs of such a deployment may be prohibitive. To avoid the cost of the computation, the sensor data from the FSN(s) could instead be transmitted, with associated meta-data, directly to the nearby CIVs for onboard processing. However, depending on the number of sensors per FSN and the number of FSNs at the junction, the volume of data to be transmitted may be significant. Alternatively, as illustrated in Figure 4, computing paradigms such as Cloud Computing [42] or MEC [39] in conjunction with Software-Defined Networking (SDN) [43] and Network Function Virtualisation (NFV) [44] technologies as part of 5G networking slicing [45] could be used. The location of the computation for the FSN(s) can have a significant bearing on the performance capabilities and cost of the IPS.
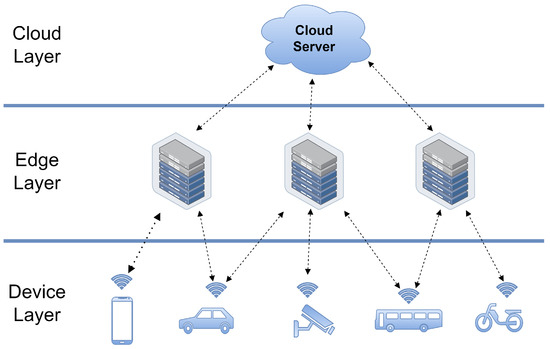
Figure 4.
Simplified View of Computing Architectures for V2X Communications, highlighting connections between nodes in the network.
2.1. Measurement Scenarios
To evaluate the trade-offs between IPS network architectures, they must first be defined and discussed. The locations of the data sources, data processing, and data consumers involved in the system must be considered. This is pertinent as these locations will have the most significant bearing on the topology of the network used to implement the system. The data sources in the case of the IPS are the FSNs and their location will be determined by the position that provides the most appropriate perspective(s) of that region. Similarly, the data consumers in this case are the CIVs that must navigate the blind or occluded junction.
The location of the computational resources in IPS can have a significant bearing on the feasibility of the system in terms of the performance capabilities and cost, i.e., deployment and maintenance costs. In this work, we evaluate and compare two different configurations or locations for the computational resources of the IPS. Specifically, the trade-offs between configurations are evaluated in terms of network performance, i.e., latency, throughput, and reliability. In the following subsections, the two configurations are presented and discussed to explore their apparent advantages and disadvantages.
2.1.1. Configuration 1: Edge Computing
The first configuration of the IPS that will be evaluated, illustrated in Figure 3, is where the computational resources are integrated within the FSN(s) or located nearby in the form of an edge server [39]. This configuration could be considered the default choice as advanced sensing systems are often deployed with their computational resources integrated into the same physical equipment. In this configuration, the sensor data are sent to the local computational resources, to be processed and converted into an object data format. This object data format represents, in a local or global coordinate system, the distinct objects within the region of interest that are of note to CIVs, e.g., other vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, animals, debris, or other possible hazards. The processed object data are then broadcast to the CIVs subscribed to the IPS, informing them of the content in the region of interest.
This configuration should have a significant advantage in terms of network performance, as the data can be sent in the form of ITS-specific packets such as Cooperative Awareness Messages (CAMs) [46] and Decentralised Event Notification Messages (DENMs) [47], which are small packets, on the order of hundreds of bytes. Thus, the latency of packets can be kept low, and the throughput requirements are also quite low. However, this configuration should also incur a significant cost, particularly regarding maintenance, as the computational resources would require substantial power, climate control, robustness, and security. Additionally, in this configuration, the system responsible for processing the sensor data is now also responsible for the quality of the decisions that can be made by the CIVs, which may not be desirable.
2.1.2. Configuration 2: Fog Computing
The second configuration of the IPS that will be evaluated, illustrated in Figure 3, is where the computational resources are located within the CIVs that connect to the IPS, also known as Vehicular Fog Computing [48,49]. This configuration can be viewed as the inverse of Configuration 1, as it offsets the challenges associated with deploying the computational resources at the FSN(s) by transferring the burden of processing sensor data to the CIVs subscribed to the IPS. Thus, in this configuration, the sensor data are transmitted directly to the CIVs subscribed to the IPS. In this configuration, more autonomy is given to the individual connected vehicles. Specifically, the CIV does not need to blindly trust the confidence intervals of the processed data coming from the FSN(s) and may verify the content of the sensor data itself.
This configuration has a significant advantage in terms of cost as the sensors alone should not require substantial power, climate control, or security. The primary cost associated with this configuration is the deployment cost, where the FSN(s) would only require power and a network connection. However, this configuration also has a significant disadvantage in terms of network performance, as the unprocessed sensor data from one or more FSNs must be broadcast to the subscribed CIVs. Thus, transmission costs will be higher and as a consequence larger deployment costs for communications hardware.
3. Experimental Methodology
In the following section, the experimental methodology used to evaluate the trade-offs between network architectures of the IPS is presented.
