Abstract
The corrosion processes of carbon steel immersed in natural seawater are influenced by microorganisms due to important biological activity. An analysis of the corrosion product layers formed on carbon steel coupons in natural or artificial seawater revealed that sulfate green rust GR(SO42−) was favored in natural environments. In this paper, the role of organic matter/bacteria on the formation and transformation of this compound are addressed. GR(SO42−) was precipitated from Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts in the presence of various marine bacterial species not involved in the redox cycle of Fe or S. Abiotic experiments were performed for comparison, first without any organic species and then with sodium acetate added as a small organic ion. The obtained aqueous suspensions were aged at room temperature for 1 week. The number of bacteria (CFU/mL) was followed over time and the solid phases were characterized by XRD. Whatever the fate of the bacteria (no activity, or activity and growth), the formation of GR(SO42−) was favored and its transformation to magnetite completely inhibited. This effect is attributed to the adsorption of organic molecules on the lateral sides of the GR(SO42−) crystals. A similar effect, though less important, was observed with acetate.
1. Introduction
Natural seawater is a biologically active medium, and it is generally acknowledged that microorganisms influence the corrosion processes of any metal or alloy immersed in a marine environment. In the case of carbon and low alloy steels, the role of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) has long been recognized [1]. This has led to the hypothesis that the long-term corrosion process of carbon steel in seawater could be controlled, at least partially, by the rate of external nutrient supply that governs bacterial activity [2,3]. More generally, it has been shown that the organic molecules released by bacteria somehow influence the behavior of metals. For instance, it has been established that in some cases, extracellular polymeric substances favor the corrosion of carbon steel [4]. Conversely, it was proposed that biofilms could form along with the corrosion products, creating a protective barrier and thus decreasing the corrosion rate [5]. Enzymes, and in particular, hydrogenases that can be present in solution (i.e., out of bacterial cells), are also known to be involved [6,7].
The various molecules associated with the presence and/or activity of microorganisms can interact with the metal itself, but also with its corrosion products. One of the consequences of the activity of SRB is the formation of iron sulfide (FeS), which precipitates from Fe2+aq ions resulting from corrosion and the sulfide species produced by SRB. For this reason, FeS was identified as another major component of the corrosion product layer formed on carbon steel coupons after just 6–12 months of immersion in the water of a seaport [8]. It could be detected locally after only 1 month [9] of immersion, and was associated with SRB in the first de-aerated regions formed inside the corrosion product layer. Due to its electronic conductivity and low overvoltage for water reduction, FeS can act as a cathodic site and promote the formation of galvanic cells [10]. Additionally, it can facilitate the influence of electroactive SRB [11].
Most studies dealing with microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) are focused on the interactions between metal and bacteria or between metal and species released or produced by bacteria [1]. The interactions between these species and the corrosion products, which may modify the properties of the corrosion product layer and thus the corrosion rate, have only been rarely addressed [12,13]. In a recent work, some differences were observed between the corrosion product layers obtained in artificial and natural seawater [14]. These differences were not only related to FeS, which can only form in natural environments as it requires the presence and activity of SRB, but also to sulfate green rust, GR(SO42−), which seemed to be favored in natural environments [14].
GR(SO42−) is one of the main corrosion products forming on carbon steel surfaces which are permanently immersed in natural seawater [5,8,9,15,16,17,18]; it is actually the first solid obtained from dissolved Fe species [9,15,17]. It is a mixed valence Fe(II-III) double layered hydroxide with chemical formula FeII4FeIII2(OH)12SO4·8H2O [19,20], and contains mainly (67%) Fe(II) ions. It is oxidized by dissolved O2, a process that leads to the formation of Fe(III)-oxyhydroxides such as goethite (α-FeOOH) and lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH), and oxides such as magnetite Fe3O4 [21,22,23]. Consequently, any species that can affect the formation and transformation of GR(SO42−) may have an indirect influence on the corrosion process.
The present study is focused on the effect of bacteria in general (i.e., bacteria not known to induce MIC processes) on the formation of GR(SO42−) and the evolution of this compound in anoxic conditions. The idea was not to address the interactions between GR(SO42−) and the bacteria involved in the redox cycles of Fe and S, which have already been documented [12,13,24,25], but to consider bacteria having no specific link with Fe and S, the characteristic elements of GR(SO42−). This study aims to contribute to a better understanding of the interactions between complex bacterial communities and the overall corrosion system through the determination of possible interactions of selected bacteria with GR(SO42−).
First, corrosion experiments were performed in artificial and natural seawater to study the composition of the corrosion product layers in each case. These layers were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and µ-Raman spectroscopy (µ-RS). Secondly, GR(SO42−) was precipitated by mixing a solution of Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts with a solution of NaOH in the presence of three bacterial strains. These strains were isolated from biofilms previously formed on carbon steel coupons immersed in natural seawater [9]. The precipitates were analyzed by XRD after 1 week and 2 months of ageing at room temperature. The bacterial growth during the ageing of the precipitate was also investigated. Finally, GR was precipitated in the presence of sodium acetate to compare the effects of a small organic anion with those observed in the presence of bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Corrosion Experiments
To compare the composition of the corrosion product layers formed on carbon steel in artificial and natural seawater, various S355GP steel coupons (5 cm × 5 cm × 1 cm) were exposed for 6 months in both kinds of environments. The nominal composition of this steel grade, commonly used for sea harbor sheet piles, is in wt.%: C ≤ 0.27, Mn ≤ 1.7, S ≤ 0.055, Si ≤ 0.6, Al ≤ 0.02 and Fe for the rest. The coupons were embedded in epoxy resin so that only one side (active area of 25 cm2) was exposed to seawater. The surface of this side was previously shot blasted (Sa 2.5, angular shot) and degreased with acetone.
First, three coupons were immersed in natural seawater for 6 months in the Minimes harbor, the marina of La Rochelle (Atlantic Ocean), using the experimental platform of the LaSIE laboratory. The coupons were immersed vertically at a depth of ~20 cm (measured from the upper edge of the coupons). As the experimental platform floats on the sea surface, the immersion depth is constant. The temperature of the water close to the coupons was measured regularly. It varied from 9 ± 2 °C at the beginning (February) to 20 ± 2 °C at the end (July) of the experiment. Secondly, three other coupons were exposed to stagnant ASTM D1141 artificial seawater [26] in 10 L tanks. The seawater was renewed after 15 days, and monthly afterwards. The tanks were set in an unheated room so that the average temperature of the water increased from 12 °C (February) to 25 °C (July) during the experiment.
