Utility of Direct Fast Scarlet Staining in the Histopathological Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Short Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
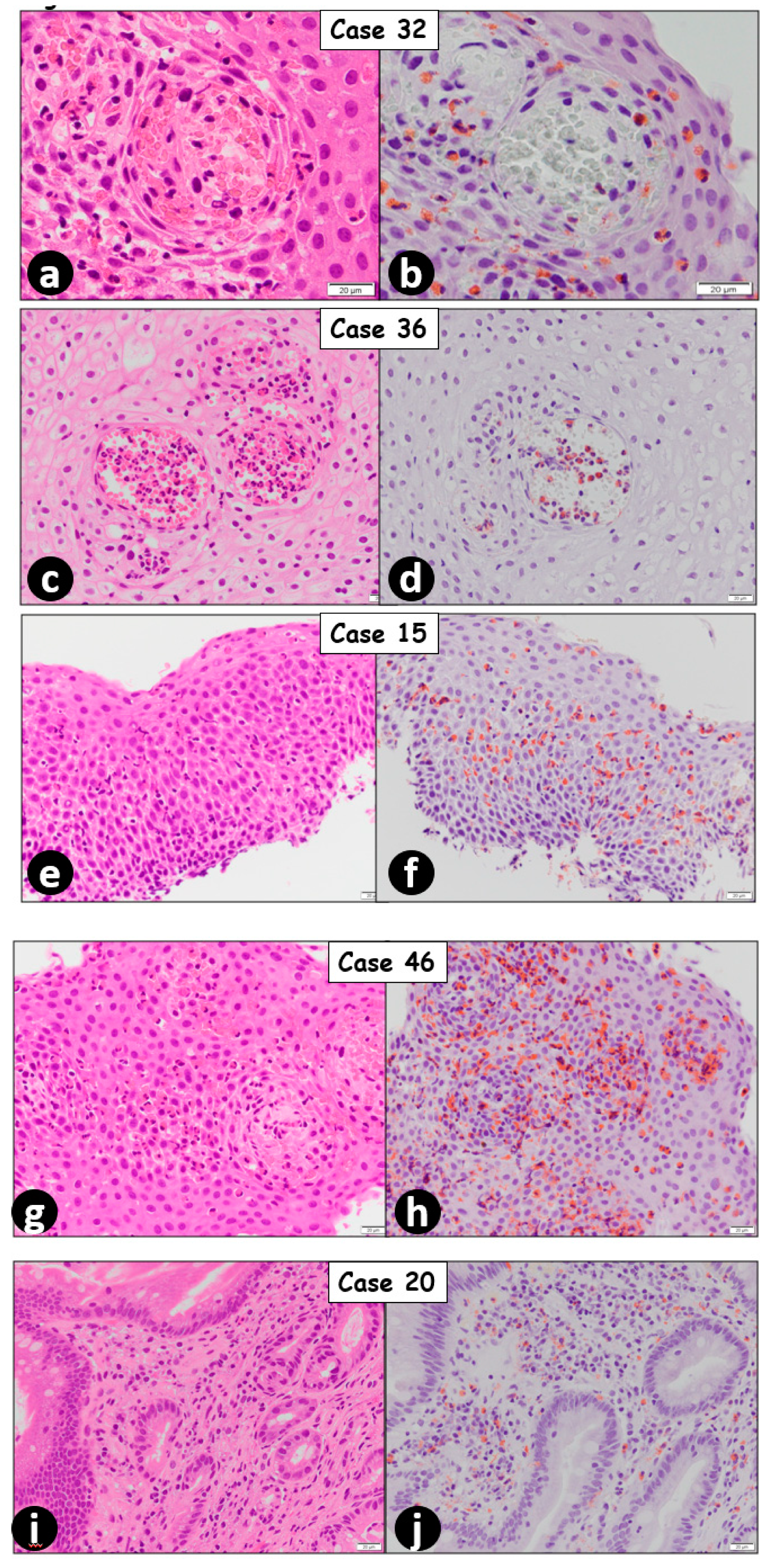
2. Results
3. Discussion
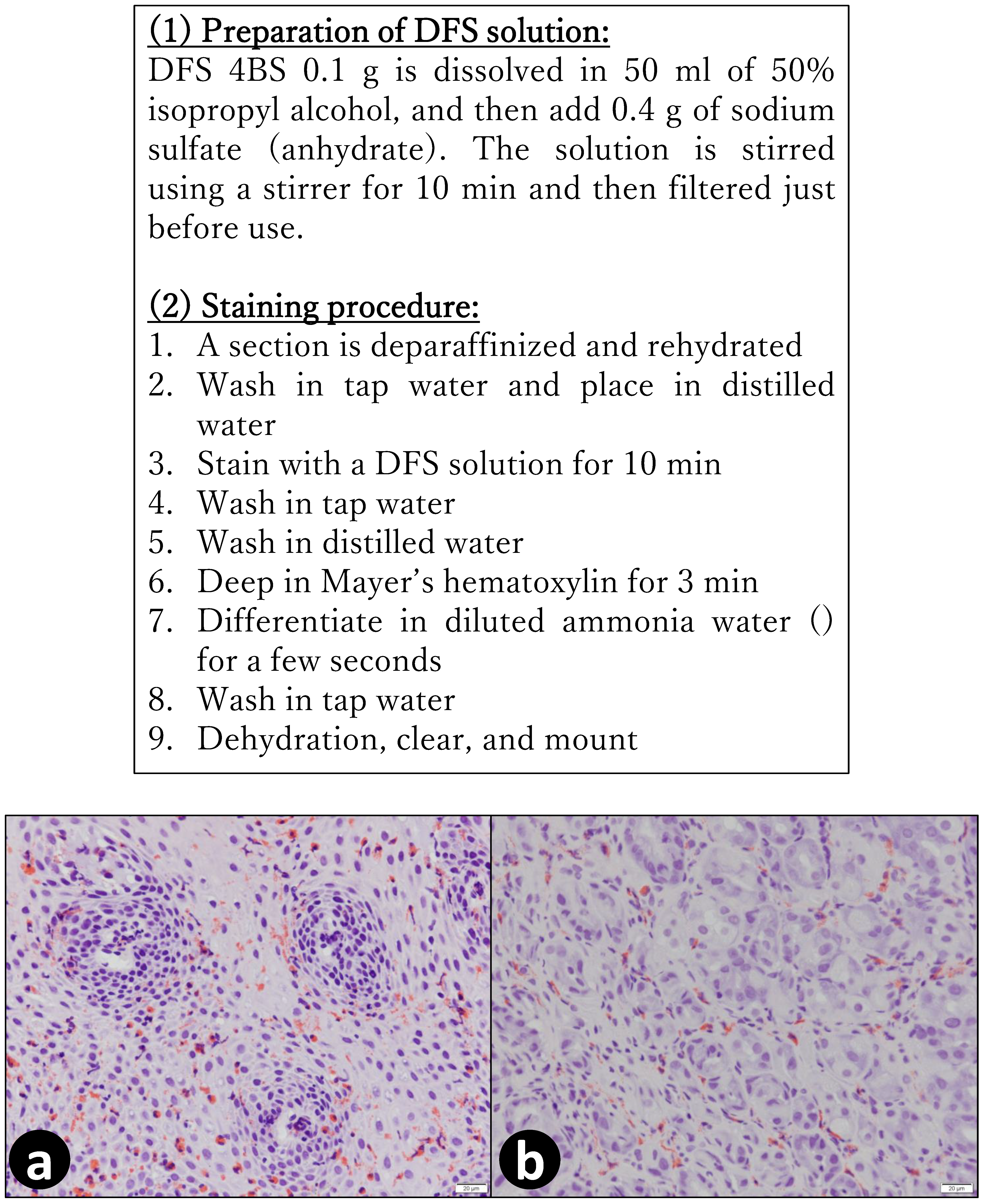
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liacouras, C.A.; Furuta, G.T.; Hirano, I.; Atkins, D.; Attwood, S.E.; Bonis, P.A.; Burks, A.W.; Chehade, M.; Collins, M.H.; Dellon, E.S.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 2011, 128, 3–20.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landres, R.T.; Kuster, G.G.; Strum, W.B. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 1978, 74, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, P.; Eggermont, E.; Marchal, G.; Geboes, K.; Jaeken, J.; Melchior, S. Eosinophilic infiltration of the oesophagus in an infant. Acta Paediatr. Belg. 1978, 31, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.G. Marked eosinophilia in esophageal mucosal biopsies. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1985, 9, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwood, S.E.; Smyrk, T.C.; Demeester, T.R.; Jones, J.B. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Collins, M.H.; Gupta, S.K.; Justinich, C.; Putnam, P.E.; Bonis, P.; Hassall, E.; Straumann, A.; Rothenberg, M.E.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: A systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1342–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, A.; von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Amil Dias, J.; Bove, M.; Gonzalez-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Numakura, T.; Moriyama, H.; Saito, R.; Shishikura, Y.; Shiihara, J.; Sugiura, H.; Ichinose, M. The first case of multiple pulmonary granulomas with amyloid deposition in a dental technician; a rare manifestation as an occupational lung disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grouls, V.; Helpap, B. Selective staining of eosinophils and their immature precursors in tissue sections and autoradiographs with Congo red. Stain Technol. 1981, 56, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, M.; Mehregan, A.H.; Mehregan, D.R. Staining of amyloid with cotton dyes. Arch. Dermatol. 