Early Detection of Corrosion-Induced Concrete Micro-cracking by Using Nonlinear Ultrasonic Techniques: Possible Influence of Mass Transport Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
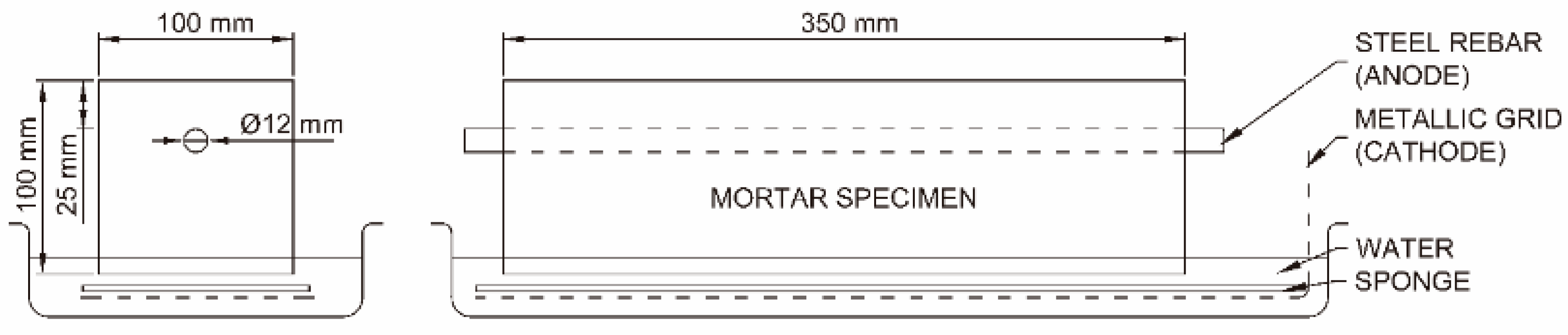
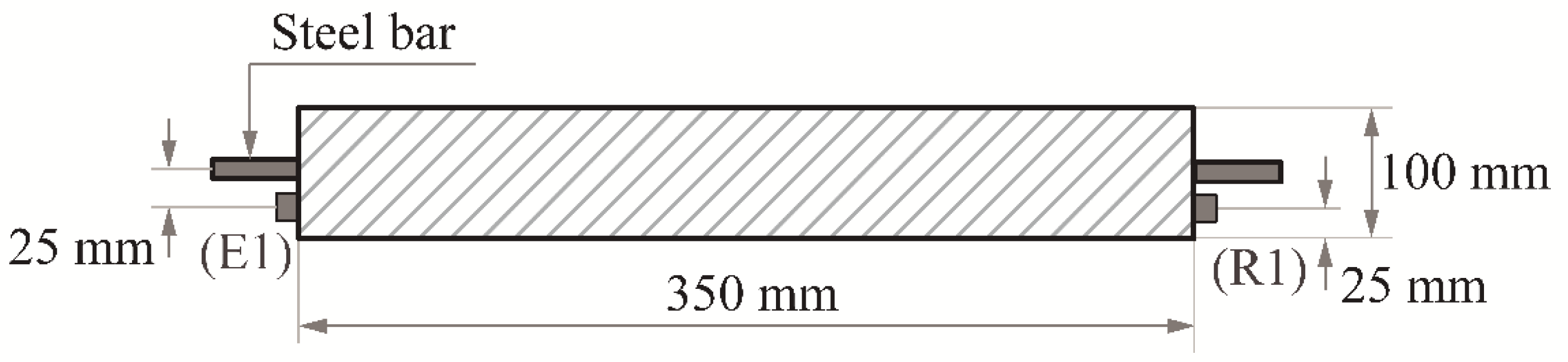
