The Corrosion Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Based Alloys—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Binary Mg-Zn Alloys
2.1. Mg-Zn System
2.2. Influence of Zn Content on the Corrosion and Mechanical Properties of Binary Mg-Zn Alloys
3. Ternary Mg-Zn-X Alloys
3.1. Influence of Microstructure on the Corrosion and Mechanical Properties
3.1.1. Mg-Zn-Ca Alloys
3.1.2. Mg-Zn-Y Alloys
3.1.3. Mg-Zn-Mn Alloys
3.1.4. Representative Mg-Zn-RE and Mg-Zn-Zr Based Alloys
3.1.5. Other Mg-Zn-X Alloys
3.2. Influence of Environment on the Corrosion Behavior
3.3. Influence of Processing
4. Strategy to Improve Properties of Mg-Zn Based Alloys
4.1. Microstructure Adjustment by Phase Composition
4.1.1. Magnesium-Based Metal Matrix Composites
4.1.2. Magnesium Bulk Metallic Glasses
4.2. Microstructure Adjustment by Production Technique
4.2.1. Squeeze Casting
4.2.2. Twin-Roll Casting
4.2.3. Rapid Solidification
4.3. Surface Treatments
- Chemical conversion coatings
- Electro-chemical coatings
- Physical techniques
5. Applications of Mg-Zn Based Alloys
6. Summary
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Secondary Phase | Alloy | Condition of Alloy | Testing Method | Potential or Relative Volta Potential | Condition of Measurement | Details about the Instrument | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgZn2 | Mg-Zn | Induction melting | Microcapillary electrochemical cell | −1.03 V (vs. SCE) | 0.1 M NaCl | - | [77] |
| Mg12ZnY | Mg3.1Zn7.6Y | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 250 mV | In air | Multimode 3D, Bruker Corporation | [88] |
| CaMgSi | Mg6Zn5Si0.8Ca | Extruded | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 384.56 mV | In air | Nanoscope III Multimode AFM | [281] |
| Mg2Si | 96.23 mV | ||||||
| MgZn2 | Mg6Zn5Si0.8Ca | Extruded | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 551.19 ± 77.85 mV | In air | Nanoscope III Multimode AFM | [282] |
| Mn5Si3 | 427.81 ± 147.88 mV | ||||||
| CaMgSi | 408.32 ± 26.35 mV | ||||||
| Mg2Si | 96.23 ± 21.91 mV | ||||||
| Grain boundary | ZE41 | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | −80 ± 5 mV | In air | Nanoscope DimensionTM 3100 AFM | [123] |
| Mg7Zn3RE | 100 ± 5 mV | ||||||
| Zr-Zn-rich | 180 ± 10 mV | ||||||
| Mg7Zn3 | Mg2Zn0.6Zr | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 120 mV | In air | Dimension Icon AFM | [283] |
| Mg(Zn, Zr) | Mg2Zn0.6Zr | Extrusion | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 50mV | In air | Dimension Icon AFM | [283] |
| MgZn2 | Mg6Zn0.5Zr | Extrusion | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 320 mV | In air | NT-MDT, Moscow | [284] |
| Zn2Zr3 | 230 mV | ||||||
| CuMgZn | Mg6Zn0.5Zr1Cu | Extrusion | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 680 mV | In air | NT-MDT, Moscow | [284] |
| MgZn2 | 510 mV | ||||||
| Zn2Zr3 | 370 mV | ||||||
| Mg75Zn20Nd5 | Mg2Zn0.2MnxNd | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 250 mV | In air | MFP 3D Infinity AFM | [285] |
| Ca2Mg6Zn3 | Mg2Zn1Ca0.2Mn | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 60 mV | In air | MFP 3D Infinity AFM | [286] |
| Ca2Mg6Zn3 | T4 | 30 mV | |||||
| MgZn2 | Mg2Zn0.2MnxCa (x = 0.38; 0.76; 1.10) | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 96 mV* | In air | MFP 3D Infinity AFM | [287] |
| Mg-Zn | ZK40 | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 50 mV | In air | Nanoscope IIIa Multimode microscope | [288] |
| Mg-Zn-Zr-Fe | Mg4Zn0.5Zr2Gd | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 430 mV | In air | Nanoscope IIIa Multimode microscope | [288] |
| (MgZn)3Gd2 | 170 mV | ||||||
| Mg-Zn-Zr-Fe | Mg4Zn0.5Zr2Nd | As-cast | Scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy | 140 mV | In air | Nanoscope IIIa Multimode microscope | |
| Mg75Zn20Nd5 | 35 mV |
| Composition/wt.% | Condition | Electrolyte | Impurity Content/wt.% | Corrosion Rate/mm year−1 | Tensile Property | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | PH | PW | YS/MPa | UTS/MPa | Elongation/% | ||||||
| Mg0.5Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.003Fe; 0.0004Cu; 0.0005Ni; 0.004Mn; 0.002Al | 3.1 | 75 | 112 | 18.4 | [46] | |||
| Mg0.5Zn | As-cast | SBF, RT | 0.004Fe; 0.004Cu; 0.001Ni | 1.2 | 1 | 38 | 95 | 4.2 | [50] | ||
| Mg0.5Zn | Backward-extrusion | SBF, RT | 0.5 | 0.5 | 62 | 145 | 17.2 | [50] | |||
| Mg0.8Zn | Extrusion | 198 | 238 | 26.5 | [26] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.004Fe; 0.0003Cu; 0.0004Ni; 0.003Mn; 0.003Al | 2.8 | 80 | 128 | 16.1 | [46] | |||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | <0.00016Fe; <0.002Cu; <0.001Mn | 0.5 | 2 | 61 | 188 | 13.8 | [10] | ||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | 9 g/L NaCl | <0.004Fe; <0.004Cu; <0.004Ni; 0.03Mn; 0.02Al | 0.9 | 1.3 | [49] | |||||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | 0.004Fe; 0.058Mn; 0.023Al; 0.031Si | 20 | 102 | 1 | [22] | |||||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.007Fe; 0.0295Cu; 0.013Mn; 0.023Al; 0.041Si | 0.07 | [42] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | SBF, RT | 0.008Fe; 0.004Cu; 0.005Ni | 4.1 | 1.1 | 43 | 99 | 6.1 | [50] | ||
| Mg1Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 1.5 | 2 | [45] | ||||||
| Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.2 | 0.3 | |||||||||
| Mg1Zn | T4 | SBF, 37 °C | 0.09 | [42] | |||||||
| Mg1Zn | Backward-extrusion | SBF, RT | 1.1 | 0.5 | 91 | 169 | 18.7 | [50] | |||
| Mg1Zn | Extrusion | 0.6 M NaCl | 1.7 | [61] | |||||||
| Mg1Zn | Hot-rolling | SBF, 37 °C | 0.9 | 2.3 | [45] | ||||||
| Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.2 | 0.6 | |||||||||
| Mg1Zn | Induction melting | In vivo | 0.4 | [157] | |||||||
| EBSS, 37 °C | 0.5 | ||||||||||
| MEM, 37 °C | 1 | ||||||||||
| MEMp, 37 °C | 1.7 | ||||||||||
| Mg1.25Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.008Fe; 0.043Mn; 0.022Al; 0.029Si | 6.5 | 3.2 | [41] | |||||
| Mg1.5Zn | As-cast | SBF, RT | 0.007Fe; 0.006Cu; 0.004Ni | 8.5 | 1.4 | 51 | 109 | 5.9 | [50] | ||
| Mg1.5Zn | Backward-extrusion | SBF, RT | 1.3 | 0.5 | 101 | 190 | 17.2 | [50] | |||
| Mg2Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.002Fe; 0.0005Cu; 0.0005Ni; 0.004Mn; 0.002Al | 2.6 | 86 | 137 | 14.5 | [46] | |||
| Mg2Zn | As-cast | 0.007Fe; 0.03Mn; 0.033Al; 0.039Si | 27 | 146 | 12.2 | [22] | |||||
| Mg2Zn | As-cast | SBF, RT | 0.004Fe; 0.003Cu; 0.007Ni | 9.7 | 1.3 | 65 | 121 | 5.3 | [50] | ||
| Mg2Zn | Backward-extrusion | SBF, RT | 1.4 | 0.6 | 111 | 198 | 15.7 | [50] | |||
| Mg2Zn | Extrusion | 0.6 M NaCl | 3.4 | [61] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.2 | [40] | |||||||
| Mg2.5Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.010Fe; 0.032Mn; 0.018Al; 0.033Si | 5.5 | 2.4 | [41] | |||||
| Mg2.6Zn | Extrusion | 208 | 263 | 25.6 | [26] | ||||||
| Mg2.65Zn | As-cast | 0.9 wt.% NaCl | 13.4 | 45 | 145 | 12 | [289] | ||||
| Mg2.9Zn | Powder metallurgy | 84 | 219 | 4.7 | [54] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.004Fe; 0.0005Cu; 0.0002Ni; 0.002Mn; 0.004Al | 2.3 | 93 | 147 | 12.4 | [46] | |||
| Mg3Zn | As-cast | 9 g/L NaCl | <0.004Fe; 0.01Cu; <0.004Ni; 0.04Mn; <0.01Al | 0.9 | 2.5 | [49] | |||||
| Mg3Zn | As-cast | 0.007Fe; 0.022Mn; 0.029Al; 0.036Si | 47 | 168 | 13.7 | [22] | |||||
| Mg3Zn | As-cast | MEM, 37 °C | 0.5 | [59] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn | As-cast | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.5 | 1.5 | [58] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 5.2 | 2 | [48] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | T4 | SBF, 37 °C | 4.8 | 1.9 | [48] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | T4 | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.4 | 1.4 | [58] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | T6 | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.4 | 1.3 | [58] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | T6 | SBF, 37 °C | 2.1 | 1.2 | 28 | 140 | 9.7 | [187] | |||
| Mg3Zn | T6 (aging for 10 h) | SBF, 37 °C | 0.0045Fe; <0.0001Cu; 0.0006Ni; <0.0001Si | 6.6 | [43] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn | T6 (aging for 50 h) | SBF, 37 °C | 7.3 | [43] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn | T6 (aging for 144 h) | SBF, 37 °C | 9.7 | [43] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn | Extrusion | 0.6 M NaCl | 8.4 | [61] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.3 | [40] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn | Bi-direction rolling | SBF, 37 °C | 2.6 | 2 | 49 | 183 | 12.6 | [187] | |||
| Mg3.3Zn | Powder metallurgy | 90 | 210 | 4.6 | [54] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn | As-cast | 0.008Fe; 0.021Mn; 0.019Al; 0.032Si | 58 | 217 | 15.8 | [22] | |||||
| Mg4Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.009Fe; 0.028Mn; 0.024Al; 0.025Si | 4.9 | 2.1 | [41] | |||||
| Mg4Zn | Powder metallurgy | 95 | 216 | 4.1 | [54] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.0072Fe; 0.0308Cu; 0.0101Mn; 0.0273Al; 0.0565Si | 0.4 | [42] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn | T4 | SBF, 37 °C | 0.1 | [42] | |||||||
| Mg4Zn | Extrusion | 0.6 M NaCl | 10 | [61] | |||||||
| Mg4Zn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.4 | [40] | |||||||
| Mg4.2Zn | Extrusion | 227 | 288 | 21 | [26] | ||||||
| Mg4.4Zn | Powder metallurgy | 68 | 155 | 8.4 | [54] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn | T6 | 57 | 209 | 14.7 | [138] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.3 | 1.3 | 76 | 195 | 8.5 | [10] | |||
| Mg5Zn | As-cast | 0.009Fe; 0.031Mn; 0.027Al; 0.034Si | 68 | 185 | 9.2 | [22] | |||||
| Mg5Zn | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl+Mg(OH)2 | 0.0034Fe; 0.0028Cu; 0.0015Ni; 0.0545Mn; 0.0105Al; 0.0296Si | 7.8 | 13.5 | 15.1 | [57] | ||||
| Salt spray (5 wt.%) | 12.4 | ||||||||||
| Mg5Zn | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.6 | 2.7 | [47] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn | T4 | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.5 | 2.3 | [47] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn | T6 (aging for 4 h) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 1.2 | 4 | [47] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn | T6 (aging for 10 h) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 1.5 | 5.5 | [47] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn | Solid solution treatment | 3.5 wt.% NaCl+Mg(OH)2 | 2.7 | 10 | 6.5 | [57] | |||||
| Salt spray (5 wt.%) | 9.1 | ||||||||||
| Mg5Zn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.5 | [40] | |||||||
| Mg5Zn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl+Mg(OH)2 | 0.000017Fe; <0.00001Cu; <0.000001Ni; 0.000011Si | 1.7 | 2.6 | [168] | |||||
| Mg6Zn | As-cast | 0.012Fe; 0.019Mn; 0.024Al; 0.033Si | 69 | 182 | 7.2 | [22] | |||||
| Mg6Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.0062Fe; 0.025Cu; 0.0077Mn; 0.0478Al; 0.0489Si | 3 | [42] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn | T4 | SBF, 37 °C | 0.8 | [42] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 6.2 | 3.5 | [48] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn | T4 | SBF, 37 °C | 4.4 | 1.4 | [48] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | 5.4 | 12.6 | [60] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | 0.0038Fe; 0.0005Cu; 0.0005Ni; 0.0085Al; 0.0004Mn; 0.0016Si | 0.16 | 0.07 | 170 | 280 | 19 | [160] | ||
| In vivo | 2.3 | ||||||||||
| Mg6Zn | Extrusion (PM) | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 0.4 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn | Extrusion (PM) + T4 | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 0.5 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn | Extrusion (PM) + T6 | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 0.4 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn | Extrusion (PM) + T5 | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 0.2 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 8.5 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 16.5 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 83 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 100.3 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg7Zn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 1.2 | 3.2 | 67 | 136 | 6 | [10] | |||
| Mg14.5Zn | Extrusion (PM) | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 1.2 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg25.3Zn | Extrusion (PM) | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 1.8 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg40.3Zn | Extrusion (PM) | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 3 | [55] | |||||||
| Mg0.8Zn0.6Ca | As-cast | HBSS, 37 °C | 0.0021Fe; 0.0021Cu; <0.0021Ni; 0.0231Mn; 0.02Al; 0.0343Si | 0.08 | 0.1 | [75] | |||||
| PBS, 37 °C | 0.02 | 0.1 | |||||||||
| Mg0.8Zn1.6Ca | As-cast | HBSS, 37 °C | <0.0006Fe; 0.0012Cu; <0.0021Ni; 0.011Mn; 0.036Al; 0.019Si | 0.1 | 0.2 | [75] | |||||
| PBS, 37 °C | 0.04 | 0.2 | |||||||||
| Mg1Zn0.5Ca | Extrusion | 105 | 210 | 44 | [72] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.004Fe; 0.058Mn; 0.023Al; 0.031Si | 2.1 | 45 | 125 | 5.7 | [23] | |||
| Mg1.2Zn0.5Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 15.8 | 8.2 | 60 | 121 | 3.2 | [176] | |||
| Mg1.2Zn0.5Ca | T6 | SBF, 37 °C | 9.6 | 4.8 | 84 | 151 | 4.9 | [176] | |||
| Mg1.8Zn0.6Ca | As-cast | HBSS, 37 °C | <0.0006Fe; 0.001Cu; <0.0021Ni; 0.0079Mn; 0.0199Al; 0.024Si | 0.03 | 0.1 | [75] | |||||
| PBS, 37 °C | 0.02 | 0.2 | |||||||||
| Mg1.8Zn1.6Ca | As-cast | HBSS, 37 °C | <0.0006Fe; 0.0011Cu; <0.0021Ni; 0.0077Mn; 0.0358Al; 0.0225Si | 0.04 | 0.2 | [75] | |||||
| PBS, 37 °C | 0.06 | 0.3 | |||||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Ca | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 10.3 | [51] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Ca | Extrusion | 118 | 211 | 24.4 | [167] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.24Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 12.1 | [290] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.24Ca | High pressure torsion | SBF, 37 °C | 0.08 | [290] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.5Ca | Rapid solidification | SBF, 37 °C | 9.6 | [291] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.007Fe; 0.03Mn; 0.033Al; 0.039Si | 2.4 | 52 | 143 | 7.3 | [23] | |||
| Mg3Zn0.2Ca | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | 0.0096Fe; 0.1302Al | 1.2 | 224 | 273 | 18.5 | [7] | |||
| Mg3Zn0.3Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.004Fe; <0.0001Cu; <0.0001Ni; <0.0001Si | 6.9 | [70] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn0.3Ca | T4 | SBF, 37 °C | 3.4 | [70] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.007Fe; 0.022Mn; 0.029Al; 0.036Si | 2.9 | 57 | 160 | 8.3 | [23] | |||
| Mg3Zn1.34Ca | Induction melting | In vivo | 0.8 | [157] | |||||||
| EBSS, 37 °C | 1.6 | ||||||||||
| MEM, 37 °C | 4.7 | ||||||||||
| MEMp, 37 °C | 3.3 | ||||||||||
| Mg3Zn2Ca | Gravity casting | 90 * | 101 | 0.4 | [215] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn2Ca | Aging | 88 * | 126 | 2 | [215] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn2Ca | Squeeze casting | 80 * | 135 | 0.9 | [215] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn2Ca | Squeeze casting + Aging | 74 * | 144 | 3.3 | [215] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn2Ca | ECAP | 166 * | 206 | 1.1 | [215] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn2Ca | Aging + ECAP | 174 * | 223 | 2.4 | [215] | ||||||
| Mg3.3Zn3.2Ca0.5RE | Squeeze casting (surface) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl, pH 11 | 0.02Fe;0.002Ni; 0.01Mn; 0.04Al; 0.02Si | 7.2 | [213] | ||||||
| Squeeze casting (core) | 6.1 | ||||||||||
| Mg3.6Zn3.5Ca0.7RE | Thixocasting (surface) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl, pH 11 | 0.009Fe;0.002Ni; 0.01Mn; 0.06Al; 0.03Si | 3 | [213] | ||||||
| Thixocasting (core) | 3.6 | ||||||||||
| Mg4Zn0.2Ca | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | 0.0095Fe; 0.1125Al | 1.3 | 243 | 295 | 18 | [7] | |||
| Mg4Zn0.5Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.007Fe; 0.022Mn; 0.029Al; 0.036Si | 70 | 180 | 12.3 | [22] | ||||
| Mg4Zn0.5Ca | As-cast | 211 | 17 | [16] | |||||||
