Experimental and Theoretical Acoustic Performance of Esparto Grass Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
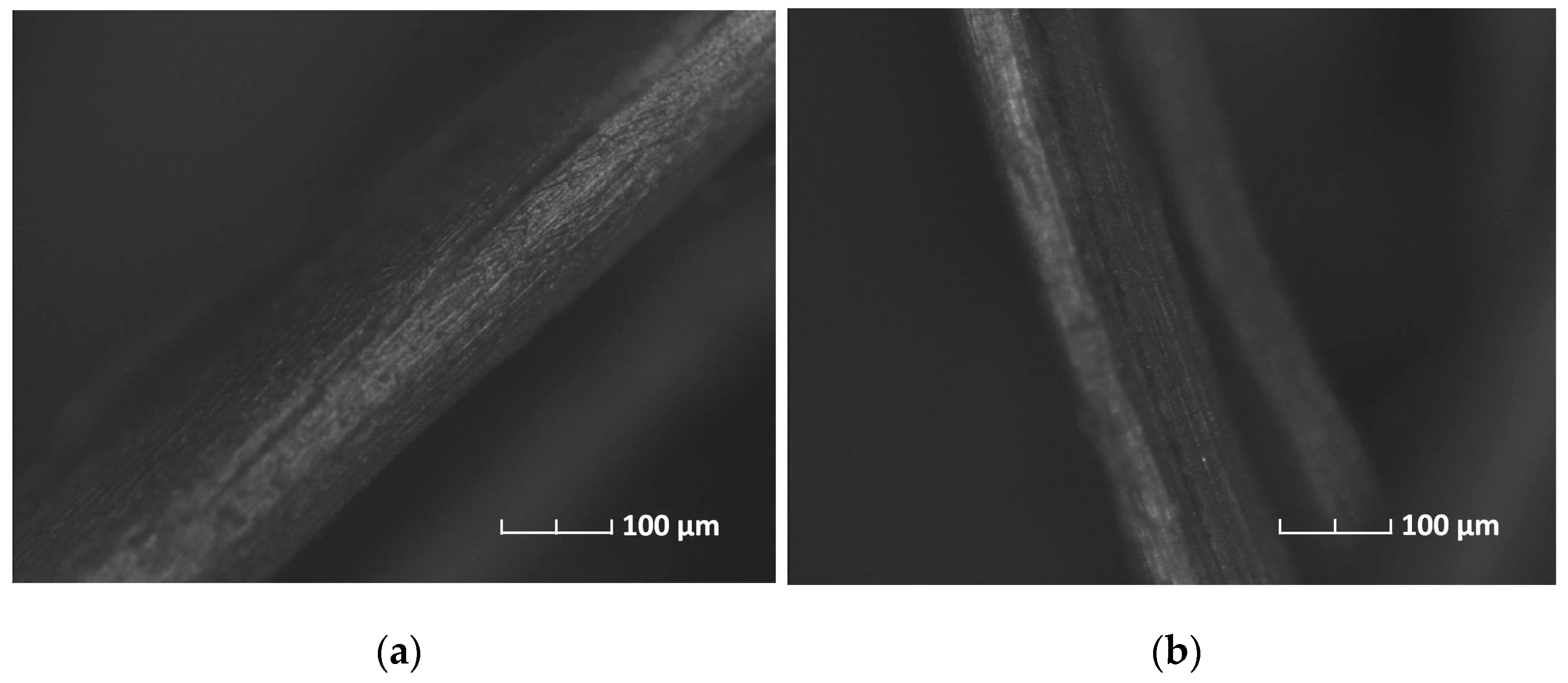
2.1. Fiber Size
2.2. Porosity
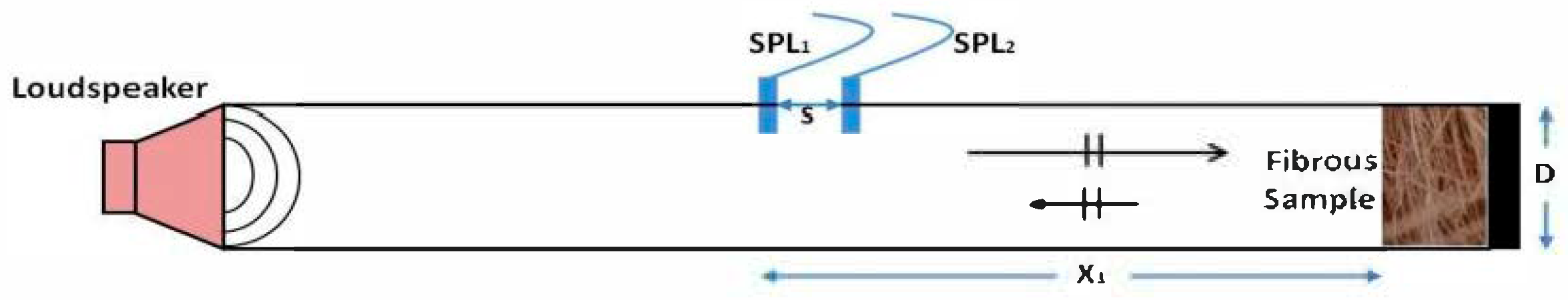
2.3. Flow Resistivity
2.4. Tortuosity
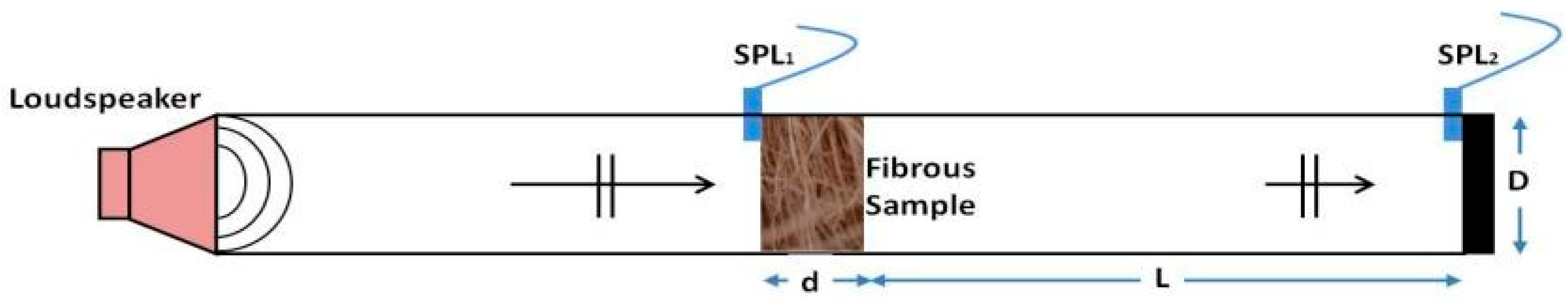
2.5. Sound Absorption Coefficient
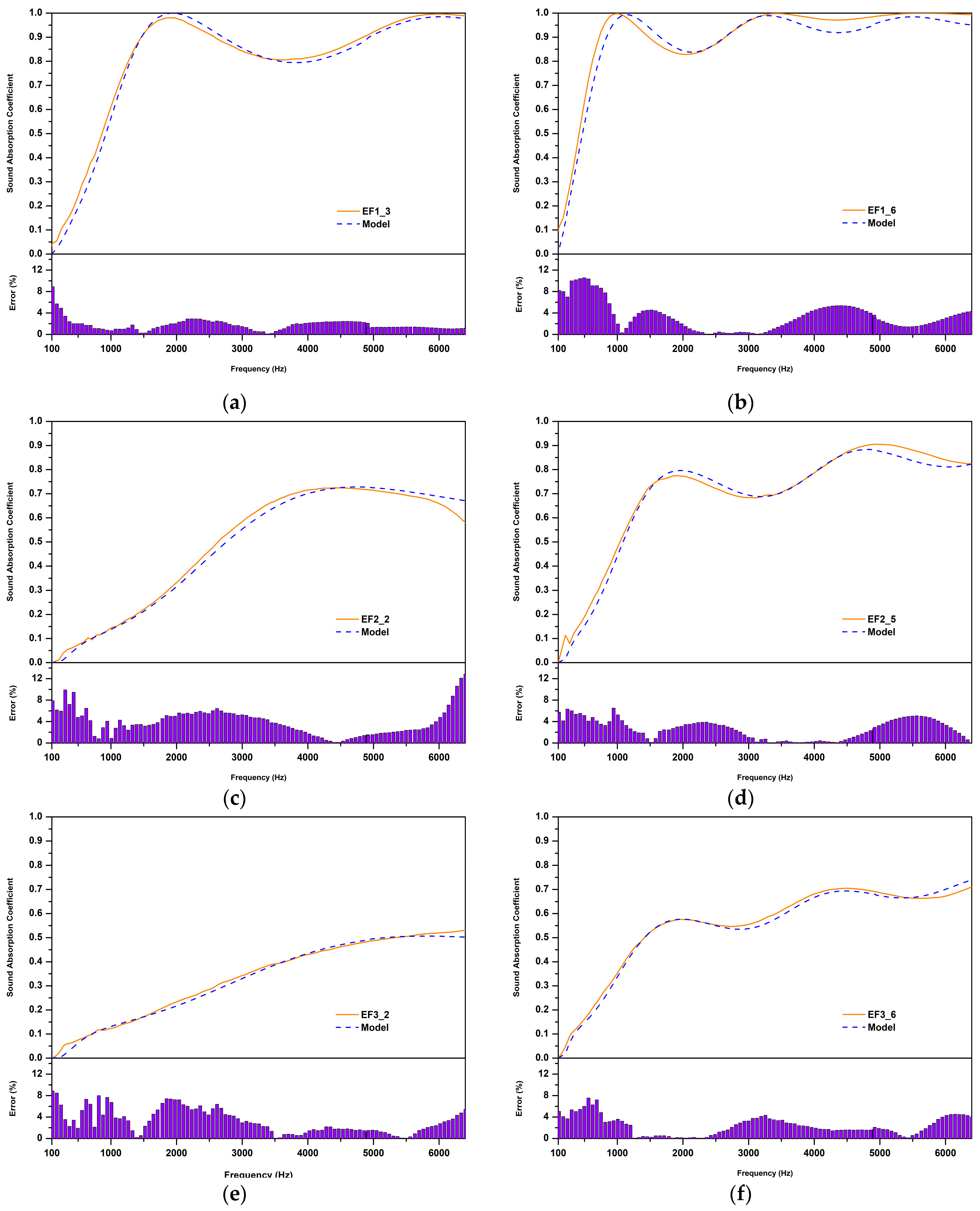
2.6. Phenomenological Model
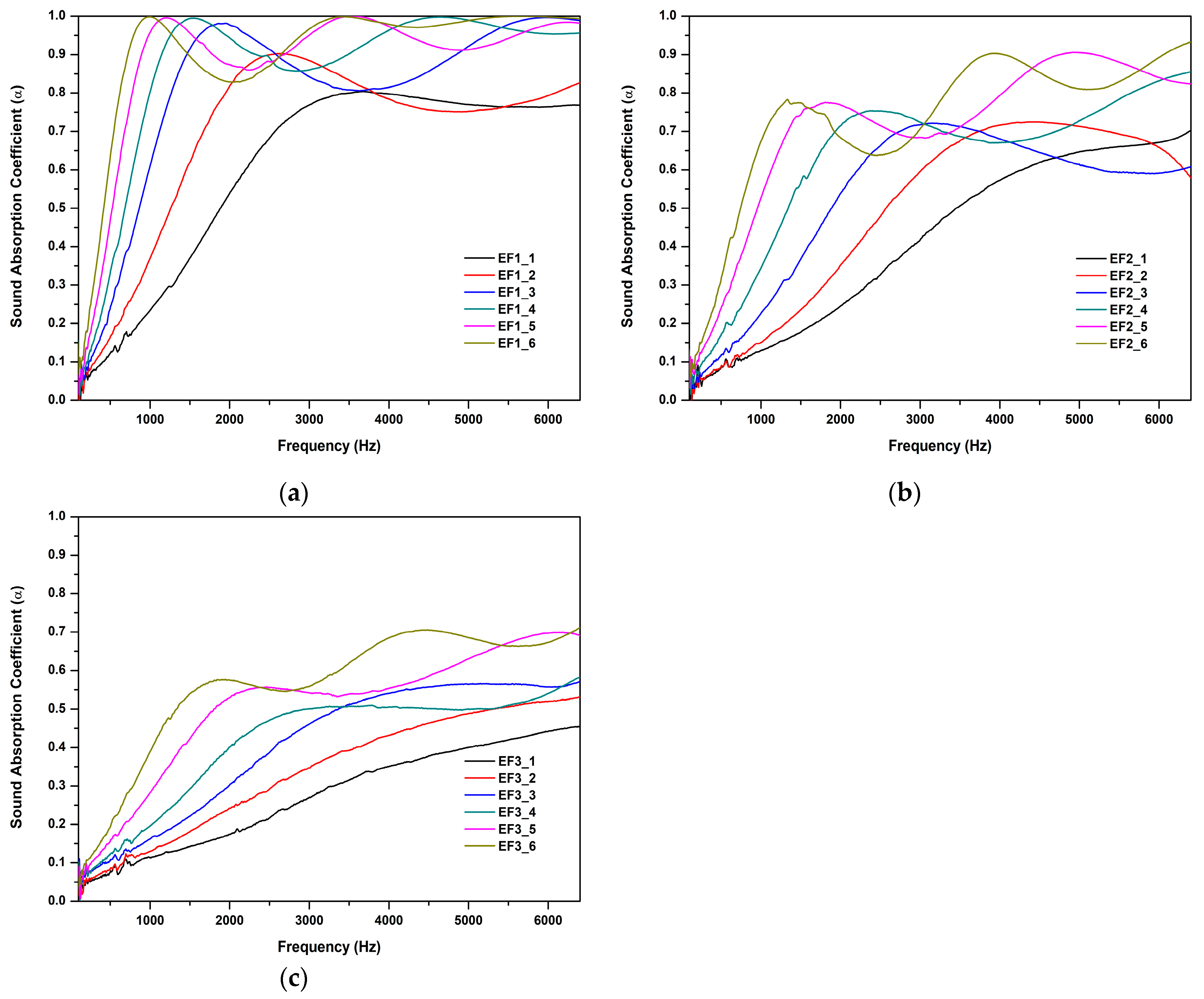
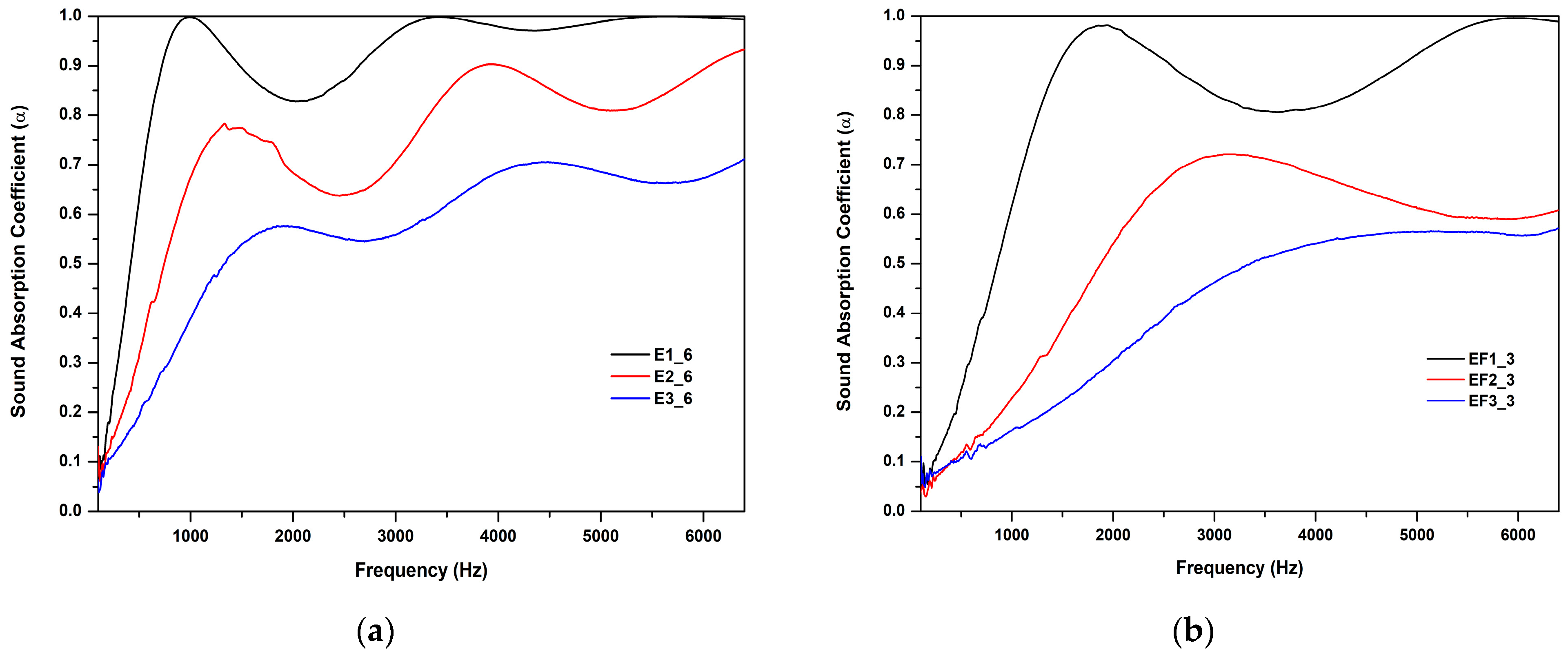
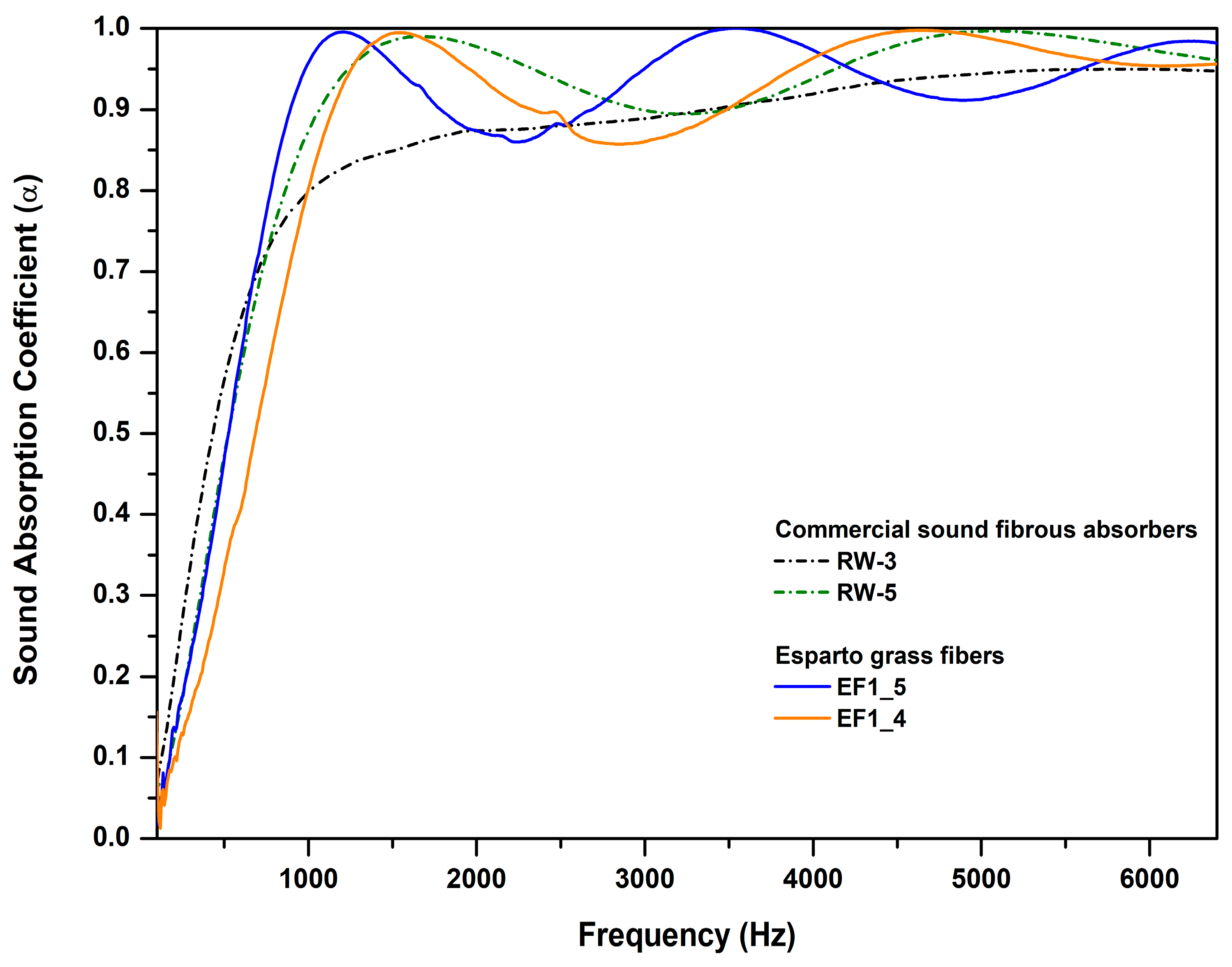
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization, Environmental Noise. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/who-compendium-on-health-and-environment/who_compendium_noise_01042022.pdf?sfvrsn=bc371498_3 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- European Environment Agency. The Health Effects of Transport Noise and Implications for Future Health Risk Assessments (Signal). Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/european-zero-pollution-dashboards/indicators/the-health-effects-of-transport-noise-and-implications-for-future-health-risk-assessments-signal (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Arruda, E.H.; Melatto, R.A.P.B.; Levy, W.; de Melo Conti, D. Circular economy: A brief