1984, 120, 1184–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madokoro, Y.; Kato, H.; Yuasa, H.; Ootaka, N.; Mori, Y.; Mitake, S. A case of eosinophilic myositis presenting with myocarditis and cardiac embolism. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2015, 55, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saga, S. Staining of granules of eosinophils by DFS. Mod. Med. Lab. (Kensa-to-Gojyutsu) 2019, 47, 499–502. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.H.; Capocelli, K.; Yang, G.Y. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders Pathology. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.A.; Alexander, J.A.; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Elias, R.M.; Locke, G.R., 3rd; Talley, N.J. Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, S.; Chan, E.S.; Watson, W. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, N.; Kinoshita, Y. Eosinophilic esophagitis in Japan: Focus on response to acid suppressive therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, K.; Haruma, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Maruyama, Y.; Ayaki, M.; Tazaki, S.; Hisamoto, N.; Manabe, N.; Kamada, T.; Kawamoto, H. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics of eosinophilic esophagitis in Japan: A case-control study. Asia Pac. Allergy 2020, 10, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Mishiro, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kinoshita, Y. Suitable biopsy site for detection of esophageal eosinophilia in eosinophilic esophagitis suspected cases. Dig. Endosc. 2016, 28, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, H.; Amano, Y.; Kushiyama, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Kinoshita, Y. Eosinophilic esophagitis investigated by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in Japanese patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Honma, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Owaki, T.; Imai, M.; Sano, T.; Iwanaga, A.; Seki, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoshida, T.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in Japanese patients: A mild and slow-progressing disorder. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, F.J. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Incidence and Prevalence. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Kao, J.Y. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Update on management and controversies. BMJ 2017, 359, j4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Katzka, D.A.; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 679–692, quiz 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genevay, M.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Rougemont, A.L. Do eosinophil numbers differentiate eosinophilic esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, N.; Okimoto, E.; Shibagaki, K.; Nagano, N.; Ishihara, S. Similarity and difference in the characteristics of eosinophilic esophagitis between Western countries and Japan. Dig. Endosc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Takahashi, C.; Imamura, S. A case of nodular cutaneous amyloidosis. Amyloid production by infiltrating plasma cells. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1993, 15, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case No. | Sex (Female/Male) | Age (Years) | No. of Eosinophils/HPF | Final Diagnosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H&E-Stained Section | DFS-Stained Section | ||||
| 1 | Female | 55 | 3 | 0 | Glycogenic acanthosis |
| 2 | Female | 81 | 0 | 4 | GERD |
| 3 | Male | 52 | 10 | 42 | EoE |
| 4 | Female | 26 | 5 | 8 | Esophageal ulcer |
| 5 | Male | 85 | 0 | 0 | GERD |
| 6 | Male | 19 | 4 | 1 | GERD |
| 7 | Female | 18 | 0 | 0 | No esophageal lesion |
| 8 | Male | 60 | 13 | 30 | EoE |
| 9 | Male | 24 | 15 | 23 | EoE |
| 10 | Male | 63 | 5 | 8 | GERD |
| 11 | Male | 49 | 3 | 8 | GERD |
| 12 | Male | 13 | 1 | 5 | GERD |
| 13 | Male | 58 | 15 | 24 | EoE |
| 14 | Male | 12 | 0 | 3 | Hiatal herniation |
| 15 | Male | 24 | 62 | 133 | EoE |
| 16 | Male | 73 | 10 | 8 | GERD |
| 17 | Female | 66 | 3 | 0 | GERD |
| 18 | Male | 24 | 2 | 6 | GERD |
| 19 | Male | 49 | 5 | 30 | EoE |
| 20 | Female | 49 | 28 | 49 | EoE * |
| 21 | Female | 53 | 16 | 55 | EoE * |
| 22 | Female | 50 | 52 | 84 | EoE |
| 23 | Female | 49 | 30 | 34 | EoE |
| 24 | Male | 22 | 25 | 120 | EoE |
| 25 | Male | 57 | 37 | 58 | EoE |
| 26 | Female | 50 | 11 | 2 | GERD |
