Per Oral Pyloromyotomy for Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature and Future Recommendations
Abstract
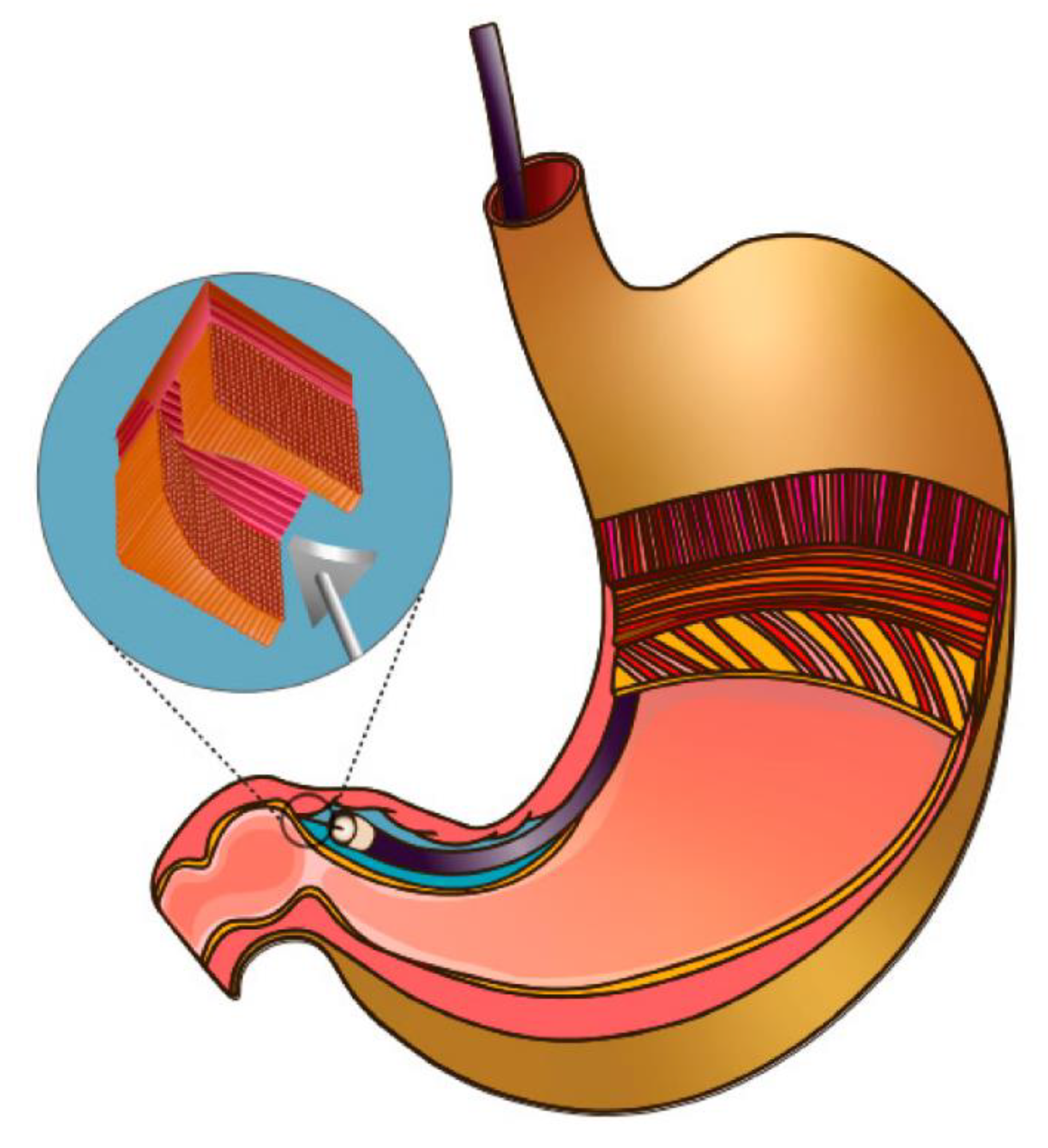
1. Introduction
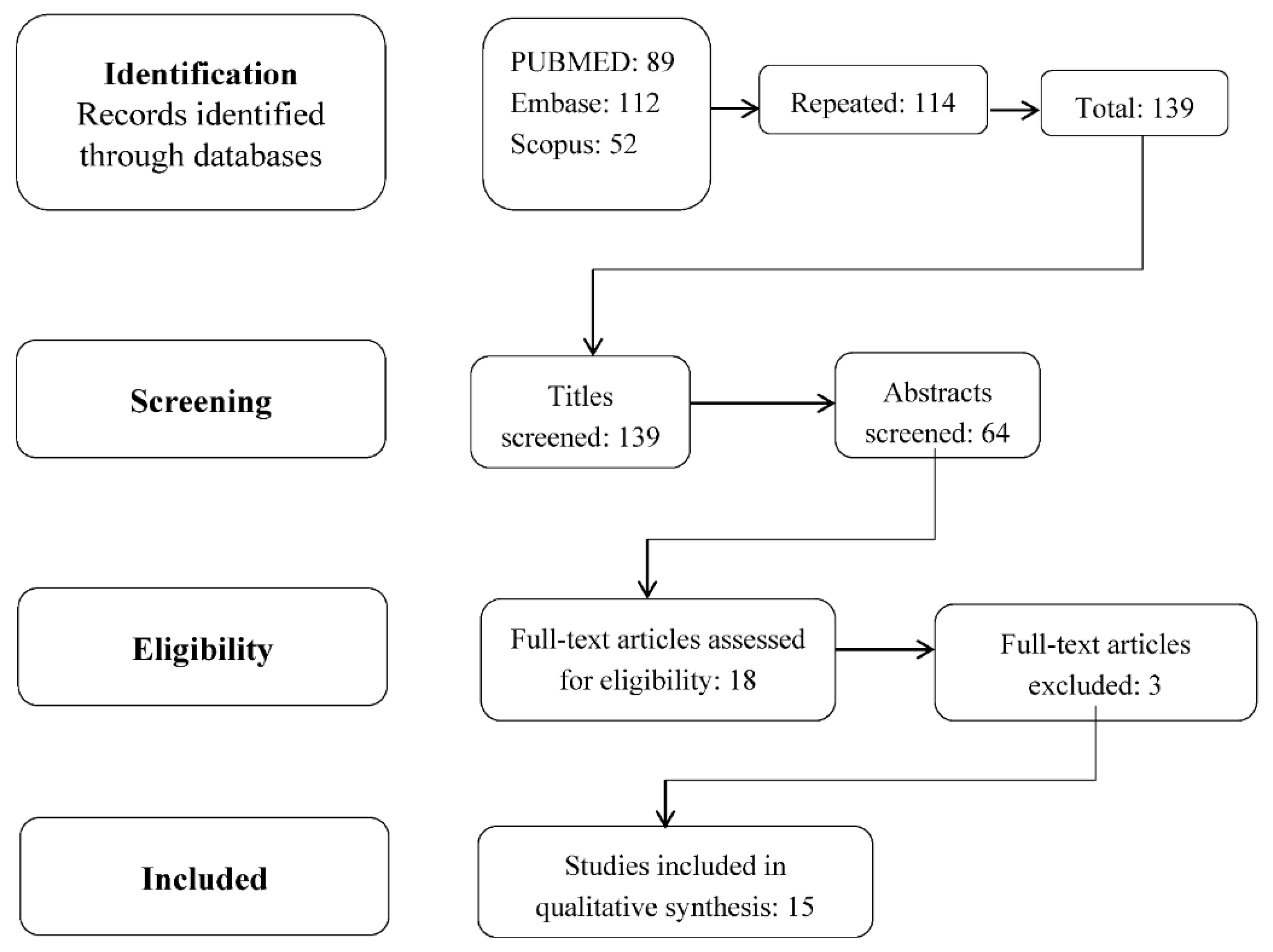
2. Methodology
3. Results and Data Synthesis
4. Discussion
5. Future Recommendations and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, J.H.; Pasricha, P.J. Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment of gastroparesis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos, D.J.; Sarosiek, I.; Loganathan, P.; McCallum, R.W. Diabetic gastroparesis: Current challenges and future prospects. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 29, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huzinga, J.D.; Lammers, W.J. Gut peristalsis is governed by a multitude of cooperating mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1–G8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, Z.; Sankineni, A.; Parkman, H.P. Assessing pyloric sphincter pathophysiology using EndoFLIP in patients with gastroparesis. Neurogastrenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, W.J.; Lin, M.S.; Agarwal, N.; Shaw, R.E. Evaluation of the pylorus with concurrent intraluminal pressure and EndoFLIP in patients with nausea and vomiting. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L.R.; Poole, D.P.; Thacker, M.; Furness, J.B. The involvement of nitric oxide synthase neurons in enteric neuropathies. Nerogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearin, F.; Camilleri, M.; Malagelada, J.R. Pyloric dysfunction in diabetics with recurrent nausea and vomiting. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.R.; Sarosiek, I.; Bashashati, M.; Alvarado, B.; McCallum, R.W. The Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Pyloroplasty Combined with Gastric Electrical Stimulation Therapy in Gastroparesis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2017, 21, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, I.; Forster, J.; Lin, Z.; Cherry, S.; Sarosiek, J.; McCallum, R. The addition of pyloroplasty as a new surgical approach to enhance effectiveness of gastric electrical stimulation therapy in patients with gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 134-e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, J.; Holvoet, L.; Caenepeel, P.; Verbeke, K.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J. Influence of intrapylotic botulinum toxin injecdtion on gastric emptying and meal-related symptoms in gastroparesis patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashab, M.A.; Stein, E.; Clarke, J.O.; Saxena, P.; Kumbhari, V.; Chander Roland, B.; Kalloo, A.N.; Stavropoulos, S.; Pasricha, P.; Inoue, H. Gastric per oral endoscopic myotomy for refractory gastroparesis:; First human endoscopic pyloromyotomy (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 78, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, Z.; Kataria, R.; Modayil, R.; Ehrlich, A.C.; Shcey, R.; Parkman, H.P.; Stavropoulos, S.N. Gastric Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the treatment of Refractory Gastroparesis: Early Experience. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Benezech, A.; Vitton, V.; Barthet, M. G-POEM with antro-pyloromyotomy for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: Mid-term follow-up and factors predicting outcome. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.B.; Fan, H.Z.; Meng, X.M.; Cristofaro, S.; Mekaroonkamol, P.; Dacha, S.; Li, L.Y.; Fu, X.L.; Zhan, S.H.; Cai, Q. Fluoroscopy-guided gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (G-POEM): A more reliable and efficient method for treatment of refractory gastroparesis. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.H.; Haskins, I.N.; Strong, A.T.; Plescia, R.L.; Allemang, M.T.; Butler, R.S.; Cline, M.S.; El-Hayek, K.; Ponsky, J.L.; Kroh, M.D. Per oral endoscopic pylormyotomy for refractory gastroparesis: Initial results from a single institution. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 5381–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaleh, M.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Xu, M.M.; Andalib, I.; Gaidhane, M.; Tyberg, A.; Saumoy, M.; Marchena, A.J.B.; Barthet, M. Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: A multicenter international experience. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomovitz, E.; Pescarus, R.; Cassera, M.A.; Sharata, A.M.; Reavis, K.M.; Dunst, C.M.; Swanström, L.L. Early human experience with per-oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (POP). Surg. Endosc. 2015, 29, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacha, S.; Mekaroonkamol, P.; Li, L.; Shahnavaz, N.; Sakaria, S.; Keilin, S.; Willingham, F.; Christie, J.; Cai, Q. Outcomes and quality-of-life assessment after gastric per-oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemang, M.T.; Strong, A.T.; Haskins, I.N.; Rodriguez, J.; Ponsky, J.L.; Kroh, M. How I Do It: Per-Oral Pyloromyotomy (POP). J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2017, 21, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, J.; Pagnon, L.; Hure, F.; Legros, R.; Crepin, S.; Fauchais, A.L.; Palat, S.; Ducrotté, P.; Marin, B.; Fontaine, S. Peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy is efficacious and safe for refractory gastroparesis: Prospective trial with assessment of pyloric function. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekaroonkamol, P.; Patel, V.; Shah, R.; Li, B.; Luo, H.; Shen, S.; Chen, H.; Shahnavaz, N.; Dacha, S.; Keilin, S.; et al. Association between duration or etiology of gastroparesis and clinical response after gastric per-oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekaroonkamol, P.; Patel, V.; Shah, R.; Li, T.; Li, B.; Tao, J.; Guan, Q.; Chen, H.; Shahnavaz, N.; Sakaria, S.; et al. 838 duration of the disease rather than the etiology of gastroparesis is the key predictive factor for linical response after gastric per oral endoscopy pyloromyotomy (GPOEM). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, AB119–AB120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, H.M.; Carbray, J.; Ujiki, M.B. Initial Experience with Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy, with Description and Video Technique. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 1706–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.T.; Landreneau, J.P.; Cline, M.; Kroh, M.D.; Rodriguez, J.H.; Ponsky, J.L.; El-Hayek, K. Per-Oral Pyloromyotomy (POP) for medically refractory post-surgial gastroparesis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, T.; Elkholy, S.; Xu, M.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Qin, W.; Cai, M.; Zhou, P. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) as a Treatment for Refractory Gastroparesis: Long-Term Outcomes. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 6409698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.; Strong, A.T.; Haskins, I.N.; Landreneau, J.P.; Allemang, M.T.; El-Hayek, K.; Villamere, J.; Tu, C.; Cline, M.S.; Kroh, M.; et al. Per-oral Pyloromyotomy (POP) for Medically Refractory Gastroparesis: Short term results from the First 100 Patients at a High Volume Center. Ann. Surg. 2018, 268, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Type | # Patients |
|---|---|---|
| Kashab 2013 [11] | Retrospective | 30 |
| Malik 2018 [12] | Case Series | 13 |
| Gonzalez 2017 [13] | Retrospective | 29 |
| Xue 2017 [14] | Single-center cohort | 14 |
| Rodriguez 2017 [15] | Prospective | 100 |
| Kahaleh 2018 [16] | Retrospective | 33 |
| Shlomovitz 2015 [17] | Retrospective | 7 |
| Dacha 2017 [18] | Retrospective | 16 |
| Allemang 2017 [19] | Retrospective | 57 |
| Jacques 2019 [20] | Prospective | 20 |
| Mekaroonkamol 2019 [21] | Retrospective | 40 |
| Mekaroonkamol 2018 [22] | Retrospective | 30 |
| Hedberg 2019 [23] | Retrospective | 17 |
| Strong 2019 [24] | Retrospective | 38 |
| Xu 2018 [25] | Retrospective single center | 16 |
| Study | Etiologies | Outcome Measures | Efficacy | Symptom Resolution | Follow up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kashab [11] | 11 Diabetic 12 post-surgical 7 idiopathic | GES Gastroparesis symptoms | 26/30 pts | Nausea 29/30 Vomiting 19/30 Abdominal pain 22/30 Weight improvement 28/30 | 5.5 |
| Malik [12] | 1 Diabetic 8 Post-surgical 4 idiopathic | GES PAGI-SYMEndoFLIP | 8/13 pts | Vomiting 4/13 Appetite improvement 4/13 | 3 |