literature review (2015–2020). SUSOC 2021, 2, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Uddala, S.; Saboor, S.; Arici, M.; Saxena, K.K. Contemporary roof pattern for energy efficient buildings: Air conditioning cost alleviation, CO2 emission mitigation potential and acceptable payback period. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawanwadeekul, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. Sustainable construction materials from leveraging water hyacinth and wastepaper for superior sound absorption and thermal insulation. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdanpilleta, M.; Leceta, I.; Martín-Garín, A.; Millán-García, J.A.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Valorized sheep wool biocomposites towards a more sustainable building sector: Thermal insulation, sound absorption, and resistance against insects. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 21, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.A.; Antonio, J. Animal-based waste for building acoustic applications: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagnoli, S.; Fabiani, C.; Frota de Albuquerque Landi, F.; Pisello, A.L. Advancing sustainable construction through comprehensive analysis of thermal, acoustic, and environmental properties in prefabricated panels with recycled PET materials. Energy Build. 2024, 312, 114218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.; Achenza, M.; Mastino, C.C.; Baccoli, R.; Frattolillo, A. Thermo-acoustic building insulation materials fabricated with recycled fibers—Jute, Wool and Loofah. Energy Build. 2023, 293, 113211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; García-Cobos, F.J.; Sánchez-Delgado, F.J.; Mota-López, M.I.; Meneses-Rodríguez, J.M.; Romero-Casado, A.; Acedo-Fuentes, P.; López-Ramos, L. Mechanical, thermal and acoustical evaluation of biocomposites made of agricultural waste for ceiling tiles. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 191, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad, S.; Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Samaei, S.E.; Khavanin, A. Sugarcane bagasse waste fibers as novel thermal insulation and sound-absorbing materials for application in sustainable buildings. Build. Environ. 2022, 211, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, M.; Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Berardi, U.; Khavanin, A.; Zaroushani, V. Waste corn husk fibers for sound absorption and thermal insulation applications: A step towards sustainable buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei, S.E.; Berardi, U.; Soltani, P.; Taban, E. Experimental and modeling investigation of the acoustic behavior of sustainable kenaf/yucca composites. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 183, 108332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawas, M.; Kerdkaew, T.; Chanlert, P. From invasive species to bio-based composites: Utilizing water hyacinth for sound absorption and insulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, E.; Amininasab, S.; Soltani, P.; Berardi, U.; Abdi, D.D.; Samaei, S.E. Use of date palm waste fibers as sound absorption material. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 41, 102752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghchiche, A. Pulping and papermaking of esparto grass. In Book Pulping and Papermaking of Nonwood Plant Fibers; Ainun, Z.M.A., Sapuan, S.M., Ilyas, R.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sair, S.; Mansouri, S.; Tanane, O.; Abboud, Y.; El Bouari, A. Alfa fiber-polyurethane composite as a thermal and acoustic insulation material for building applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousshine, S.; Ouakarrouch, M.; Bybi, A.; Laaroussi, N.; Garoum, M.; Tilioua, A. Acoustical and thermal characterization of sustainable materials derived from vegetable, agricultural, and animal fibers. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 187, 108520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakarrouch, M.; Bousshine, S.; Bybi, A.; Laaroussi, N.; Garoum, M. Acoustic and thermal performances assessment of sustainable insulation panels made from cardboard waste and natural fibers. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 199, 109007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, J.P.; del Rey, R.; Alba, J.; Oltra, R. Sound-Absorption Properties of Materials Made of Esparto Grass Fibers. Sustainability. 2020, 12, 5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingard, K.U.; Dear, T.A. Measurement of acoustic flow resistance. J. Sound Vib. 1985, 103, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, M.; Korkmaz, Y. Sound absorption properties of bilayered nonwoven composites. Fiber Polym. 2015, 16, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; Acedo-Fuentes, P.; García-Cobos, F.J.; Sánchez-Delgado, F.J.; Mota-López, M.I.; Meneses-Rodríguez, J.M. The recycling of surgical face masks as sound porous absorbers: Preliminary evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Plona, T.J.; Scala, C.; Pasierb, F.; Kojima, H. Tortuosity and acoustic slow waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attenborough, K. Models for the acoustical characteristics of air filled granular materials. Acta Acust. 