Protective Coatings for Metals in Scientific—Technical Heritage: The Collection of the Spanish National Museum of Science and Technology (MUNCYT)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterisation of the Metals and Original Coatings
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Substrates and Coatings
2.2.2. Thickness
2.2.3. Artificial Ageing
2.3. Evaluation Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
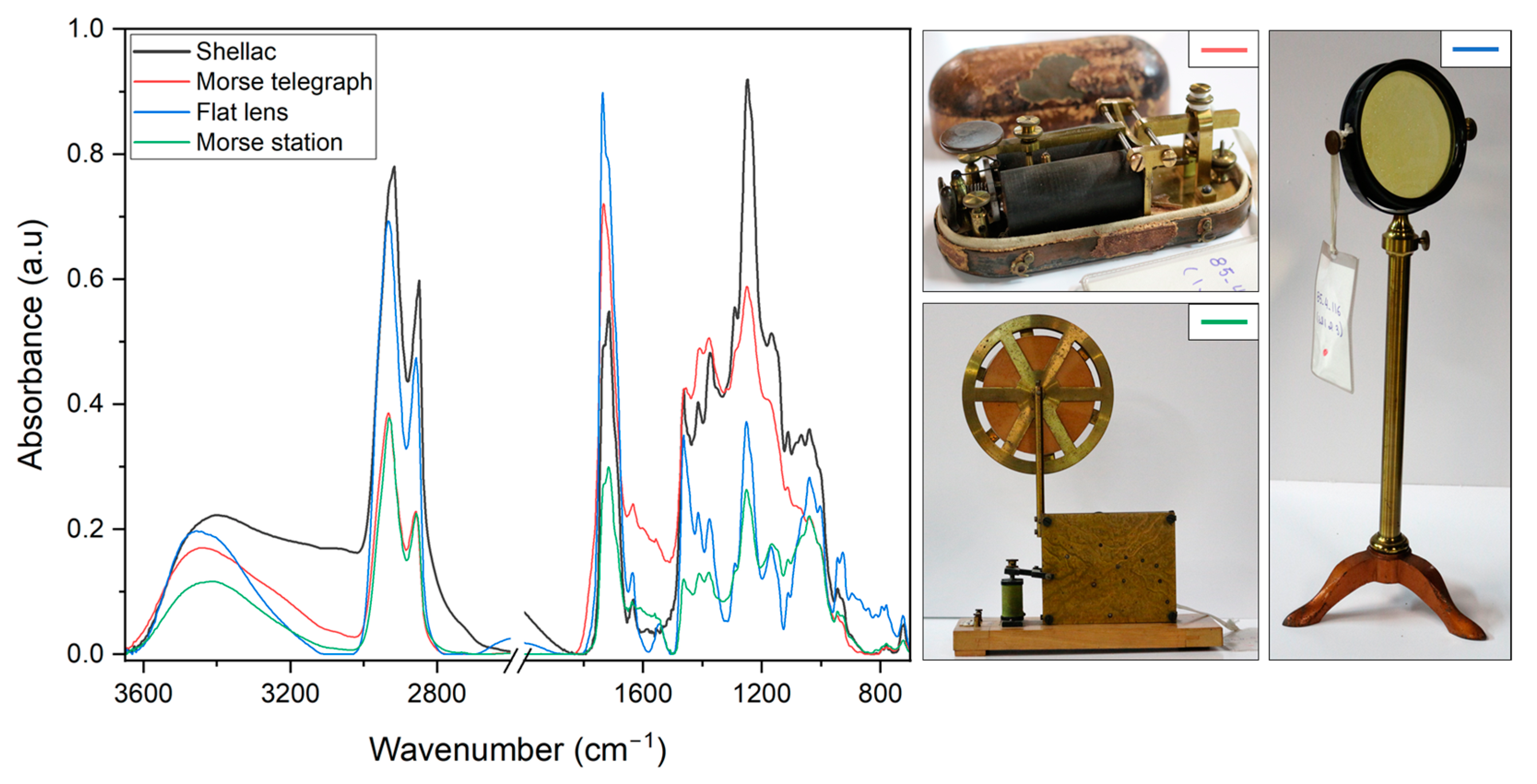
3.1. Section I: Materials Characterization
