Experimental Investigation into the Active Narrowband Reshaping of a Ship Model’s Acoustic Signature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
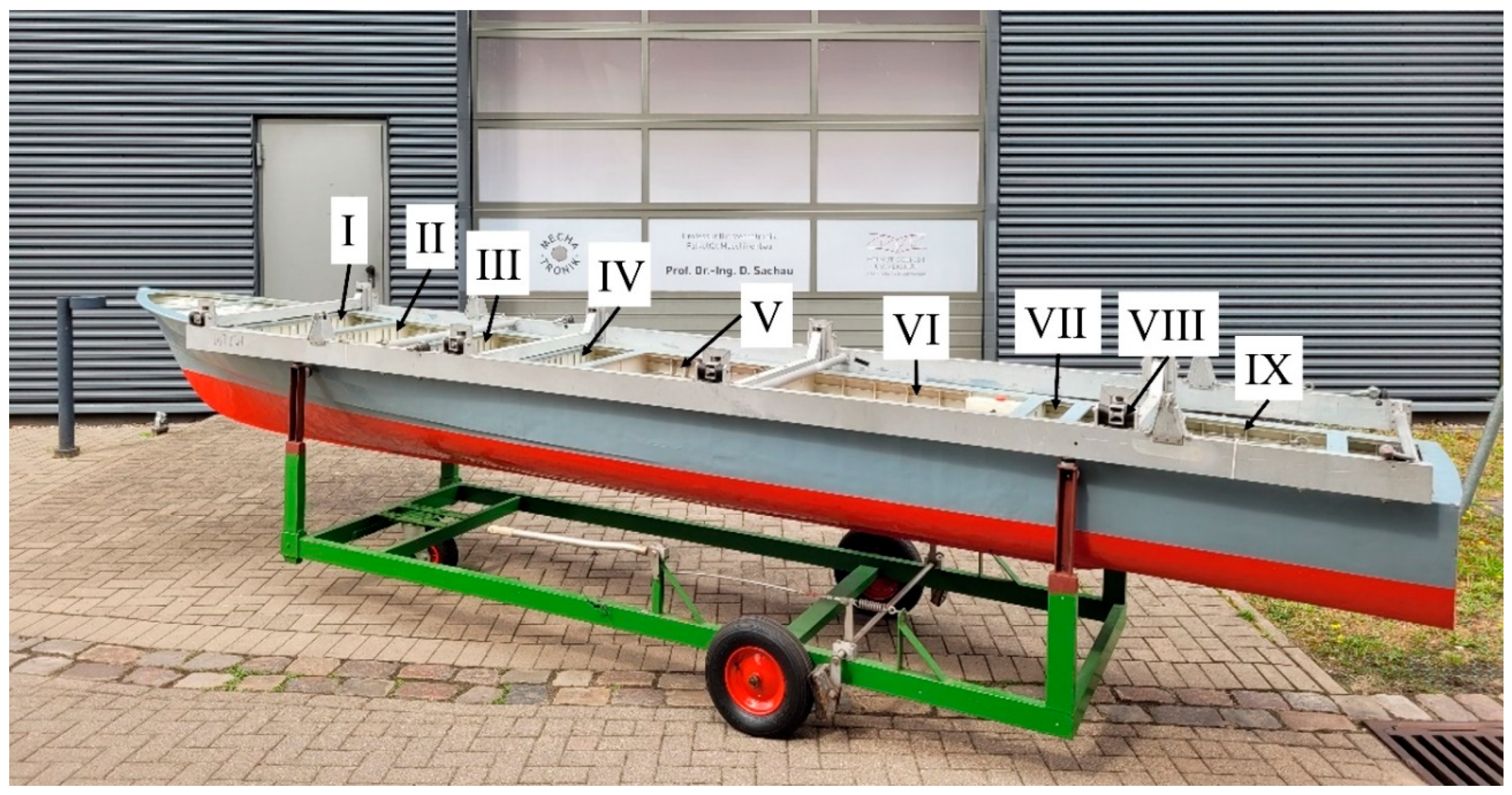
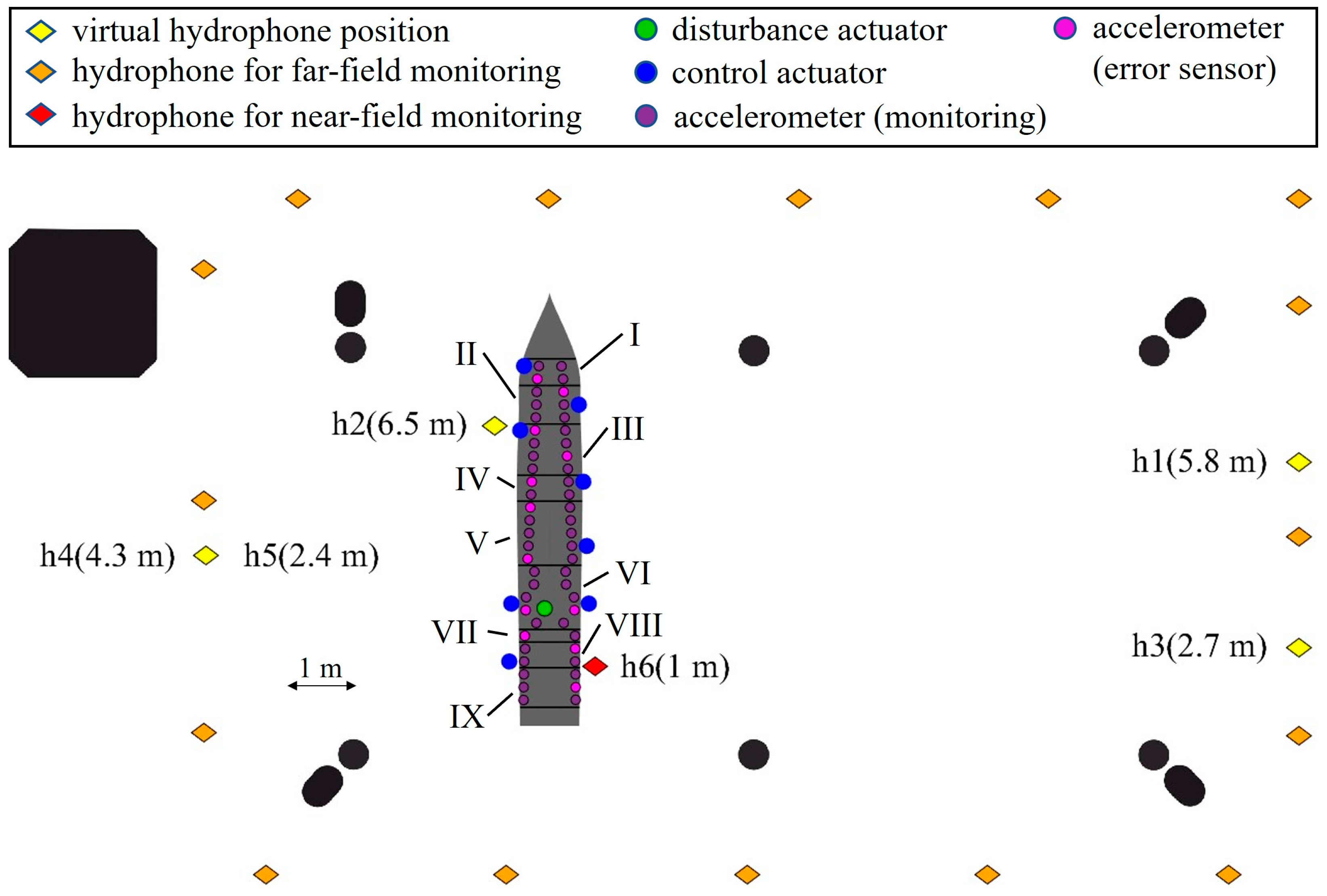
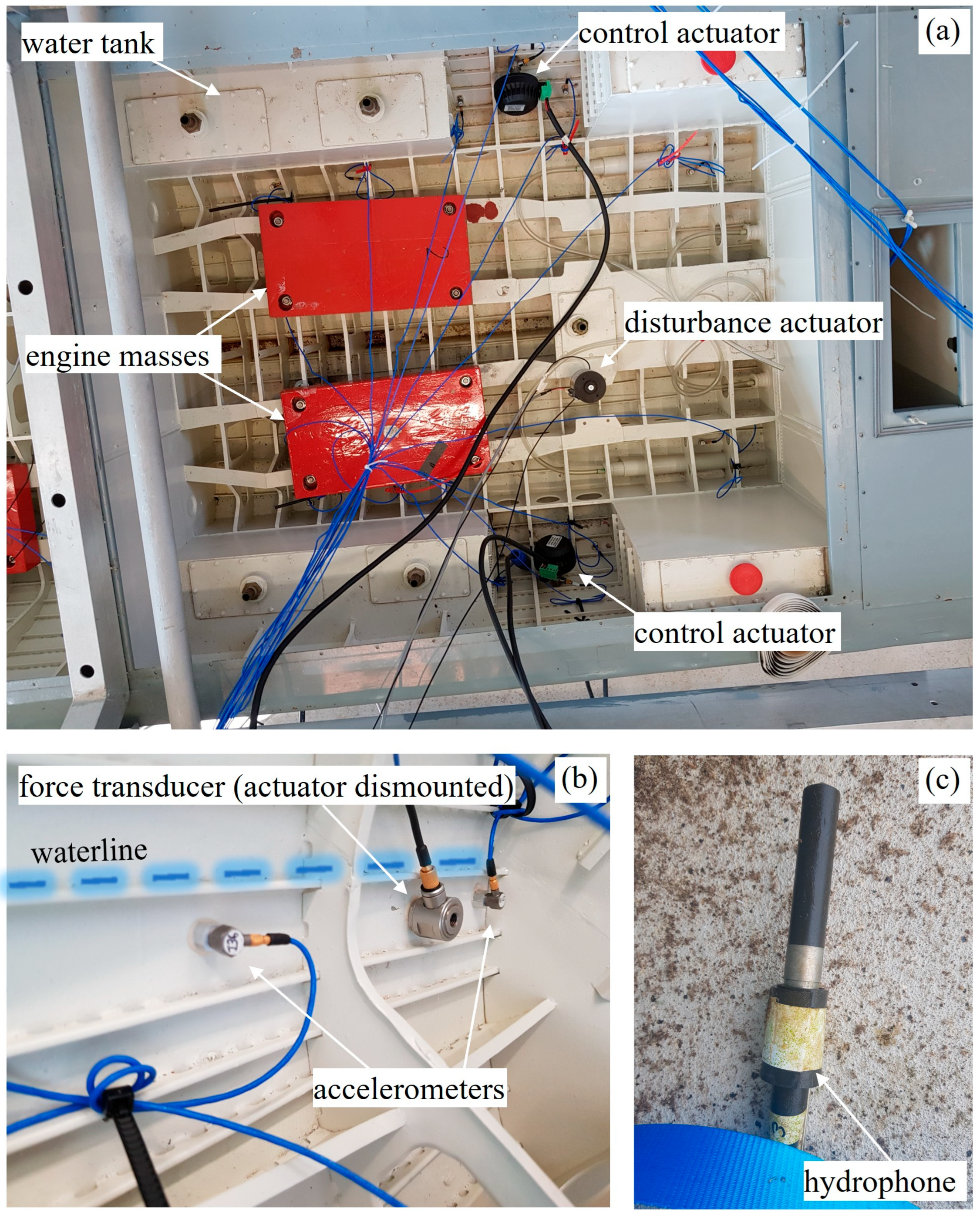
2. Experiment
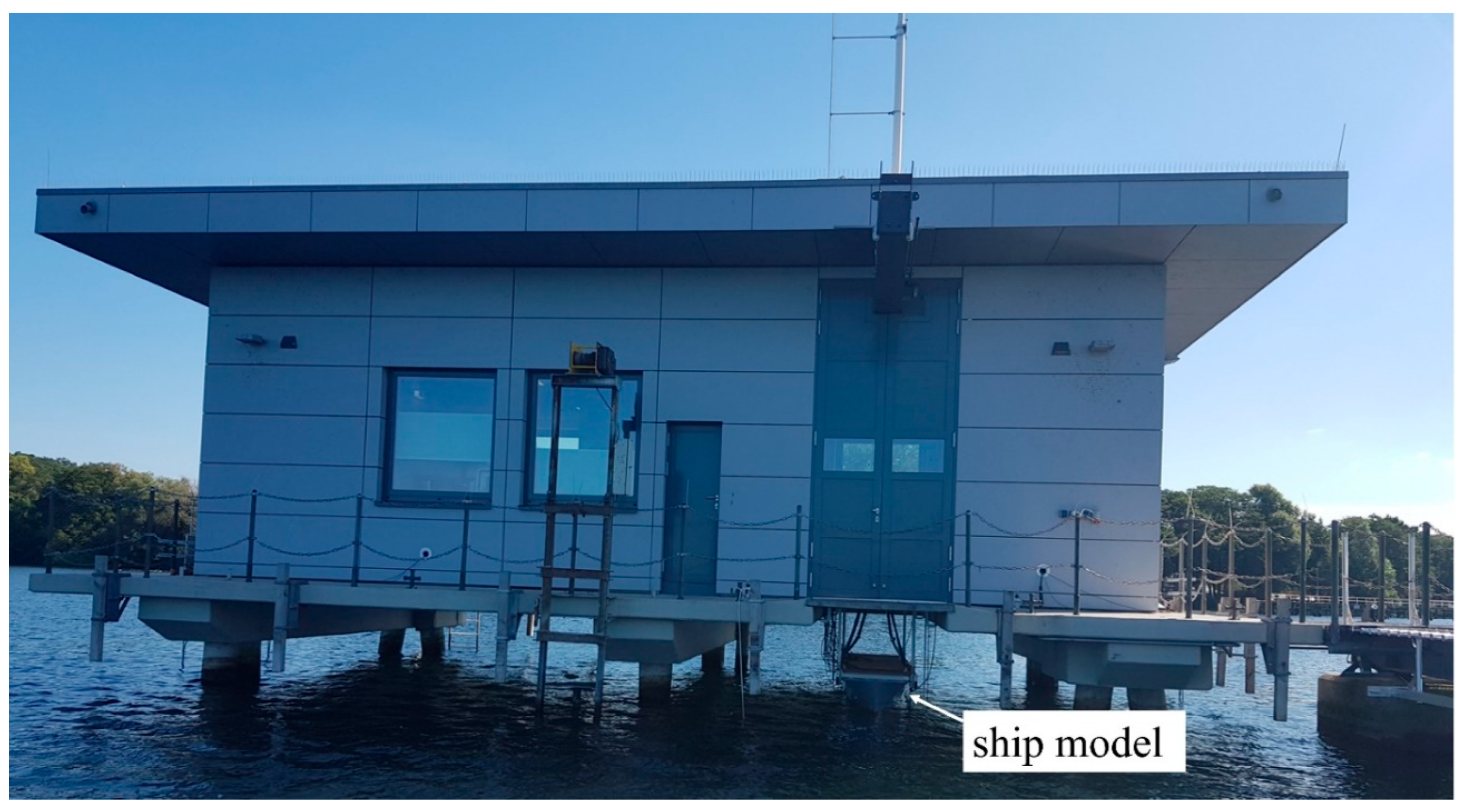
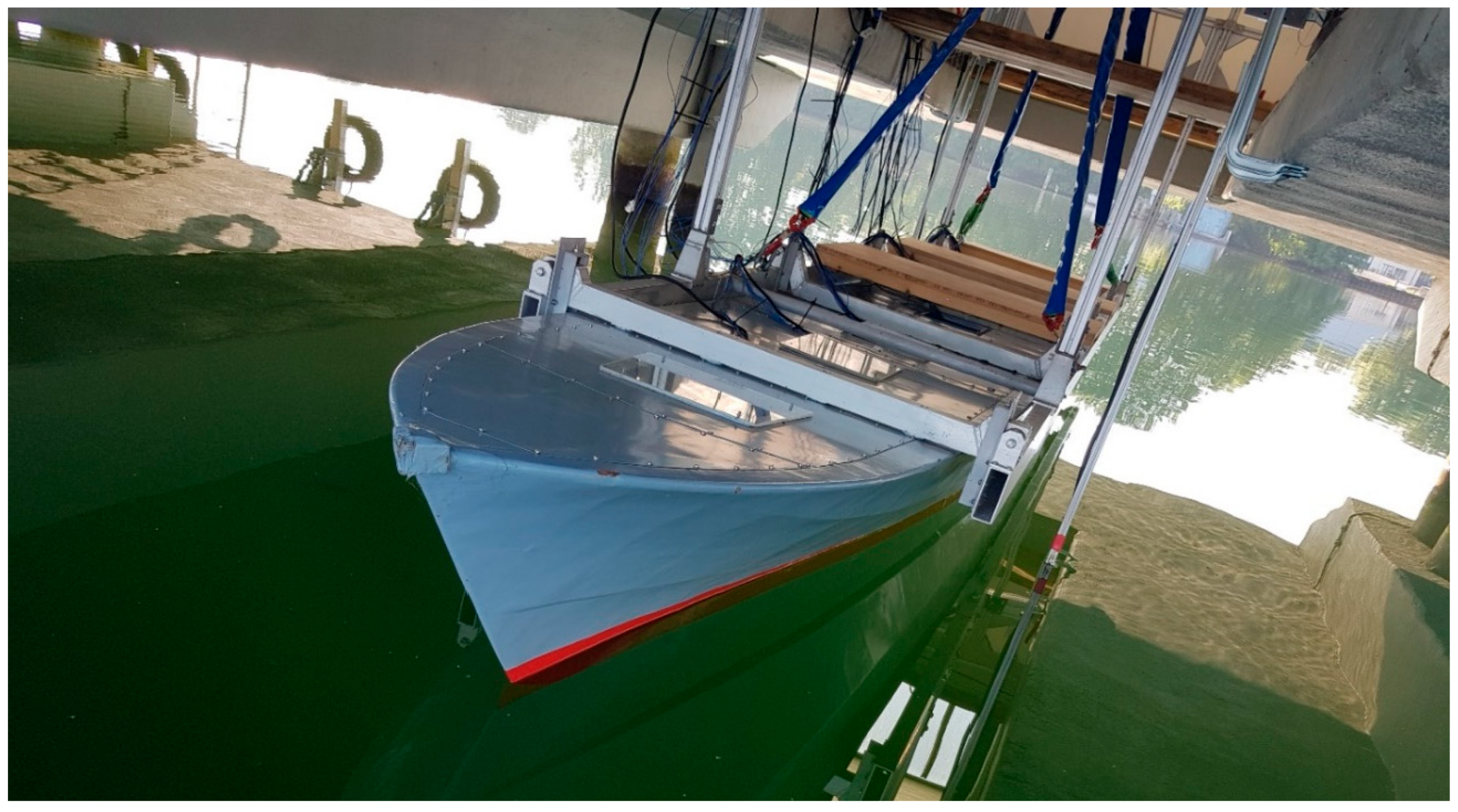
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Signal Processing
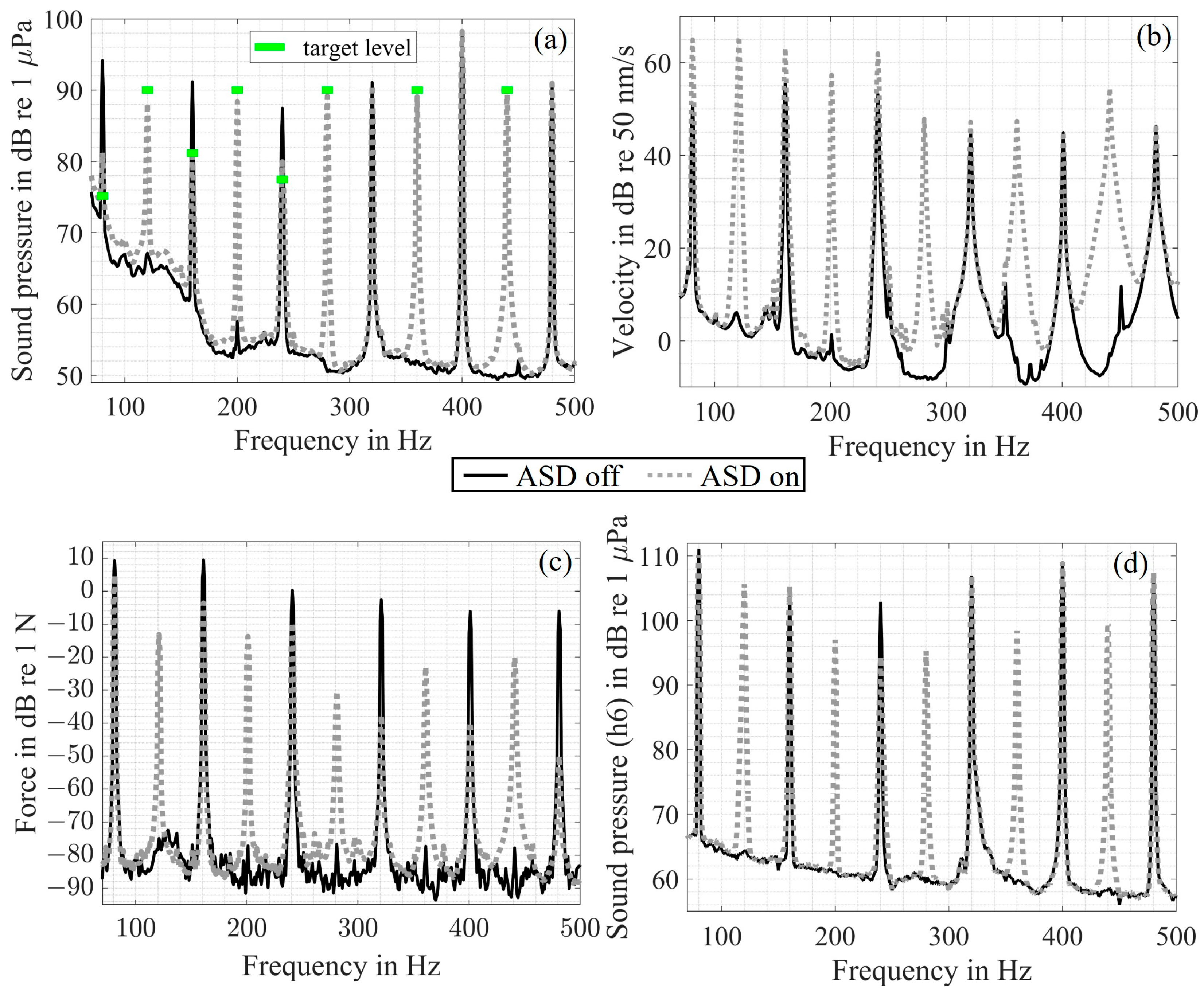
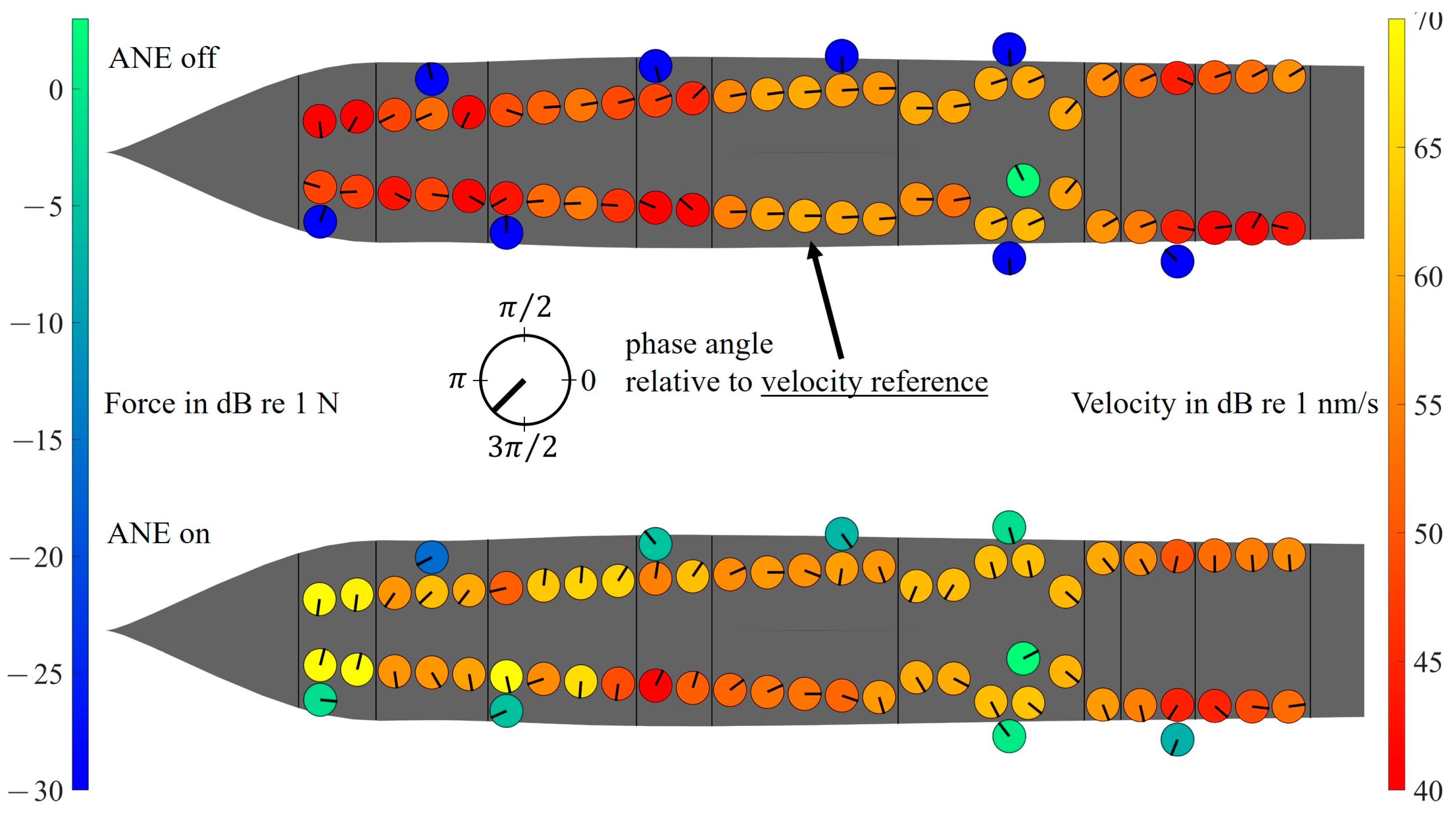
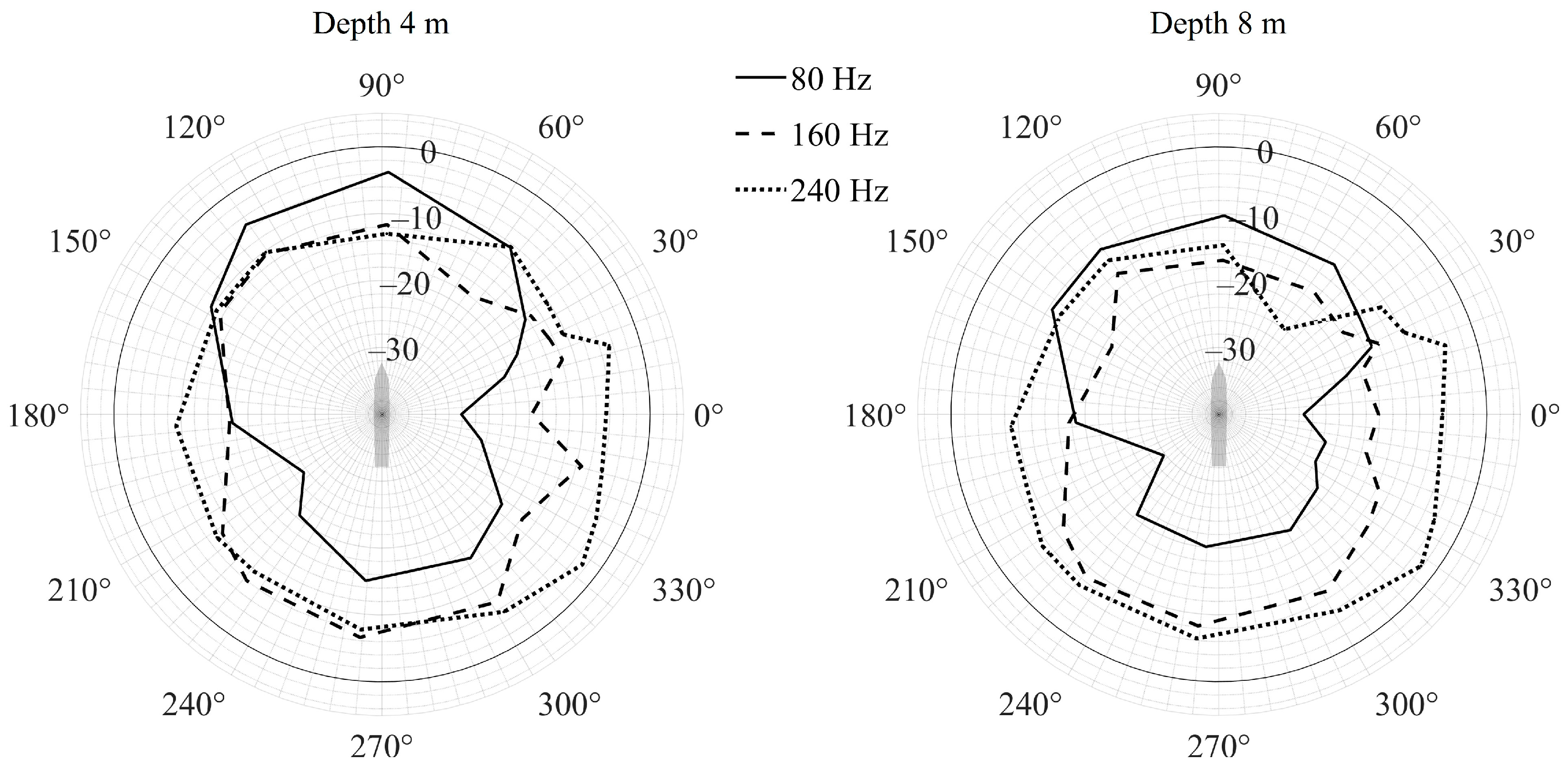
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AVC | Active vibration control |
| ASAC | Active Structural Acoustic Control |
| FxLMS | Filtered Reference Least Mean Square |
| ASD | Active Sound Design |
| ANE | Active Noise Equalizer |
| ASI | Active Sound Injection |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| CSVD | Compact Singular Value Decomposition |
| RMS | Root Mean Square |
| CMIF | Complex Mode Indicator Function |
Appendix A
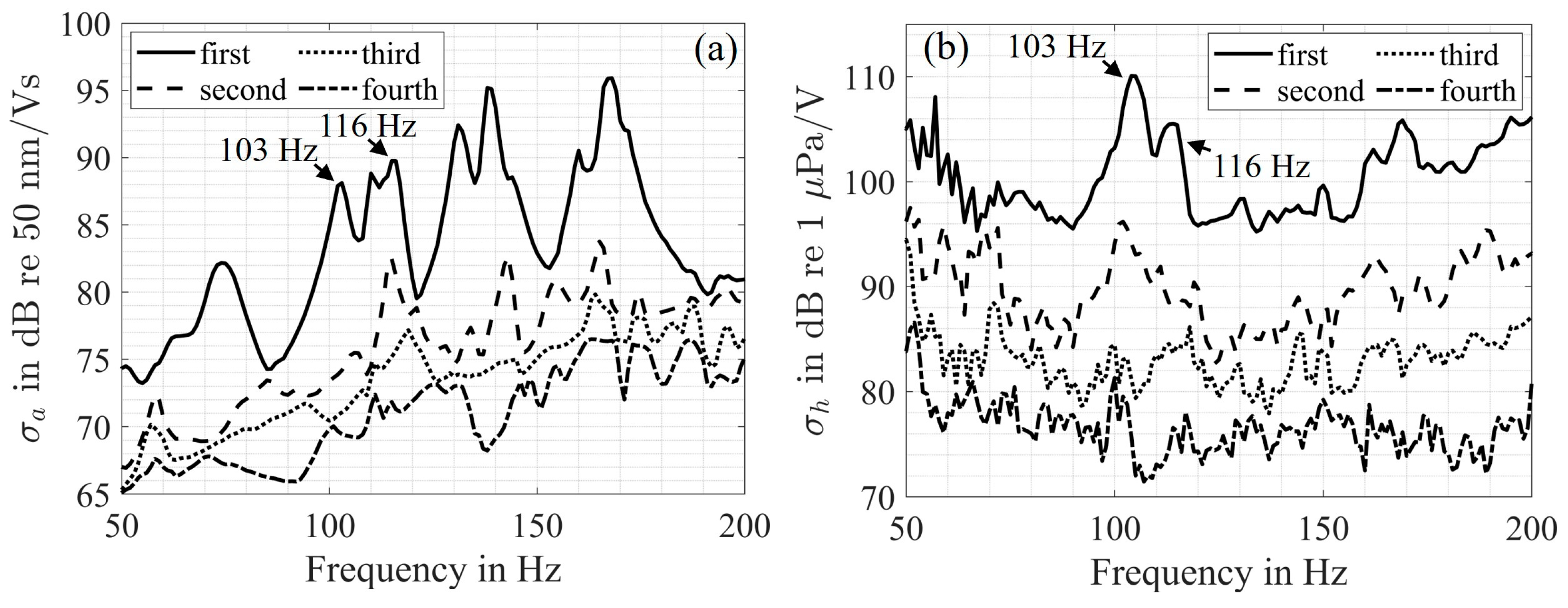

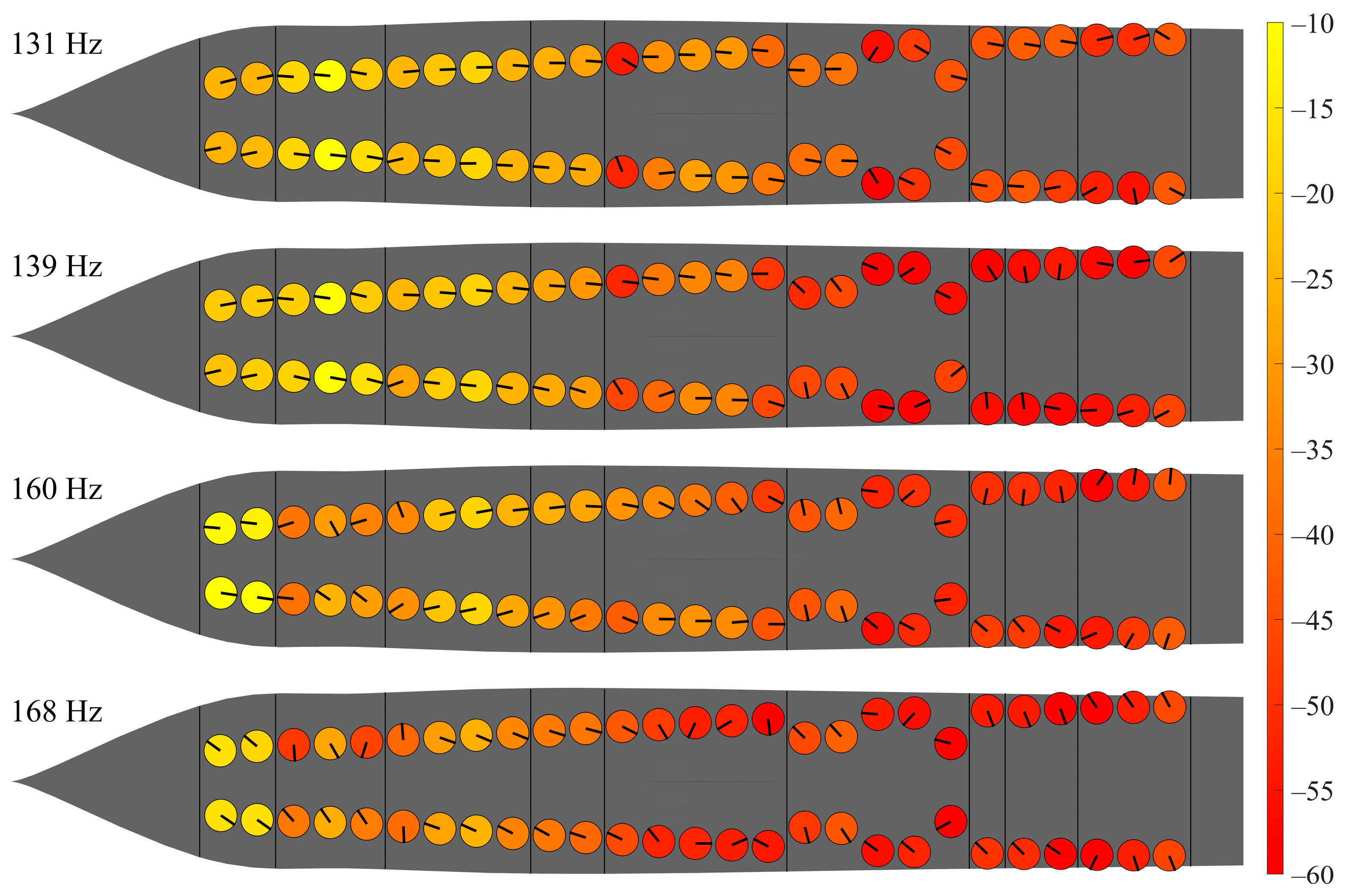
Appendix B
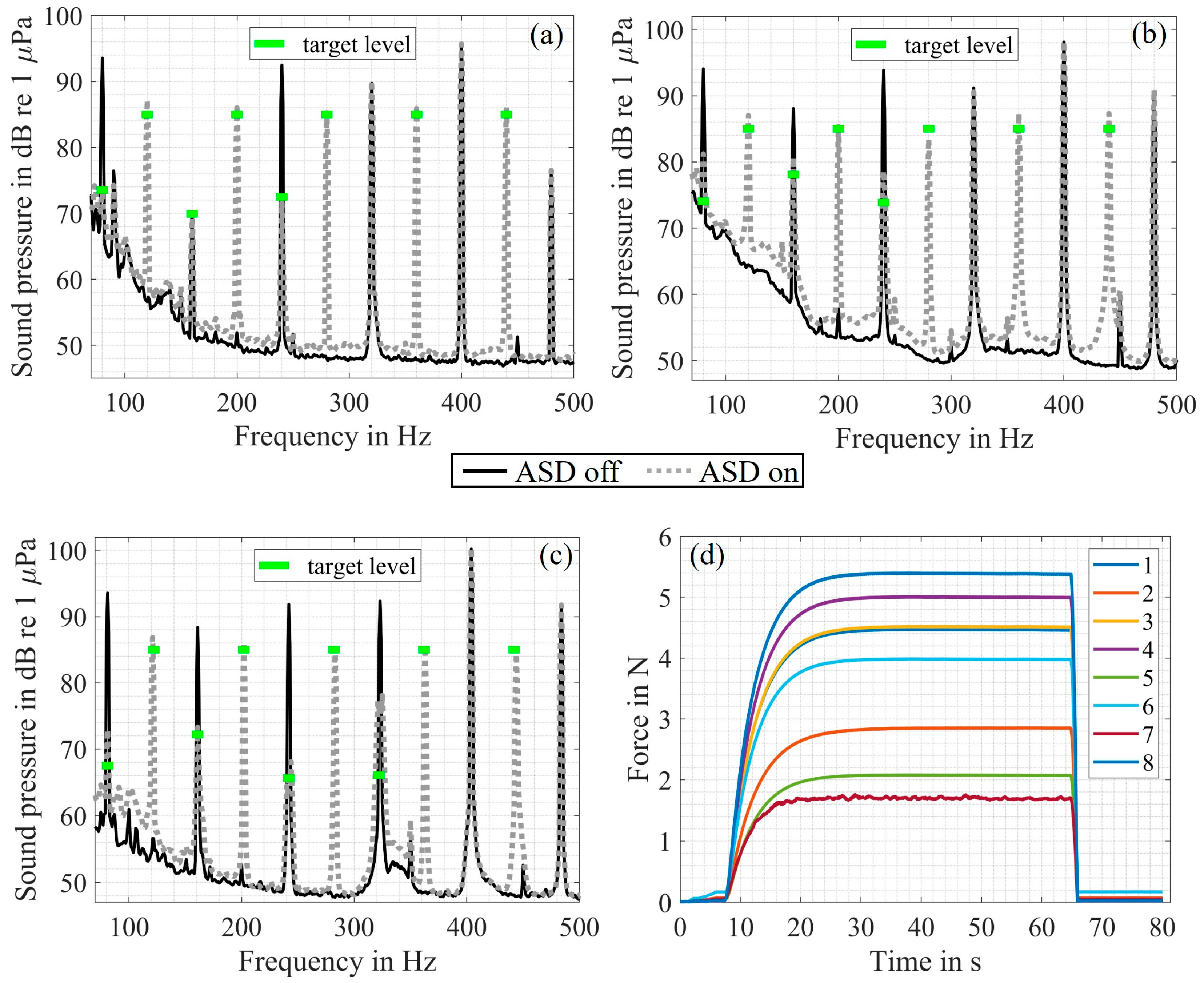
References
- Żak, A. Ships classification basing on acoustic signatures. WSEAS Trans. Signal Process. Arch. 2008, 4, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Grushetsky, I.V.; Kalyu, V.A.; Shlemov, Y.F.; Tarovik, V.I. Underwater noise radiation, mechanisms, and control. In Encyclopedia of Maritime and Offshore Engineering; Carlton, J., Jukes, P., Choo, Y.