| Gonzalez [13] | 7 Diabetic 5 post-surgical 15 idiopathic 2 other | GES GCSI | 23/29 pts | All GCSI | 6 |
| Rodriguez [15] | 12 Diabetic 8 post-surgical 27 idiopathic | GES GCSI | Not documented | All GCSI | 3 |
| Kahaleh [16] | 7 Diabetic 12 post-surgical 13 idiopathic 1 other | GES GCSI | 28/33 pts | All GCSI | 11.5 |
| Schlomovitz [17] | 2 post-surgical 4 idiopathic 1 other | GES Gastroparesis Symptoms | 6/7 pts | Nausea 7/7 | 6.5 |
| Dacha [18] | 9 Diabetic 1 post-surgical 5 idiopathic 1 post-infectious | GES GCSI SF36 | 13/16 pts | nausea and vomiting and early satiety significantly improved but not bloating | 12 |
| Jacques [20] | 10 diabetic 1 post-surgical 4 idiopathic 5 other | GES GCSI | 20/20 pts | All GCSI | 3 |
| Mekaroonkamol [22] | 12 Diabetic 5 post-surgical 12 idiopathic 1 post-infectious | GES GCSISF36 | 24/30 pts | Nausea and early satiety | 18 |
| Study | Gpoem Duration (min) | Myotomy Length (cm) | Hospital Stay (Days) | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kashab [11] | 72 ± 42 | 2.6 ± 2.3 | 3.3 | 1 pneumoperitoneum 1 pre-pyloric ulcer |
| Malik [12] | 119 ± 23 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 1.4 | 1 pulmonary embolism |
| Gonzalez [13] | 47 | not documented | not documented | 5 pneumoperitoneum 2 bleeding 1 perigastric abscess 1 pre-pyloric stricture |
| Kahaleh [16] | 77.6 (37–255) | 3.34 | 5.4 | 1 bleeding 1 ulcer |
| Schlomovitz [17] | 90–120 | not documented | not documented | 1 pre-pyloric ulcer 1 bleeding |
| Mekaroonkamol [22] | 48.3 ± 16.5 | not documented | 2.4 ± 1 | 1 pneumoperitoneum |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chavez, L.O.; Galura, G.; Robles, A.; Bustamante-Bernal, M.A.; McCallum, R. Per Oral Pyloromyotomy for Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature and Future Recommendations. Gastrointest. Disord. 2020, 2, 415-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040038
Chavez LO, Galura G, Robles A, Bustamante-Bernal MA, McCallum R. Per Oral Pyloromyotomy for Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature and Future Recommendations. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2020; 2(4):415-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleChavez, Luis O., Gian Galura, Alejandro Robles, Marco A. Bustamante-Bernal, and Richard McCallum. 2020. "Per Oral Pyloromyotomy for Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature and Future Recommendations" Gastrointestinal Disorders 2, no. 4: 415-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040038
APA StyleChavez, L. O., Galura, G., Robles, A., Bustamante-Bernal, M. A., & McCallum, R. (2020). Per Oral Pyloromyotomy for Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature and Future Recommendations. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 2(4), 415-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord2040038