3.1. Measurement Setup
With the network architecture configurations defined, the measurement setup used to evaluate them can be presented. Given that this work aims to evaluate the network architectures of the IPS and not the sensing modalities or application layer functions, a pseudo-IPS is used to conduct measurements. This pseudo-IPS, illustrated in Figure 5, consists of a single pseudo-FSN connected (via 1 Gb Ethernet) to a private 5G NR standalone network from DruidSoftware (Wicklow, Ireland—v5.2.4.0-1.P1) [50] with a single gNodeB serving a pseudo-CIV. Windows-based PCs are used to represent both the pseudo-FSN and pseudo-CIV in this measurement setup. Connectivity is provided via a VirtualAccess GW1400 [51] (Sub-6GHz, i.e., 3.5 GHz) rugged automotive cellular router featuring a Quectel RM500Q [52] modem. To appropriately approximate a sub-urban or urban blind road junction or blind corner scenario, the pseudo-CIV is located ∼50 m away from the gNobeB and repeatedly traverses a ∼20 m path, as illustrated in Figure 5. Additionally, given the spectrum allocation changes in 5G NR [53,54], two connectivity options are investigated for Configuration 2, Sub-6GHz (FR1) and mmWave (FR2). In addition to the Sub-6GHz (3.5 GHz) connectivity option, connectivity for mmWave spectrum (26 GHz) is provided by a MicroAmp [55] CPE router featuring a Quectel RM530N [56] modem.
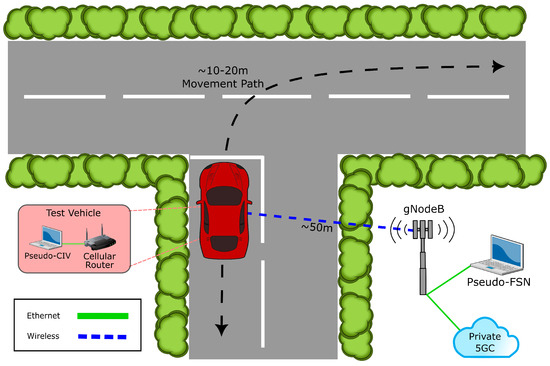
Figure 5.
Pseudo–IPS setup with a private 5G NR standalone network used to conduct measurements.
Two different software tools, ping and iPerf3 [57], were used to conduct the measurements for this study. A custom application was written to generate ICMP packets at a frequency of 1 Hz and record the round-trip-time (RTT) and thus the end-to-end (E2E) latency. iPerf3 was used to collect throughput measurements. An iPerf3 server was installed on the pseudo-FSN and the iPerf3 client was installed on the pseudo-CIV, where UDP streams were used to more closely align with the CAM [46], DENM [47] or CPM [58] packets used in V2X communications, sent from the pseudo-FSN to the pseudo-CIV. These tools were not run in parallel to avoid the effects of packet collisions or routing delays from the scheduling of the various ICMP and UDP packets.
3.2. Measurement Plan
To evaluate the outlined configurations for the IPS, a series of potential measurement runs were identified. Each of the identified measurement runs was chosen to encapsulate data rates that would potentially be generated by an FSN in each of the outlined configurations. For each of the selected data rates, as described in Table 1, 3 measurement runs of 3 min in duration were conducted using iPerf. In the case of the additional mmWave setup for Configuration 2, an additional set of measurements was repeated using the sensor data rates where the Sub-6Hz setup notably drops in performance. Latency measurements were conducted with the ping utility in the same format, i.e., 3 runs, each 3 min in length, repeated before each of the aforementioned iPerf measurement runs.

Table 1.
Data rates for measurement runs.
In Configuration 1, where only object data are transmitted from the FSN(s) to the CIV(s), data rates were chosen to represent the amount of activity in the scene, i.e., a little, some, or a lot of activity. Using the specifications for the CAM message type (300 bytes for each CAM at 10 Hz [8,46,59]) results in a data rate of ∼25 kbps. For the purposes of this work, this data rate will represent a moderate amount of activity in a scene, thus data rates for a quiet and busy scene can be represented by half (5 Hz–12.5 kbps) and double (20 Hz–50 kbps) the data rate for a moderate scene, respectively.
In Configuration 2, where sensor data are transmitted from the FSN(s) to the CIV(s), data rates were chosen based on common camera architectures with varying resolutions, frame rates, and compression levels. While it is unlikely that any of these specific camera architectures will satisfy all of the possible FSN scenarios, they will serve as reference points of known video performance for given data rates in Table 1.
Current generation CCTV Cameras [60] use high resolution (8MP) sensors with low frame rates (10–20 frame/s) and high compression ratios (H.265), yielding up to 8 Mbps of bandwidth, enabling the storage of large volumes of data. Mobile phones [61] and action cameras [62] most commonly capture 8 MP videos at 30 frames/s with a lower compression ratio (H.265), yielding up to 50 Mbps bandwidth to achieve higher image quality at the expense of storage. Recent trends towards HDR displays have also pushed manufacturers of consumer cameras to implement HDR video captures, that require more storage of colour information (more bits per pixel). Capturing HDR video, with 10 or 12 bits per pixel, causes the bit rate to increase to approximately 150 Mbps. Current production vehicles with advanced ADAS features commonly have HDR cameras (12-bit) [63] to deal with the challenging dynamic range conditions of the outdoors and typically have 2 MP sensors that capture 30 frames/s. These camera systems minimise latency by not compressing the image and therefore have by far the largest bit rate of approximately 800 Mbps, which is set to rise to 3 Gbps for next-generation 4 K video cameras.