At the end of the experiment, the coupons immersed in the Minimes harbor were carried to the lab in a tank full of natural seawater sampled in situ with the coupons. Then, all coupons were removed from the seawater (artificial or natural) and rapidly transferred to a freezer and stored at −24 °C before analysis. With this procedure, already used in previous works [9,16,17], the samples can be analyzed in a frozen state so that the corrosion product layers, that contain a lot of water, can be easily handled. Due to the complexity of the corrosion product layers forming on steel in seawater [8,9,15,16,17,18], two methods were used to identify the corrosion products, namely µ-Raman spectroscopy (µ-RS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). For each type of seawater, one coupon was analyzed by µ-RS and another by XRD.
µ-RS analysis was carried out at room temperature using a Horiba Raman spectrometer (LabRam HR evo, Horiba, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a confocal microscope and a Peltier-based cooled charge coupled device (CCD) detector. A solid-state diode pumped green laser (wavelength = 532 nm) was used with laser power reduced to 10% (0.6 mW) of the maximum to prevent the transformation of the analyzed compounds into hematite α-Fe2O3. This transformation can take place due to an excessive heating [27,28]. The acquisition time depended on the nature of the analyzed phase, and thus, varied from 60 s to 2 min. At least 20 zones (diameter of 3–6 μm) were analyzed on the same sample using a 50× long working distance objective. The analysis was achieved without specific protection from air because the time required for analysis was short. Additionally, the samples remained wet during the procedure, which minimized oxidation.
For the XRD analysis, the whole corrosion product layer was scraped from the surface of the coupon and ground in a mortar (it was initially solid, as it was frozen) until a homogenous wet paste was obtained. This paste was then analyzed as described in Section 2.5.
2.2. Preparation of Green Rust Precipitates
Green rust compounds can be precipitated by mixing a solution of Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts with NaOH solution [19]. Based on this, a method was developed to prepare GR(SO42−) under conditions simulating seawater, i.e., using Fe(II) and Fe(III) chlorides and adding sodium chloride and sodium sulfate to obtain a suspension with overall chloride and sulfate concentrations similar to those typical of seawater [23,29]. In the present study, this method was used once again. The concentrations of reactants are listed in Table 1, together with the distribution of the reactants in the two prepared solutions.

Table 1.
Concentrations of reactants used to prepare the initial green rust precipitate (mol L−1), expressed with respect to the total volume of solution (200 mL = solution 1 + solution 2), and considered bacterial strains.
To obtain the GR precipitate, solution 1 (100 mL) was added to solution 2 (100 mL) and the overall 200 mL of suspension was vigorously stirred for 30 s at room temperature (RT = 21 ± 1 °C). After stirring, the suspension was poured into a flask, filled to the rim. The flask was hermetically sealed to avoid any oxidation by air of the precipitates during ageing periods of 1 week and 2 months. The aged precipitates were finally filtered for analysis by XRD. They were sheltered from air with a plastic membrane during filtration to avoid the oxidation of the obtained GR compounds.
The NaOH, FeCl2·4H2O and FeCl3·6H2O concentrations used here correspond to the stoichiometry of the precipitation of the sulfate GR. This reaction can be written as:
4Fe2+ + 2Fe3+ + 12OH− + SO42− + 8H2O → FeII4 FeIII2 (OH)12 SO4·8H2O
2.3. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
Considering that the influence of microorganisms/organic matter may depend significantly on the bacterial species present, three different bacterial strains (belonging to different families of bacteria) were considered: Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004, Micrococcus IVA008 and Bacillus IVA016. They were previously isolated from the biofilm covering carbon steel coupons immersed for 1 week (Pseudoalteromonas) or 2 weeks (Micrococcus and Bacillus) in natural seawater (La Rochelle marina, Atlantic Ocean) [9]. Each strain was previously identified by sequencing the 16S rRNA gene (accession numbers in the GenBank database: KJ814569 for Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004, KJ814564 for Micrococcus IVA008 and KJ814540 for Bacillus IVA016) [9]). These bacteria do not belong to the families of bacteria classically described as SRB, iron oxidizing bacteria (IOB) or iron reducing bacteria (IRB). The three considered strains were cultured in aerobic conditions, and consequently, were not SRB that can only grow in anaerobic conditions (or in an environment with a low oxygen concentration).
For bacterial growth, the culture medium used, called Marine Broth, was composed of ammonium nitrate 0.0016 g L−1, anhydrous magnesium chloride 8.8 g L−1, bacteriological peptone 5 g L−1, boric acid 0.022 g L−1, anhydrous calcium chloride 1.8 g L−1, disodium phosphate 0.008 g L−1, potassium bromide 0.08 g L−1, potassium chloride 0.55 g L−1, sodium bicarbonate 0.16 g L−1, sodium chloride 19.4 g L−1, sodium fluoride 0.0024 g L−1, sodium silicate 0.004 g L−1, sodium sulfate 3.24 g L−1, strontium chloride 0.034 g L−1, yeast extract 1 g L−1 and ferric citrate 0.1 g L−1. The culture medium was sterilized for 20 min at 115 °C.
A concentrated suspension (5 mL) of the three bacteria was first prepared. For each strain, 200 mL of Marine Broth was inoculated with bacteria at 2%, from an overnight culture in Marine Broth, and incubated at 30 °C under constant stirring (orbital shaker, 160 rpm). After 24 h of incubation, all three bacterial suspensions were centrifuged for 20 min at 5000× g. The centrifugation pellet was finally set again in suspension in 5 mL of ASTM D1141 artificial seawater [26]. The final suspension of bacteria was then added to NaOH solution 1 (see Table 1).
2.4. Numeration of Bacteria
Quantification of bacteria was performed at four stages of the process: (1) after 24 h of growth independently for each strain, (2) once the bacteria had been concentrated, (3) right after mixing solutions 1 and 2, i.e., right after the formation of the GR precipitate, and (4) after the 1-week ageing period at RT (see Section 2.2) in a hermetically sealed flask. For aged samples, because of decantation, the solid phase(s) settled at the bottom of the flask. Consequently, the supernatant liquid phase and the decanted precipitate (solid phase) could be sampled and analyzed separately.
