Abstract
The conventional corrosion management process consists of defining the expected process conditions, identifying potential corrosion threats, and estimating their likely rate, then using that information to develop mitigation plans and inspection schedules. The Virtual Corrosion Engineer (VCE) project aims to improve this process by utilizing online monitoring data to automate the running of the best available corrosion models and provide a continuously updated dashboard in real time. This paper provides an overview of the VCE, together with a brief discussion of the underlying models for two exemplar damage mechanisms, High-Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA) and Under Deposit Corrosion (UDC) in steam generators.
1. Introduction
Despite massive efforts over many years, corrosion remains one of the primary causes of unexpected plant downtime. The conventional corrosion management process consists of defining the expected process conditions, identifying potential Damage Mechanisms (DMs) and estimating their likely rate, then using that information to develop mitigation plans and inspection schedules. Over time, inspection results are fed back to corrosion engineers, initial threat assessments are updated, and the cycle is repeated [1,2]. However, online corrosion monitoring and real-time corrosion prediction can provide complementary information on much shorter time frames [3,4,5,6]. The Virtual Corrosion Engineer (VCE) is a project within Shell to develop and implement a new software tool that will help to improve this process. A key concept behind this project is to change from a system based largely on the initial selection of the most likely DMs in the expected conditions to a continuously updated assessment of all potential DMs in the actual conditions as measured by process monitoring instrumentation. This driver for the project is captured in the motto ‘everything, everywhere, all the time’. In practice, the conventional and VCE systems will run in parallel, with the VCE providing a faster feedback loop for the decision-making process, as shown schematically in Figure 1.
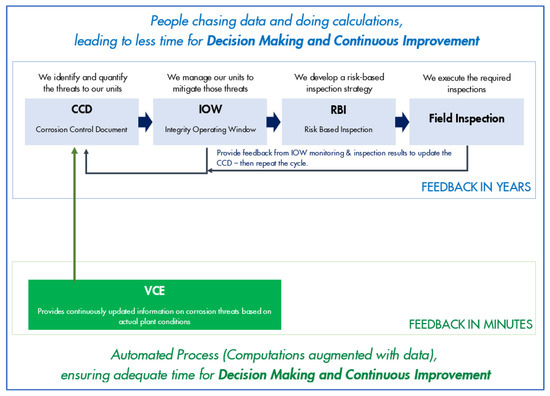
Figure 1.
The corrosion and integrity management workflow, including the conventional feedback loop from inspections, together with faster feedback from the Virtual Corrosion Engineer.
The ability to achieve these goals comes from combining modern computing power with the very extensive instrumentation that is nowadays present in large-scale industrial plants. In the conventional process, it is extremely time-consuming for engineers to identify all the relevant process data, make a judgement of the likely DMs, and then use their knowledge or run available models to estimate corrosion rates or susceptibility to failure. In the VCE process, work is performed up front to automate the connection between monitoring data and corrosion models so that assessment results are updated continuously, without human intervention. Because of this automation, there is no need to preselect only the most likely DMs; computers today are more than capable of simultaneously running models for all remotely plausible DMs at speeds sufficient to provide results every hour or so. In the most challenging cases, such as in furnaces or heat exchangers where the raw process monitoring data must be further processed to estimate metal temperatures, daily updates are still achievable. The resulting VCE assessments still need review and interpretation by human engineers, but the overall process is significantly more efficient.
To enable the review by human engineers, VCE results are displayed in an interactive web-based dashboard that shows high-level Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and provides functionality for data drilling down to view the underlying calculations and input data in various formats. Of course, this concept can only be truly valuable if the implemented corrosion models are reliable and if the required input data are available, preferably, for process conditions, via online monitoring. Where any of the required input data are not monitored in the plant, then the VCE calculations are based on expected values or off-line process simulation results, as would be the case in any normal corrosion threat assessment. For the corrosion models, the general approach in this project is not to develop new theories but to use available models that are already accepted by the industry. However, for some damage mechanisms, additional model development is required to deliver the project’s long-term goals. This paper provides a brief discussion of the underlying models for two exemplar damage mechanisms, High-Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA) and Under Deposit Corrosion (UDC) in steam generators.
