Abstract
Reliable prognostic biomarkers are needed to support the early diagnosis of brain injury in extremely preterm infants, and to develop effective neuroprotective protocols that are tailored to the progressing phases of injury. Experimental and clinical research shows that severity of neuronal damage is correlated with changes in the electroencephalogram (EEG) after hypoxic-ischemia (HI). We have previously reported that micro-scale sharp-wave EEG waveforms have prognostic utility within the early hours of post-HI recordings in preterm fetal sheep, before injury develops. This article aims to investigate whether these subtle EEG patterns are translational in the early hours of life in clinical recordings from extremely preterm newborns. This work evaluates the existence and morphological similarity of the sharp-waves automatically identified throughout the entire duration of EEG data from a cohort of fetal sheep 6 h after HI (n = 7, at 103 ± 1 day gestation) and in recordings commencing before 6 h of life in extremely preterm neonates (n = 7, 27 ± 2.0 weeks gestation). We report that micro-scale EEG waveforms with similar morphology and characteristics (r = 0.94) to those seen in fetal sheep after HI are also present after birth in recordings started before 6 h of life in extremely preterm neonates. This work further indicates that the post-HI sharp-waves show rapid morphological evolution, influenced by age and/or severity of neuronal loss, and thus that automated algorithms should be validated against such signal variations. Finally, this article discusses the need for more focused research on the early assessment of EEG changes in preterm infants to help determine the timing of brain injury to identify biomarkers that could assist in targeting novel therapies for particular phases of injury.
1. Introduction
Preterm infants continue to have a high risk of disability in survivors, despite progressively improved survival [1]. Experimental and clinical research in full-term and pre-term and neonates shows that the severity of hypoxia-ischemia (HI) is associated with the severity of injury in the white and grey matter [2,3], and, in turn, with changes in the electroencephalogram (EEG) after HI [4,5]. Studies in large animals (e.g., fetal sheep) support the value of continuous EEG monitoring for assessing early diagnosis and prognosis [6,7]. The use of fetal sheep allows for comprehensive physiological assessment at different gestational ages, from pre- to full-term age, in order to acquire continuous EEG and electrocardiography (ECG) recordings without confounding by anaesthesia or other medications [8].
Our understanding of the evolution of HI brain injury has mostly been established in animal studies and validated in human newborns with magnetic resonance spectroscopy [7,9]. Typically, an HI event is followed by a ‘latent’ phase of suppression of EEG activity and hypometabolism, followed after 6 to 8 h by a secondary deterioration associated with high amplitude seizures (HAS) (Figure 1a) [7] and failure of mitochondrial function [10]. After 3 days, this may be followed by a long term ‘tertiary’ phase with remodeling, persistent inflammation, and epigenetic changes [11].
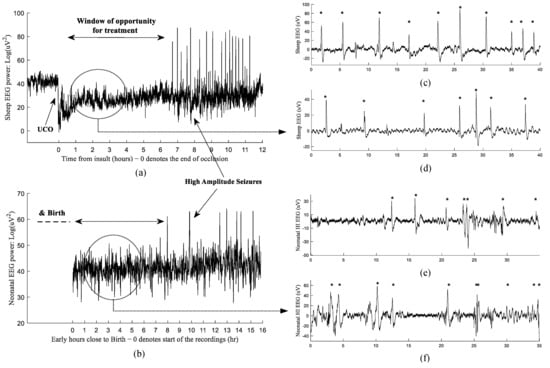
Figure 1.
Examples of the changes in EEG power after hypoxia-ischemia induced by umbilical cord occlusion (UCO) in preterm fetal sheep (a) and during the first day of life after birth in an extremely preterm human neonate (b). Examples of post HI micro-scale sharp-waves along profoundly suppressed EEG in 1024 Hz recordings of preterm fetal sheep model (c,d) and in 256 Hz neonatal EEG from an at risk preterm infant (e,f). The HI sharp-waves are indicated with ‘*’.
Currently, no specific neuroprotection/neurorepair treatments have been proven to be effective for premature infants. In full-term babies, the first 6 h after hypoxia-ischemia (HI) provides a ‘window of opportunity’ when therapeutic hypothermia can significantly improve outcomes [12,13]. It is important to appreciate that the ideal windows for other interventions in the very preterm brain are likely to be different. The development of effective treatments requires accurately targeting the right phases of injury. For example, our animal experiments indicate that early signatures of the injury emerge in the form of micro-scale EEG waveforms superimposed on a suppressed background during the latent phase before the bursts of high-amplitude seizures [6].
Therefore, there is a need to identify biological markers that could indicate the timing of the injury in order to further develop effective treatments associated with different phases of the injury. Currently, we lack reliable early biomarkers while HAS (seen in both experimental and clinical evolving EEG—Figure 1a,b) can be a good indicator of the start of the secondary phase, at least in most cases. Another drawback of HAS are that they are a sign of the closure of the best window of opportunity for treatment in the preterm brain [7,10]. Nevertheless, encouragingly there is some animal evidence that, in specific situations, very late treatment starting after the secondary phase may be beneficial [14]. Anticonvulsant therapy for HAS may improve outcomes, but this remains surprisingly controversial [2]. Thus, HAS should mainly be thought of as useful markers of secondary deterioration after acute brain injury.
