Evaluation of Acoustic Features after Refurbishment Works Inside Two Historical Opera Theatres Located in Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Documentary Background
2.1. The History of the Teatro Nuovo of Spoleto
2.2. The History of the Teatro Alighieri of Ravenna
3. Architectural Organization
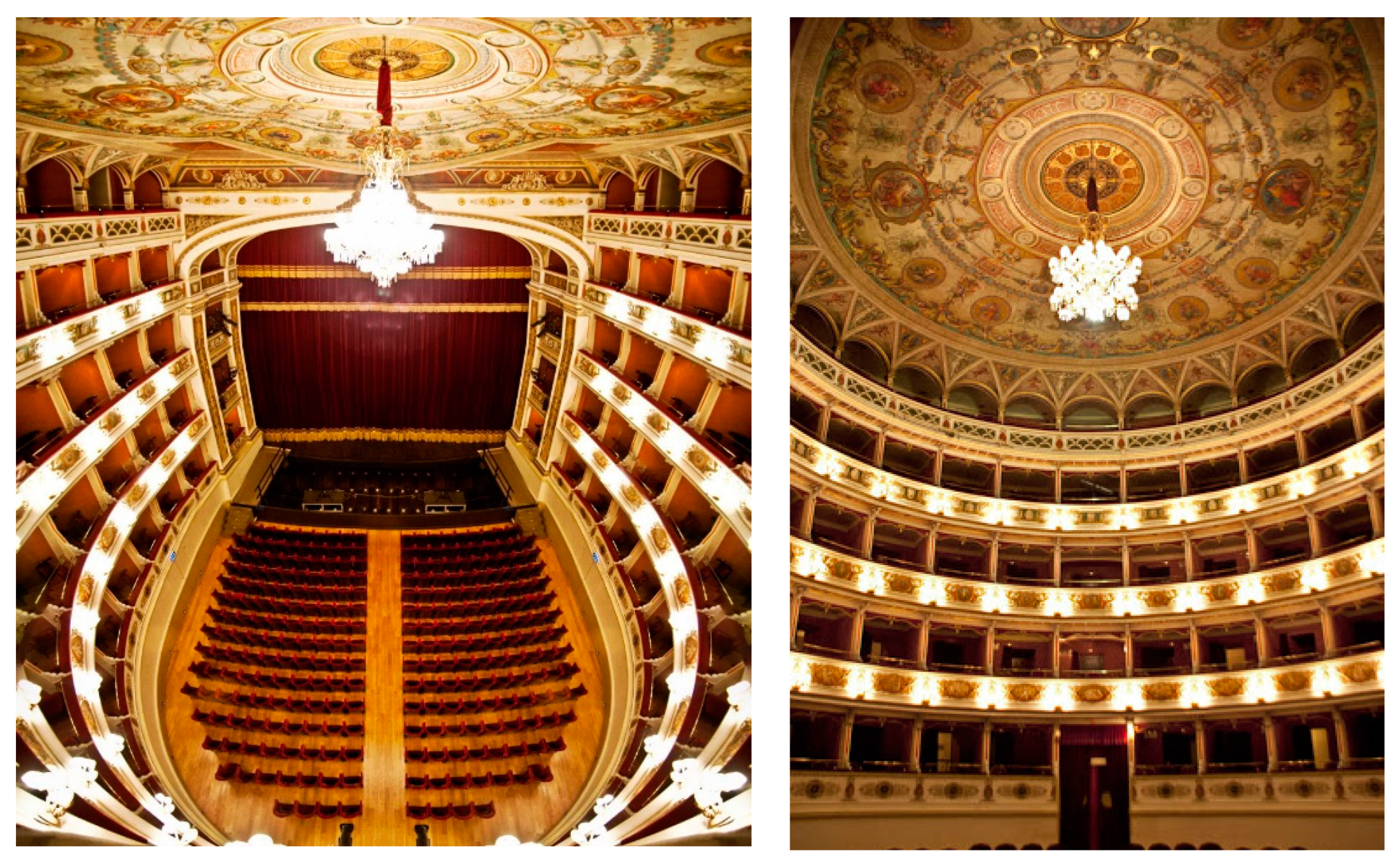
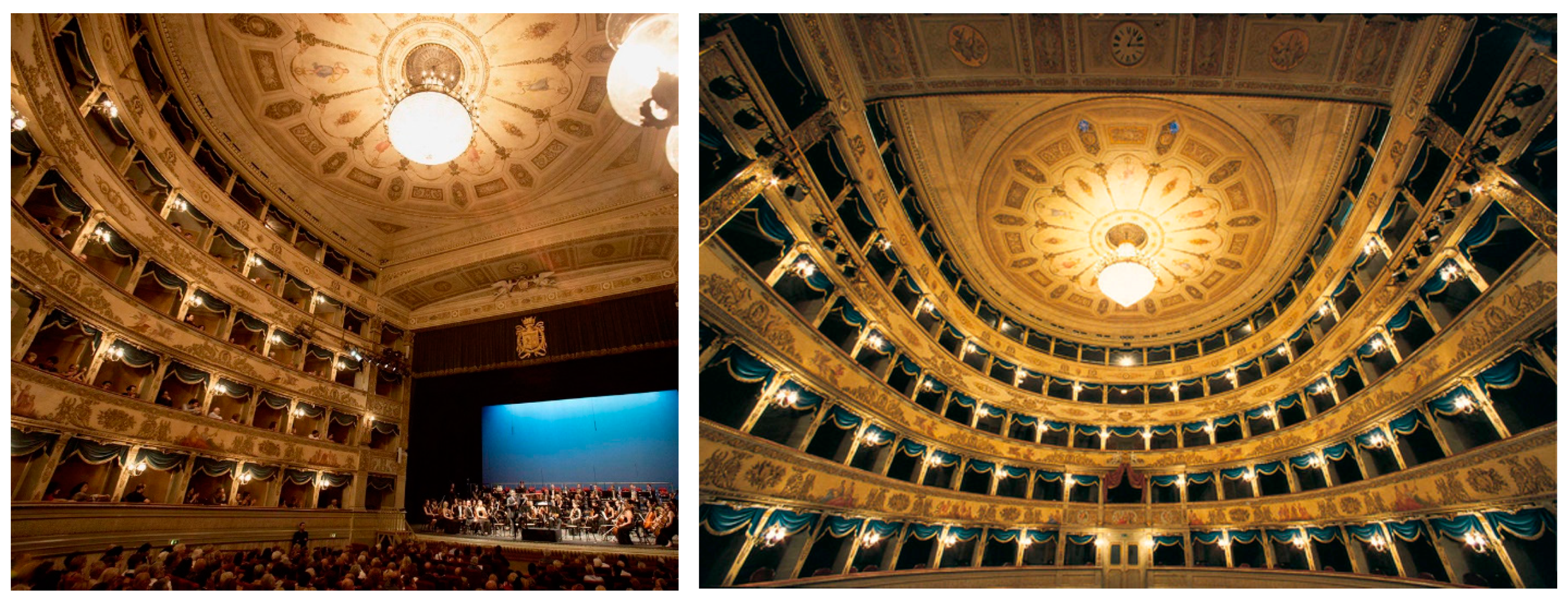
3.1. Geometry and Architectural Features Inside the Teatro Nuovo of Spoleto
3.2. Geometry and Architectural Features Inside the Teatro Alighieri of Ravenna
3.3. Functional Differences and Analogies
3.3.1. Alterations Applied in Teatro Nuovo
3.3.2. Potential Changes Tested in Teatro Alighieri
- ▪
- Omnidirectional sound source (B&K4224);
- ▪
- Binaural dummy head (Sennheiser MKE2002 set);
- ▪
- Radiomicrophones (Nady 201 VHF—LT Lavalier Bodypack Transmitter, Wireless System Receiver);
- ▪
- MLSSA audio board (A2D160) and related software (MLSSA 10.0C) for the post-processing;
- ▪
- Personal Computer (Toshiba 3200).
4. Measurements
4.1. Equipment and Instrumentation
- ▪
- Pre-equalised omnidirectional loudspeaker (Look Line);
- ▪
- Binaural dummy head (Neumann KU-100);
- ▪
- B-Format microphone (Soundfield MK-V);
- ▪
- Personal Computer connected to the loudspeaker and the microphones.
