The Predictive Factors of Responsiveness to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
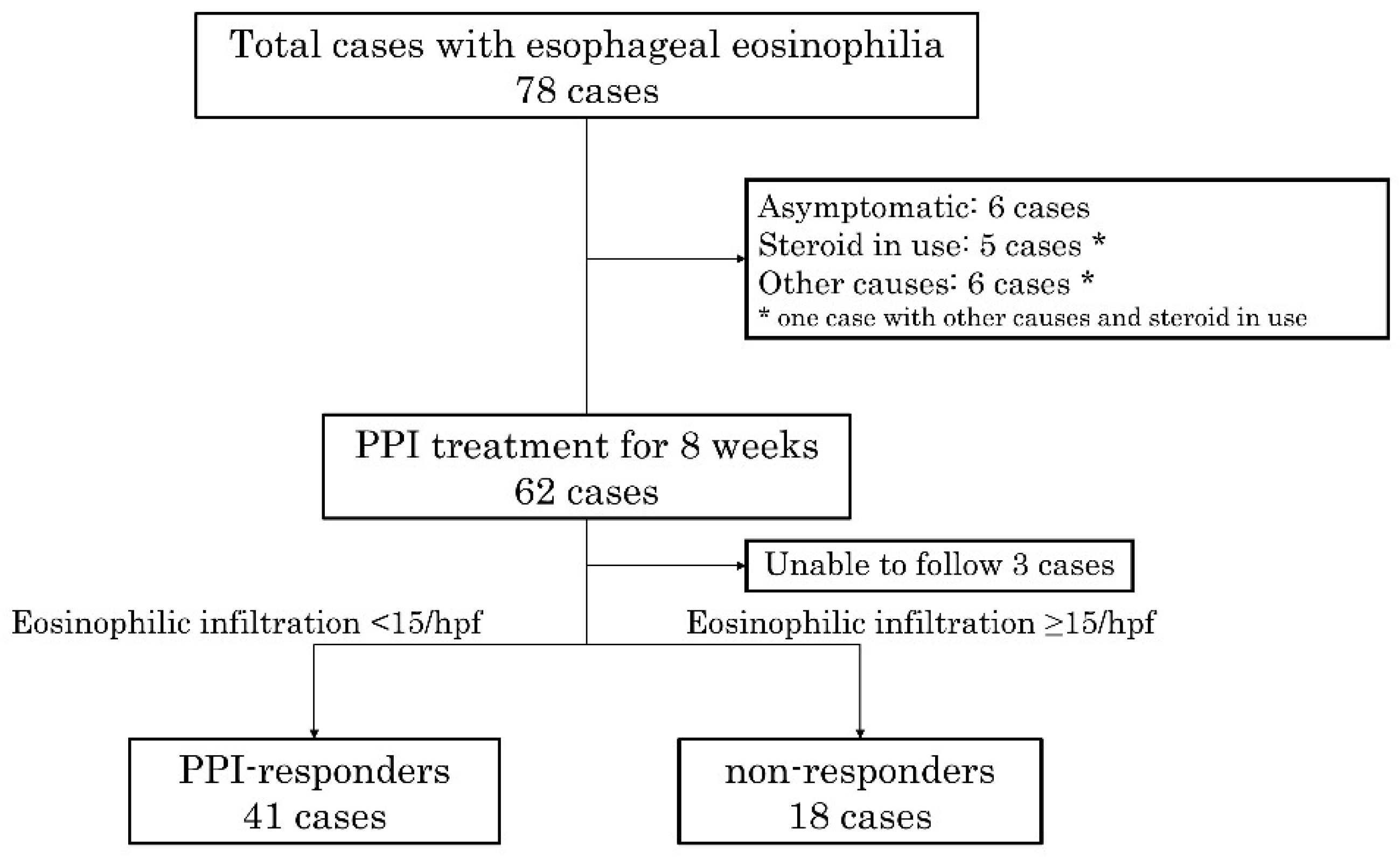
2.1. Study Subjects
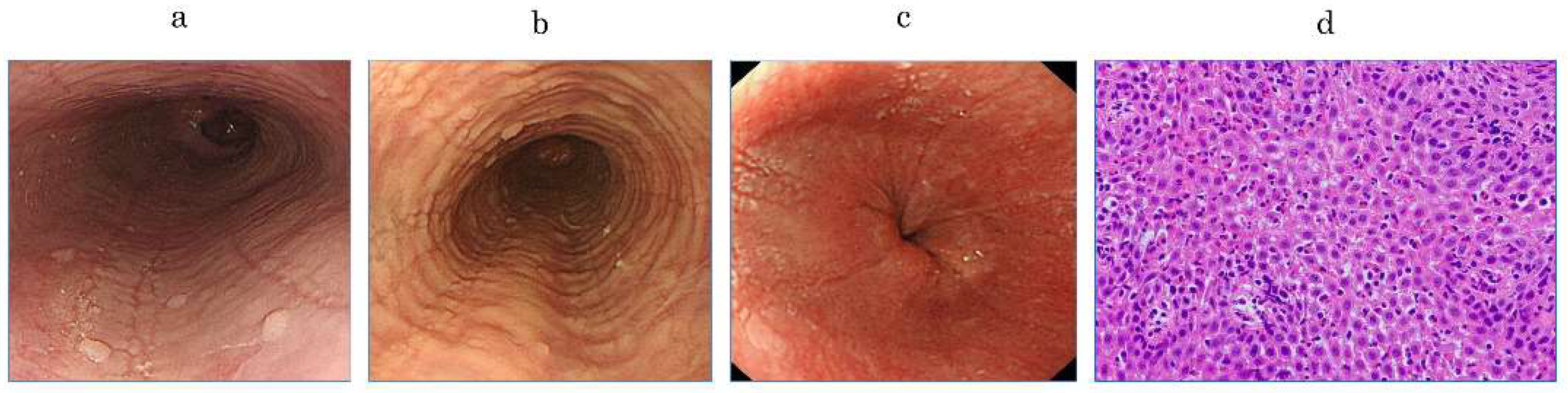
2.2. Endoscopic Agreement
2.3. Rate of PPI-Responders and Non-Responders and Their Characteristics
2.4. Factors Associated with PPI-Responders in Patients with Esophageal Eosinophilia
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Study Design
4.2. Endoscopic Assessment and Biopsy Protocol
4.3. Definition of PPI Responsiveness
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGowan, E.C.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis from an Allergy Perspective: How to Optimally Pursue Allergy Testing & Dietary Modification in the Adult Population. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.E. Molecular, genetic, and cellular bases for treating eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Ferrando-Lamana, L.; Ripoll, C.; Hernandez-Alonso, M.; Mateos, J.M.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Duenas, C.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, N.; Quintana, E.M.; Gonzalez-Nunez, M.A. Esophageal eosinophilic infiltration responds to proton pump inhibition in most adults. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.; Perez-Martinez, I.; Tenias, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Sugawa, T.; Tanaka, F.; Tatsuwaki, H.; Okuyama, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamamori, K.; Wada, R.; Ohtani, K.; Uno, H.; et al. A multicenter study on the prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis and PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilic infiltration. Intern. Med. 2012, 51, 3235–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, K.; Adachi, K.; Kowari, K.; Mishima, Y.; Imaoka, H.; Kadota, C.; Koshino, K.; Miyake, T.; Kadowaki, Y.; Furuta, K.; et al. A Japanese case of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomomatsu, Y.; Yoshino, J.; Inui, K.; Wakabayashi, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Miyoshi, H.; Kosaka, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Torii, Y. Clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis: Ten Japanese cases. Dig. Endosc. 2013, 25, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Katzka, D.A.; Dellon, E.S. Proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: A historical perspective on a novel and evolving entity. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2015, 107, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Katzka, D.A. American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 679–692, quiz 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, A.; von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Amil Dias, J.; Bove, M.; Gonzalez-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Molina-Infante, J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Zevit, N.; Spechler, S.J.; Attwood, S.E.; Straumann, A.; Aceves, S.S.; et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moawad, F.J.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Ally, M.R.; Chen, Y.J.; Maydonovitch, C.L.; Wong, R.K. Eosinophilic oesophagitis and proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia have similar clinical, endoscopic and histological findings. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiao, D.; Ishimura, N.; Maruyama, R.; Ishikawa, N.; Nagase, M.; Oshima, N.; Aimi, M.; Okimoto, E.; Mikami, H.; Izumi, D.; et al. Similarities and differences among eosinophilic esophagitis, proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia, and reflux esophagitis: Comparisons of clinical, endoscopic, and histopathological findings in Japanese patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Speck, O.; Woodward, K.; Gebhart, J.H.; Madanick, R.D.; Levinson, S.; Fritchie, K.J.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics do not reliably differentiate PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis in patients undergoing upper endoscopy: A prospective cohort study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Katzka, D.A.; Gisbert, J.P. Review article: Proton pump inhibitor therapy for suspected eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Arias, A.; Molina-Infante, J. Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitor Drugs for Inducing Clinical and Histologic Remission in Patients with Symptomatic Esophageal Eosinophilia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 13–22.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Speck, O.; Woodward, K.; Covey, S.; Rusin, S.; Gebhart, J.H.; Chen, X.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. Markers of eosinophilic inflammation for diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis and proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: A prospective study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Rivas, M.D.; Hernandez-Alonso, M.; Vinagre-Rodriguez, G.; Mateos-Rodriguez, J.M.; Duenas-Sadornil, C.; Perez-Gallardo, B.; Ferrando-Lamana, L.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, N.; Banares, R.; et al. Proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia correlates with downregulation of eotaxin-3 and Th2 cytokines overexpression. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, T.; Dellon, E.S.; Moawad, F.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Rothenberg, M.E. Transcriptome analysis of proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia reveals proton pump inhibitor-reversible allergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakura, N.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tanaka, F.; Tanigawa, T.; Yamagami, H.; Shiba, M.; Tominaga, K.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, K.; Koike, T.; et al. Basophil infiltration in eosinophilic oesophagitis and proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savarino, E.V.; Tolone, S.; Bartolo, O.; de Cassan, C.; Caccaro, R.; Galeazzi, F.; Nicoletti, L.; Salvador, R.; Martinato, M.; Costantini, M.; et al. The GerdQ questionnaire and high resolution manometry support the hypothesis that proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia is a GERD-related phenomenon. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedika, R.R.; Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Potential anti-inflammatory effects of proton pump inhibitors: A review and discussion of the clinical implications. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2312–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rhijn, B.D.; Weijenborg, P.W.; Verheij, J.; van den Bergh Weerman, M.A.; Verseijden, C.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; de Jonge, W.J.; Smout, A.J.; Bredenoord, A.J. Proton pump inhibitors partially restore mucosal integrity in patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia but not eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1815–1823.