4. Results
The aim of the analysis in this work is to estimate the general performance characteristics of the identified network architecture configurations so that their performance and the trade-offs between them can be evaluated. To accomplish this, we analyse two key metrics: latency and throughput. First, the results of the experimental methodology will be presented. Following this, the findings as they relate to the outlined configurations will be discussed. It should be noted that the figures presented in this analysis use a log axis for display purposes. In addition, the upper and lower fences of the box plots presented in this section are determined by Equations (1) and (2) [64], where IQR is the inter-quartile range.
4.1. Latency
Latency is often viewed, in addition to reliability, as the dominant metric for safety-critical use cases and applications [65]. In the context of ITS, delayed packets can lead to an intelligent vehicle making a misinformed decision based on out-of-date information. Particularly in safety-critical ITS applications, this can lead to accidents, or in non-safety ITS applications can lead to decreases in traffic efficiency and fuel economy. Table 2 and Figure 6 present the latency performance statistics and distributions for each of the Sub-6GHz and mmWave connectivity setups used to evaluate the network architectures of the IPS concept.

Table 2.
Latency Performance Statistics.
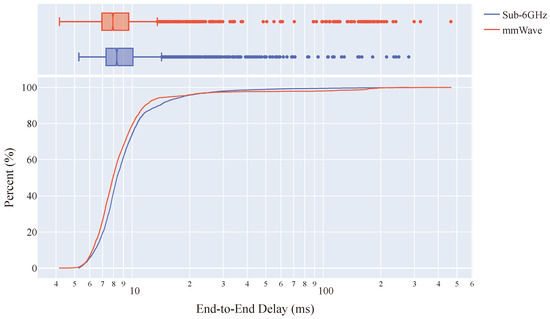
Figure 6.
eCDF + marginal box plot of E2E latency performance distribution for Sub-6GHz and mmWave connectivity setups (Sub-6GHz: 8.32 ms, mmWave: 7.93 ms median latency).
Between the two connectivity setups, the mmWave setup achieved on average the lowest latencies, as shown by the quartiles in Table 2, with a minimum latency at 4.17 ms. However, the Sub-6GHz setup displayed a higher degree of reliability and stability, resulting in a larger kurtosis (Sub-6GHz: 182.65, mmWave: 82.43) and lower maximum latency (Sub-6GHz: 279.91 ms, mmWave: 465.16 ms) compared to the mmWave setup. This stability difference between devices is highlighted by the distribution of outliers in Figure 6. Given that both connectivity setups use the same 5G NR core network, this apparent performance difference between the two connectivity setups is likely found in the wireless channel, where the shorter wavelengths of the mmWave setup provide a slight latency improvement. Additionally, as a consequence of these shorter wavelengths, the mmWave setup was slightly less reliable, again highlighted by the concentration of outliers around 100–200 ms in the box plot of Figure 6.
Regarding Packet Delay Variation (PDV) or jitter, in Table 3 it is clear that the overall jitter of both devices is quite low with 95.75% (Sub-6GHz) and 96.53% (mmWave) of packets having a jitter lower than 20 ms. While there is little difference in the median jitter of both devices (∼0.44 ms), there is a notable difference in the maximum observed jitter, i.e., the worst case is 272.63 ms (Sub-6GHz) and 457.42 ms (mmWave), indicating that the mmWave setup has slightly less reliability. This is further highlighted by the larger positive skew (Sub-6GHz: 9.20, mmWave: 8.04) as can be seen from the empirical CDF curves in Figure 7, again indicating that the Sub-6GHz setup has a higher degree of reliability than the mmWave setup.

Table 3.
Jitter Performance Statistics.
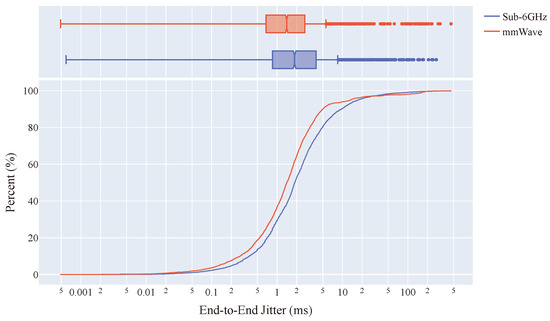
Figure 7.
eCDF + marginal box plot of E2E jitter performance distribution for Sub-6GHz and mmWave connectivity setups (Sub-6GHz: 1.85 ms, mmWave: 1.41 ms median jitter).
