Intelligent Face Recognition: Comprehensive Feature Extraction Methods for Holistic Face Analysis and Modalities
Abstract
1. Introduction
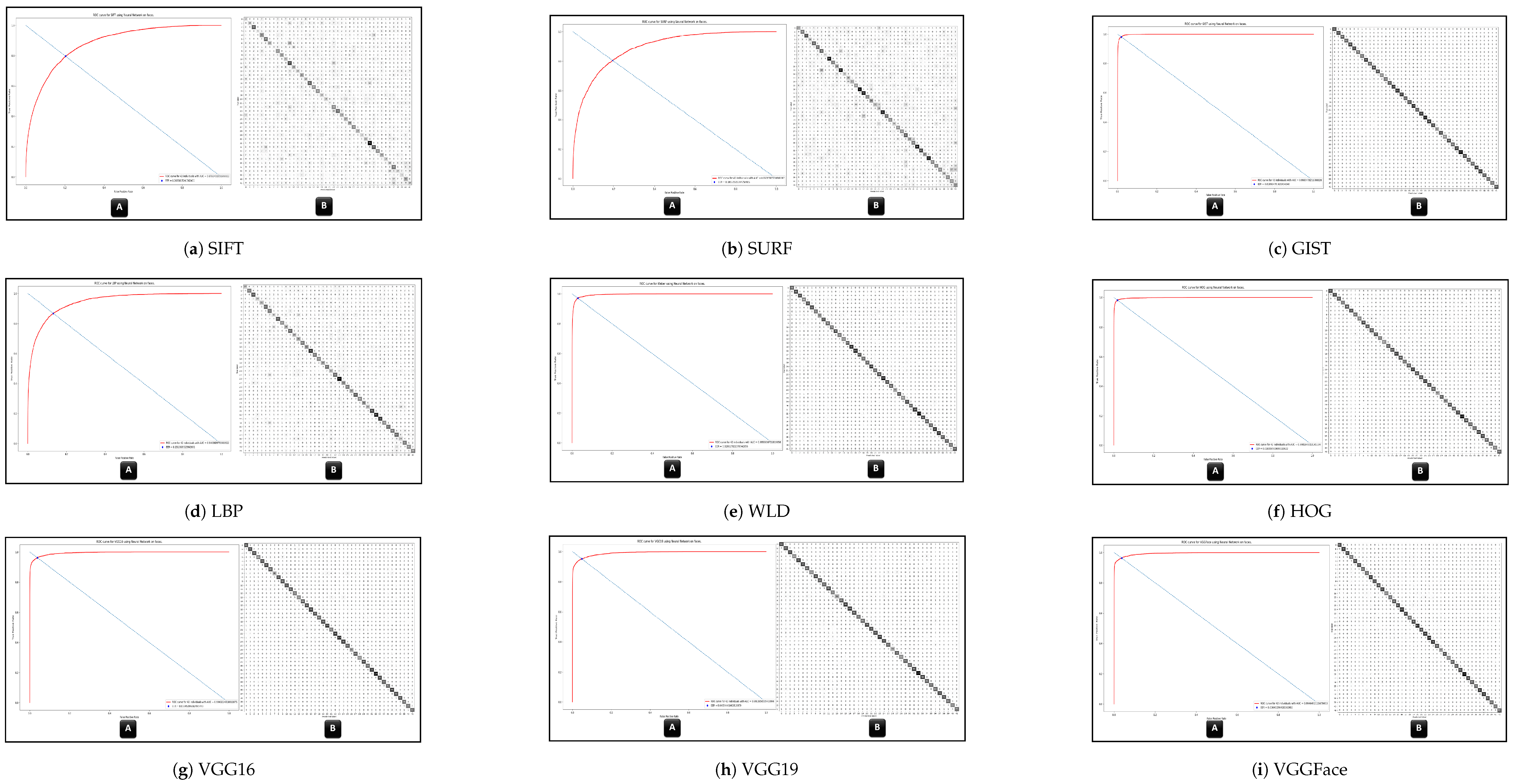
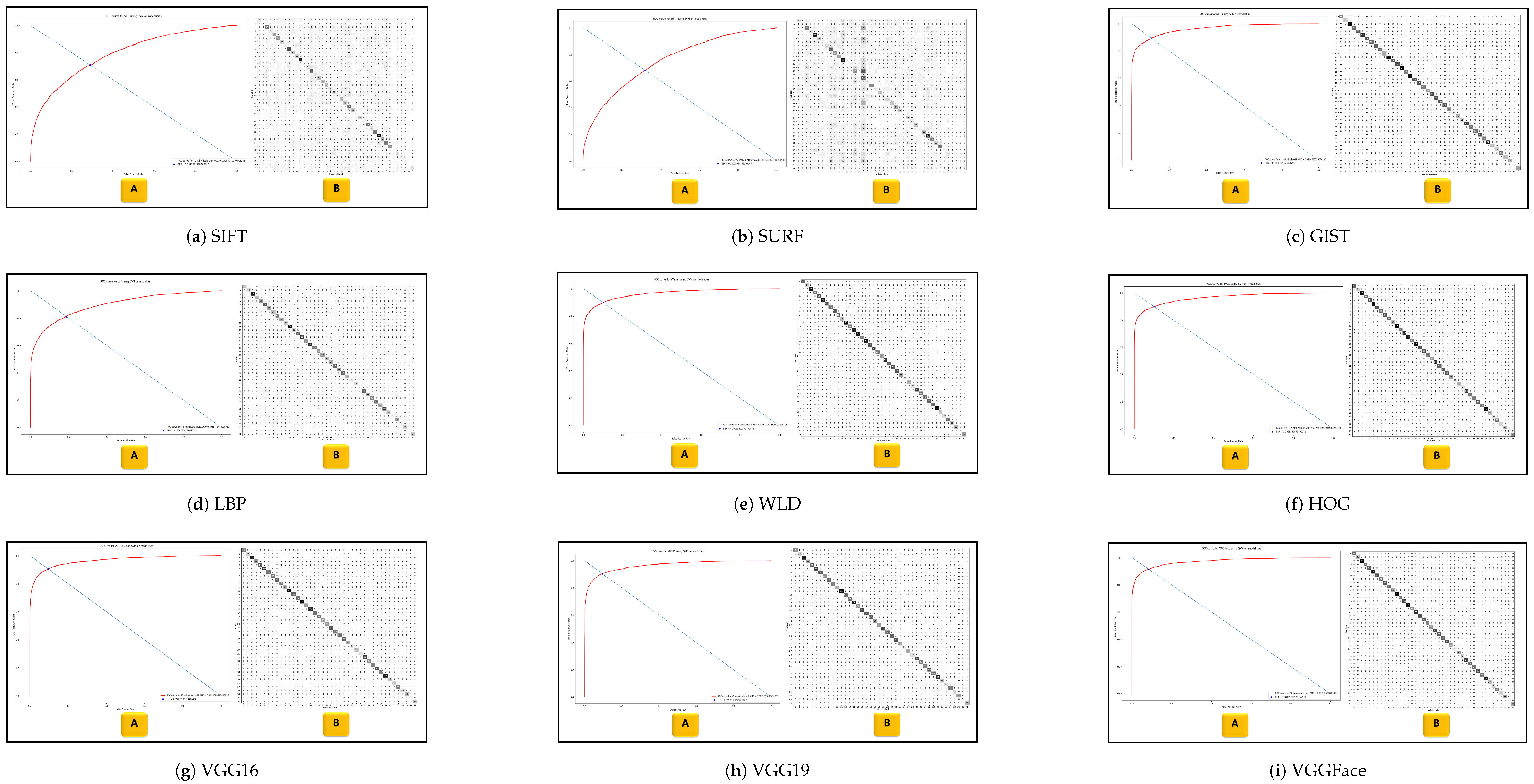
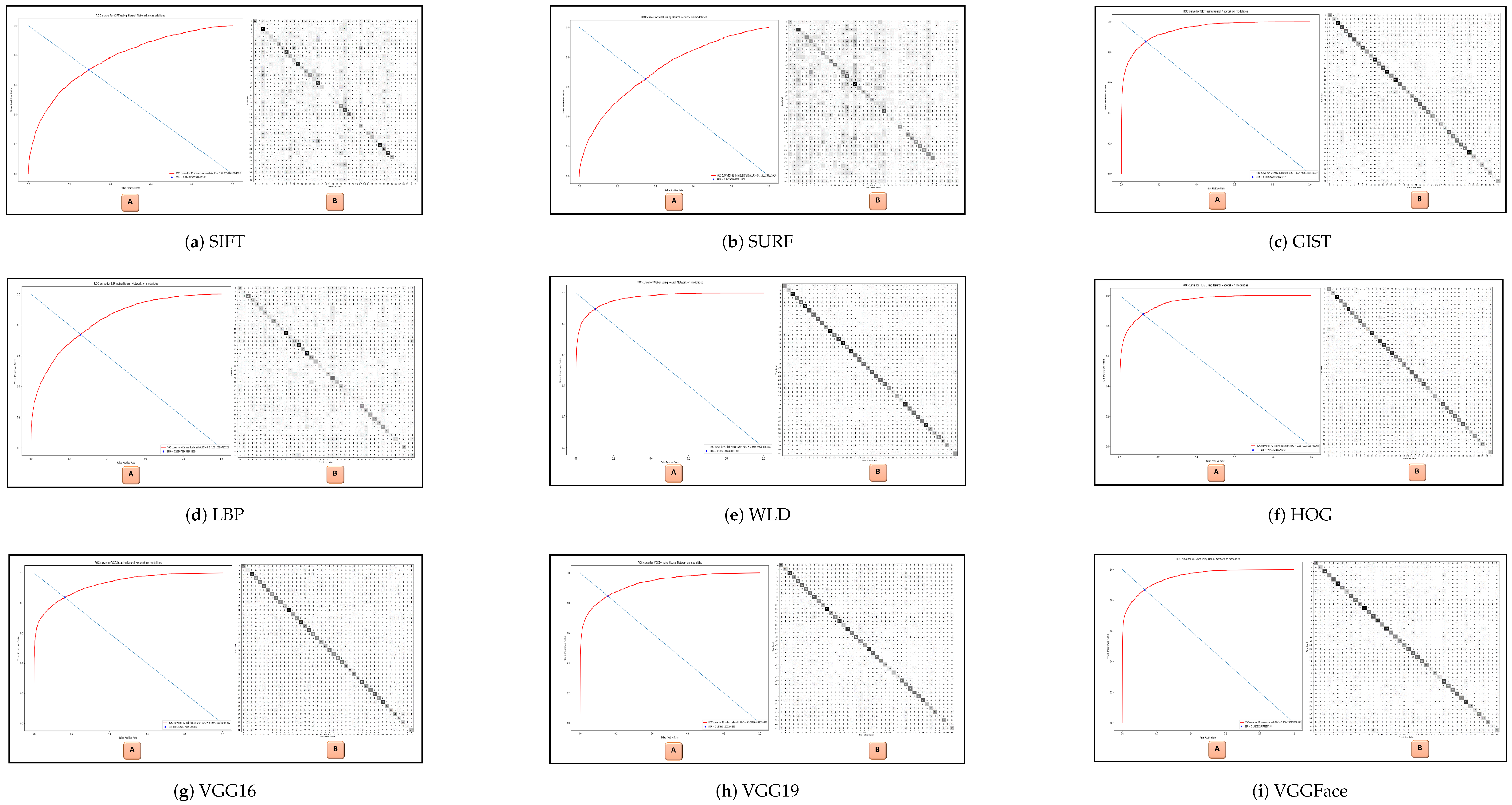
- Experiment 1: Comprehensive evaluations are conducted on ten feature extraction methods. These methods include SIFT, SURF, and GIST as global features. On the other hand, the other three methods are utilized for local features: LBP, WLD, and HOG. The deep learning (CNN) features are classified into VGG16, VGG19, VGG-face, and SNN, also known as face embeddings. Two classifiers, MLP and SVM, are used for both whole faces and face modalities in the in-house database.