Our team has previously shown that in preterm fetal sheep these EEG waveforms emerge in the form of micro-scale sharp-waves and gamma spike transients, and that they are significantly correlated with the subcortical brain damage post HI injury [6,15]. Our team has successfully developed and validated automated advanced signal processing technology, based on deep-learning, for the identification, quantification, and localization of these patterns in preterm fetal sheep data (accuracy > 99%) [15,16]. We have previously shown that micro-scale sharp-waves, in particular, contain timing information related to the evolution of injury in the latent phase after HI. Following this, in fetal sheep the phase of secondary deterioration is associated with a fully stochastic EEG background regardless of age and that HAS in this phase are not necessarily associated with clinical signs. In the preterm brain, these seizures are most often discrete events, and they are less likely to show clinical seizures than term infants [9,10,17].
Real-time manual identification and assessments of EEG data is challenging and requires expert clinical knowledge [18,19,20,21,22]. This is even more challenging when subtle waveforms, often with complex morphological patterns, need to be quantified [23,24]. Hence, there is a significant need for developing automated signal processing techniques to assist with reliable assessments of EEG in suspected cases of brain injury [4,19,25,26,27,28,29]. One approach is to focus on automatic identification and quantification of micro-scale EEG patterns as well as seizures in order to determine the timing and effectively target treatment for infants who might benefit [9,15,17,25,26,30,31].
The primary aim of this study was to explore the potential translational relevance of subtle EEG patterns during the first 6 h of life, specifically focusing on their presence and significance in clinical recordings obtained from extremely preterm newborns. By closely examining these EEG patterns in this vulnerable population, this study seeks to determine whether they exhibit consistent characteristics and whether these patterns could serve as reliable indicators of neurological development similar to those seen in our fetal sheep models.
Therefore, this article will delve into whether the micro-scale sharp-waves observed in preterm fetal sheep models after HI are also evident within the initial 6 h of life in clinical recordings from extremely preterm newborns. The study will then discuss how these subtle waveforms may represent early signatures of preterm brain injury, and how automated algorithms could be useful for the identification and quantification of these patterns in clinical recordings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
Animal ethics: all procedures on animals were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the University of Auckland (R1942) under the New Zealand Animal Welfare Act and were carried out in accordance with the Code of Animal ethical conduct established by the Ministry of Primary Industries of New Zealand Government.
Human ethics: Ethics approval was granted by the Health and Disability Ethics Committees (HDEC), New Zealand (ethics number 13/NTB/49).
2.2. Experimental Protocols
In this study, a total of seven preterm Romney/Suffolk fetal sheep at the gestational ages of 103 ± 1 days were used (full term gestation: 145 days). The surgical procedures were conducted using aseptic techniques, as previously described [10]. Prior to surgery, the ewes were fasted for 18 h, with access to water. They were administered long-acting oxytetracycline (20 mg/kg, Phoenix Pharm, Auckland, New Zealand) intramuscularly 30 min before the start of surgery. Anesthesia was induced using intravenous propofol (5 mg/kg, AstraZeneca Limited, Auckland, New Zealand) and maintained with 2–3% isoflurane in oxygen. Throughout the procedure, the depth of anesthesia, maternal heart rate, and respiration were closely monitored by trained staff. To maintain fluid balance, the ewes received a continuous infusion of isotonic saline (at approximately 250 mL/h).
Following a midline abdominal incision, the fetuses were exposed and an inflatable silicone occluder (OC16HD, 16 mm, In Vivo Metric, Healdsburg, CA, USA) was loosely placed around the umbilical cord to allow for post-surgical occlusion, inducing fetal hypoxic-ischemic (HI) injury [6,8]. EEG electrodes, consisting of two pairs of electrodes made from a 7-stranded stainless-steel wire (AS633–7SSF; Cooner Wire Co.: Los Angeles, CA, USA), were placed on the dura over the parasagittal parietal cortex. A reference electrode was sewn over the occiput. Additional instruments, such as thermistors for temperature measurement, were placed accordingly (data not used in this study). The surgical incisions were closed, and antibiotics (80 mg Gentamicin, Pharmacia and Upjohn, Rydalmere, New South Wales, Australia) were administered into the amniotic sac. Post-operative care included housing the sheep together in separate metabolic cages with ad libitum access to food and water. The room temperature was maintained at 16 ± 1 °C, with a humidity level of 50 ± 10%, and a 12 h light/dark cycle (lights on at 06:00 h).
Sheep received intravenous antibiotics daily for four days (600 mg benzylpencillin sodium, Novartis Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand, and 80 mg gentamicin) to ensure post-operative maternal care and minimize the risk of infection. The patency of fetal catheters was maintained by continuous infusion of heparinized saline, while the maternal catheter was flushed daily to maintain patency.
