Optical Characteristics of Directly Deposited Gold Nanoparticle Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis and Gold Nanoparticle Film Preparation
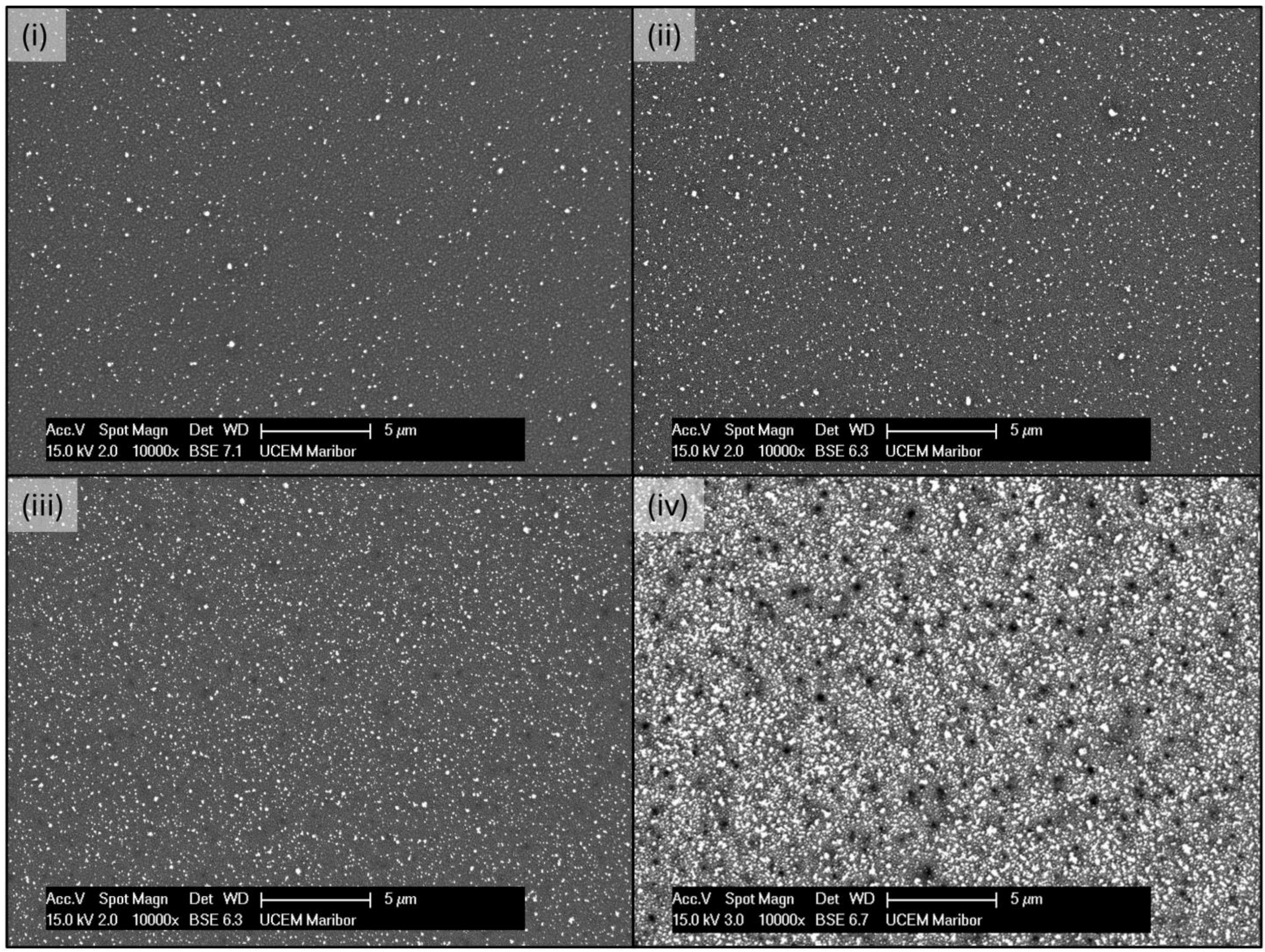
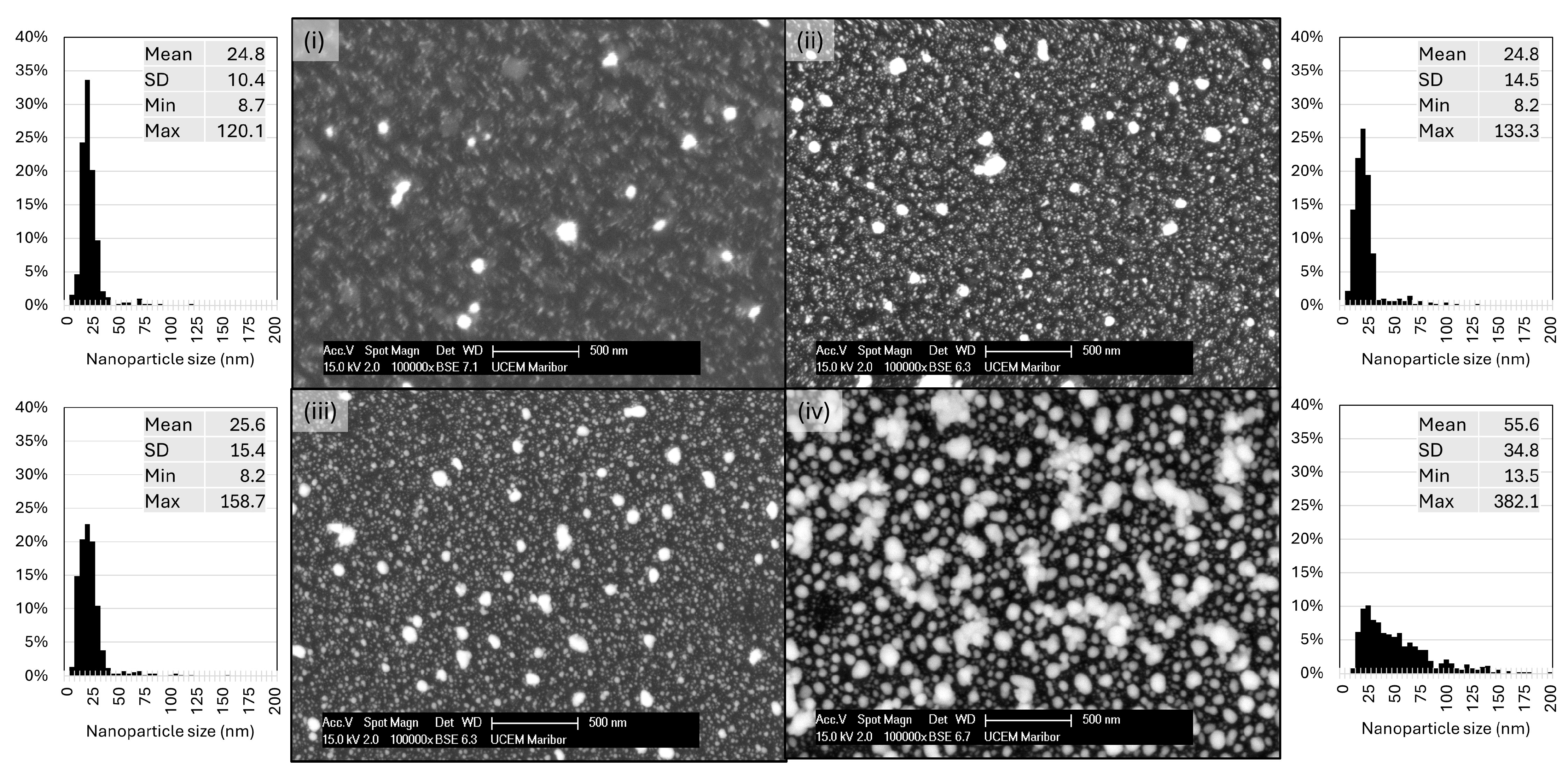
2.2. Morphological Characterisation
2.3. Optical Characterisation