In each case, a 100 µL sample was prepared by serial dilutions (10−1 to 10−6) of the cell suspension in artificial seawater and inoculated on a solid culture medium composed of Marine Broth with 1.2% (w/v) agar. After incubation at 30 °C in aerobic conditions, bacterial growth was evaluated by counting the number of colony forming units (CFU) (three replicates). The results are expressed in CFU mL−1.
2.5. XRD Analysis of the Precipitates
XRD analysis was performed with an Inel EQUINOX 6000 diffractometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a CPS 590 detector that detects the diffracted photons simultaneously on a 2θ range of 90°. Co-Kα radiation (λ = 0.17903 nm) was used at 40 kV and 40 mA, with the XRD analysis being performed at RT with a constant angle of incidence (5 degrees) for 45 min. To prevent the oxidation of GR compounds during preparation and analysis, the wet paste obtained after filtration of the sample was mixed with a few drops of glycerol. With this procedure, the GR particles were coated with glycerol and sheltered from the oxidizing action of O2 [30]. The angular scale was calibrated using the diffraction peaks of magnetite (if present).
The crystalline phases were identified via the ICDD-JCPDS (International Center for Diffraction Data—Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards) database, and the peaks indexed according to the corresponding file. The parameters of the diffraction peaks, i.e., interplanar distance, intensity and full width at half maximum, were determined via a computer fitting of the experimental diffraction patterns. The diffraction peaks were fitted with pseudo-Voigt functions to take into account the evolution of the peak profile with increasing diffraction angle. The fitting procedure was achieved using the OriginPro 2016 software (OriginLab).
µ-Raman spectroscopy was not used for the characterization of the precipitates because (i) this method is not suitable to distinguish between the various GR compounds [31], and (ii) the bacterial cells and associated organic matter mixed with the solid phases induce an important fluorescence phenomenon that makes it difficult to acquire usable data.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Corrosion Product Layers Formed in Artificial/Natural Seawater
As already reported in previous studies, the corrosion product layer forming on carbon steel in seawater is, in most cases, a bilayer, composed of an inner black stratum which is in contact with the metal surface and an outer orange stratum which is in contact with the marine medium [8,9,15,16,17,18]. The layers obtained in this study verified this general trend too.
The results given by µ-RS are described first, and two typical µ-RS spectra are displayed in Figure 1. Table 2 lists all the components identified by µ-RS in the corrosion product layers of the analyzed coupons. Because a large number of zones were analyzed in each layer, three kinds of components could be identified: the main ones, frequently occurring ones and minor ones which were rarely observed.
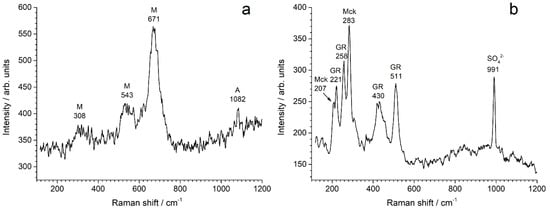
Figure 1.
Raman spectra (examples) obtained during the analysis of the corrosion product layers formed after 6 months in: (a) artificial and (b) natural seawater. M = magnetite, A = aragonite, Mck = nanocrystalline mackinawite and GR = green rust, with the position (in cm−1) of the corresponding Raman peak.

Table 2.
µ-RS analysis of the corrosion product layers formed after 6 months in artificial/natural seawater: synthesis of the results.
For the coupon left for 6 months in artificial seawater, the main identified component was magnetite Fe3O4. A typical spectrum is shown in Figure 1a. The three characteristic peaks of magnetite are clearly seen, with the most intense one at 671 cm−1 and two smaller ones at 308 and 543 cm−1, as reported in literature data [27,28,32]. Magnetite was mainly identified in the inner black stratum of the corrosion product layer. Lepidocrocite γ-FeOOH and aragonite were also frequently identified, mainly in the outer orange stratum. Aragonite is not a corrosion product, as it is a form of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), but it is often associated with corrosion products in the cathodic zones of the metal surface [14,17,18]. The small increase of the interfacial pH in these zones is sufficient to induce the precipitation of aragonite from the dissolved Ca2+ and carbonate species present in seawater. The main peak of aragonite at 1082 cm−1 [33] is visible on the spectrum of Figure 1a. More rarely, green rusts, i.e., ferrihydrite (FeOOH·H2O) and chukanovite (Fe2(OH)2CO3), were also identified, but only in the inner black stratum.
For the coupon left 6 months in natural seawater, only the inner black stratum of the corrosion product layer was analyzed. In the outer orange layer, the biofouling mixed with the corrosion products induced an important fluorescence phenomenon that made it difficult to acquire useful data. The FeOOH phases, mainly present in the outer orange layer, thus do not appear in Table 2 for this coupon (except for ferrihydrite, identified as a minor component). In this case, the main compounds identified in the black inner stratum were nanocrystalline mackinawite (FeS) and magnetite. Nanocrystalline mackinawite is the iron sulfide that forms from the dissolved Fe(II) species [34,35] produced by the corrosion of steel, and the dissolved sulfide species produced by SRB. Its Raman spectrum is characterized by two peaks, i.e., the main one at 283 cm−1 and the other at 207 cm−1 [35], as illustrated by Figure 1b. The spectrum of (well) crystallized mackinawite is slightly different, with the main peak occurring at 300 cm−1 [35]. GR compounds were also frequently identified. In Figure 1b, the spectral signature of nanocrystalline mackinawite is accompanied by that of a GR compound that may be GR(SO42−) or GR(CO32−). Both GRs have similar spectra, with two main peaks at 430–535 cm−1 and 510–515 cm−1 and two smaller ones at ~220 cm−1 and ~260 cm−1 [36,37]. The characteristic sulfate ion peak at 991 cm−1 does not demonstrate that this GR is GR(SO42−), as it could correspond to sulfate ions adsorbed on the surface of GR(CO32−) crystals.
It must be kept in mind that Figure 1 only shows one selected spectrum from each coupon. Magnetite was identified by µRS as one of the main components of the corrosion product layer in both cases, as reported in Table 2. However, in some cases, given the small size of the zone analyzed by µRS, magnetite was not observed. This means that some small regions of the corrosion product layer did not contain magnetite, as illustrated in Figure 1b.
The results given by XRD, consistent with those given by µ-RS, are presented in Figure 2. The first pattern (a) is that of the corrosion product layer formed in stagnant artificial seawater. The most intense diffraction peaks are unambiguously those of magnetite. Numerous diffraction peaks of aragonite and lepidocrocite are clearly seen. Finally, both GR(SO42−) and GR(CO32−) may be identified, but only owing to their main diffraction peak (GR001 or GRC003) that is very weak.