Data were recorded and saved continuously at 1024 Hz sampling frequency for off-line analysis using custom data acquisition programs (LabView for Windows, National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA). The raw EEG recordings were initially low-pass filtered by using a 6th order anti-aliasing Butterworth filter with a cut-off set at 500 Hz. The signal was then amplified by a gain ×10,000 and then high-pass filtered by a first-order filter with a cut-off frequency set at 1.6 Hz. The recordings were then digitized at 4096 Hz, low-pass filtered using a 10th-order low-pass inverse Chebyshev at 128 Hz (in software), and then decimated down to 1024 Hz sample rate, before saving to file. Data from the last stage were recorded for 72 h and then decoded into Matlab for analysis. Here, we used the experimental EEG recordings during the first 6 h after HI.
2.3. Clinical Protocols
Here we used data from a random subset (n = 7) of an observational cohort study of 33 extremely preterm infants born at ≤28 weeks estimated gestation at Starship Children’s Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand, from 2014 to 2017. All infants received routine clinical and nursing care. The EEG recordings were started as early as possible after birth and continued for 3 days (median age of starting recordings 4:29 h, range 2:45 to 5:29). The infants’ EEG activity was monitored through EEG leads placed symmetrically on the left and right sides of the skull. The EEGs were recorded on the reBRM2 monitor (research version of the BRM2; BrainZ Instruments, Auckland, New Zealand). The EEG signals from the right and left sides were amplified by a factor of 5000 and filtered using a first-order high-pass filter with a −3 dB frequency at 1 Hz, as well as a fourth-order low-pass Butterworth filter with a −3 dB frequency at 50 Hz. The computer digitized the signal at a sampling rate of 256 Hz. Data were collected continuously for a duration of 48 h from the point of initiation. However, we exclusively analyzed recordings from the first 6 h after birth.
In order to avoid any conflict between clinical care requirements and research activities, the EEG electrodes were placed by experienced neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) nurses on call for this project and available in addition to the standard clinical team. Physiological instability in the infant, drug administration and blood sampling, or infant cares were recorded.
Administration of antenatal and postnatal treatments such as sedatives and steroids were documented. Infants with congenital or genetic abnormalities, or scalp injury/infection were excluded.
2.4. Micro-Scale Sharp-Wave EEG Waveforms—An HI Biomarker
We have previously shown that micro-scale sharp-wave EEG patterns with amplitudes between 20–80 μV and a duration between 70 and 250 ms (frequency range: 4 to 14.3 Hz, in the (4–8 Hz), (8–12 Hz), and lower-beta band (i.e., 12–14.3 Hz)) were superimposed on a suppressed EEG background, within the latent phase of fetal sheep data (103 ± 1 days, human brain maturation equivalent ~28–30 weeks) which are a reliable marker for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) (see Figure 1c,d) [6,15]. We have shown that EEG sharp-waves can help to predict the latent phase of injury after an HI insult, where a larger number of sharp-waves within the first 30 min post-HI is associated with greater subcortical neuronal survival in the caudate nucleus (r = 0.80). Conversely, greater numbers of sharp-wave activity between 2–4 h after HI are associated with more damage and a reduced neuronal survival in the same subcortical region (r = −0.83) [6]. This experimental observation highlights the significance of these micro-scale EEG waveforms in a suppressed background as early indicators of HIE, emphasizing the necessity to explore their presence in bedside monitoring, at birth.
This study investigated the potential “translatability” of micro-scale sharp wave EEG patterns within the critical early postnatal period, with a specific focus on documenting their presence within clinical recordings derived from profoundly premature neonates. To achieve this, we examined the comparability of EEG power signal behaviour as well as these sharp-wave EEG patterns within neonatal clinical recordings, compared to our animal data.
Here, in a preliminary analysis of a subset (n = 7) of an observational cohort study of EEG recordings in 33 extremely preterm infants born at ≤28 weeks estimated gestation, we investigated whether the micro-scale EEG waveforms previously reported in our fetal sheep models were also present within the first 6 h after birth. The micro-scale sharp waves were initially detected using our deep learning-based sharp wave identifiers from animal experiments [15,16]. Sharp-waves were automatically identified throughout the entire duration of EEG recordings, starting from the initiation of neonatal recording and continuing 6 h post-birth. Similarly, sharp-waves were automatically identified throughout the entire duration of EEG post-hypoperfusion phase (30 min after the HI event), extending for 6 h post-HI, in the preterm fetal sheep data.
A total of 5191 sharp waves were extracted from the clinical EEG set, while 6086 sharp waves were extracted from the experimental EEG set in the fetal sheep data. Sharp wave patterns from each baby and fetal sheep were centralized at their peaks. The sharp waves per subject were then averaged, and correlations were calculated between the average pattern of all subjects within the neonatal and fetal sheep groups. The matrix of correlation coefficients between the average of sharp patterns in all subjects was calculated using Matlab’s ‘corrcoef’ function.
Here we used Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r, between −1 to +1) to report the correlation coefficient (i.e., the strength in the ‘degree of similarity’—morphological characteristics) between the average of micro-scale sharp-waves seen in our fetal sheep models post-HI, and the ‘similar’ patterns observed in the early hours (<6 h) of birth.
Thus, the current paper focuses on the ‘signal observation’ aspects of the work and does not investigate the potential correlations between the quantifications and timing of these EEG patterns with neonatal outcomes.