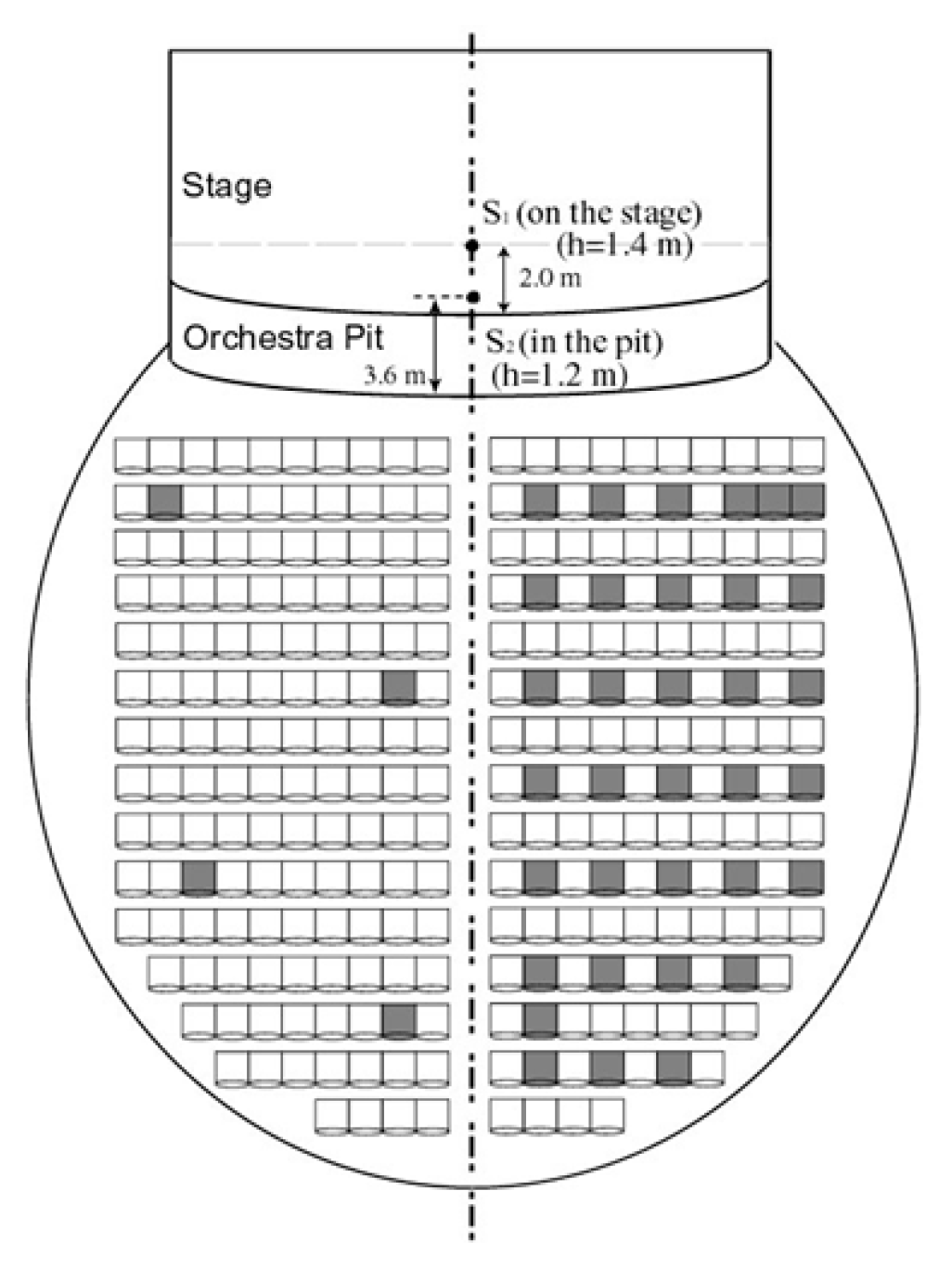
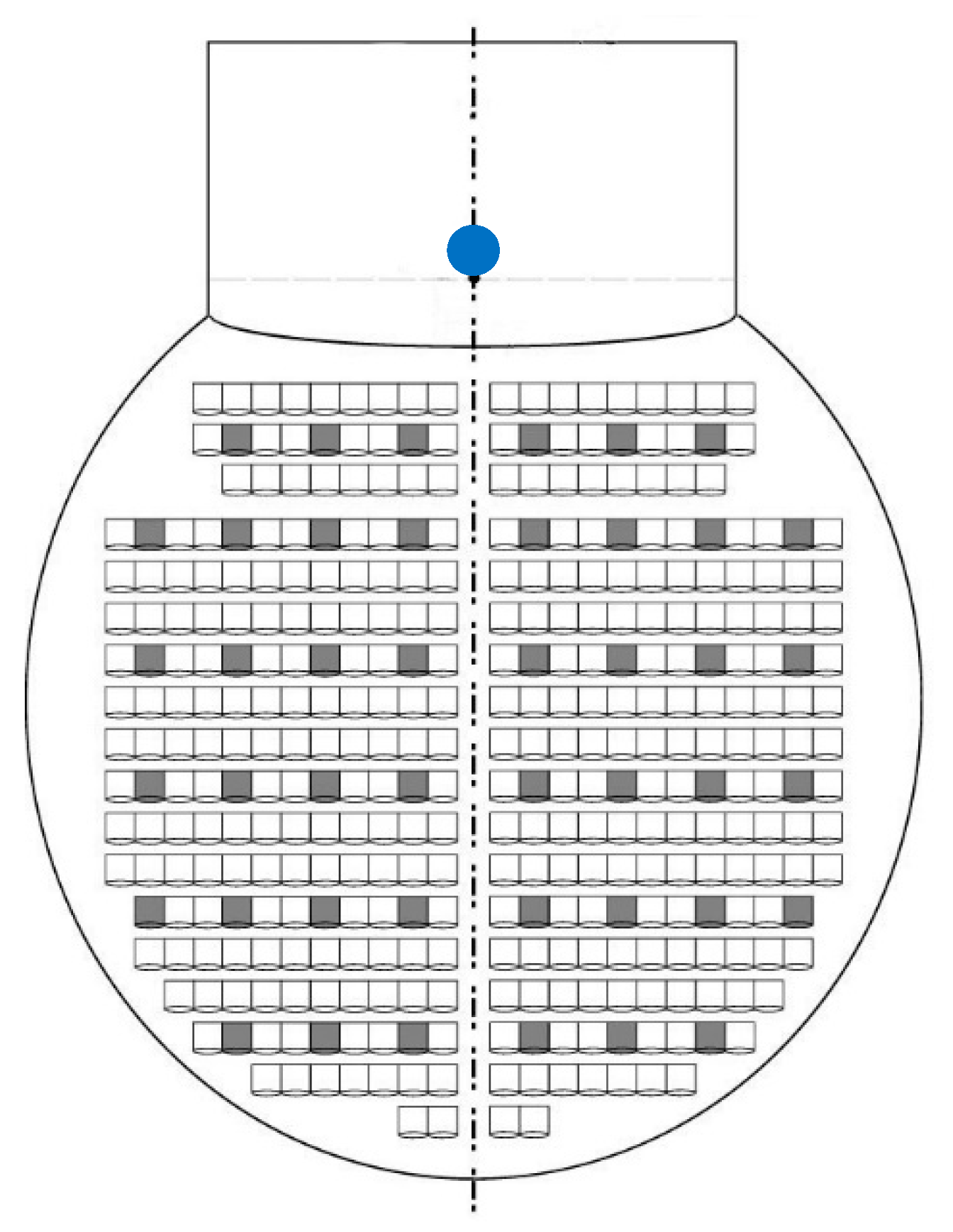
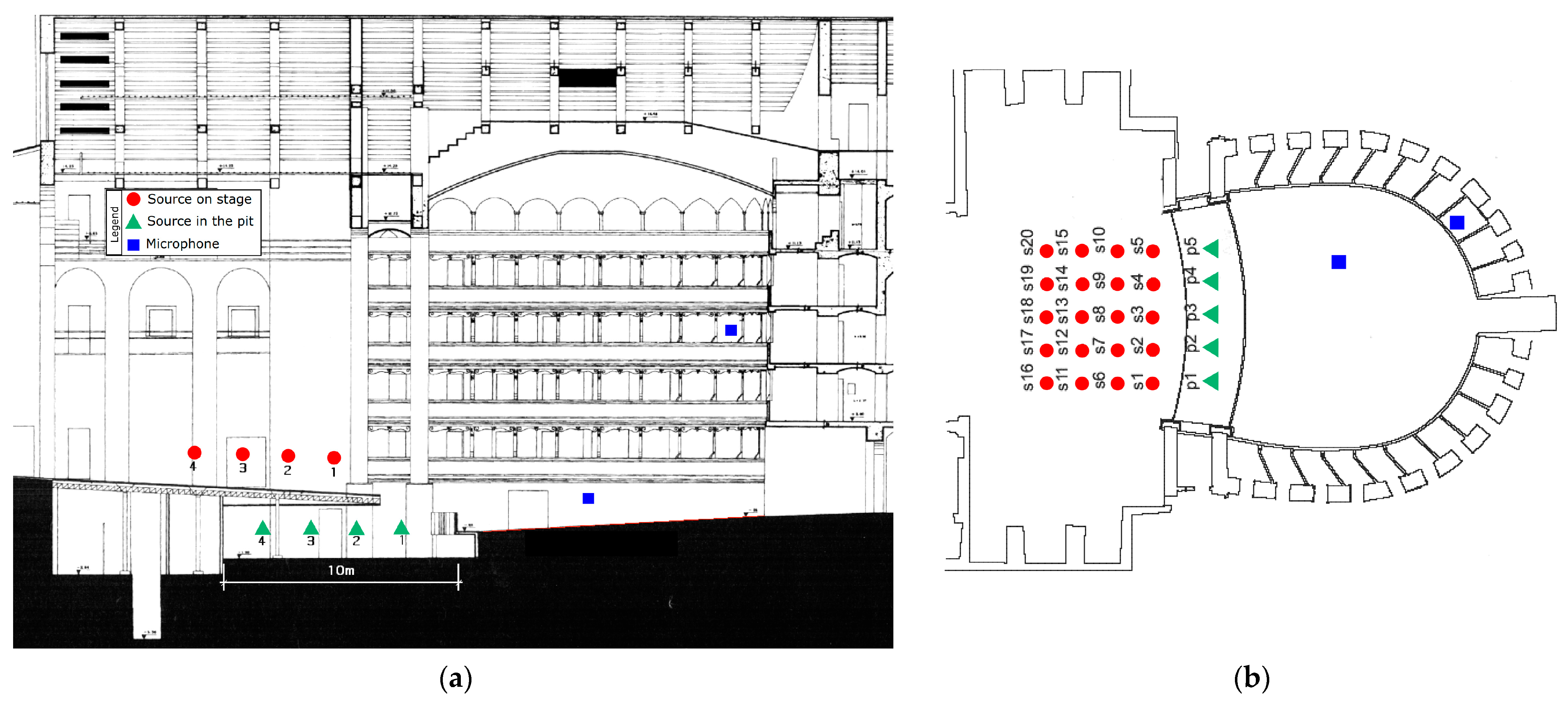
4.2. Sound Source and Microphones Positions in Spoleto
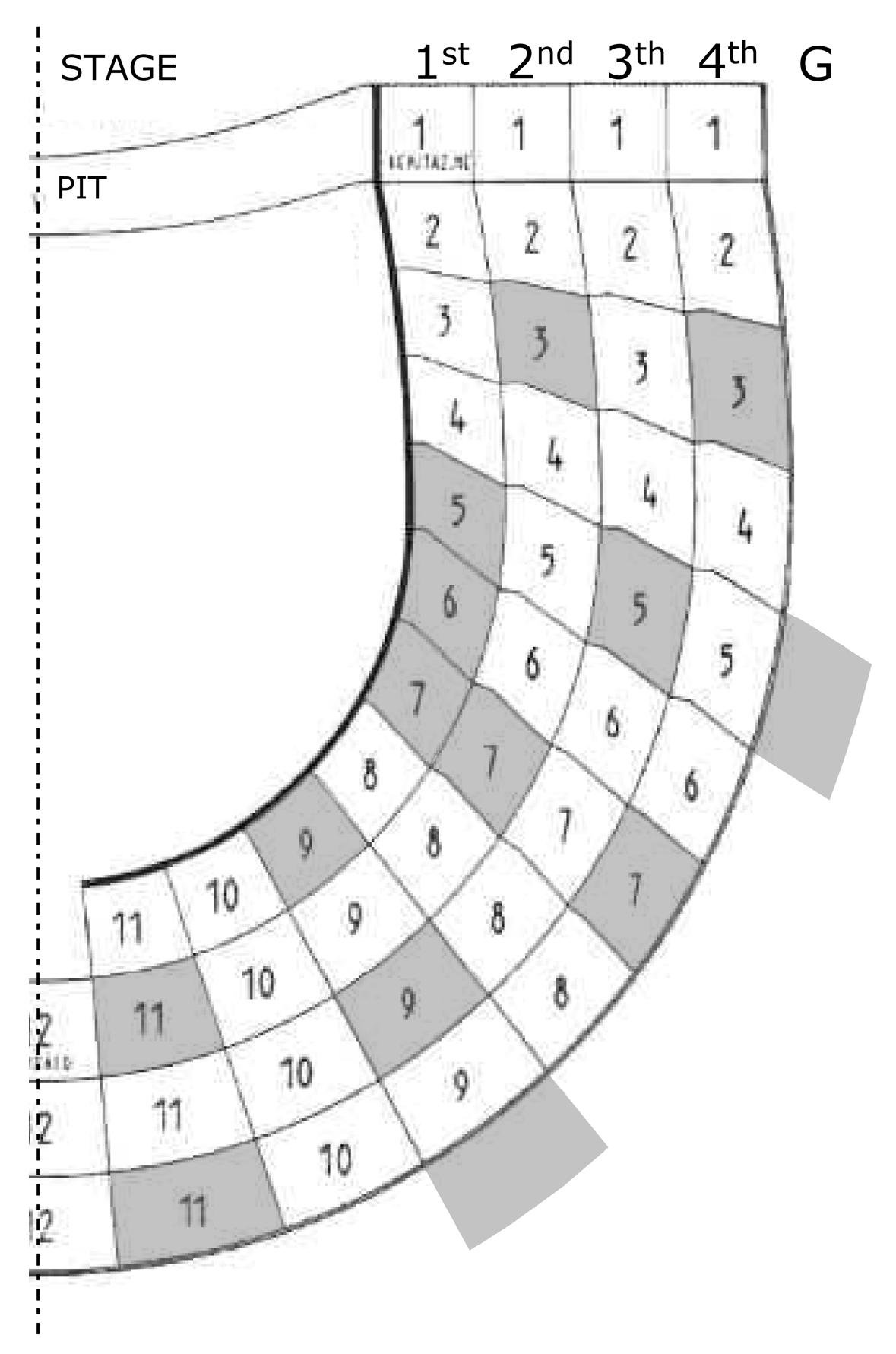
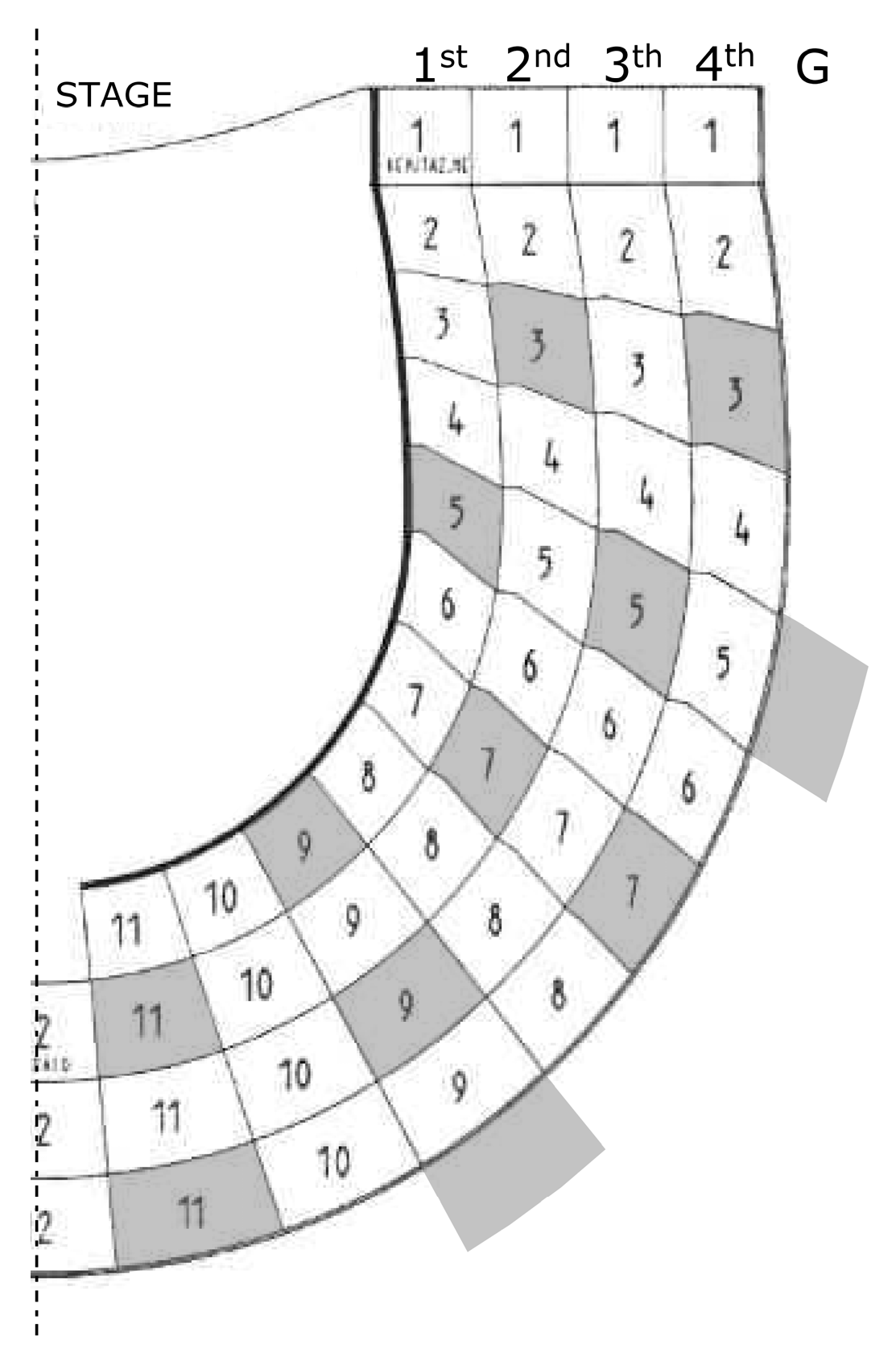
4.3. Sound Source and Microphones Positions in Ravenna
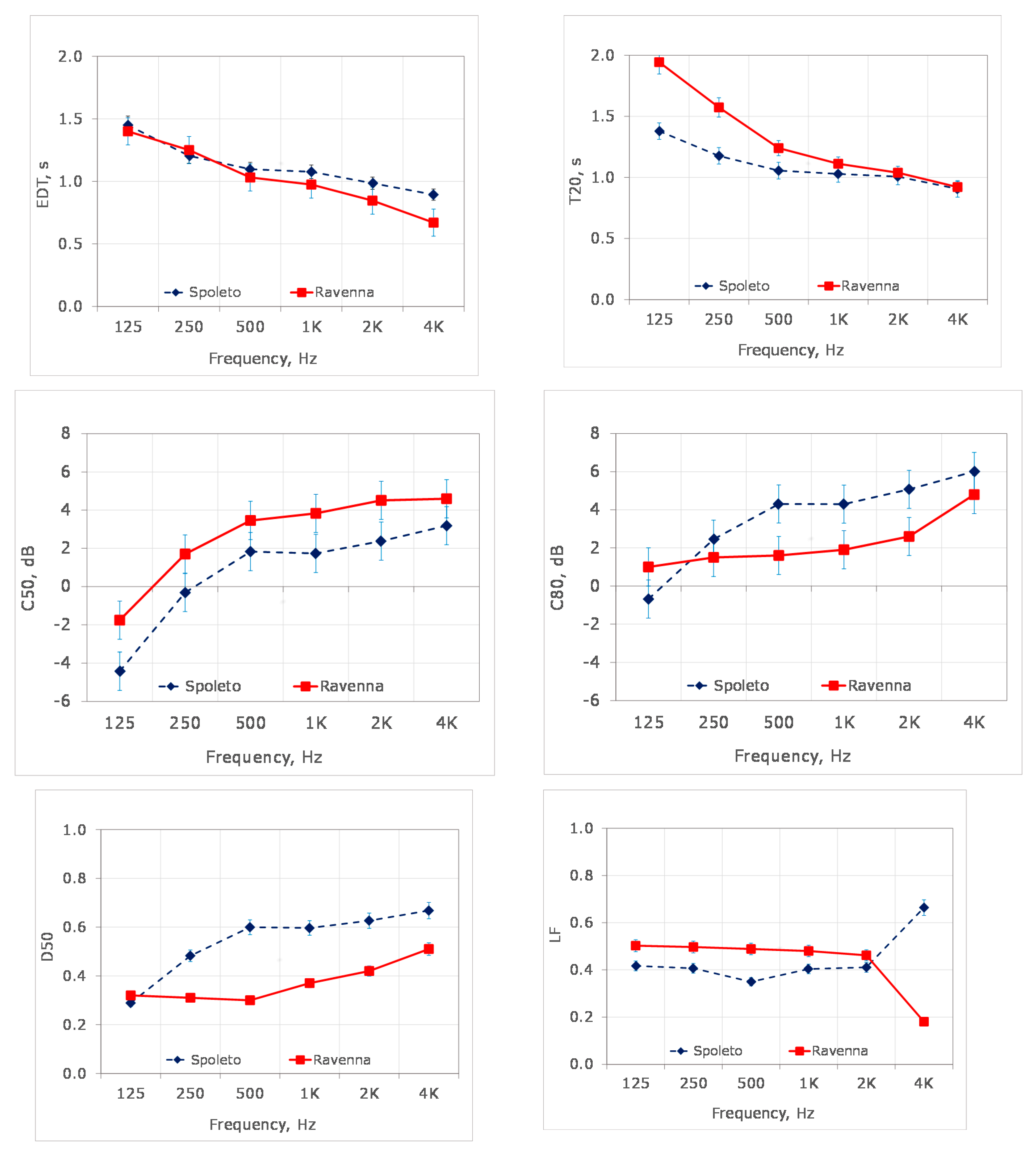
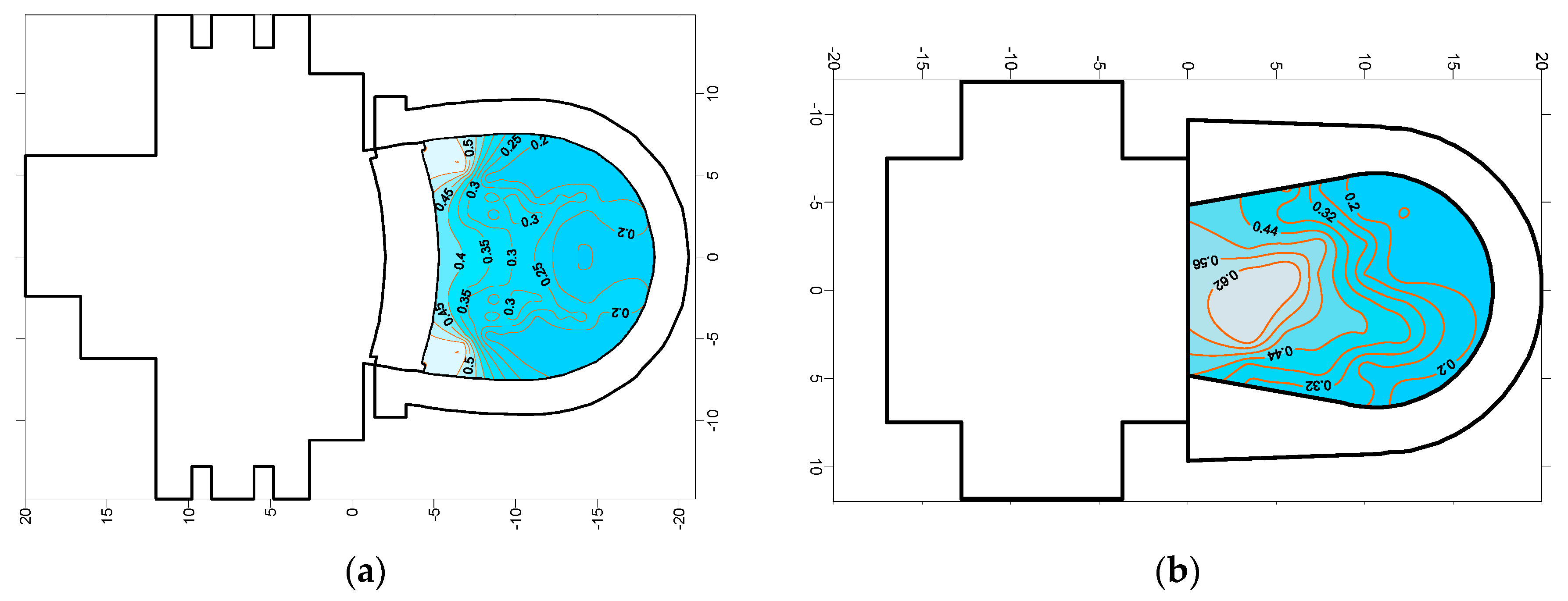
5. Measured Results
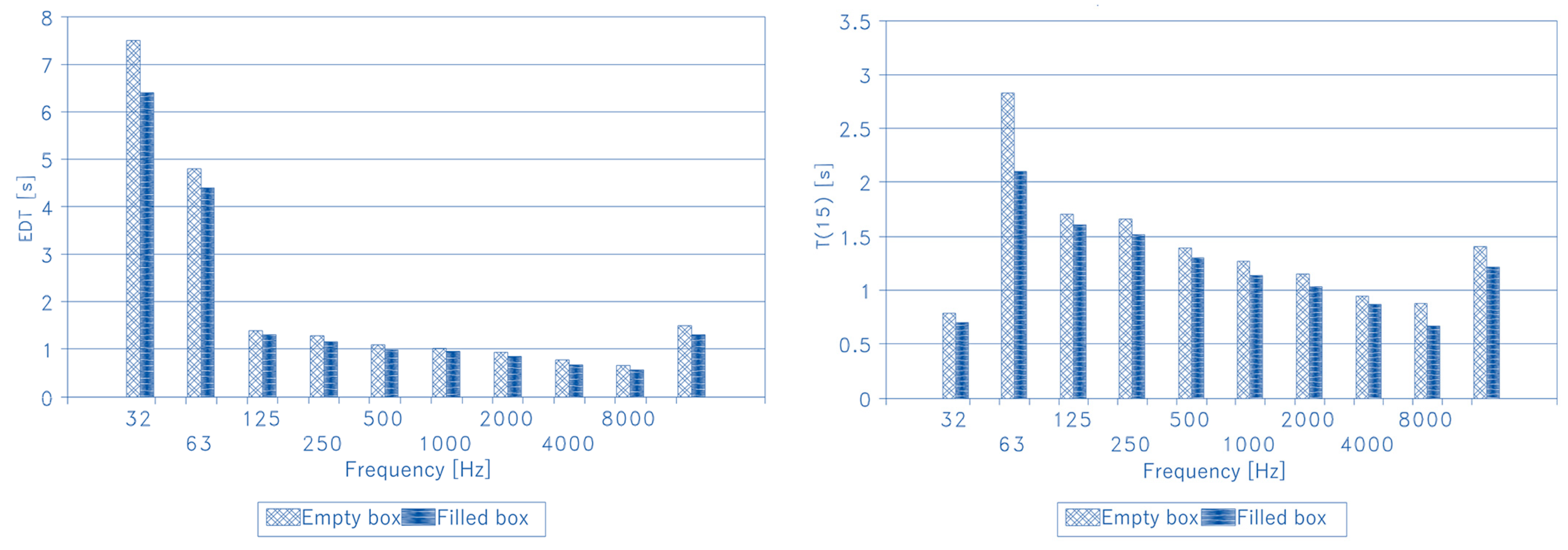
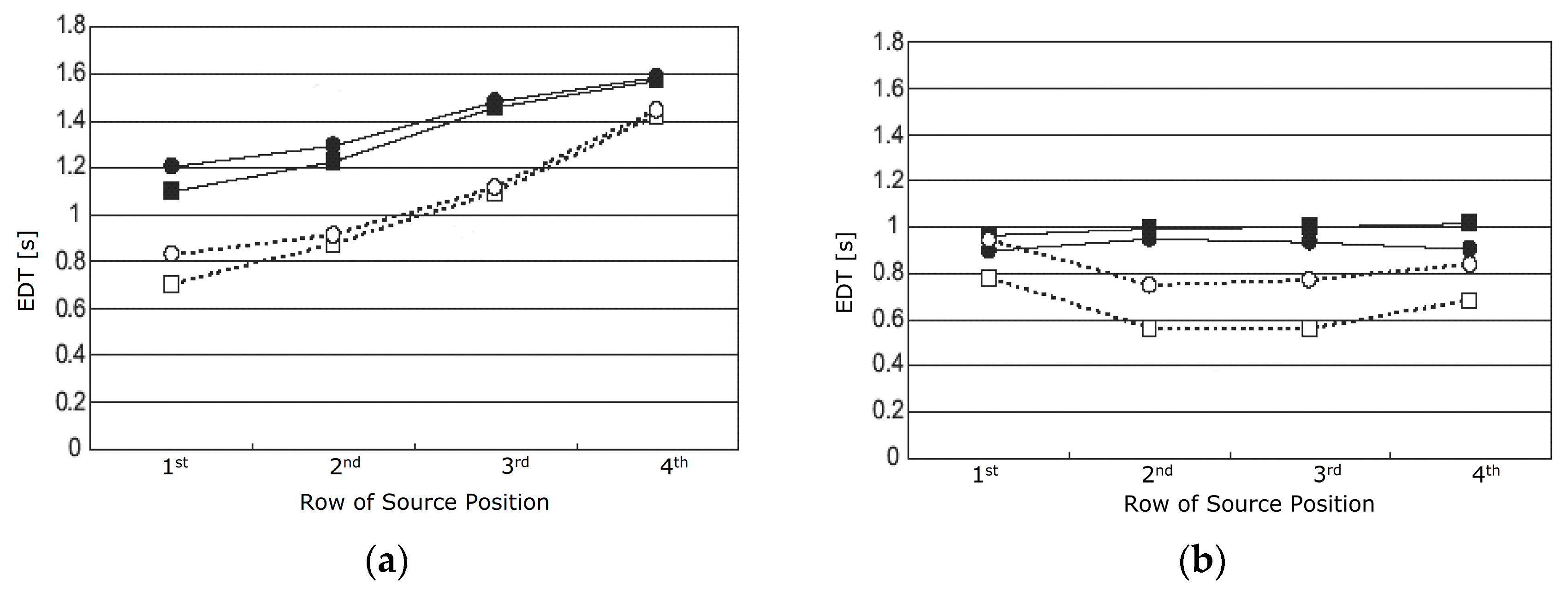
5.1. Early Decay Time (EDT)
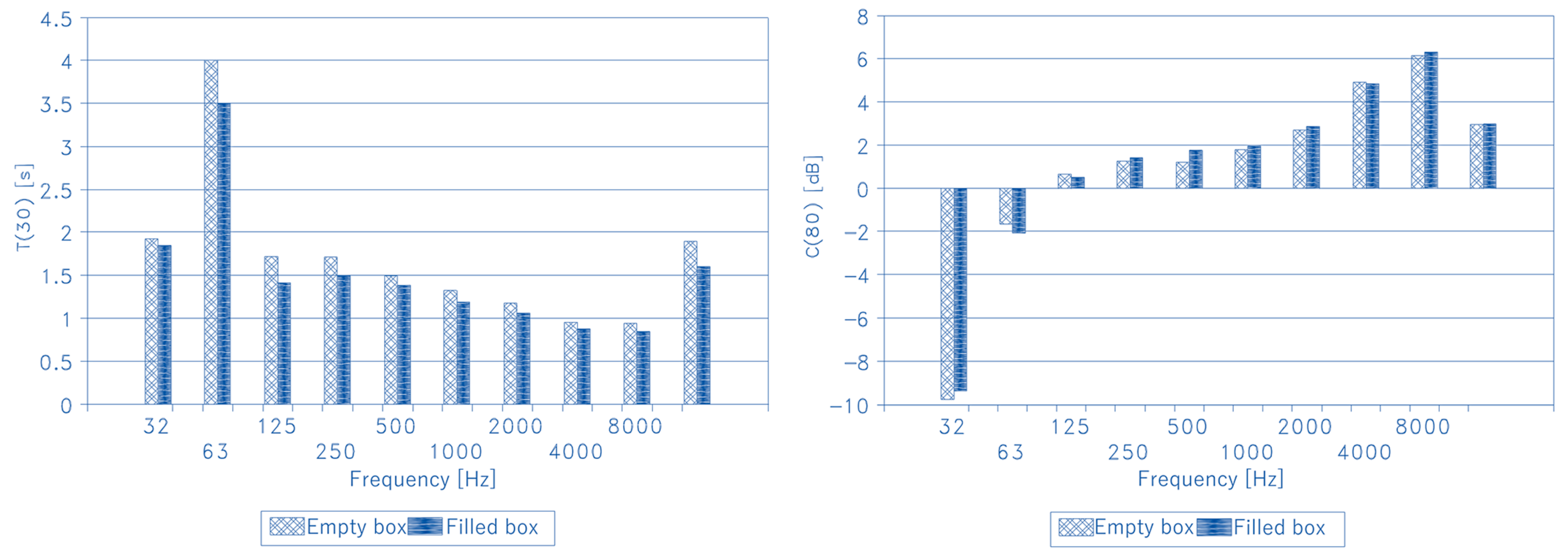
5.2. Reverberation Time
5.3. Clarity Indexes (C50 and C80)
5.4. Definition (D50)
5.5. Lateral Energy Fraction (LF)
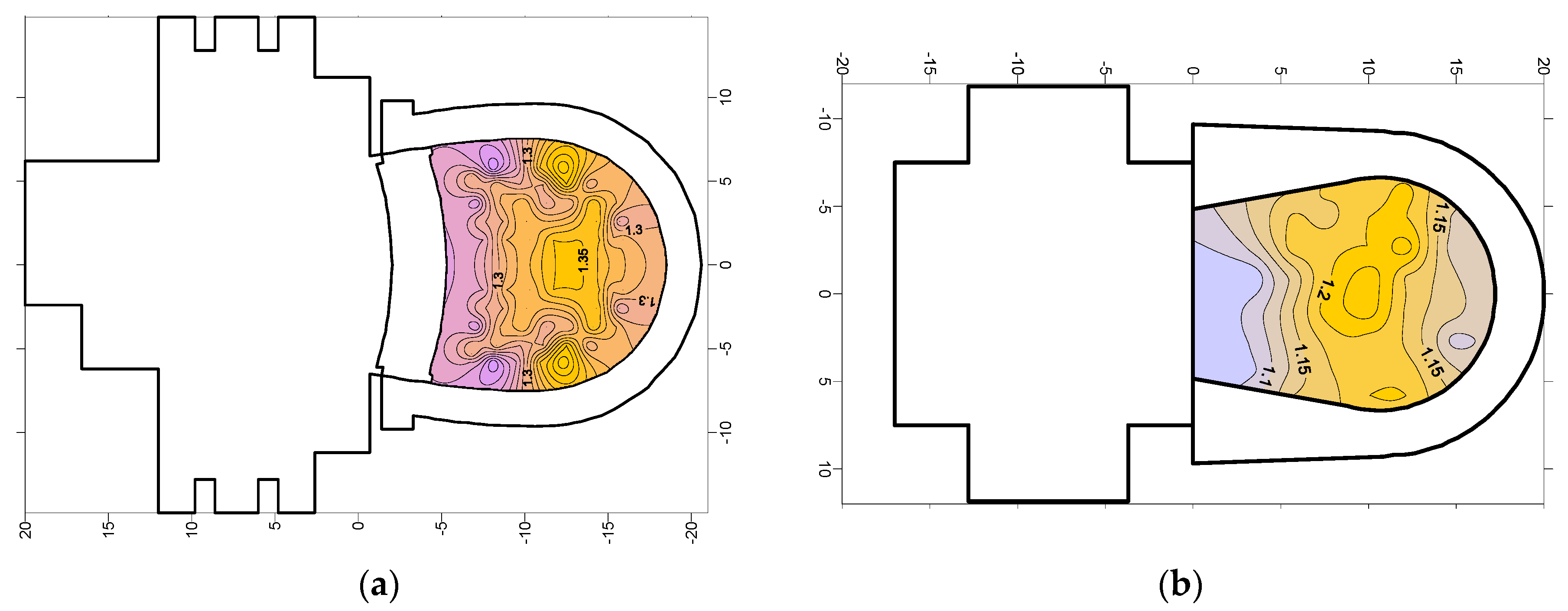
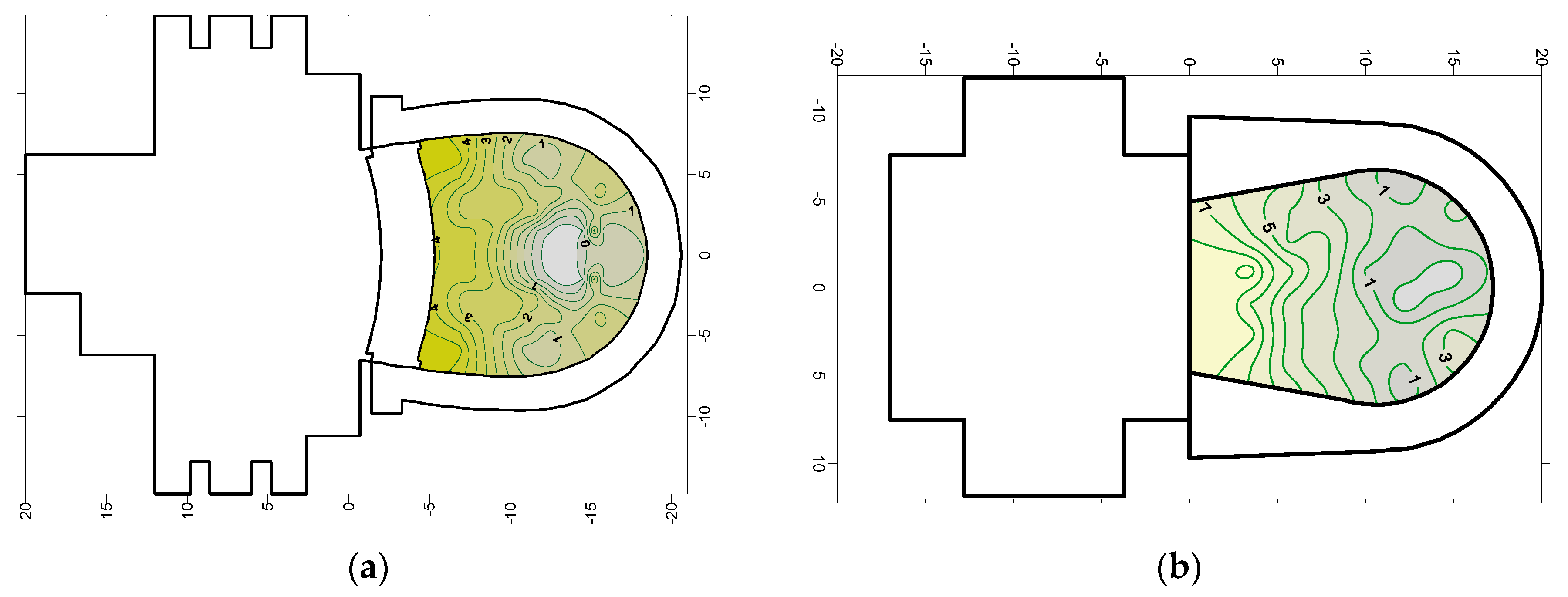
5.6. Acoustic Maps
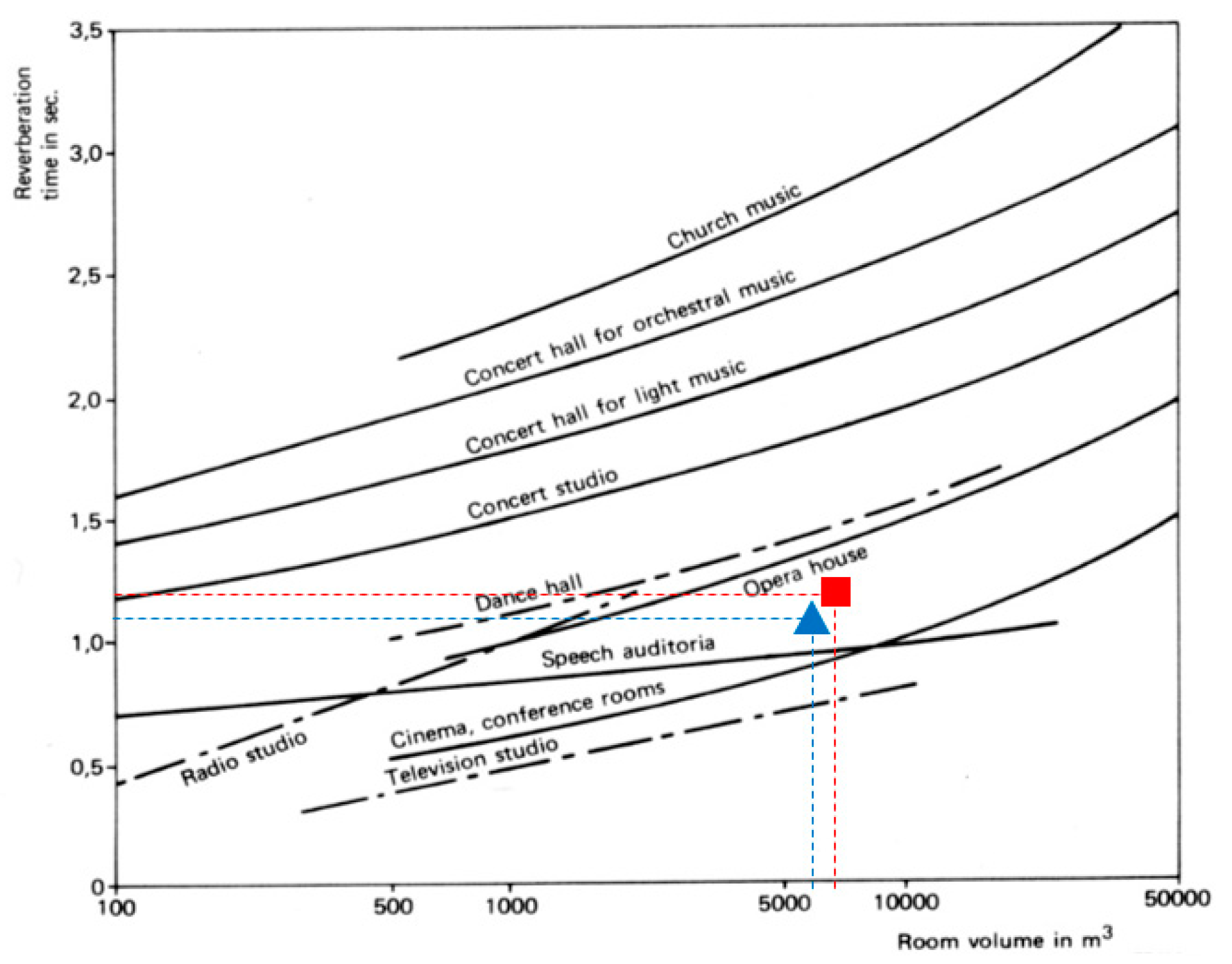
6. Acoustical Limits in Teatro Nuovo of Spoleto
- ▪
- The EDT represents the decay time of the first 10 dB of the sound energy emitted in the room by the impulse, and consequently it is very sensible to the geometric details of the room volume [34];
- ▪
- The EDT has been used by Gade in many binaural RIR measurements for performing arts spaces [35];
- ▪
- Since the EDT becomes lower by increasing the distance between the source and the receiver, it is considered the appropriate parameter to compare different positions in the same room [34];
- ▪
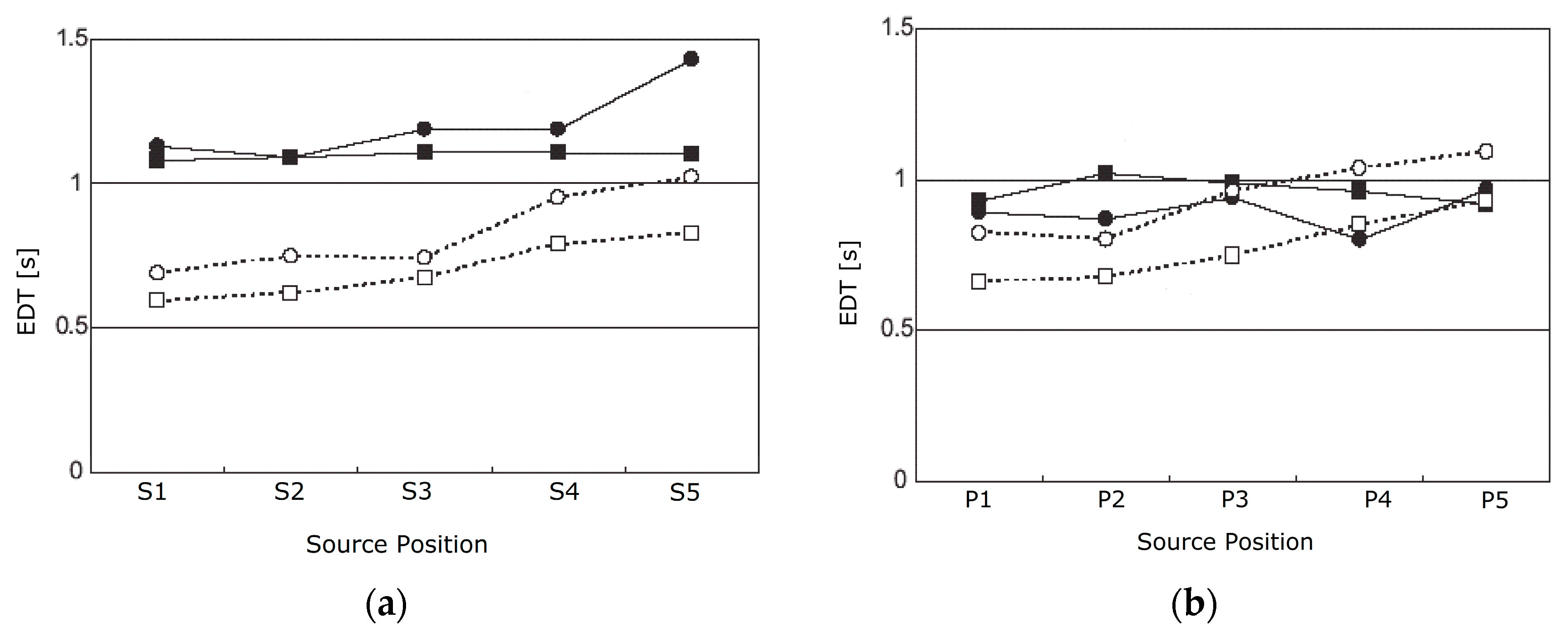
6.1. EDT and ITDG Analysis by Averaging the Values of Each Row of Source Positions
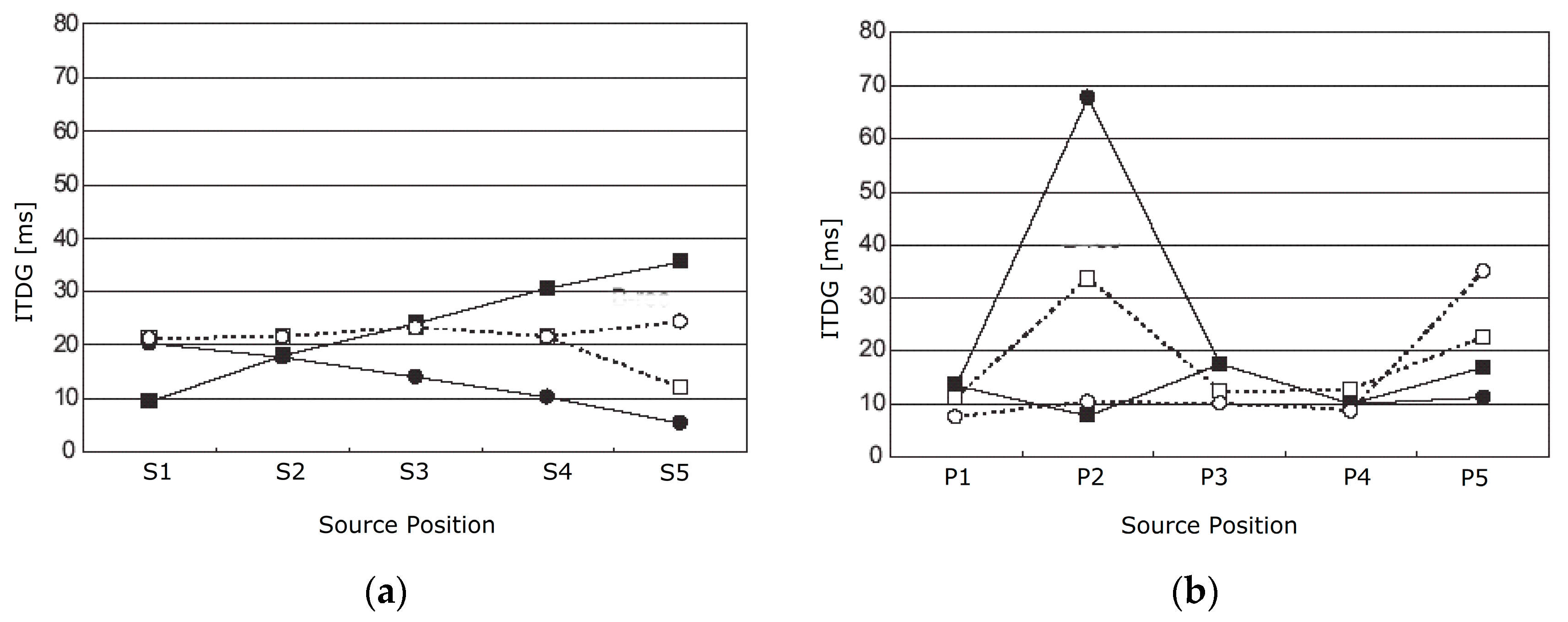
6.2. EDT and ITDG Analysis at Each Sound Source Position along the First Row on the Stage and in the Orchestra Pit
