Abstract
Plummer-Vinson syndrome (PVS) is defined by the classic triad of dysphagia, esophageal web, and iron deficiency. It is a rare entity that remains poorly understood, and we describe our experience in diagnosing and management. Treatment for patients with PVS begins with aggressive dilation of the esophageal web (stricture), which has specific histopathology findings, thus helping to restore nutrition and facilitate iron absorption while also identifying other possible etiologies of iron deficiency, specifically underlying autoimmune conditions. We have reviewed the literature to place our experience in perspective and conclude that PVS now warrants a re-definition and a new perspective, which we discuss in this article.
1. Introduction
Plummer-Vinson syndrome (PVS), or Kelly-Patterson syndrome (in the United Kingdom), is a rare entity defined by the classic tried of dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia, and esophageal webs. It is typically described in Caucasian females between the ages of 40 and 70 [1], and named after Dr. Henry Stanley Plummer and Dr. Porter Paisley Vinson from the Mayo Clinic. In 1912 Dr. Plummer [2] published a case series first describing it in patients with long standing iron deficiency anemia, dysphagia, and “spasm” of the upper esophagus. Dr. Vinson in 1919 then published a series of cases with “angulation” of the esophagus attributed to a similar entity as Dr. Plummer had previously described [3]. The term Paterson-Kelly syndrome comes from two British laryngologists, Dr. Donald Ross Paterson and Dr. Adam Brown-Kelly, who published a case series independently in 1919 describing the same syndrome and identifying the association with esophageal cancer [4,5]. However, the term PVS seems to be the current preferred term.
Despite over 100 years of knowledge of this syndrome, the pathophysiology of the web formation remains poorly understood, with theories focusing on iron deficiency or part of an autoimmune spectrum. Dysphagia associated with PVS is accompanied by iron deficiency which frequently resolves gradually with iron replacement [6]. In some patients, however, the web does not resolve and requires endoscopy with dilation to reverse the dysphagia and restore enteral nutrition [7,8,9,10]. From our clinical experience we have not found a true “esophageal web” in PVS, but rather a tight fibrotic stricture with chronic inflammatory cells on biopsy at the level of the upper esophageal sphincter requiring aggressive dilation and sometimes repeat dilations to sustain resolution. We also identify other important clinical and autoimmune characteristics, suggesting that the pathophysiology of this syndrome needs to be updated and the understanding of this entity given redefinition.
2. Results
Three patients with PVS were identified after reviewing 134 esophagogastroduodenoscopies (EGD) performed by a single gastroenterologist over the course of 15 months. The demographics of all patients who underwent EGD during the period included in the study are summarized in Table 1. All three patients were Hispanic females, mean age 52.7 (46 to 57). The initial presenting complaint for all three patients was chronic dysphagia. All three patients had reported iron deficiency anemia. Two of the three patients were already on iron replacement at time of referral and their anemia had resolved at time of initial evaluation in our system. All patients had a prior history of an underlying autoimmune disorder including celiac disease, pernicious anemia, systemic lupus erythematosus, and autoimmune dementia. Specifically, the following antibody profiles were elucidated in our patients: positive antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-parietal cell antibodies, and intrinsic factor antibodies (Table 2).

Table 1.
Demographics data of the 134 patients who underwent upper endoscopies over the 15-month period of the study.

Table 2.
Initial presenting labs of the three patients found to have Plummer-Vinson syndrome (PVS) and the dose of iron replacement they were started on.
Barium swallow demonstrated a focal linear filling defect in the posterior aspect of proximal esophagus suggestive of an esophageal web with moderate luminal narrowing (Figure 1a,b). High-resolution esophageal manometry showed some retrograde movement into the pharynx with wet swallows and intermittent coughing with weak pharyngeal contractions. The smooth muscle portion of the esophagus had normal manometric findings (Figure 2).