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Accelerated Corrosion Tests
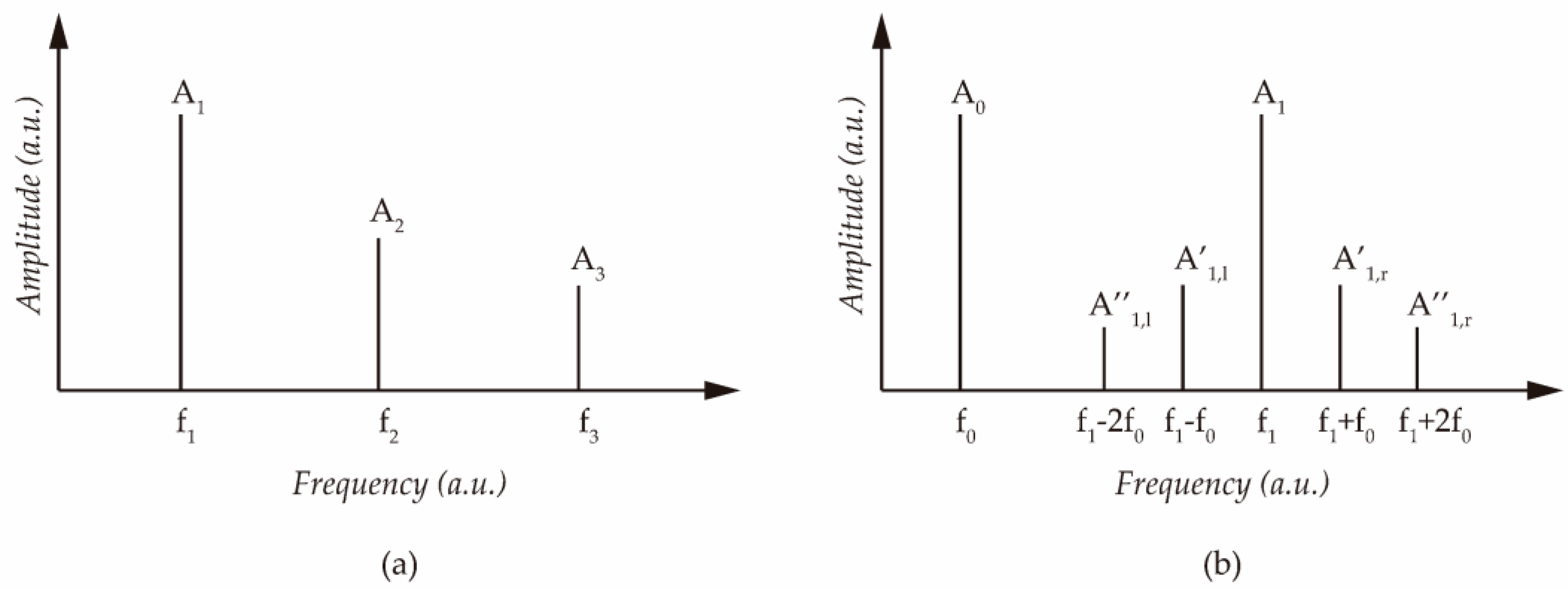
2.3. The Assessment of Material Damage through Nonlinear Elastic Wave Features
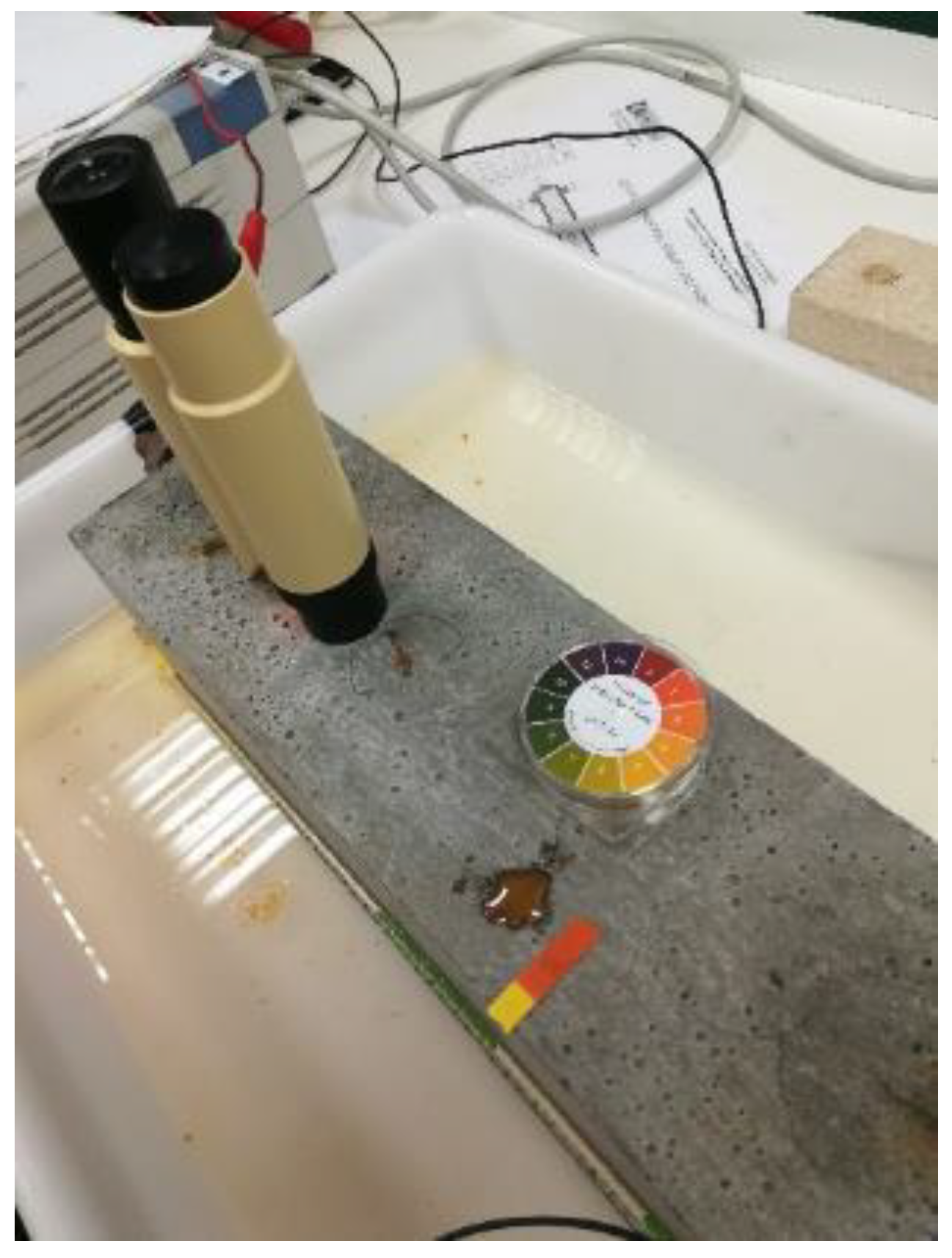
2.4. Nonlinear Ultrasonic Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
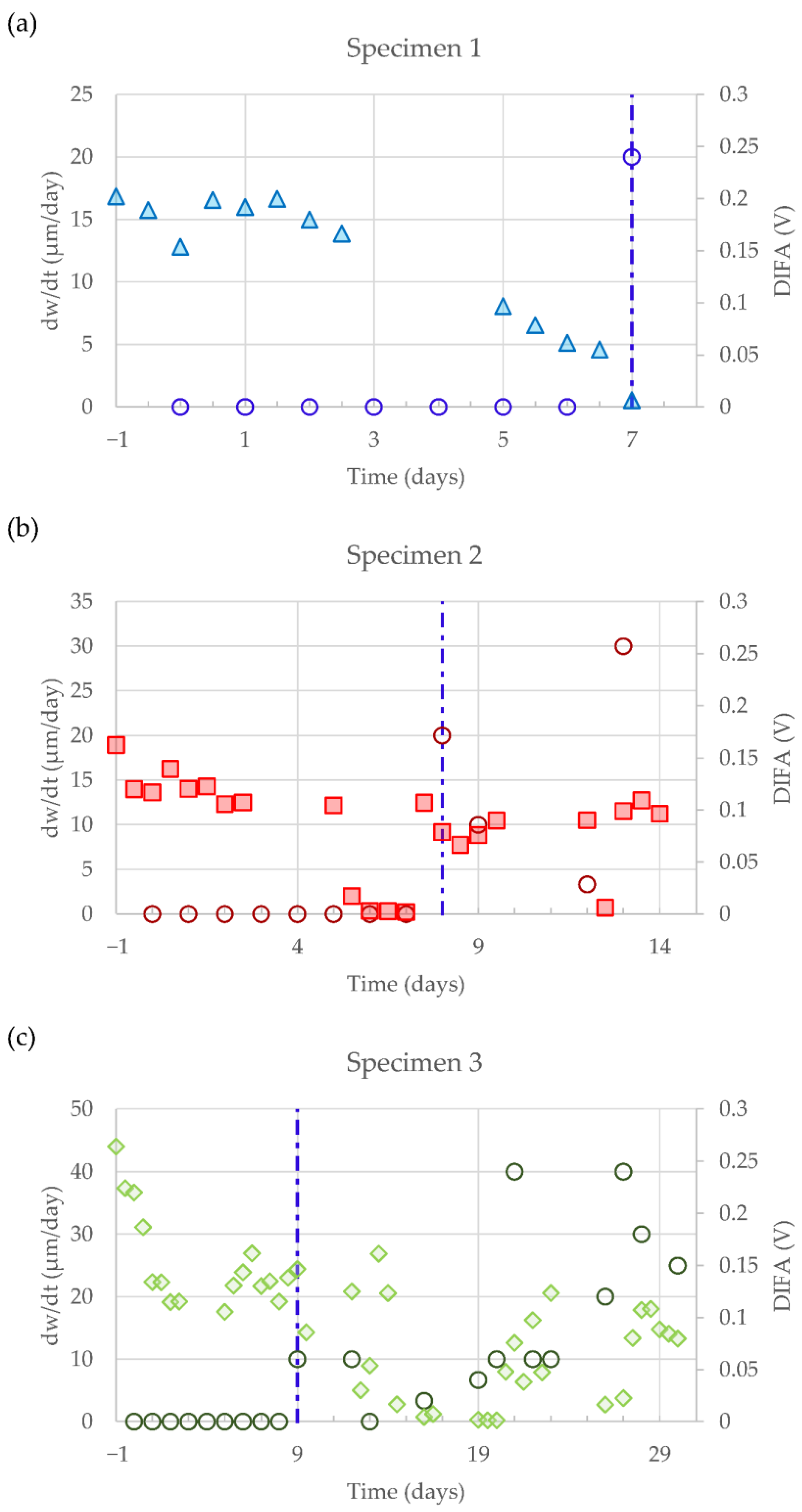
