General Practitioners and Gut Microbiota: Surveying Knowledge and Awareness in Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchesi, J.R.; Adams, D.H.; Fava, F.; Hermes, G.D.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Hold, G.; Quraishi, M.N.; Kinross, J.; Smidt, H.; Tuohy, K.M.; et al. The gut microbiota and host health: A new clinical frontier. Gut 2016, 65, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Cremon, C.; Barbaro, M.R.; Fuschi, D.; Bellacosa, L.; Marasco, G.; Stanghellini, V.; Castellazzi, A.M.; Valsecchi, C. The role of microbiota in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 167–183. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, Z.Y.; Lal, S.K. The human gut microbiome—A potential controller of wellness and disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carding, S.; Verbeke, K.; Vipond, D.T.; Corfe, B.M.; Owen, L.J. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Francavilla, R.; Piccolo, M.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Giannelli, G.; Gobbetti, M. Autism spectrum disorders and intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B. The role of the gut microbiota in psychological disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 52, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Savarino, E.V.; Marabotto, E.; Zentilin, P.; Furnari, M.; Bodini, G.; De Maria, C.; Pellegatta, G.; Coppo, C.; Savarino, E. Proton pump inhibitors, Helicobacter pylori and the Gut microbiota. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 903–913. [Google Scholar]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernberg, C.; Löfmark, S.; Edlund, C.; Jansson, J.K. Long-term impacts of antibiotic exposure on the human intestinal microbiota. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Wang, J.; Darzi, Y.; Faust, K.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Vandeputte, D.; et al. Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation. Science 2016, 352, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, S.; Frauwallner, A.; Varga, L.; Langerholc, T.; Rogelj, I.; Lorber, M.; Lewis, P.; Povalej Bržan, P. Health Professionals’ Knowledge of Probiotics: An International Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Gwee, K.A.; Holtmann, G.; Li, Y.; Park, S.J.; Simadibrata, M.; Sugano, K.; Cohen, H.; Quigley, E.M.M. Physician Perceptions on the Use of Antibiotics and Probiotics in Adults: An International Survey in the Asia-Pacific Area. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 722700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geest, A.; Flach, J.; Claassen, E.; Sijlmans, A.W.; Van de Burgwal, L.; Larsen, O. European General Practitioners perceptions on probiotics: Results of a multinational survey. PharmaNutrition 2020, 11, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Gasbarrini, A. Antibiotics as deep modulators of gut microbiota: Between good and evil. Gut 2016, 65, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.V.; Dickinson, H.O.; Eccles, M.P. Response rates in postal surveys of healthcare professionals between 1996 and 2005: An observational study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2009, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2025, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, G.; Flores, G.A.; Venanzoni, R.; Angelini, P. The Impact of Antibiotic Therapy on Intestinal Microbiota: Dysbiosis, Antibiotic Resistance, and Restoration Strategies. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Tillisch, K.; Gupta, A. Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.F.; Murphy, E.F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Lucey, A.J.; Humphreys, M.; Hogan, A.; Hayes, P.; O’Reilly, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; Wood-Martin, R.; et al. Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut 2014, 63, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders and the Microbiome: The Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Obesity, Lipid Metabolism, and Metabolic Health-Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.N.; Liu, X.T.; Liang, Z.H.; Wang, J.H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Islam, M.; Rahman, A.; Ripon, A.R.; Hossain, M.S. Gut microbiota in obesity and related complications: Unveiling the complex interplay. Life Sci. 2023, 334, 122211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Arora, K.; Prakash, S. Microbial Medicine: Prebiotic and Probiotic Functional Foods to Target Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmiguel, C.; Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A. Gut Microbiome and Obesity: A Plausible Explanation for Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, N.; Zhong, J.; Gong, W.; Zheng, W.; Wu, Y.H.; Myers, A.; et al. Smoking-related gut microbiota alteration is associated with obesity and obesity-related diseases: Results from two cohorts with sibling comparison analyses. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.; Dalamaga, M.; Stratigou, T.; Karampela, I.; Tsigalou, C. Do Antibiotics Cause Obesity Through Long-term Alterations in the Gut Microbiome? A Review of Current Evidence. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Vela, J.; Solis-Urra, P.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Álvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Olivares-Arancibia, J.; Plaza-Diaz, J. Impact of Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Harris, L.A.; Lacy, B.E.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Moayyedi, P. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The efficacy of prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics and antibiotics in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, G.; Cremon, C.; Bellini, M.; Corsetti, M.; Di Nardo, G.; Falangone, F.; Fuccio, L.; Galeazzi, F.; Iovino, P.; Sarnelli, G.; et al. Italian guidelines for the management of irritable bowel syndrome: Joint Consensus from the Italian Societies of: Gastroenterology and Endoscopy (SIGE), Neurogastroenterology and Motility (SINGEM), Hospital Gastroenterologists and Endoscopists (AIGO), Digestive Endoscopy (SIED), General Medicine (SIMG), Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Pediatric Nutrition (SIGENP) and Pediatrics (SIP). Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Hasler, W.L. Rome IV-Functional GI disorders: Disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, R.; Barbara, G.; Pace, F.; Annese, V.; Bassotti, G.; Binda, G.A.; Casetti, T.; Colecchia, A.; Festi, D.; Fiocca, R.; et al. Italian consensus conference for colonic diverticulosis and diverticular disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2014, 2, 413–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahner, E.; Bellisario, C.; Hassan, C.; Zullo, A.; Esposito, G.; Annibale, B. Probiotics in the Treatment of Diverticular Disease. A Systematic Review. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Sgamato, C.; Amato, A.; Beltrame, B.; Binda, G.A.; Germanà, B.; Leandro, G.; Pasquale, L.; Peralta, S.; Viggiani, M.T.; et al. Italian guidelines for the diagnosis and management of colonic diverticulosis and diverticular disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 1989–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gao, L.; Yin, Z.; Ye, S.; Zhao, H.; Peng, Q. Probiotics and rifaximin for the prevention of travelers’ diarrhea: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, S.; Deans, A.; Padua-Zamora, A.; Gregorio, G.V.; Li, C.; Dans, L.F.; Allen, S.J. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD003048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Scott, K.P.; de Meij, T.; Forslund-Startceva, S.K.; Knight, R.; Koren, O.; Little, P.; Johnston, B.C.; Łukasik, J.; Suez, J.; et al. Antibiotic-perturbed microbiota and the role of probiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 22, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Eusebi, L.H.; Pellegrino, R.; Palladino, G.; Frazzoni, L.; Dajti, E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Di Mario, F.; Zagari, R.M.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: Guidelines of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology (SIGE) and the Italian Society of Digestive Endoscopy (SIED). Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi-Rad, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Yadegar, A.; Smith, S.M.; Zali, M.R. The double-edged sword of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota structure in Helicobacter pylori management. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2108655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.T.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Siegel, C.A.; Barnes, E.L.; Long, M.D. ACG Clinical Guideline Update: Ulcerative Colitis in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 120, 1187–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevinho, M.M.; Yuan, Y.; Rodríguez-Lago, I.; Sousa-Pimenta, M.; Dias, C.C.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Jairath, V.; Magro, F. Efficacy and safety of probiotics in IBD: An overview of systematic reviews and updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 12, 960–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bager, P.; Escher, J.; Forbes, A.; Hébuterne, X.; Hvas, C.L.; Joly, F.; Klek, S.; Krznaric, Z.; Ockenga, J.; et al. ESPEN guideline on Clinical Nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 352–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G. Probiotics in inflammatory bowel diseases: Emphasis on mechanisms and clinical application. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1620079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabitska, I.; Petakh, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Oksenych, V.; Kainov, D.E.; Kamyshnyi, O. The interplay of gut microbiota, obesity, and depression: Insights and interventions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, F.; Hasani, S.; Aghili, Z.S.; Asgary, S. The potential preventive effect of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on cardiovascular risk factors through modulation of gut microbiota: A Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 4569–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Bäckhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; de Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M.; et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcari, S.; Mullish, B.H.; Asnicar, F.; Ng, S.C.; Zhao, L.; Hansen, R.; O′Toole, P.W.; Raes, J.; Hold, G.; Putignani, L.; et al. International consensus statement on microbiome testing in clinical practice. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 10, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, G.; Bruni, A.; Nardone, O.M.; Lopetuso, L.R. Insights into Probiotic Prescription among Gastroenterologists and Other Healthcare Professionals: Evidence from an Italian Survey. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | Total [n = 457] | GPs < 45 yrs Old [n = 292] | GPs > 45 yrs Old [n = 165] | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major factors | ||||