3. Results
This study reports that micro-scale sharp-wave transients are present in the recordings taken within the first 6 h after birth in extremely preterm infants. We found that these clinical transients had a nearly identical morphology (r = 0.94, Figure 1e,f) to the sharp-waves seen in the experimental data from sheep fetuses (n = 7, 103 ± 1 days, Figure 2). The example micro-scale sharp-waves shown in Figure 2A were recorded at around 3 h post birth using conventional 256 Hz neonatal recordings from an extremely premature infant. For comparison, Figure 2B shows examples of experimental micro-scale sharp waves at around 2 h post-HI in 1024 Hz recordings from a preterm fetal sheep, as well as the high level of morphological similarities between these micro-scale patterns in preterm infants and fetal sheep.
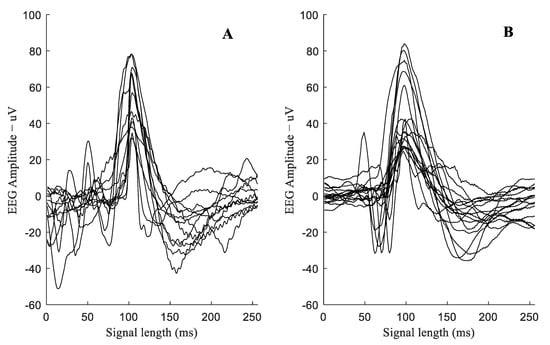
Figure 2.
Examples of micro-scale EEG sharp-waves in 256 Hz neonatal recordings from a premature infant at ~3 h post birth ((A)—12 patterns), and in 1024 Hz recordings from preterm fetal sheep model at ~2 h post-HI ((B)—12 patterns). The low level of noise in the experimental data in B reflects the more controlled environment of these studies.
Examples of EEG sections showing sharp-waves in the amplitude range of 20–70 µV in the clinical and experimental recordings are shown in Figure 3. As can be seen in the EEG sections on the left column of Figure 3, the clinical EEG recordings show greater complexity (spectral components associated with neuronal activity) compared to the EEG sections after acute-HI (25 min occlusion) from fetal sheep models, collected under a much more controlled environment, on the right-hand side column of this figure.
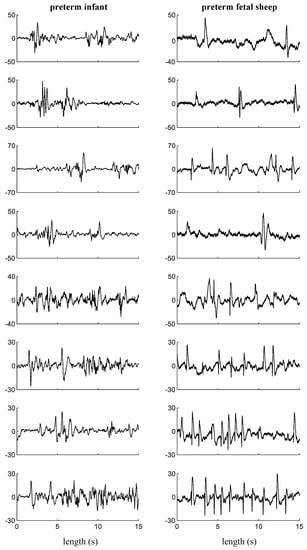
Figure 3.
Examples of EEG sections containing micro-scale sharp-waves in neonatal recordings from premature infants at about 2–6 h after birth (left column), and in experimental recordings from preterm fetal sheep model at about 2–6 h after HI (right column). Y-axis: EEG amplitude (µV).
Furthermore, Figure 1c,d and 1e,f show examples of the post-HI EEG signals in a preterm fetal sheep and during the first day of life after birth in an extremely preterm human neonate, respectively. The EEG sections in Figure 1a,b also illustrate the similarity of the EEG signal’s behavior in the post-HI recordings of fetal sheep vs. early hours post birth recordings in a preterm human data (i.e., the overall EEG recovery and the existence of high amplitude seizures). The emergence of the micro-scale sharp-waves along profoundly suppressed EEG signals could be reliable evidence as to how these EEG patterns are translational in human neonates.
The importance of this ‘EEG pattern similarity’ associated with their emergence in the very early hours of birth lies in factors that we have shown in our fetal sheep models, which show how these early EEG signatures are associated with subcortical neuronal damage, post-HI event.
The correlation coefficients between the average sharp-wave patterns in all subjects (including both neonates and fetal sheep data) are presented in Table 1. The gray-highlighted cells in the table indicate out-of-group correlations for each baby versus each sheep. The average overall out-of-group correlation was calculated as r = 0.94.

Table 1.
Correlation coefficients between all subjects (neonates and fetal sheep data).
4. Discussion
4.1. Insights on the Utility of Computer-Aided Diagnostic Algorithms
EEG is a highly complex and detailed signal that requires experienced clinicians, pediatrics, or neonatal EEG specialists to interpret [32,33]. Therefore, the current clinical utility of this technology at the neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) is limited to units with access to experts. EEG monitoring is also a critically time-consuming process that requires meticulous attention to detail, adding to the burden for human interpretation. Research shows that a simplified 2–4 channel EEG system can be more practical at NICUs [34]. Despite these limitations, EEG provides useful information related to the evolution of HI injury and could contain potential biomarkers related to evolution of HIE [6,35]. Therefore, there is currently a growing interest in the application of automated algorithms for the assessment and grading of the post HI EEG background [4,34]. However, there is limited evidence for how automated deep-learning-based algorithms could help to identify and quantify HI-related markers in the post-HI EEG; furthermore, there is a question as to what extent these strategies could translate across different stages of brain maturation.