2. High-Temperature Hydrogen Attack
High-Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA) is the irreversible degradation of the mechanical properties of steel by exposure to hydrogen at high temperatures. At elevated temperatures, some of the molecular hydrogen in the process environment dissociates into atomic hydrogen, which can diffuse into the steel and then react with carbon in the steel to form methane. The generated methane molecules are too large to diffuse through the steel and create internal pressures that can cause fissuring, cracking, and eventual failure of the affected equipment. HTHA has been encountered in carbon steels and low alloy Cr-Mo steels, whereas austenitic stainless steels are considered immune. In the oil and gas industry, the so-called “Nelson Curves” are used to guide the operating conditions where HTHA can occur. These curves are published in API Recommended Practice 941 [7] and are empirical, based on reported occurrences of HTHA. Within Shell, internal standards define HTHA susceptibility zones (e.g., high, medium, low, etc.) with reference to the Nelson Curves and describe the recommended actions for equipment operating in each zone.
In the VCE project, the challenge was to provide a continuously updated visualization of this HTHA susceptibility assessment. Having identified the relevant equipment and the materials of their construction, the relevant process data consisted of the operating metal temperature (T) and the partial hydrogen pressure (pH2) in the process environment, as a function of time since plant start-up. Two different methods were then considered to determine the susceptibility zone for each equipment item. In the first method, the representative operating condition for comparison with the Nelson curves is taken as the 97.5th percentile in pH2 and the 97.5th percentile in T. However, this method is not always suitable for equipment with variable conditions or significantly different operating modes since the T and pH2 obtained this way are not necessarily coincident and may be misleading. In the second method, the entire operating history is reviewed as a function of time, and the total number of operating hours spent in each susceptibility zone is counted. The susceptibility rating is then given by the highest zone where the equipment has operated for a cumulative total of >1000 h in (or above) that zone. This method considers only coincident values of T and pH2 and is hence more robust, but it is much more challenging to carry out this type of assessment for plants that have operated for many years and generated large amounts of data. For visualization of results from the second method, the ‘VCE Concurrent Point’ has been defined as the worst case actual operating condition within the assigned zone. Figure 2 shows the results as displayed in the VCE for one equipment item at a plant operating for about ten years.
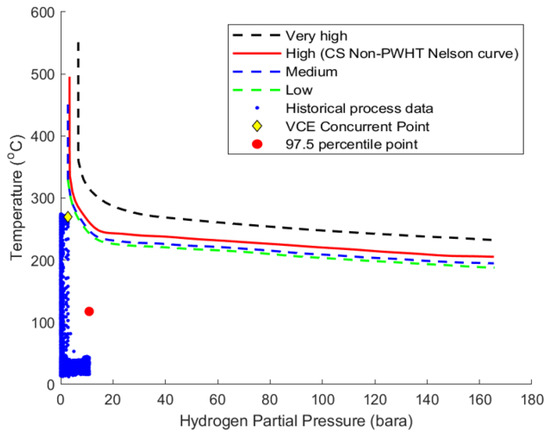
Figure 2.
VCE visualization of the HTHA threat assessment for a single equipment item operating for a period of several years.
The cloud of blue data points are the actual operating conditions at 1 h intervals throughout the full operating history, the red point shows the representative operating condition from the 97.5th percentile method, and the yellow diamond shows the VCE concurrent point. This equipment operates in several different modes that involve relatively high pH2, but only one of those modes also involves a relatively high T. As a result, the 97.5th percentile method identifies a point that is quite some distance away from any of the actual operating conditions for this equipment and hence cannot reasonably be considered representative. It would not, for example, be possible to recommend operational changes based on the location of this point. In contrast, the VCE Concurrent Point is positioned at an actual operating condition and provides a much better representation of the result. In all cases, the VCE uses the second method (counting hours in each zone) to assess susceptibility to HTHA. The equipment in Figure 2 has only a low susceptibility to HTHA.
