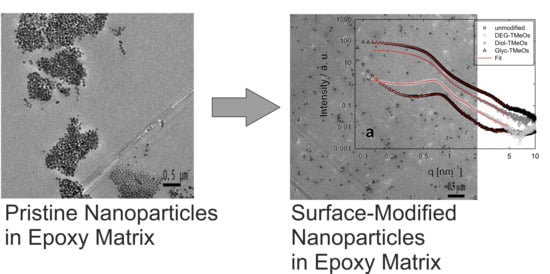
Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: The Influence of Interface Modification on the Dispersion Structure—A Small-Angle-X-ray-Scattering Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
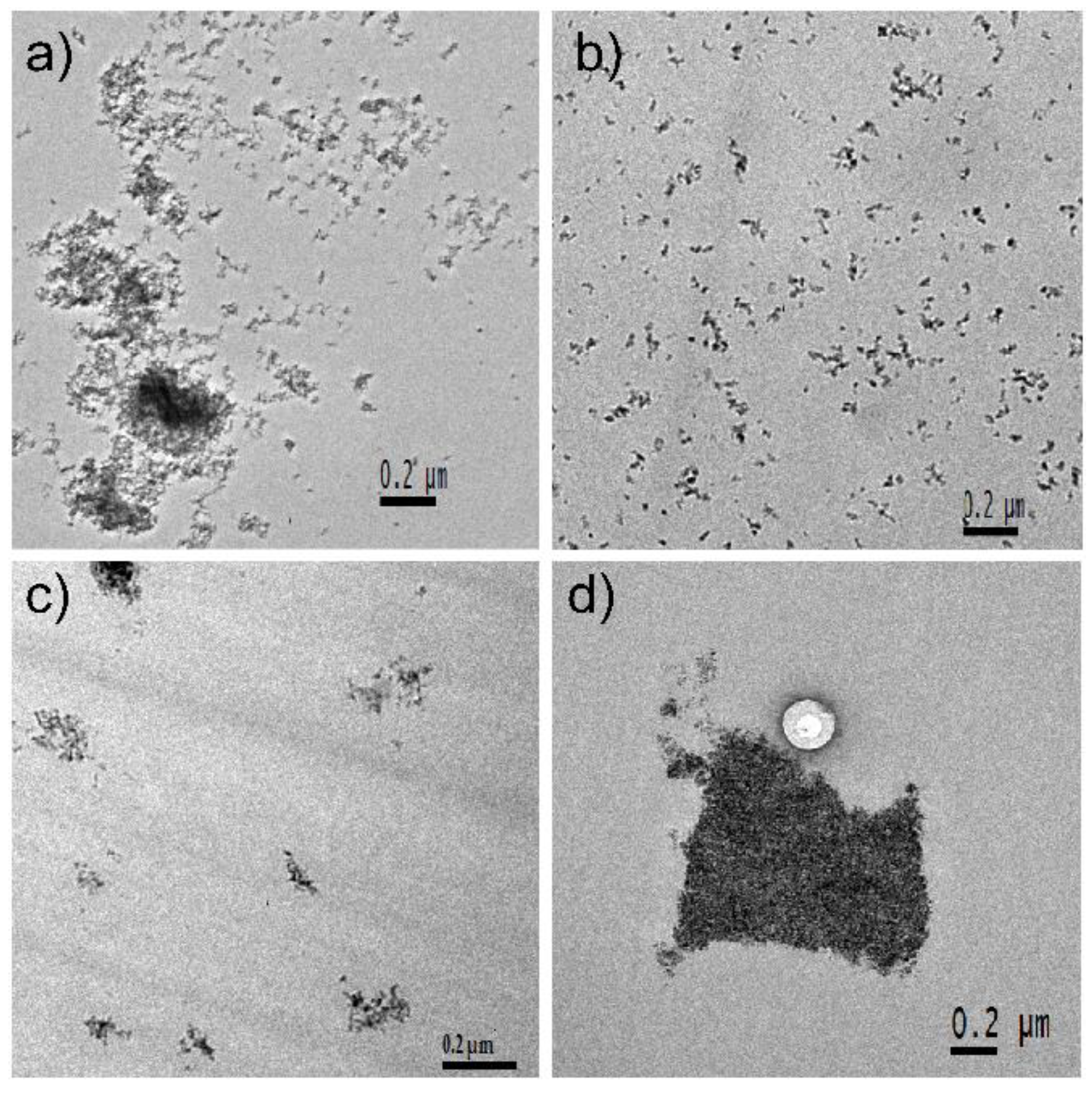
3.1. Nanoparticles
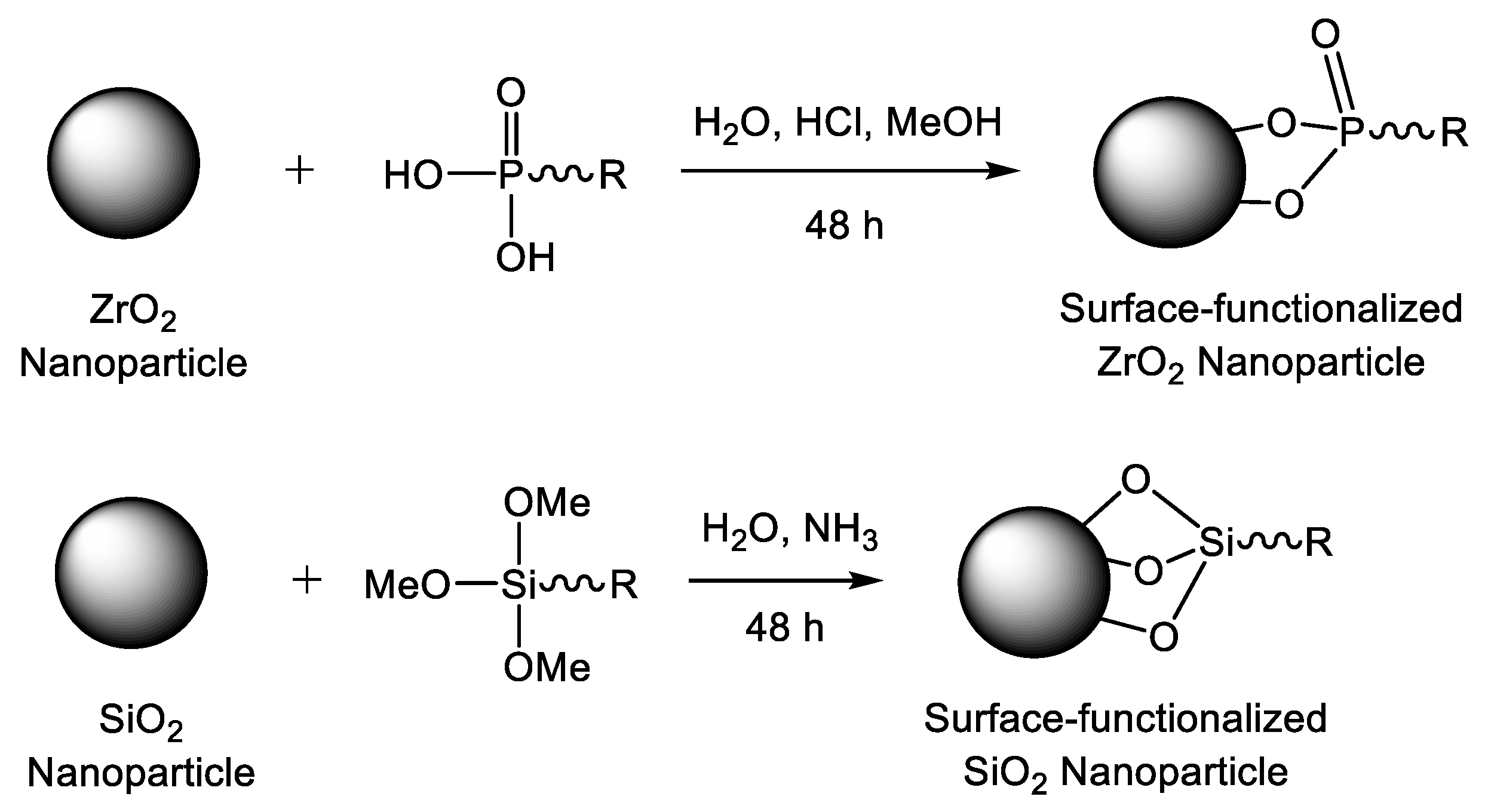
3.2. Chemical Tailoring of the Nanoparticle Surface with Coupling Agents
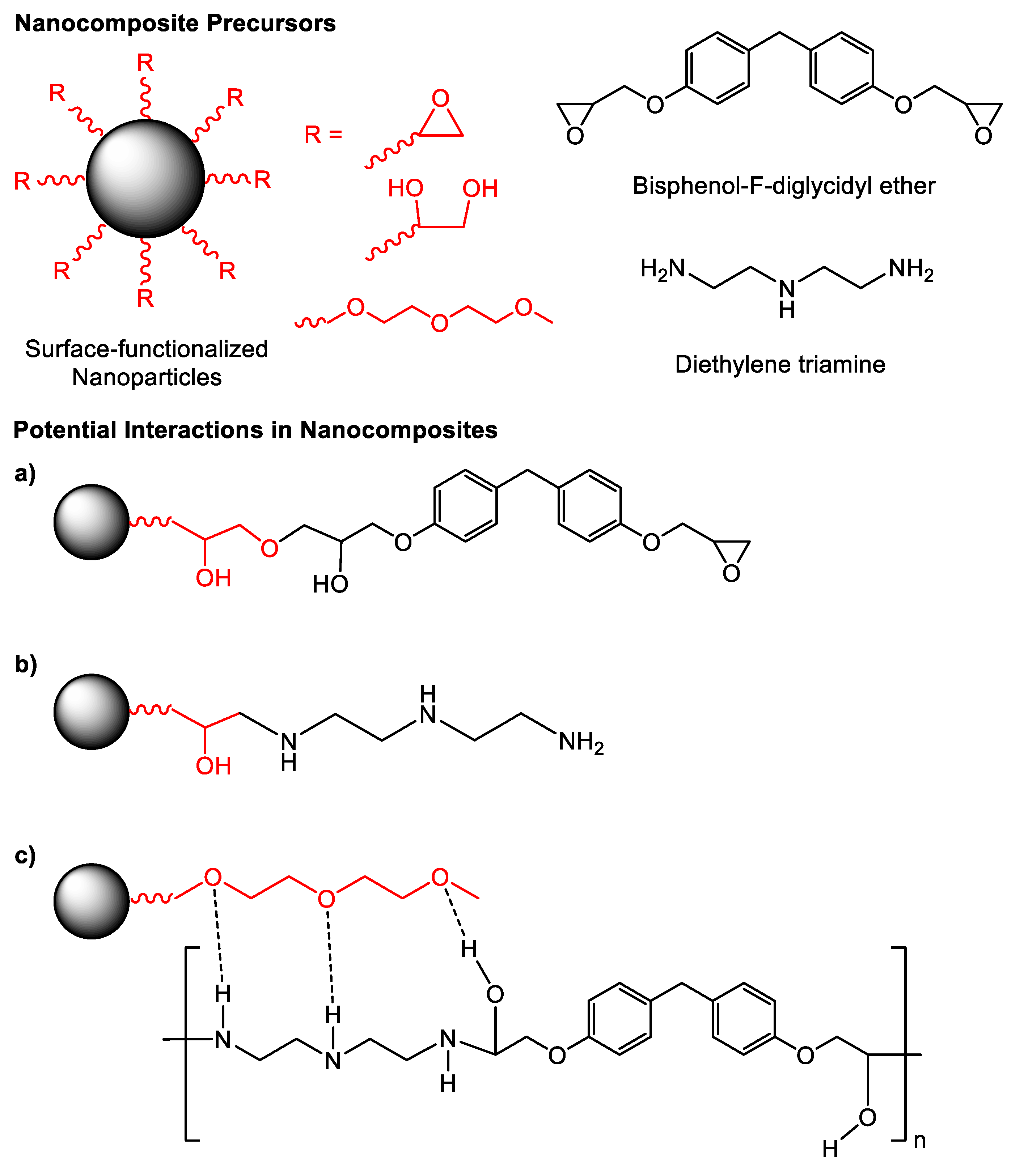
3.3. Preparation of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites
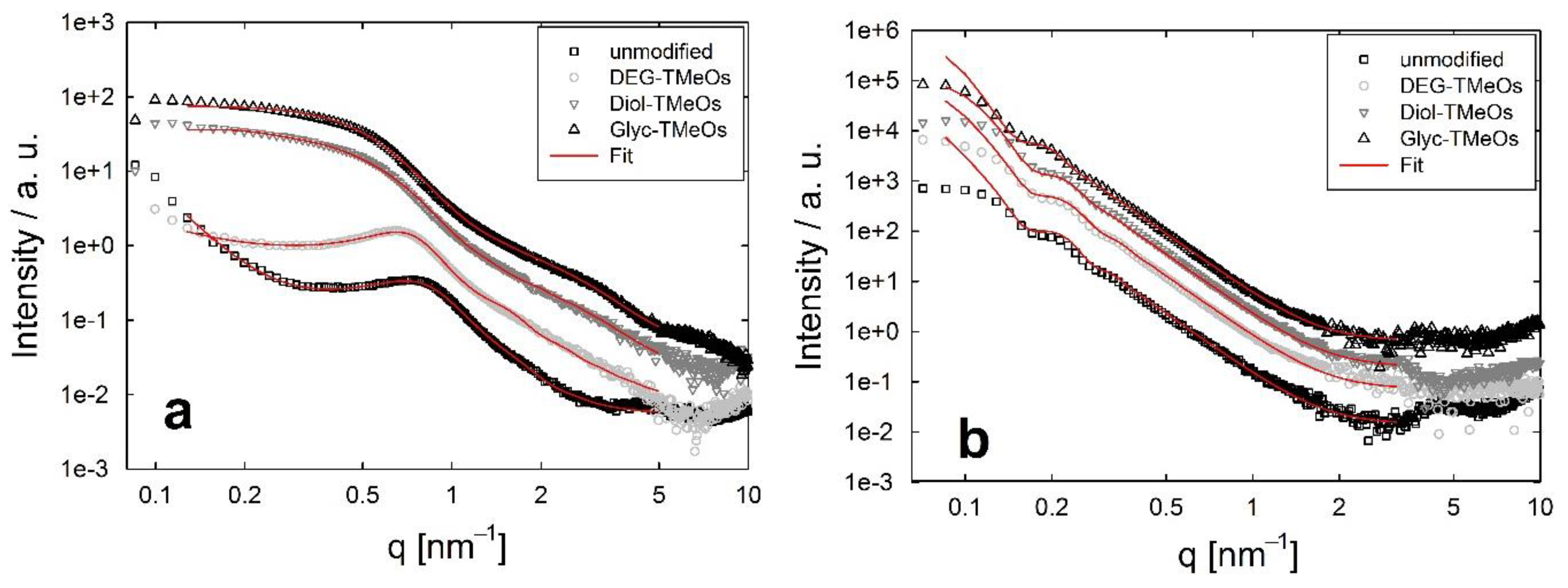
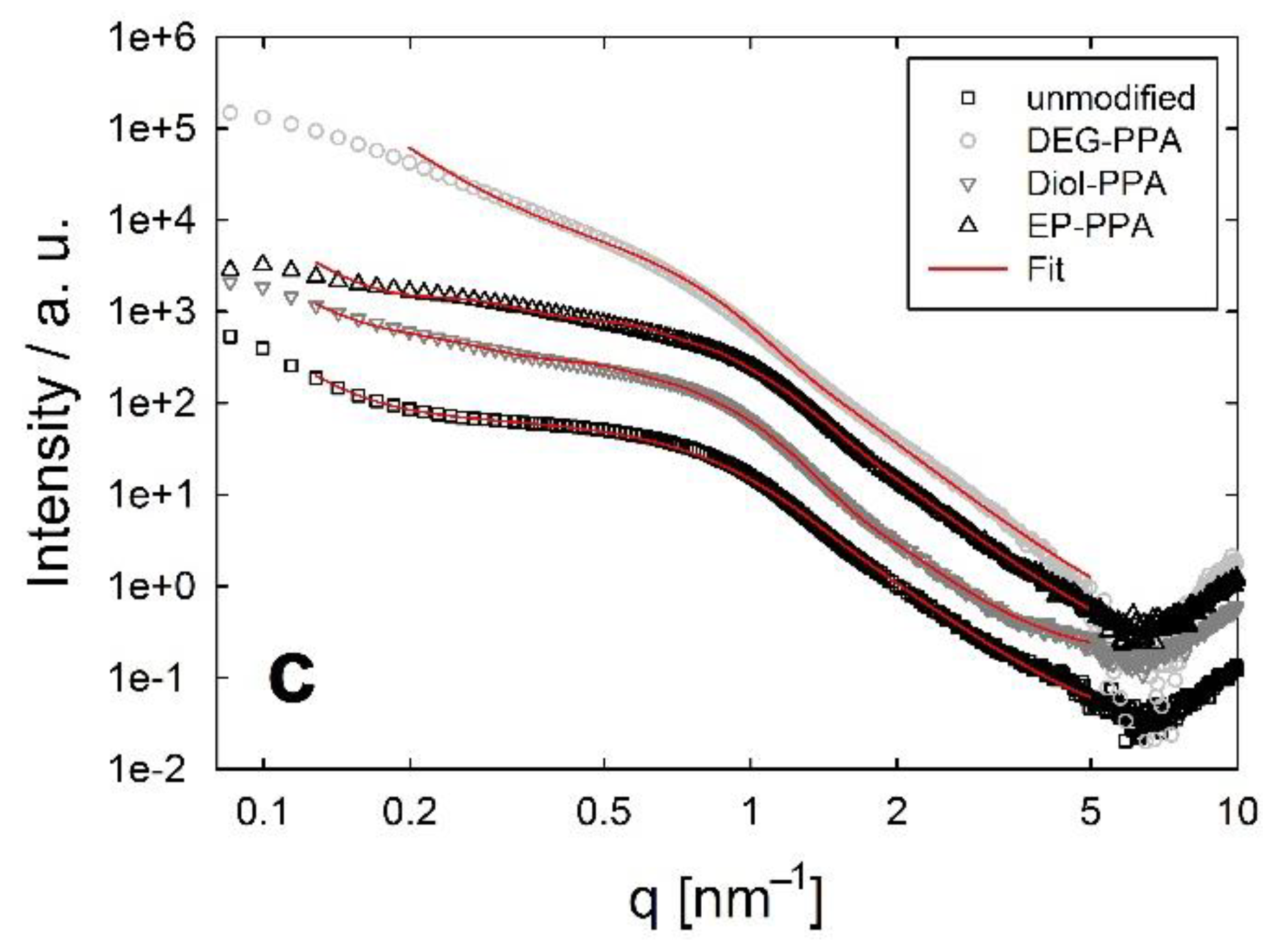
3.4. Structural Investigations Using Small Angle X-ray-Scattering (SAXS)
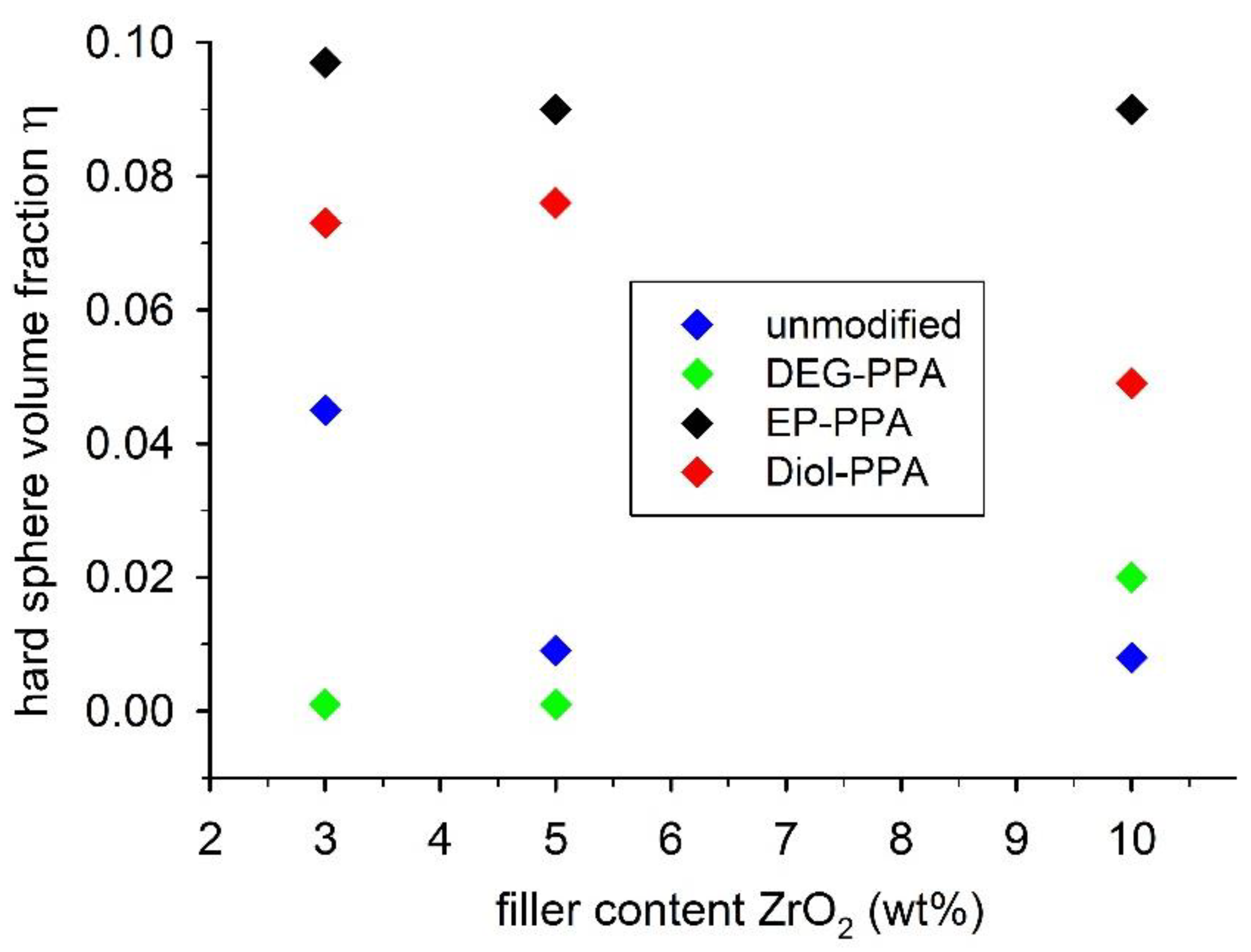
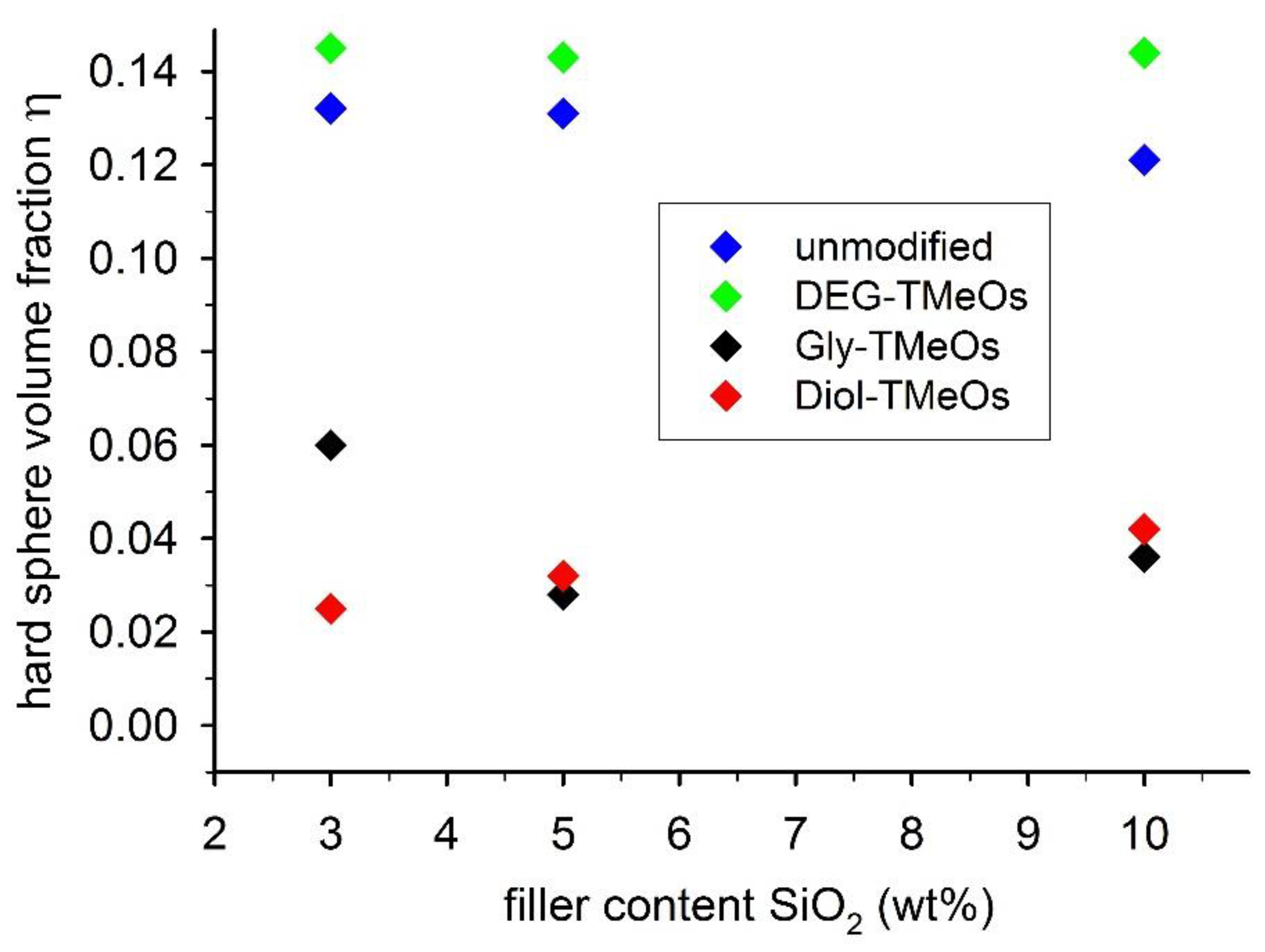
4. Discussion
4.1. ZrO2 Nanocrystals
4.2. Spherical SiO2 Nanoparticles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, F.L.; Li, X.; Park, S.J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Shyha, I.; Inam, F. Mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of graphene-epoxy nanocomposites-a review. Polymers 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Ma, C.; Gu, J.; Guo, J.; Yan, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Z. An overview of multifunctional epoxy nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 5890–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irzhak, T.F.; Irzhak, V.I. Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2017, 59, 791–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, R.; Tian, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.-H. A review of the electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanofiller-reinforced polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1036–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, A.J.; Lee, J.Y. Polymer nanocomposites: The “nano” effect on mechanical properties. Polym. Rev. 2007, 47, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S. Epoxy resin composites with surface-modified silicon dioxide nanoparticles: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrusciel, J.J.; Lesniak, E. Modification of epoxy resins with functional