Studies show that the severity of neurological damage can be predicted based on the first 12 h EEG recordings from a two-channel EEG-set initiated within the early hours of birth [34,36,37,38]. Importantly, in a cohort of term infants with HIE, TH was more efficacious if initiated within less than 3 h of birth [12]. Our team also has a successful track record on developing and validating advanced technology, based on deep-learning, for the identification, quantification, and localization of micro-scale EEG patterns in the latent phase of preterm fetal sheep (0–7 h post-HI) [9,17,25]. Our data-driven techniques include 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (1D-CNN), Wavelet-Fourier CNNs (WF-CNN), and a highly accurate state-of-the-art 2D Wavelet-Scalogram CNN (WS-CNN) approach that infuses spectrally rich feature maps of EEG sections into a deep CNN classifier for pattern recognition.
Further, the literature indicates an extensive set of clinical and experimental work on the application of data-driven deep-learning-based classifiers for seizure identification in term and preterm infants [27,39,40,41,42] as well as adults [43]. Our team has also recently developed and validated a generalized seizure (HAS) detector algorithm, using data from fetal sheep, that can accurately identify post-HI stereotypic seizures regardless of age or use of TH [44]. HAS are common in clinical recordings and TH can partially suppress these seizures in both animals and human neonates [44,45,46,47,48]. Therefore, automated seizure detector algorithms hold clinical utility to help identify the secondary phase of injury (in some cases, albeit not all). However, HAS identification has almost no utility for detecting the latent phase of injury where the earlier initiation of therapeutic treatment, prior to the emergence of HAS, has been shown to be most effective. The strong morphological similarity between the clinical and experimental seizures makes our pre-clinically validated seizure detector, reported in [44], a good candidate for the identification of clinical seizures in the secondary phase (see Figure 1).
The reliability of our pattern classifiers still needs to be tested on clinical EEG recordings for the identification of micro-scale sharp-wave and HAS. This is particularly important for micro-scale seizures occurring in the latent phase, as they are subject to higher complexities (Figure 3) and rapid morphological evolution, influenced by age and/or severity of neuronal loss.
4.2. Implications and Future Direction
This study demonstrates that micro-scale EEG sharp-wave patterns, previously reported by our team in the recordings from preterm fetal sheep after HI, also exist with similar morphology and characteristics in the early hours of post-birth clinical data of preterm neonates. This cohort was selected to include only infants whose recordings started within 6 h of birth. Future studies will examine the evolution of the EEG after 6 h of life. We demonstrated that the morphology of micro-scale sharp waves observed in the initial hours of post-birth neonatal EEG in extremely preterm newborns and post-HI fetal sheep EEG data are notably consistent (with an average overall correlation of r = 0.94 across all subjects from the two groups). The reader should note that preterm brain injury is multifactorial and commonly involves hypoxia-ischemia (HI) and exposure to infection, alone or in combination [49,50]. To make matters worse, the preterm infant may be injured in utero, survive, and remain unborn with developing brain injury. However, serial EEG recordings support the concept that EEG abnormalities are most often closely related to the time of birth (~53.8%), with some injury occurring well before birth (19.2%); while postnatal injury occurs, it is less common (23%) [51]. Although most interventions are most effective if they are started in the latent phase, there is now preclinical evidence in preterm fetal sheep that anti-inflammatory therapy delayed until 72 h after HI can attenuate surprisingly severe delayed white matter injury [14].
One important factor to consider is that the pattern of evolution of sharp-waves after HI can be markedly affected by the severity of neuronal injury within the latent phase, and therefore early and continuous monitoring can play a pivotal role in the early assessment of the injury. This important factor must be carefully considered in future studies, as being consistent with maturation of neural connectivity, EEG characteristics and the associated patterns’ morphology (including seizures) are highly influenced by age and severity of the injury [2,52,53]. Thus, there is a significant need to design more focused research into the early assessment of EEG patterns (along with other electrophysiological data) to precisely determine timing of the injury in preterm infants with signs of disturbed brain function. Through such investigations, a deeper understanding of the early neurological processes in extremely preterm infants could emerge, thereby potentially paving the way for more targeted interventions and enhanced care strategies in neonatal healthcare.
5. Study limitations
While this study offers valuable insights into the potential translatability of micro-scale sharp waves in neonatal EEG and highlights the necessity for the utility of computer-aided algorithms for EEG interpretation in the context of HIE, there are several limitations that merit careful consideration.
The study’s implications and future directions acknowledge the multifactorial nature of preterm brain injury and emphasize the challenge of accurately timing interventions due to the intricate interplay of contributing factors. While the presence of micro-scale EEG sharp-wave patterns in post-birth clinical data is highlighted, it is important to note that the study’s focus on infants with recordings initiated within six hours of birth limits the understanding of the evolution of these patterns beyond that timeframe.
This temporal constraint does not fully account for injuries that might have occurred prior to birth, thereby complicating the interpretation of EEG abnormalities and their relationship to birth time. Furthermore, the study’s assertion that early and continuous monitoring plays a pivotal role in assessing injury is indeed significant; however, it necessitates careful consideration in light of the ongoing development of neural connectivity and the intricate interrelationship between EEG characteristics and the severity of the injury.