| Mg4Zn0.5Ca | Extrusion | 273 | 34 | [16] | |||||||
| Mg4Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.008Fe; 0.021Mn; 0.019Al; 0.032Si | 83 | 175 | 8.7 | [22] | ||||
| Mg4Zn1.5Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.009Fe; 0.031Mn; 0.027Al; 0.034Si | 83 | 167 | 7.1 | [22] | ||||
| Mg4Zn2Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.012Fe; 0.019Mn; 0.024Al; 0.033Si | 90 | 143 | 2.1 | [22] | ||||
| Mg4Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.008Fe; 0.021Mn; 0.019Al; 0.032Si | 4.4 | 63 | 182 | 9.1 | [23] | |||
| Mg5Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.009Fe; 0.031Mn; 0.027Al; 0.034Si | 6.2 | 65 | 173 | 8.2 | [23] | |||
| Mg5Zn1Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | <0.0016Fe; <0.002Cu; <0.001Mn | 0.28 | 1.36 | 87 | [5] | ||||
| Mg5Zn2Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.34 | 1.84 | 93 | [5] | |||||
| Mg5Zn3Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 0.44 | 3.23 | 83 | [5] | |||||
| Mg5.25Zn0.6Ca | Extrusion | 178 | 276 | 25.9 | [193] | ||||||
| Mg5.25Zn0.6Ca | Extrusion + ECAP-A | 246 | 332 | 15.5 | [193] | ||||||
| Mg5.25Zn0.6Ca | Extrusion + ECAP-B | 180 | 287 | 21.9 | [193] | ||||||
| Mg5.25Zn0.6Ca | Extrusion + ECAP-C | 131 | 228 | 12.6 | [193] | ||||||
| Mg5.25Zn0.6Ca | Extrusion | 220 | 21.4 | [292] | |||||||
| Mg5.25Zn0.6Ca0.3Mn | Extrusion | 272 | 18.9 | [292] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.012Fe; 0.019Mn; 0.024Al; 0.033Si | 9.2 | 67 | 145 | 4.5 | [23] | |||
| Mg6Zn1Ca | Rapid solidification | PBS, RT | 2.9 | [230] | |||||||
| Mg6.6Zn0.19Ca | Extrusion | 148 | 275 | 26 | [293] | ||||||
| Mg5.7Zn0.17Ca0.84Zr | Extrusion | 310 | 357 | 18 | [293] | ||||||
| Mg10Zn1Ca | Rapid solidification | PBS, RT | 3.1 | [230] | |||||||
| Mg20Zn1Ca | Rapid solidification | PBS, RT | 4.7 | [230] | |||||||
| Mg46Zn10Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.4 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg49Zn10Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.04 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg51Zn10Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.04 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg54Zn10Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.03 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg56Zn10Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.4 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg46Zn15Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.05 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg49Zn15Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.2 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg51Zn15Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.1 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg54Zn15Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.1 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg56Zn15Ca | Induction melting | MEM, RT | 0.4 | [294] | |||||||
| Mg51Zn10Ca | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.18 | [295] | |||||||
| Mg50Zn10Ca2.6Y | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.19 | [295] | |||||||
| Mg47Zn10Ca7.7Y | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.19 | [295] | |||||||
| Mg50Zn10Ca | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.06 | 12.2 | [296] | ||||||
| Mg50Zn10Ca2.6Y | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.2 | 28.3 | [296] | ||||||
| Mg50Zn10Ca5.2Y | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.4 | 60.1 | [296] | ||||||
| Mg51Zn12Ca | Rapid solidification | SBF, 37 °C | 5.2 | 1.8 | [297] | ||||||
| Mg51Zn12Ca | Rapid solidification + Annealing | SBF, 37 °C | 9.2 | 10.4 | [297] | ||||||
| Mg54Zn10Ca | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.2 | [211] | |||||||
| Mg47Zn12Ca | Induction melting | SBF, 37 °C | 0.4 | [211] | |||||||
| Mg54Zn10Ca | Induction melting (22 mm) | SBF, 37 °C | 35 | [298] | |||||||
| Mg54Zn10Ca | Induction melting (8 mm) | SBF, 37 °C | 0.2 | [298] | |||||||
| Mg59Zn12Ca | Induction melting (22 mm) | SBF, 37 °C | 5.1 | [298] | |||||||
| Mg59Zn12Ca | Induction melting (8 mm) | SBF, 37 °C | 0.1 | [298] | |||||||
| Mg0.5Zn1Y | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 1.9 | 25.1 | 27.9 | [87] | |||||
| Mg0.9Zn1.6Y | As-cast | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 59 | 97 | 6.3 | [88] | ||
| Mg1Zn2Y | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.2 | 1.9 | 2.4 | [87] | |||||
| Mg1.3Zn5Y | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 5.8 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg1.5Zn0.2Y | Extrusion + Rolling | 0.011Fe;0.0006Cu; 0.001Ni; 0.024Mn; 0.02Al; 0.0091Si | 139 | 222 | 23 | [94] | |||||
| Mg1.5Zn0.2Y | Extrusion + Rolling | 0.011Fe;0.006Cu; 0.001Ni; 0.024Mn; 0.019Al; 0.0073Si | 178 | 225 | 18 | [94] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.36Y | Extrusion | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.04 | 0.7 | 197 | 260 | 23 | [53] | |||
| Mg2Zn0.82Y | Extrusion | Hank’s, 37 °C | <0.015Fe; <0.001Cu; <0.0005Ni | 0.1 | 2 | 212 | 265 | 25 | [53] | ||
| Mg2Zn1.54Y | Extrusion | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.05 | 0.8 | 214 | 265 | 27 | [53] | |||
| Mg2Zn4Y | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 8.1 | 88.8 | 110.4 | [87] | |||||
| Mg2Zn5Y | Gravity casting | 0.17 M NaCl | 33.8 | [300] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y | Injection casting | 0.17 M NaCl | 12.5 | [300] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y | Rapid solidification (10 m s−1) | 0.17 M NaCl | 5.1 | [300] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y | Rapid solidification (20 m s−1) | 0.17 M NaCl | 1.4 | [300] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y | Rapid solidification (40 m s−1) | 0.17 M NaCl | 1.2 | [300] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y1.3Al | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 0.6 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y2.6Al | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 0.3 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y3.9Al | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 0.1 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y1.3Nd | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 1 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y1.3Si | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 0.8 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg2.1Zn5.2Y | As-cast | 0.1 M NaCl | 1.5 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 95 | 141 | 5.2 | [88] | ||
| Mg2.6Zn5Y | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 2.4 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg2.6Zn5.2Y | As-cast | DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.2 | [89] | |||||||
| Mg2.6Zn5.2Y0.5Zr | As-cast | DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.1 | [89] | |||||||
| Mg2.6Zn5.2Y0.5Zr | Extruded | DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.2 | [89] | |||||||
| Mg2.6Zn2.6Y | As-cast | 102 | 16 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg2.6Zn2.6Y | Rolling | 261 | 12 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg2.6Zn2.6Y | Rolling + Annealing | 190 | 25 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg3Zn0.6Y | Rolling | 121 | 226 | 30.2 | [108] | ||||||
| Mg3.1Zn5.2Y | As-cast | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.6 | 2.1 | 9.5 | 107 | 148 | 3 | [88] | ||
| Mg3.3Zn5Y | Rapid solidification | 0.17 M NaCl | 13.5 | [299] | |||||||
| Mg4Zn0.7Y | Rolling | 209 | 258 | 17.4 | [74] | ||||||
| Mg3.24Zn3.34Y0.67Zr | As-cast | 127 | 185 | 3 | [301] | ||||||
| Mg3.93Zn4.14Y0.69Zr | As-cast | 168 | 226 | 2 | [301] | ||||||
| Mg4.87Zn5.03Y0.73Zr | As-cast | 150 | 195 | 1.9 | [301] | ||||||
| Mg5.95Zn6.08Y0.64Zr | As-cast | 121 | 165 | 1.4 | [301] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn8Y | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 3.8 | 71.3 | 80.5 | [87] | |||||
| Mg5Zn0.5Y | Rolling | 157 | 306 | 23.4 | [93] | ||||||
| Mg5.2Zn5.2Y | As-cast | 130 | 11 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg5.2Zn5.2Y | Rolling | 317 | 10 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg5.2Zn5.2Y | Rolling + Annealing | 217 | 22 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg5.2Zn10Y | As-cast | DMEM + FBS, 37 °C | 0.07 | [89] | |||||||
| Mg4.4Zn2.4Y6.2RE | Extrusion | PBS | 0.00246Fe; 0.1Mn | 0.4 | 4.9 | [302] | |||||
| Mg5.7Zn1Y3.8RE | Extrusion | PBS | 0.00139Fe; 0.1Mn | 0.1 | 2.5 | [302] | |||||
| Mg6Zn1.2Y | Rolling | 157 | 259 | 29.3 | [108] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.5Y0.5Zr | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 285 | 340 | 10.2 | [180] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.5Y0.5Zr | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + Peak-aging | 289 | 336 | 15.5 | [180] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.5Y0.5Zr | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 278 | 336 | 108 | [180] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.5Y0.5Zr | Extrusion (at 350 °C) + Peak-aging | 290 | 332 | 17.9 | [180] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.5Y0.5Zr | Extrusion (at 400 °C) | 258 | 325 | 14.6 | [180] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.5Y0.5Zr | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + Peak-aging | 277 | 326 | 16.9 | [180] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.2Y0.4Zr | As-cast | 157 | 237 | 3 | [177] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1.2Y0.4Zr | Extrusion | 203 | 290 | 16.7 | [177] | ||||||
| Mg6.7Zn1.3Y0.6Zr | As-forged | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.5 | 2.2 | 202 | 280 | 17 | [303] | |||
| Mg6.7Zn1.3Y0.6Zr | As-forged+T4 | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.3 | 1.3 | 183 | 262 | 22 | [303] | |||
| Mg7.7Zn10.7Y | As-cast | DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.08 | [89] | |||||||
| Mg7.7Zn7.7Y | As-cast | 177 | 10 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg5.2Zn5.2Y | Rolling | 380 | 6 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg5.2Zn5.2Y | Rolling+Annealing | 293 | 15 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg8Zn1.6Y | Rolling | 173 | 270 | 26.9 | [108] | ||||||
| Mg8Zn14Y | As-cast | 0.9 | [304] | ||||||||
| Mg8Zn6Y6Gd | As-cast | 1.1 | [304] | ||||||||
| Mg8Zn5Y8Gd | As-cast | 1.5 | [304] | ||||||||
| Mg8Zn4Y12Gd | As-cast | 1.5 | [304] | ||||||||
| Mg8.6Zn1.6Y | Rolling | 1.1 | 210 | 355 | 23.4 | [90] | |||||
| Mg10Zn2Y | Rolling | 181 | 276 | 21.9 | [108] | ||||||
| Mg10.8Zn1.9Y | Rolling | 220 | 370 | 19.7 | [90] | ||||||
| Mg10.8Zn1.9Y0.5Zr | Rolling | 180 | 325 | 23.5 | [90] | ||||||
| Mg11Zn2Y | Rolling | 220 | 370 | 17.2 | [93] | ||||||
| Mg10.5Zn2.1Y | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 200 | 300 | [92] | |||||||
| Mg10.5Zn2.1Y | Extrusion +Heat-treatment | 197 | 297 | 18 | [305] | ||||||
| Mg11Zn2Y | Extrusion (Ratio: 10) | 232 | 258 | 4.5 | [86] | ||||||
| Mg11Zn2Y | Extrusion (Ratio: 15) | 236 | 312 | 13.2 | [86] | ||||||
| Mg11Zn2Y | Extrusion (Ratio: 20) | 240 | 336 | 15.6 | [86] | ||||||
| Mg12Zn2.4Y | Rolling | 189 | 285 | 21.3 | [108] | ||||||
| Mg12Zn1.2Y0.4Zr | As-cast | 172 | 216 | 0.8 | [177] | ||||||
| Mg12Zn1.2Y0.4Zr | Extrusion | 231 | 320 | 13 | [177] | ||||||
| Mg15.5Zn2.6Y | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 210 | 320 | [92] | |||||||
| Mg15.5Zn2.6Y | Extrusion +Heat-treatment | 213 | 321 | [305] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn5Y0.6Zr | Extrusion | 233 | 290 | 17.2 | [306] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn5Y0.6Zr | Extrusion | 322 | 345 | 18.3 | [306] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Y0.6Zr | Extrusion | 244 | 283 | 20.2 | [306] | ||||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | 1 N NaCl | 0.006Fe; <0.002Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.02Mn; 0.004Al; <0.001Cr | 2.1 | 13.5 | 12 | [118] | ||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.0056Fe; 0.0014Cu; 0.0002Ni; 0.02Mn: 0.0101Al | 0.24 | 1.6 | 2.3 | [113] | ||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | 0.2 M Na2SO4 + 0.1 M NaCl (30 °C) | 0.006Fe; <0.002Cu; 0.02Mn; <0.001Ni; 0.004Al | 5.4 | [117] | ||||||
| 0.2 M Na2SO4 + 1.0 M NaCl (30 °C) | 10 | ||||||||||
| 0.6 M Na2SO4 + 0.1 M NaCl (30 °C) | 8.49 | ||||||||||
| 0.6 M Na2SO4 + 1.0 M NaCl(30 °C) | 14.3 | ||||||||||
| 1.0 M Na2SO4 + 0.1 M NaCl(30 °C) | 12.3 | ||||||||||
| 0.1 M Na2SO4 + 1.0 M NaCl (30 °C) | 18.4 | ||||||||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | 0.1 M NaCl (pH3) | 0.006Fe; <0.002Cu; 0.02Mn; <0.001Ni; 0.004Al | 3.7 | 9.7 | [119] | |||||
| 0.1 M NaCl (pH7) | 0.63 | 2.3 | |||||||||
| 0.1 M NaCl (pH11) | 0.22 | 1.5 | |||||||||
| 1 M NaCl (pH3) | 5 | 20 | |||||||||
| 1 M NaCl (pH7) | 1.6 | 14 | |||||||||
| 1 M NaCl (pH11) | 0.6 | 8 | |||||||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C (pH6.6) | 0.0056Fe; 0.0014Cu; 0.0002Ni; 0.02Mn: 0.0101Al | 1.5 | 3.4 | [148] | |||||
| Hank’s, 37 °C (pH6.9) | 2.3 | 4.2 | |||||||||
| Hank’s, 37 °C (pH7.4) | 2.9 | 1.5 | |||||||||
| Hank’s, 37 °C (pH8.2) | 3.2 | 1.5 | |||||||||
| ZE41 | T5 | 0.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.003Fe | 0.1 | [120] | ||||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | 0.001 M NaCl | 0.1Cu; 0.01Ni; 0.15Mn | 0.07 | [122] | ||||||
| ZE41 | T4 | 0.001 M NaCl | 0.1 | [122] | |||||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | 0.2 M Na2SO4 | pH2 | 0.006Fe; <0.002Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.02Mn; 0.004Al | 12 | [150] | |||||
| pH5 | 5.4 | ||||||||||
| pH7 | 2.8 | ||||||||||
| pH9 | 2 | ||||||||||
| pH12 | 1.3 | ||||||||||
| 0.6 M Na2SO4 | pH2 | 15 | |||||||||
| pH5 | 9.3 | ||||||||||
| pH7 | 6.2 | ||||||||||
| pH9 | 4.7 | ||||||||||
| pH12 | 3.9 | ||||||||||
| 1.0 M Na2SO4 | pH2 | 20.1 | |||||||||
| pH5 | 14.2 | ||||||||||
| pH7 | 11.1 | ||||||||||
| pH9 | 8.1 | ||||||||||
| pH12 | 7.1 | ||||||||||
| ZE41 | As-cast | 3 wt.% NaCl | 0.006Fe; <0.002Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.02Mn; 0.004Al | 1.1 | 46 | [15] | |||||
| Interrupted 3 wt.% NaCl salt spray (1 min spray, 119 min humid) | 47 | ||||||||||
| Interrupted 3 wt.% NaCl salt spray (15 min spray, 105 min humid) | 2.7 | ||||||||||
| Mg1Zn0.3Zr | Rolling | 194 | 254 | 15.6 | [74] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.6Zr | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 0.3 | 51 | 195 | 18.1 | [283] | |||
| Mg2Zn0.6Zr | Extrusion | Hank’s, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 0.1 | 194 | 258 | 17.6 | [283] | |||
| Mg2Zn0.8Zr | Extrusion | 221 | 271 | 24.5 | [307] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn0.6Zr | As-cast | 215 | 300 | 9 | [125] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn0.8Zr | Extrusion + Aging | SBF, 37 °C | 0.04 | 245 | 8.8 | [206] | |||||
| Mg3Zn0.8Zr0.5β-TCP | Extrusion + Aging | SBF, 37 °C | 0.05 | 260 | 10.3 | [206] | |||||
| Mg3Zn0.8Zr1 β-TCP | Extrusion + Aging | SBF, 37 °C | 0.03 | 280 | 10.5 | [206] | |||||
| Mg3Zn0.8Zr1.5 β-TCP | Extrusion + Aging | SBF, 37 °C | 0.04 | 275 | 6.3 | [206] | |||||
| Mg4Zn0.5Zr | As-cast | DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.002Fe; 0.014Cu; 0.018Ni; 0.003Mn; 0.007Si | 0.8 | 1.1 | [308] | |||||
| Mg4Zn0.5Zr | Heat-treatment | DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.9 | 0.5 | [308] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn0.5Zr | Indirect chill casting | 0.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.00113Fe; 0.00141Cu; 0.00128Ni | 2.9 | 102 | 225 | 12.8 | [288] | |||
| Mg4Zn0.5Zr2Gd | Indirect chill casting | 0.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.00069Fe; 0.00292Cu; <0.003Ni | 1.8 | 100 | 228 | 17.9 | [288] | |||
| Mg4Zn0.5Zr2Nd | Indirect chill casting | 0.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.0011Fe; 0.00148Cu; 0.00282Ni | 4.1 | 99 | 148 | 3.9 | [288] | |||
| Mg4Zn0.7Zr | As-cast | 0.03Cu; 0.01Ni; 0.2Si | 108 | 216 | 16 | [132] | |||||
| Mg4Zn0.7Zr3Nd | As-cast | 144 | 202 | 6 | [132] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn0.6Zr | As-cast | 235 | 315 | 8 | [125] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn0.3Zr | Extrusion + Heat-treatment | 5 wt.% NaCl | 9.8 | [129] | |||||||