4.2. Throughput
In addition to latency and jitter, throughput is another important metric when evaluating a communications system’s ability to maintain QoS. Several of the advanced V2X communications use cases, such as remote driving, sensor sharing, and vehicle platooning, require the transmission of unprocessed sensor data, i.e., videos or point clouds. As such, these advanced V2X communications use cases are infeasible if the communications system is unable to maintain a minimum throughput for the duration required. Statistics for the download performance of both connectivity setups are presented in Table 4 and Table 5. Additionally, the corresponding distributions for both connectivity setups are presented in Figure 8 and Figure 9 (Sub-6GHz), and Figure 10 (mmWave).

Table 4.
Sub-6GHz Throughput Statistics.

Table 5.
mmWave Throughput Statistics.
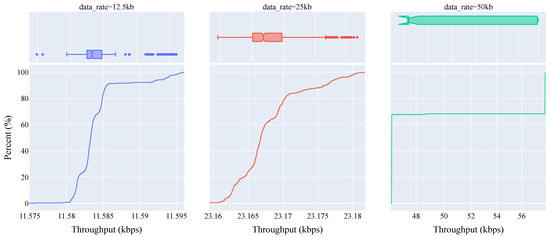
Figure 8.
eCDF plot of throughput performance distribution for object data using the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup (Quiet: 11.583 kbps, Moderate: 23.166 kbps, Busy: 46.336 kbps median throughput).
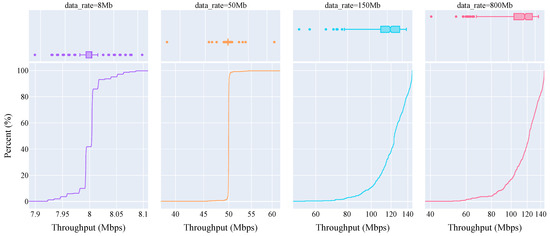
Figure 9.
eCDF plot of throughput performance distribution for sensor data using the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup (CCTV: 8.004 Mbps, Action: 49.997 Mbps, Consumer: 123.915 Mbps, Automotive: 122.780 Mbps median throughput).
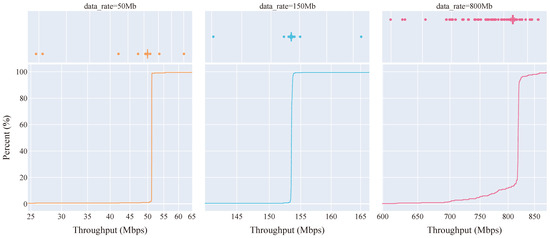
Figure 10.
eCDF plot of throughput performance distribution for sensor data using the mmWave connectivity setup (Action: 51.196 Mbps, Consumer: 153.540 Mbps, Automotive: 818.829 Mbps median throughput).
As can be seen from Table 4, the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup maintains a high degree of reliability at all three of the chosen scenarios, i.e., quiet (12.5 kbps), moderate (25 kbps) and busy (50 kbps). Particularly for quiet and moderate scenarios, the standard deviation is as low as 3–4 bytes. However, there is a notable increase in the standard deviation of the busy scenario, highlighted by the abrupt shift from ∼46 kbps to ∼57 kbps in the eCDF curve of Figure 8 at ∼67%. This is an apparent artefact of the iPerf tool, wherein an integer multiple of the Ethernet MTU size (1448 bytes with 52 bytes overhead) is used to achieve a given data rate. As such, this 1448 MTU size results in a data rate of 11.584 kbps, giving the 11.583 kbps (1 MTU) and 23.166 kbps (2 MTU) median throughputs for the quiet and moderate scenarios. In the case of the busy scenario, the abrupt change in the eCDF curve is a result of the iPerf tool using 4 MTUs (46.336 kbps) and 5 MTUs (57.920 kbps) with a ratio of 3:2 (∼67%) to approximate the desired average data rate of 50 kbps (50.017 kbps actual mean throughput).
Unlike the object data, as can be seen in Table 4, the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup did not maintain the same degree of reliability across all of the chosen sensor data rates. The highest degree of reliability was maintained for the CCTV Camera sensor data rate (8 Mbps), as is noted from the standard deviation of 22 bytes. As discussed regarding the object data, there is a distinct pattern in the eCDF curve and outliers in the box plot of the CCTV (8 Mbps) data rate in Figure 9, which is the same artefact of the MTU size used by iPerf. The reliability of the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup begins to notably deviate when the Action Camera (50 Mbps) data rate is considered. In Table 4, it can be seen that the mean throughput is 50.001 Mbps; however, the kurtosis value (167.687) is notably higher than all other data rates. The outliers that result in this increased kurtosis value are shown in the box plot for this data rate in Figure 9. Given that the test setup used a line-of-sight (LOS) connection between the pseudo-CIV and the gNodeB, these outliers may be caused by asynchronous interference from the environment. The reliability of the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup is significantly challenged when considering the final two sensor data rates, i.e., Consumer Camera (150 Mbps) and Automotive Camera (800 Mbps). It is evident that the maximum throughput of the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup is reached as an average throughput of ∼120 Mbps could not be appreciably exceeded in either case.