- Experiment 2: The best result feature extraction method (VGG16), as determined in Experiment 1, is employed to evaluate exclusively whole faces on the LFW and Pins databases, utilizing both MLP and One-vs-All SVM classifiers for assessment.
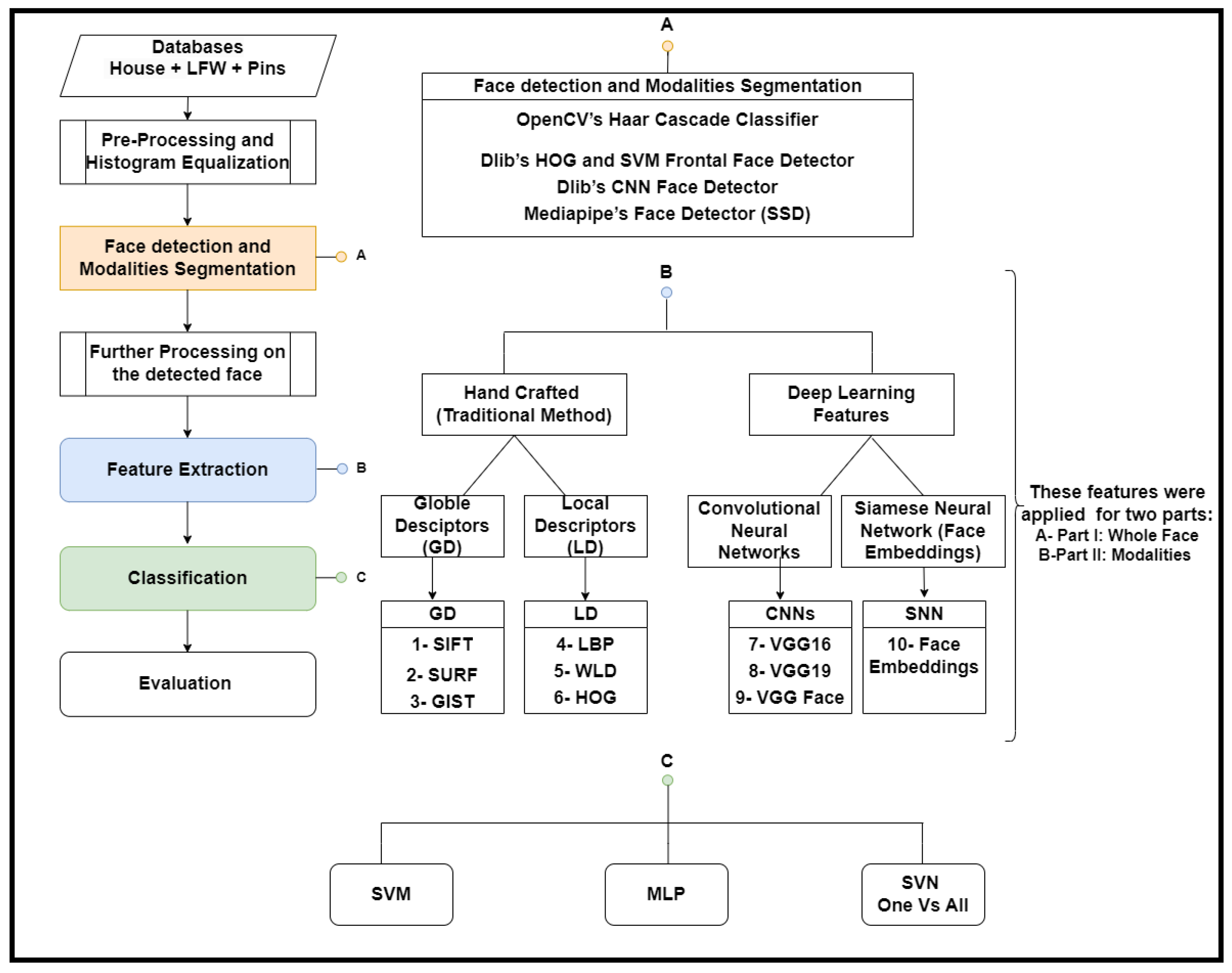
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Preprocessing and Histogram Equalization
2.2. Face Detection and Modalities Segmentation
2.3. Further Preprocessing
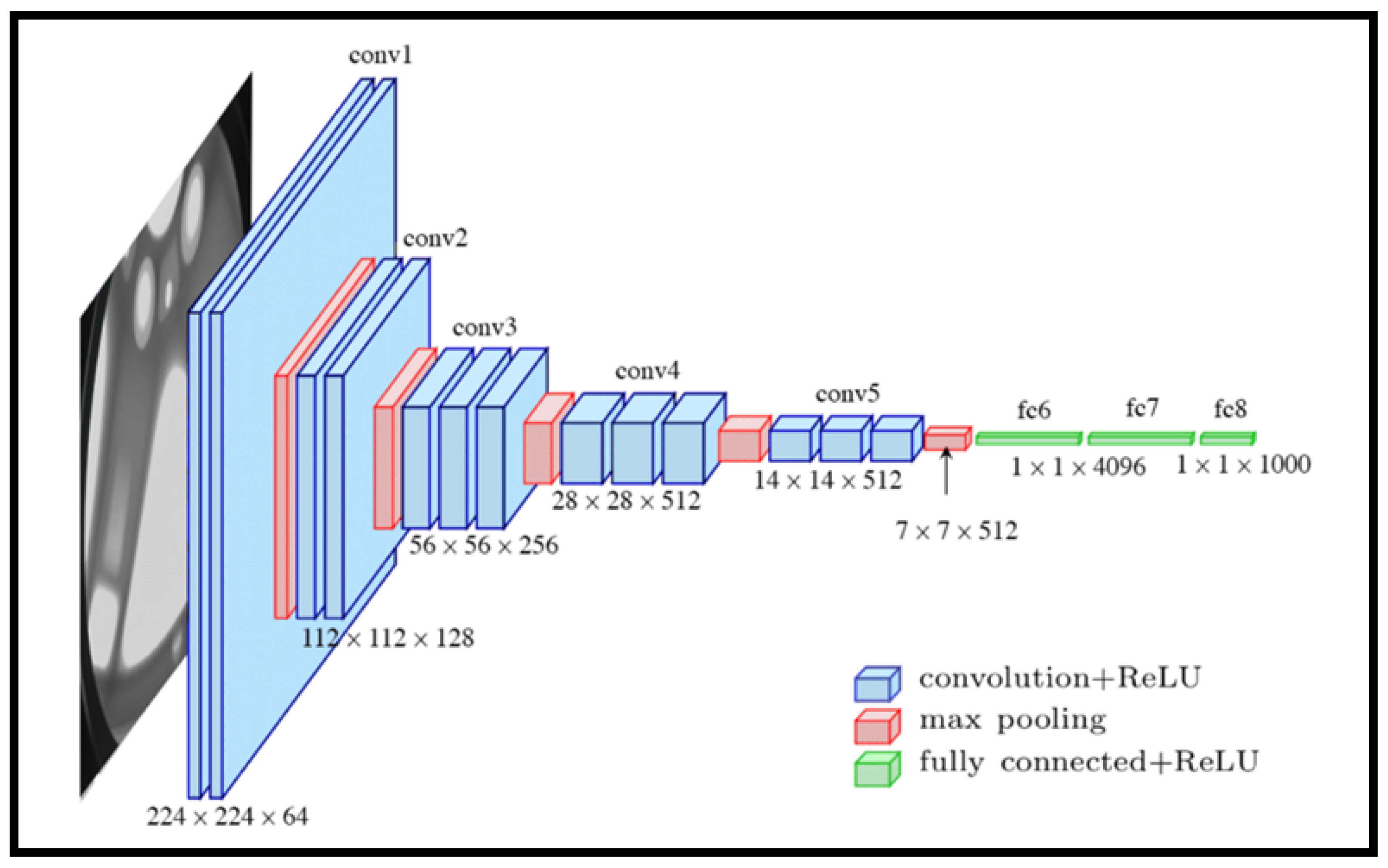
2.4. Feature Extraction Methods
2.5. Classification Methods
3. Databases
3.1. In-House Database
3.2. Labelled Faces in the Wild (LFW) Database
3.3. Pins Face Recognition Database
3.4. Training Process and Data Splitting
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Data and Code Availability
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Walker, D.L.; Palermo, R.; Callis, Z.; Gignac, G.E. The association between intelligence and face processing abilities: A conceptual and meta-analytic review. Intelligence 2023, 96, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignac, G.E.; Shankaralingam, M.; Walker, K.; Kilpatrick, P. Short-term memory for faces relates to general intelligence moderately. Intelligence 2016, 57, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, A.; Sommer, W.; Schacht, A.; Wilhelm, O. Perceiving and remembering emotional facial expressions—A basic facet of emotional intelligence. Intelligence 2015, 50, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, V.; Kumar, N.; Srivastava, A.R. Single sample face recognition using deep learning: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 1063–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Guest, R.; Deravi, F. Presentation-Level Privacy Protection Techniques for Automated Face Recognition-A Survey. Acm Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Lu, X.; Gao, S. 3D face recognition: A comprehensive survey in 2022. Comput. Vis. Media 2023, 9, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolf, J.N.; Boutros, F.; Elliesen, J.; Theuerkauf, M.; Damer, N.; Alansari, M.; Hay, O.A.; Alansari, S.; Javed, S.; Werghi, N.; et al. EFaR 2023: Efficient Face Recognition Competition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.04168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, D.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Xu, F. Deep learning based single sample face recognition: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 2723–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, I.; Dev, A.; Mohapatra, A. Forensic Facial Recognition: Review and Challenges. In Proceedings of International Conference on Data Science and Applications: ICDSA 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2023; Volume 2, pp. 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Mulpuri, S.K.; Neelima, K.N.L.; Lakshmi, D.G.; Anuradha, T.; Gudapati, G.; Bulla, S. Review Paper on Facial Recognition Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 23–25 January 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shree, M.; Dev, A.; Mohapatra, A. Review on Facial Recognition System: Past, Present, and Future. In Proceedings of International Conference on Data Science and Applications: ICDSA 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 807–829. [Google Scholar]