| Mg5Zn0.3Zr1Nd | Extrusion + Heat-treatment | 5 wt.% NaCl | 9 | [129] | |||||||
| Mg5Zn0.3Zr2Nd | Extrusion + Heat-treatment | 5 wt.% NaCl | 4.7 | [129] | |||||||
| Mg5Zn0.3Zr0.5Y | Extrusion + Heat-treatment | 5 wt.% NaCl | 5.4 | [129] | |||||||
| Mg5Zn0.3Zr1Y | Extrusion + Heat-treatment | 5 wt.% NaCl | 9 | [129] | |||||||
| Mg5Zn0.6Zr | As-cast | 88 | 236 | 18.2 | [136] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn0.6Zr1Nd | As-cast | 102 | 196 | 7.3 | [136] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn0.6Zr2Nd | As-cast | 89 | 133 | 2.9 | [136] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn0.6Zr2Nd0.5Y | As-cast | 94 | 203 | 9.1 | [136] | ||||||
| Mg5Zn0.6Zr2Nd1Y | As-cast | 102 | 219 | 12.1 | [136] | ||||||
| Mg5.3Zn0.48Zr | Extrusion | PBS, 37 °C | 5.6 | [189] | |||||||
| Mg5.3Zn0.48Zr | Extrusion+ECAP | PBS, 37 °C | 3.8 | [189] | |||||||
| Mg5.3Zn0.48Zr | Extrusion | PBS, 37 °C | 1.4 | 290 | 340 | 15.1 | [191] | ||||
| Mg5.3Zn0.48Zr | Extrusion+ECAP | PBS, 37 °C | 1.3 | 219 | 285 | 32.4 | [191] | ||||
| Mg5.45Zn0.45Zr | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.4 | 0.9 | [126] | ||||||
| DMEM, 37 °C | 0.7 | ||||||||||
| DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 1.3 | ||||||||||
| Mg5.45Zn0.45Zr | Extrusion | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.2 | 0.3 | [126] | ||||||
| DMEM, 37 °C | 0.3 | ||||||||||
| DMEM+FBS, 37 °C | 0.5 | ||||||||||
| Mg5.54Zn0.56Zr | Extrusion | 237 | 312 | 15.5 | [309] | ||||||
| Mg5.54Zn0.56Zr | Extrusion +T5 | 273 | 329 | 16.5 | [309] | ||||||
| Mg5.6Zn0.5Zr | Laser rapid solidification (420 J/mm3) | Hank’s, 37 °C | 1 | [229] | |||||||
| Mg5.6Zn0.5Zr | Laser rapid solidification (500 J/mm3) | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.8 | [229] | |||||||
| Mg5.6Zn0.5Zr | Laser rapid solidification (600 J/mm3) | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.2 | [229] | |||||||
| Mg5.6Zn0.5Zr | Laser rapid solidification (750 J/mm3) | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.7 | [229] | |||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr0.74Y | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 263 | 326 | 12.9 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr0.74Y | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 268 | 331 | 14.6 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr0.74Y | Extrusion (at 400 °C) | 257 | 327 | 14.5 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr1.35Y | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 285 | 341 | 10.2 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr1.35Y | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 279 | 338 | 10.8 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr1.35Y | Extrusion (at 400 °C) | 258 | 327 | 14.6 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr1.72Y | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 267 | 335 | 15.3 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr1.72Y | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 263 | 330 | 12.8 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.4Zr1.72Y | Extrusion (at 400 °C) | 283 | 338 | 10.1 | [310] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.6Zr | High strain-rate rolling | 223 | 311 | 18.3 | [133] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.6Zr0.2Gd | High strain-rate rolling | 227 | 307 | 25.3 | [133] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.6Zr0.5Gd | High strain-rate rolling | 235 | 318 | 23.2 | [133] | ||||||
| Mg5.5Zn0.6Zr0.8Gd | High strain-rate rolling | 242 | 327 | 22 | [133] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | As-cast | 108 | 233 | 9.6 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | T4 | 84 | 272 | 15.7 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | T6 | 165 | 281 | 10.9 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + T5 | 261 | 340 | 19.8 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | Extrusion (at350 °C) + T5 | 269 | 343 | 19.2 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + T5 | 273 | 341 | 18.3 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr | Extrusion + T6 | 222 | 311 | 15.8 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | As-cast | 99 | 212 | 7.7 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | T4 | 78 | 262 | 16.1 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | T6 | 146 | 276 | 13.2 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + T5 | 252 | 321 | 20 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | Extrusion (at 350 °C) + T5 | 258 | 324 | 19.8 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + T5 | 261 | 325 | 19.9 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg5.79Zn0.35Zr1.3Gd | Extrusion + T6 | 239 | 306 | 18.8 | [135] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Zr | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 1.9 | [124] | |||||||
| SBF, 37 °C | 9.6 | ||||||||||
| Mg6.01Zn0.49Zr | Extrusion | 209 | 315 | 19.3 | [134] | ||||||
| Mg5.94Zn0.37Zr0.96Y | Extrusion | 246 | 325 | 22.3 | [134] | ||||||
| Mg5.73Zn0.39Zr1.63Y | Extrusion | 229 | 313 | 15.6 | [134] | ||||||
| Mg5.50Zn0.43Zr2.2Y | Extrusion | 261 | 313 | 17.6 | [134] | ||||||
| Mg5.30Zn0.41Zr3.59Y | Extrusion | 292 | 330 | 20.7 | [134] | ||||||
| Mg5.88Zn0.48Zr | Extrusion | 289 | 346 | 16.4 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.57Zn0.52Zr0.45Yb | Extrusion | 322 | 367 | 15.3 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.64Zn0.47Zr0.93Yb | Extrusion | 355 | 382 | 6.9 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg6.03Zn0.56Zr1.78Yb | Extrusion | 412 | 418 | 2.7 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.88Zn0.48Zr | T5 | 315 | 352 | 14.3 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.57Zn0.52Zr0.45Yb | T5 | 324 | 367 | 15.1 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.64Zn0.47Zr0.93Yb | T5 | 323 | 371 | 14.8 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg6.03Zn0.56Zr1.78Yb | T5 | 359 | 397 | 10.6 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.88Zn0.48Zr | T6 | 266 | 332 | 14.3 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.57Zn0.52Zr0.45Yb | T6 | 302 | 356 | 15.1 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg5.64Zn0.47Zr0.93Yb | T6 | 314 | 368 | 14.9 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg6.03Zn0.56Zr1.78Yb | T6 | 312 | 378 | 10.5 | [311] | ||||||
| Mg9Zn0.6Zr | Extrusion | 263 | 351 | 25 | [175] | ||||||
| Mg9Zn0.6Zr | Aging | 313 | 352 | 20 | [175] | ||||||
| Mg9Zn0.6Zr0.5Er | Extrusion | 313 | 366 | 22 | [175] | ||||||
| Mg9Zn0.6Zr0.5Er | Aging | 342 | 372 | 18 | [175] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn3Gd | As-cast | 9g/L NaCl | <0.004Fe; <0.004Cu; <0.004Ni; 0.3Al; 0.02Mn | 1.2 | 0.83 | [49] | |||||
| Mg3Zn3Gd | As-cast | <0.004Fe; <0.004Cu; <0.004Ni; <0.01Al; 0.02Mn | 1.9 | 5.29 | [49] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn1Gd | Rolling | 182 | 231 | 29.2 | [185] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn1Gd | Rolling | 189 | 233 | 27.2 | [185] | ||||||
| Mg2.6Zn6.5Gd | Induction melting | 288 | 335 | 9.2 | [312] | ||||||
| Mg2.6Zn6.5Gd | Extrusion (Homogenized for 0.5 h) | 303 | 352 | 8.3 | [312] | ||||||
| Mg2.6Zn6.5Gd | Extrusion (Homogenized for 5 h) | 336 | 391 | 7 | [312] | ||||||
| Mg2.6Zn6.5Gd | Extrusion (Homogenized for 10 h) | 345 | 380 | 6.9 | [312] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn0.5Gd | T6 | 98 | 160 | 2.2 | [138] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn1Gd | T6 | 110 | 189 | 4.1 | [138] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn1.5Gd | T6 | 113 | 231 | 8.3 | [138] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn2Gd | T6 | 121 | 215 | 6.4 | [139] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn3Gd | T6 | 92 | 194 | 6.3 | [139] | ||||||
| Mg4.5Zn5Gd | T6 | 80 | 154 | 5.6 | [139] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 214 | 311 | 16.5 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd | Extrusion (at 400 °C) | 199 | 302 | 14.6 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + T4 | 170 | 284 | 15.6 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + T6 | 188 | 285 | 15.3 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + T4 | 166 | 275 | 16.3 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + T6 | 190 | 274 | 15.7 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd3.9Cu | Extrusion (at 300 °C) | 222 | 297 | 10.4 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd3.9Cu | Extrusion (at 400 °C) | 223 | 299 | 11.4 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd3.9Cu | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + T4 | 164 | 258 | 11.1 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd3.9Cu | Extrusion (at 300 °C) + T6 | 161 | 248 | 10.6 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd3.9Cu | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + T4 | 174 | 266 | 16.3 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg8.9Zn1.6Gd3.9Cu | Extrusion (at 400 °C) + T6 | 172 | 257 | 12.3 | [313] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn0.1Ce | Rolling | 191 | 216 | 19.8 | [74] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn0.3RE0.5Zr | Rolling | 203 | 234 | 23.7 | [74] | ||||||
| Mg4Zn1RE0.5Zr | Rolling | 258 | 291 | 8.8 | [74] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn0.5Mn | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 1.6 | [112] | |||||||
| Mg1Zn1Mn | As-cast | <0.01Fe; <0.005Cu; <0.005Ni; <0.3Al | 44 | 175 | 12.1 | [314] | |||||
| Mg1Zn1Mn | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.005Cu; <0.005Ni; <0.3Al | 0.06 | 247 | 280 | 21.8 | [133] | |||
| Mg1.5Zn0.5Mn | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 1.1 | [112] | |||||||
| Mg1.5Zn1Mn | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 0.9 | [112] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.003Fe; 0.002Mn; <0.001Ni; 0.1Al; 0.02Si | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.1 | [113] | ||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 3.4 | [51] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 3.7 | [109] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | Extrusion Aging | SBF, 37 °C | 3.1 | [109] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn1Mn | As-cast | 58 | 181 | 11.1 | [314] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn1Mn | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.005Cu; <0.005Ni; <0.3Al | 0.2 | 249 | 284 | 20.9 | [133] | |||
| Mg2Zn1Mn | Rolling | 127 | 236 | 24.3 | [74] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn1Mn0.3Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 1.7 | 59 | 162 | 7.4 | [52] | ||||
| Mg2Zn1Mn0.5Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 1.3 | 73 | 188 | 9.1 | [52] | ||||
| Mg2Zn1Mn1Ca | As-cast | Hank’s, 37 °C | 0.07 | 81 | 136 | 2.7 | [52] | ||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 8.4 | 20.4 | [287] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn0.38Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 7 | 15.4 | [287] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn0.76Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 10.1 | 23.5 | [287] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 13.1 | 27.8 | [287] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | 6.6 | 14.6 | [315] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn0.38Ca | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | 6.3 | 11.8 | [315] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn0.76Ca | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | 8.1 | 18.6 | [315] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | 9.2 | 23.5 | [315] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | As-cast | SBF, 37 °C | 13.1 | 129 | 1.5 | [286] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | Solid solution treatment (at 300 °C) | SBF, 37 °C | 11.1 | 148 | 3 | [286] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | Solid solution treatment (at 360 °C) | SBF, 37 °C | 10.6 | [286] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | Solid solution treatment (at 420 °C) | SBF, 37 °C | 5.9 | 198 | [286] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | Solid solution treatment (at 460 °C) | SBF, 37 °C | 8.1 | 220 | [286] | ||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.1Ca | Solid solution treatment (at 500 °C) | SBF, 37 °C | 8.8 | [286] | |||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | As-cast | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 8.4 | 102 | [285] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn0.6Nd | As-cast | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 1.2 | 178 | [285] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.2Nd | As-cast | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 2.2 | 208 | [285] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.8Nd | As-cast | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 3.8 | 215 | [285] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 6.6 | 158 | [316] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn0.6Nd | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 0.8 | 224 | [316] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.2Nd | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 1.8 | 228 | [316] | |||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Mn1.8Nd | Solid solution treatment | Kokubo solution, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.01Cu; <0.01Ni | 3.1 | 235 | [316] | |||||
| Mg3Zn1Mn | As-cast | 66 | 217 | 15.5 | [314] | ||||||
| Mg3Zn1Mn | Extrusion | SBF, 37 °C | <0.01Fe; <0.005Cu; <0.005Ni; <0.3Al | 0.4 | 276 | 316 | 10.5 | [133] | |||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.46 | 8.3 | [114] | |||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn0.5Si | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 1.25 | 26.7 | [114] | |||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn1Si | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.54 | 13.5 | [114] | |||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn2Si | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.47 | 9.5 | [114] | |||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn | Induction melting | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.1 | 108 | 335 | 20.3 | [111] | ||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn | Rapid solidification | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.01 | 154 | 460 | 20.5 | [111] | ||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn | Extrusion | Hank’s | 0.2 | 1 | [317] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn | Extrusion + Aging | Hank’s | 0.3 | 1.3 | [317] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn | Twin roll casting + T4 | 170 | 284 | 17.1 | [217] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn | Twin roll casting + T6 | 256 | 310 | 16.2 | [217] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn1Al | Twin roll casting + T4 | 216 | 308 | 17.3 | [217] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn1Al | Twin roll casting + T6 | 307 | 330 | 16.2 | [217] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn3Al | Twin roll casting + T4 | 227 | 327 | 7.8 | [217] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Mn1Al | Twin roll casting + T6 | 319 | 360 | 6.3 | [217] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 5.9 | 3.1 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 7.3 | 0.27 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn0.5Si | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 28.3 | 16.9 | [115] | ||||||