As previously mentioned, given the noted deviation in reliability beginning at the Action Camera (50 Mbps) data rate, the previous measurements from where the deviation began were repeated using the mmWave connectivity setup and are detailed in Table 5 and Figure 10. From these repeated mmWave measurements, there is a significant increase in reliability compared to the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup in Table 4. Most notably, the mmWave connectivity setup achieved the desired mean throughputs for all three of the chosen data rates, i.e., Action Camera (51.084 Mbps mean), Consumer Camera (153.557 Mbps mean), and Automotive Camera (811.110 Mbps mean). To a lesser extent, a comparable irregularity in outlier data, characterised by notably high kurtosis values, that is found for the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup is also found for the mmWave connectivity setup regarding the Action Camera (50 Mbps) and Consumer Camera (150 Mbps) data rates. As such, it is possible that the process responsible for these outliers may not be related to the wireless channel, given that the anomaly is present in both connectivity setups. Additionally, it is unlikely that the wired link between the pseudo-FSN and the pseudo-CIV is responsible for the outliers, as the only node between them is the gNodeB which has no other traffic to serve. Thus, it is more likely that the outliers are a consequence of the operation of the iPerf tool as it attempts to generate packets for a given data rate.
4.3. Discussion
With the latency and throughput performance results of both connectivity setups presented, the findings and insights as they relate to the network architecture configurations must be discussed.
From the results presented, it is clear that Configuration 1, where the computational resources are located at or near the FSN(s) and object data are transmitted to the CIV(s), is entirely feasible from a network performance perspective. In particular, the mean latency (10.60 ms) measured for the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup is well within the stringent requirements for V2X applications as specified by the 3GPP [8,9]. Additionally, even with the ∼120 Mbps effective maximum mean throughput achieved by the Sub-6GHz, this bandwidth would allow for either a further increase in CAM reporting frequency beyond the busy scenario (20 Hz) for a single FSN, or for several FSN(s) to report simultaneously in the busy scenario.
Unlike the findings for Configuration 1, the results reveal that Configuration 2, where the computational resources are located within the CIV(s) and sensor data are transmitted across the network, may not be feasible from a network performance perspective. Similar to Configuration 1, the latency performance results for both connectivity setups are within the requirements for V2X applications [8,9]. However, the throughput performance results for both connectivity setups demonstrate that the bandwidth requirements for different sensor data rates impose a trade-off for Configuration 2 depending on the image quality needs of the object detection algorithms. If the image quality provided by the CCTV Camera (8 Mbps) and Action Camera (50 Mbps) data rates is sufficient for the application, then Configuration 2 is likely feasible with the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup. It should be noted that given the effective maximum throughput (∼120 Mbps) found for the Sub-6GHz connectivity setup, there is a limit of ∼15 CCTV Cameras (8 Mbps) or ∼2 Action Cameras (50 Mbps) sensors that could be supported simultaneously by the network. However, if the image quality, i.e., resolution, frame rate, and compression codec, provided by these data rates is not sufficient and sensors of a calibre similar to the Consumer Camera (150 Mbps) or Automotive Camera (800 Mbps) data rates are required, then the use of a mmWave connectivity setup will be required. It should be noted that while the mmWave connectivity setup can afford a significantly higher bandwidth, this comes at the cost of radio robustness in terms of effective transmission range and susceptibility to noise and interference. Thus, if a mmWave connectivity setup is to be used, it will likely have to be deployed at the region of interest to mitigate the aforementioned shortcomings.
These findings highlight the scalability of the IPS system. Within the constraints of the single channel used in this study, Configuration 1 can support a large number of FSNs (∼2400) during a busy scene (20 Hz CAMs). Whereas, Configuration 2 can support significantly fewer FSNs during a busy scene due to the bandwidth requirements of the chosen sensor, i.e., ∼15 CCTV Cameras (8 Mbps) FSNs or ∼2 Action Cameras (50 Mbps) FSNs. Given that the IPS uses a publish-subscribe model, the number of CIVs using the IPS system does not contribute to the scalability of the system. Thus, only the available bandwidth and sensor performance requirements predicate the scalability of the system. As previously mentioned, future technologies such as an mmWave connectivity setup leveraged via carrier aggregation could provide scalability support for the substantial sensor requirements of Configuration 2. Additionally, considerations towards security and privacy will notably affect the performance and scalability of the IPS system. The introduction of security and privacy measures, i.e., encryption, authentication, and access control, will necessarily increase the latency and bandwidth required to access and use the IPS system.
5. Limitations and Future Work
The results and findings presented in this work are primarily limited by the fact that only a single data source (FSN) and single data consumer (CIV) were studied. Also, the 5G SA network utilized for this work was proprietary, and as such technical details regarding the core network are unavailable. It should be noted that latency and throughput measurements were analysed separately and that no real data streams were analysed. In addition, the cellular sidelink was not included as part of this measurement campaign as it is not representative of what is currently available in cellular-capable vehicles. Regardless, these results and findings can be used to advise MNOs and automotive manufacturers on which V2X communications applications can be implemented now and on the challenges that must be addressed to support all V2X communications applications in the future.