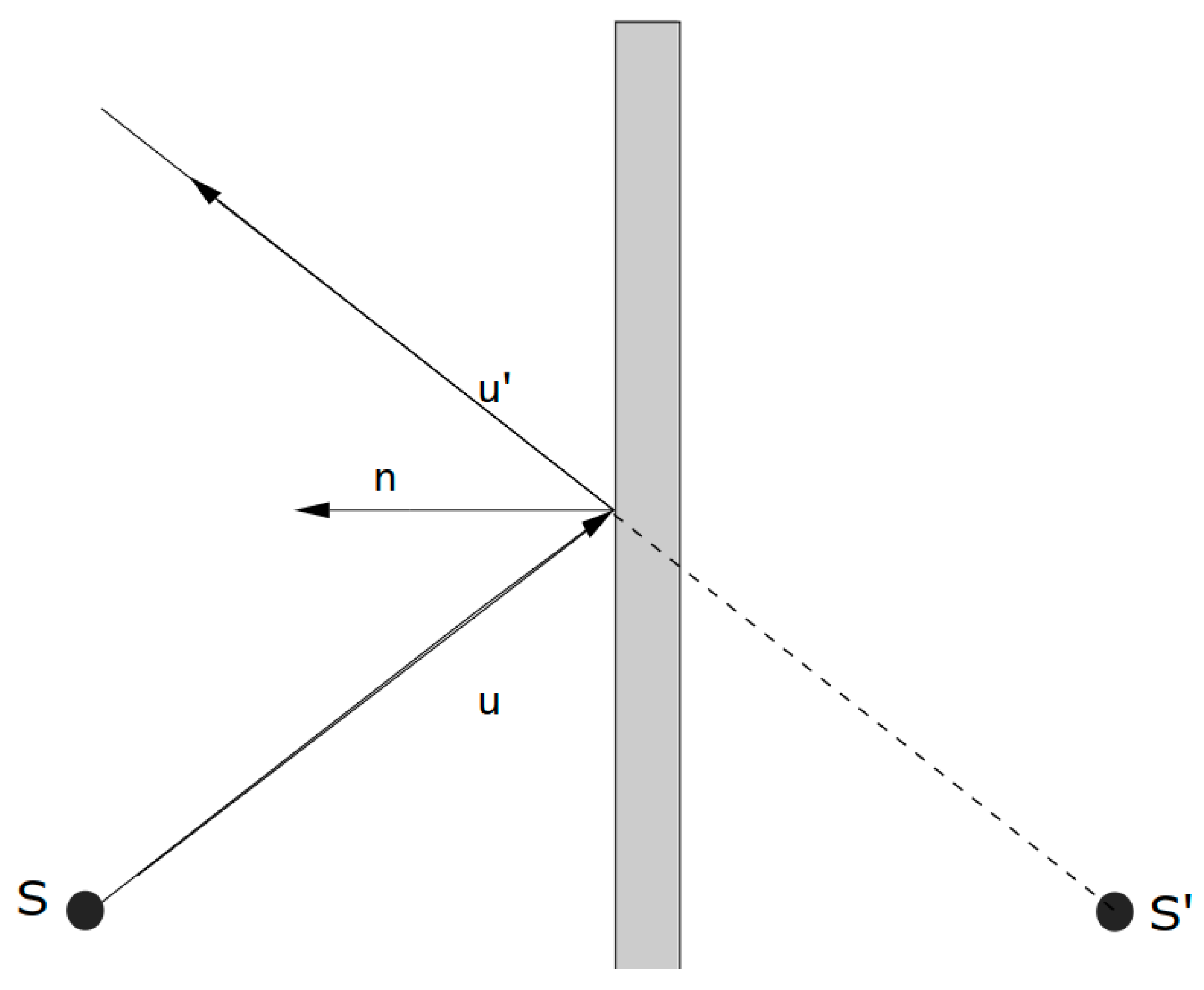
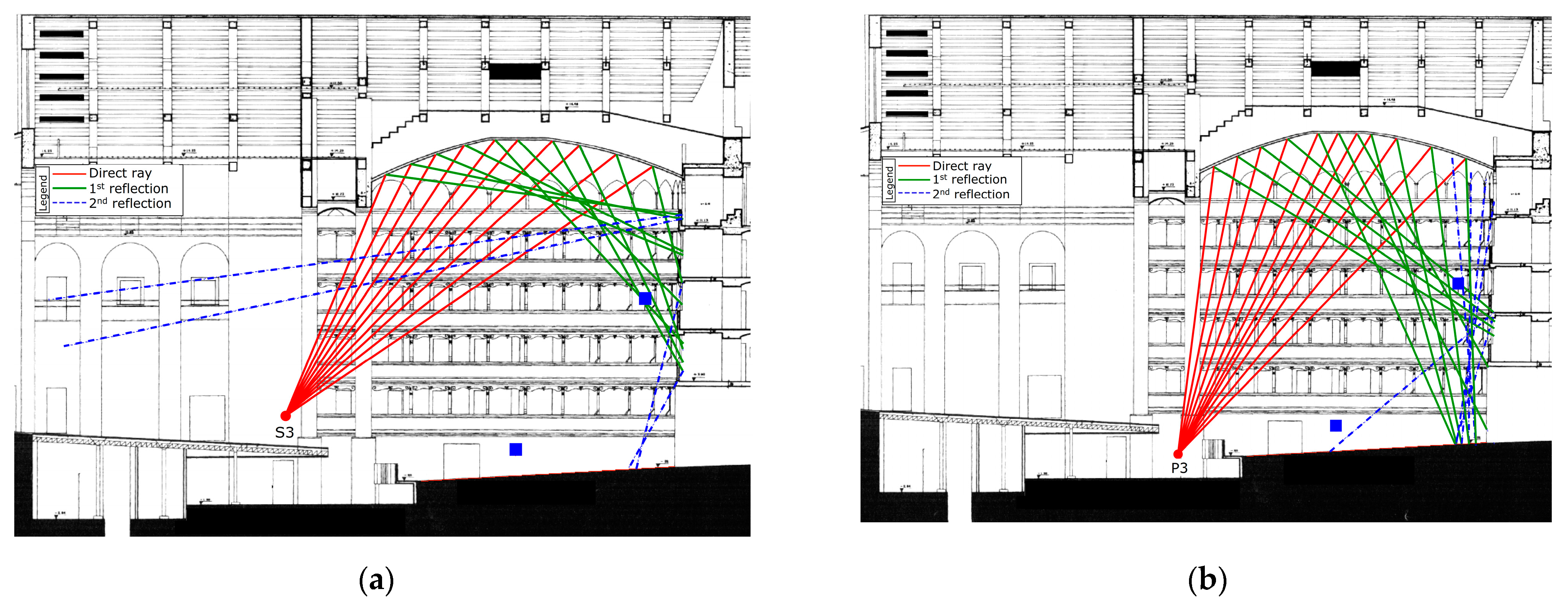
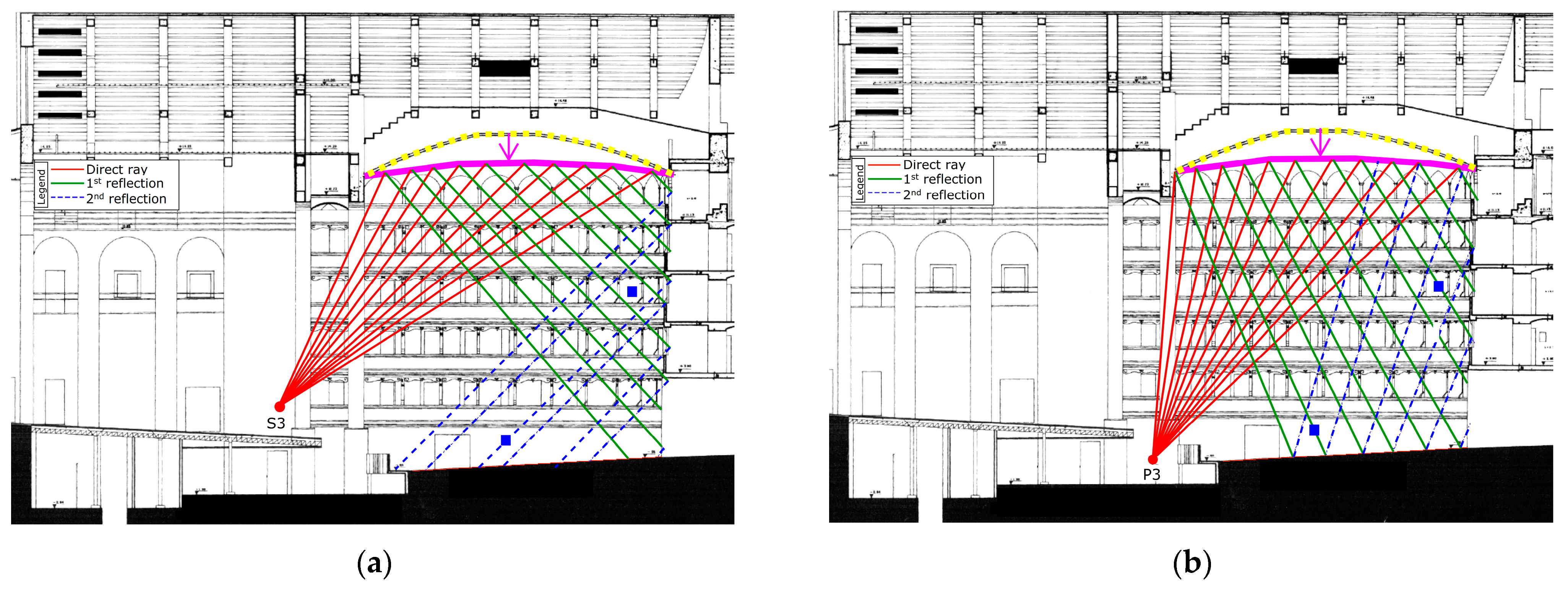
6.3. Geometrical Analysis of the Early Reflections Hitting the Ceiling at the Vertical-Longitudinal Section
7. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vecco, M. A definition of Cultural Heritage: From the tangible to the intangible. J. Cult. Herit. 2010, 11, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordevic, Z. Intangigle tangibility: Acoustical heritage in architecture. Struct. Integr. Life 2016, 6, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin, L.; Farina, A. Acoustics of the former teatro la Fenice in Venice. AES J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1997, 45, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Chiuini, G. Teatri Storici in Umbria: L’architettura; Electa: Milan, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, G. Teatri D’italia, 1st ed.; Bramante: Milan, Italy, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Sansi, O. Il Teatro Nuovo di Spoleto. Notizie Cronistoriche dal 1840 al 1864. Brigata Spoletina Degli Amici Dell’arte e del Paesaggio; Premiata tipografia dell’Umbria: Spoleto, Italy, 1914. [Google Scholar]
- Pavoni, G. Notizie Cronistoriche del Teatro Nuovo di Spoleto—1927, V—1942 XX, 1st ed.; Accademia Spoletina: Spoleto, Italy, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri, P.; Pizzaroli, N. Il teatro Alighieri; Essegi: Galliera Veneta, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi, A.; Garai, M.; Tronchin, L. Influenza di Cavità Risonanti Poste Sotto la Fossa