3.2. Section II: Coatings Evaluation
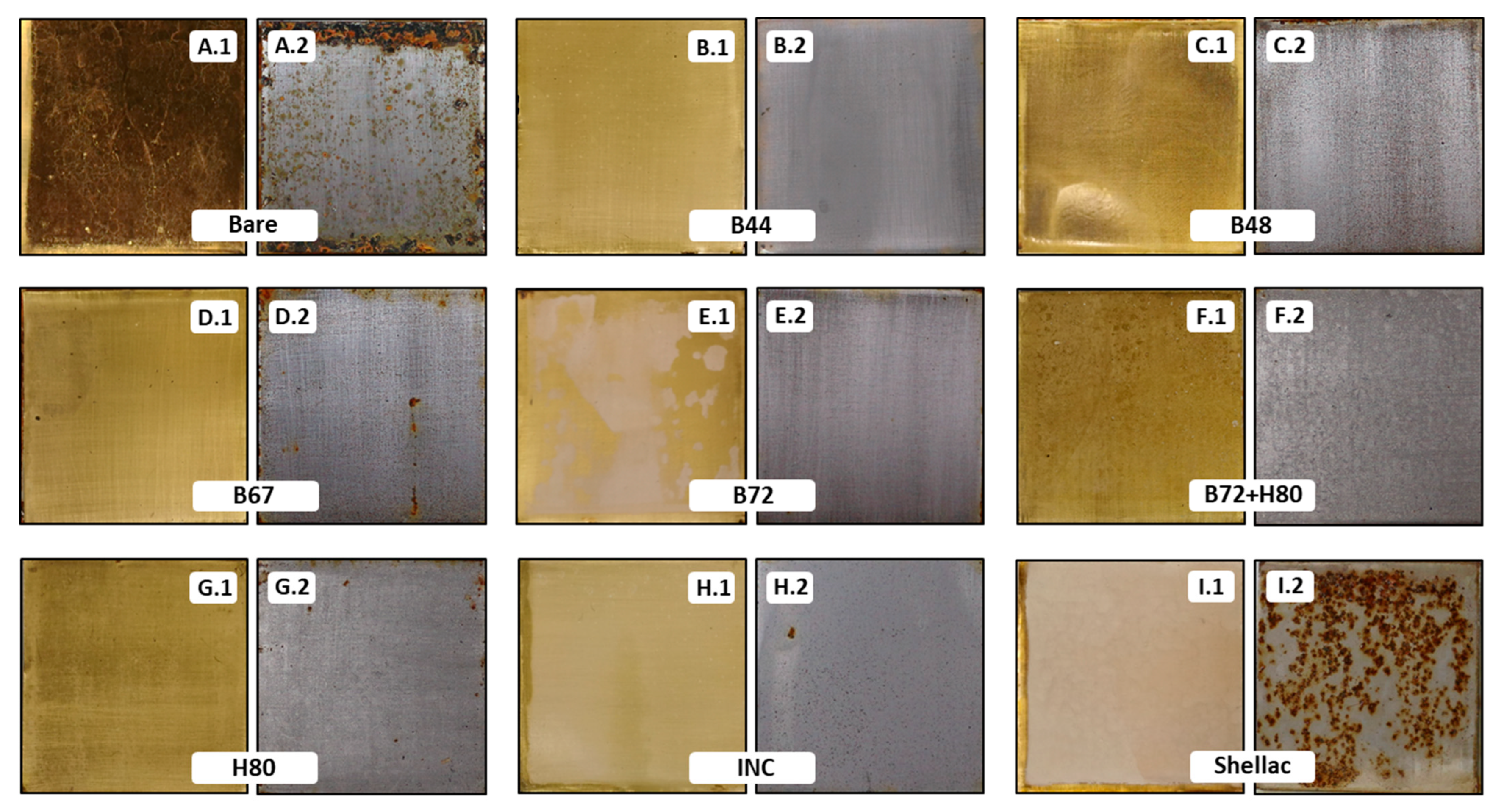
3.2.1. Visual Changes
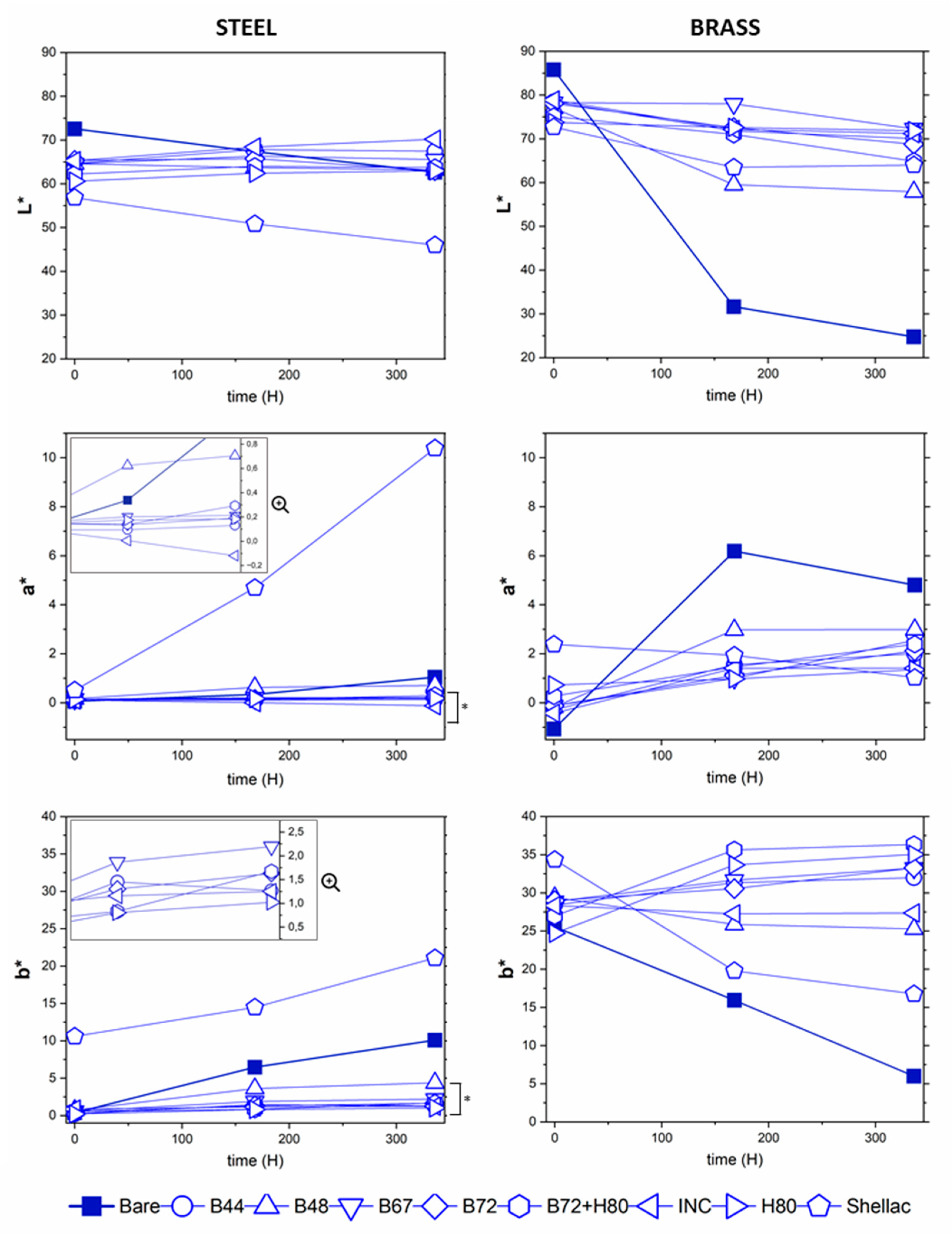
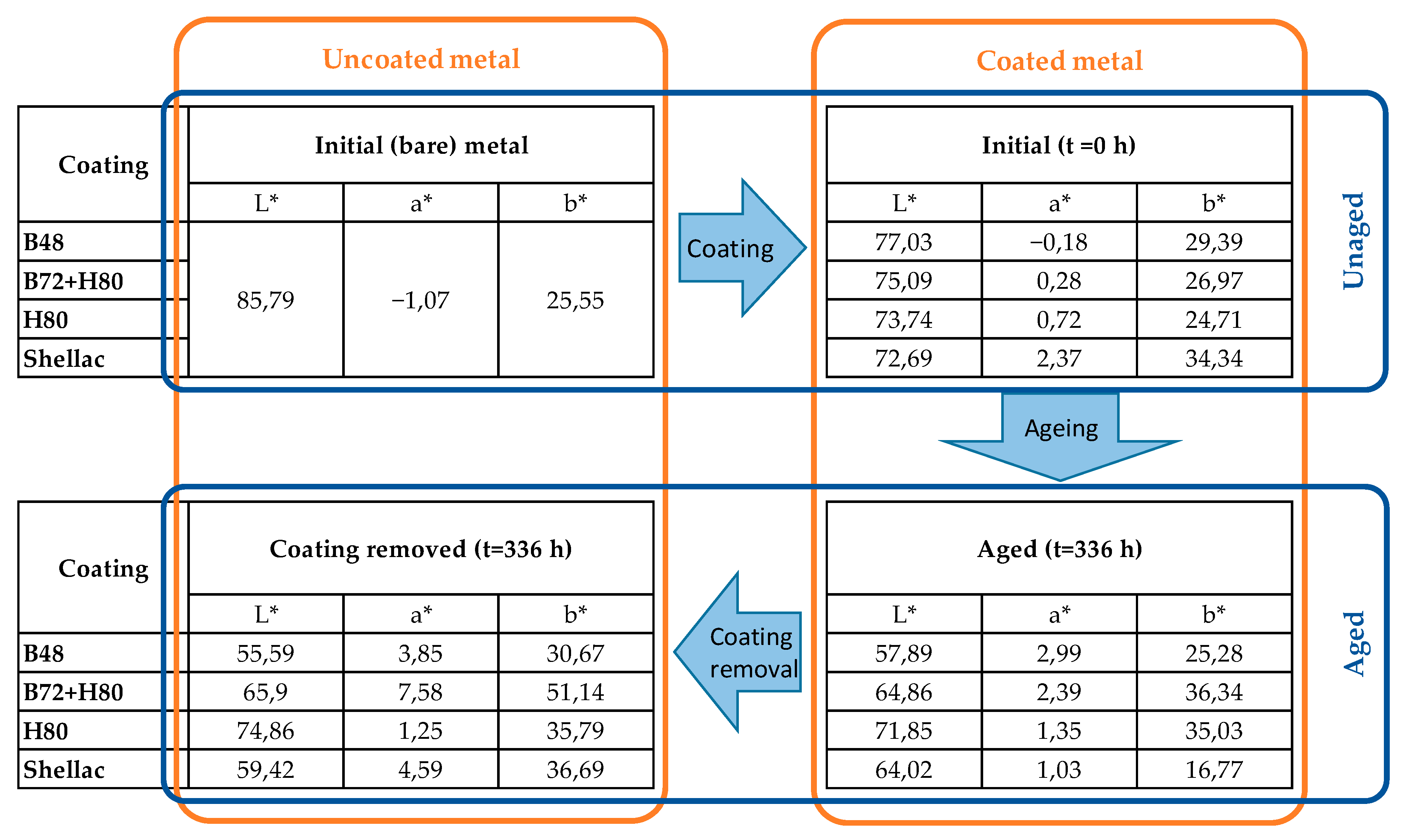