| 27 | Male | 25 | 6 | 15 | EoE |
| 28 | Female | 60 | 15 | 24 | EoE * |
| 29 | Male | 43 | 13 | 45 | EoE |
| 30 | Male | 35 | 22 | 21 | EoE |
| 31 | Female | 48 | 25 | 48 | EoE |
| 32 | Male | 80 | 3 | 27 | EoE |
| 33 | Female | 49 | 12 | 23 | EoE |
| 34 | Female | 50 | 13 | 26 | EoE |
| 35 | Female | 72 | 5 | 0 | GERD |
| 36 | Male | 25 | 98 | 183 | EoE |
| 37 | Female | 18 | 55 | 143 | EoE |
| 38 | Male | 49 | 3 | 0 | Barrett’s esophagus |
| 39 | Male | 55 | 0 | 0 | GERD |
| 40 | Male | 14 | 30 | 20 | EoE |
| 41 | Female | 51 | 10 | 1 | GERD |
| 42 | Male | 15 | 27 | 32 | EoE |
| 43 | Male | 14 | 62 | 96 | EoE |
| 44 | Female | 46 | 3 | 1 | Glycogenic acanthosis |
| 45 | Female | 51 | 15 | 31 | EoE |
| 46 | Female | 51 | 14 | 32 | EoE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, T.; Watanabe, N.; Kato, T.; Aoki, R.; Ogiso, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Tomita, E. Utility of Direct Fast Scarlet Staining in the Histopathological Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Short Report. Gastrointest. Disord. 2020, 2, 448-455. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040040
Tanaka T, Watanabe N, Kato T, Aoki R, Ogiso T, Sugiyama A, Tomita E. Utility of Direct Fast Scarlet Staining in the Histopathological Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Short Report. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2020; 2(4):448-455. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040040
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Takuji, Naoki Watanabe, Tomohiro Kato, Ryogo Aoki, Tomio Ogiso, Akihiko Sugiyama, and Eiichi Tomita. 2020. "Utility of Direct Fast Scarlet Staining in the Histopathological Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Short Report" Gastrointestinal Disorders 2, no. 4: 448-455. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040040
APA StyleTanaka, T., Watanabe, N., Kato, T., Aoki, R., Ogiso, T., Sugiyama, A., & Tomita, E. (2020). Utility of Direct Fast Scarlet Staining in the Histopathological Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Short Report. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 2(4), 448-455. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040040