Importantly, the intricate and complex nature of EEG signals necessitates the involvement of experienced clinicians, pediatricians, or neonatal EEG specialists for precise interpretation, underscoring the need for a thorough clinical validation phase before the technology can be implemented in specialized units. The clinical specialists’ expertise and experiences can be incorporated into automatic analysis studies for data interpretation. Moreover, the demanding and time-consuming nature of EEG monitoring further highlights the challenges associated with human interpretation. Despite the interest in automated algorithms to assess post-HIE EEG backgrounds, there remains a scarcity of robust evidence on the effectiveness of deep-learning-based algorithms in identifying and quantifying HIE-related markers across different stages of brain maturation.
Additionally, the study’s pattern classifiers, developed using experimental data from preterm fetal sheep, need validation against extensive and reliable clinical EEG recordings, particularly for identifying micro-scale sharp-wave patterns and seizures during and after the latent phase, respectively, which are influenced by complex factors such as brain maturity (age) and neuronal loss severity.
Addressing this limitation could involve the development of robust machine-learning architectures and their validation using substantial clinical datasets.
6. Conclusions
This study highlights the presence of micro-scale EEG sharp-wave patterns, as previously observed in experimental data from preterm fetal sheep after HIE, in clinical recordings obtained within the first six hours after birth in extremely preterm neonates. We report the morphological and timing similarities between the clinical and experimental sharp-wave patterns, supporting the translational utility of these patterns as biomarkers of neural dysfunction. These findings emphasize the need for reliable automated algorithms that can accurately identify and quantify clinical EEG sharp-waves as a potential candidate prognostic biomarker for disturbed brain function in the early stages of recovery from injury.
The study also illustrates the limitations of current clinical EEG interpretation, which require experienced clinicians and neonatal EEG specialists. Automated algorithms can address these limitations and provide practical solutions for accurate and efficient assessment of encephalopathy-related EEG patterns. Such advances would facilitate early interventions and individualized treatment protocols targeted at specific phases of brain injury, which ultimately are likely to be essential to help improve outcomes for preterm infants. The integration of advanced signal processing technology with clinical practice holds promise for improving prognostic accuracy, facilitating timely interventions, and ultimately enhancing the long-term outcomes of preterm infants at risk of HIE.
We conclude that there is a need for more targeted studies specifically aimed at the early assessment of EEG recordings, and other electrophysiological data, to precisely determine the timing and severity of brain injury in extremely preterm infants displaying signs of HIE.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.A., L.B., A.J.G. and M.R.B.; Methodology, H.A., L.B., A.J.G., M.R.B., R.B., D.R. and B.A.L.; Software, H.A.; Validation, L.B., A.J.G., M.R.B., R.B. and B.A.L.; Formal analysis, H.A.; Investigation, L.B., A.J.G., M.R.B. and R.B.; Resources, L.B., A.J.G. and M.R.B.; Data curation, H.A.; Writing—original draft, H.A.; Writing—review and editing, H.A., L.B., A.J.G. and M.R.B.; Visualization, H.A.; Supervision, L.B., A.J.G. and M.R.B.; Funding acquisition, L.B. and A.J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. Grant numbers: HRC 17/601 and HRC 22/559.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable for this article—data are unavailable due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the use of the New Zealand eScience Infrastructure (NeSI) high-performance computing facilities for the results of this research. URL: https://www.nesi.org.nz (accessed on 4 September 2023). The authors acknowledge the technical support from Mark Gunning from the Lab of the Department of Physiology at the University of Auckland for his assistance with acquiring the fetal sheep data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zayegh, A.M.; Doyle, L.W.; Boland, R.A.; Mainzer, R.; Spittle, A.J.; Roberts, G.; Hickey, L.M.; Anderson, P.J.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; the Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group. Trends in survival, perinatal morbidities and two-year neurodevelopmental outcomes in extremely low-birthweight infants over four decades. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2022, 36, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, M.S.; Hamid, M.Y.; Steppe, D.A.; Beggarly, M.E.; Painter, M.J. Ictal and interictal electrographic seizure durations in preterm and term neonates. Epilepsia 1993, 34, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLaGarza-Pineda, O.; Mailo, J.A.; Boylan, G.; Chau, V.; Glass, H.C.; Mathur, A.M.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Soul, J.S.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Chang, T. Management of seizures in neonates with neonatal encephalopathy treated with hypothermia. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 26, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raurale, S.A.; Boylan, G.B.; Mathieson, S.R.; Marnane, W.P.; Lightbody, G.; O’Toole, J.M. Grading hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal EEG with convolutional neural networks and quadratic time-frequency distributions. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 046007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raurale, S.A.; Boylan, G.B.; Lightbody, G.; O’Toole, J.M. Grading the severity of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborn EEG using a convolutional neural network. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. (EMBC) 2020, 2020, 6103–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Drury, P.P.; Lear, C.A.; Gunn, A.J.; Davidson, J.O.; Bennet, L.; Unsworth, C.P. EEG sharp waves are a biomarker of striatal neuronal survival after hypoxia-ischemia in preterm fetal sheep. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.K.; Lear, C.A.; Galinsky, R.; Wassink, G.; Davidson, J.O.; Juul, S.; Robertson, N.J.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L. The fetus at the tipping point: Modifying the outcome of fetal asphyxia. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 5571–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heuij, L.G.; Wassink, G.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L. Using pregnant sheep to model developmental brain damage. Prenat. Postnatal Determ. Dev. 2016, 31, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar]