Orchestrale: Il Caso del Teatro Alighieri di Ravenna (The Influence of Resonating Cavities under the Orchestra Pit: The Case of the Alighieri Theatre in Ravenna); Nardini: Firenze, Italy, 1997; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin, L.; Merli, F.; Manfren, M.; Nastasi, B. The sound diffusion in Italian Opera Houses: Some examples. Build. Acoust. 2020, 27, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, A.; Shimokura, R.; Cesare, M. Acoustical measurements in “Teatro Nuovo” (Spoleto, Italy), changing sound source position in performance area. J. Temporal Des. Arch. Environ. 2006, 5, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Barba Sevillano, A.; Gimenez, A.; Lacatis, R.; Cibrian, R. Resonant cavities and acoustic vases in Italian Opera Houses; the “Teatro Principal” of Valencia and the eighteen century treatises about theatres. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokura, R.; Tronchin, L.; Cocchi, A.; Soeta, Y. Subjective diffuseness of music signals convolved with binaural impulse response. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 3382-1: Acoustics—Measurement of Room Acoustic Parameters; Part 1: Performance Spaces; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin, L. Variability of room acoustic parameters with thermo-hygrometric conditions. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 177, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, G.B.; Embrechts, J.J.; Archambeau, D. Comparison of different impulse response measurement techniques. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2002, 50, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. Simultaneous measurement of impulse response and distortion with a swept-sine technique. In Proceedings of the 108th Audio Engineering Society (AES) Convention, Paris, France, 19–22 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.S. Review of objective room acoustics measures and future needs. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Centre of Acoustics and Music Research (CIARM). Guidelines for Acoustical Measurements inside Historical Opera Houses: Procedures and Validation; International Centre of Acoustics and Music Research (CIARM): Ferrara, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, V.L. Acoustical criteria for auditoriums and their relation to model techniques. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1970, 47, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.K.; Jeon, J.Y. Subjective and objective evaluations of a scattered sound filed in a scale model opera house. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 1528–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ryu, J.K. The effect of stage absorption on reverberation times in opera house seating areas. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.; Lee, J. Energy relations in concert auditoriums. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 84, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, V.L. A group of objective acoustical criteria for concert halls. Appl. Acoust. 1981, 14, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, L.; Muller, A. Principle and Applications of Room Acoustics; Peninsula Publishing: Westport, CT, USA, 1982; pp. 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti, L.; Masetti, L. Teatri Storici: Dal Restauro allo Spettacolo (Historical Theatres: From Renovation to Performance); Nardini: Fiesole, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.sfu.ca/sonic-studio-webdav/cmns/Handbook%20Tutorial/Sound-Environment.html (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Reichardt, W.; Abel Alim, O.; Schmidt, W. Definition and basis of making an objective evaluation to distinguish between useful and useless clarity defining musical performances. Acta Acust. 1975, 3, 126–137. [Google Scholar]
- Thiele, R. Richtungsverteilungs und zeitfolge del schallruckewurfe in raumen. Acta Acust. 1953, 3, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, M. Subjective effects of first reflections in concert halls—The need for lateral reflections. J. Sound Vib. 1971, 15, 472–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.; Marshall, A.H. Spatial impression due to early lateral reflections in concert halls: The deviation of a physical measure. J. Sound Vib. 1981, 77, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouis, D. Acoustical parameters used for the subjective assessment of musical performance spaces. J. New Music Res. 2006, 35, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y. Concert Hall Acoustic; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kuttruff, H. Room Acoustics, 4th ed.; Spon Press: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gade, A.C. Proceedings of the Sabine Centennial Symposium; Acoustical Society of America: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Lokki, T.; Pätynen, J. Auditory