PID Controller Parameter Tables for Time-Delayed Systems Optimized Using Hill-Climbing
Abstract
1. Introduction and Related Research
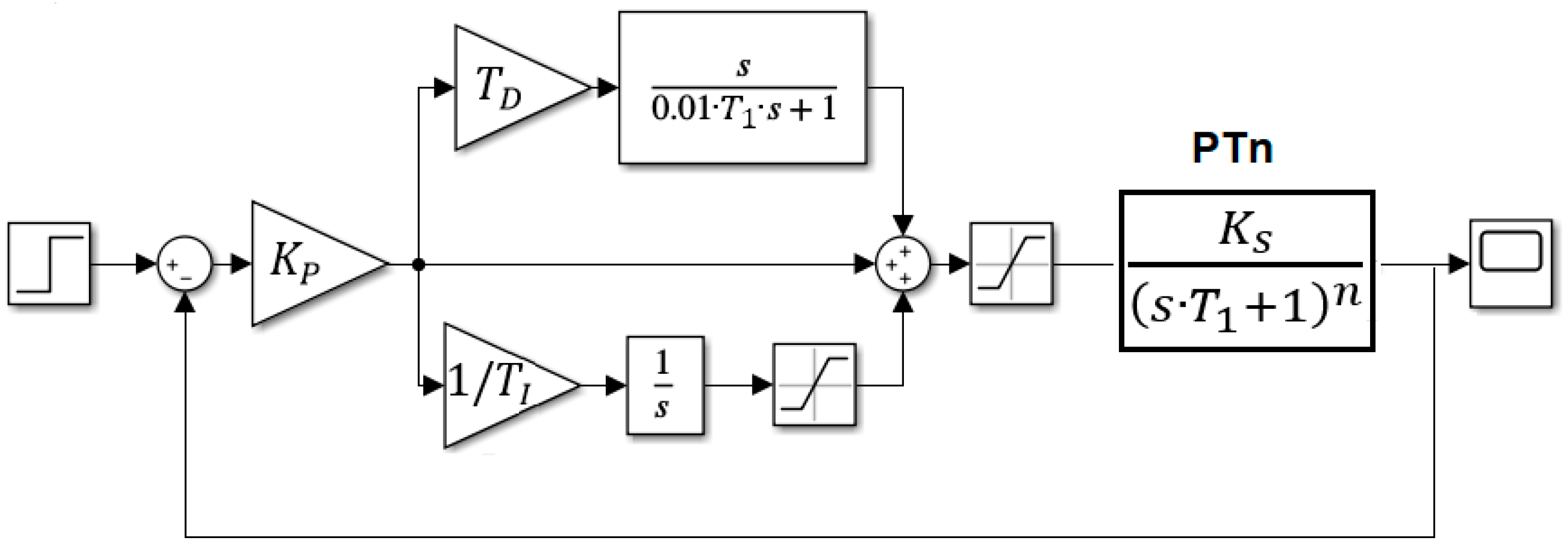
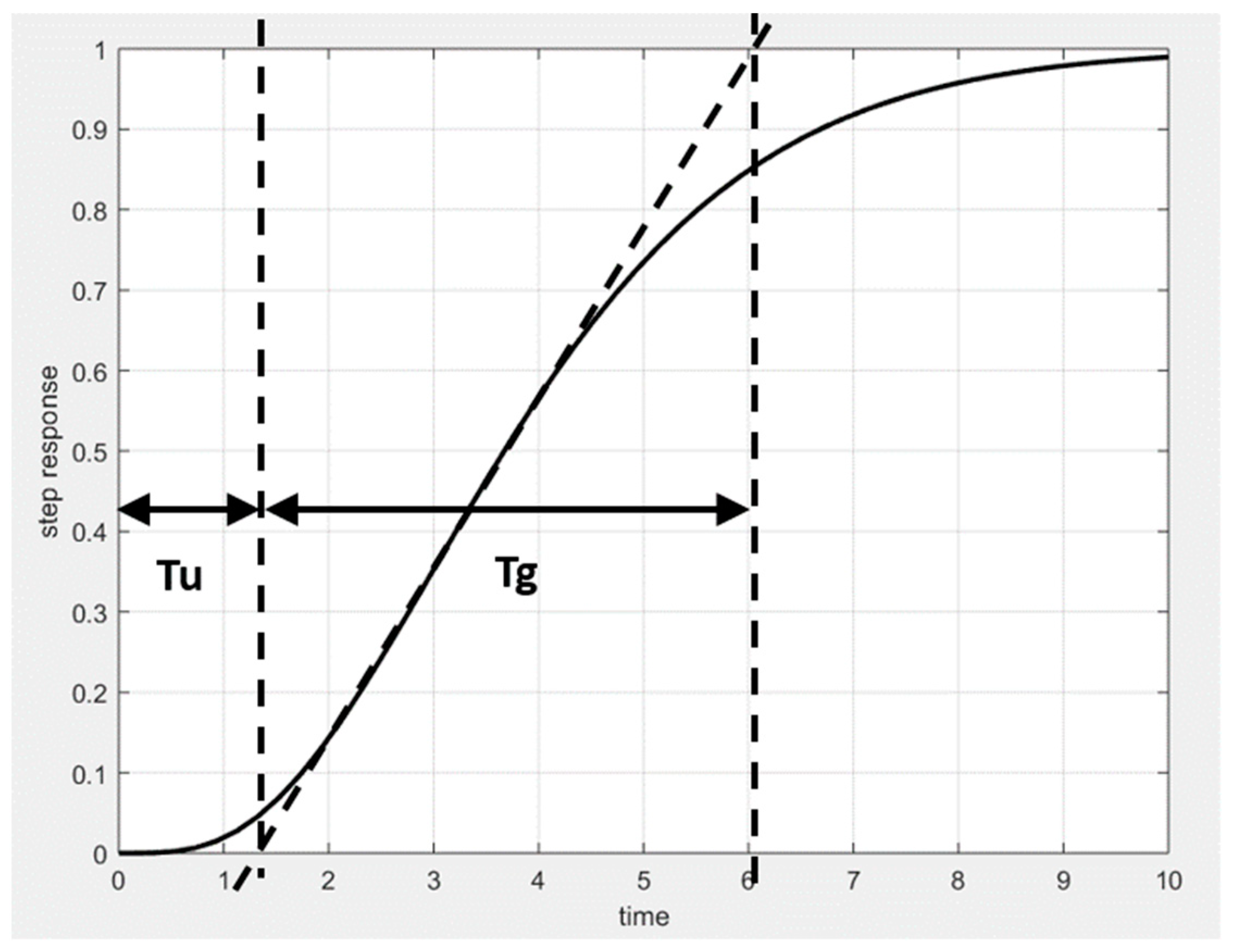
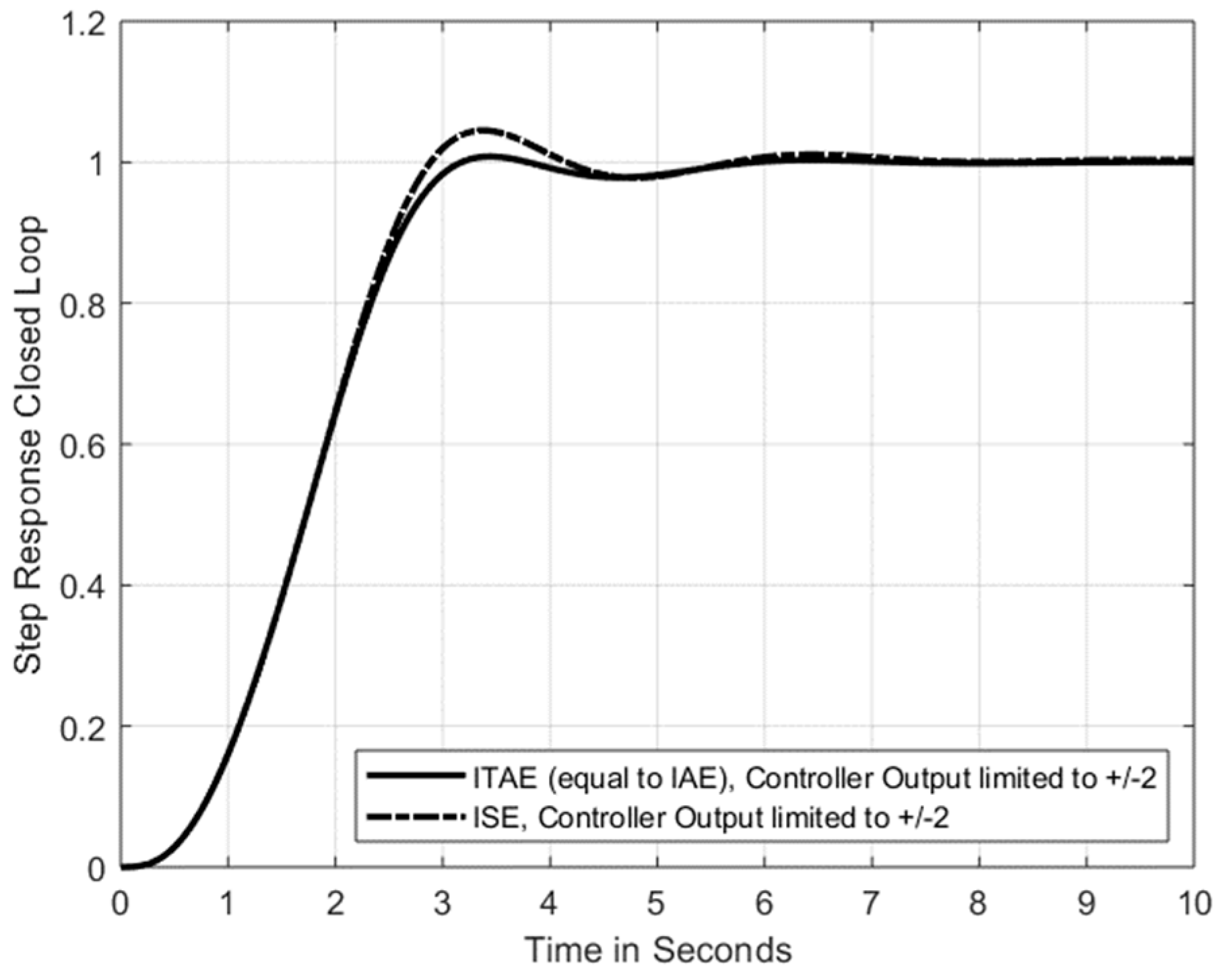
2. PTn Systems and ITAE, IAE and ISE Criteria
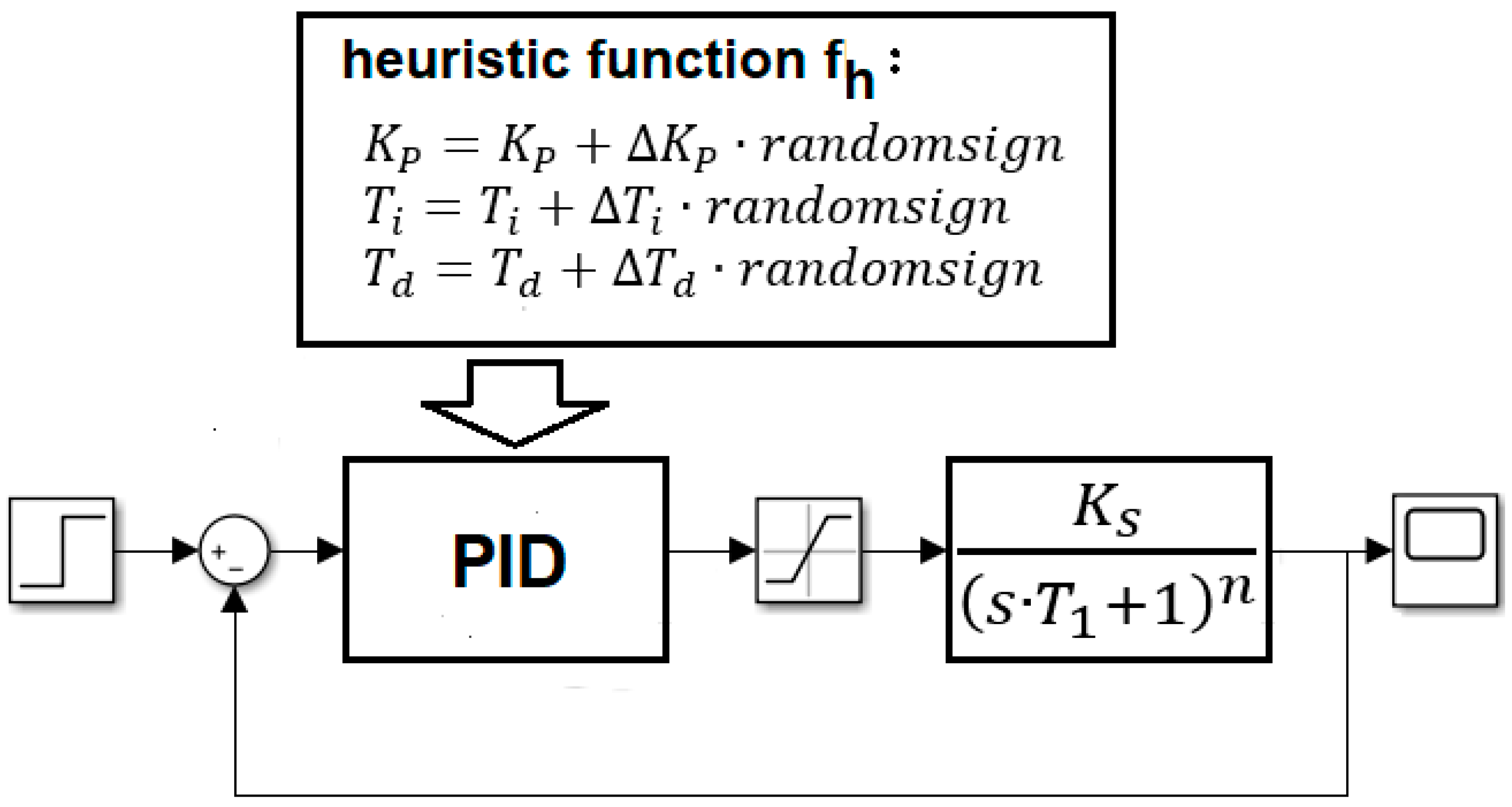
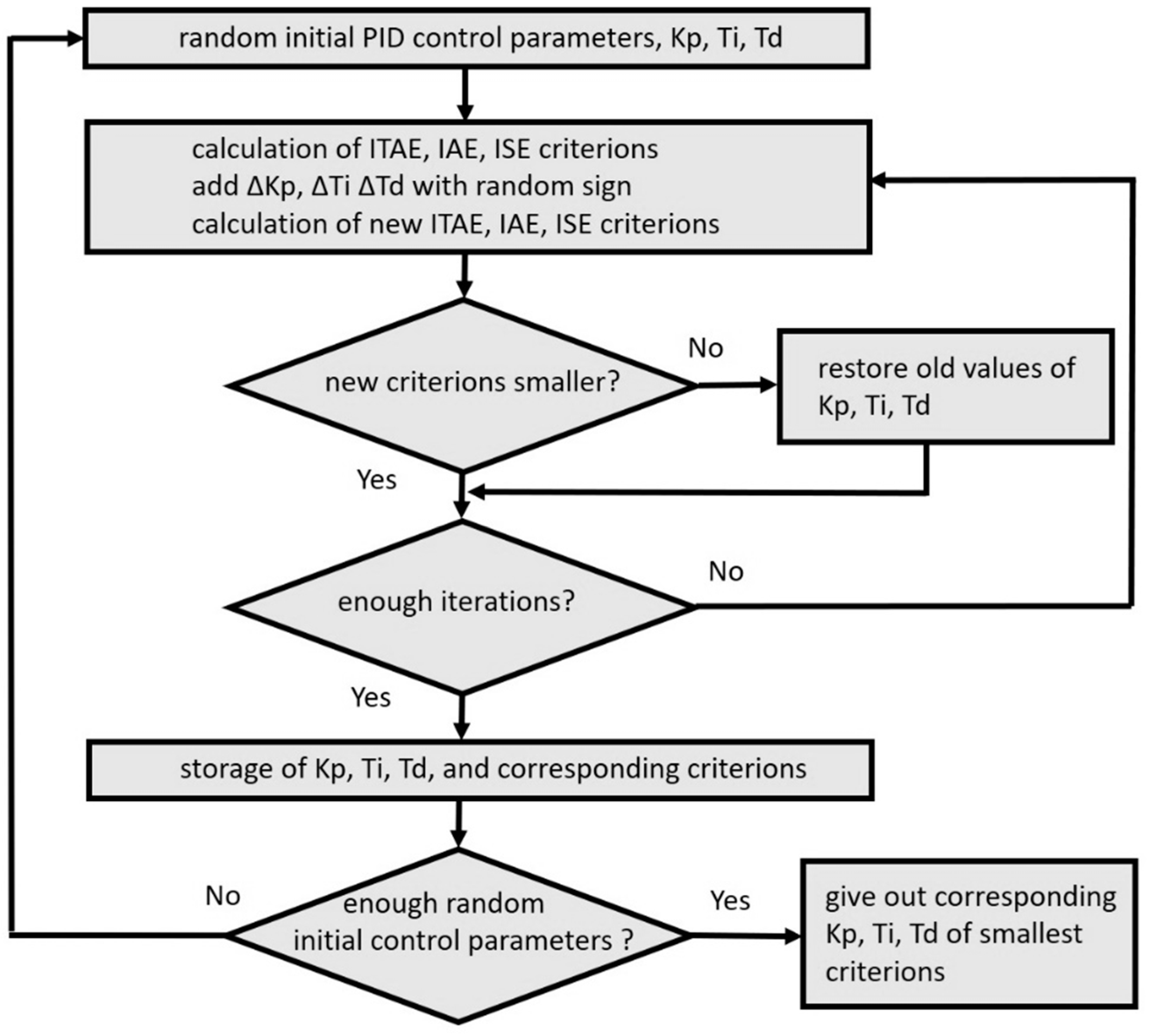
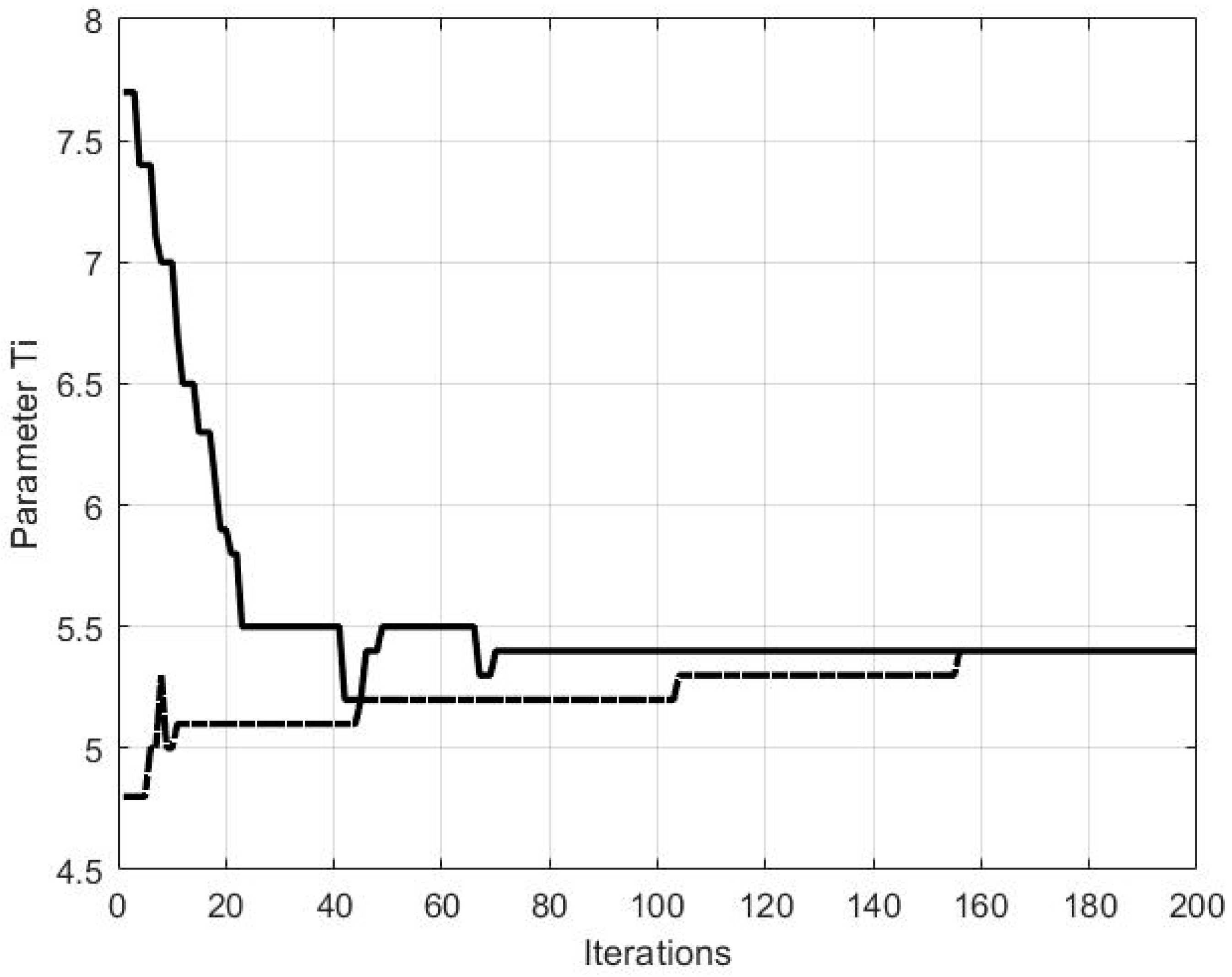
3. The Hill-Climbing Method for Calculating the PID Controller Parameters
4. Results: Calculated PID Parameters for the Minimized IAE, ITAE and ISE Criteria
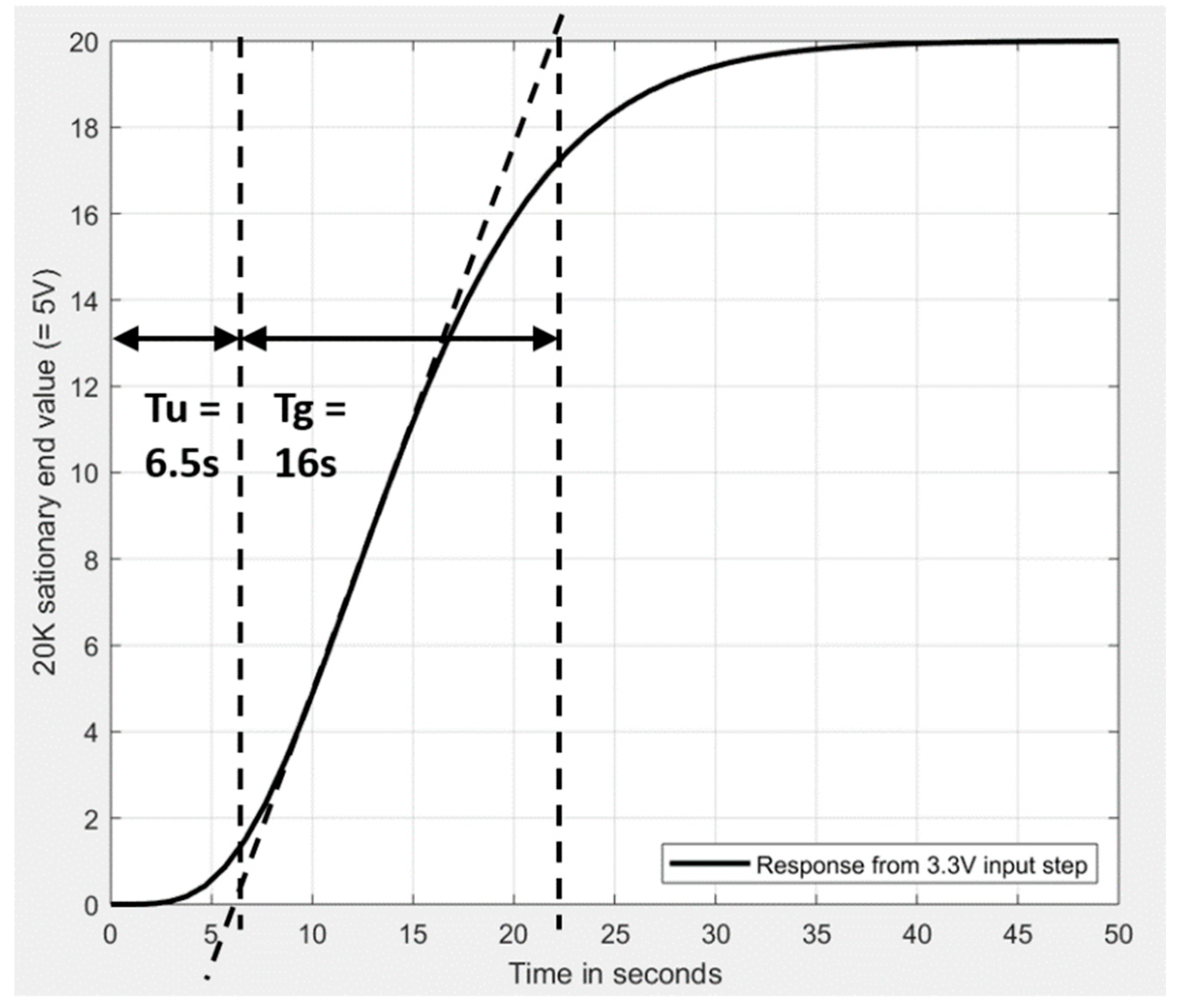
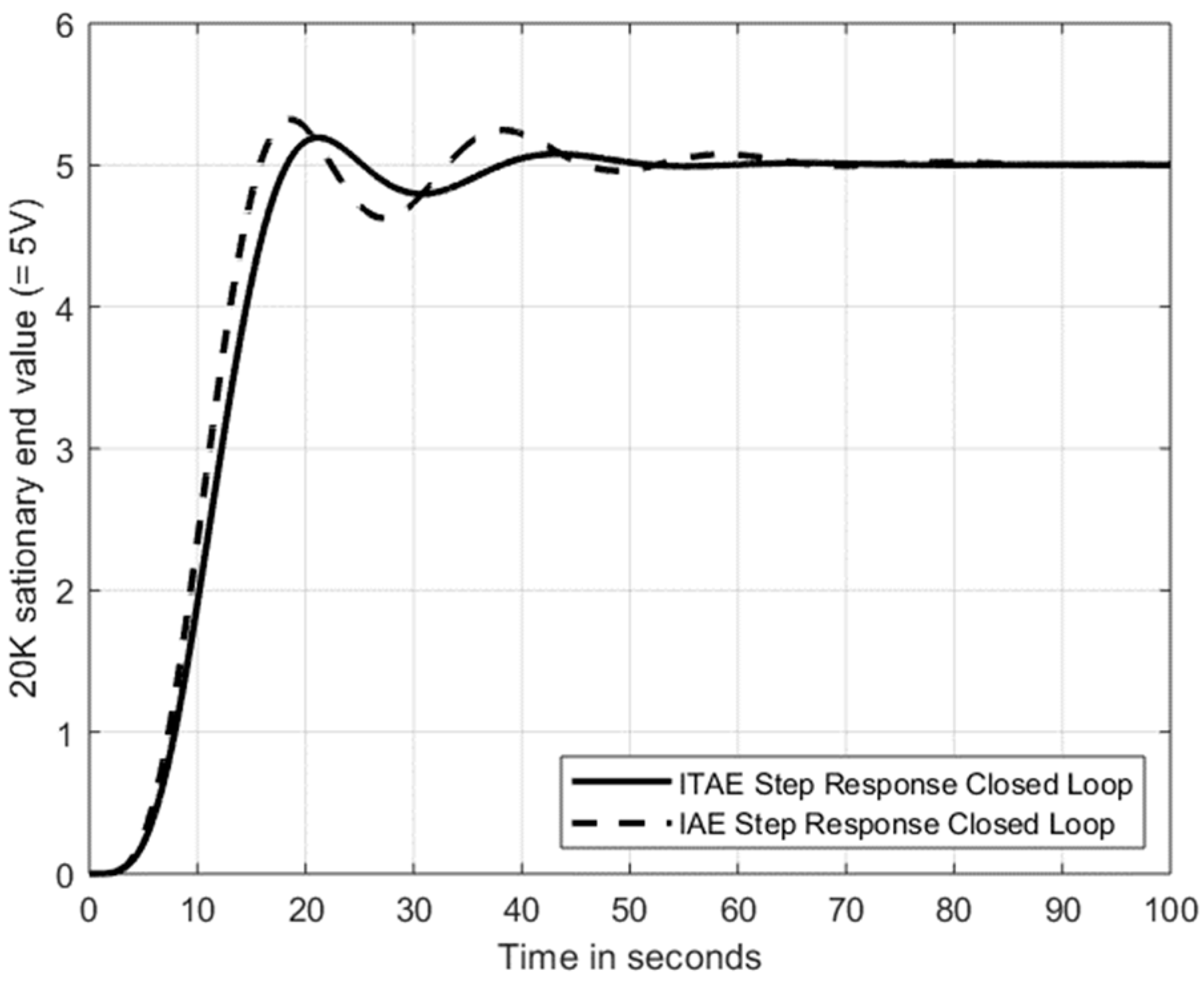
5. Applications for the Use of the Table: PID-Controlled PT3 and PT5
6. Discussion and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ziegler, J.G.; Nichols, N.B. Optimum settings for automatic controllers. ASME Trans. 1942, 64, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, K.L.; Hrones, J.A.; Reswick, J.B. On the Automatic Control of Generalized Passive Systems. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. ASME 1972, 74, 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Zamani, M.; Sadati, N.; Ghartemani, M.K. Design of H∞ PID controller using particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2009, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Maruta, I.; Sugie, T. Robust PID controller tuning based on the constrained particle particle swarm optimization. Automatica 2008, 44, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, I.; Kim, T.-H.; Sugie, T. Fixed-structure H∞ controller synthesis: A meta-heuristic approach using simple constrained particle swarm optimization. Automatica 2009, 45, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Han, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-M. Network-Based Modeling and Proportional–Integral Control for Direct-Drive-Wheel Systems in Wireless Network Environments. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 2462–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H. Tuning of digital PID controllers using particle swarm optimization algorithm for a CAN-based DC motor subject to stochastic delays. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5637–5646. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.-D.; Shih, S.-P. PID controller design of nonlinear systems using an improved particle swarm optimization approach. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, A.T.; Ammar, H.H.; Ibrahim, Z.F.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Mohamed, N.A.; Taha, M.A. Implementation of PID controller with PSO tuning for autonomous vehicle. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Cairo, Egypt, 26–28 October 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Sang, Z.-K.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhao, R. High Precision Temperature Control Performance of a PID Neural Network-Controlled Heater Under Complex Outdoor Conditions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 195, 117234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbayomy, K.M.; Jiao, Z.; Zhang, H. PID controller optimization by GA and its performances on the electro-hydraulic servo control system. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2008, 21, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, E.; Naghavi, N. Offline auto-tuning of a PID controller using extended classifier system (XCS) algorithm. J. Adv. Comput. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, K.M.; Zepherin, R.A.; Shantha, M. Comparison of PID Controller Tuning Methods with Genetic Algorithm for FOPTD System. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2014, 4, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, E.A.; Olaiya, O.O. Cohen- Coon PID Tuning Method, A Better Option to Ziegler Nichols- PID Tuning Method. Comput. Eng. Intell. Syst. 2017, 2, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ozana, S.; Docekal, T. PID Controller Design Based on Global Optimization Technique with Additional Constraints. J. Electr. Eng. 2016, 67, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Büchi, R. Modellierung und Regelung von Impact Drives für Positionierungen im Nanometerbereich. Doctoral Dissertation, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, L.R.; Flesch, R.C.; Normey-Rico, J.E. Controlling industrial dead-time systems: When to use a PID or an advanced controller. ISA Trans. 2020, 99, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.G. Tuning PID Controllers using the ITAE Criterion. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2005, 21, 867–873. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, G.J.; Datta, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. PID Controllers for Time-Delay Systems; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-8176-4266-8. [Google Scholar]
- Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 111–114. ISBN 0-13-790395-2. [Google Scholar]
- Unbehauen, H. Regelungstechnik; Vieweg: Braunschweig, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zacher, S.; Reuter, M. Regelungstechnik Für Ingenieure; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]


| PTn | PT2 | PT3 | PT4 | PT5 | PT6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg/Tu | 9.71 | 4.61 | 3.14 | 2.44 | 2.03 |
| Tg/T1 | 2.72 | 3.69 | 4.46 | 5.12 | 5.70 |
| Tu/T1 | 0.28 | 0.8 | 1.42 | 2.10 | 2.81 |
| PT1 | +/−2 | +/−3 | +/−5 | +/−10 |
| IAE | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| IAE | Ti = 3.1·T1 | Ti = 2·T1 | Ti = 1.3·T1 | Ti = 1·T1 |
| IAE | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) |
| ITAE | Kp·Ks = 9.3 | Kp·Ks = 9.5 | Kp·Ks = 9.1 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| ITAE | Ti = 2.9·T1 | Ti = 1.9·T1 | Ti = 1.2·T1 | Ti = 1·T1 |
| ITAE | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) |
| ISE | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 9.8 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| ISE | Ti = 2.7·T1 | Ti = 1.6·T1 | Ti = 1.5·T1 | Ti = 0.2·T1 |
| ISE | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) | Td = 0 (PI) |
| PT2, Tg/Tu = 9.71 | +/−2 | +/−3 | +/−5 | +/−10 |
| IAE | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| IAE | Ti = 9.6·T1 | Ti = 7.3·T1 | Ti = 5.6·T1 | Ti = 3.7·T1 |