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–12. ISBN 9781118476352. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, J.; Zhu, S.; He, L.; Yu, X. Application of chaos method to line spectra reduction. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 286, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Möser, M. Taschenbuch der Technischen Akustik; Heckl, M., Müller, H.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Chapter 17; ISBN 9783642973574. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, H.F. Electronic control of noise, vibration, and reverberation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B. Anti-noise: The Essex breakthrough. Chart. Mech. Engr. 1983, 30, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, H.; Wendt, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Kessissoglou, N. Active structural cloaking using equivalent feedback cancellation. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 602, 118950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-S.; Lee, S.-M.; Chung, K.-Y. Ship vibration control using a force-adjustable mechanical actuator. J. Vib. Control 1999, 5, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winberg, M.; Johansson, S.; Håkansson, L.; Claesson, I.; Lagö, T. Active vibration isolation in ships: A pre-analysis of sound and vibration problems. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2005, 10, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauba, M.; Herold, S.; Koch, T.; Mayer, D.; Melz, T. Design and application of an active vibration control system for a marine engine mount. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Noise and Vibration Engineering, Leuven, Belgium, 15–17 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Brennan, M.J.; Liu, Z. Active vibration isolation of a Diesel generator in a small marine vessel: An experimental study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basten, T.; Berkhoff, A.P.; Vermeulen, R. Active vibration control for underwater signature reduction of a navy ship. In Proceedings of the 17th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Cairo, Egypt, 18–22 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Seiler, R.D. Structure-borne noise reduction of gearboxes in maritime application. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress on Acoustics, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Wei, D.; Tian, Y.; Yang, L. The research on the transverse vibration active control model of ship propulsion shaft with the active control force on the bearing support. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyalyshev, A.I.; Dubini, A.I.; Tartakovskii, B.D. Active acoustic reduction of a plate. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1986, 32, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, C.R.; Hansen, C.H.; Snyder, S.D. Experiments on active control of sound radiation from a panel using a piezoceramic actuator. J. Sound Vib. 1991, 150, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.R.; Elliott, S.J.; Nelson, P.A. Active