3. Under Deposit Corrosion in Steam Generators
Most significant industrial facilities operate an extensive steam system comprising multiple steam generators (typically waste heat boilers, cooling the main process stream) and multiple steam users (including both heat exchangers using steam to heat the main process flow and turbines generating electrical power). One of the most critical potential damage mechanisms in such systems is the Under Deposit Corrosion (UDC) of steam generator tubes [8,9,10,11,12]. The primary cause of UDC is the deposition of a porous layer of magnetite particles on the waterside surface of the tubes, on top of the protective magnetite film formed in situ on the tube surfaces. The magnetite particles are generated by corrosion elsewhere in the system (e.g., in the feedwater piping) and then transported into the steam generator, where they deposit onto the heat transfer surfaces [12,13,14,15,16]. Beneath this layer, a wick-boiling process leads to a concentration of ionic contaminants (such as chlorides) that are present in the steam-generator water. As the deposits become thicker, the degree of concentration beneath the deposit increases and can reach factors as high as 10,000 times the bulk concentration [17]. At some point, the concentration reaches a critical threshold level and causes the initiation of UDC. In this paper, we focus on chloride-driven UDC. To mitigate the risks of chloride-driven UDC, industry guidance [17,18] is first, to manage Boiler Feed Water (BFW) quality to minimize the risk of Flow Assisted Corrosion (FAC) and hence reduce the amount of iron (both dissolved ferrous ions and solid magnetite particles) that enters the steam generator; second, to minimize the chloride concentration in the Boiler Water (BW); and, finally, to monitor the extent of deposition and to chemically clean the boiler before the deposits reach the levels necessary to initiate UDC. For the critical deposit loading threshold before cleaning is required, experience-based values of around 35 mg cm−2 are typically suggested [17,18]. However, there are expected to be significant differences for other types of steam generators due to variation in factors such as the pressure, heat-flux, circulation rate, and whether the water is inside or outside the tubes. In recent work [19], we have examined a selection of industrial waste heat boiler tubes that had suffered from UDC and estimated that rapid UDC had occurred above a deposit loading of ~50 mg cm−2.
In the VCE project, the initial focus has been on trending deposit loading measurements and predicting the dates at which accepted critical deposit loading thresholds will be reached, as shown schematically in Figure 3. However, it is desirable to have more direct real-time measures of the potential for UDC initiation, taking into account short-term variations in process variables such as the BW pH and chloride concentration. Below we summarise a potential approach to this calculation.
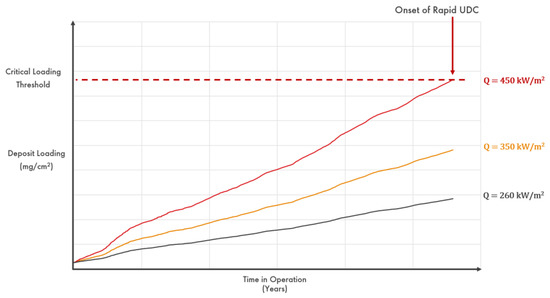
Figure 3.
Schematic showing trending of boiler tube deposit loading data for different heat flux (Q) values, with the red dotted line indicating the critical value before which cleaning must be carried out to avoid the onset of UDC.
Wick-Boiling and the Critical Deposit Threshold for UDC
In an industrial steam system, the boiler feedwater is first demineralized, then de-oxygenated, and then dosed with chemicals for pH control. For a system using an All Volatile Treatment (AVT) regime, the Boiler Water might be around 250–300 °C, with a bulk pH of ~9–9.5 and ~100–300 ppb chloride. If wick-boiling occurs beneath surface deposits, then the volatile treatment chemicals (amines and ammonia) are predominantly evaporated out of the aqueous phase, leaving behind a solution that consists mainly of the nonvolatile contaminant species, which can become highly concentrated. For pressurized water reactors, Gonzalez and Spekkens [20] developed a theoretical model for the concentration process, which is shown schematically in Figure 4. Water flows through the porous deposit layer to the hot metal surface where boiling takes place. The resulting steam bubbles then flow back through the deposit through ‘chimney-like passages. Contaminants are transported to the hot surface with the water by convection and can then be transported away by diffusion, or in droplets of water entrained with the steam, or by vaporization. For a given thickness of deposit, the steady-state condition is reached when the efflux of contaminants balances the influx, as shown by Equation (1):
where:
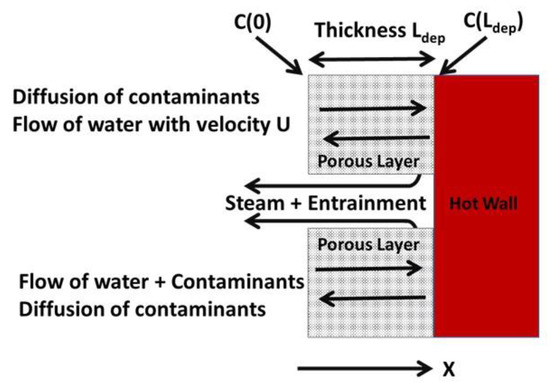
Figure 4.