- Waelen, R.A. The struggle for recognition in the age of facial recognition technology. AI Ethics 2023, 3, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, M.H.M.; Zaini, N.; Mazalan, L.; Ahamad, A.H. Online attendance system based on facial recognition with face mask detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 34437–34457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikromovich, H.O.; Mamatkulovich, B.B. Facial recognition using transfer learning in the deep CNN. Open Access Repos. 2023, 4, 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, T.V. Smart attendance system based on improved facial recognition. J. Robot. Control (JRC) 2023, 4, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahan, J.M.; Abbas, E.I.; Abood, Z.M. A facial recognition using a combination of a novel one dimension deep CNN and LDA. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 3594–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, M.; Tavakoli Tafti, K.; Soltani, P. Evaluation of histogram equalization and contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization effect on image quality and fractal dimensions of digital periapical radiographs. Oral Radiol. 2023, 39, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Paul, G.C. Tripartite sub-image histogram equalization for slightly low contrast gray-tone image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 134, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, S.M.; Bhardwaj, V.; Jain, A.; Sharma, V.; Reddy, T.J.; Virender. A Comparative Analysis of Face Detection Algorithms and Real-Time Facial Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 3–5 August 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bedair, A.; Abdel-Nasser, M. Gamma Effect in Face Detection Methods. SVU-Int. J. Eng. Sci. Appl. 2023, 4, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.S.; Sengupta, D.; Ghosh, A.; Chaudhuri, A. MTCNN++: A CNN-based face detection algorithm inspired by MTCNN. Vis. Comput. 2023, 40, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.T.; Ali, N.H.M. Deploying Facial Segmentation Landmarks for Deepfake Detection. J. Al-Qadisiyah Comput. Sci. Math. 2023, 15, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, N.P.; Krishna, E.P.; Chakravarthi, S.S. Facial Landmarks Detection System with OpenCV Mediapipe and Python using Optical Flow (Active) Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 12–13 May 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Anami, B.S.; Sagarnal, C.V. A fusion of hand-crafted features and deep neural network for indoor scene classification. Malays. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 36, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjdira, B.; Ali, A.M.; Koubaa, A. Streamlined Global and Local Features Combinator (SGLC) for High Resolution Image Dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 1854–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Selvi, A.; Thilagamani, S. Scale Invariant Feature Transform with Crow Optimization for Breast Cancer Detection. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2023, 36, 2973–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzid, H.; le Goic, G.; Bekkari, A.; Mansouri, A.; Mammass, D. A new SURF-based algorithm for robust registration of multimodal images data. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raat, E.; Kyle-Davidson, C.; Evans, K. Using global feedback to induce learning of gist of abnormality in mammograms. Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic. 2023, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanwal, S.; Diwakar, M. Triangle and orthogonal local binary pattern for face recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 36179–36205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z. High-boost-based local Weber contrast method for infrared small target detection. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.; Subedi, R.; Gaire, R.R.; Vazquez, E.; Stoyanov, D. Histogram of Oriented Gradients meet deep learning: A novel multi-task deep network for 2D surgical image semantic segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 85, 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.R.; Saranya, N.; Priyadharshini, M.; Gilchrist, D.; Rahman, M.K. Face recognition using CNN and siamese network. Meas. Sensors 2023, 27, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ean, I.C.K.; Abu Hassan, M.F.; Yusof, Y.; Nadzri, N.Z. Deep CNN-Based Facial Recognition for a Person Identification System Using the Inception Model. In Industrial Revolution in Knowledge Management and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.; Wadekar, S.; Warbhe, S.; Dalal, S.; Mirajkar, R.; Sathe, S. Facial Recognition System Using Transfer Learning with the Help of VGG16. In AI, IoT, Big Data and Cloud Computing for Industry 4.0; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bewoor, M.; Patil, S.; Kushwaha, S.; Tandon, S.; Trivedi, S.; Pawar, A. Face recognition using open CV and VGG 16 transfer learning. Aip Conf. Proc. 2023, 2890, 020019. [Google Scholar]
- Khajuria, O.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, M. Facial Emotion Recognition using CNN and VGG-16. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Lalitpur, Nepal, 26–28 April 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Melinda, M.; Oktiana, M.; Nurdin, Y.; Pujiati, I.; Irhamsyah, M.; Basir, N. Performance of ShuffleNet and VGG-19 Architectural Classification Models for Face Recognition in Autistic Children. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2023, 13, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.; Savithadevi, M.; Sridevi, M.; Sridhar, R. A novel facial emotion recognition model using segmentation VGG-19 architecture. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 15, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, U.K.; Bendre, A.; Ganguli, S.; Rai, R.N. Prosthetic Face Recognition using a Siamese Neural Network Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Computing and Communication Systems (I3CS), Shillong, India, 16–18 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Saeed, M.; El Saddik, A.; Gueaieb, W. ARTriViT: Automatic Face Recognition System Using ViT-Based Siamese Neural Networks with a Triplet Loss. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 32nd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Helsinki, Finland, 19–21 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Traore, M.M.; Traore, D. Face Recognition efficiency Based on Support Vector Machine using Skin Color Information. Maghrebian J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2023, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, A.; Mahdianpari, M.; Abdul Rahman, A. Hyperspectral image classification using multi-layer perceptron mixer (MLP-MIXER). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, T.; Yadav, J. Large-scale orthogonal integer wavelet transform features-based active support vector machine for multi-class face recognition. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2023, 72, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al_Dujaili, M.J.; Salim ALRikabi, H.T.; Abed, N.K.; Niama ALRubeei, I.R. Gender Recognition of Human from Face Images Using Multi-Class Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2023, 17, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.; Woo, W.L.; Dlay, S.S.; Chambers, J.A. Multi-dimensional i-vector closed set speaker identification based on an extreme learning machine with and without fusion technologies. In Proceedings of the 2017 Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys), London, UK, 7–8 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1141–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.S. Robust Text Independent Closed Set Speaker Identification Systems and Their Evaluation. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.S.; Al-Sumaidaee, S.A.M.; Al-Nima, R.R.O. Classifications of signatures by radial basis neural network. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2022, 11, 3294–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.S. Multi-Modal Ocular Recognition in Presence of Occlusion in Mobile Devices; University of Missouri-Kansas City: Kansas City, MO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.S.; Al-Ani, J.A. Convolutional neural network for ethnicity classification using ocular region in mobile environment. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th Computer Science and Electronic Engineering (CEEC), Colchester, UK, 19–21 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.S.; Rattani, A.; Derakhshani, R. Comparison of squeezed convolutional neural network models for eyeglasses detection in mobile environment. J. Comput. Sci. Coll. 2018, 33, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.S.; Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.; Alshehabi Al-Ani, J.; Chambers, J.A. Comprehensive Evaluations of Student Performance Estimation via Machine Learning. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.; Mohammad, A.S.; Woo, W.L. Ensemble System of Deep Neural Networks for Single-Channel Audio Separation. Information 2023, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nima, R.R.O.; Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.; Han, T.; Woo, W.L. Road tracking enhancements for self-driving cars applications. Aip Conf. Proc. 2023, 2839, 040004. [Google Scholar]
- Devnath, L.; Arora, P.; Carraro, A.; Korbelik, J.; Keyes, M.; Wang, G.; Guillaud, M.; MacAulay, C. Recognizing Epithelial Cells in Prostatic Glands Using Deep Learning. Cells 2025, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, R.; Janzen, I.; Devnath, L.; Khattra, S.; Myers, R.; Lam, S.; MacAulay, C. MA19. 11 Predicting Future Lung Cancer Risk with Low-Dose Screening CT Using an Artificial Intelligence Model. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, B.; Guo, J. Fine-grained face verification: FGLFW database, baselines, and human-DCMN partnership. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 66, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.; Muhammad, G.; Alhumyani, H.; Alshamrani, S.S.; Cheikhrouhou, O.; Ibrahim, S.; Hossain, M.S. Deep learning-based intelligent face recognition in IoT-cloud environment. Comput. Commun. 2020, 152, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, W. Dual Gaussian Modeling for Deep Face Embeddings. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 161, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastmalchi, H.; Aghaeinia, H. Super-resolution of very low-resolution face images with a wavelet integrated, identity preserving, adversarial network. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2022, 107, 116755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Tao, D. Robust face recognition via multimodal deep face representation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2015, 17, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zafeiriou, S. Marginal loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C.; Lin, C.W. Identity-aware face super-resolution for low-resolution face recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Bai, T.; Wei, Z.; Huang, C. Targeting ultimate accuracy: Face recognition via deep embedding. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.07310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Kan, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Recursive spatial transformer (rest) for alignment-free face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3772–3780. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, C.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y. Feature-improving generative adversarial network for face frontalization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 68842–68851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Lee, H.; Learned-Miller, E. Learning hierarchical representations for face verification with convolutional deep belief networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 2518–2525. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Hybrid deep learning for face verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1489–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deepid3: Face recognition with very deep neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.00873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Deng, W.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Tao, X.; Huang, Y. Fair loss: Margin-aware reinforcement learning for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 10052–10061. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Hybrid deep learning for computing face similarities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Wu, S.; Xu, Y. Face recognition using both visible light image and near-infrared image and a deep network. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2017, 2, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Kot, A. Deep coupled resnet for low-resolution face recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taigman, Y.; Yang, M.; Ranzato, M.; Wolf, L. Deepface: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1701–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1891–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deeply learned face representations are sparse, selective, and robust. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2892–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhi, O.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2015-Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2015, Swansea, UK, 7–10 September 2015; British Machine Vision Association: Durham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, H. Additive margin softmax for face verification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, X.; Gong, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Cosface: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5265–5274. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeshkumar, G.; Braveen, M.; Venkatesh, R.; Shermila, P.J.; Prabu, B.G.; Veerasamy, B.; Bharathi, B.; Jeyam, A. Smart office automation via faster R-CNN based face recognition and internet of things. Meas. Sensors 2023, 27, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, B.A.; Kurnaz, S. An investigational FW-MPM-LSTM approach for face recognition using defective data. Image Vis. Comput. 2023, 132, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.R.; Wadhwa, A.S.; Tyagi, N. Brain inspired face recognition: A computational framework. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2023, 78, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussaad, L.; Boucetta, A. Deep-learning based descriptors in application to aging problem in face recognition. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikha, O.; Bharath, B. VGG16-random Fourier hybrid model for masked face recognition. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 12795–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdana, A.B.; Prahara, A. Face recognition using light-convolutional neural networks based on modified Vgg16 model. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference of Computer Science and Information Technology (ICoSNIKOM), Medan, Indonesia, 28–29 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Sun, K.; Gao, F.; Zhu, S. Face biometric quality assessment via light CNN. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 107, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Feature Extractor | MLP on Faces | MLP on Modalities | SVM on Faces | SVM on Modalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | 70.5% | 53.0% | 34.8% | 59.9% |
| SURF | 79.5% | 41.7% | 41.1% | 46.3% |
| GIST | 99.4% | 94.4% | 92.6% | 96.3% |
| LBP | 88.1% | 25.5% | 68.1% | 85.7% |
| WLD | 97.7% | 94.6% | 97.7% | 95.8% |
| HOG | 98.4% | 93.3% | 99.5% | 97.3% |
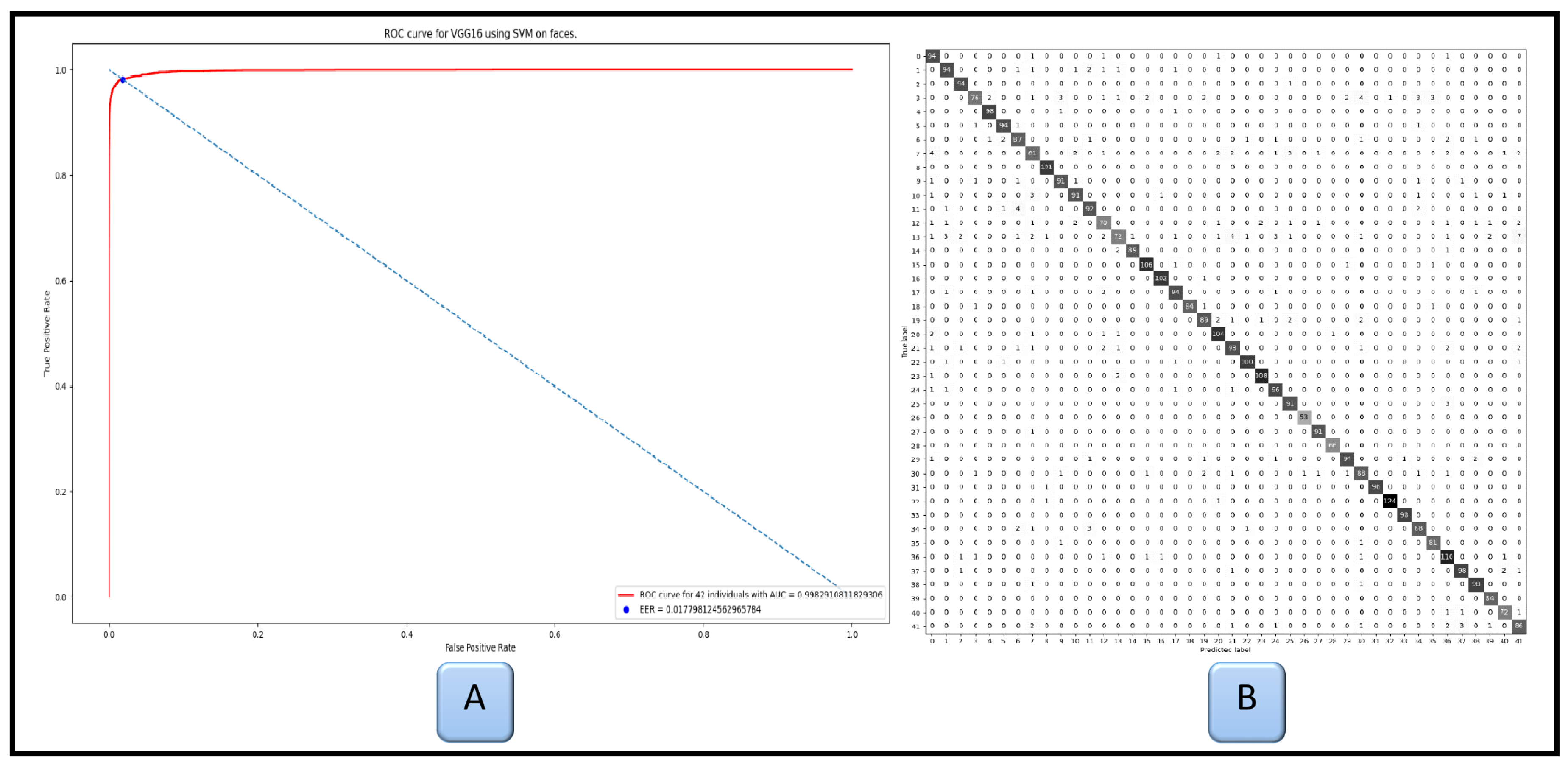
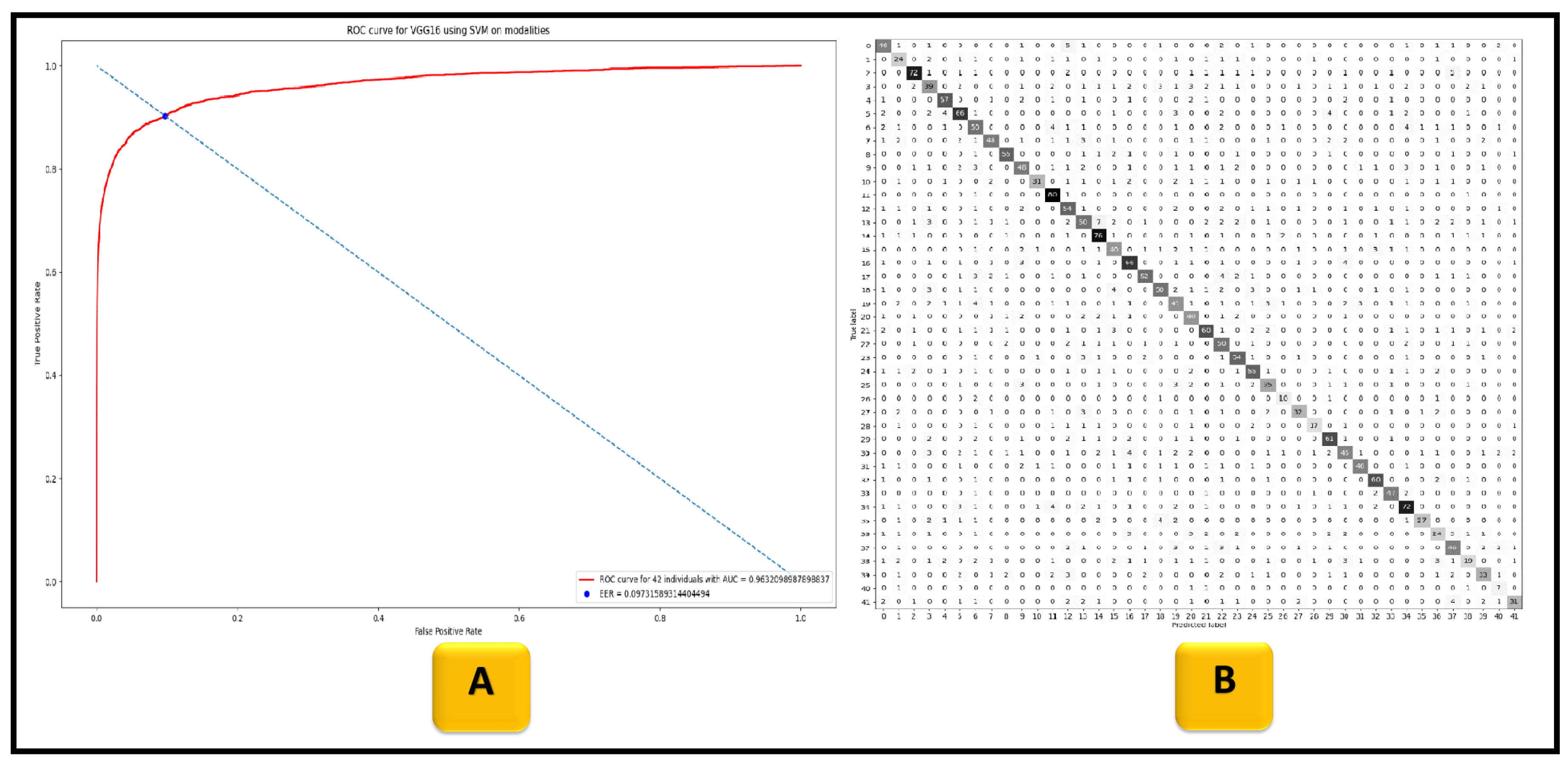
| VGG16 | 98.2% | 94.0% | 99.8% | 96.4% |
| VGG19 | 96.4% | 94.8% | 99.7% | 96.9% |