| 4.1 | 0.36 | [116] | |||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn0.5Si0.2Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 25.5 | 9.1 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 5.4 | 0.42 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn0.5Si0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 21.1 | 7.1 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 4.5 | 0.42 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn1Si | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 15.6 | 12.3 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 3.2 | 0.36 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn1Si0.2Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 22.3 | 10.3 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 2.7 | 0.38 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn1Si0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 25.9 | 12.1 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 3.8 | 0.49 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn2Si | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 18.9 | 12.6 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 2.7 | 0.52 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn2Si0.2Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 16.9 | 12.2 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 2.6 | 0.59 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Mn2Si0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 21.9 | 14.3 | [115] | ||||||
| 0.01M NaOH | 3.6 | 0.78 | [116] | ||||||||
| Mg2Zn0.2Si | As-cast | Ringer’s solution, 37 °C | 12.3 | [51] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Si | As-cast | 135 | 183 | 5.8 | [318] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Si0.1Ca | As-cast | 149 | 213 | 5.1 | [318] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Si0.25Ca | As-cast | 161 | 220 | 5.2 | [318] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn1Si0.5Ca | As-cast | 146 | 197 | 4.7 | [318] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn4Si | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 4.2 | 2.8 | [319] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn4Si0.1Sr | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 4.1 | 2.5 | [319] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn4Si0.5Sr | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.003 | 1.5 | [319] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn4Si1Sr | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 0.1 | 1.6 | [319] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn4Si1.5Sr | As-cast | 3.5 wt.% NaCl | 5 | 1 | [319] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn3Si1Mn0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.73 | [282] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Si1Mn0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.42 | [282] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Si1Mn0.6Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.44 | [282] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Si1Mn0.8Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.49 | [282] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn10Si1Mn0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.39 | [282] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 7.3 | 101 | 190 | 8.5 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn0.5Sn | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 8.6 | 118 | 225 | 8.9 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn1Sn | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 7 | 122 | 215 | 7.8 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn2Sn | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 6.8 | 127 | 206 | 7 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn3Sn | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 6.4 | 137 | 203 | 6.5 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn0.5Sn0.2Ca | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 5.3 | 115 | 220 | 8 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn2Al0.2Mn3Sn0.2Ca | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 3.8 | 135 | 255 | 9 | [320] | ||||
| Mg8Zn5Al0.2Mn | As-cast | 1 M NaCl | 11.9 | 106 | 142 | 3.5 | [320] | ||||
| Mg6Zn5Al4RE | As-cast | 140 | 242 | 6.4 | [321] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn7Al4RE | As-cast | 93 | 168 | 3.2 | [321] | ||||||
| Mg8Zn5Al4RE | As-cast | 95 | 174 | 3.1 | [321] | ||||||
| Mg10Zn5Al4RE | As-cast | 93 | 159 | 1.8 | [321] | ||||||
| Mg8Zn4Al | As-cast | 125 | 174 | 3.85 | [322] | ||||||
| Mg8Zn4Al0.5Sn | As-cast | 137 | 185 | 4.05 | [322] | ||||||
| Mg8Zn4Al1Sn | As-cast | 149 | 194 | 4.32 | [322] | ||||||
| Mg8Zn4Al2Sn | As-cast | 163 | 180 | 3.13 | [322] | ||||||
| Mg1Zn0.2Sr | Backward-extrusion | SBF | 0.53 | 1.8 | 89 | 187 | 11 | [140] | |||
| Mg1Zn0.5Sr | Backward-extrusion | SBF | 0.71 | 2.8 | 93 | 211 | 11.8 | [140] | |||
| Mg1Zn0.8Sr | Backward-extrusion | SBF | 2.4 | 3.9 | 117 | 210 | 11.5 | [140] | |||
| Mg1Zn1Sr | Backward-extrusion | SBF | 5.1 | 6.3 | 130 | 249 | 12.6 | [140] | |||
| Mg2Zn0.1Sr | As-cast | SBF; 37 °C | 0.025Fe; <0.001Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.065Al | 8.9 | 6.4 | 58 | 179 | 11.5 | [141] | ||
| Mg2Zn0.2Sr | As-cast | SBF; 37 °C | 0.033Fe; <0.001Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.058Al | 7.6 | 5.6 | 66 | 186 | 14.4 | [141] | ||
| Mg2Zn0.3Sr | As-cast | SBF; 37 °C | 0.018Fe; <0.001Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.072Al | 9.5 | 6.8 | 66 | 179 | 10.7 | [141] | ||
| Mg2Zn0.4Sr | As-cast | SBF; 37 °C | 0.026Fe; <0.001Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.061Al | 13.1 | 7 | 64 | 176 | 10.4 | [141] | ||
| Mg2Zn0.5Sr | As-cast | SBF; 37 °C | 0.033Fe; <0.001Cu; <0.001Ni; 0.074Al | 14.9 | 7.5 | 52 | 153 | 6.3 | [141] | ||
| Mg2Zn0.5Sr | Aging | HBSS | 0.2 | 62 | 142 | 8.9 | [143] | ||||
| Mg4Zn0.5Sr | Aging | HBSS | 0.4 | 104 | 169 | 3 | [143] | ||||
| Mg6Zn0.5Sr | Aging | HBSS | 10.6 | 128 | 209 | 3.6 | [143] | ||||
| Mg4Zn1Sr | As-cast | SBF; 37 °C | 9.4 | 2.3 | 250 | 5 | [142] | ||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 33.3 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 48.1 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 88.4 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn1Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 106.2 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn2Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 40 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn2Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 58.5 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn2Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 97.8 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn2Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 111.2 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn3Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 42.7 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn3Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 66 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn3Ag | Extrusion (at 275 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 85.4 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn3Ag | Extrusion (at 350 °C) + Aging | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 102.9 | [144] | |||||||
| Mg6Zn3Si0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.73 | [281] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Si0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.42 | [281] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Si0.6Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.44 | [281] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn5Si0.8Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.48 | [281] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn10Si0.4Ca | Extrusion | 3.5 wt.% NaCl saturated with Mg(OH)2 | 0.04Fe(max); 0.005Ni(max); 0.05Cu(max) | 0.4 | [281] | ||||||
| Mg6Zn3Cu | Squeeze casting | Salt spray | 11.7 | [323] | |||||||
| Mg1.3Zn3.9La | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0229Fe | 1.5 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg2.6Zn3.9La | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0231Fe | 2.3 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg3.9Zn3.9La | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0234Fe | 3.4 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg5.2Zn3.9La | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0234Fe | 6.3 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg1.3Zn5.2Yb | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0237Fe | 0.8 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg2.6Zn5.2Yb | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0237Fe | 1.4 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg3.9Zn5.2Yb | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0237Fe | 2.8 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg5.2Zn5.2Yb | Rapid solidification | 1 wt.% NaCl | 0.0239Fe | 4.1 | [228] | ||||||
| Mg12Zn4Al0.5Ca | Gravity casting | 118 | 151 | 1.3 | [214] | ||||||
| Mg12Zn4Al0.5Ca | Squeeze casting | 113 | 211 | 5.2 | [214] | ||||||
References
- Song, G.L.; Atrens, A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 1999, 1, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusieva, K.; Davies, C.; Scully, J.; Birbilis, N. Corrosion of magnesium alloys: The role of alloying. Int. Mater. Rev. 2015, 60, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Lorimer, G.; Robson, J. Review on research and development of magnesium alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 2008, 21, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulekci, M.K. Magnesium and its alloys applications in automotive industry. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2008, 39, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Li, N.F.; Lei, T.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, C. Effects of Ca on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties and biocompatibility of Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Geng, L.; Jiao, X. Preparation and characterization of a new biomedical Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, F.; Chen, M. The influence of Zn content on the corrosion and wear performance of Mg-Zn-Ca alloy in simulated body fluid. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zheng, Y. Novel magnesium alloys developed for biomedical application: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Hu, T.; Chu, P. In vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys in a simulated physiological environment: A review. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lei, T.; Li, N.; Feng, F. Effects of Zn on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger, M.; Dehm, G. Trends in the development of new Mg alloys. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 505–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W.; Zhang, P.; Watzinger, B.; Grossmann, B.; Haldenwanger, H. Comparative study of creep of the die-cast Mg-alloys AZ91, AS21, AS41, AM60 and AE42. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 319, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Kad¶, B.K.; Viswanathan, S. Design perspectives for creep-resistant magnesium die-casting alloys. Philos. Mag. 2004, 84, 3843–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rahman, S.S.A. Neuropathology of aluminum toxicity in rats (glutamate and GABA impairment). Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 47, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Davies, C.; Nie, J.; Birbilis, N. Influence of composition and processing on the corrosion of magnesium alloys containing binary and ternary additions of zinc and strontium. Corrosion 2014, 71, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, A.; Dong, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–4.0Zn–0.5Ca alloy. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferkamp, H.; Bach, F.W.; Kaese, V.; Möhwald, K.; Niemeyer, M.; Schreckenberger, H.; Tai, P.T. Magnesium Corrosion–Processes, Protection of Anode and Cathode. In Magnesium-Alloys and Technology; Kainer, K., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weiheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 226–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mordike, B.; Lukác, P. Physical metallurgy. In Magnesium Technology: Metallurgy, Design Data, Applications; Friedrich, H.E., Mordike, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.-Z.; Zhang, W.-Z. Investigation on the microstructure of a τ-Mg32 (Al, Zn) 49 strengthened Mg–Zn–Al alloy with relatively low Zn content. Phase Transit. 2012, 85, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.-S.; Guo, Z.-X.; Pan, F.-S. Solidification microstructural constituent and its crystallographic morphology of permanent-mould-cast Mg-Zn-Al alloys. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2006, 16, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.D. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: Zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Geng, L. Research on Mg-Zn-Ca alloy as degradable biomaterial. In Biomaterials-Physics and Chemistry; Pignatello, R., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011; pp. 183–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Geng, L. Mechanical properties, degradation performance and cytotoxicity of Mg–Zn–Ca biomedical alloys with different compositions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, H. Comment on Mg-Zn (magnesium-zinc). J. Phase Equilib. 1994, 15, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Hort, N.; Vogt, C.; Cohen, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somekawa, H.; Osawa, Y.; Mukai, T. Effect of solid-solution strengthening on fracture toughness in extruded Mg–Zn alloys. Scripta Mater. 2006, 55, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, M.; Schmid-Fetzer, R. Mg-rich phase equilibria of Mg–Mn–Zn alloys analyzed by computational thermochemistry. ZMetl 2006, 97, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.-P.; Murakami, Y.; Niikura, A. The Zn-Mg-Y phase diagram involving quasicrystals. Philos. Mag. A 2000, 80, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, S.; Lal, A. The Mg-Zn-Zr system (magnesium-zinc-zirconium). J. Phase Equilib. 1993, 14, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, I.; Shiotani, N.; Uda, M.; Mizoguchi, T.; Katoh, H. The crystal structure of Mg51Zn20. J. Solid State Chem. 1981, 36, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Nie, J. Structure and thermal stability of primary intermetallic particles in an Mg–Zn casting alloy. Scripta Mater. 2007, 57, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komura, Y.; Tokunaga, K. Structural studies of stacking variants in Mg-base Friauf–Laves phases. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1980, 36, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, S. Die Kristallstruktur von Mg2Zn11-Isomorphie zwischen Mg2Zn11 und Mg2Cu6Al5. Acta Chem. Scand. 1949, 3, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallot, J.; Graf, R. X-Ray Investigation of the Equilibrium Phase in a 60% Zinc Containing Magnesium-Zinc Alloy. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. 1966, 262, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.; Byrne, J. Precipitate strengthening mechanisms in magnesium zinc alloy single crystals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1969, 4, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, C.; Blake, A. The Strength of Concentrated Mg–Zn Solid Solutions. Phys. Status Solidi. A 2002, 194, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J. Transmission electron microscopy study of age hardening in a Mg-5 wt.% Zn alloy. Acta Metall. 1965, 13, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, N.T.; Staiger, M.P.; Nisbet, D.; Davies, C.H.; Birbilis, N. Performance-driven design of biocompatible Mg alloys. JOM 2011, 63, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, G.; Kruger, J. Corrosion studies of rapidly solidified magnesium alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Han, E.-H.; Shan, D.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. The effect of Zn concentration on the corrosion behavior of Mg–xZn alloys. Corros. Sci. 2012, 65, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.; Hamzah, E.; Fereidouni-Lotfabadi, A.; Daroonparvar, M.; Yajid, M.; Mezbahul-Islam, M.; Kasiri-Asgarani, M.; Medraj, M. Microstructure and bio-corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn and Mg–Zn–Ca alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasek, J.; Vojtech, D.; Pospisilova, I. Structural and corrosion characterization of biodegradable Mg-Zn alloy castings. Kovove Mater. 2012, 50, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Bradshaw, A.