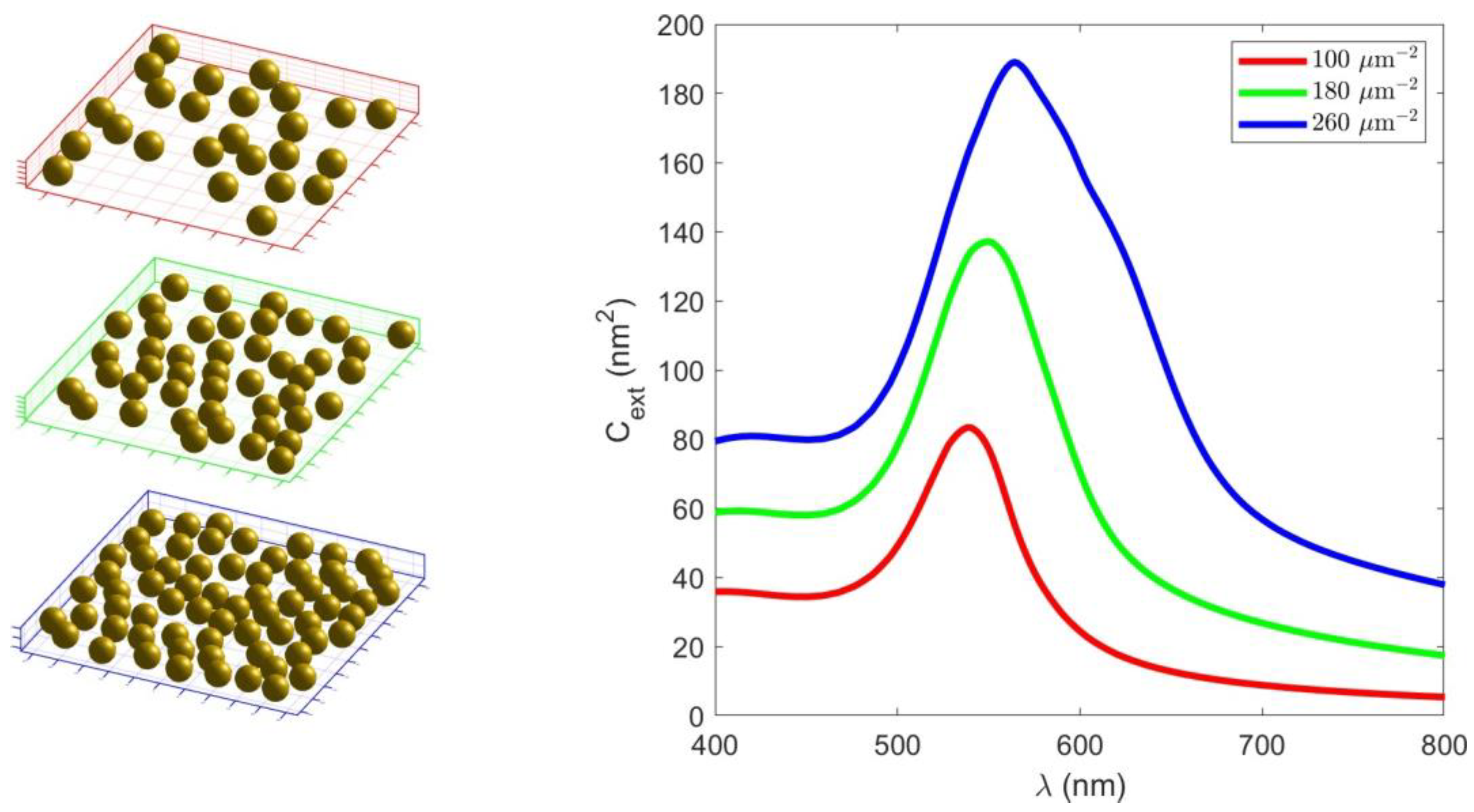
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characterisation
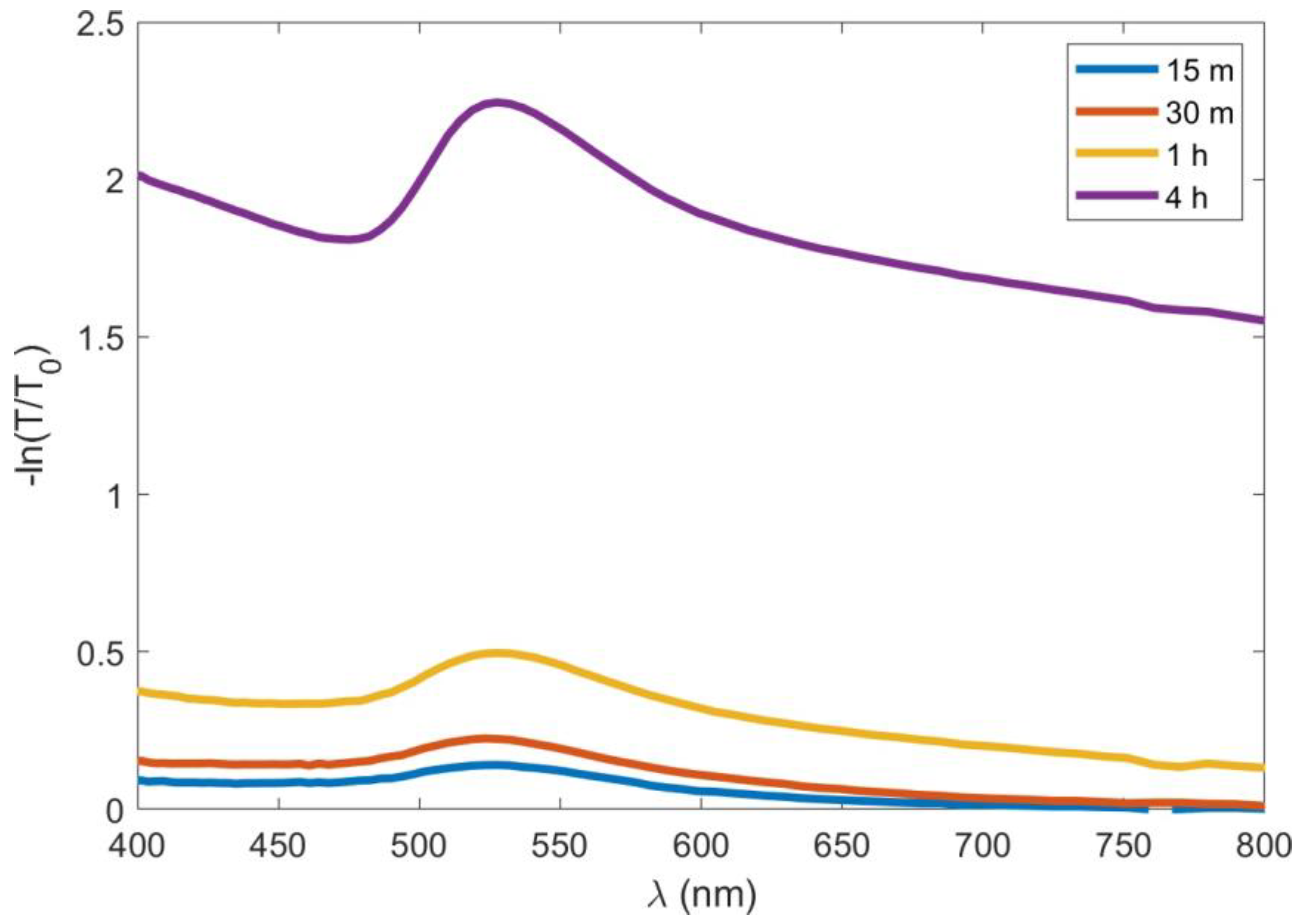