silanes, polysiloxanes, silsesquioxanes, silica and silicates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 41, 67–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Bernardo, L.; Amaro, A.; Lopes, S. Mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites using alumina as reinforcement—A review. J. Nano Res. 2015, 30, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, A.P. Graphene and carbon nanotube reinforced epoxy nanocomposites: A review. Polymer 2019, 180, 121724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, I.; Manshoor, B.; Khalid, A.; Araby, S. From clay to graphene for polymer nanocomposites—A survey. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.-B.; Luo, J.-Q.; Wang, Q.-W.; Xu, B.; Hong, S.; Yu, Z.-Z. Highly Electrically Conductive Three-Dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene/Reduced Graphene Oxide Hybrid Aerogels with Excellent Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Performances. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11193–11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliozberg, Y.; Andzelm, J.; Hatter, C.B.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Hall, A. Interface binding and mechanical properties of MXene-epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 192, 108124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatter, C.B.; Shah, J.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y. Micromechanical response of two-dimensional transition metal carbonitride (MXene) reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 182, 107603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althues, H.; Henle, J.; Kaskel, S. Functional inorganic nanofillers for transparent polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Mohammed, R.D.; Taylor, A.C.; Eger, C.; Sprenger, S.; Egan, D. The effect of silica nano particles and rubber particles on the toughness of multiphase thermosetting epoxy polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5083–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.P.; Hoa, S.V.; Pugh, M. Fracture toughness and water uptake of high-performance epoxy/nanoclay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.G.; Luo, W.B. Fracture surface analysis on nano-SiO2/epoxy composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.; Haupert, F.; Schlarb, A.K. Improvement of tensile properties and toughness of an epoxy resin by nanozirconium-dioxide reinforcement. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 3245–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Fan, P. Synthesis and characterization of epoxy resin modified with nano-SiO2 and γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxy silane. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5269–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Morgan, A.B. Mild processing and characterization of silica epoxy hybrid nanocomposite. Polymer 2009, 50, 6265–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.C.; Riang, L.; Chou, I.C.; Ma, C.C.M.; Chiang, C.L.; Yang, C.C. The Poss Side Chain Epoxy Nanocomposite: Synthesis and Thermal Properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. Glass transition and relaxation behavior of epoxy nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3849–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, M.; Feichtenschlager, B.; Pabisch, S.; Svehla, J.; Koch, T.; Seidler, S.; Peterlik, H.; Kickelbick, G. Study of the effect of the concentration, size and surface chemistry of zirconia and silica nanoparticle fillers within an epoxy resin on the bulk properties of the resulting nanocomposites. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouault, N.; Dalmas, F.; Said, S.; Di Cola, E.; Schweins, R.; Jestin, J.; Boue, F. Direct Measurement of Polymer Chain Conformation in Well-Controlled Model Nanocomposites by Combining SANS and SAXS. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 9881–9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouault, N.; Vallat, P.; Dalmas, F.; Said, S.; Jestin, J.; Boue, F. Well-Dispersed Fractal Aggregates as Filler in Polymer-Silica Nanocomposites: Long-Range Effects in Rheology. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Hall, L.M.; Schweizer, K.S.; Zukoski, C.F. Long Wavelength Concentration Fluctuations and Cage Scale Ordering of Nanoparticles in Concentrated Polymer Solutions. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 10123–10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, A.; Ribot, F.; Matejka, L.; Whelan, P.; Starovoytova, L.; Plestil, J.; Steinhart, M.; Slouf, M.; Hromadkova, J.; Kovarova, J.; et al. Preparation of Novel, Nanocomposite Stannoxane-Based Organic-Inorganic Epoxy Polymers containing Ionic bonds. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevigny, C.; Dalmas, F.; Di Cola, E.; Gigmes, D.; Bertin, D.; Boue, F.; Jestin, J. Polymer-Grafted-Nanoparticles Nanocomposites: Dispersion, Grafted Chain Conformation, and Rheological Behavior. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlik, H.; Fratzl, P. Small-angle X-ray scattering to characterize nanostructures in inorganic and hybrid materials chemistry. Monatsh. Chem. 2006, 137, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucage, G.; Kammler, H.K.; Pratsinis, S.E. Particle size distributions from small-angle scattering using global scattering functions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2004, 37, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.S. Analysis of small-angle scattering data from colloids and polymer solutions: Modeling and least-squares fitting. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 70, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M. Analysis of structures of rubber-filler systems with combined scattering methods. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A.; Dahmouche, K.; Soares, B.G. Nanostructure and dynamic mechanical properties of silane-functionalized montmorillonite/epoxy nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, G.P.; Genix, A.-C.; Paupy-Peyronnet, N.; Degrandcourt, C.; Couty, M.; Oberdisse, J. Revealing nanocomposite filler structures by swelling and small-angle X-ray scattering. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 186, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Buonocore, G.; Lavorgna, M.; Kaciulis, S.; Balijepalli, S.K.; Zhan, Y.; Xia, H.; Ambrosio, L. The role of reduced graphene oxide on chemical, mechanical and barrier properties of natural rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 102, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chonung, K.; Wang, G.L.; Wei, P.; Jiang, P.K. Epoxy/Nano-Silica Composites: Curing Kinetics, Glass Transition Temperatures, Dielectric, and Thermal-Mechanical Performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Hong, S.I.; Choe, C.R.; Park, M.; Rim, S.; Kim, J. Preparation and characterization of epoxy composites filled with functionalized nanosilica particles obtained via sol-gel process. Polymer 2001, 42, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, O.; Simon, G.P.; Dusek, K. Epoxy Layered Silicate Nanocomposites. In Inorganic Polymeric Nanocomposites and Membranes; Guida-Pietrasanta, F., Boutevin, B., Nuyken, O., Becker, O., Simon, G.P., Dusek, K., Rusanov, A.L., Likhatchev, D., Kostoglodov, P.V., Müllen, K., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 29–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mascia, L.; Prezzi, L.; Haworth, B. Substantiating the role of phase bicontinuity and interfacial bonding in epoxy-silica nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, K.; Endo, T. A review of our development of dental adhesives—Effects of radical polymerization initiators and adhesive monomers on adhesion. Dent. Mater. J. 2010, 29, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Terahara, A.; Hakuta, Y.; Matsui, K.; Hayashi, H.; Ueno, N. Transparent poly(bisphenol A carbonate)-based nanocomposites with high refractive index nanoparticles. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Nii, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Harada, M. Thermal and optical properties of epoxy/zirconia hybrid materials synthesized via in situ polymerization. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutin, P.H.; Lafond, V.; Popa, A.F.; Granier, M.; Markey, L.; Dereux, A. Selective Surface Modification of SiO2-TiO2 Supports with Phosphonic Acids. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5670–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, N.; Hentschke, R. Modelling Filler Dispersion in Elastomers: Relating Filler Morphology to Interface Free Energies via SAXS and TEM Simulation Studies. Polymers 2018, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabisch, S. Increased Structural Order in Nanocomposites. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeev, A.Y.; Helmy, R.; Marcinko, S. Self-Assembled Monolayers of Organosilicon Hydrides Supported on Titanium, Zirconium, and Hafnium Dioxides. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7521–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabisch, S.; Feichtenschlager, B.; Kickelbick, G.; Peterlik, H. Effect of interparticle interactions on size determination of zirconia and silica based systems—A comparison of SAXS, DLS, BET, XRD and TEM. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 521, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percus, J.K.; Yevick, G.J. Analysis of classical statistical mechanics by means of collective co.ovrddot.ordinates. Phys. Rev. 1958, 110, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinning, D.J.; Thomas, E.L. Hard-sphere interactions between spherical domains in diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram Research, Inc. Mathematica; Wolfram Research, Inc.: Champaign, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogeras, I.M.; Vassilikou-Dova, A.; Christakis, I.; Pietkiewicz, D.; Brostow, W. Thermophysical properties and molecular relaxations in cured epoxy resin + PEO blends: Observations on factors controlling miscibility. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-H. Wettability and conformation of reactive polysiloxanes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 27, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickelbick, G. The search of a homogeneously dispersed material-the art of handling the organic polymer/metal oxide interface. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 46, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, R.; Fadeev, A.Y. Self-Assembled Monolayers Supported on TiO2: Comparison of C18H37SiX3 (X = H, Cl, OCH3), C18H37Si(CH3)2Cl, and C18H37PO(OH)2. Langmuir 2002, 18, 8924–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtenschlager, B.; Lomoschitz, C.J.; Kickelbick, G. Tuning the Self-Assembled Monolayer Formation on Nanoparticle Surfaces showing different Curvature: Comparison of Spherical Silica Particles with Plane-Crystal-Shaped Zirconia Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegel, B.; Kiefer, W.; Hofacker, S.; Schottner, G. FT-Raman Spectroscopic Investigations on the Organic Crosslinking in Hybrid Polymers. Part II: Reactions of Epoxy Silanes. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2002, 24, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamibayashi, M.; Ogura, H.; Otsubo, Y. Shear-thickening flow of nanoparticle suspensions flocculated by polymer bridging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 321, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, M.; Kamalin, O.; Schoonheydt, R.A.; Wostyn, K.; Clays, K.; Persoons, A.; Dekany, I. Ordering and optical properties of monolayers and multilayers of silica spheres deposited by the Langmuir-Blodgett method. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 3268–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, M.E.; Tuteja, A.; Duxbury, P.M.; Hawker, C.J.; Van Horn, B.; Guan, Z.; Chen, G.; Krishnan, R.S. General strategies for nanoparticle dispersion. Science 2006, 311, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Coupling Agent Structure | Coupling Agent Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
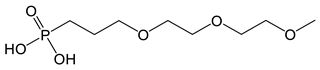 | 1-(3-diethylene glycol monomethyl ether) propoxy phosphonic acid | DEG-PPA |
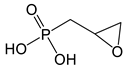 | oxiran-2-ylmethyl phosphonic acid | Ep-PPA |
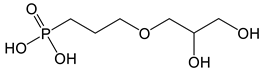 | (3-(2,3-dihydroxypropoxy)propyl) phosphonic acid | Diol-PPA |
 | 1-(3-diethylene glycol monomethyl ether) propoxy trimethoxysilane | DEG-TMeOs |
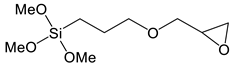 | 3-glycidoxy propyl trimethoxysilane | Gly-TMeOs |
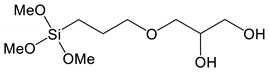 * * | (3-(2,3-dihydroxypropoxy)propyl) trimethoxysilane | Diol-TMeOs |
| Coupling Agent | Substrate | Mass Loss TGA 200–800 °C [wt%] | Grafting Density [molecules/nm2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEG-PPA | ZrO2 | 9.5%/16.7% | 3.1 |
| Ep-PPA | ZrO2 | 11.8%/9.4% | 8.8 |
| Diol-PPA | ZrO2 | 10.5%/10.0% | 3.4 |
| DEG-TMeOs | small SiO2/large SiO2 | 16.6%/11.0% | 0.7/2.2 |
| Gly-TMeOs | small SiO2/large SiO2 | 16.6%/9.6% | 1.0/1.8 |