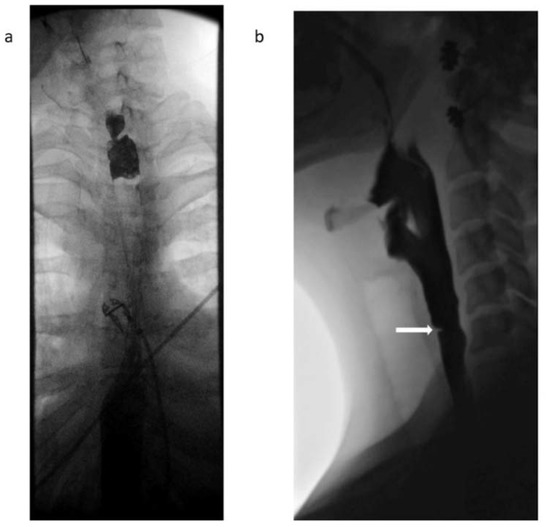
Figure 1.
(a): Barium swallow from patient 2 showing proximal esophageal narrowing at level of C6-C7. (b) Lateral view of the neck obtained during esophagram with barium demonstrates an eccentric thin mucosal membrane located anteriorly projecting into the esophageal lumen at the level of C6, expected location of the cricopharyngeus impression.
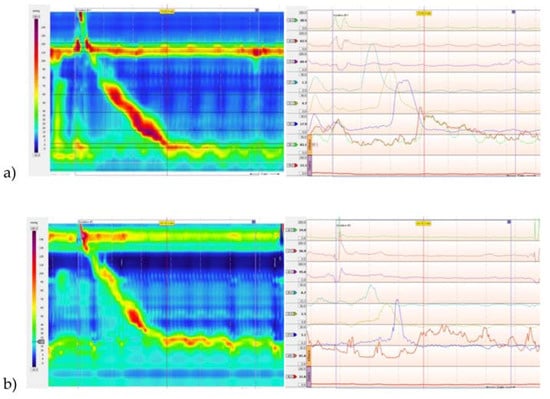
Figure 2.
(a) High-resolution esophageal motility study from patient 1 showing normal lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure with normal relaxation of the LES. The amplitude of the peristaltic contractions are normal in the smooth muscle portion of the esophagus. Striated muscle function was not normal and there appeared to be some retrograde movement into the pharynx with wet swallows and intermittent coughing. The fleck of red above the upper sphincter with the swallow suggests some retention and pharyngeal presence of the water swallowed—corresponding to food if the patient was eating. The upper sphincter relaxation appeared to be present but pharyngeal contractions were weak. (b) Example of a normal high-resolution esophageal motility study.
In patient 1 the EGD demonstrated a tight proximal fibrotic stricture that was dilated to 12 mm with a through the scope balloon dilator technique (Table 3).

Table 3.
Initial endoscopy findings and the interventions performed on the three patients with Plummer Vinson Syndrome.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in patient 2 showed a tight stenosis just below the cricopharyngeus (Figure 3), preventing passage of either an adult or neonatal endoscope. Savary dilators passed with fluoroscopic monitoring and over a guidewire were used to dilate the tight stenosis to 8 mm initially and on subsequent endoscopes up to 20 mm in diameter (Table 3).
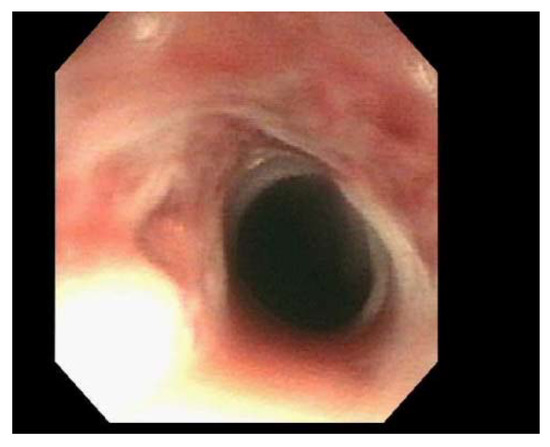
Figure 3.
Endoscopic visualization of a tight stenosis at the cricopharyngeus preventing passage of a standard adult endoscope, prior to dilation with Savor dilators. This endoscopy image is from patient 2.