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Jones, I. The role of β1′ precipitates in the bio-corrosion performance of Mg–3Zn in simulated body fluid. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 614, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avedesian, M.M.; Baker, H. ASM Speciality Handbook: Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1999; Volume 59, p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xi, T. In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koç, E.; Kannan, M.B.; Ünal, M.; Candan, E. Influence of zinc on the microstructure, mechanical properties and in vitro corrosion behavior of magnesium–zinc binary alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Han, E.-H.; Shan, D.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. The role of second phases in the corrosion behavior of Mg–5Zn alloy. Corros. Sci. 2012, 60, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.; Hamzah, E.; Medraj, M.; Idris, M.; Lotfabadi, A.; Daroonparvar, M.; Yajid, M. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and corrosion behaviour of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasek, J.; Vojtěch, D. Structural characteristics and corrosion behavior of biodegradable Mg–Zn, Mg–Zn–Gd alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, N.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H. Effects of backward extrusion on mechanical and degradation properties of Mg–Zn biomaterial. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2012, 10, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalbino, F.; De Negri, S.; Saccone, A.; Angelini, E.; Delfino, S. Bio-corrosion characterization of Mg–Zn–X (X = Ca, Mn, Si) alloys for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Yang, L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion properties of Mg–Zn–Mn–Ca alloy for biomedical application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 497, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; He, W.; Du, H.; Yang, K. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloys with low Zn content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 488, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehlert, C.; Knittel, K. The microstructure, tensile properties, and creep behavior of Mg–Zn alloys containing 0–4.4 wt.% Zn. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 417, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Cao, H.; Kang, Y.; Yu, K.; Xiao, T.; Luo, J.; Deng, Y.; Fang, H.; Xiong, H.; Dai, Y. Effects of Zn concentration and heat treatment on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of as-extruded Mg-Zn alloys produced by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, H.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y. In vitro degradation, hemolysis and MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion of biodegradable Mg–Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Shi, Z.; Song, G.-L.; Liu, M.; Atrens, A. Corrosion behaviour in salt spray and in 3.5% NaCl solution saturated with Mg(OH)2 of as-cast and solution heat-treated binary Mg–X alloys: X = Mn, Sn, Ca, Zn, Al, Zr, Si, Sr. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 60–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-B.; Shan, D.-Y.; Song, Y.-W.; Han, E.-H. Effects of heat treatment on corrosion behaviors of Mg-3Zn magnesium alloy. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2010, 20, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-B.; Kirkland, N.; Krebs, H.; Thiriat, M.; Virtanen, S.; Nisbet, D.; Birbilis, N. In vitro corrosion survey of Mg–x Ca and Mg–3Zn–y Ca alloys with and without calcium phosphate conversion coatings. Corros. Eng. Sci. Techn. 2012, 47, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, Y. In vitro and in vivo corrosion and histocompatibility of pure Mg and a Mg-6Zn alloy as urinary implants in rat model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 414–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, H.-Y.; Kang, J.-Y.; Yang, J.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S. Limitations in the use of the potentiodynamic polarisation curves to investigate the effect of Zn on the corrosion behaviour of as-extruded Mg–Zn binary alloy. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.; Birbilis, N. Effect of grain size on corrosion: A review. Corrosion 2010, 66, 075005–075005-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op’t Hoog, C.; Birbilis, N.; Estrin, Y. Corrosion of pure Mg as a function of grain size and processing route. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Zhang, M.X.; Estrin, Y. Surface grain size effects on the corrosion of magnesium. In Key Engineering Materials; Hoog, C.O.T., Birbilis, N., Zhang, M.X., Eds.; Trans Tech Publ.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ambat, R.; Aung, N.N.; Zhou, W. Evaluation of microstructural effects on corrosion behaviour of AZ91D magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1433–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K.; Cohen, S. The relation between microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg–Y–RE–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 431, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Ralston, K.; Virtanen, S.; Fraser, H.; Davies, C. Grain character influences on corrosion of ECAPed pure magnesium. Corros. Eng. Sci. Techn. 2010, 45, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-C.; Liu, M.; Song, G.; Atrens, A. Influence of the β-phase morphology on the corrosion of the Mg alloy AZ91. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1939–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Atrens, A.; Dargusch, M. Influence of microstructure on the corrosion of diecast AZ91D. Corros. Sci. 1998, 41, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Bradshaw, A.; Chiu, Y.; Jones, I. Effects of secondary phase and grain size on the corrosion of biodegradable Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 480–486. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, W. Enhancement of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg–Ca alloys through microstructural refinement by indirect extrusion. Corros. Sci. 2014, 82, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Geng, L.; Lu, C. Effects of calcium on texture and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 539, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Peng, Q. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of backward extruded Mg-Zn-Ca alloys in different media. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2013, 8, 2551–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Bohlen, J.; Nürnberg, M.R.; Senn, J.W.; Letzig, D.; Agnew, S.R. The texture and anisotropy of magnesium–zinc–rare earth alloy sheets. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2101–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zander, D.; Zumdick, N.A. Influence of Ca and Zn on the microstructure and corrosion of biodegradable Mg–Ca–Zn alloys. Corros. Sci. 2015, 93, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, P.-R.; Han, H.-S.; Yang, G.-F.; Kim, Y.-C.; Hong, K.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Jung, J.-Y.; Ahn, J.-P.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Cho, S.-Y. Biodegradability engineering of biodegradable Mg alloys: Tailoring the electrochemical properties and microstructure of constituent phases. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Südholz, A.; Kirkland, N.; Buchheit, R.; Birbilis, N. Electrochemical properties of intermetallic phases and common impurity elements in magnesium alloys. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2011, 14, C5–C7. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, S.; Muddle, B.; Nie, J. Precipitation-hardened Mg–Ca–Zn alloys with superior creep resistance. Scripta Mater. 2005, 53, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Ohkubo, T.; Mukai, T.; Hono, K. TEM and 3DAP characterization of an age-hardened Mg–Ca–Zn alloy. Scripta Mater. 2005, 53, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Guo, C.; Chai, L.; Sherman, V.R.; Qin, X.; Ding, Y.; Meyers, M.A. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of hot extruded Mg–2.5 Zn–1Ca alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2015, 195, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, Y.; Kobata, M.; Iwasaki, H.; Mabuchi, M. Tensile properties from room temperature to 673 K of Mg-0.9 mass% Ca alloy containing lamella Mg2Ca. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 2643–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Jurey, C.; Xu, Z.; Dong, Z.; Collins, B.; Yun, Y.; Sankar, J. Understanding corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Ca alloys from subcutaneous mouse model: Effect of Zn element concentration and plasma electrolytic oxidation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, G.; Varsani, V.; Fan, Z. Thermodynamic modelling of the Y–Zn and Mg–Zn–Y systems. Calphad 2006, 30, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, D.H. Effects of Zn/Y ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3801–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.; Kim, T. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of rapidly solidified Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, H.; Yoon, E.; Chae, H.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Kim, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a Mg–Zn–Y alloy produced by a powder metallurgy route. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S95–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, W.; Chen, C.; Kang, J. Corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Y alloy with long-period stacking ordered structures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, D.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, B.; Sheng, L.; Chen, X.-B.; Han, E. Effect of volume fraction of LPSO phases on corrosion and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shi, L.-l.; Xu, J. Mg–Zn–Y alloys with long-period stacking ordered structure: In vitro assessments of biodegradation behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, D.; Lee, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, W.; Kim, D. Application of quasicrystalline particles as a strengthening phase in Mg–Zn–Y alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 342, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Han, E. Effects of icosahedral phase formation on the microstructure and mechanical improvement of Mg alloys: A review. Progr. Nat. Sci. 2012, 22, 364–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Watanabe, M.; Kato, A.; Tsai, A. Microstructure and strength of quasicrystal containing extruded Mg–Zn–Y alloys for elevated temperature application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 385, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, W. Deformation behavior of Mg–Zn–Y alloys reinforced by icosahedral quasicrystalline particles. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, Y.; Sassa, K.; Mabuchi, M. Texture and stretch formability of a rolled Mg–Zn alloy containing dilute content of Y. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 513, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Ma, A.; Jiang, J.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Q. Review on long-period stacking-ordered structures in Mg-Zn-RE alloys. Rare Metals 2012, 31, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shi, L.-l.; Xu, J. Biodegradable Mg–Zn–Y alloys with long-period stacking ordered structure: Optimization for mechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2013, 18, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoi, T.; Inazawa, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Hirohashi, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg--Zn--Y alloy sheet prepared by hot-rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, Y.; Yamasaki, M. Formation and mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1RE2 alloys with long-period stacking ordered structure. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded Mg-Zn-Y alloys with 14H long period ordered structure. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Lin, D.; Zeng, X.; Lu, C. Effects of yttrium and zinc addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Y–Zn alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 45, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Hirohashi, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y rolled sheet with a Mg12ZnY phase. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Lin, D.; Zeng, X.; Lu, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 440, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Rapidly solidified powder metallurgy Mg97Zn1Y2Alloys with excellent tensile yield strength above 600 MPa. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, M.; Ando, S.; Nishida, M. Dislocation structure in rapidly solidified Mg97Zn1Y2 alloy with long period stacking order phase. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms in Mg–Zn–Y alloy with a long period stacking ordered structure. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 4760–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Yokotani, N.; Umakoshi, Y. Plastic deformation behavior of Mg12YZn with 18R long-period stacking ordered structure. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, E.; Garcés, G.; Onorbe, E.; Pérez, P.; Adeva, P. High-strength Mg–Zn–Y alloys produced by powder metallurgy. Scripta Mater. 2009, 60, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.T.; Kim, D.H. Effect of volume fraction of qusicrystal on the mechanical properties of quasicrystal-reinforced Mg–Zn–Y alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-B.; Wu, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.-F. Corrosion and wear behavior of an Mg–2Zn–0.2 Mn alloy in simulated body fluid. Rare Metals 2015, 34, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.-s.; Zhang, E.-l.; Zeng, S.-y. Effect of Zn on mechanical property and corrosion property of extruded Mg-Zn-Mn alloy. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2008, 18, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Ma, C.; Guo, S. Improving mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg-6Zn-Mn magnesium alloy by rapid solidification. Mater. Lett. 2013, 92, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalbino, F.; De Negri, S.; Scavino, G.; Saccone, A. Microstructure and in vitro degradation performance of Mg–Zn–Mn alloys for biomedical application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, N.I.Z.; Atrens, A.D.; Martin, D.; Atrens, A. Corrosion of high purity Mg, Mg2Zn0. 2Mn, ZE41 and AZ91 in Hank’s solution at 37 °C. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3542–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K. The role of Mg2Si on the corrosion behavior of wrought Mg–Zn–Mn alloy. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisitsyn, V.; Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K. The role of Ca microalloying on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg–6Zn–Mn–(0.5–2) Si alloys. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisitsyn, V.; Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K. Some particularities of the corrosion behaviour of Mg–Zn–Mn–Si–Ca alloys in alkaline chloride solutions. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinodi, N.; Shetty, A.N. Electrochemical investigations on the corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy ZE41 in a combined medium of chloride and sulphate. J. Magnes. Alloys 2013, 1, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.C.; Liu, M.; Song, G.-L.; Atrens, A. Influence of Microstructure on Corrosion of As-cast ZE41. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-C.; Liu, M.; Song, G.-L.; Atrens, A. Influence of pH and chloride ion concentration on the corrosion of Mg alloy ZE41. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3168–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, M.B.