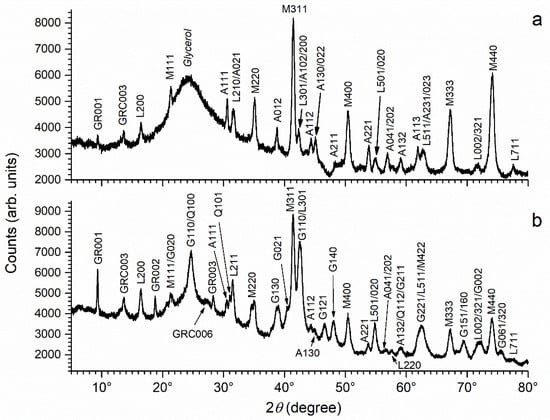
Figure 2.
XRD pattern of the corrosion product layers formed after 6 months in: (a) artificial and (b) natural seawater. GR = GR(SO42−), GRC = GR(CO32−), A = aragonite, G = goethite, L = lepidocrocite, M = magnetite and Q = quartz, with the corresponding Miller index.
For the coupon immersed in natural seawater, corresponding to pattern (b), the main diffraction peaks are those of magnetite and goethite. If compared with pattern (a), the diffraction peaks of aragonite are slightly less intense, while those of lepidocrocite and GR(CO32−) appear slightly more intense. Finally, the diffraction peaks of GR(SO42−) are much more intense in pattern (b). As noted previously [8,17], the XRD analysis did not allow us to detect mackinawite FeS, because this phase remains in a nanocrystalline state.
In conclusion, the main observed difference between both kinds of coupons is the presence of FeS in the corrosion product layer formed in natural conditions a result of bacterial (SRB) activity. This FeS phase is nanocrystalline and was only identified via µ-RS analysis. However, the XRD analysis revealed other differences. In particular, it confirmed that the formation of GR(SO42−) was indeed favored in the natural seawater of the harbor site.
3.2. Characterization of the Precipitate Obtained in Abiotic Conditions
In this section, and in Section 3.3 and Section 3.4, the precipitates obtained by mixing NaOH with Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts are characterized.
Under the abiotic conditions considered here, and as previously studied [23], the initial precipitate was composed of a mixture of GR(Cl−) and GR(SO42−). After 1 week of ageing, the proportion of GR(Cl−) drastically decreased. The XRD pattern presented in Figure 3 confirms this result: only the main peaks of GR(Cl−) are seen and their intensity is very small with respect to that of the peaks of GR(SO42−). However, the ageing induced the formation of a small amount of magnetite Fe3O4. This evolution was attributed to the respective stability of the three phases [23], i.e., magnetite is more stable than GR(SO42−), which, in turn, is more stable than GR(Cl−) in the conditions considered here.
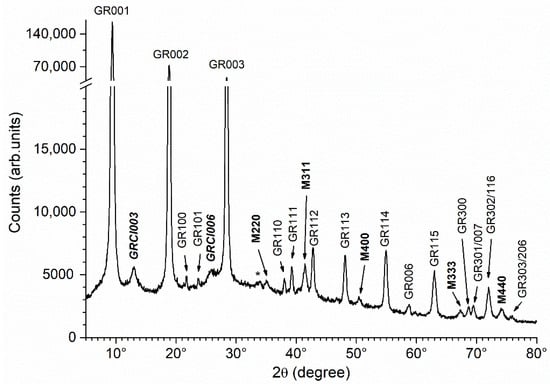
Figure 3.
XRD pattern of the precipitate obtained without addition of bacteria or organic compounds, after 1 week of ageing at RT. GR = GR(SO42−), GRCl = GR(Cl−) and M = magnetite, with the corresponding Miller index. * = unidentified peak.
This XRD pattern will be used below as a reference. The intensities of the diffraction peaks M311, GRCl003, GR001 and GR112 were determined by computer fitting as described in Section 2.5. The results of this analysis are presented in Table 3, with the intensity of the main peak of GR(SO42−), i.e., GR001, being arbitrarily set as 100 in each case.

Table 3.
Abiotic precipitate aged for 1 week: characteristics of the diffraction peaks GR001 and GR112 of GR(SO42−), GRCl003 of GR(Cl−) and M311 of magnetite; 2θ = diffraction angle, in degree, d = interplanar distance (Å), FWHM = full width a half maximum, in degree, and I = peak intensity, with I = 100 for GR001.
The interplanar distance d001 obtained for GR(SO42−) corresponded to the c parameter of the hexagonal cell. It was determined here at 11.00 Å, a value consistent with literature data [20]. The intensity of the GR112 peak was abnormally small, due to the preferential orientation of the GR particles. These particles comprised thin hexagonal platelets perpendicular to the c axis of the crystal structure [16]. For this reason, they were usually parallel to the sample holder. This preferential orientation increased the intensity of the 00l diffraction peaks. The interplanar distance d003 found for GR(Cl−) was also consistent with literature data [38].
3.3. Influence of Bacteria
The results of the study of bacterial growth and quantification are presented in Table 4. Each bacterial strain grew rapidly in the culture medium, reaching between 1.7 and 3.3 × 109 CFU mL−1 after 24 h at 30 °C, and showing similar cell concentrations for the three strains. All the initial concentrated suspensions of bacteria contained more than 3 × 1011 CFU mL−1 of bacteria prior to mixing with the reagents used to prepare the GR precipitate. However, the results obtained after precipitation proved to be highly dependent on the considered bacterial strain. For Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004, no viable culturable bacteria could be enumerated. The same result was obtained for this strain 1 week later in both the precipitate and supernatant. In the first case, the Fe solid phases were precipitated and aged in a medium where the bacteria did not grow, likely because of cellular death due to the immersion of the bacteria in the NaOH solution 1.

Table 4.
Numeration of bacteria (CFU mL−1).
In contrast, both Micrococcus IVA008 and Bacillus IVA016 remained viable and culturable throughout the experiments, even though the cell concentration after precipitation decreased from the initial concentrated suspension. In both cases, the results obtained in the precipitate after 1 week of ageing were similar to those obtained right after precipitation. A slight increase of the bacterial concentration was even observed, in particular for Micrococcus IVA008. In contrast, no viable culturable bacteria could be enumerated in the supernatant after ageing. This shows that the bacteria were mostly associated with the solid phases, more likely bound to the particles of Fe compounds. In this second case, the Fe compounds were precipitated and aged in a medium where bacteria survived and even developed.