| Antibiotics | 95.4% | 94.5% | 97.0% | - |
| Dietary habits | 90.6% | 92.8% | 86.7% | - |
| Gastrointestinal infections | 88.8% | 88.0% | 90.3% | - |
| Stress | 77.0% | 83.9% | 64.8% | 0.001 |
| Intermediate factors (p = 0.001 vs. major factors) | ||||
| Immunosuppressive drugs | 64.3 | 63.0% | 66.4% | - |
| Obesity | 59.1% | 66.1% | 46.7% | 0.001 |
| Cigarette smoking | 57.1% | 63.7% | 45.5% | 0.001 |
| Minor factors (p = 0.005 vs. intermediate factors) | ||||
| Physical activity | 47.3% | 50.0% | 42.4% | - |
| Insomnia | 33.9% | 41.1% | 19.4% | 0.001 |
| Biologic drug therapies | 33.5% | 38.4% | 24.8% | 0.013 |
| What is your age? | <35 yrs; 35–44 yrs; 45–54 yrs; 55–64 yrs; >64 yrs |
| In which region of Italy do you work? | North-East; North-West; Center; South; Islands |
| Which of the following factors do you believe can cause intestinal dysbiosis, defined as an imbalance in the gut bacterial flora? (Multiple answers allowed) |
|
| Are you familiar with the scientific evidence and current recommendations regarding the use of probiotics? (Single answer) |
|
| Which of the following best defines probiotics? (Single answer) |
|
| Which of the following best defines prebiotics? (Single answer) |
|
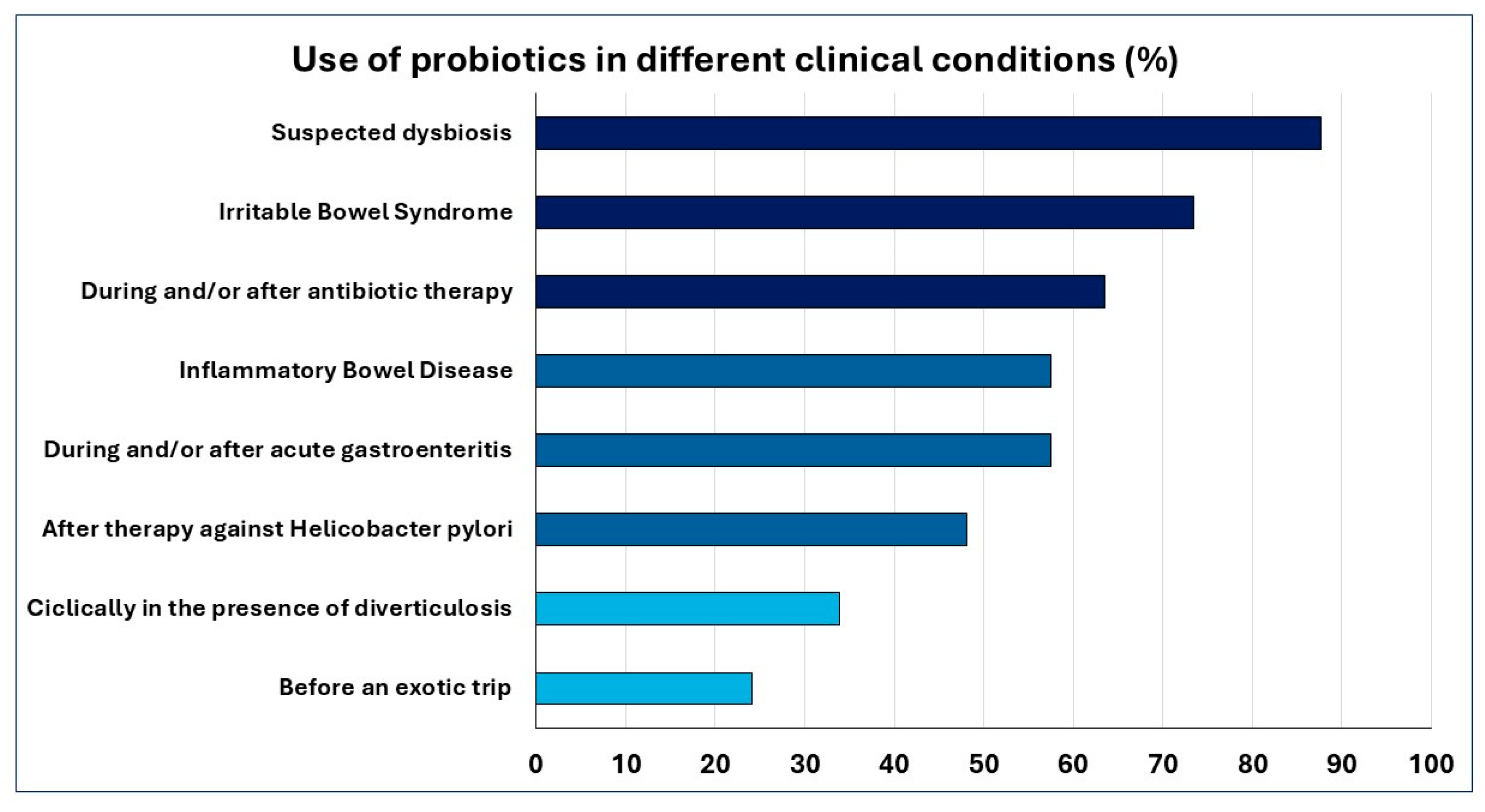
| In your opinion, in which clinical conditions is the use of probiotics indicated? (Multiple answers allowed) |
|
| In your opinion, in which clinical conditions is the use of prebiotics indicated? (Multiple answers allowed) |
|
| Which criteria do you consider when prescribing probiotics? (Multiple answers allowed) |
|
| Are you familiar with the fecal microbiota test? (Single answer) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tosetti, C.; Belvedere, A.; Berardino, M.; Bertolusso, L.; Cantarini, R.; Carofiglio, F.; Di Bella, F.; Franchi, D.; Furnari, A.; Marturano, A.; et al. General Practitioners and Gut Microbiota: Surveying Knowledge and Awareness in Italy. Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040060
Tosetti C, Belvedere A, Berardino M, Bertolusso L, Cantarini R, Carofiglio F, Di Bella F, Franchi D, Furnari A, Marturano A, et al. General Practitioners and Gut Microbiota: Surveying Knowledge and Awareness in Italy. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2025; 7(4):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleTosetti, Cesare, Alessandra Belvedere, Massimo Berardino, Luciano Bertolusso, Rosanna Cantarini, Francesco Carofiglio, Floriana Di Bella, Daniele Franchi, Andrea Furnari, Alessandro Marturano, and et al. 2025. "General Practitioners and Gut Microbiota: Surveying Knowledge and Awareness in Italy" Gastrointestinal Disorders 7, no. 4: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040060
APA StyleTosetti, C., Belvedere, A., Berardino, M., Bertolusso, L., Cantarini, R., Carofiglio, F., Di Bella, F., Franchi, D., Furnari, A., Marturano, A., Mastronuzzi, T., Barone, R., Disclafani, G., Dubini, S., Prastaro, M., Scoglio, R., Rossi, A., & Grattagliano, I. (2025). General Practitioners and Gut Microbiota: Surveying Knowledge and Awareness in Italy. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 7(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040060