Control of Vibration; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Snyder, S.D.; Hansen, C.H.; Fuller, C.R. Active control of far-field sound radiated by a rectangular panel: A general analysis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.D.; Tanaka, N. To absorb or not to absorb: Control source power output in active noise control systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 94, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheer, J.; Daley, S. Active structural acoustic control using the remote sensor method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 744, 012184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, U.O.; Brenna, D.P.; Koko, T.S.; Besli, O.; Masson, P.; Renault, S. Active Noise and Vibration Control Literature Survey: Controller Technologies. Canadian National Defence Contractor Report, DREA CR 1999-177. 1999. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA636599.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Morgan, D. An analysis of multiple correlation cancellation loops with a filter in the auxiliary path. In Proceedings of the ICASSP ‘80. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 16–18 April 1980; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Denver, CO, USA, 1980; pp. 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, J.C. Active adaptive sound control in a duct: A computer simulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 70, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmacher, R. Active design of automotive engine sound. Audio Engineering Society Convention 112. In Proceedings of the Audio Engineering Society Convention 112, München, Germany, 10–13 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, L.E.; Elliott, S.J. Adaptive algorithms for active sound-profiling. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera-Sánchez, J.A.; de Oliveira, L.P.R. A multi-harmonic amplitude and relative-phase controller for active sound quality control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2014, 45, 542–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Tsai, J. Residual noise shaping technique for active noise control systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 1665–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.J.; Kuo, S.M. An active harmonic noise equalizer. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 27–30 April 1993; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.C.; Jo, E.S.; Hong, S.; Csakan, M. Development of personalized engine sound system using active sound design technology. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars Mech. Syst. 2015, 8, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Multiple-harmonic amplitude and phase control method for active noise and vibration reshaping. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 3173–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungnad, S.; Sachau, D.; Zerbs, C.; Müller, A.; Homm, A. Active control of target sound fields using structural-acoustic brightness applied to a ship model’s acoustic signature. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2024, 155, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, C.; Cheer, J.; Daley, S. An experimental investigation into active structural acoustic cloaking of a flexible cylinder. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 170, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittek, G. Measuring facilities and model testing techniques in ship’s acoustic research. In Proceedings of the winter annual meeting of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Hydroacoustic Facilities, Instrumentation, and Experimental Techniques, Atlanta, Georgia, 1–6 December 1991; pp. 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ungnad, S.; Wandel, M. Evaluation of robust position optimization of loudspeakers and microphones for an adaptive active noise control system. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2016: 45th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering: Towards a Quiter Future, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016; Kropp, W., Ed.; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Akustik e.V: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 3903–3909. [Google Scholar]
- Ungnad, S.; Müller, A.; Zerbs, C.; Sachau, D.; Homm, A. Simulation of the active manipulation of acoustic signatures based on measured data. In Proceedings of the DAGA 2022, Online, 21–24 March 2022; pp. 723–726. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Randall, R.B. Frequency Analysis; Brüel & Kjaer: Naerum, Denmark, 1987; Chapter 7. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, S.J.; Boucher, C.C.; Nelson, P.A. The behavior of a multiple channel active control system. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Tahernezhadi, M.; Ji, L. Frequency-domain periodic active noise control and equalization. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1997, 5, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Rank-Deficient and Discrete Ill-Posed Problems; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, S.J. Signal Processing for Active Control; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; Chapter 4.4. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.A. Active control of acoustic fields and the Reproduction of Sound. J. Sound Vib. 1994, 177, 447–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-H. Generation of an acoustically bright zone with an illuminated region using multiple sources. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewins, D.J. Modal testing: Theory, Practice and Application, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Maidanik, G. Response of ribbed panels to reverberant acoustic fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 809–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bies, D.A. Uses of anechoic and reverberant rooms for the investigation of noise sources. Noise Control Eng. 1976, 7, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachau, D.; Jukkert, S.; Hövelmann, N. Development and experimental verification of a robust active noise control system for a diesel engine in submarines. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 375, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Simanowski, K.; Delf, S.; Homm, A. Experimental investigation of acoustic emissions from a ship hull. In Proceedings of the DAGA 2025, Copenhagen, Denmark, 17 March 2025; pp. 916–919. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ungnad, S.; Sachau, D.; Zerbs, C.; Müller, A.; Homm, A. Experimental Investigation into the Active Narrowband Reshaping of a Ship Model’s Acoustic Signature. Acoustics 2025, 7, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020034
Ungnad S, Sachau D, Zerbs C, Müller A, Homm A. Experimental Investigation into the Active Narrowband Reshaping of a Ship Model’s Acoustic Signature. Acoustics. 2025; 7(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleUngnad, Steffen, Delf Sachau, Carsten Zerbs, Andreas Müller, and Anton Homm. 2025. "Experimental Investigation into the Active Narrowband Reshaping of a Ship Model’s Acoustic Signature" Acoustics 7, no. 2: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020034
APA StyleUngnad, S., Sachau, D., Zerbs, C., Müller, A., & Homm, A. (2025). Experimental Investigation into the Active Narrowband Reshaping of a Ship Model’s Acoustic Signature. Acoustics, 7(2), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020034