The XRD analysis of the precipitates obtained after 1 week of ageing in the presence of bacteria provided results independent of the bacterial strain. The pattern obtained for the precipitate aged with Micrococcus IVA008 is displayed in Figure 4. It is mainly composed of the diffraction peaks of GR(SO42−) that may all be clearly seen. Numerous additional, very small peaks are present, but they do not correspond to other expected Fe compounds, i.e., GR(Cl−) and magnetite, that are formed in abiotic conditions (Figure 3). These peaks were likely due to the various compounds, organic and inorganic, present in the concentrated bacterial suspension introduced in the system (see Section 2.3 for instance, where the composition of the culture medium is given). Only one small peak could be tentatively identified: located at 2θhkl = 13.756°, i.e., dhkl = 7.47 Å, it may correspond to the main diffraction peak of GR(CO32−) [30,39], i.e., GRC003, as mentioned in Figure 4. NaHCO3 is present in the culture medium and bacteria produce carbonate species through their metabolic activity by oxidizing organic matter.
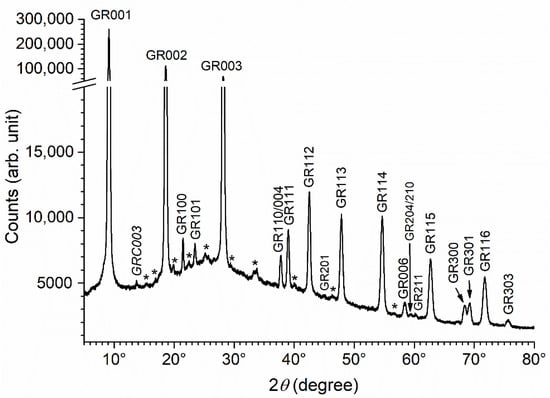
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of the precipitate obtained with bacterial strain Micrococcus IVA008 after 1 week of ageing at RT. GR = GR(SO42−) and GRC = GR(CO32−), with the corresponding Miller index. * = unidentified peaks.
The XRD patterns obtained for the precipitates aged with bacterial strains Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004 and Bacillus IVA016 are both displayed in Figure 5. These patterns, like the previous one, did not show any trace of the diffraction lines of GR(Cl−) or magnetite. Numerous additional small peaks are also seen, located at similar positions regardless of the bacteria species. The main peak of GR(CO32−) was not seen in the case of Bacillus IVA016. It was very small in the case of Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004, but could nonetheless be identified.
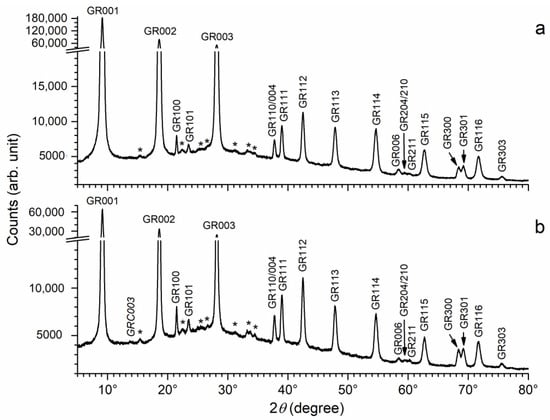
Figure 5.
XRD pattern of the precipitates obtained with bacterial strain Bacillus IVA016 (a) and Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004 (b) after 1 week of ageing at RT. GR = GR(SO42−) and GRC = GR(CO32−), with the corresponding Miller index. * = unidentified peaks.
In conclusion, the presence of bacteria and associated organic matter prevented the formation of magnetite during ageing. The absence of GR(Cl−) showed that the bacteria and associated organic matter either accelerated the transformation of GR(Cl−) to GR(SO42−) or prevented the formation of GR(Cl−) during the precipitation reaction.
The precipitates were also aged for 2 months at RT. Once again, the results were similar for all bacterial strains. The pattern obtained for the precipitate aged 2 months with bacterial strain Micrococcus IVA008 is displayed in Figure 6 as an example. It was very similar to that of the precipitate aged 1 week, i.e., the main diffraction peaks were those of GR(SO42−), and the peaks of GR(Cl−) and magnetite were not seen. This demonstrates that the effects of the bacteria and the associated organic matter can persist for long periods. This may explain why GR(SO42−) is favored in natural marine environments, as shown in Section 3.1.
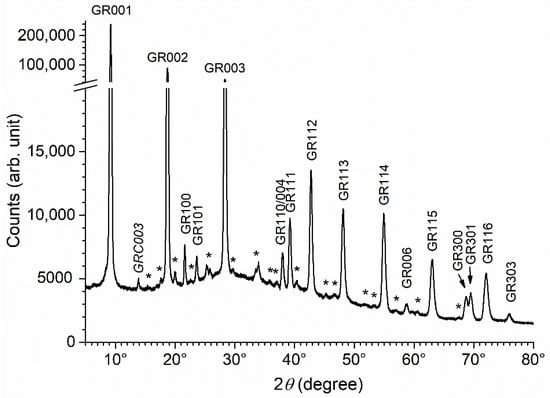
Figure 6.
XRD pattern of the precipitate obtained with bacterial strain Micrococcus IVA008 after 2 months of ageing at RT. GR = GR(SO42−) and GRC = GR(CO32−), with the corresponding Miller index. * = unidentified peaks.
Finally, it can be noted that the numerous unidentified diffraction peaks, as well as the main peak of GR(CO32−), were, compared to those of GR(SO42), more intense after 2 months of ageing. This can be observed visually by comparing Figure 4 and Figure 6. To be more accurate, the intensities of the GR001 and GRC003 peaks were determined in each case by computer fitting, as described in Section 2.5. If the intensity of the GR001 peak was arbitrarily set at 100 in each case, then the intensity of the GRC003 peak slightly increased from 0.40(±0.01) to 0.45(±0.01) during ageing (from 1 week to 2 months). This may be attributed to weak bacterial activity.