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of ZE41 and QE22 magnesium alloys. In Materials Science Forum; Dieringa, H., Hort, N., Kainer, K.U., Eds.; Trans Tech Publ.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Neil, W.; Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P.; Hutchinson, C.; Hinton, B. Corrosion of magnesium alloy ZE41–The role of microstructural features. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, W.; Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P.; Hutchinson, C.; Hinton, B. Corrosion of heat treated magnesium alloy ZE41. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coy, A.; Viejo, F.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G. Susceptibility of rare-earth-magnesium alloys to micro-galvanic corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3896–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamesh, M.I.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M.; Chu, P.K. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of biodegradable Mg–Y–RE and Mg–Zn–Zr alloys in Ringer’s solution and simulated body fluid. Corros. Sci. 2015, 91, 160–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Z.; Leeflang, M.; Zhou, J.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.; Duszczyk, J. In vitro degradation behavior and cytocompatibility of Mg–Zn–Zr alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2623–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.; Ruan, L. In vitro degradation performance and biological response of a Mg–Zn–Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Kaese, V.; Haferkamp, H.; Switzer, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wirth, C.; Windhagen, H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.-C.; Sha, W.; Qiao, L.-Y.; Yong, W. Corrosion behavior of Mg and Mg-Zn alloys in simulated body fluid. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2008, 18, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-W.; Duo, J.; Xiang, Y.-Z.; Yang, H.-Y.; Ding, W.-J.; Peng, Y.-H. Influence of Nd and Y additions on the corrosion behaviour of extruded Mg-Zn-Zr alloys. Int. J. Min. Metal Mater. 2011, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.D.R.S.; del Rosario, M. The Role of Intermetallic Phases in the Corrosion of Magnesium-Rare Earth Alloys; Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Cao, P.; Yan, T.; Xu, X. Effect of Y and Ce additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 644, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z. Effect of neodymium on mechanical behavior of Mg-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2003, 22, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Hongge, Y.; Jihua, C.; Bin, S.; Yi, Z.; Yanjin, S.; Zhaojie, M. Effects of minor Gd addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of the high strain-rate rolled Mg–Zn–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, P.; Gao, S.; Wei, Y.; Pan, F. Influence of Y on the phase composition and mechanical properties of as-extruded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 47, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Peng, L.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of the microstructure and mechanical properties of a ZK60 alloy with and without 1.3 wt.% gadolinium addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 433, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Effect of Nd and Y addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Ding, W. Effects of Zn/Gd ratio and content of Zn, Gd on phase constitutions of Mg alloys. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Xiao, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Influences of Gd on the microstructure and strength of Mg–4.5 Zn alloy. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the Mg–4.5 Zn–xGd (x= 0, 2, 3 and 5) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 459, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Han, Z.; Fang, D. Microstructures, mechanical and cytocompatibility of degradable Mg–Zn based orthopedic biomaterials. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Effects of Sr on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Mg-2Zn-xSr alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, R.-G.; Cipriano, A.F.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Lock, J.; Tie, D.; Zhao, T.; Cui, T.; Liu, H. Development and evaluation of a magnesium–zinc–strontium alloy for biomedical applications—Alloy processing, microstructure, mechanical properties, and biodegradation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3661–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, H.S.; Wong, J.; Manuel, M.V. Investigation of the mechanical and degradation properties of Mg–Sr and Mg–Zn–Sr alloys for use as potential biodegradable implant materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2012, 7, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Kaya, A.; Na, Y.; Shin, K. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Ag alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfpour, M.; Emamy, M.; Dehghanian, C.; Tavighi, K. Influence of Cu addition on the structure, mechanical and corrosion properties of Cast Mg-2% Zn alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 2136–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zeng, Z.; Scully, J.; Williams, G.; Birbilis, N. Simultaneously improving the corrosion resistance and strength of magnesium via low levels of Zn and Ge additions. Corros. Sci. 2018, 140, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, P.; Blawert, C.; Hou, R.; Scharnagl, N.; Bohlen, J.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Microstructural influence on corrosion behavior of MgZnGe alloy in NaCl solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Shi, Z.; Atrens, A. The influence of pH on the corrosion rate of high-purity Mg, AZ91 and ZE41 in bicarbonate buffered Hanks’ solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 101, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taltavull, C.; Shi, Z.; Torres, B.; Rams, J.; Atrens, A. Influence of the chloride ion concentration on the corrosion of high-purity Mg, ZE41 and AZ91 in buffered Hank’s solution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinodi, N.; Shetty, A.N. Investigation of influence of medium ph and sulfate ion concentrations on corrosion behavior of magnesium alloy ZE41. Surf. Eng. Appl. Elect. 2014, 50, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Ravikiran, V. Evaluation of electrochemical and surface characteristics of conversion coatings on ZM21 magnesium alloy. Surf. Eng. 2006, 22, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.J.; Horstemeyer, M.; Wang, P.T. Comparison of corrosion pitting under immersion and salt-spray environments on an as-cast AE44 magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3624–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Martin, H.J.; Hicks, A.; Seely, D.; Walton, C.A.; Lawrimore, W.B., II; Wang, P.T.; Horstemeyer, M. Corrosion behaviour of extruded AM30 magnesium alloy under salt-spray and immersion environments. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, C.A.; Martin, H.J.; Horstemeyer, M.; Wang, P.T. Quantification of corrosion mechanisms under immersion and salt-spray environments on an extruded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2012, 56, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-C.; Schmutz, P.; Brunner, S.; Liu, M.; Song, G.-l.; Atrens, A. An exploratory study of the corrosion of Mg alloys during interrupted salt spray testing. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.; Hou, R.Q.; Nidadavolu, E.P.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Feyerabend, F. Magnesium degradation under physiological conditions–Best practice. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Shadanbaz, S.; Kirkland, N.T.; Stace, E.; Woodfield, T.; Staiger, M.P.; Dias, G.J. Magnesium alloys: Predicting in vivo corrosion with in vitro immersion testing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzi, A.C.; Gerber, I.; Schinhammer, M.; Löffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. On the in vitro and in vivo degradation performance and biological response of new biodegradable Mg–Y–Zn alloys. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.H.M.; Luthringer, B.J.; Feyerabend, F.; Willumeit, R. Mg and Mg alloys: How comparable are in vitro and in vivo corrosion rates? A review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, C.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y. Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seuss, F.; Seuss, S.; Turhan, M.; Fabry, B.; Virtanen, S. Corrosion of Mg alloy AZ91D in the presence of living cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 99, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, R.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Garamus, V.M.; Frant, M.; Koll, J.; Feyerabend, F. Adsorption of Proteins on Degradable Magnesium-Which Factors are Relevant? ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 42175–42185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willumeit, R.; Fischer, J.; Feyerabend, F.; Hort, N.; Bismayer, U.; Heidrich, S.; Mihailova, B. Chemical surface alteration of biodegradable magnesium exposed to corrosion media. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2704–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hiromoto, S. Effect of inorganic salts, amino acids and proteins on the degradation of pure magnesium in vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.S.; Jafari, S.; Harandi, S.E. Corrosion fatigue fracture of magnesium alloys in bioimplant applications: A review. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 137, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhong, S.; Xi, T.; Chen, L. Corrosion fatigue behaviors of two biomedical Mg alloys–AZ91D and WE43–in simulated body fluid. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4605–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Z. Fatigue behaviors of HP-Mg, Mg–Ca and Mg–Zn–Ca biodegradable metals in air and simulated body fluid. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Hofstetter, J.; Cao, F.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Dargusch, M.S.; Atrens, A. Corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of ultra-high-purity Mg5Zn. Corros. Sci. 2015, 93, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, L.; Raman, R.S. Mechanical integrity of magnesium alloys in a physiological environment: Slow strain rate testing based study. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 103, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, N.; Atrens, A.; Dietzel, W.; Song, G.; Kainer, K. Stress corrosion cracking in magnesium alloys: Characterization and prevention. JOM 2007, 59, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, D.B.; Dhamotharan, S.; Kumar, G.S.; Gopalakrishnan, P.; Ravi, K. Stress corrosion cracking of biodegradable Mg-4Zn alloy in simulated body fluid at different strain rates-a fractographic investigation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Raman, R.S.; Davies, C.H. Stress corrosion cracking of an extruded magnesium alloy (ZK21) in a simulated body fluid. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 201, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, Y.; Ding, W.; Lu, C. Effects of extrusion on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Gd alloy reinforced with quasicrystalline particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 474, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Song, G.; Atrens, A. Corrosion resistance of anodised single-phase Mg alloys. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2006, 201, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; Pan, F. Effects of trace Er addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Zr alloy. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4043–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Klarner, A.D.; Poorganji, B.; Dean, D.; Luo, A.A.; Elahinia, M. Microstructural, mechanical and corrosion characteristics of heat-treated Mg-1.2 Zn-0.5 Ca (wt%) alloy for use as resorbable bone fixation material. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2017, 69, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Han, E.-H.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y. Influence of higher Zn/Y ratio on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Somekawa, H.; Mukai, T. Compressive strength and yield asymmetry in extruded Mg–Zn–Ho alloys containing quasicrystal phase. Scripta Mater. 2007, 56, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; You, B.S.; Mishra, R.K.; Sachdev, A.K. Effects of extrusion parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–(Mn)–Ce/Gd alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 598, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Precipitation behavior and mechanical properties of a Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloy processed by thermo-mechanical treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 395, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Bae, D.; Kim, D. Precipitates in a Mg–Zn–Y alloy reinforced by an icosahedral quasicrystalline phase. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 359, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, L.; Davis, B.; Humphreys, F.; Lorimer, G. The deformation, recrystallisation and texture of three magnesium alloy extrusions. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, S.; Horton, J.; Lillo, T.; Brown, D. Enhanced ductility in strongly textured magnesium produced by equal channel angular processing. Scripta Mater. 2004, 50, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Sassa, K.; Kamiya, A.; Mabuchi, M. Press formability of a rolled AZ31 Mg alloy sheet with controlled texture. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, R.; Han, E. Room-temperature ductility and anisotropy of two rolled Mg–Zn–Gd alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Yun, Y.-S.; Suh, B.-C.; Kim, N.-J.; Kim, W.-T.; Kim, D.-H. Comparison of static recrystallization behavior in hot rolled Mg–3Al–1Zn and Mg–3Zn–0.5 Ca sheets. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 589, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Bhushan, B.; Jayaganthan, R.; Gopinath, P.; Agarwal, R.; Lahiri, D. Strengthening of Mg based alloy through grain refinement for orthopaedic application. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2016, 59, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Aibin, M.; Saito, N.; Zhixin, S.; Dan, S.; Fumin, L.; Nishida, Y.; Donghui, Y.; Pinghua, L. Improving corrosion resistance of RE-containing magnesium alloy ZE41A through ECAP. J. Rare Earth. 2009, 27, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaed, E.; Hashempour, M.; Fabrizi, A.; Dellasega, D.; Bestetti, M.; Bonollo, F.; Vedani, M. Microstructure, texture evolution, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of ECAP processed ZK60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2014, 37, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.Y.; Xu, S.W.; Qiao, X.G.; Gan, W.M.; Wu, K.; Kamado, S.; Kojima, Y.; Brokmeier, H.G. Equal channel angular pressing of magnesium alloy containing quasicrystal phase. In Materials Science Forum; Horita, Z., Ed.; Trans Tech Publ.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 527–532. [Google Scholar]