| IAE | Td = 0.3·T1 | Td = 0.3·T1 | Td = 0.3·T1 | Td = 0.2·T1 |
| ITAE | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 9.6 | Kp·Ks = 9.8 |
| ITAE | Ti = 9.6·T1 | Ti = 7.3·T1 | Ti = 5.4·T1 | Ti = 4.7·T1 |
| ITAE | Td = 0.3·T1 | Td = 0.3·T1 | Td = 0.3·T1 | Td = 0.3·T1 |
| ISE | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| ISE | Ti = 9.7·T1 | Ti = 7.3·T1 | Ti = 5.1·T1 | Ti = 4.6·T1 |
| ISE | Td = 0.2·T1 | Td = 0.2·T1 | Td = 0.2·T1 | Td = 0.1·T1 |
| PT3, Tg/Tu = 3.61 | +/−2 | +/−3 | +/−5 | +/−10 |
| IAE | Kp·Ks = 5.4 | Kp·Ks = 7 | Kp·Ks = 8.4 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| IAE | Ti = 9.4·T1 | Ti = 10·T1 | Ti = 9.8·T1 | Ti = 9.7·T1 |
| IAE | Td = 0.7·T1 | Td = 0.7·T1 | Td = 0.7·T1 | Td = 0.7·T1 |
| ITAE | Kp·Ks = 5.4 | Kp·Ks = 7 | Kp·Ks = 8.2 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| ITAE | Ti = 9.4·T1 | Ti = 10·T1 | Ti = 9.6·T1 | Ti = 9.7·T1 |
| ITAE | Td = 0.7·T1 | Td = 0.7·T1 | Td = 0.7·T1 | Td = 0.7·T1 |
| ISE | Kp·Ks = 6.1 | Kp·Ks = 8.1 | Kp·Ks = 10 | Kp·Ks = 10 |
| ISE | Ti = 10·T1 | Ti = 9.8·T1 | Ti = 10·T1 | Ti = 7.8·T1 |
| ISE | Td = 0.6·T1 | Td = 0.6·T1 | Td = 0.6·T1 | Td = 0.6·T1 |
| PT4, Tg/Tu = 3.14 | +/−2 | +/−3 | +/−5 | +/−10 |
| IAE | Kp·Ks = 2 | Kp·Ks = 2.9 | Kp·Ks = 3.3 | Kp·Ks = 3.3 |