3.4. Influence of Acetate Ions
The XRD pattern of the precipitate obtained with sodium acetate added as a reactant and after 1 week of ageing is displayed in Figure 7. The main diffraction peaks are once again those of GR(SO42−), even though the acetate to sulfate concentration ratio, [CH3COO−]/[SO42−], was equal to 2. Actually, it is well known that the double layered structure of GR compounds exhibits a stronger affinity for divalent anions [40,41], which explains why GR(SO42−) forms instead of GR(Cl−) in seawater, even though the [Cl−]/[SO42−] is high (about 19). The formation of GR(SO42−) in this experiment was consistent with the findings in previous works.
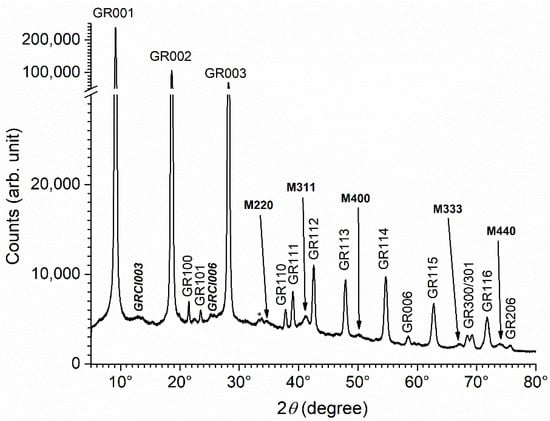
Figure 7.
XRD pattern of the precipitate obtained with acetate after 1 week of ageing at RT. GR = GR(SO42−), GRCl = GR(Cl−), M = magnetite, with the corresponding Miller index. * = unidentified peaks.
As for the precipitate obtained in abiotic conditions without acetate, most of the diffraction peaks of magnetite were seen, together with the main peaks of GR(Cl−), i.e., GRCl003 and GRCl006. From Figure 3 and Figure 7, it can be seen that the addition of acetate decreased the intensity of the diffraction peaks of GR(Cl−) and magnetite with respect to those of GR(SO42). The data obtained via computer fitting of diffraction peaks GR001, GR112, GRCl003 and M311 confirmed this (Table 5). The intensity of the main peak of magnetite decreased from 4.6 (Table 3) to 2.0, and that of GR(Cl−) from 7.0 to 1.8. The intensity of the GR112 lines, in contrast, increased from 3.2 to 5.9, which shows that the preferential orientation is less pronounced. If the intensity of the magnetite and GR(Cl−) diffraction peaks were expressed with respect to the 112 diffraction peak of GR(SO42), the decrease due to the acetate ions would appear more significant.

Table 5.
Precipitate obtained with acetate and aged 1 week: characteristics of the diffraction peaks GR001 and GR112 of GR(SO42−), GRCl003 of GR(Cl−) and M311 of magnetite; 2θ = diffraction angle, in degree, d = interplanar distance (Å), FWHM = full width a half maximum, in degree, and I = peak intensity, with I = 100 for GR001.
In conclusion, acetate ions induced the same effects as bacteria, but these effects were smaller and did not completely prevent the formation of magnetite and GR(Cl−).
4. Discussion
GR compounds are metastable with respect to magnetite [19,42,43]. For instance, depending on pH and dissolved Fe2+ concentration, the precipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ can yield either GR(SO42−) or the two-phase system Fe3O4 + Fe(OH)2 [19]. GR compounds are also likely to be spontaneously transformed into magnetite. GR(CO32−) was observed to transform spontaneously under anoxic conditions, resulting in either a mixture of magnetite and siderite (FeCO3) [42] or a mixture of magnetite, chukanovite (Fe2(OH)2CO3) and siderite [43], depending on the pH and the concentration of the carbonate species. The metastability of GR(SO42−) with respect to magnetite explains why the ageing of GR(SO42−) in the experimental abiotic conditions considered here induced the formation of a small proportion of Fe3O4.
However, it was demonstrated that the adsorption of phosphate ions on the lateral sides of the GR(CO32−) particles could prevent their transformation to magnetite [44]. Similarly, lactate ions proved to have a strong effect during the oxidation of GR(SO42−), which was attributed to the adsorption of the lactate ions, through their carboxyl group, on the surface of the GR crystals [37]. It can therefore be proposed that acetate ions adsorb similarly on the lateral sides of the GR(SO42−) hexagonal platelets (Figure 8) and hinder the formation of magnetite during ageing. The organic polymeric substances associated with bacteria may therefore have similar effects. The bioreduction of lepidocrocite γ-FeOOH by Shewanella putrefaciens was studied, and it was observed that the formation of GR compounds was favored, with respect to the formation of magnetite, in the presence of polyacrylic acid or polyacrylamide [45]. Polyacrylic acid, which can model extracellular polymeric substances found in biofilms, was also observed to inhibit, albeit moderately, the reactivity of GR compounds towards methyl red [46]. This reactivity was assumed to mainly involve the Fe(II) reactive sites present on the lateral sides of the GR crystals. Polyacrylic acid, like acetate ions, carries a negatively charged carboxyl group. This confirms that GR compounds can be stabilized by carboxylates.
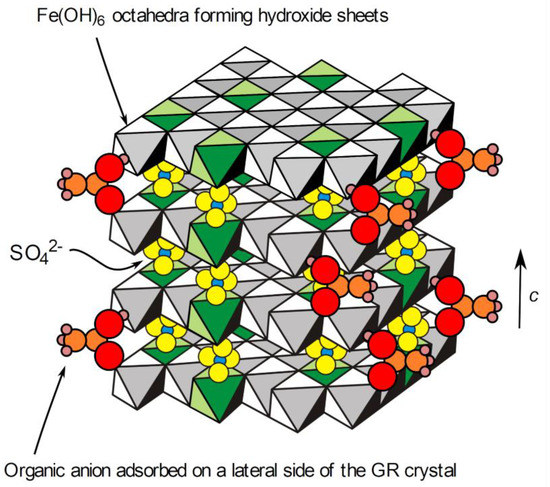
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of a GR(SO42−) crystal with adsorbed acetate ions. The interlayers are actually composed of two layers of SO42− ions and include water molecules that were omitted for clarity. The octahedra in green are those built on Fe(III) cations.