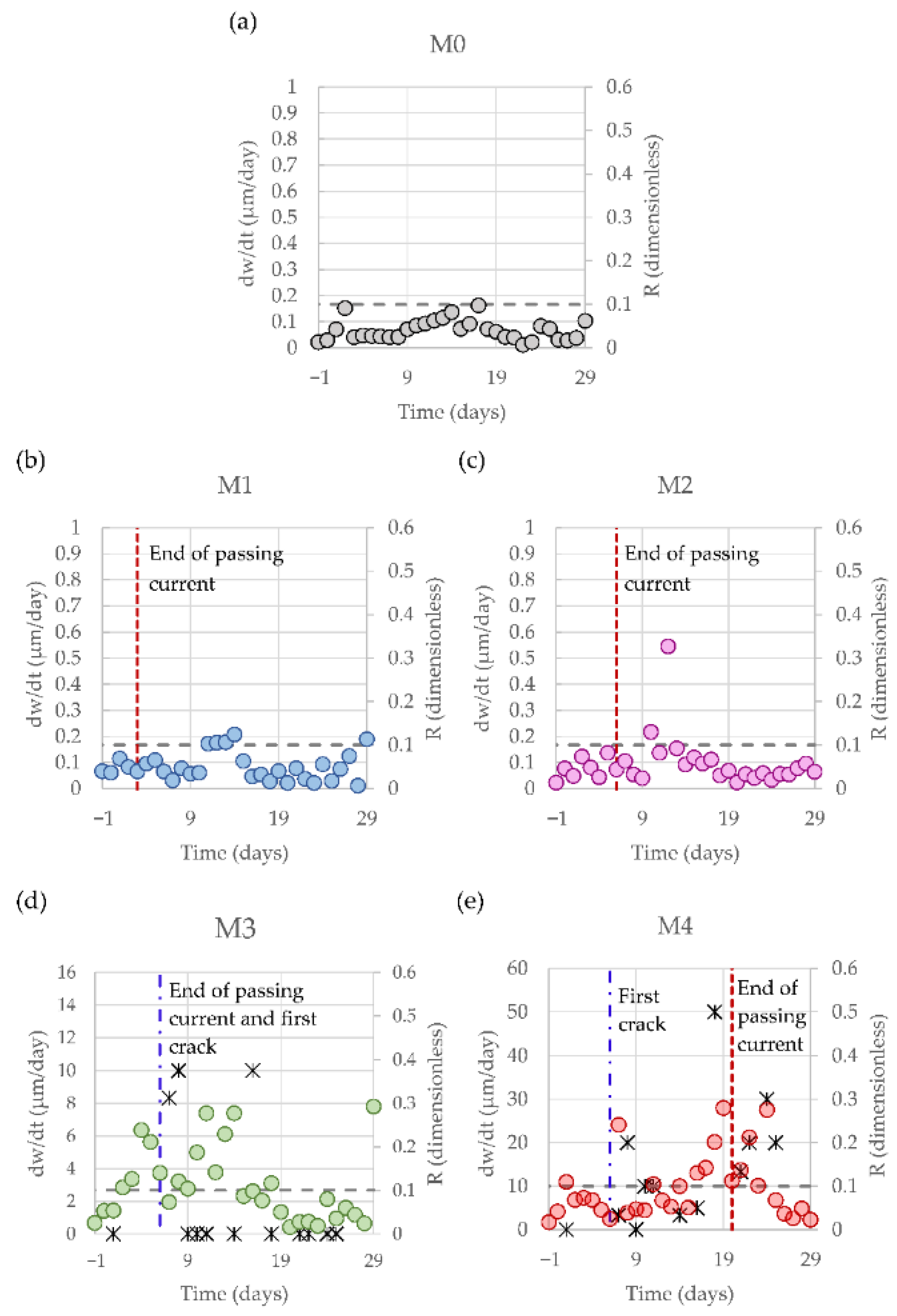
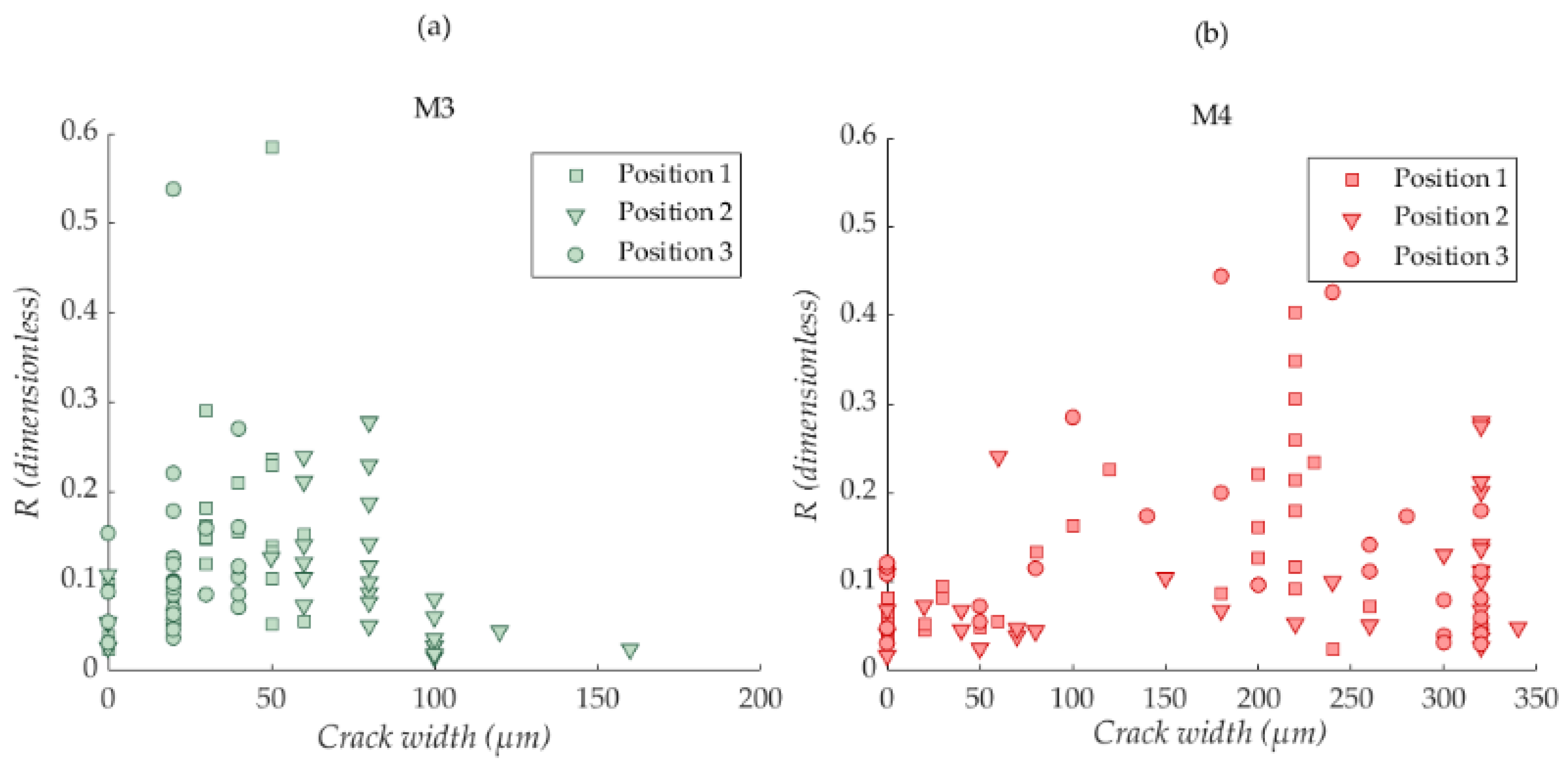
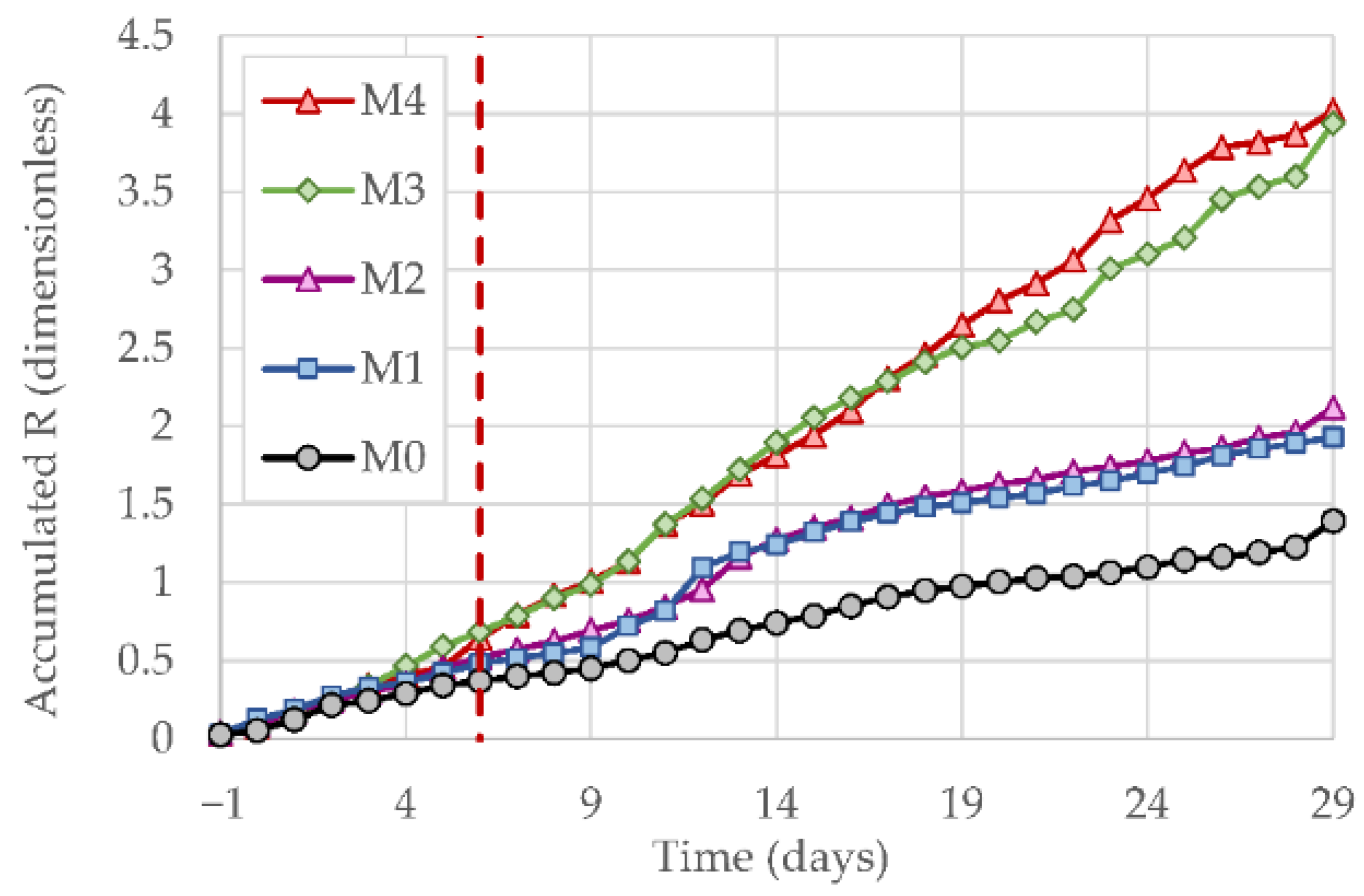
3.1. Correlation between the NLU Observations and the Corrosion-Induced Cracking Process
3.2. Possible Influence of Active Mass Transport Processes on the Evolution of the NLU Parameters during the Accelerated Corrosion Tests
3.3. Consequences for the Possible Application of the NLU Techniques to Engineering Practices in the Field of the Detection of the Corrosion-Induced Damage of Reinforced Concrete Structures
3.4. Influence of the Electrochemical Parameters Governing the Activity of the Steel Reinforcement Corrosion on the Suitability of the NLU Techniques to Assess the Corrosion-Induced Damage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ACI Committee 222R-96; Corrosion of Metals in Concrete. American Concrete Institute (ACI): Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 1996.