- Mostaed, E.; Vedani, M.; Hashempour, M.; Bestetti, M. Influence of ECAP process on mechanical and corrosion properties of pure Mg and ZK60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable stent applications. Biomaterials 2014, 4, e28283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, L.; Zheng, M.; Chang, H.; Hu, X.; Wu, K.; Xu, S.; Kamado, S.; Kojima, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 523, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zheng, M.; Hu, X.; Wu, K.; Xu, S.; Kamado, S.; Kojima, Y. Influence of ECAP routes on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 4250–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.V.; Zhu, Y.T.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Lowe, T.C.; Valiev, R.Z. Influence of ECAP routes on the microstructure and properties of pure Ti. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 299, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Feyerabend, F.; Maier, P.; Fischer, J.; Störmer, M.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Hort, N. Biodegradable magnesium–hydroxyapatite metal matrix composites. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poddar, P.; Srivastava, V.; De, P.; Sahoo, K. Processing and mechanical properties of SiC reinforced cast magnesium matrix composites by stir casting process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 460, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, R.; Surappa, M. Fabrication and characterisation of pure magnesium-30 vol.% SiCP particle composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 276, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Lopez, C.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.; Lyon, P.; Karimzadeh, H.; Wilks, T. The corrosion behaviour of Mg alloy ZC71/SiCp metal matrix composite. Corros. Sci. 1995, 37, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Lopez, C.; Habazaki, H.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.; Karimzadeh, H.; Lyon, P.; Wilks, T. An investigation of microgalvanic corrosion using a model magnesium-silicon carbide metal matrix composite. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, F.; Trabanelli, G.; Grassi, V.; Frignani, A. Corrosion behavior in sodium sulfate and sodium chloride solutions of SiCp reinforced magnesium alloy metal matrix composites. Corrosion 2004, 60, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Han, Y. Mechanical and in vitro degradation behavior of ultrafine calcium polyphosphate reinforced magnesium-alloy composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, T.; Schwartz, A.; Wadsworth, J. Superplasticity in a 17 vol.% SiC particulate-reinforced ZK60A magnesium composite (ZK60/SiC/17p). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 208, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianxi, H.; Erde, W. Fabrication and mechanical properties of SiCw/ZK51A magnesium matrix composite by two-step squeeze casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 278, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-B.; Chen, M.-F.; Ye, X.-Y. Fabrication and corrosion behavior of HA/Mg-Zn biocomposites. Front. Mater. Sci. 2010, 4, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, M.; Wei, J.; Liu, D. In vitro corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility of nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced Mg–Zn–Zr composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.-Y.; Yue, S.; Chen, M.-F.; Liu, D.-B.; Ye, X.-Y. Microstructure and properties of biodegradable β-TCP reinforced Mg-Zn-Zr composites. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2011, 21, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, S.C.; Frutos, E.; González-Carrasco, J.L.; Muñoz, M.; Multigner, M.; Chao, J.; Benavente, R.; Lieblich, M. Novel PLLA/magnesium composite for orthopedic applications: A proof of concept. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Dai, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Z. In vitro corrosion behavior and in vivo biodegradation of biomedical β-Ca3(PO4)2/Mg–Zn composites. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Wei, Y.; Guo, S.; Fusheng, P. Enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of a Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glass composite by Fe particle addition. Mater. Lett. 2013, 91, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Shiflet, G.; Guo, F.; Poon, S. Mg–Ca–Zn bulk metallic glasses with high strength and significant ductility. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 1935–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Corrosion of, and cellular responses to Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glasses. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamado, S.; Ikeya, N.; Rudi, R.S.; Araki, T.; Kojima, Y. Application of semi-solid forming to Mg-Zn-Al-Ca alloys. In Materials Science Forum; Kojima, Y., Aizawa, T., Kamado, S., Eds.; Trans Tech Publ.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Blawert, C.; Morales, E.D.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K.U. Comparison of corrosion properties of squeeze cast and thixocast MgZnRE alloys. In Materials Science Forum; Ke, W., Han, E.H., Han, Y.F., Eds.; Trans Tech Publ.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 697–700. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, C. Effects of processing parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of squeeze-cast Mg–12Zn–4Al–0.5 Ca alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležal, P.; Zapletal, J.; Fintová, S.; Trojanová, Z.; Greger, M.; Roupcová, P.; Podrábský, T. Influence of processing techniques on microstructure and mechanical properties of a biodegradable Mg-3Zn-2Ca alloy. Materials 2016, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-M.; Yu, H.-S.; Kang, S.-B.; Min, G.-H.; Jin, Y.-X. Effect of rolling temperature on microstructure and texture of twin roll cast ZK60 magnesium alloy. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2010, 20, 2086–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Bae, G.; Kang, D.; Jung, I.-H.; Shin, K.; Kim, N.J. Microstructure and tensile properties of twin-roll cast Mg–Zn–Mn–Al alloys. Scripta Mater. 2007, 57, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-R.; Min, W.; Kang, S.-B.; Cho, J.-H. Microstructure comparison of ZK60 alloy under casting, twin roll casting and hot compression. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2010, 20, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, H.; Davey, K.; Rasgado, M.; Haga, T.; Izawa, S. Semi-solid manufacturing process of magnesium alloys by twin-roll casting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 155, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Park, W.-J.; Kim, C.; You, B.; Kim, N.J. The twin-roll casting of magnesium alloys. JOM 2009, 61, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, G.; Ürgen, M. Corrosion behaviour of magnesium AZ31 sheet produced by twin roll casting. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, C.; Bae, J.; Kim, N.; Hono, K. Microstructures and tensile properties of a twin roll cast and heat-treated Mg–2.4 Zn–0.1 Ag–0.1 Ca–0.1 Zr alloy. Scripta Mater. 2011, 64, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N. Critical assessment 6: Magnesium sheet alloys: Viable alternatives to steels? Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Bae, G.; Kang, D.; You, B.; Kim, N.J. Superplastic deformation behavior of twin-roll cast Mg–6Zn–1Mn–1Al alloy. Scripta Mater. 2009, 61, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Victoria-Hernandez, J.; Jiang, P.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Luthringer-Feyerabend, B.; Yi, S.; Letzig, D.; Feyerabend, F. In vitro evaluation of the ZX11 magnesium alloy as potential bone plate: Degradability and mechanical integrity. Acta Biomater. 2019, 97, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria-Hernández, J.; Yi, S.; Klaumünzer, D.; Letzig, D. Recrystallization behavior and its relationship with deformation mechanisms of a hot rolled Mg-Zn-Ca-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 761, 138054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaumünzer, D.; Marx, A.; Schauerte, O.; Wollenberg, A.; Letzig, D.; Yi, S.; Victoria-Hernández, J.; Uggowitzer, P.; Knwon, O.-D.; Kim, J.J.; et al. Magneisum Alloy Sheet Produced by Twin Roll Casting. EP3205736A1, 22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, M.; Hayashi, N.; Izumi, S.; Kawamura, Y. Corrosion behavior of rapidly solidified Mg–Zn–rare earth element alloys in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Yang, Y.; Wu, P.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, P.; Liu, X.; Peng, S. Laser rapid solidification improves corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Chen, S.; Sankar, J. Development and microstructural characterizations of Mg–Zn–Ca alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornberger, H.; Virtanen, S.; Boccaccini, A. Biomedical coatings on magnesium alloys—A review. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2442–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, H.Y.; Abbott, T.; Easton, M.A.; Birbilis, N. Corrosion-resistant electrochemical platings on magnesium alloys: A state-of-the-art review. Corrosion 2012, 68, 518–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Harimkar, S.P. Laser surface engineering of magnesium alloys: A review. JOM 2012, 64, 716–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Cui, F.-z.; Lee, I.S.; Wang, X. Plasma surface modification of magnesium alloy for biomedical application. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2010, 205, S182–S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Luan, B. Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys—A critical review. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 336, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.-G.; Zhang, S.; Bu, J.-F.; Lin, C.-J.; Song, G.-L. Recent progress in corrosion protection of magnesium alloys by organic coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 73, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Birbilis, N.; Abbott, T. Review of corrosion-resistant conversion coatings for magnesium and its alloys. Corrosion 2011, 67, 035005-1–035005-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lai, Y.; Qin, L. Surface modification of magnesium alloys developed for bioabsorbable orthopedic implants: A general review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Hall, C.; Murphy, P. Surface treatments for controlling corrosion rate of biodegradable Mg and Mg-based alloy implants. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 2015, 16, 053501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommiers-Belin, S.; Frayret, J.; Uhart, A.; Ledeuil, J.; Dupin, J.-C.; Castetbon, A.; Potin-Gautier, M. Determination of the chemical mechanism of chromate conversion coating on magnesium alloys EV31A. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 298, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, C.; Liu, Y. Molybdate/phosphate composite conversion coating on magnesium alloy surface for corrosion protection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ger, M.; Hwu, W.; Sung, Y.; Liu, Y. Study of vanadium-based chemical conversion coating on the corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 101, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, S.; Luo, J.; Fukuda, Y.; Nakae, H. A chromium-free conversion coating of magnesium alloy by a phosphate–permanganate solution. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2006, 200, 5407–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, W.; Lin, C. Effect of permanganate concentration on the formation and properties of phosphate/permanganate conversion coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2013, 70, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, G.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, H. A chrome-free conversion coating for magnesium–lithium alloy by a phosphate–permanganate solution. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2008, 202, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Q.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B. Composite anticorrosion coatings for AZ91D magnesium alloy with molybdate conversion coating and silicon sol–gel coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 66, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, J.; Lei, T.; Xiao, T. Optimization of process factors for self-healing vanadium-based conversion coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Chang, S.-H.; Tong, X.; Li, G.; Shi, Z. Analysis of characteristics of vanadate conversion coating on the surface of magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 617, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lin, H.; Lin, K.; Lai, W. Formation and properties of stannate conversion coatings on AZ61 magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dai, C.-l.; Liu, Y.-l.; Zhu, J. Study of Silicate and Tungstate Composite Conversion Coating on Magnesium Alloy. Eletroplating Pollut. Control 2007, 27, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Tsai, C.; Huang, Y.; Lin, C. Formation mechanism and properties of titanate conversion coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, C226–C232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.-Y.; Chu, Y.-R.; Lin, C.-S. Permanganate conversion coating on AZ31 magnesium alloys with enhanced corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 2015, 93, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Liu, B.; Peng, Z. Preparation of superhydrophobic zinc coating for corrosion protection. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2014, 454, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.C. Method of preparing copper plating layer having high adhesion to magnesium alloy using electroplating. US7368047B2, 6 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Macary, R.L. Method of chrome plating magnesium and magnesium alloys. US8152985B2, 10 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Ouyang, Y.; He, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z. Studies on influence of zinc immersion and fluoride on nickel electroplating on magnesium alloy AZ91D. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7773–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.-L.; Shi, Z. Corrosion mechanism and evaluation of anodized magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Ghali, E.; Song, G. Anodizing treatments for magnesium alloys and their effect on corrosion resistance in various environments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Blawert, C.; Kainer, K.U.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Investigation of the formation mechanisms of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on Mg alloy AM50 using particles. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 196, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Blawert, C.; Huang, Y.; Ovri, H.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Kainer, K.U. Plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on Mg alloy with addition of SiO2 particles. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, T.; Meng, G.; Wang, F. Corrosion protection of Mg–5Li alloy with epoxy coatings containing polyaniline. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2906–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, V.-T.; Lai, P.; Moore, B.; Muscat, R.; Russo, M. Corrosion protection of magnesium by electroactive polypyrrole/paint coatings. Synthetic Met. 2000, 110, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.M.; Yeung, K.W.; Lam, K.O.; Tam, V.; Chu, P.K.; Luk, K.D.; Cheung, K.M. A biodegradable polymer-based coating to control the performance of magnesium alloy orthopaedic implants. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2084–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoche, H.; Groß, S.; Oechsner, M. Development of new PVD coatings for magnesium alloys with improved corrosion properties. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 259, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zeng, X.; Yuan, G. Growth and corrosion of aluminum PVD-coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4325–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, H.; Sen, S. The effect of PVD coatings on the corrosion behaviour of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-l.; Wang, C.-S.; Yao, M.; Liu, H.-B. The resistance to wear and corrosion of laser-cladding Al2O3 ceramic coating on Mg alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 5306–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignat, S.; Sallamand, P.; Grevey, D.; Lambertin, M. Magnesium alloys laser (Nd: YAG) cladding and alloying with side injection of aluminium powder. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 225, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Kim, H. Laser surface modification of Ti and TiC coatings on magnesium alloy. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2014, 115, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, T.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Li, S. Structure, micro-hardness and corrosion behaviour of the Al–Si/Al2O3 coatings prepared by laser plasma hybrid spraying on magnesium alloy. Vacuum 2015, 117, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterman, J.; Staiger, M. Coating systems for magnesium-based biomaterials—State of the art. In Magnesium Technology 2011; Neelameggham, A.R., Mathaudhu, S.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Aghion, E.; Bronfin, B. Magnesium alloys development towards the 21st century. In Materials Science Forum; Kojima, Y., Aizawa, T., Kamado, S., Eds.; Trans Tech Publ.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, A.A. Magnesium casting technology for structural applications. J. Magnes. Alloys 2013, 1, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, A.; Renaud, J.; Nakatsugawa, I.; Plourde, J. Magnesium castings for automotive applications. JOM 1995, 47, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, B.; Luo, A.; Krajewski, P. Magnesium alloys for lightweight powertrains and automotive bodies. In Advanced Materials in Automotive Engineering; Rowe, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 150–209. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, A.; Shinoda, T. A new magnesium alloy for automotive powertrain applications. SAE Trans. 1998, 107, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Klaumünzer, D.; Hernandez, J.V.; Yi, S.; Letzig, D.; Kim, S.-h.; Kim, J.J.; Seo, M.H.; Ahn, K. Magnesium Process and Alloy Development for Applications in the Automotive Industry. In Magnesium Technology 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Biocompatibility of bio-Mg-Zn alloy within bone with heart, liver, kidney and spleen. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; He, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Biocompatibility of magnesium-zinc alloy in biodegradable orthopedic implants. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 28, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraus, T.; Fischerauer, S.F.; Hänzi, A.C.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F.; Weinberg, A.M. Magnesium alloys for temporary implants in osteosynthesis: In vivo studies of their degradation and interaction with bone. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K. Influence of Si, Ca and Ag addition on corrosion behaviour of new wrought Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K. The role of Si and Ca on new wrought Mg–Zn–Mn based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-X.; Song, R.-B.; Cai, C.-H.; Li, J.-Y. Enhanced Strength and Corrosion Resistance of Mg–2Zn–0.6Zr Alloy with Extrusion. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. 2019, 32, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, S.-M.; Kim, B.; Park, S.S. Influence of Intermetallic Particles on the Corrosion Properties of Extruded ZK60 Mg Alloy Containing Cu. Metals 2018, 8, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J. Microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion behavior and film formation mechanism of Mg-Zn-Mn-xNd in Kokubo’s solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 730, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J. Effects of microstructure transformation on mechanical properties, corrosion behaviors of Mg-Zn-Mn-Ca alloys in simulated body fluid. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2018, 80, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J. Effects of Calcium addition on phase characteristics and corrosion behaviors of Mg-2Zn-0.2 Mn-xCa in simulated body fluid. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzolin, R.; Mohedano, M.; Mendis, C.; Mingo, B.; Tolnai, D.; Blawert, C.; Kainer, K.; Pinto, H.; Hort, N. As cast microstructures on the mechanical and corrosion behaviour of ZK40 modified with Gd and Nd additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zou, Z. Effects of tensile and compressive deformation on corrosion behaviour of a Mg–Zn alloy. Corros. Sci. 2015, 90, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guan, S.; Ren, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, B. Homogeneous corrosion of high pressure torsion treated Mg–Zn–Ca alloy in simulated body fluid. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, R.; Chen, M. Effects of solidification cooling rate on the corrosion resistance of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Progr. Nat. Sci. 2014, 24, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, L.; Zheng, M.; Xu, S.; Kamado, S.; Du, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, K.; Gan, W.; Brokmeier, H.; Wang, G. Effect of Mn addition on microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, T.; Mendis, C.; Hono, K.; Kamado, S. Effect of Zr addition on the mechanical properties of as-extruded Mg–Zn–Ca–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Laws, K.; Birbilis, N.; Ferry, M. Potentiodynamic polarisation study of bulk metallic glasses based on the Mg–Zn–Ca ternary system. Corros. Eng. Sci. Techn. 2012, 47, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Guo, S.; Huang, S.; Zhou, X.; Pan, F. The Y-doped MgZnCa alloys with ultrahigh specific strength and good corrosion resistance in simulated body fluid. Mater. Lett. 2012, 81, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Wei, Y.; Xi, X.; Cai, K.; Pan, F. Effects of Y on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Bio-corrosion Properties of Mg–Zn–Ca Bulk Metallic Glass. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, M.J.; Pang, J.; Wang, Z.; Jarfors, A.W. In vitro corrosion behaviors of Mg67Zn28Ca5 alloy: From amorphous to crystalline. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, M.; Sarwat, S.G.; Udhayabanu, V.; Subramanian, S.; Raj, B.; Ravi, K. Role of partially amorphous structure and alloying elements on the corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glass for biomedical applications. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Izumi, S.; Kawamura, Y. Development of High Strength and Highly Corrosion-Resistant Bulk Nanocrystalline Mg-Zn-Y Alloys with Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase. ECS Trans. 2009, 16, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y. Relation between corrosion behavior and microstructure of Mg–Zn–Y alloys prepared by rapid solidification at various cooling rates. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Tang, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Han, E. Effect of W-phase on the mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 461, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.; Onofre, E.; Cabeza, S.; Llorente, I.; Del Valle, J.; García-Alonso, M.; Adeva, P.; Escudero, M. Corrosion behaviour of Mg–Zn–Y–Mischmetal alloys in phosphate buffer saline solution. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Chen, X.; Han, E.; Dong, C. Effect of heat treatment on the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of an as-forged Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloy. Corros. Sci. 2015, 92, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Wang, C.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-M. Microstructures, corrosion and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Y–(Gd) alloys. T. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 2015, 25, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kato, A.; Tsai, A. Quasicrystal strengthened Mg–Zn–Y alloys by extrusion. Scripta Mater. 2003, 49, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, P.; Gao, S.; Huang, X.; Shi, Z.; Pan, F. Effects of Zn on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and damping capacity of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Liu, D.-B.; Liu, Y.-C.; Zheng, W.-B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.-F. Effect of corrosion on mechanical behaviors of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy in simulated body fluid. Front. Mater. Sci. 2014, 8, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Saha, P.; Chou, D.-T.; Lee, B.; Collins, B.E.; Tan, Z.; Dong, Z.; Kumta, P.N. In vitro degradation and cytotoxicity response of Mg–4% Zn–0.5% Zr (ZK40) alloy as a potential biodegradable material. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8534–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Dong, J.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Z.; Zhai, C.; Ding, W. High cycle fatigue behavior of as-extruded ZK60 magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 44, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Lu, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y. Effects of yttrium on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 373, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Cheng, N.; Li, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZK60–Yb magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 478, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Anan, T.; Yoshimoto, S.; Kawamura, Y. Mechanical properties of warm-extruded Mg–Zn–Gd alloy with coherent 14H long periodic stacking ordered structure precipitate. Scripta Mater. 2005, 53, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Ding, W. Effect of quasicrystal and Laves phases on strength and ductility of as-extruded and heat treated Mg–Zn–Gd-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Yin, D.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, K. Microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties and biocompatibility of Mg–Zn–Mn alloys for biomedical application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of Homogenization on Microstructure Characteristics, Corrosion and Biocompatibility of Mg-Zn-Mn-xCa Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.-y.; Liaw, P.K.; Xu, Y.-z.; Lai, H.-y. Effects of heat treatment on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of the Mg-2Zn-0.2 Mn-xNd alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 769, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, S. In vitro degradation behavior and cytocompatibility of Mg-6Zn-Mn alloy. Mater. Lett. 2018, 228, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangyin, Y.; Manping, L.; Wenjiang, D.; Inoue, A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Si-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 357, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengqi, C.; Ziquan, L.; Jinsong, L.; Menghui, W.; Beibei, S.; Bijun, W. Corrosion Behavior of as-Cast Mg-6Zn-4Si Alloy with Sr Addition. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2017, 46, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jihua, C.; Zhenhua, C.; Hongge, Y.; Fuquan, Z.; Yingliang, C. Effects of Sn and Ca additions on microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of the as-cast Mg-Zn-Al-based alloy. Mater. Corros. 2008, 59, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jia, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. The microstructures and mechanical properties of cast Mg–Zn–Al–RE alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, L33–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Pan, F. Effects of Sn addition on as-cast microstructure, mechanical properties and casting fluidity of ZA84 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Kailas, S.V.; Seshan, S.; Fleury, E. Properties of squeeze cast Mg-6Zn-3Cu alloy and its saffil alumina short fibre reinforced composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 41, 3743–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
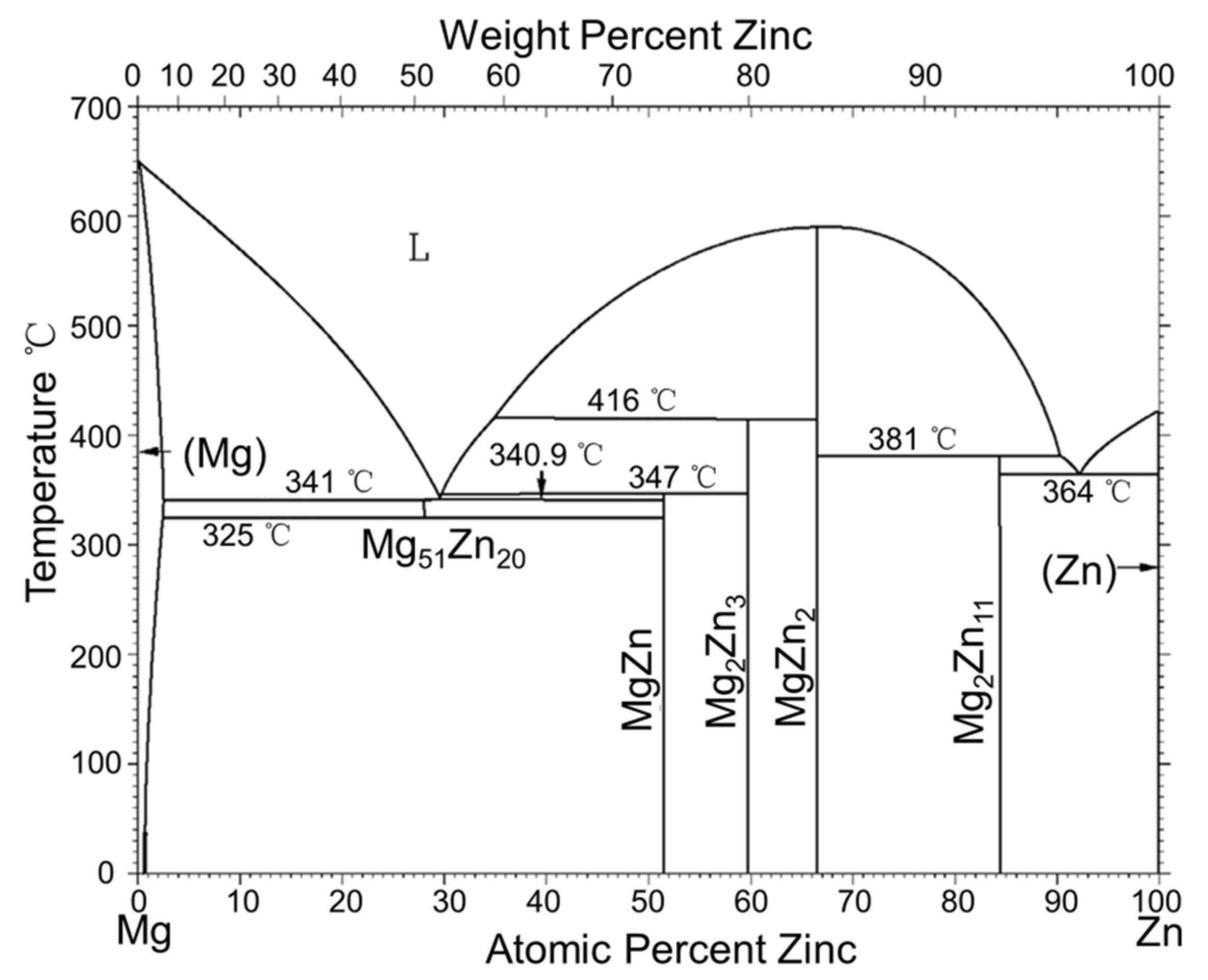
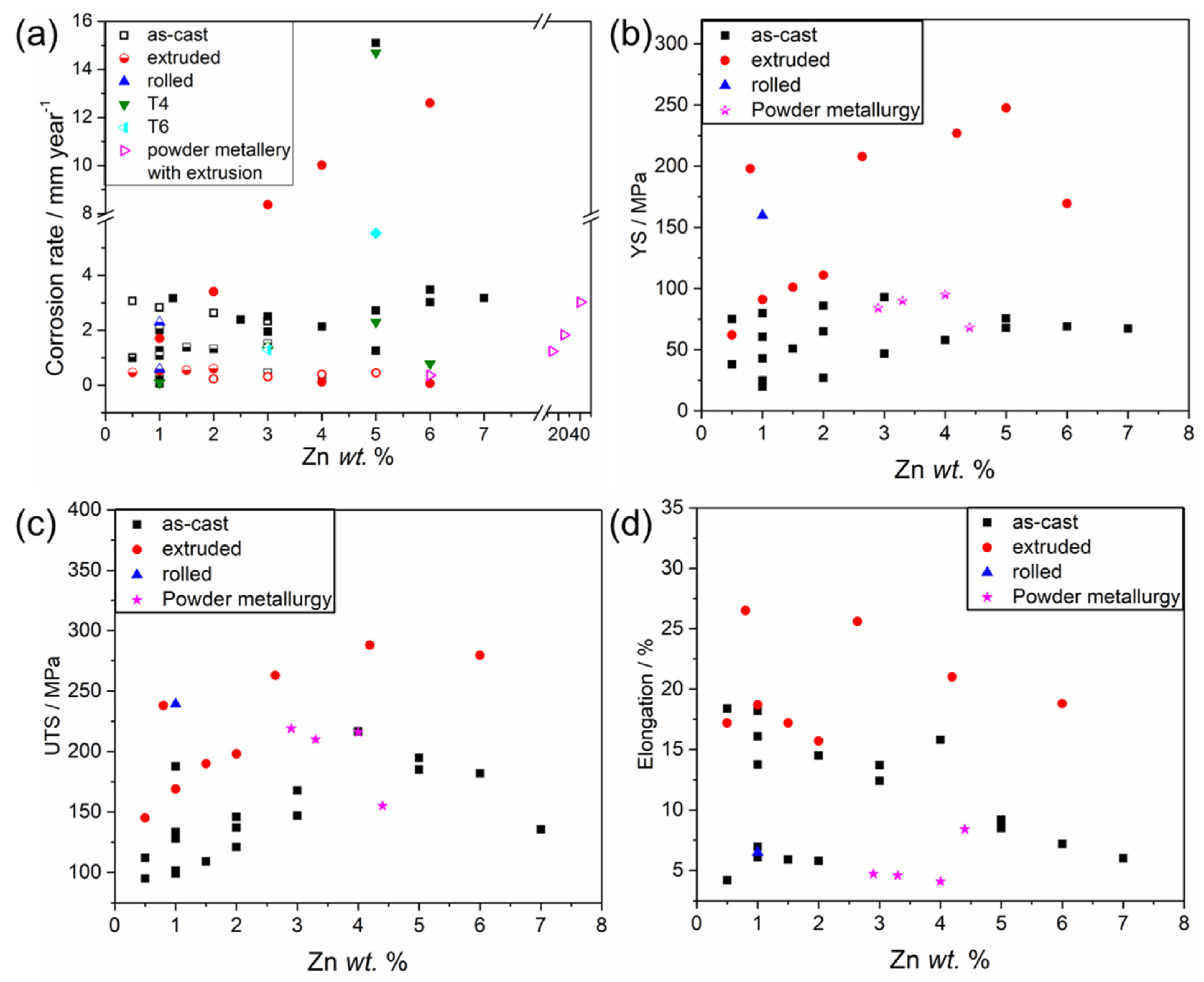
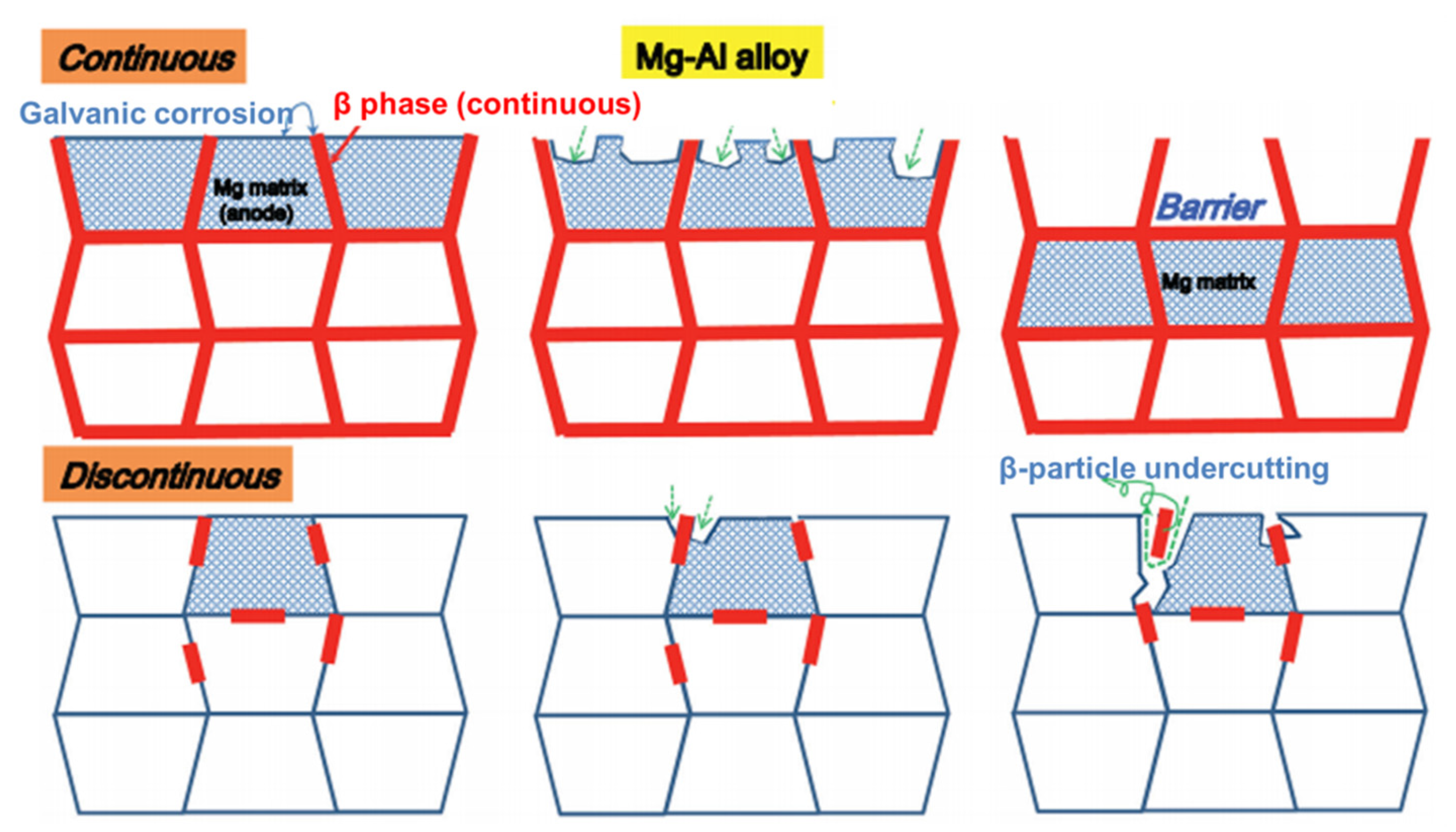
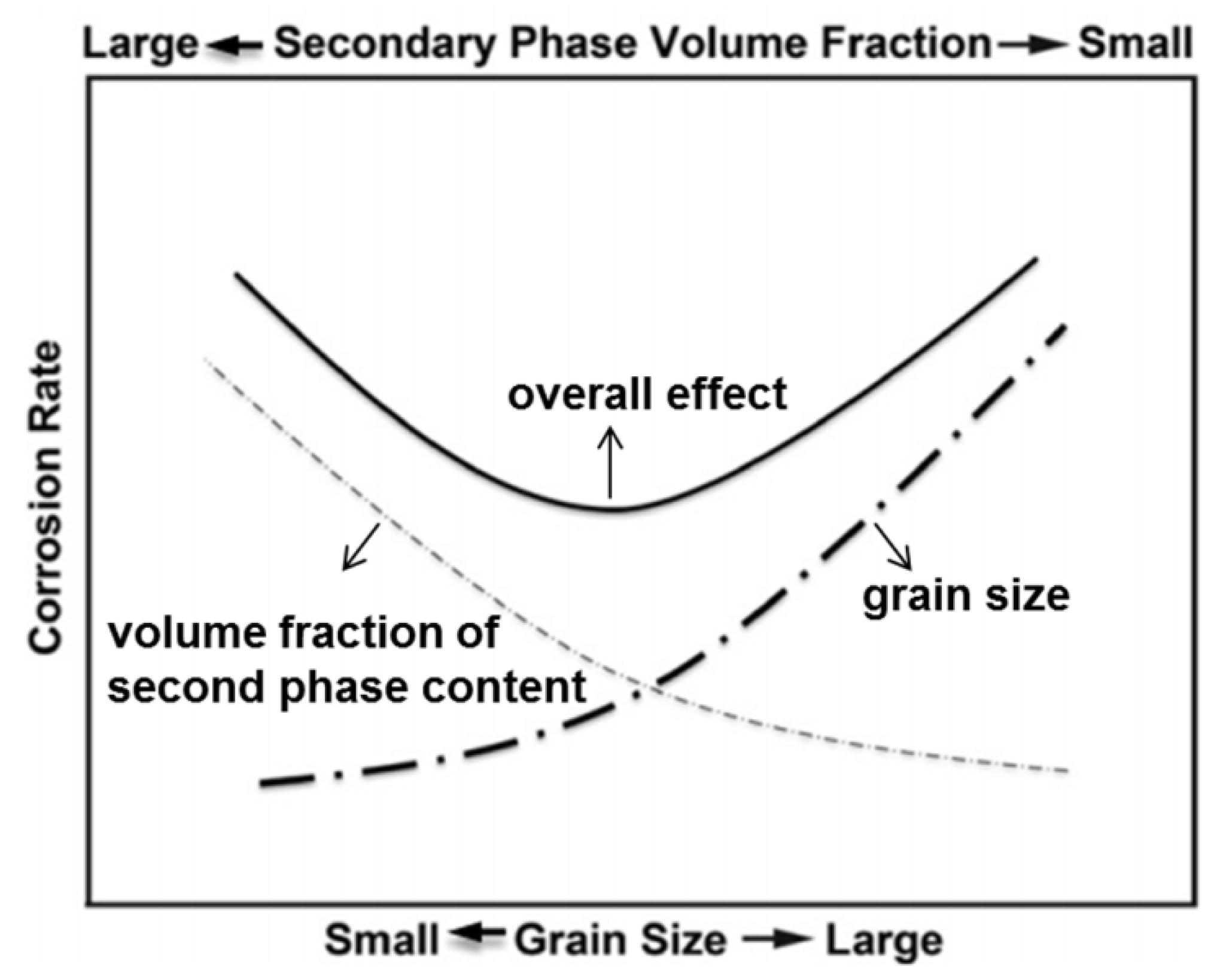

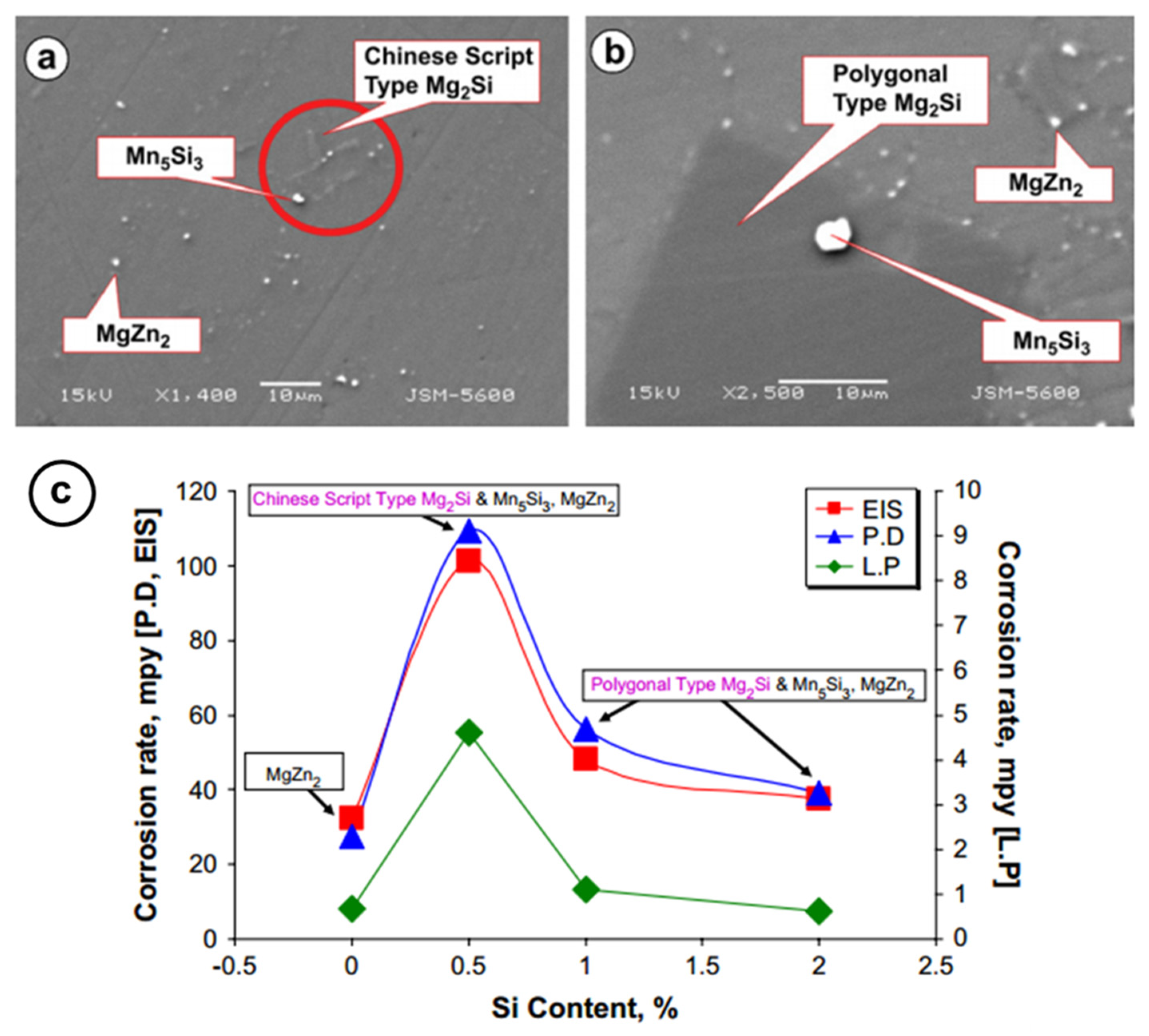
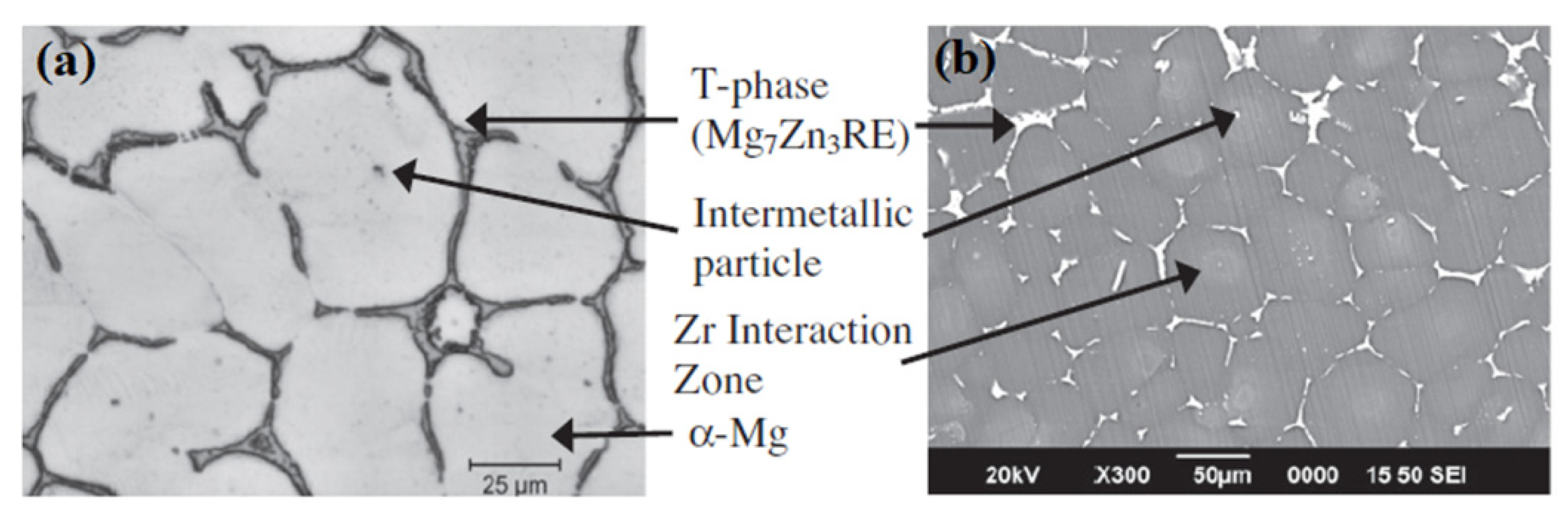
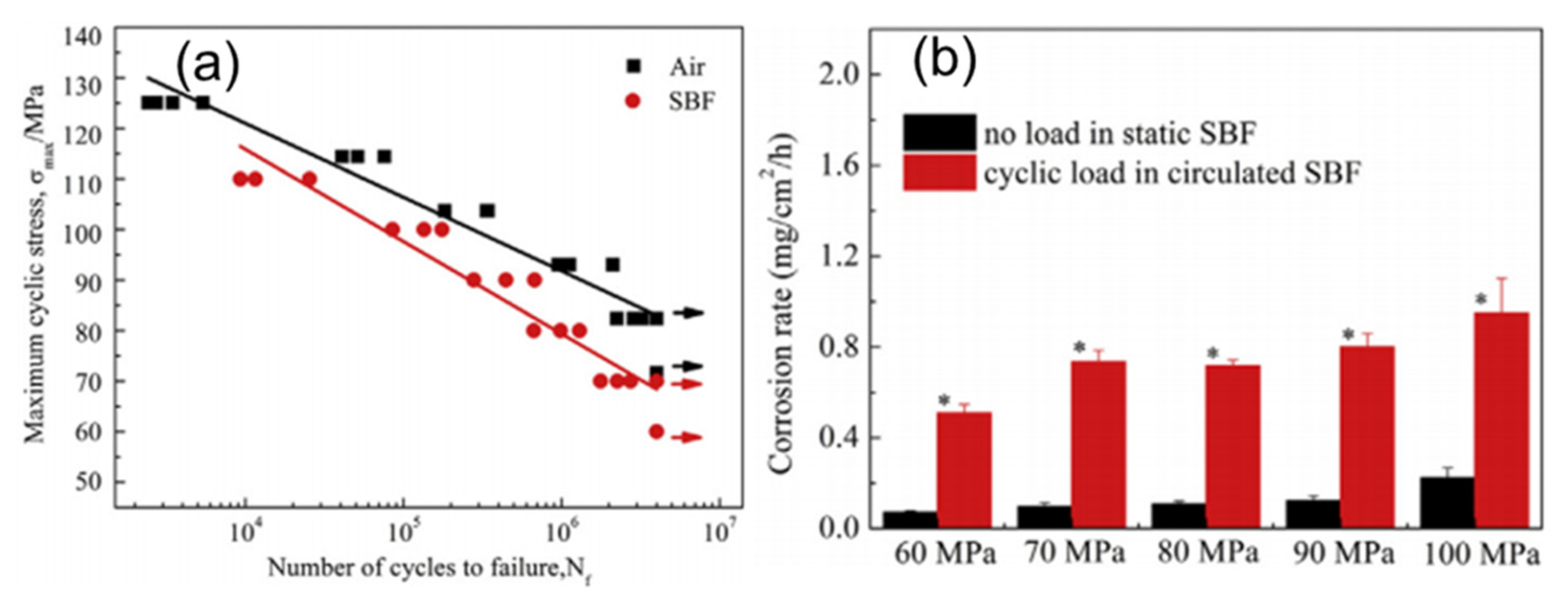
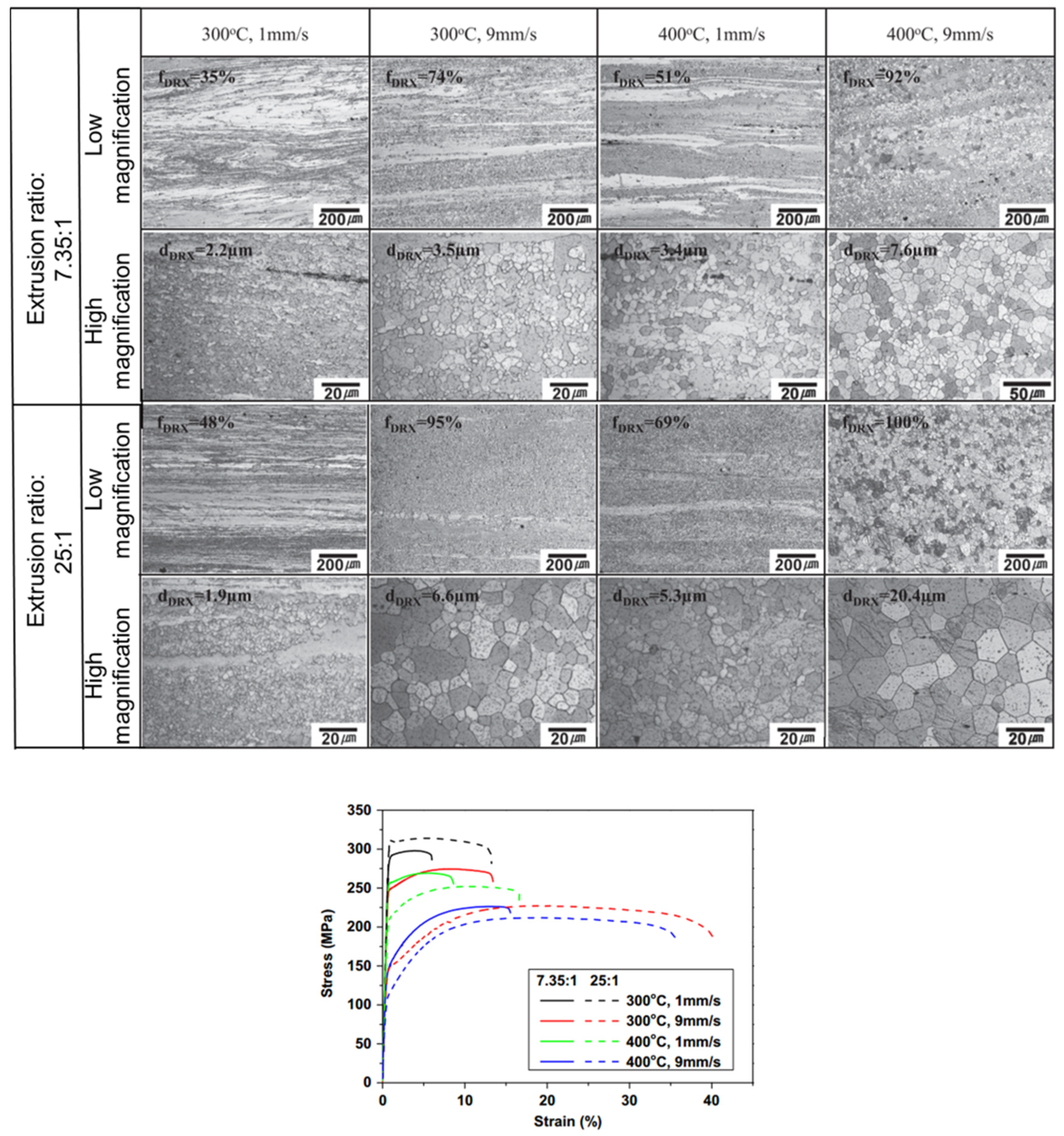
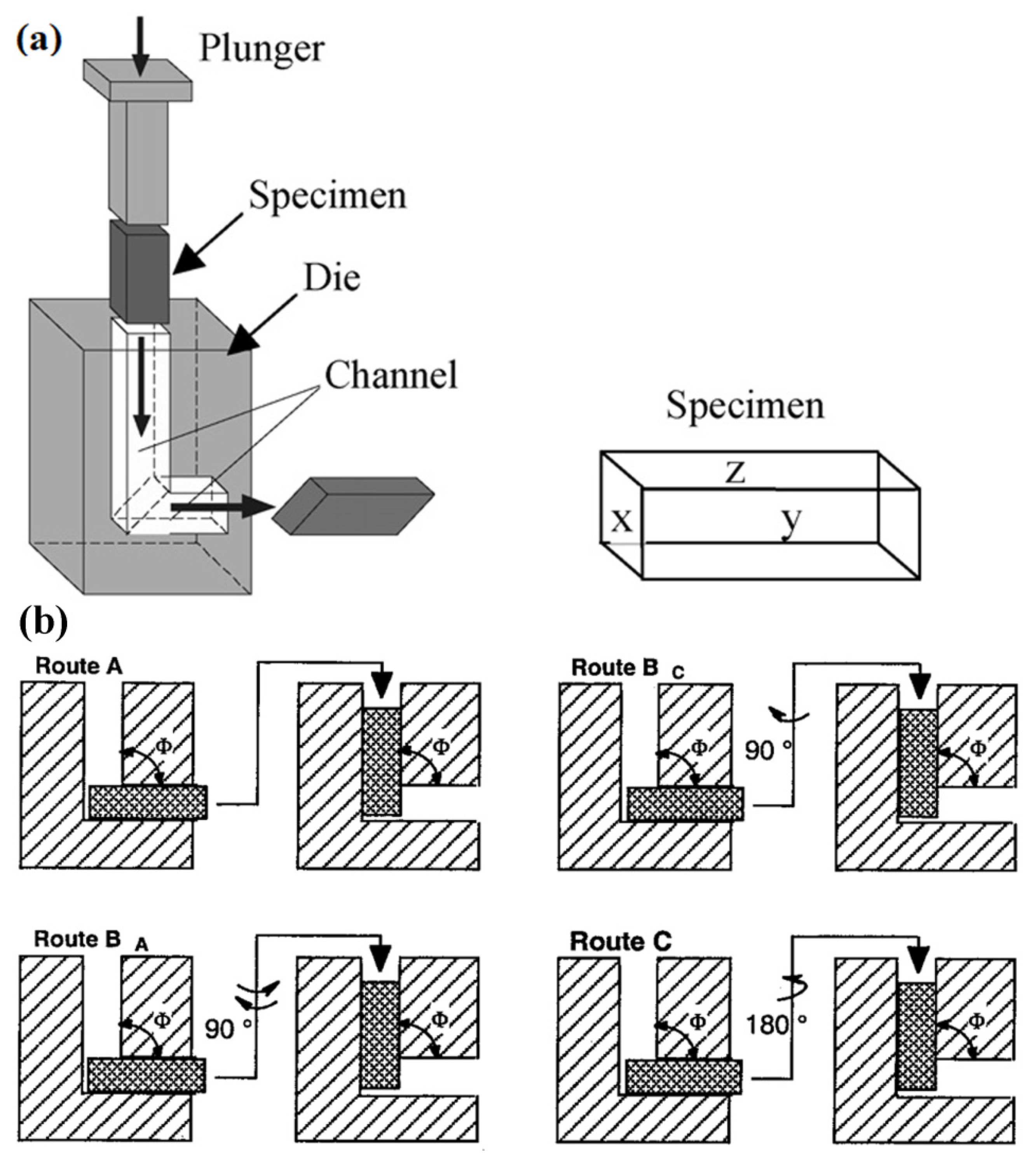
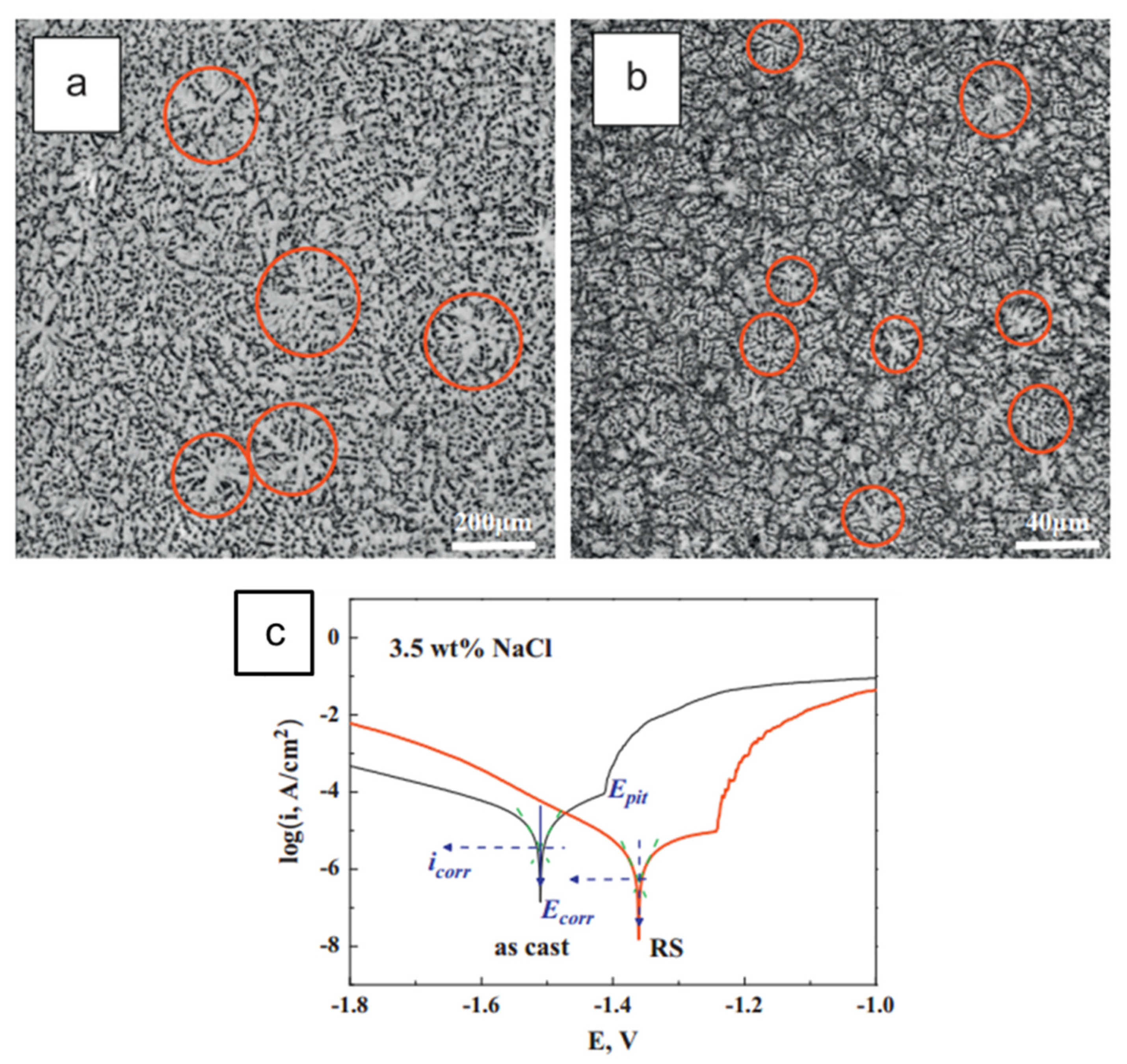

| Composition | Condition | Containing Phases | Mechanical Properties (Room Temperature) | Refs. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YS/MPa | UTS/MPa | Elongation/% | ||||
| Mg97Zn1Y2 (at.%) | Rapidly solidified powder metallurgy | LPSO phase | 610 | - | 5 | [103] |
| Mg97Zn1Y2 (at.%) | High-frequency induction melting + warm extrusion | LPSO phase | 350 | 410 | 6 | [98] |
| Mg97Zn1Y2 (at.%) | Conventional casting + extrusion | LPSO phase | - | 400 | 12.5 | [100] |
| Mg97Zn1Y2 (at.%) | Conventional casting + ECAP | LPSO phase | 400 | 450 | 2.5 | [102] |
| Mg3.1Zn7.6Y (wt.%) | Conventional casting | LPSO phase | 107 | 148 | 3 | [88] |
| Mg94Zn2Y4 (wt.%) | Conventional casting | LPSO phase | 155 | 236 | 3.7 | [96] |
| Mg94Zn3Y3 (wt.%) | Conventional casting + hot-rolling | LPSO phase + W-phase | 380 | - | 6 | [97] |
| Mg96Zn2Y2 (wt.%) | High-frequency induction melting + extrusion | LPSO phase + W-phase | 390 | 420 | 5 | [99] |
| Mg1.5Zn0.8Y (wt.%) | Conventional casting + hot-rolling | W-phase | 178 * | 225 | 18 | [94] |
| Mg2Zn1.54Y (wt.%) | Conventional casting + extrusion | W-phase | 214 | 266 | 27 | [53] |
| Mg2Zn0.82Y (wt.%) | Conventional casting + extrusion | W-phase + I-phase | 213 | 266 | 25 | [53] |
| Mg2Zn0.36Y (wt.%) | Conventional casting + extrusion | I-phase | 197 | 261 | 23 | [53] |
| Mg96.27Zn3.3Y0.43 (at.%) | Rapidly solidified powder metallurgy + extrusion | I-phase | 412 | 445 | 13 | [107] |
| Mg95Zn4.3Y0.7 (at.%) | Conventional casting + hot-rolling | I-phase | 220 * | 370 | 19.7 | [90] |
| Mg12Zn2.4Y (wt.%) | Conventional casting + hot-rolling | I-phase | 189 | 286 | 21.3 | [108] |
| Ingredient | Ringer’s Solution | Hanks’ Solution | DMEM | EBSS | SBF | PBS | MEM | Blood Plasma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg2+ | - | 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.4 | 1 | - | 0.4 | 1 |
| Na+ | 156 | 142 | 154 | 144 | 142 | 153 | 143 | 140 |
| K+ | 5.8 | 5.8 | 6.24 | 5.4 | 5 | 5 | 5.4 | 5 |
| Ca2+ | 2.2 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.5 | - | 1.8 | 2.5 |
| Cl− | 164 | 145 | 118 | 125 | 109 | 140 | 125 | 100 |
| HCO3− | 2.4 | 4.2 | 44.05 | 26 | 27 | - | 26 | 22–30 |
| H2PO4− | - | 0.4 | 1.04 | 1 | - | 2 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| HPO42− | - | 0.3 | - | - | 1 | 8 | - | - |
| SO42− | - | 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.4 | 1 | - | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Glucose | - | - | 5.55 | 5.6 | - | - | 5.6 | 5 |
| Amino acid (g/L) | - | 11.01 (mM/L) | - | - | - | 0.95 | Variable | |
| Proteins (g/L) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 35–50 |
| Vitamins (mg/L) | - | - | - | 8.1 | Variable | |||
| Phenol red | - | - | - | 0.03 | - | - | 0.03 | - |
| Refs. | [51] | [113] | [126] | [157] | [158] | [158] | [157] | [157] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, P.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M.L. The Corrosion Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Based Alloys—A Review. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 92-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd1010007
Jiang P, Blawert C, Zheludkevich ML. The Corrosion Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Based Alloys—A Review. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2020; 1(1):92-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd1010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Pingli, Carsten Blawert, and Mikhail L. Zheludkevich. 2020. "The Corrosion Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Based Alloys—A Review" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 1, no. 1: 92-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd1010007
APA StyleJiang, P., Blawert, C., & Zheludkevich, M. L. (2020). The Corrosion Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Based Alloys—A Review. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 1(1), 92-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd1010007