| IAE | Ti = 5.2·T1 | Ti = 6.5·T1 | Ti = 7.1·T1 | Ti = 6.9·T1 |
| IAE | Td = 1.1·T1 | Td = 1.2·T1 | Td = 1.3·T1 | Td = 1.3·T1 |
| ITAE | Kp·Ks = 1.9 | Kp·Ks = 2.4 | Kp·Ks = 2.3 | Kp·Ks = 2.1 |
| ITAE | Ti = 5·T1 | Ti = 5.9·T1 | Ti = 5.7·T1 | Ti = 5·T1 |
| ITAE | Td = 1.1·T1 | Td = 1.2·T1 | Td = 1.2·T1 | Td = 1.1·T1 |
| ISE | Kp·Ks = 2.8 | Kp·Ks = 3.6 | Kp·Ks = 4.9 | Kp·Ks = 5.2 |
| ISE | Ti = 6.6·T1 | Ti = 7·T1 | Ti = 7.1·T1 | Ti = 7·T1 |
| ISE | Td = 1.2·T1 | Td = 1.2·T1 | Td = 1.4·T1 | Td = 1.4·T1 |
| PT5, Tg/Tu = 2.44 | +/−2 | +/−3 | +/−5 | +/−10 |
| IAE | Kp·Ks = 1.7 | Kp·Ks = 1.8 | Kp·Ks = 1.8 | Kp·Ks = 1.7 |
| IAE | Ti = 5.8·T1 | Ti = 5.9·T1 | Ti = 5.8·T1 | Ti = 5.5·T1 |
| IAE | Td = 1.6·T1 | Td = 1.6·T1 | Td = 1.6·T1 | Td = 1.6·T1 |
| ITAE | Kp·Ks = 1.4 | Kp·Ks = 1.4 | Kp·Ks = 1.4 | Kp·Ks = 1.4 |
| ITAE | Ti = 5.3·T1 | Ti = 5.2·T1 | Ti = 5.2·T1 | Ti = 5.0·T1 |
| ITAE | Td = 1.4·T1 | Td = 1.4·T1 | Td = 1.4·T1 | Td = 1.4·T1 |
| ISE | Kp·Ks = 1.9 | Kp·Ks = 2.6 | Kp·Ks = 2.5 | Kp·Ks = 2.5 |
| ISE | Ti = 5.9·T1 | Ti = 6.5·T1 | Ti = 6.3·T1 | Ti = 6.1·T1 |
| ISE | Td = 1.7·T1 | Td = 1.8·T1 | Td = 1.8·T1 | Td = 1.8·T1 |
| PT6, Tg/Tu = 2.03 | +/−2 | +/−3 | +/−5 | +/−10 |
| IAE | Kp·Ks = 1.3 | Kp·Ks = 1.3 | Kp·Ks = 1.3 | Kp·Ks = 1.3 |