- Suda, K.; Misra, S.; Motohashi, K. Corrosion products of reinforcing bars embedded in concrete. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Andrade, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Díez, J.M. Factors controlling cracking of concrete affected by reinforcement corrosion. Mater. Struct. 1998, 31, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Weyers, R.E. Modeling the time-to-corrosion cracking in chloride contaminated reinforced concrete structures. ACI Mater. J. 1998, 95, 675–681. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Polder, R. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Uomoto, T.; Misra, S. Behavior of concrete beams and columns in marine environment when corrosion of reinforcing bars takes place. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Concrete in Marine Environment, St. Andrews, NB, Canada, 21–26 August 1988; ACI: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 1988; pp. 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- EHE-08; Spanish Structural Concrete Code. Ministerio de Fomento: Madrid, Spain, 2010. (In Spanish)
- ASTM C 876-91; Standard Test Method for Half-Cell Potential of Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1991.
- Elsener, B.; Andrade, C.; Gulikers, J.; Polder, R.; Raupach, M. Recommendation on half-cell potential measurements. Mater. Struct. 2003, 36, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; González, J.A. Quantitative measurements of corrosion rate of reinforcing steels embedded in concrete using polarization resistance measurements. Werkst. Korros. 1978, 29, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.A.; Marco, A.J.; de Vera, G.; Campos, S. Measurements of rebar corrosion rates in the concrete structure of a building with 40 years’ service life in a marine environment. In Measurement and Interpretation of the On-Site Corrosion Rate, Proceedings of the International Workshop MESINA, Madrid, Spain, 22–23 January 1999; Andrade, C., Alonso, C., Fullea, J., Polimón, J., Rodriguez, J., Eds.; RILEM Publications: Cachan, France, 2000; pp. 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, A.; Chai, H.K.; Aggelis, D.G.; Alver, N. Non-destructive evaluation for corrosion monitoring in concrete: A review and capability of acoustic emission technique. Sensors 2015, 15, 19069–19101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mukherjee, A. Longitudinal guided waves for monitoring chloride corrosion in reinforcing bars in concrete. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 9, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Ribakov, Y. Non-destructive evaluation of concrete in damaged and undamaged states. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.T.; Su, P.J. Detection of the corrosion damage of rebar in concrete using impact-echo method. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, I.; Campanella, G.; Proverbio, E. Identification of corrosion mechanisms by univariate and multivariate statistical analysis during long term acoustic emission monitoring on a pre-stressed concrete beam. Corros. Sci. 2013, 73, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, M. Recommendation of RILEM TC 212-ACD: Acoustic emission and related NDE techniques for crack detection and damage evaluation in concrete. Mater. Struct. 2010, 43, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, P.B. Fatigue damage assessment by nonlinear ultrasonic materials characterization. Ultrasonics 1998, 36, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, K.Y. Nonlinear ultrasonic techniques for non-destructive assessment of microdamage in materials: A review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2009, 10, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, T.; Eiras, J.N.; Li, W.; Liu, P.; Sohn, H.; Payá, J. Fundamentals of nonlinear acoustical techniques and sideband peak count. In Nonlinear Ultrasonic and Vibro-Acoustical Techniques for Nondestructive Evaluation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Abeele, K.; De Visscher, J. Damage assessment in reinforced concrete using spectral and temporal nonlinear vibration techniques. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Garnier, V.; Moysan, J.; Johnson, P.A. Applying nonlinear resonant ultrasound spectroscopy to improving thermal damage assessment in concrete. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, EL125–EL130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eiras, J.N.; Kundu, T.; Popovics, J.S.; Payá, J. Cement-based material characterization using nonlinear single-impact resonant acoustic spectroscopy (NSIRAS). In Nonlinear Ultrasonic and Vibro-Acoustical Techniques for Nondestructive Evaluation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 487–508. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.A.; Ribakov, Y. Non-linear ultrasonic evaluation of damaged concrete based on higher order harmonic generation. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 4095–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; In, C.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kurtis, K.E.; Jacobs, L.J. Air-coupled detection of nonlinear Rayleigh surface waves in concrete-Application to microcracking detection. NDT E Int. 2014, 67, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, J.D.; Woodward, C.B.; White, K.R. Nonlinear ultrasonic testing with resonant and pulse velocity parameters for early damage in concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2005, 102, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Scalerandi, M.; Griffa, M.; Antonaci, P.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Lura, P. Nonlinear elastic response of thermally damaged consolidated granular media. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 154902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warnemuende, K.; Wu, H.C. Actively modulated acoustic non-destructive evaluation of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.N.; Yang, C.L. Damage assessment of concrete using a noncontact nonlinear wave modulation technique. NDT E Int. 2019, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Abeele, K.E.A.; Johnson, P.A.; Sutin, A. Nonlinear elastic wave spectroscopy (NEWS) techniques to discern material damage, part I: Nonlinear wave modulation spectroscopy (NWMS). Res. Nondestr. Eval. 2000, 12, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yao, Y.P. Experimental characterization of granite damage using nonlinear ultrasonic techniques. NDT E Int. 2014, 67, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonaci, P.; Bruno, C.L.; Gliozzi, A.S.; Scalerandi, M. Monitoring evolution of compressive damage in concrete with linear and nonlinear ultrasonic methods. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Loreto, G.; Kim, J.Y.; Kurtis, K.E.; Wall, J.J.; Jacobs, L.J. In situ nonlinear ultrasonic technique for monitoring microcracking in concrete subjected to creep and cyclic loading. Ultrasonics 2018, 88, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Thirumalaiselvi, A.; Sasmal, S.; Kundu, T. Nonlinear ultrasonics-based technique for monitoring damage progression in reinforced concrete structures. Ultrasonics 2021, 115, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yin, T.; Kim, J.Y.; Xu, Z.; Yao, Y. Characterization of thermal damage in sandstone using the second harmonic generation of standing waves. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 91, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Ulrich, T.J.; Le Bas, P.Y.; Saleh, T.; Guimaraes, M. Quantitative linear and nonlinear resonance inspection techniques and analysis for material characterization: Application to concrete thermal damage. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.; Kim, J.Y.; Kurtis, K.E.; Jacobs, L.J. Drying shrinkage in concrete assessed by nonlinear ultrasound. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 92, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jayapalan, A.R.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kurtis, K.E.; Jacobs, L.J. Nonlinear wave modulation spectroscopy method for ultra-accelerated alkali-silica reaction assessment. ACI Mater. J. 2009, 106, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Jayapalan, A.R.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kurtis, K.E.; Jacobs, L.J. Rapid evaluation of alkali-silica reactivity of aggregates using a nonlinear resonance spectroscopy technique. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.N.; Kundu, T.; Bonilla, M.; Payá, J. Nondestructive monitoring of ageing of alkali resistant glass fiber reinforced cement (GRC). J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2013, 32, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovés, V.; Soriano, L.; Borrachero, M.V.; Eiras, J.; Payá, J. Preliminary study on short-term sulphate attack evaluation by non-linear impact resonance acoustic spectroscopy technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskoy, D.M.; Ferroni, K.; Sutin, A.; Sheppard, K.A. Nonlinear Acoustic Technique for Crack and Corrosion Detection in Reinforced Concrete. In Nondestructive Characterization of Materials VIII; Green, R.E., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, C.; Amin, M.N. Evaluating rebar corrosion using nonlinear ultrasound. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2008; Volume 975, pp. 1314–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Korenska, M.; Matysik, M.; Vyroubal, P.; Pospisil, K. Assessment of reinforcement corrosion using nonlinear ultrasonic spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 5th NDT Progress—International Workshop of NDT Experts, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–14 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Antonaci, P.; Bruno, C.L.E.; Scalerandi, M.; Tondolo, F. Effects of corrosion on linear and nonlinear elastic properties of reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 51, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.Á.; Miró, M.; Carbajo, J.; Poveda, P.; de Vera, G.; Ramis, J. Use of non-linear ultrasonic techniques to detect cracks due to steel corrosion in reinforced concrete structures. Materials 2019, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Climent-Llorca, M.Á.; Miró-Oca, M.; Poveda-Martínez, P.; Ramis-Soriano, J. Use of higher-harmonic and intermodulation generation of ultrasonic waves to detecting cracks due to steel corrosion in reinforced cement mortar. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2020, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, M.; Eiras, J.N.; Poveda, P.; Climent, M.Á.; Ramis, J. Detecting cracks due to steel corrosion in reinforced cement mortar using intermodulation generation of ultrasonic waves. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Alonso, C.; Molina, F.J. Cover cracking as a function of bar corrosion: Part I—Experimental test. Mater. Struct. 1993, 26, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, F.J.; Alonso, C.; Andrade, C. Cover cracking as a function of bar corrosion: Part II—Numerical model. Mater. Struct. 1993, 26, 532–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, F.; Andrade, C. Corrosion induced cracking: Effect of different corrosion rates on crack width evolution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Garnier, V.; Moysan, J. Effect of water saturation and porosity on the nonlinear elastic response of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J. Nonlinear ultrasonic characterization of material deterioration of asphalt mixture during cracking-healing cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 308, 125056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE-EN 197-1, equivalent to the European Standard EN 197-1; Cement. Part 1: Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación: Madrid, Spain, 2011. (In Spanish)
- Climent, M.A.; Viqueira, E.; de Vera, G.; López-Atalaya, M.M. Analysis of acid-soluble chloride in cement, mortar, and concrete by potentiometric titration without filtration steps. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.A.; de Vera, G.; Viqueira, E.; López-Atalaya, M.M. Generalization of the possibility of eliminating the filtration step in the determination of acid-soluble chloride content in cement and concrete by potentiometric titration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossoni, G.; Harichandran, R. Current efficiency in accelerated corrosion testing of concrete. Corrosion 2012, 68, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G1-03; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Jhang, K.Y. Applications of nonlinear ultrasonics to the NDE of material degradation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2000, 47, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.; Goble, T. Signals and noise. In Telecommunications Engineer’s Reference Book; Mazda, F.F., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1993; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar]