spatial impression in concert halls. In The Technology of Binaural Understanding, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin, L.; Bevilacqua, A. Acoustic study of different sceneries at the São Carlos National Theatre of Lisbon. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 180, 108102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, A.; Wanniarachchi, W.K.I.L. Image source method based acoustic simulation for 3d room environment. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 8, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Aretz, M.; Dietrich, P.; Vorländer, M. Application of the mirror source method for low frequency sound prediction in rectangular rooms. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, B.; Jones, D. A simple image method for calculating the distribution of sound pressure levels within an enclosure. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1972, 26, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.; Berkley, D. Image method for efficiently simulating small-room acoustics. J. Acust. Soc. Am. 1979, 65, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, S. Filippo Marignoli e Ireneo Aleandri Nella Tela di un Inedito Pittore Spoletino.XXXI-XXXII, 1st ed.; Accademia Spoletina: Spoleto, Italy, 1990; pp. 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Prodi, N.; Pompoli, R. Acoustics in the restoration of Italian historical opera houses: A review. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 21, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianniello, C. An acoustic catalogue of historical Italian theatres for opera. In Proceedings of the Forum Acusticum, 4th European Congress on Acoustics, Budapest, Hungary, 29 August–2 September 2005. [Google Scholar]


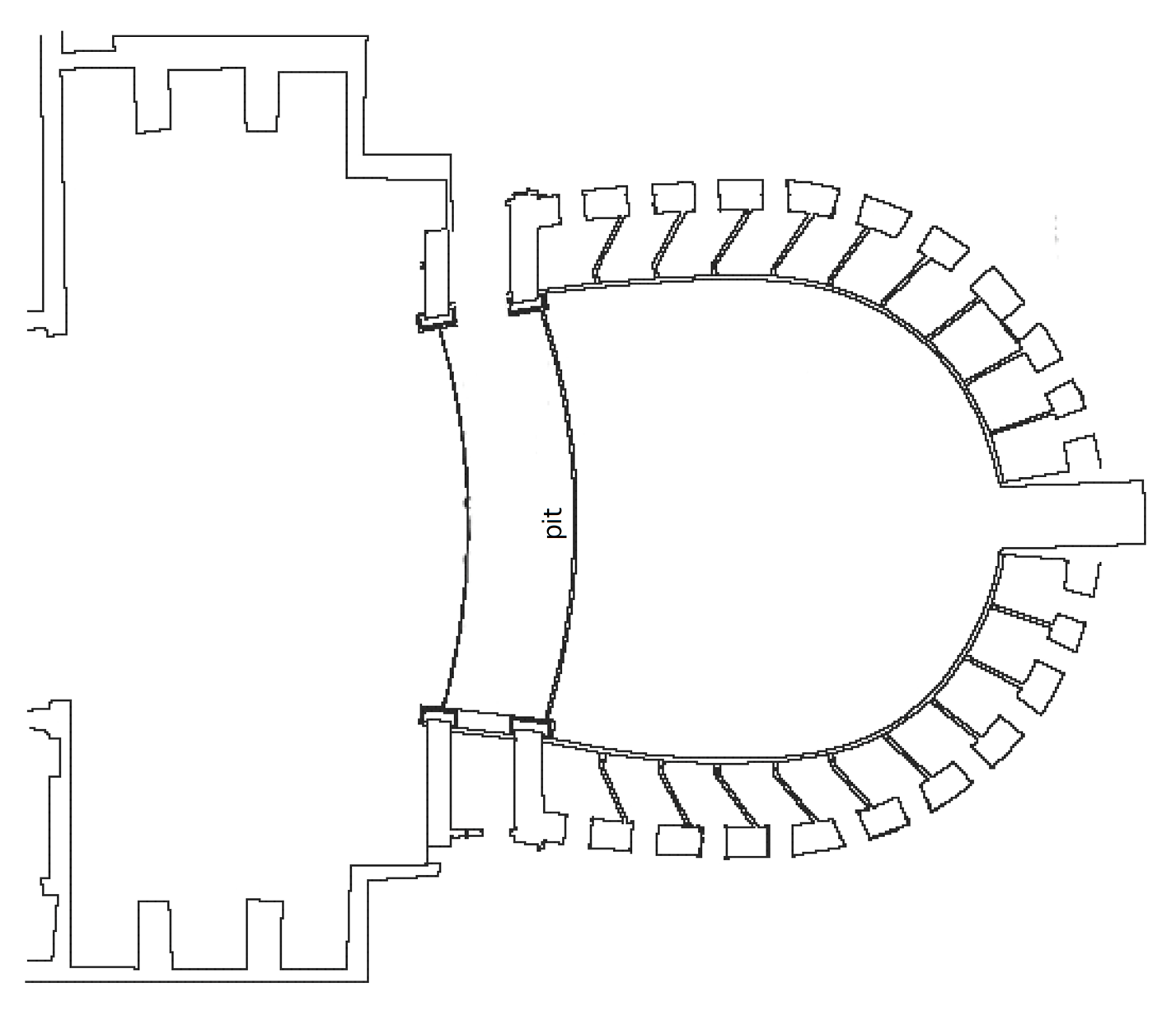
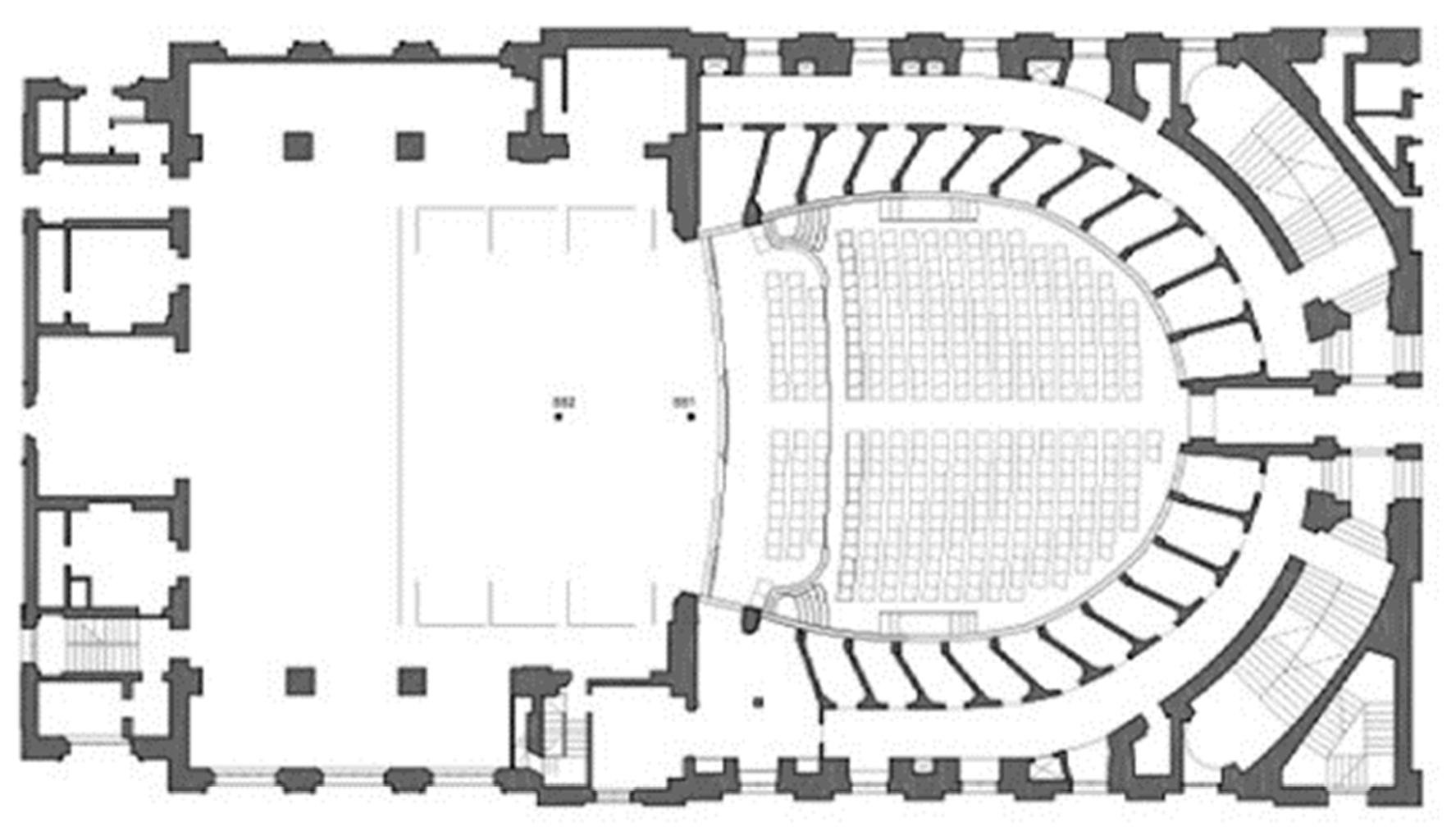

| Description | Teatro Nuovo (Spoleto) | Teatro Alighieri (Ravenna) |
|---|---|---|
| Type of plan layout | Horseshoe box | Horseshoe box |
| Total capacity (no. of seats) | 800 | 1026 |
| Inclination of stalls area (%) | 5% | 5% |
| Stage dimension (m) [L × W] | 29 × 20.5 | 25 × 22 |
| Volume (m3) | 6300 | 7100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bevilacqua, A.; Tronchin, L. Evaluation of Acoustic Features after Refurbishment Works Inside Two Historical Opera Theatres Located in Italy. Acoustics 2021, 3, 316-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics3020022
Bevilacqua A, Tronchin L. Evaluation of Acoustic Features after Refurbishment Works Inside Two Historical Opera Theatres Located in Italy. Acoustics. 2021; 3(2):316-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics3020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleBevilacqua, Antonella, and Lamberto Tronchin. 2021. "Evaluation of Acoustic Features after Refurbishment Works Inside Two Historical Opera Theatres Located in Italy" Acoustics 3, no. 2: 316-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics3020022
APA StyleBevilacqua, A., & Tronchin, L. (2021). Evaluation of Acoustic Features after Refurbishment Works Inside Two Historical Opera Theatres Located in Italy. Acoustics, 3(2), 316-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics3020022