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Collins, M.H.; Gupta, S.K.; Justinich, C.; Putnam, P.E.; Bonis, P.; Hassall, E.; Straumann, A.; Rothenberg, M.E.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: A systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1342–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liacouras, C.A.; Furuta, G.T.; Hirano, I.; Atkins, D.; Attwood, S.E.; Bonis, P.A.; Burks, A.W.; Chehade, M.; Collins, M.H.; Dellon, E.S.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 3–20.e6, quiz 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Aceves, S.S. Clinical implications and pathogenesis of esophageal remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 43, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaka, M.; Kimura, T.; Kudo, M.; Takeda, H.; Mitani, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Miki, K.; Graham, D.Y. Relationship of Helicobacter pylori to serum pepsinogens in an asymptomatic Japanese population. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, T.; Malaty, H.M.; Graham, D.Y.; Hosogaya, S.; Misawa, K.; Furihata, K.; Ota, H.; Sei, C.; Tanaka, E.; Akamatsu, T.; et al. Acquisition versus loss of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: Results from an 8-year birth cohort study. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Yagi, M.; Yaoita, T.; Nishise, S.; Ueno, Y. Diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in clinical practice. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; He, H. Kappa coefficient: A popular measure of rater agreement. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2015, 27, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Moy, N.; Heckman, M.G.; Thomas, C.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Achem, S.R. Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: Validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut 2013, 62, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundell, L.R.; Dent, J.; Bennett, J.R.; Blum, A.L.; Armstrong, D.; Galmiche, J.P.; Johnson, F.; Hongo, M.; Richter, J.E.; Spechler, S.J.; et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: Clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut 1999, 45, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahrilas, P.J.; Kim, H.C.; Pandolfino, J.E. Approaches to the diagnosis and grading of hiatal hernia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 22, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, K.; Takemoto, T. An endoscopic recognition of the atrophic border and its significance in chronic gastritis. Endoscopy 1969, 1, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PPI-Responders (n = 41) | Non-Responders (n = 18) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics (n, % or median, IQR) | |||
| Age (years) | 46 (26–73) | 44 (28–72) | 0.779 |
| Male sex | 27 (65.9) | 12 (66.7) | 1 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.7 (17.9–37.2) | 23.8 (18.7–39.1) | 0.242 |
| Smoking habits | 14 (34.1) | 5 (27.8) | 0.766 |
| Drinking habits | 27 (67.5) | 11 (61.1) | 0.767 |
| Duration of illness (months) | 9 (1–240) | 12 (1–60) | 0.844 |
| Indications of endoscopy | |||
| GI screening/further examination for upper GI symptoms | 28 (68.3)/13 (31.7) | 6 (33.3)/12 (66.7) | 0.021 |
| Allergy (n, %) | |||
| Any | 28 (68.3) | 14 (77.8) | 0.545 |
| Asthma | 7 (17.1) | 4 (22.2) | 0.721 |
| Rhinitis | 21 (51.2) | 6 (33.3) | 0.262 |
| Dermatitis | 4 (9.8) | 3 (16.7) | 0.664 |
| Food | 7 (17.1) | 6 (33.3) | 0.187 |