In the future, the current dataset can be further bolstered by the inclusion of an increased number of data sources and consumers, where a more realistic pseudo-FSN with actual sensors is used. Thus, a deeper analysis of more specific factors in different working conditions such as static obstructions, environmental factors, and vehicle telemetries will be carried out to isolate the parameters that have the greatest effect on the KPIs studied in this work. Additionally, the use of cloud computing or the MEC paradigm [39] as alternate locations for the computation resources may be of value to provide insights into the cost and network performance trade-offs associated with moving the data away from the locality of interest. Lastly, when available, a re-creation of the measurements conducted can be repeated using the cellular sidelink to more accurately represent the whole capabilities of cellular technology as a V2X communications system.
6. Conclusions
In this work, we present a study conducted to assess the network architectures of an IPS, a small-scale V2I use case for blind road junction or blind corner scenarios. This small-scale system is intended to be used to focus on considerations for developing sufficient QoS for V2X communications applications and use cases at a larger scale. This study was conducted by collecting network measurements between a pseudo-FSN (Fixed Sensor Node) and a pseudo-CIV (Connected Intelligent Vehicle) using a private 5G NR network with two connectivity setups, Sub-6GHz and mmWave. Several measurement runs were conducted to evaluate the feasibility and trade-offs between two identified configurations of the IPS network architecture.
Results demonstrate that the IPS system is feasible, though there is nuance in how it could be implemented that affects feasibility. Regarding the nuance, the primary determinant of how the system should be implemented is the cost of deployment and maintenance of the system. In the ideal case, i.e., Configuration 1, if deploying the necessary computation resources alongside the FSN(s) at the region of interest is feasible from a cost perspective, then the IPS system will yield the highest performance, i.e., up to ∼2400 FSNs reporting at 20 Hz. However, if it is not possible to deploy the necessary computation resources with the FSN(s) and instead the burden of sensor processing is imposed on the CIV(s), i.e., Configuration 2, then the IPS may still be feasible albeit with some trade-offs. In this case, the secondary determinant of how the system should be implemented is the required image quality for the object detection algorithms. Results show that if lower resolution or compressed sensor data can be tolerated then the IPS remains feasible, though with reduced performance, i.e., ∼15 CCTV Cameras (8 Mbps) FSNs or ∼2 Action Cameras (50 Mbps), relative to the instance where the computational resources are local to the FSN(s). However, if higher resolution or uncompressed sensor data are required, then as a result of the ∼120 Mbps limit of the Sub-6GHz channel, the IPS is likely not feasible to implement without the deployment of mmWave connectivity to increase throughput capacity (∼800 Mbps). However, it should be noted, that even with mmWave connectivity, very few high-resolution sensors can be supported, i.e., ∼5 Consumer Camera (150 Mbps) FSNs or ∼1 Automotive Camera (800 Mbps) FSNs. Aside from the discussed implementation nuance, IPS presents a meaningful application to allow progress toward large-scale V2X applications.
Consequently, these findings and insights emphasise some key considerations that need to be investigated thoroughly to realise a system like the IPS, regardless of the chosen configuration. Primarily, results highlight a strong incentive to reduce the costs associated with the deployment and maintenance of the computational resources needed for sensor processing. Moreover, the limitations found when transferring sensor data highlight the importance of compression techniques to make use of the available bandwidth. Finally, there is significant motivation to understand the trade-offs associated with using mmWave spectrum bands, as they may have a key role in enabling V2X communications applications like the IPS to be deployed in many ITS use cases and scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C., M.G. and B.D.; methodology, J.C., D.M. and B.D.; software, J.C., D.M. and S.H.; validation, J.C.; formal analysis, J.C.; investigation, J.C., D.M., S.H. and J.L.; resources, J.C.; data curation, J.C., D.M., S.H. and J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; writing—review and editing, J.C., D.M., S.H., J.L., P.D., E.W., M.G., E.J. and B.D.; visualization, J.C.; supervision, M.G., E.J., B.D. and E.W.; project administration, M.G. and E.J.; funding acquisition, M.G. and E.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was produced by the Connaught Automotive Research (CAR) group at the University of Galway and was supported, in part, by Science Foundation Ireland grants 13/RC/2094_P2 and 18/SP/5942, and co-funded under the European Regional Development Fund through the Southern & Eastern Regional Operational Programme to Lero—the Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre for Software (www.lero.ie, accessed on 22 January 2024).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Sean Hassett is employed by the company DruidSoftware. Author Enda Ward is employed by the company Valeo. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cruise. Cruise Self Driving Cars. 2023. Available online: https://getcruise.com/ (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Waymo. Waymo Driver. 2023. Available online: https://waymo.com/waymo-driver/ (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Tesla. Artificial Intelligence & Autopilot. 2023. Available online: https://www.tesla.com/AI (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Uber. Uber AV. 2023. Available online: https://www.uber.com/us/en/autonomous/ (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- 3GPP. Release 16. 2023. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-16 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- 3GPP. Release 17. 2023. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-17 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- IEEE. IEEE Draft Standard for Information technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems Local and Metropolitan Area Networks–Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment: Enhancements for Next Generation V2X; Technical Report 802.11bd; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP. Service Requirements for V2X Services. TS 22.185, 3GPP. 2023. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2989 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- 3GPP. Service Requirements for Enhanced V2X Scenarios. TS 22.186, 3GPP. 2023. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3180 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- 3GPP. 3GPP. 2023. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/ (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Santa, J.; Skarmeta, A.; Sánchez-Artigas, M. Architecture and evaluation of a unified V2V and V2I communication system based on cellular networks. Comput. Commun. 2008, 31, 2850–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Release 14. 2023. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-14 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- 3GPP. Release 15. 2023. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-15 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Gaber, A.; Nassar, W.; Mohamed, A.M.; Mansour, M.K. Feasibility Study of Teleoperated Vehicles Using Multi-Operator LTE Connection. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Innovative Trends in Communication and Computer Engineering (ITCE), Aswan, Egypt, 8–9 February 2020; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, M.; Gimenez, L.C.; Rodriguez, I.; Sorensen, T.B.; Mogensen, P. From LTE to 5G for Connected Mobility. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, R.; Schrammar, N.; Wang, K.; Karapantelakis, A.; Mokrushin, L.; Feljan, A.V.; Fersman, E. Feasibility assessment to realise vehicle teleoperation using cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; IEEE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016; pp. 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.; Mullins, D.; Deegan, B.; Horgan, J.; Ward, E.; Denny, P.; Eising, C.; Jones, E.; Glavin, M. Feasibility Study of V2X Communications in Initial 5G NR Deployments. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 75269–75284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Study on LTE Support for Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Services, 2023. TS 22.885, 3GPP. 2023. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2898 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Neumeier, S.; Walelgne, E.A.; Bajpai, V.; Ott, J.; Facchi, C. Measuring the Feasibility of Teleoperated Driving in Mobile Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Network Traffic Measurement and Analysis Conference (TMA), Paris, France, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mämmelä, O.; Ojanperä, T.; Mäkelä, J.; Martikainen, O.; Väisänen, J. Evaluation of LiDAR Data Processing at the Mobile Network Edge for Connected Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), Valencia, Spain, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykönen, P.; Lumiaho, A.; Kutila, M.; Scholliers, J.; Kakes, G. V2X-supported automated driving in modern 4G networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 3–5 September 2020; pp. 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daengsi, T.; Ungkap, P.; Wuttidittachotti, P. A Study of 5G Network Performance: A Pilot Field Trial at the Main Skytrain Stations in Bangkok. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science Technology (ICAICST), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 29–30 June 2021; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, A.; Kuroda, S.; Ushida, K.; Kudo, R.; Tateishi, K.; Yamashita, H.; Kantou, T. Field Experiments on Sensor Data Transmission for 5G-Based Vehicle-Infrastructure Cooperation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 88th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Chicago, IL, USA, 27–30 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalay, Z.; Ficzere, D.; Tihanyi, V.; Magyar, F.; Soós, G.; Varga, P. 5G-Enabled Autonomous Driving Demonstration with a V2X Scenario-in-the-Loop Approach. Sensors 2020, 20, 7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutila, M.; Kauvo, K.; Pyykönen, P.; Zhang, X.; Martinez, V.G.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, S. A C-V2X/5G Field Study for Supporting Automated Driving. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Nagoya, Japan, 11–17 July 2021; pp. 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukhwas, D. Road junction convex mirrors. Appl. Ergon. 1987, 18, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhalwar, S.; Ruby, S.; Salgar, S.; Padiri, B. Image Processing based Traffic Convex Mirror Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fifth International Conference on Image Information Processing (ICIIP), Shimla, India, 15–17 November 2019; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Steinhauser, F.; Hinz, G.; Knoll, A. Traffic Mirror-Aware POMDP Behavior Planning for Autonomous Urban Driving. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Aachen, Germany, 5–9 June 2022; pp. 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wu, G.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Oguchi, K.; Barth, M.J. Infrastructure-Based Object Detection and Tracking for Cooperative Driving Automation: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Aachen, Germany, 5–9 June 2022; pp. 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.Y. Cooperative driving at adjacent blind intersections. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 12 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narksri, P.; Takeuchi, E.; Ninomiya, Y.; Takeda, K. Crossing Blind Intersections from a Full Stop Using Estimated Visibility of Approaching Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, K.; Morales, Y.; Akai, N.; Takeuchi, E.; Takeda, K. Learning How to Drive in Blind Intersections from Human Data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomitckii, D.; Barneto, C.B.; Turunen, M.; Allén, M.; Koucheryavy, Y.; Valkama, M. Millimeter-Wave Automotive Radar Scheme with Passive Reflector for Blind Corner Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Strohbeck, J.; Herrmann, M.; Buchholz, M. Motion Planning for Connected Automated Vehicles at Occluded Intersections With Infrastructure Sensors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 17479–17490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabek, C.; Kosmalska, A.; Weiss, G.; Ishigooka, T.; Otsuka, S.; Mizuochi, M. Safe Interaction of Automated Forklifts and Humans at Blind Corners in a Warehouse with Infrastructure Sensors. In Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security; Habli, I., Sujan, M., Bitsch, F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaktheerangkoon, S.; Nakorn, K.N.; Rojviboonchai, K. Performance study of IEEE 802.11p in blind corner scenario. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS), Phuket, Thailand, 24–27 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, M.; Müller, J.; Herrmann, M.; Strohbeck, J.; Völz, B.; Maier, M.; Paczia, J.; Stein, O.; Rehborn, H.; Henn, R.W. Handling Occlusions in Automated Driving Using a Multiaccess Edge Computing Server-Based Environment Model From Infrastructure Sensors. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2022, 14, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annu; Rajalakshmi, P.; Tammana, P. Optimizing Latency for Real-time Traffic and Road Safety Applications through MEC-based V2X System. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart Applications, Communications and Networking (SmartNets), Istanbul, Türkiye, 25–27 July 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A Survey on Mobile Edge Computing: The Communication Perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, D.J.; Velasco-Hernandez, G.; Barry, J.; Walsh, J. Sensor and Sensor Fusion Technology in Autonomous Vehicles: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETSI. Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Local Dynamic Map (LDM); Rationale for and Guidance on Standardization. TR 102 863, ETSI. 2011. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_tr/102800_102899/102863/01.01.01_60/tr_102863v010101p.pdf8 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Srivastava, P.; Khan, R. A Review Paper on Cloud Computing. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 2018, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, D.; Ramos, F.M.V.; Veríssimo, P.E.; Rothenberg, C.E.; Azodolmolky, S.; Uhlig, S. Software-Defined Networking: A Comprehensive Survey. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 14–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijumbi, R.; Serrat, J.; Gorricho, J.L.; Bouten, N.; De Turck, F.; Boutaba, R. Network Function Virtualization: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 236–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dulaimi, A.; Wang, X. 5G Networks: Fundamental Requirements, Enabling Technologies, and Operations Management; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- EN 302 637-2; Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 2: Specification of Cooperative Awareness Basic Service. ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2019.
- EN 302 637-3; Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 3: Specifications of Decentralized Environmental Notification Basic Service. ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2019.
- Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Kim, B.G.; Lin, C.W.; Shiraishi, S.; Xie, J.; Han, Z. Architectural Design Alternatives based on Cloud/Edge/Fog Computing for Connected Vehicles. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 2349–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlam, H.F.; Walters, R.J.; Wills, G.B. Fog Computing and the Internet of Things: A Review. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DruidSoftware. Raemis™—Cellular Network Technology. 2023. Available online: https://druidsoftware.com/raemis-cellular-network-technology/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- VirtualAccess. GW1450 Series 5G Router. 2023. Available online: https://virtualaccess.com/gw1450-series-5g-router/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Quectel. Quectel RM50xQ Series. 2023. Available online: https://www.quectel.com/product/5g-rm50xq-series (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- 3GPP. NR; User Equipment (UE) Radio Transmission and Reception; Part 1: Range 1 Standalone. TS 38.101-1, 3GPP. 2023. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3283 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- 3GPP. NR; User Equipment (UE) Radio Transmission and Reception; Part 2: Range 2 Standalone. TS 38.101-2, 3GPP. 2023. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3284 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- MicroAmp. MicroAmp 5G mmWave. 2023. Available online: https://microamp-solutions.com/products (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Quectel. Quectel RM530N=GL Series. 2023. Available online: https://www.quectel.com/product/5g-rm530n-gl (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- iPerf. iPerf—The TCP, UDP and SCTP Network Bandwidth Measurement Tool. 2023. Available online: https://iperf.fr/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- TS 103 324; Intelligent Transport System (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Collective Perception Service; Release 2. ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2023.
- Sepulcre, M.; Gozalvez, J.; Thandavarayan, G.; Coll-Perales, B.; Schindler, J.; Rondinone, M. On the Potential of V2X Message Compression for Vehicular Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 214254–214268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikvision. 4MP Fixed Turret Network Camera. 2023. Available online: https://www.hikvision.com/uk/products/IP-Products/Network-Cameras/Pro-Series-EasyIP-/ds-2cd2347g2h-liu/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Google. Google Pixel 6a. 2023. Available online: https://store.google.com/ie/product/pixel_6a?hl=en-GB (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Hikvision. Compact 4K Camcorder. 2023. Available online: https://uk.jvc.com/pro/camcorders/4k/GY-HM170E/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Imaging, L. LI-AR0823-GM2B-120H. 2023. Available online: https://leopardimaging.com/product/automotive-cameras/front-view-cameras/li-ar0823-gm2b/li-ar0823-gm2b-120h/ (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Tukey, J.W. Exploratory Data Analysis. In The Concise Encyclopedia of Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communications. 2023. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/technologies/urlcc-2022 (accessed on 25 September 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).