| IAE | Ti = 5.9·T1 | Ti = 5.8·T1 | Ti = 5.8·T1 | Ti = 5.6·T1 |
| IAE | Td = 1.9·T1 | Td = 1.9·T1 | Td = 1.9·T1 | Td = 1.9·T1 |
| ITAE | Kp·Ks = 1.1 | Kp·Ks = 1.1 | Kp·Ks = 1.1 | Kp·Ks = 1.1 |
| ITAE | Ti = 5.5·T1 | Ti = 5.5·T1 | Ti = 5.4·T1 | Ti = 5.3·T1 |
| ITAE | Td = 1.7·T1 | Td = 1.7·T1 | Td = 1.7·T1 | Td = 1.7·T1 |
| ISE | Kp·Ks = 1.8 | Kp·Ks = 1.8 | Kp·Ks = 1.8 | Kp·Ks = 1.8 |
| ISE | Ti = 6.8·T1 | Ti = 6.5·T1 | Ti = 6.5·T1 | Ti = 6.3·T1 |
| ISE | Td = 2.1·T1 | Td = 2.1·T1 | Td = 2.1·T1 | Td = 2.1·T1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Büchi, R. PID Controller Parameter Tables for Time-Delayed Systems Optimized Using Hill-Climbing. Signals 2022, 3, 146-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3010010
Büchi R. PID Controller Parameter Tables for Time-Delayed Systems Optimized Using Hill-Climbing. Signals. 2022; 3(1):146-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBüchi, Roland. 2022. "PID Controller Parameter Tables for Time-Delayed Systems Optimized Using Hill-Climbing" Signals 3, no. 1: 146-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3010010
APA StyleBüchi, R. (2022). PID Controller Parameter Tables for Time-Delayed Systems Optimized Using Hill-Climbing. Signals, 3(1), 146-156. https://doi.org/10.3390/signals3010010