- De Wel, O.; Van Huffel, S.; Lavanga, M.; Jansen, K.; Dereymaeker, A.; Dudink, J.; Gui, L.; Hüppi, P.S.; de Vries, L.S.; Naulaers, G.; et al. Relationship between early functional and structural brain developments and brain injury in preterm infants. Cerebellum 2021, 20, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.O.; Gonzalez, F.; Gressens, P.; Gunn, A.J. Guidelines NBS, Publications Committee. Update on mechanisms of the pathophysiology of neonatal encephalopathy. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 26, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, B.; Gressens, P. Tertiary mechanisms of brain damage: A new hope for treatment of cerebral palsy? Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoresen, M.; Tooley, J.; Liu, X.; Jary, S.; Fleming, P.; Luyt, K.; Jain, A.; Cairns, P.; Harding, D.; Sabir, H. Time is brain: Starting therapeutic hypothermia within three hours after birth improves motor outcome in asphyxiated newborns. Neonatology 2013, 104, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, A.J.; Laptook, A.R.; Robertson, N.J.; Barks, J.D.; Thoresen, M.; Wassink, G.; Bennet, L. Therapeutic hypothermia translates from ancient history in to practice. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lear, C.A.; Lear, B.A.; Davidson, J.O.; Sae-Jiw, J.; Lloyd, J.M.; Dhillon, S.K.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L. Tumour necrosis factor blockade after asphyxia in foetal sheep ameliorates cystic white matter injury. Brain 2023, 146, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P.; Bennet, L. Advanced deep learning spectroscopy of scalogram infused CNN classifiers for robust identification of post-hypoxic epileptiform EEG spikes. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P.; Bennet, L. Wavelet Spectral Time-Frequency Training of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Accurate Identification of Micro-Scale Sharp Wave Biomarkers in the Post-Hypoxic-Ischemic EEG of Preterm Sheep. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 2020, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; Rennie, J.M.; de Vries, L.S.; Blennow, M.; Foran, A.; Shah, D.K.; Pressler, R.M.; Kapellou, O.; Dempsey, E.M.; Mathieson, S.R.; et al. Neonatal seizure management: Is the timing of treatment critical? J. Pediatr. 2022, 243, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Mou, C. Survey on the research direction of EEG-based signal processing. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1203059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelc, K.; Gajewska, A.; Napiórkowski, N.; Dan, J.; Verhoeven, C.; Dan, B. Multiscale entropy as a metric of brain maturation in a large cohort of typically developing children born preterm using longitudinal high-density EEG in the first two years of life. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.M.; Pinchefsky, E.; Tse, I.; Marchi, V.; Kohonen, J.; Kauppila, M.; Airaksinen, M.; Tapani, K.; Nevalainen, P.; Hahn, C.; et al. Building an open source classifier for the neonatal EEG background: A systematic feature-based approach from expert scoring to clinical visualization. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 675154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dib, M.; Abend, N.S.; Austin, T.; Boylan, G.; Chock, V.; Cilio, M.R.; Greisen, G.; Hellström-Westas, L.; Lemmers, P.; Pellicer, A.; et al. Neuromonitoring in neonatal critical care part I: Neonatal encephalopathy and neonates with possible seizures. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 94, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, J.; Mikkonen, K.; Metsäranta, M.; Toiviainen-Salo, S.; Vanhatalo, S.; Lauronen, L.; Nevalainen, P. Poor aEEG background recovery after perinatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy predicts postneonatal epilepsy by age 4 years. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 143, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlif, M.S.; Mesbah, M.; Colditz, P.B.; Boashash, B. Neonatal EEG seizure detection using a new signal structural complexity measure based on matching pursuit decomposition with nonstationary dictionary. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 224, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramacki, A.; Gramacki, J. A deep learning framework for epileptic seizure detection based on neonatal EEG signals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P. Latent phase detection of hypoxic-ischemic spike transients in the EEG of preterm fetal sheep using reverse biorthogonal wavelets & fuzzy classifier. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2019, 29, 1950013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L.; Unsworth, C.P. Latent phase identification of high-frequency micro-scale gamma spike transients in the hypoxic ischemic EEG of preterm fetal sheep using spectral analysis and fuzzy classifiers. Sensors 2020, 20, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; O’Toole, J.M.; Proietti, J.; Livingstone, V.; Mitra, S.; Marnane, W.P.; Finder, M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B.; et al. Machine learning for the early prediction of infants with electrographic seizures in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, A.A.; Pavel, A.M.; O’toole, J.M.; Walsh, B.H.; Korotchikova, I.; Livingstone, V.