In patient 3 the EGD showed two benign areas of intrinsic stenosis at 15 and 20 cm from the incisors that were smooth and not ulcerated. The endoscope could not be passed with either adult or pediatric endoscopes (Figure 4a). Dilation was performed with Savary dilators up to 11 mm with a guidewire under fluoroscopic monitoring (Table 3). These webs were biopsied during EGD with the microscopy showing chronic inflammatory cells, consisting of mostly intramucosal lymphocytes, and evidence of regenerating esophageal squamous epithelial changes, consisting of basal zone hyperplasia and elongation of the papillae (Figure 4b).
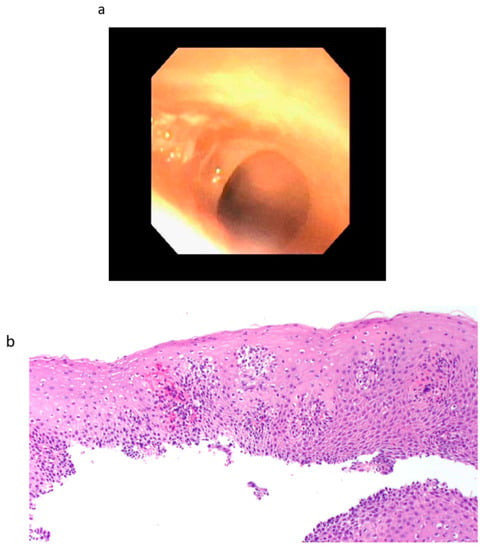
Figure 4.
(a) Endoscopic finding from patient 3 of a tight stenosis in the upper esophagus prior to dilation with Savory dilators. (b) Microscopic section (Hematoxylin and Eosin stain; 20X) from biopsy of the esophageal web (stricture) in patient 3, showing chronic inflammatory cells (mostly lymphocytes). In addition, regenerative changes are also seen, consisting of basal zone hyperplasia and elongation of papillae.
Following initial dilations, all patients were placed on oral iron supplementation and possible underlying causes of their anemia were investigated. One patient had a positive tissue transglutaminase antibody test for celiac disease, one had pernicious anemia with positive intrinsic factor and anti-parietal cell antibody, and the third had a positive anti-nuclear antibody finding. Two of the patients required subsequent EGDs with dilation for return of dysphagia after 39 days and 55 days and a 20 mm size dilation was achieved. Following serial dilation of the esophageal stricture and correction of iron replacement, all three patients have had sustained relief of dysphagia with up to one year of follow up.
3. Discussion
These three cases of PVS that we present all required an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy with challenging dilations of an esophageal stricture leading to resolution of this dysphagia. Patients were thus able to resume full oral feedings that included iron replacement. All EGDs showed a tight proximal stricture at or just below the upper esophageal sphincter level requiring endoscopic dilation in two cases with Savary dilator methods and fluoroscopy with guidewire in order to break the fibrotic strictures; one continues to require intermittent dilations. Pathology from biopsy of these strictures documented inflammation and fibrosis.
These cases are also unique because they all involved Hispanic females instead of the typically described demographics of PVS involving only Caucasian females. Our three patients all had evidence of abnormal autoimmune serology, including thyroid disease, celiac disease, achlorhydria, and atrophic gastritis or a positive anti-nuclear antibody. These have all been reported in the literature to be more prevalent in PVS patients [11,12]. However, what is particularly relevant in these PVS patients is the findings of celiac disease, pernicious anemia, achlorhydria, and atrophic gastritis, which were all autoimmune conditions that can explain why there is an accompanying iron deficiency anemia.