- Raichel, D.R. The Science and Applications of Acoustics (AIP Series in Modern Acoustics and Signal Processing); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 625–626. [Google Scholar]
- Pieczonka, A.L.; Klepka, A.; Martowicz, A.; Staszewski, W.J. Nonlinear vibroacoustic wave modulations for structural damage detection: An overview. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Abeele, K.E.A.; Carmeliet, J.; Ten Cate, J.A.; Johnson, P.A. Nonlinear elastic wave spectroscopy (NEWS) techniques to discern material damage, Part II: Single-mode nonlinear resonance acoustic spectroscopy. Res. Nondestruct. Eval. 2000, 12, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Sutin, A.; Guyer, R.; Talmant, M.; Laugier, P.; Johnson, P.A. Nonlinear resonant ultrasound spectroscopy (NRUS) applied to damage assessment in bone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 3946–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aymerich, F.; Staszewski, W.J. Experimental study of impact-damage detection in composite laminates using a cross-modulation vibroacoustic technique. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 2010, 9, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakel, 2019, IDK09 Transducer. Available online: http://www.dakel.cz (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Miró, M. Application of Non-Linear Ultrasonic Techniques to the Detection of Cracking of Concrete Due to Steel Corrosion. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 2021. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Segovia, E.G.; de Vera, G.; Miró, M.; Ramis, J.; Climent, M.Á. Cement mortar cracking under accelerated steel corrosion test: A mechanical and electrochemical model. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 896, 115222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalerandi, M.; Gliozzi, A.S.; Bruno, C.L.E.; Masera, D.; Bocca, P. A scaling method to enhance detection of a nonlinear elastic response. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 101912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldred, J.M.; Rangan, B.V.; Buenfeld, N.R. Effect of initial moisture content on wick action through concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalaiselvi, A.; Sasmal, S.; Kundu, T. Detection of initiation of corrosion induced damage in concrete structures using nonlinear ultrasonic techniques. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 151, 1341. [Google Scholar]
- Garcés, P.; Andrade, M.C.; Sáez, A.; Alonso, M.C. Corrosion of reinforcing steel in neutral and acid solutions simulating the electrolytic environments in the micropores of concrete in the propagation period. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polder, R.B. Test methods for on-site measurement of resistivity of concrete—A RILEM TC-154 technical recommendation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2001, 15, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuutti, K. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete; Swedish Foundation for Concrete Research: Stockholm, Sweden, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Elsener, B.; Böhni, H. Corrosion of steel in mortar studied by impedance measurements. Mater. Sci. Forum. 1986, 8, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.J.; Sykes, J.M. A galvanostatic pulse technique for investigation of steel corrosion in concrete. Corros. Sci. 1988, 28, 1051–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material | Amount (g) |
|---|---|
| Cement (CEM I 52,5 R SR(3)) | 450 |
| Standard siliceous sand | 1350 |
| Deionized water | 225 (w/c = 0.5) |
| NaCl | 14.8 (2% Cl− relative to cement weight) |
| Series of Experiments | Specimen | C (mm) | (c/ø) | Icorr (μA/cm2) | t50 (Days) | Time of Passing Current (Days) | Time of Cracking (Days) | Duration of the NLU Survey (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 0.83 | 40 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 8 |
| 2 | 10 | 0.83 | 40 | 12 | 14 | 8 | 15 | |
| 3 | 10 | 0.83 | 40 | 12 | 30 | 9 | 31 | |
| 2 | M0 | 25 | 2.1 | 100 | 8.4 | 0 | - | 30 |
| M1 | 25 | 2.1 | 100 | 8.4 | 3 | - | 30 | |
| M2 | 25 | 2.1 | 100 | 8.4 | 6 | - | 30 | |
| M3 | 25 | 2.1 | 100 | 8.4 | 6 | 6 | 30 | |
| M4 | 25 | 2.1 | 100 | 8.4 | 20 | 6 | 30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Climent, M.-Á.; Miró, M.; Eiras, J.-N.; Poveda, P.; de Vera, G.; Segovia, E.-G.; Ramis, J. Early Detection of Corrosion-Induced Concrete Micro-cracking by Using Nonlinear Ultrasonic Techniques: Possible Influence of Mass Transport Processes. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2022, 3, 235-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd3020014
Climent M-Á, Miró M, Eiras J-N, Poveda P, de Vera G, Segovia E-G, Ramis J. Early Detection of Corrosion-Induced Concrete Micro-cracking by Using Nonlinear Ultrasonic Techniques: Possible Influence of Mass Transport Processes. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2022; 3(2):235-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd3020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleCliment, Miguel-Ángel, Marina Miró, Jesús-Nuño Eiras, Pedro Poveda, Guillem de Vera, Enrique-Gonzalo Segovia, and Jaime Ramis. 2022. "Early Detection of Corrosion-Induced Concrete Micro-cracking by Using Nonlinear Ultrasonic Techniques: Possible Influence of Mass Transport Processes" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 3, no. 2: 235-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd3020014
APA StyleCliment, M.-Á., Miró, M., Eiras, J.-N., Poveda, P., de Vera, G., Segovia, E.-G., & Ramis, J. (2022). Early Detection of Corrosion-Induced Concrete Micro-cracking by Using Nonlinear Ultrasonic Techniques: Possible Influence of Mass Transport Processes. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 3(2), 235-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd3020014