| VGGFace | 93.0% | 96.3% | 99.7% | 97.9% |
| Face embeddings | 46.1% | None | 46.3% | None |
| Method | F1 Score | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Database |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | 97.3% | 97.4% | 97.3% | 97.4% | Pins |
| SVM O vs. All | 98.4% | 98.5% | 98.4% | 98.4% | Pins |
| MLP | 99.5% | 99.5% | 99.6% | 99.5% | LFW |
| SVM O vs. All | 99.7% | 99.8% | 99.7% | 99.7% | LFW |
| References | Database | Model Used | Accuracy % |
|---|---|---|---|
| [56] | LFW | DCMN | 98.03% |
| FGLFW | DCMN | 91.00% | |
| [57] | LFW | Tree-Based Deep | 95.84% |
| FEI | 98.65% | ||
| ORL | 99.19% | ||
| [58] | Training: CASIAWebFace | DGM | Training: CASIA |
| LFW | 99.27% | ||
| CFP-FF | 99.26% | ||
| CFP-FP | 86.97% | ||
| CPLF | 93.09% | ||
| Trained on VGG Face | Trained on VGG Face | ||
| LFW | 99.62% | ||
| CFP-FF | 99.63% | ||
| CFP-FP | 92.45% | ||
| CPLF | 96.37% | ||
| [59] | LFW | IPA | 86.10% |
| WIPA | 86.00% | ||
| [60] | LFW | MM-DFR | 99.02% |
| [61] | LFW | Marginal Loss | 99.48% |
| YTF | 95.98% | ||
| AgeDB | 98.95% | ||
| CACD | 95.75% | ||
| [62] | LFW | Light CNN | 98.98% |
| [63] | LFW | CNN and deep metric learning | 99.77% |
| [64] | LFW | ReST | 99.03% |
| YTF | 95.40% | ||
| [65] | LFW | FI-GAN | 98.30% |
| CFP | 94.20% | ||
| [66] | LFW | Hand-crafted and Deep learning. | 87.77% |
| [67] | LFW | hybrid ConvNet-RBM model | 92.52% |
| [68] | LFW | DeepID3 | 99.53% |
| [69] | LFW | Fair loss-Cos | 99.53% |
| YTF | 96.20% | ||
| [70] | LFW | CNN-RBM | 93.80% |
| [71] | LFW | VGGNet | 98.99% |
| YTF | 97.30% | ||
| [72] | LFW | Deep coupled ResNet | 99.00% |
| [73] | LFW | Deep face | 97.35% |
| [74] | LFW | Deep ID | 97.40% |
| [75] | LFW | Deep ID2 | 99.50% |
| [76] | LFW | VGGFace | 98.90% |
| [77] | LFW | FaceNet | 99.60% |
| [78] | LFW | AMS loss, Caffe | 94.50% |
| [79] | LFW | CosFace | 99.73% |
| YTF | 97.60% | ||
| [80] | NA | faster R-CNN | 99.30% |
| [81] | NA | FW-MPM-LSTM | 99.58% |
| [82] | ORL | BIFR | 98.50% |
| [83] | face-aging FG-NET | Deep CNN models | 98.21% |
| [84] | 1-Face dataset by robotics lab | VGG16-random Fourier hybrid model | 97.46% |
| 2-Head pose image dataset | 97.63% | ||
| 3-Georgia tech face dataset | 97.55% | ||
| [85] | ROSE-Youtu Face Liveness Detection Database + In House | Light-CNN Based on Modified VGG16 | 94.40% |
| [86] | CASIA, FLW | Light CNN | 99.00% |
| Proposed | House | VGG16+SVM | 99.80% |
| Proposed | House | VGG16+MLP | 98.20% |
| Proposed | LFW | VGG16+SVM | 99.70% |
| Proposed | LFW | VGG16+MLP | 99.50% |
| Proposed | Pins | VGG16+SVM | 98.40% |
| Proposed | Pins | VGG16+MLP | 97.40% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarullah, T.G.; Mohammad, A.S.; Al-Kaltakchi, M.T.S.; Alshehabi Al-Ani, J. Intelligent Face Recognition: Comprehensive Feature Extraction Methods for Holistic Face Analysis and Modalities. Signals 2025, 6, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals6030049
Jarullah TG, Mohammad AS, Al-Kaltakchi MTS, Alshehabi Al-Ani J. Intelligent Face Recognition: Comprehensive Feature Extraction Methods for Holistic Face Analysis and Modalities. Signals. 2025; 6(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals6030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarullah, Thoalfeqar G., Ahmad Saeed Mohammad, Musab T. S. Al-Kaltakchi, and Jabir Alshehabi Al-Ani. 2025. "Intelligent Face Recognition: Comprehensive Feature Extraction Methods for Holistic Face Analysis and Modalities" Signals 6, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals6030049
APA StyleJarullah, T. G., Mohammad, A. S., Al-Kaltakchi, M. T. S., & Alshehabi Al-Ani, J. (2025). Intelligent Face Recognition: Comprehensive Feature Extraction Methods for Holistic Face Analysis and Modalities. Signals, 6(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals6030049






_Al-Kaltakchi.jpg)