The pathogenesis of web formation remains poorly understood and there have been multiple proposed theories with iron deficiency being the most extensively studied and widely accepted hypothesis. It has been proposed that reduction in activity of iron-dependent oxidative enzymes due to iron deficiency, results in gradual degradation of the pharyngeal muscles and atrophy of the mucosa overlying them, leading to the development of webs [13,14,15]. However, this theory does not explain why webs are located in the upper esophagus that is lined with stratified squamous epithelium, which has relatively slower turnover compared to the mucosa of the small or large intestine [15]. Esophageal webs have also been described in patients with epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica recessive (EBDR) in the absence of iron deficiency and were responsive to balloon dilation [16]. Another theory that has been proposed is the possible existence of ectopic gastric mucosa in the upper esophagus causing local inflammation and web formation. However, transition of ectopic gastric mucosa to an inflammatory state requires H. Pylori infection, and this was not observed in our patients or the literature [17]. Finally, it has been hypothesized that the associated autoimmune syndromes could contribute to increased inflammation, leading to web formation in the proximal esophagus. Our series documented this “rich” serological presence of autoimmune entities and could also explain the potential for chronicity that was observed in one of our patients who had positive ANA serology.
Because PVS is a rare syndrome, the data on modern day prevalence is limited. PubMed was used to review the latest literature on PVS. Analysis of case reports published in the English language literature during 1999–2005 revealed 28 adult patients with PVS [1]. Twenty of these patients underwent a dilation of the esophageal web; in one patient the web was disrupted endoscopically using biopsy forceps [1,18], and in one patient the web was resected using microlaryngosurgery. [1,19] These findings suggest that esophageal “webs” did not resolve with iron replacement in most cases and required dilation or disruption for resolution. A study performed in South Wales in the 1960s screened 1994 men and 2346 women for post-cricoid web in patients complaining of dysphagia. They found that 8.4–22.4% of women with dysphagia and none of the men had a post cricoid web [20]. Another recent large retrospective study performed in Morocco reviewed all 135 cases of PVS at a single center managed between 1993 and 2011. All of these patients underwent endoscopic dilation and iron replacement with 69% reporting complete resolution of dysphagia at follow-up visit [21]. A retrospective study performed over the course of 10 years in Bangalore, India identified 132 patients with PVS and found 85.6% to be women. They also found that 90.7% of patients with PVS had complete relief of their dysphagia with a single session of Savary-Gilliard bougie dilation [10]. These studies highlight how rare this syndrome is and the poor data regarding its actual prevalence. Therefore, one theory that could be proposed to explain the decreasing prevalence of PVS is that “modern” medicine focuses on a better nutritional diet, as well as improved early recognition of iron deficiency [15]. Particularly the evolving presence of celiac disease, not a frequently recognized entity in the past, but a very important and under-recognized etiology of unexplained iron deficiency in women. There has been an increased awareness of this entity along with widespread empiric use of gluten-free diets in recent years [15]. In addition, iron supplements are invariably promoted in the average diet.
Historically, there is a reported association between PVS with squamous cell carcinoma in the post cricoid location with rates of malignant transformation reported between 4–16% [1,10,15,20,22]. The exact mechanism for progression to cancer is unknown. One hypothesis was the limited expertise available to reverse strictures by successful dilations. Therefore, chronic inflammation in the stricture continued with some patients progressing to malignant degeneration [22]. Therefore this background of iron deficiency could be explained by poor nutrition due to chronicity of the non-dilated esophageal stricture. Currently, there are no formal guidelines for surveillance endoscopies to screen for squamous cell carcinoma. Some experts have recommended annual EGDs for screening, while others recommend an EGD evaluation if symptoms return [1,15,21].
In conclusion, our new observations give fresh perspectives and definition to an “old entity,” namely: (1) Hispanic females can present with PVS, in contrast to primarily Caucasian females described in the literature; (2) The association between PVS and autoimmune syndromes offers an explanation for their iron deficiency; (3) The “web” is actually a tight fibrotic stricture requiring aggressive endoscopic dilation to restore and maintain oral nutrition, which then permits more iron absorption from food. We hope our colleagues Plummer, Vinson, Kelly, and Patterson can rest in peace knowing these important observations are still being unraveled and new explanations are being advanced to fully explain their very astute observations.