1993, 64, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10534-2: 2023; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes. Part 2: Two-Microphone Technique for Normal Sound Absorption Coefficient and Normal Surface Impedance. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R. Characterizing and modelling the sound absorption of the cellulose acetate fibers coming from cigarette butts. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cobos, F.J.; Maderuelo-Sanz, R. Prediction of sound absorption performance of fibers coming from cigarette butts using a phenomenological model. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 7056S–7071S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwikker, C.; Kosten, C.W. Sound Absorbing Materials; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of Propagation of Elastic Waves in a Fluid-Saturated Porous Solid. I. Low- Frequency Range. J Acoust. Soc. America 1956, 28, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Mechanics of deformation and acoustic propagation in porous media. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 1482–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfretzschner, J.; Rodríguez, R.M. Acoustic properties of rubber crumbs. Polym. Test. 1999, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Koplik, J.; Dashen, R. Theory of dynamic permeability and tortuosity in fluid saturated porous media. J. Fluid. Mech. 1987, 176, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Cano, A.; Haurie, L.; Velasco, J.I. Esparto wool as reinforcement in hybrid polyurethane composite foams. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 34, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhir, S.; Koubaa, A.; Khadhri, A.; Ksontini, M.; Smiti, S. Variations in the morphological characteristics of Stipa tenacissima fiber: The case of Tunisia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 37, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, P.; Taban, E.; Faridan, M.; Samaei, S.E.; Amininasab, S. Experimental and computational investigation of sound absorption performance of sustainable porous material: Yucca Gloriosa fiber. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 157, 106999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.; Fatima, S.; Tandon, N. A study of areca nut leaf sheath fibers as a green sound-absorbing material. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 169, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