Schematic of the wick-boiling model proposed by Gonzalez and Spekkens [20].
- Φ is dimensionless porosity
- τ is dimensionless tortuosity
- D is molecular diffusion constant in m2 s−1
- C(x) is the concentration at depth x in the layer in mol m−3
- Ccov is a dimensionless coverage factor indicating the fraction of the surface that is covered by the porous layer (i.e., the area that is not occupied by the ‘chimneys’ that allow steam to escape from the metal surface);
- Q is heat flux in W m−2
- ρw,l is liquid water density in kg m−3
- ∆Hv is vaporization enthalpy in J kg−1
- H is Henry’s constant
- εE is the entrainment coefficient
- Ldep is the porous layer thickness in m.
For any contaminant species, the Concentration Factor (CF) is the ratio of its concentration beneath the deposits to its concentration in bulk and can be determined by rearranging Equation (1) to give:
For fully dissociated ionic species such as chlorides, vaporization and entrainment are considered negligible [19], and hence Equation (2) reduces to:
where the factor α is given by:
Thus, if the composition of the bulk Boiler Water is known, then Equation (1) enables the calculation of the concentration of nonvolatile ionic species beneath the deposit. In modern high-pressure boilers, these species are likely to include chloride ions, sodium ions, and possibly phosphate ions. Hence, for any bulk boiler water composition, for a specific heat-flux and deposit thickness, it is then possible to calculate the local pH that is created beneath the deposit [17]. Figure 5 shows an example of the calculated concentration factor for chloride ions and the associated local pH, for specific bulk chemistry and certain assumptions about the physical properties of the deposit [19].
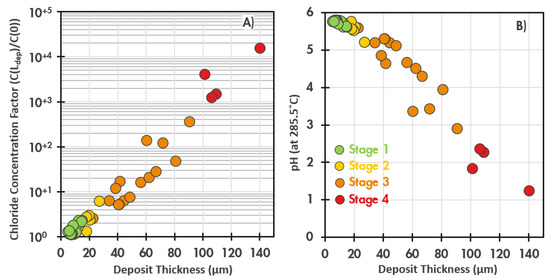
Figure 5.
(A) Calculated concentration factor and (B) pH beneath the porous deposits as a function of the deposit thickness, for a boiler operating under an All Volatile Treatment regime at ~75 bar, with a bulk pH of 9.4 and bulk chloride concentration of ~120 ppb, Stage 4 indicates the onset of rapid UDC [19]. Note: the neutral pH at 286 °C is 5.7.
Although the current industry approach is based on fixed values of the critical deposit loading, it is also recognized that the progression of UDC is, in reality, more directly governed by the chemistry beneath the deposit. Moreover, for carbon steel or low alloy steel tubes, the most critical factor in the local chemistry is the local pH. For the example in Figure 5, with deposit thickness < 30 μm, the chloride concentration factor is not high, and the local pH remains within the range of 5.6–5.8, which is close to the at-temperature pH of the bulk water (5.8). However, when the concentration factor exceeds ~1000, the pH falls below 2.7. From the analysis of corroded low alloy steel tubes extracted from these boilers, the transition to rapid UDC was estimated to occur at about this point [19]. Taking this as the definition of the underlying ‘critical pH’ value required for rapid UDC, it is then possible to calculate the deposit thickness required to generate that local pH (and hence cause UDC) as a function of various operating parameters, as shown in Figure 6.
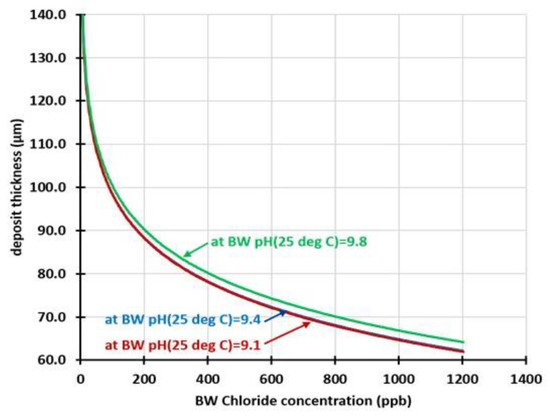
Figure 6.
The critical deposit thickness required to generate the local pH beneath the deposit required to cause rapid UDC, as a function of the bulk pH and chloride concentration, for the boiler design and tube materials considered in Figure 5 [19].