| Diol-TMeOs | small SiO2/large SiO2 | 16.7%/9.4% | 0.9/1.5 |
| Hard Sphere Volume Fraction η from SAXS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Type | Filler wt% | Unmodified | DEG-PPA | EP-PPA | Diol-PPA |
| small ZrO2 | 3 | 0.045 | 0.001 | 0.097 | 0.073 |
| 5 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.090 | 0.076 | |
| 10 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.090 | 0.049 | |
| Filler wt% | Unmodified | DEG-TMeOs | Gly-TMeOs | Diol-TMeOs | |
| small SiO2 | 3 | 0.132 | 0.145 | 0.060 | 0.025 |
| 5 | 0.131 | 0.143 | 0.028 | 0.032 | |
| 10 | 0.121 | 0.144 | 0.036 | 0.042 | |
| large SiO2 | 3 | 0.174 | 0.160 | 0.148 | 0.099 |
| 5 | 0.223 | 0.148 | 0.121 | 0.090 | |
| 10 | 0.156 | 0.188 | 0.079 | 0.110 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feichtenschlager, B.; Pabisch, S.; Svehla, J.; Peterlik, H.; Sajjad, M.; Koch, T.; Kickelbick, G. Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: The Influence of Interface Modification on the Dispersion Structure—A Small-Angle-X-ray-Scattering Study. Surfaces 2020, 3, 664-682. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3040044
Feichtenschlager B, Pabisch S, Svehla J, Peterlik H, Sajjad M, Koch T, Kickelbick G. Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: The Influence of Interface Modification on the Dispersion Structure—A Small-Angle-X-ray-Scattering Study. Surfaces. 2020; 3(4):664-682. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeichtenschlager, Bernhard, Silvia Pabisch, Jakob Svehla, Herwig Peterlik, Muhammad Sajjad, Thomas Koch, and Guido Kickelbick. 2020. "Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: The Influence of Interface Modification on the Dispersion Structure—A Small-Angle-X-ray-Scattering Study" Surfaces 3, no. 4: 664-682. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3040044
APA StyleFeichtenschlager, B., Pabisch, S., Svehla, J., Peterlik, H., Sajjad, M., Koch, T., & Kickelbick, G. (2020). Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: The Influence of Interface Modification on the Dispersion Structure—A Small-Angle-X-ray-Scattering Study. Surfaces, 3(4), 664-682. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces3040044