| Blood test (n, % or median, IQR) | |||
| WBC (/μL) | 5600 (3500–9200) | 5500 (4400–8400) | 0.787 |
| Eosinophil (/μL) | 307.5 (100.8–1002.8) | 380.8 (110–918.4) | 0.615 |
| Eosinophil (%) | 5 (1.8–15.0) | 5.9 (2.1–14.1) | 0.551 |
| IgE (IU/mL) | 120 (5–2100) | 230 (28–550) | 0.176 |
| Positive radioallergosorbent test | 14 (40) | 8 (53.3) | 0.536 |
| Helicobacter pylori infection | 10 (24.4) | 6 (33.3) | 0.533 |
| Symptoms (n, %) | |||
| Dysphagia | 29 (70.7) | 16 (88.9) | 0.189 |
| Heartburn | 12 (29.3) | 3 (16.6) | 0.354 |
| Chest pain | 6 (14.6) | 4 (22.2) | 0.475 |
| PPI-Responders (n = 41) | Non-Responders (n = 18) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endoscopic findings and histological feature (n, % or median, IQR) | |||
| EREFS findings | |||
| Linear furrows | 37 (90.2) | 17 (94.4) | 1 |
| grade 0 | 4 | 1 | |
| grade 1 | 37 | 17 | |
| Rings | 12 (29.3) | 11 (61.1) | 0.041 |
| grade 0 | 29 | 7 | |
| grade 1 | 11 | 7 | |
| grade 2 | 1 | 4 | |
| grade 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| White plaques | 20 (48.8) | 12 (66.7) | 0.262 |
| grade 0 | 21 | 6 | |
| grade 1 | 15 | 8 | |
| grade 2 | 5 | 4 | |
| Edema | 35 (85.7) | 17 (94.4) | 0.422 |
| grade 0 | 6 | 1 | |
| grade 1 | 35 | 17 | |
| Strictures | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| grade 0 | 41 | 18 | |
| grade 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Reflux esophagitis | 17 (41.5) | 1 (5.6) | 0.006 |
| Los Angeles classification | |||
| grade A | 12 | 1 | |
| grade B | 4 | 0 | |
| grade C | 1 | 0 | |
| grade D | 0 | 0 | |
| Hiatal hernia | 6 (14.6) | 4 (22.2) | 0.475 |
| Atrophic gastritis | 11 (26.8) | 4 (22.2) | 1 |
| Maximum eosinophil count (per hpf) | 35 (15–110) | 40 (20–170) | 0.537 |
| Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | |
| Food allergy | 0.223 | 0.029–1.690 | 0.146 |
| GI screening | 6.740 | 1.200–37.900 | 0.030 |
| Dysphagia | 0.145 | 0.011–1.890 | 0.141 |
| Presence of rings | 0.081 | 0.029–0.501 | 0.007 |
| Presence of reflux esophagitis | 9.490 | 1.010–89.100 | 0.049 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hashimoto, A.; Sugawa, T.; Iwakura, N.; Uemura, R.; Sawada, A.; Otani, K.; Taira, K.; Hosomi, S.; Nagami, Y.; Tanaka, F.; et al. The Predictive Factors of Responsiveness to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastrointest. Disord. 2019, 1, 220-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord1010017
Hashimoto A, Sugawa T, Iwakura N, Uemura R, Sawada A, Otani K, Taira K, Hosomi S, Nagami Y, Tanaka F, et al. The Predictive Factors of Responsiveness to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2019; 1(1):220-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord1010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleHashimoto, Atsushi, Takashi Sugawa, Narika Iwakura, Risa Uemura, Akinari Sawada, Koji Otani, Koichi Taira, Shuhei Hosomi, Yasuaki Nagami, Fumio Tanaka, and et al. 2019. "The Predictive Factors of Responsiveness to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis" Gastrointestinal Disorders 1, no. 1: 220-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord1010017
APA StyleHashimoto, A., Sugawa, T., Iwakura, N., Uemura, R., Sawada, A., Otani, K., Taira, K., Hosomi, S., Nagami, Y., Tanaka, F., Kamata, N., Yamagami, H., Tanigawa, T., Watanabe, T., & Fujiwara, Y. (2019). The Predictive Factors of Responsiveness to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 1(1), 220-230. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord1010017