From a VCE perspective, if such calculations could be validated, it would be possible to deliver online estimates of changes in UDC risk due to short-term excursions in operational variables (such as bulk pH and chloride concentration), which are routinely monitored. However, further work is required before this approach is considered robust enough for practical implementation.
4. Summary and Conclusions
The conventional corrosion management process consists of defining the expected process conditions, identifying potential corrosion threats, and estimating their likely rate, then using that information to develop mitigation plans and inspection schedules. Eventually, over time, inspection results are fed back to corrosion engineers, initial threat assessments are updated, and then the cycle is repeated. The Virtual Corrosion Engineer both improves the accuracy of this process and massively speeds up the feedback cycle by taking advantage of the enormous quantity of process information that is already collected and digitally stored every day and automating various data-handling actions that must otherwise be completed manually during a corrosion assessment. The VCE utilizes actual monitoring data to run the best available corrosion models and provides a continuously updated dashboard in real time. The overall goal is not to remove the need for real engineers but to arm those people with the most accurate and up to date information in the most efficient possible way, thus freeing up their time to focus on decision-making and continuous improvement of the underlying models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.L. and A.T.; methodology, A.T. and W.H.; software, A.T., V.V. and P.S.; formal analysis, J.P., V.V., P.S. and A.R.; writing—original draft preparation, N.L.; writing—All; project administration, A.T. and W.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The VCE project is internally funded within Shell. The work on UDC model development is a part of Shell’s in-kind contribution to grant NPRP12S-0228-190182, funded by the Qatar Foundation under the National Priorities Research Program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Qatar Foundation had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- API Recommended Practice 580, Risk Based Inspection, 3rd ed.; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- AS/NZ Standard 3788, Pressure Equipment—In Service Inspection, 4th ed.; Standards New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2006.
- Britton, C.F. Corrosion Monitoring and Inspection. In Shreir’s Corrosion, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 3117–3166. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, D.D.; Engelhardt, G.R. Predictive Modeling of Corrosion. In Shreir’s Corrosion, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1630–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, R.D.; Eden, D.C.; Amidi, S.; Delve, D. Implementation of Real-Time Corrosion Monitoring with Industrial Process Control & Automation; Paper NACE-07268; CORROSION: Nashville, TN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, P.; Kane, R.D.; Castillo, M.; Lagad, V. Improving Amine Unit Reliability with On-Line Corrosion Monitoring & Modeling; Paper NACE-08421; CORROSION: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- API Recommended Practice 941, Steels for Hydrogen Service at Elevated Temperatures and Pressures in Petroleum Refineries and Petrochemical Plants, 8th ed.; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Dooley, R.B.; Bursik, A. Caustic Gouging. Powerpl. Chem. 2010, 12, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, R.B.; Bursik, A. Acid Phosphate Corrosion. Powerpl. Chem. 2010, 12, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, R.B.; Bursik, A. Underdeposit Corrosion. Powerpl. Chem. 2009, 11, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, R.B.; Bursik, A. Hydrogen Damage. Powerpl. Chem. 2010, 12, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, C.W. AECL. Nucl. Rev. 2013, 2, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deposition in Boilers: Review of Soviet and Russian Literature; EPRI TR-1004193; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2003.
- Deposition on Drum Boiler Tube Surfaces; EPRI TR-1010186; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2005.
- Deposition on Drum Boiler Tube Surfaces; EPRI TR-1008083; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2004.
- Raman, B.; Hall, D.M.; Shulder, S.J.; Caravaggio, M.F.; Lvov, S.N. An experimental study of deposition of suspended magnetite in high temperature–high pressure boiler type environments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 508, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive Cycle Chemistry Guidelines for Fossil Plants; EPRI TR-1021767; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2011.
- International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam. IAPWS TGD7-16, Technical Guidance Document: HRSG High Pressure Evaporator Sampling for Internal Deposit Identification and Determining the Need to Chemical Clean. Available online: http://www.iapws.org/index.html (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Ramesh, A.; Laycock, N.; Shenai, P.; Barnes, A.; van Santen, H.; Thyagarajan, A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Ryan, M.P. Critical Deposit Loading Thresholds for Under Deposit Corrosion in Steam Generators. 2021, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, F.; Spekkens, P. Concentration processes under tubesheet sludge piles in nuclear steam generators. Nucl. J. Can. 1986, 1, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).