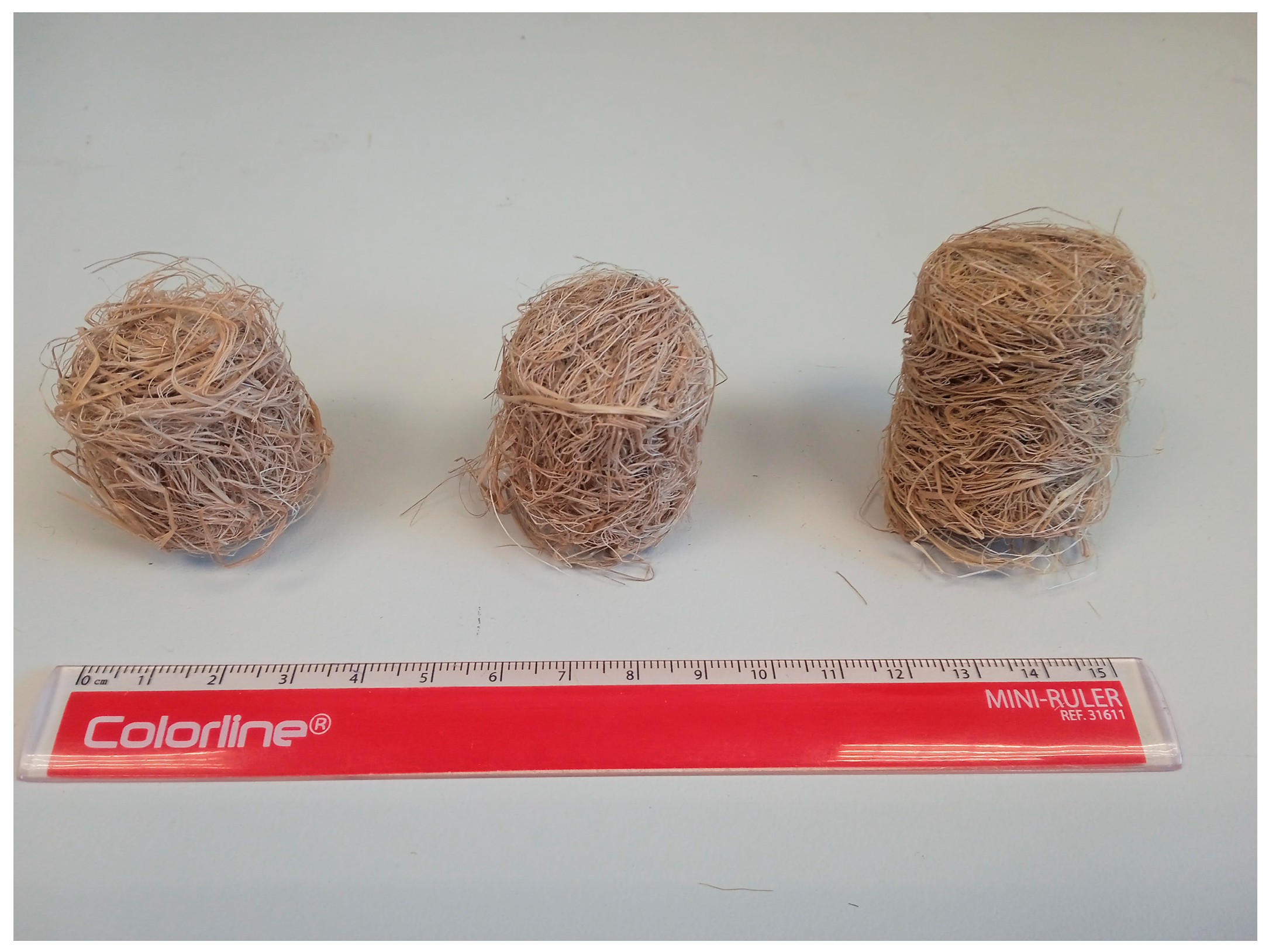

| Sample ID | ρm (kg/m3) | ϕ (%) | α∞ | σ (Pa s/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF1 | 199.8 ± 8.1 | 84.6 ± 1.2 | 1.091 ± 0.009 | 13,199 ± 227 |
| EF2 | 104.0 ± 6.2 | 91.9 ± 1.4 | 1.044 ± 0.010 | 3692 ± 163 |
| EF3 | 56.8 ± 3.5 | 95.6 ± 1.1 | 1.023 ± 0.005 | 917 ± 82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; Meneses-Rodríguez, J.M. Experimental and Theoretical Acoustic Performance of Esparto Grass Fibers. Acoustics 2025, 7, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020032
Maderuelo-Sanz R, Meneses-Rodríguez JM. Experimental and Theoretical Acoustic Performance of Esparto Grass Fibers. Acoustics. 2025; 7(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaderuelo-Sanz, Rubén, and Juan Miguel Meneses-Rodríguez. 2025. "Experimental and Theoretical Acoustic Performance of Esparto Grass Fibers" Acoustics 7, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020032
APA StyleMaderuelo-Sanz, R., & Meneses-Rodríguez, J. M. (2025). Experimental and Theoretical Acoustic Performance of Esparto Grass Fibers. Acoustics, 7(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7020032