4. Materials and Methods
All endoscopies performed at University Medical Center in El Paso, Texas between April of 2019 and June of 2020 performed by gastroenterologist Dr. Richard McCallum were reviewed for findings of esophageal web formation. All patients found to have an esophageal web and the clinical presentation consistent with Plummer-Vinson syndrome were included in the study. The initial clinical presentation was reviewed and documented. The three patients found to have Plummer-Vinson syndrome were followed in clinic for at least 12 months after the initial endoscopy and their response to therapy was reviewed and compared.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D.H. and R.M.; methodology, J.D.H. and R.M.; validation, J.D.H., O.P., J.D., and R.M.; formal analysis, J.D.H. and V.B.; investigation, J.D.H. and R.M.; writing–original draft preparation, J.D.H. and V.B.; writing–review & editing, J.D.H., V.B., and R.M.; supervision, R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Novacek, G. Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2006, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, H.S. Diffuse dilation of the oesophagus without anatomical stenosis (cardiospasm) a report of 91 cases. JAMA 1912, 58, 2013–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, P.P. A case of cardiospasm with dilation and angulation of oesophagus. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1919, 3, 623–627. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.B. Spasm at the entrance of the oesophagus. J. Laryngol. Rhinol. Otol. 1919, 34, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, D.R. A clinical type of dysphagia. J. Laryngol. Rhinol. Otol. 1919, 34, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, M. The association between webs, iron and post-cricoid carcinoma. Postgrad. Med. J. 1974, 50, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, D.; Bansal, D.; Malu, A. Revisiting Plummer Vinson syndrome. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyler, A.R.; Yurdaydin, C.; Bahar, K.; Goren, A.; Soykan, I.; Uzunalimoglu, O. Dilation therapy of upper esophageal webs in two cases of Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Endoscopy 1996, 28, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M.; Kohmoto, M.; Arafa, U.A.; Shiba, M.; Watanabe, T.; Tominaga, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Saeki, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Plummer-Vinson syndrome successfully treated by endoscopic dilatation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 2348–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Malipatel, R.; Devarbhavi, H. Plummer-Vinson syndrome: A decade’s experience of 132 cases from a single center. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2020. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Midha, V.; Sood, N.; Bansal, M. Paterson Kelly syndrome in celiac disease. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2005, 53, 991–992. [Google Scholar]
- Medrano, M. Dysphagia in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and iron deficiency anemia. MedGenMed 2002, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamura, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Inaki, S.; Mori, T. Esophageal web in Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Laryngoscope 1988, 98, 994–998. [Google Scholar]
- Atmatzidis, K.; Papaziogas, B.; Pavlidis, T.; Mirelis, C.; Papaziogas, T. Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Dis. Esophgagus 2003, 16, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Bakshi, S.S.; Soni, N.; Chhavi, N. Iron deficiency anemia and Plummer-Vinson syndrome: Current insights. J. Blood Med. 2017, 8, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillemeier, C.; Touloukian, R.; McCallum, R.; Gryboski, J. Esophageal web: A previously unrecognized complication of epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatrics 1981, 67, 678–682. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, J.T.; Monto, R.W. Syndrome of anemia, dysphagia and glossitis (plummer vinson syndrome). N. Eng. J. Med. 1953, 249, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, T.; Shibata, T.; Okubo, M.; Yoshioka, D.; Ishizuka, T.; Sumi, K.; Kawamura, T.; Nagasaka, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Arisawa, T.; et al. A case of plummer-vinson syndrome showing rapid improvement of Dysphagia and esophageal web after two weeks of iron therapy. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2014, 8, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanai, F.M.; Mohamed, A.E.; Karawi, M.A. Dysphagia caused by Plummer-Vinson syndrome. Endoscopy 2001, 33, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitahara, S.; Ohmae, Y.; Ogura, M.; Matumury, Y. The operation of upper esophageal web in Plummer-Vinson syndrome: A case report. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1999, 26, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.R.; Sinacori, J.T. Plummer-Vinson syndrome heralded by postcricoid carcinoma. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2007, 28, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.M. The importance of plummer-vinson syndrome in the aetiology of carcinoma of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Postgrad. Med. J. 1961, 37, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).