Our results showed that the presence of bacteria cells led to stronger effects, because it prevented the formation of magnetite even after 2 months of ageing in anoxic conditions. This effect was the same whether the bacteria were dead (Pseudoalteromonas IIIA004) or alive and active (Micrococcus IVA008 and Bacillus IVA016). The only difference observed was the formation of a very small amount of GR(CO32−), which resulted from the presence of NaHCO3 in the culture medium and/or the oxidation of organic substances to carbonate by the microorganisms. In the study of the reactivity of GR compounds toward methyl red, it was demonstrated that bacterial cells had a stronger effect on the reactivity of GR(SO42−) than polyacrylic acid [46]. This is fully consistent with what was observed here by comparing the results obtained in the presence of bacteria and those obtained with acetate. The stronger effect of bacterial cells and/or associated organic species, in particular with respect to the much smaller CH3COO− ions, may have been due to a higher steric effect that would more efficiently hinder the interaction between the GR crystal surfaces (in particular lateral sides) and solution, as illustrated schematically in Figure 8. The transformation of GR(SO42−) to magnetite requires the release in solution of the SO42− ions present in the interlayers of the GR structure, which was assumed to be hindered by the adsorption of anionic species on the lateral sides of the crystals [44]. Voluminous adsorbed species obviously induce a stronger barrier effect than small ones.
The presence of the bacteria, and to a lesser extent, of acetate ions, also led to the absence of GR(Cl−) after 1 week of ageing. Two mechanisms can be proposed to explain this. First, it can be proposed that the bacterial cells and/or the associated organic species accelerate the transformation of GR(Cl−) to GR(SO42−). However, since bacteria cells tend to stabilize GR crystals, preventing their transformation, this first assumption seems unlikely. The second hypothesis is that bacterial cells and/or associated organic species inhibit the formation of GR(Cl−). During the precipitation reaction, all of the anionic species present in solution may initially adsorb on the Fe-hydroxide sheets that constitute the basic elements of the GR structure [18] (see also Figure 8). In the reference abiotic experiment, only Cl− ions could compete with SO42− to adsorb on these hydroxides sheets, which led to the formation of a small amount of GR(Cl−), together with GR(SO42−). Over time, GR(Cl−) transformed spontaneously to the more stable GR(SO42−) [23]. When bacteria or acetate were added to the reactants, other species could compete with Cl− and SO42−. It can therefore be postulated, in particular with bacteria and the numerous associated organic species, that the preferential adsorption of monovalent organic anionic species on the hydroxide sheets prevented the formation of GR(Cl−) and favored the formation of GR(SO42−), with SO42 being the main divalent available anionic species.
5. Conclusions
Aqueous suspensions of GR(SO42−) were obtained by mixing a solution of Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts with a NaOH solution and ageing for 1 week in anoxic conditions. Bacterial cells (dead or still alive and active) and/or associated organic species, for instance, extracellular polymeric substances, prevented the transformation of GR(SO42−) to magnetite in anoxic conditions. Similar effects, albeit less important, were observed with acetate ions added to the system. It is proposed that the adsorption of organic species on the lateral sides of the GR(SO42−) crystals hinders the release of SO42− ions into solution, a process required for the transformation of GR(SO42−) to magnetite. After further ageing (up to two months) in the presence of bacterial cells, magnetite was not observed either.
GR(Cl−) was observed as a minor component together with GR(SO42−) in the absence of bacteria or acetate. Acetate ions decreased the amount of obtained GR(Cl−) whereas bacteria prevented completely its formation. This suggests that monovalent organic anionic species compete with Cl− during the precipitation reaction and prevent the formation of GR(Cl−), consequently favoring that of the more stable GR(SO42−).
The corrosion product layer formed on carbon steel in a natural marine environment appeared to be enriched in GR(SO42−) with respect to the layer formed in artificial seawater. This may be a consequence of the interaction between GR(SO42−), and, more generally, GR compounds, with bacterial cells and associated organic matter.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R., M.J., R.S., I.L. and S.S.; methodology, P.R., M.J., R.S., I.L. and S.S.; validation, P.R., M.J., R.S., I.L. and S.S.; formal analysis, J.D., J.V., P.R., M.J., I.L. and S.S.; investigation, J.D., J.V., P.R. and M.J.; data curation, P.R., M.J., I.L. and S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, P.R.; writing—review and editing, P.R., M.J., I.L., R.S. and S.S.; visualization, P.R.; supervision, P.R., M.J., I.L., R.S. and S.S.; project administration, P.R., M.J., R.S., I.L. and S.S.; funding acquisition, P.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Nielsen, P.H.; Hamilton, W.A. Role of sulfate-reducing bacteria in corrosion of mild steel: A review. Biofouling 1995, 8, 165–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E.; Wells, T. Models for the anaerobic phases of marine immersion corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E.; Jeffrey, R. Corrosion of long vertical steel strips in the marine tidal zone and implications for ALWC. Corros. Sci. 2012, 65, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, I.B.; Zinkevich, V.; Tapper, R.; Gubner, R. The direct involvement of extracellular compounds from a marine sulphate-reducing bacterium in deterioration of steel. Geomicrobiol. J. 1998, 15, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, E.; Kervadec, D.; Gil, O.; Lefevre, Y.; Malard, S. Interactions between steels and sulphide-producing bacteria-Corrosion of carbon steels and low-alloy steels in natural seawater. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.V.R.; Singh, R.; Nigam, R.K. Mössbauer spectroscopy of corrosion products of mild steel due to microbiologically influenced corrosion. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1999, 242, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanna, M.; Basseguy, R.; Delia, M.-L.; Girbal, L.; Demuez, M.; Bergel, A. New hypotheses for hydrogenase implication in the corrosion of mild steel. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pineau, S.; Sabot, R.; Quillet, L.; Jeannin, M.; Caplat, C.; Dupont-Morral, I.; Refait, P. Formation of the Fe(II-III) hydroxysulphate green rust during marine corrosion of steel associated to molecular detection of dissimilatory sulphite-reductase. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanneluc, I.; Langumier, M.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Refait, P.; Sablé, S. On the bacterial communities associated with the corrosion product layer during the early stages of marine corrosion of carbon steel. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 99, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Miller, J.D.A. Nature of sulfides and their corrosive effect on ferrous metals: A review. Br. Corros. J. 1975, 10, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enning, D.; Venzlaff, H.; Garrelfs, J.; Dinh, H.T.; Meyer, V.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Hassel, A.W.; Stratmann, M.; Widdel, F. Marine sulfate-reducing bacteria cause serious corrosion of iron under electroconductive biogenic mineral crust. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1772–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zegeye, A.; Huguet, L.; Abdelmoula, A.; Carteret, C.; Mullet, M.; Jorand, F. Biogenic hydroxysulfate green rust, a potential electron acceptor for SRB activity. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 5450–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langumier, M.; Sabot, R.; Obame-Ndong, R.; Jeannin, M.; Sablé, S.; Refait, P. Formation of Fe(III)-containing mackinawite from hydroxysulphate green rust by sulphate reducing bacteria. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2694–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboscq, J.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Refait, P. Localized corrosion of carbon steel in seawater: Processes occurring in cathodic zones. Mater. Corros. 2019, 70, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Du, M.; Hou, B. Corrosion of carbon steel influenced by anaerobic biofilm in natural seawater. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Nguyen, D.D.; Jeannin, M.; Sablé, S.; Langumier, M.; Sabot, R. Electrochemical formation of green rusts in deaerated seawater-like solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 6481–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; François, E.; Sabot, R. Localized corrosion of carbon steel in marine media: Galvanic coupling and heterogeneity of the corrosion product layer. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.M.; Jeannin, M.; Rémazeilles, C.; Sabot, R. Corrosion of carbon steel in marine environments: Role of the corrosion product layer. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Géhin, A.; Abdelmoula, M.; Génin, J.-M.R. Coprecipitation thermodynamics of iron(II–III) hydroxysulphate green rust from Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; François, M.; Refait, P.; Renaudin, G.; Lelaurain, L.; Génin, J.M. Structure of the Fe(II-III) layered double hydroxysulphate green rust two from Rietveld analysis. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detournay, J.; De Miranda, L.; Dérie, R.; Ghodsi, M. The region of stability of green rust II in the electrochemical potential-pH equilibrium diagram of iron in sulphate medium. Corros. Sci. 1975, 15, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, A.A.; Génin, J.-M.R. The mechanism of oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in sulphated aqueous media: Importance of the initial ratio of reactants. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 965–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M. Role of Al(III) and Cr(III) on the formation and oxidation of the Fe(II–III) hydroxysulfate green rust. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ona-Nguema, G.; Carteret, C.; Benali, O.; Abdelmoula, M.; Génin, J.-M.R.; Jorand, F. Competitive formation of hydroxycarbonate green rust I vs hydroxysulphate green rust 2 in Shewanella putrefaciens cultures. Geomicrobiol. J. 2004, 21, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, A.; Ona-Nguema, G.; Carteret, C.; Huguet, L.; Abdelmoula, M.; Jorand, F. Formation of hydroxysulphate green rust 2 as a single iron(II-III) mineral in microbial culture. Geomicrobiol. J. 2005, 22, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM D1141-98(2013); Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- De Faria, D.L.A.; Silva, S.V.; Oliveira, M.T.D. Raman micro spectroscopy study of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebanova, O.N.; Lazor, P. Raman study of magnetite (Fe3O4): Laser-induced thermal effects and oxidation. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Duboscq, J.; Aggoun, K.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M. Influence of Mg2+ ions on the formation of green rust compounds in simulated marine environments. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2021, 2, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.C.B. Composition, stabilisation, and light absorption of Fe(II)-Fe(III) hydroxycarbonate (green rust). Clay Miner. 1989, 24, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; François, E.; Sabot, R. Corrosion of carbon steel at the mud zone/seawater interface: Mechanisms and kinetics. Corros. Sci. 2018, 130, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicot, D.; Mendoza, J.; Zaoui, A.; Louis, G.; Lepingle, V.; Roudet, F.; Lesage, J. Mechanical properties of magnetite (Fe3O4), hematite (α-Fe2O3) and goethite (α-FeO·OH) by instrumented indentation and molecular dynamics analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, Z.; Makreski, P.; Gajic, B. Identification and spectra–structure determination of soil minerals: Raman study supported by IR spectroscopy and X-ray powder diffraction. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohfuji, H.; Rickard, D. High resolution transmission electron microscopic study of synthetic nanocrystalline mackinawite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 241, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdoiseau, J.A.; Jeannin, M.; Sabot, R.; Rémazeilles, C.; Refait, P. Characterisation of mackinawite by Raman spectroscopy: Effects of crystallisation, drying and oxidation. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3247–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, L.; Sagon, G.; Lecomte, S.; Chausse, A.; Messina, R. A Raman and infrared study of a new carbonate green rust obtained by electrochemical way. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Gadouleau, M.; Guo, Q.; Sicre, E.; Refait, P. Influence of lactate ions on the formation of rust. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Abdelmoula, M.; Génin, J.-M.R. Mechanisms of formation and structure of green rust one in aqueous corrosion of iron in the presence of chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, J.R.; McEnaney, B.; Smith, D.C. Crystal structure of green rust formed by corrosion of cast iron. Nature 1976, 259, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S. Anion-exchange properties of hydrotalcite-like compounds. Clays Clay Miner. 1983, 31, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiboure, A.; Schöllhorn, R. Formation and anion exchange reactions of layered transition metal hydroxides [Ni1-xMx](OH)2(CO3)x/2(H2O)z (M=Fe,Co). Rev. Chim. Miner. 1986, 23, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, O.; Abdelmoula, M.; Refait, P.; Génin, J.-M.R. Effect of orthophosphate on the oxidation products of Fe(II)-Fe(III) hydroxycarbonate; the transformation of green rust to ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Reffass, M.; Landoulsi, J.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M. Role of nitrite species during the formation and transformation of the Fe(II-III) hydroxycarbonate Green Rust. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2014, 459, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocher, F.; Géhin, A.; Ruby, C.; Ghanbaja, J.; Abdelmoula, M.; Génin, J.-M.R. Coprecipitation of Fe(II-III) hydroxycarbonate green rust stabilised by phosphate adsorption. Solid State Sci. 2004, 6, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorand, F.P.A.; Sergent, A.-S.; Rémy, P.-P.; Bihannic, I.; Ghanbaja, J.; Lartiges, B.; Hanna, K.; Zegeye, A. Contribution of anionic vs. neutral polymers to the formation of green rust 1 from γ-FeOOH bioreduction. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémy, P.-P.; Etique, M.; Hazotte, A.A.; Sergent, A.-S.; Estrade, N.; Cloquet, C.; Hanna, K.; Jorand, F.P.A. Pseudo-first-order reaction of chemically and biologically formed green rusts with HgII and C15H15N3O2: Effects of pH and stabilizing agents (phosphate, silicate, polyacrylic acid, and bacterial cells). Water Res. 2015, 70, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).