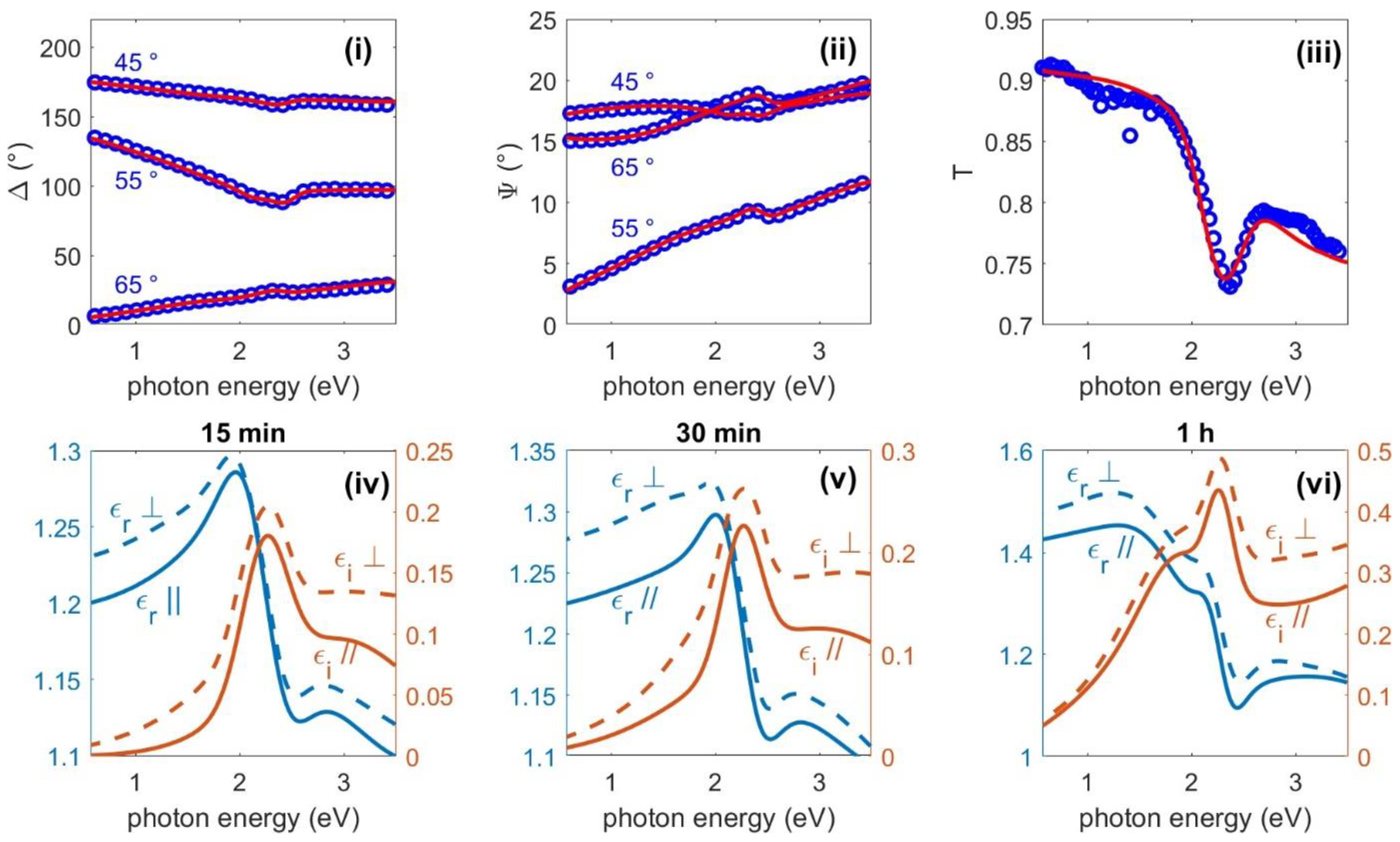
3.2. Optical Characterisation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The initially deposited AuNPs were small, with sizes of about 10–20 nm. As a higher number of particles were deposited, larger particles were formed and grown through coalescence and aggregation.