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B. Multichannel EEG abnormalities during the first 6 hours in infants with mild hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cainelli, E.; Di Bono, M.G.; Bisiacchi, P.S.; Suppiej, A. Electroencephalographic functional connectivity in extreme prematurity: A pilot study based on graph theory. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J.; Unsworth, C.P. Robust Wavelet Stabilized ‘Footprints of Uncertainty’ for Fuzzy System Classifiers to Automatically Detect Sharp Waves in the EEG after Hypoxia Ischemia. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2017, 27, 1650051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Mathieson, S.R.; Raurale, S.A.; Magarelli, F.; Marnane, W.P.; Lightbody, G.; Boylan, G.B. Neonatal EEG graded for severity of background abnormalities in hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.; Osselton, J.W.; Shaw, J.C. EEG Technology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhatalo, S.; Stevenson, N.J.; Pressler, R.M.; Abend, N.S.; Auvin, S.; Brigo, F.; Cilio, M.R.; Hahn, C.D.; Hartmann, H.; Hellström-Westas, L.; et al. Why monitor the neonatal brain—That is the important question. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.K.; Mackay, M.T.; Lavery, S.; Watson, S.; Harvey, A.S.; Zempel, J.; Mathur, A.; Inder, T.E. Accuracy of bedside electroencephalographic monitoring in comparison with simultaneous continuous conventional electroencephalography for seizure detection in term infants. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidis, E.; Lloyd, R.O.; Boylan, G.B. EEG—A Valuable Biomarker of Brain Injury in Preterm Infants. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 39, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Fu, N.; Chen, W.; Liang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, J. Prognostic value of electroencephalography in hypothermia-treated neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 93, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, E.; van der Stoel, M.; Nagaraj, S.B.; Ghassemi, M.M.; Jing, J.; O’Reilly, U.-M.; Scirica, B.M.; Lee, J.W.; Cash, S.S.; Westover, M.B. Quantitative EEG reactivity and machine learning for prognostication in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, A.; Lai, M.M.; Azemi, G.; Boashash, B.; Colditz, P.B. EEG background features that predict outcome in term neonates with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: A structured review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’shea, A.; Ahmed, R.; Lightbody, G.; Pavlidis, E.; Lloyd, R.; Pisani, F.; Marnane, W.; Mathieson, S.; Boylan, G.; Temko, A. Deep Learning for EEG Seizure Detection in Preterm Infants. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2021, 31, 2150008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’shea, A.; Lightbody, G.; Boylan, G.; Temko, A. Neonatal seizure detection from raw multi-channel EEG using a fully convolutional architecture. Neural Netw. 2020, 123, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; Rennie, J.M.; de Vries, L.S.; Blennow, M.; Foran, A.; Shah, D.K.; Pressler, R.M.; Kapellou, O.; Dempsey, E.M.; Mathieson, S.R.; et al. A machine-learning algorithm for neonatal seizure recognition: A multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.H.; Cherian, P.J.; Caicedo, A.; Naulaers, G.; De Vos, M.; Van Huffel, S. Neonatal seizure detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2019, 29, 1850011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adeli, H. Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 100, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, H.; Dhillon, S.K.; Davidson, J.; Gunn, A.J.; Bennet, L. 2D Wavelet-scalogram deep-learning for seizures pattern identification in the post-hypoxic-ischemic EEG of preterm fetal sheep. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC’23); IEEE EMBC 2023, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 24–27 July 2023. in press. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, R.O.; O’Toole, J.M.; Pavlidis, E.; Filan, P.M.; Boylan, G.B. Electrographic seizures during the early postnatal period in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2017, 187, 18–25.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wusthoff, C.J.; Dlugos, D.J.; Gutierrez-Colina, A.; Wang, A.; Cook, N.; Donnelly, M.; Clancy, R.; Abend, N.S. Electrographic seizures during therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J. Child Neurol. 2011, 26, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, G.B.; Kharoshankaya, L.; Wusthoff, C.J. Seizures and hypothermia: Importance of electroencephalographic monitoring and considerations for treatment. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophelders, D.R.; Gussenhoven, R.; Klein, L.; Jellema, R.K.; Westerlaken, R.J.; Hütten, M.C.; Vermeulen, J.; Wassink, G.; Gunn, A.J.; Wolfs, T.G. Preterm brain injury, antenatal triggers, and therapeutics: Timing is key. Cells 2020, 9, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, C.M.; Pierro, A.; Eaton, S. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of neonates with medically and surgically treated necrotizing enterocolitis. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007, 92, F193–F198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, A.L.; Stoll, B.J. Neonatal sepsis: Progress towards improved outcomes. J. Infect. 2014, 68, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Okumura, A.; Hayakawa, F.; Kato, T.; Itomi, K.; Kuno, K.; Watanabe, K. Relation between the date of cyst formation observable on ultrasonography and the timing of injury determined by serial electroencephalography in preterm infants with periventricular leukomalacia. Brain Dev. 2001, 23, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janáčková, S.; Boyd, S.; Yozawitz, E.; Tsuchida, T.; Lamblin, M.-D.; Gueden, S.; Pressler, R. Electroencephalographic characteristics of epileptic seizures in preterm neonates. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2721–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrizi, S.; Holmes, G.L.; Orzalesi, M.; Allemand, F. Neonatal seizures: Characteristics of EEG ictal activity in preterm and fullterm infants. Brain Dev. 2003, 25, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).