How Time Window Influences Biometrics Performance: An EEG-Based Fingerprint Connectivity Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Datasets
2.2. Pre-Processing
2.3. Epoch Segmentation
2.4. Functional Connectivity Analysis
2.5. Performance Evaluation
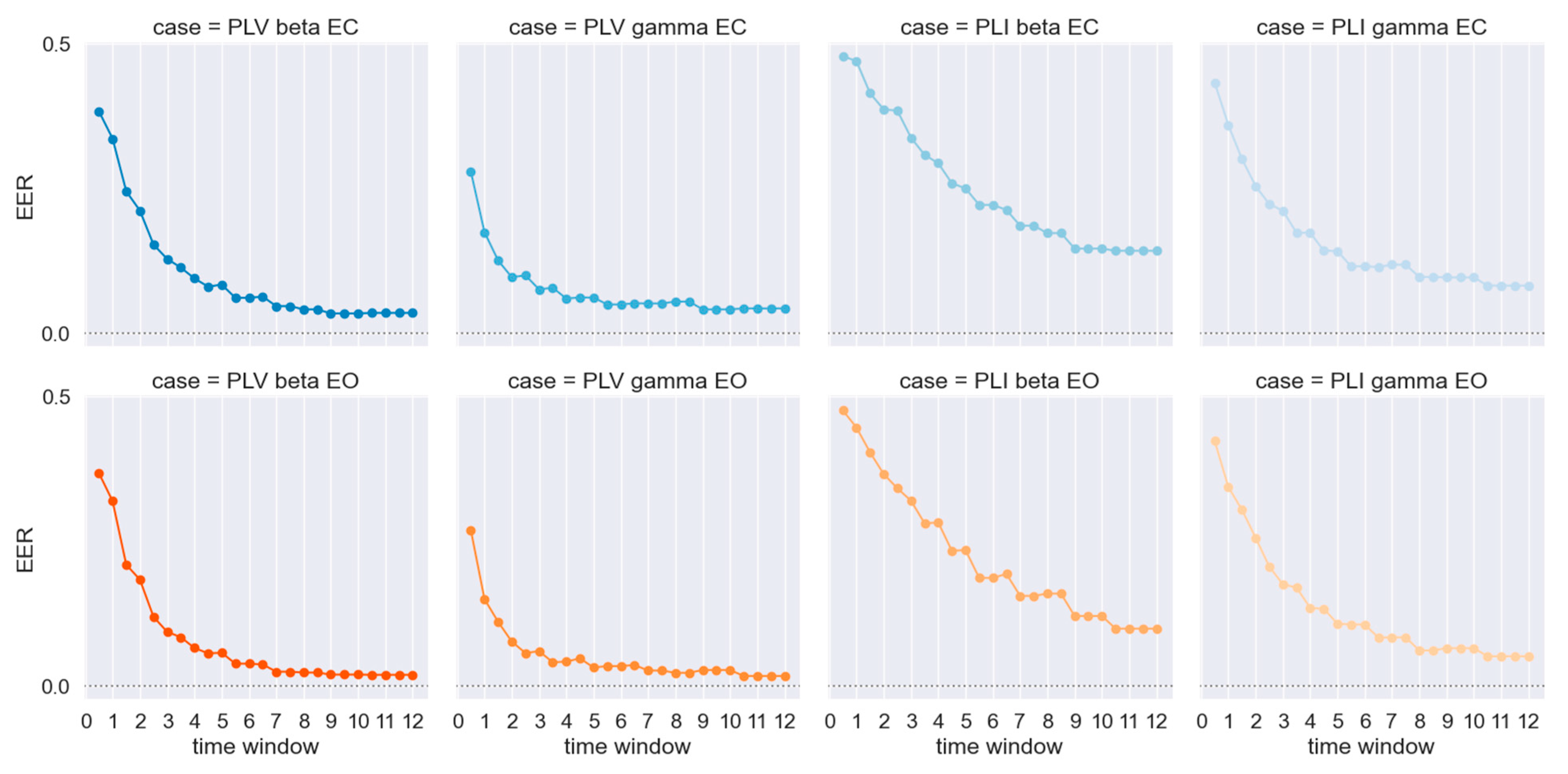
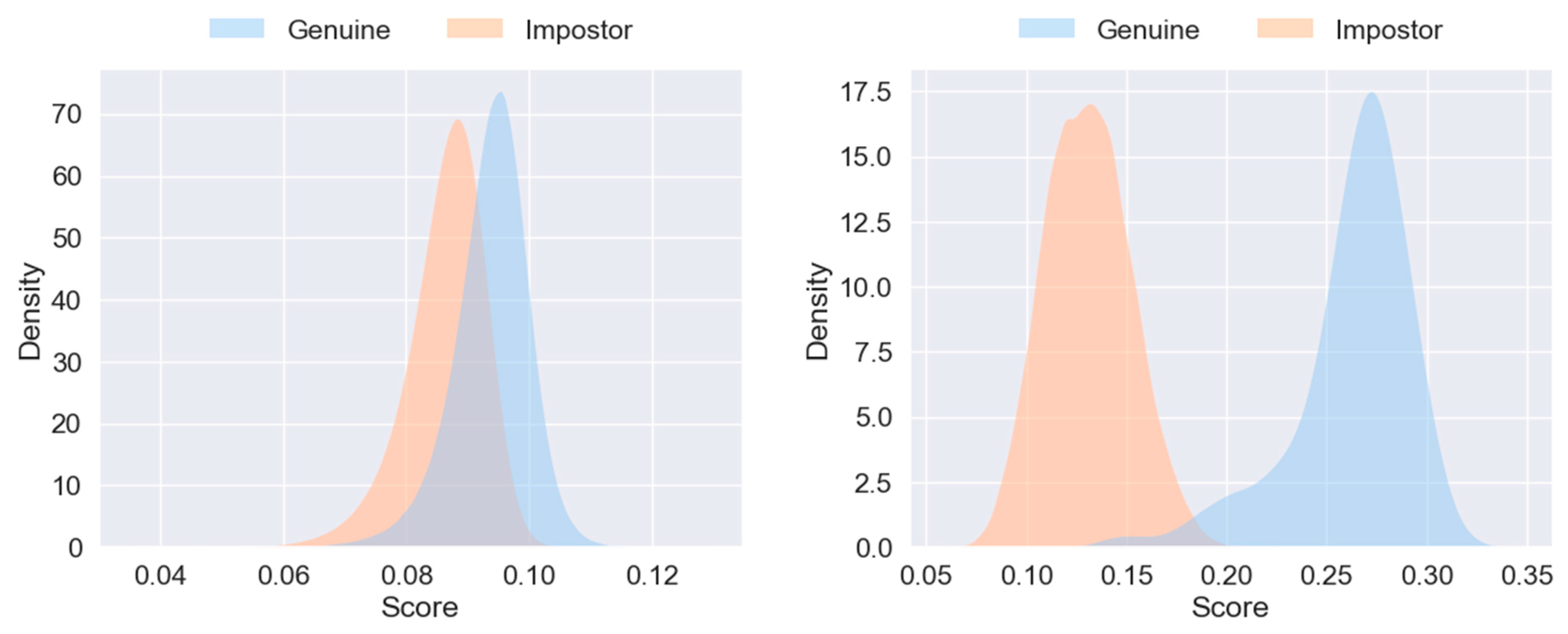
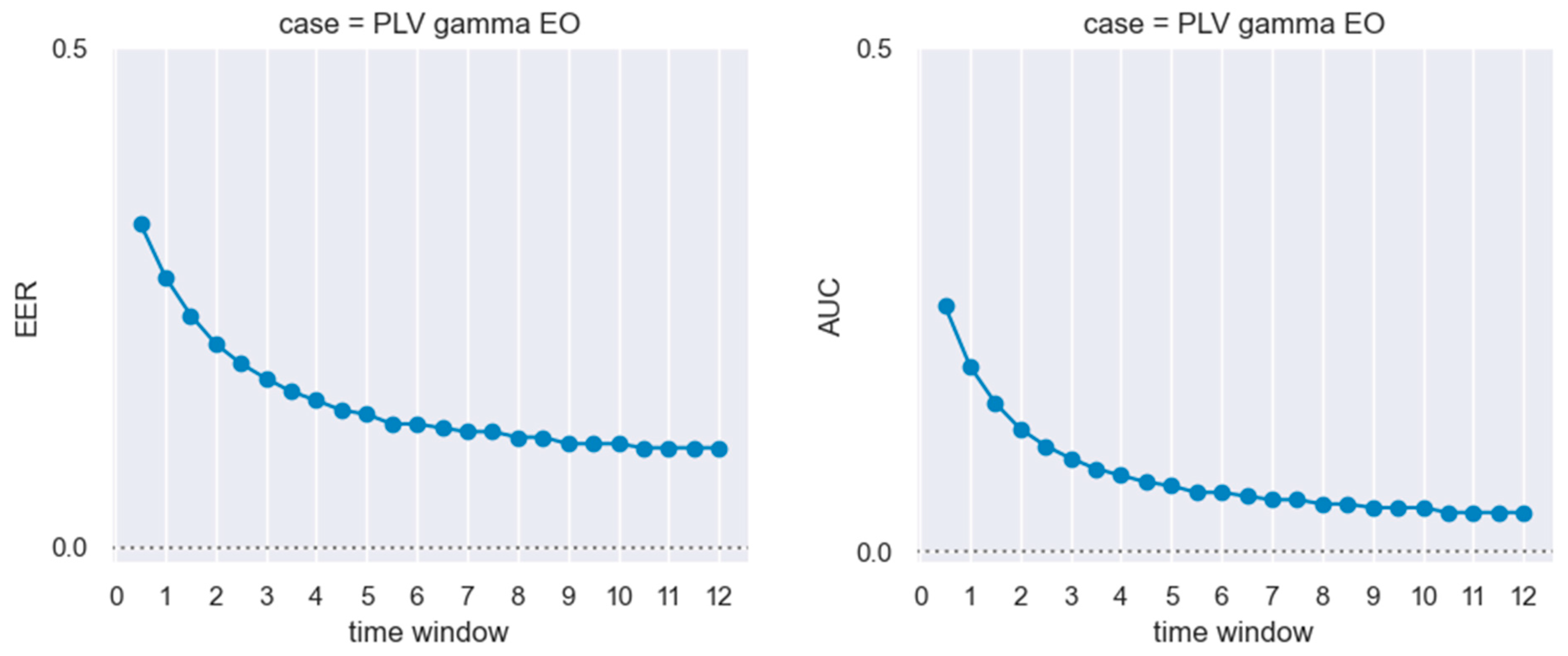
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maiorana, E.; La Rocca, D.; Campisi, P. On the Permanence of EEG Signals for Biometric Recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaly Bidgoly, A.; Jalaly Bidgoly, H.; Arezoumand, Z. A Survey on Methods and Challenges in EEG Based Authentication. Comput. Secur. 2020, 93, 101788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-L.; Kuo, P.-C.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S. Challenges and Future Perspectives on Electroencephalogram-Based Biometrics in Person Recognition. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo-Banos, M.; Alonso, J.B.; Ticay-Rivas, J.R.; Travieso, C.M. Electroencephalogram Subject Identification: A Review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 6537–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidas, C.A.; Lyras, D. A Review of EEG-Based User Authentication: Trends and Future Research Directions. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 22917–22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amico, E.; Goñi, J. The Quest for Identifiability in Human Functional Connectomes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saia, R.; Carta, S.; Fenu, G.; Pompianu, L. Influencing Brain Waves by Evoked Potentials as Biometric Approach: Taking Stock of the Last Six Years of Research. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 11625–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Mao, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, P. Review on EEG-Based Authentication Technology. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, e5229576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Flynn, P.; Ross, A.A. Handbook of Biometrics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-71041-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kida, T.; Tanaka, E.; Kakigi, R. Multi-Dimensional Dynamics of Human Electromagnetic Brain Activity. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Pani, S.M.; Didaci, L.; Marcialis, G.L. Robustness of Functional Connectivity Metrics for EEG-Based Personal Identification over Task-Induced Intra-Class and Inter-Class Variations. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Hillebrand, A.; Demuru, M.; Didaci, L.; Marcialis, G.L. An EEG-Based Biometric System Using Eigenvector Centrality in Resting State Brain Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Abbass, H.A. BrainPrint: EEG Biometric Identification Based on Analyzing Brain Connectivity Graphs. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 105, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, D.L.; Campisi, P.; Vegso, B.; Cserti, P.; Kozmann, G.; Babiloni, F.; Fallani, F.D.V. Human Brain Distinctiveness Based on EEG Spectral Coherence Connectivity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, S.M.; Ciuffi, M.; Demuru, M.; Cava, S.M.L.; Bazzano, G.; d’Aloja, E.; Fraschini, M. Subject, Session and Task Effects on Power, Connectivity and Network Centrality: A Source-Based EEG Study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 59, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J.; Nolte, G.; Daffertshofer, A. Phase Lag Index: Assessment of Functional Connectivity from Multi Channel EEG and MEG with Diminished Bias from Common Sources. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachaux, J.P.; Rodriguez, E.; Martinerie, J.; Varela, F.J. Measuring Phase Synchrony in Brain Signals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1999, 8, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, C.; Garrido, M.I.; Gramfort, A.; Maurits, N.; Michel, C.M.; Pang, E.; Salmelin, R.; Schoffelen, J.M.; Valdes-Sosa, P.A.; Puce, A. Issues and Recommendations from the OHBM COBIDAS MEEG Committee for Reproducible EEG and MEG Research. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, A.; Chella, F.; Guidotti, R.; Ermolova, M.; D’Andrea, A.; Stenroos, M.; Romani, G.L.; Pizzella, V.; Marzetti, L. Looking through the Windows: A Study about the Dependency of Phase-Coupling Estimates on the Data Length. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 016039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Demuru, M.; Crobe, A.; Marrosu, F.; Stam, C.J.; Hillebrand, A. The Effect of Epoch Length on Estimated EEG Functional Connectivity and Brain Network Organisation. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 036015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. Eugene PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsigiannis, S.; Ramzan, N. DREAMER: A Database for Emotion Recognition Through EEG and ECG Signals From Wireless Low-Cost Off-the-Shelf Devices. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraschini, M.; Meli, M.; Demuru, M.; Didaci, L.; Barberini, L. EEG Fingerprints under Naturalistic Viewing Using a Portable Device. Sensors 2020, 20, 6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crobe, A.; Demuru, M.; Didaci, L.; Marcialis, G.L.; Fraschini, M. Minimum Spanning Tree Andk-Core Decomposition as Measure of Subject-Specific EEG Traits. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2016, 2, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Didaci, L.; Pani, S.M.; Frongia, C.; Fraschini, M. How Time Window Influences Biometrics Performance: An EEG-Based Fingerprint Connectivity Study. Signals 2024, 5, 597-604. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030033
Didaci L, Pani SM, Frongia C, Fraschini M. How Time Window Influences Biometrics Performance: An EEG-Based Fingerprint Connectivity Study. Signals. 2024; 5(3):597-604. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleDidaci, Luca, Sara Maria Pani, Claudio Frongia, and Matteo Fraschini. 2024. "How Time Window Influences Biometrics Performance: An EEG-Based Fingerprint Connectivity Study" Signals 5, no. 3: 597-604. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030033
APA StyleDidaci, L., Pani, S. M., Frongia, C., & Fraschini, M. (2024). How Time Window Influences Biometrics Performance: An EEG-Based Fingerprint Connectivity Study. Signals, 5(3), 597-604. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals5030033