- The uniaxial anisotropic model showed better agreement with the ellipsometric measurement data compared to the isotropic model.
- For all AuNP films, a distanced peak at 2.2 eV can be observed in the imaginary part of the dielectric function that corresponds to the LSPR of a single AuNP.
- The perpendicular effective dielectric function showed larger values than the effective parallel dielectric function.
- The effective thickness from the ellipsometry measurements of the AuNP layer for samples deposited at 15, 30 and 60 min were 79, 97 and 110 nm. The AuNP layer deposited after 4 h showed very large depolarisation values due to large scattering, and was not able to be fitted with the used model.
- The higher values of the transmittance and extinction cross-section are related to the longer AuNP deposition times.
- The enhanced electromagnetic response between AuNPs is associated with an increase in their density through the formation of clusters and irregular structures.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Maragò, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface Plasmon Resonance in Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U.J. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance: Nanostructures, Bioassays and Biosensing—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated Absorption and Scattering Properties of Gold Nanoparticles of Different Size, Shape, and Composition: Applications in Biological Imaging and Biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size, Shape, and Dielectric Environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J. Foundations of Colloid Science; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780198505020. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, M.L.; Righini, M.; Quidant, R. Plasmon Nano-Optical Tweezers. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Review of Some Interesting Surface Plasmon Resonance-Enhanced Properties of Noble Metal Nanoparticles and Their Applications to Biosystems. Plasmonics 2007, 2, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, A.; Kumar, A.R. The Performance Enhancement of Surface Plasmon Resonance Optical Sensors Using Nanomaterials: A Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 458, 214424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lou, X.-Y.; Liang, F.; Yang, Y.-W. Surface-Functionalized Gold and Silver Nanoparticles for Colorimetric and Fluorescent Sensing of Metal Ions and Biomolecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 459, 214461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, C. Detection of Chemical Pollutants in Water Using Gold Nanoparticles as Sensors: A Review. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugunan, A.; Thanachayanont, C.; Dutta, J.; Hilborn, J.G. Heavy-Metal Ion Sensors Using Chitosan-Capped Gold Nanoparticles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chah, S.; Hammond, M.R.; Zare, R.N. Gold Nanoparticles as a Colorimetric Sensor for Protein Conformational Changes. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X. Noble Metal Nanomaterials for NIR-Triggered Photothermal Therapy in Cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejabat, M.; Samie, A.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. An Overview on Gold Nanorods as Versatile Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khursheed, R.; Dua, K.; Vishwas, S.; Gulati, M.; Jha, N.K.; Aldhafeeri, G.M.; Alanazi, F.G.; Goh, B.H.; Gupta, G.; Paudel, K.R.; et al. Biomedical Applications of Metallic Nanoparticles in Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles: Optical Properties and Implementations in Cancer Diagnosis and Photothermal Therapy. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, R.; Shao, M.; Zhuo, S.; Wen, C.; Wang, S.; Lee, S.-T. Highly Reproducible Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering on a Capillarity-Assisted Gold Nanoparticle Assembly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3337–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ali, M.R.K.; Chen, K.; Fang, N.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles in Biological Optical Imaging. Nano Today 2019, 24, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Cronin, S.B. A Review of Surface Plasmon Resonance-Enhanced Photocatalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, D.; Cerrillo, J.L.; Durini, S.; Gascon, J. Fundamentals and Applications of Photo-Thermal Catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 2173–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Tan, X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Recent Progress on Metal-Enhanced Photocatalysis: A Review on the Mechanism. Research 2024, 2021, 9794329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghlara, H.; Rostami, R.; Maghoul, A.; SalmanOgli, A. Noble Metal Nanoparticle Surface Plasmon Resonance in Absorbing Medium. Optik 2015, 126, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.E.; Aherne, D.; Gara, M.; Ledwith, D.M.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Kelly, J.M.; Blau, W.J.; Brennan-Fournet, M.E. Versatile Solution Phase Triangular Silver Nanoplates for Highly Sensitive Plasmon Resonance Sensing. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, E.E. Brownian Movement and Thermophoresis of Nanoparticles in Liquids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 81, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, B.; Aminossadati, S.M. Brownian Motion of Nanoparticles in a Triangular Enclosure with Natural Convection. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and Zeta Potential—What They Are and What They Are Not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, R.I.; Napper, D.H. Depletion Stabilization and Depletion Flocculation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 75, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkenschuh, E.; Friess, W. Freeze-Drying of Nanoparticles: How to Overcome Colloidal Instability by Formulation and Process Optimization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 165, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beirowski, J.; Inghelbrecht, S.; Arien, A.; Gieseler, H. Freeze Drying of Nanosuspensions, 2: The Role of the Critical Formulation Temperature on Stability of Drug Nanosuspensions and Its Practical Implication on Process Design. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 4471–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelen, Ž.; Krajewski, M.; Zupanič, F.; Majerič, P.; Švarc, T.; Anžel, I.; Ekar, J.; Liou, S.-C.; Kubacki, J.; Tokarczyk, M.; et al. Melting Point of Dried Gold Nanoparticles Prepared with Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis and Lyophilisation. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20220568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Parramon, J.; Okorn, B.; Salamon, K.; Janicki, V. Plasmonic Resonances in Copper Island Films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Parramon, J.; Janicki, V.; Zorc, H. Tuning the Effective Dielectric Function of Thin Film Metal-Dielectric Composites by Controlling the Deposition Temperature. J. Nanophotonics 2011, 5, 051805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipovskii, A.A.; Shustova, O.V.; Zhurikhina, V.V.; Svirko, Y. On the Modeling of Spectral Map of Glass-Metal Nanocomposite Optical Nonlinearity. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 12040–12047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedl, E.; Bregović, V.B.; Rakić, I.Š.; Mandić, Š.; Samec, Ž.; Bergmann, A.; Sancho-Parramon, J. Optical Properties of Annealed Nearly Percolated Au Thin Films. Opt. Mater. 2023, 135, 113237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Galván, A.; Järrendahl, K.; Dmitriev, A.; Pakizeh, T.; Käll, M.; Arwin, H. Optical Response of Supported Gold Nanodisks. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubaš, M.; Fabijanić, I.; Kenđel, A.; Miljanić, S.; Spadaro, M.C.; Arbiol, J.; Janicki, V.; Sancho-Parramon, J. Unifying Stability and Plasmonic Properties in Hybrid Nanoislands: Au–Ag Synergistic Effects and Application in SERS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| AuNP Deposition Time | 15 Min | 30 Min | 1 h | 4 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNP layer effective thickness from ellipsometric measurements | 79 nm | 97 nm | 110 nm | Not measurable/large scattering |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parramon, J.S.; Švarc, T.; Majerič, P.; Jelen, Ž.; Rudolf, R. Optical Characteristics of Directly Deposited Gold Nanoparticle Films. Surfaces 2024, 7, 369-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces7020023
Parramon JS, Švarc T, Majerič P, Jelen Ž, Rudolf R. Optical Characteristics of Directly Deposited Gold Nanoparticle Films. Surfaces. 2024; 7(2):369-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces7020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleParramon, Jordi Sancho, Tilen Švarc, Peter Majerič, Žiga Jelen, and Rebeka Rudolf. 2024. "Optical Characteristics of Directly Deposited Gold Nanoparticle Films" Surfaces 7, no. 2: 369-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces7020023
APA StyleParramon, J. S., Švarc, T., Majerič, P., Jelen, Ž., & Rudolf, R. (2024). Optical Characteristics of Directly Deposited Gold Nanoparticle Films. Surfaces, 7(2), 369-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces7020023