3.2.2. Aesthetic Changes
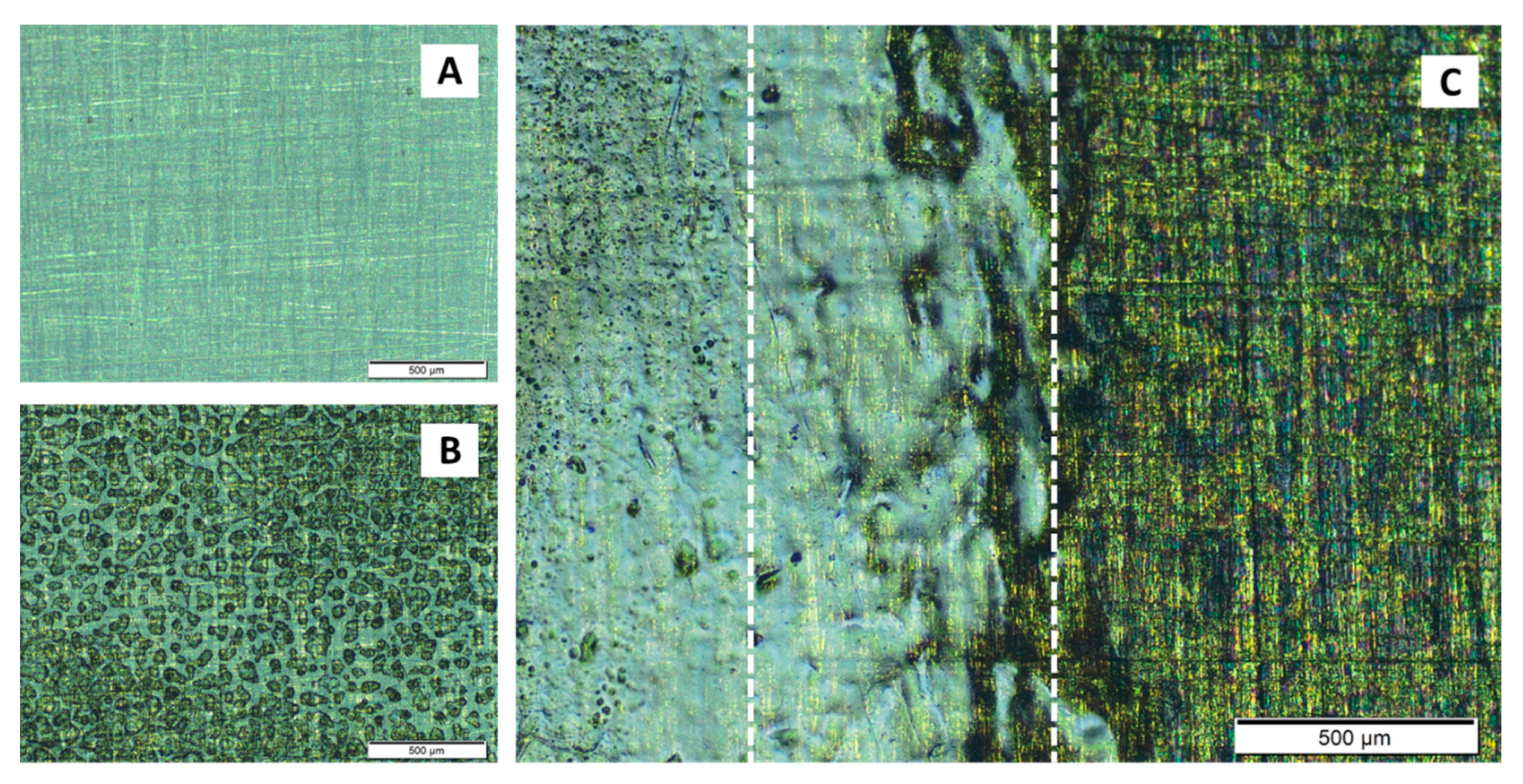
3.2.3. Changes at the Microscopic Scale
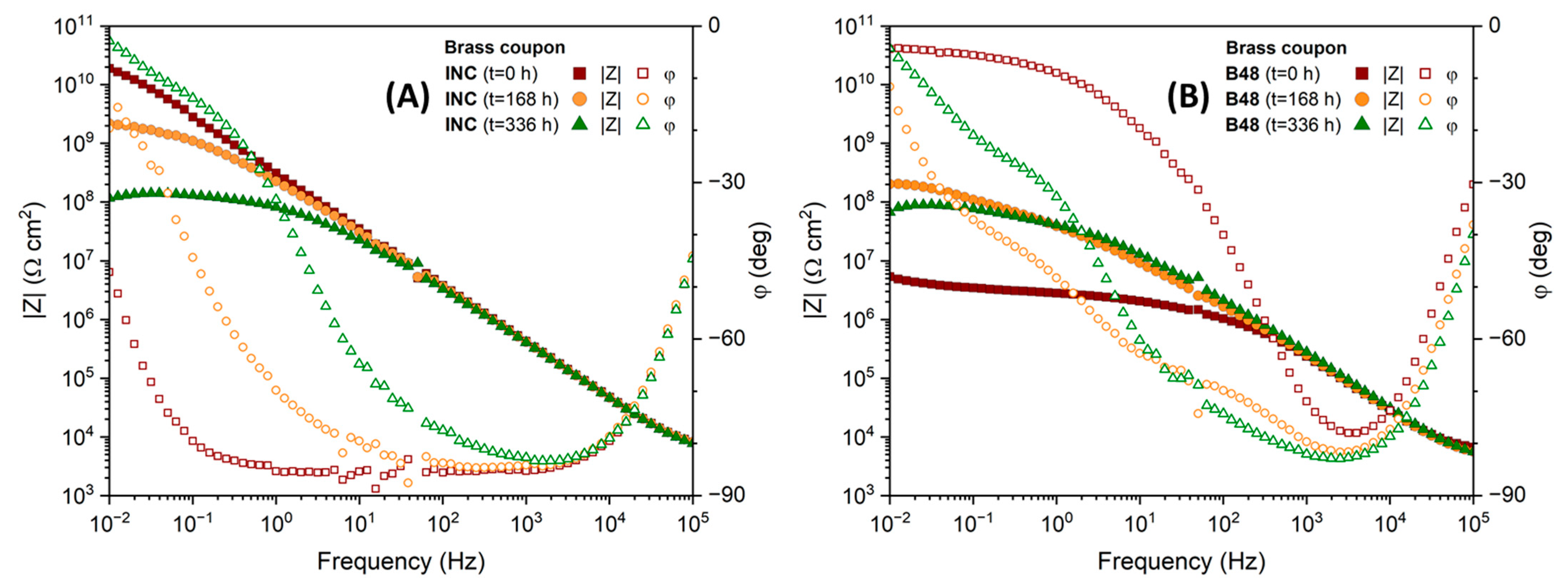
3.2.4. Protective Capacity
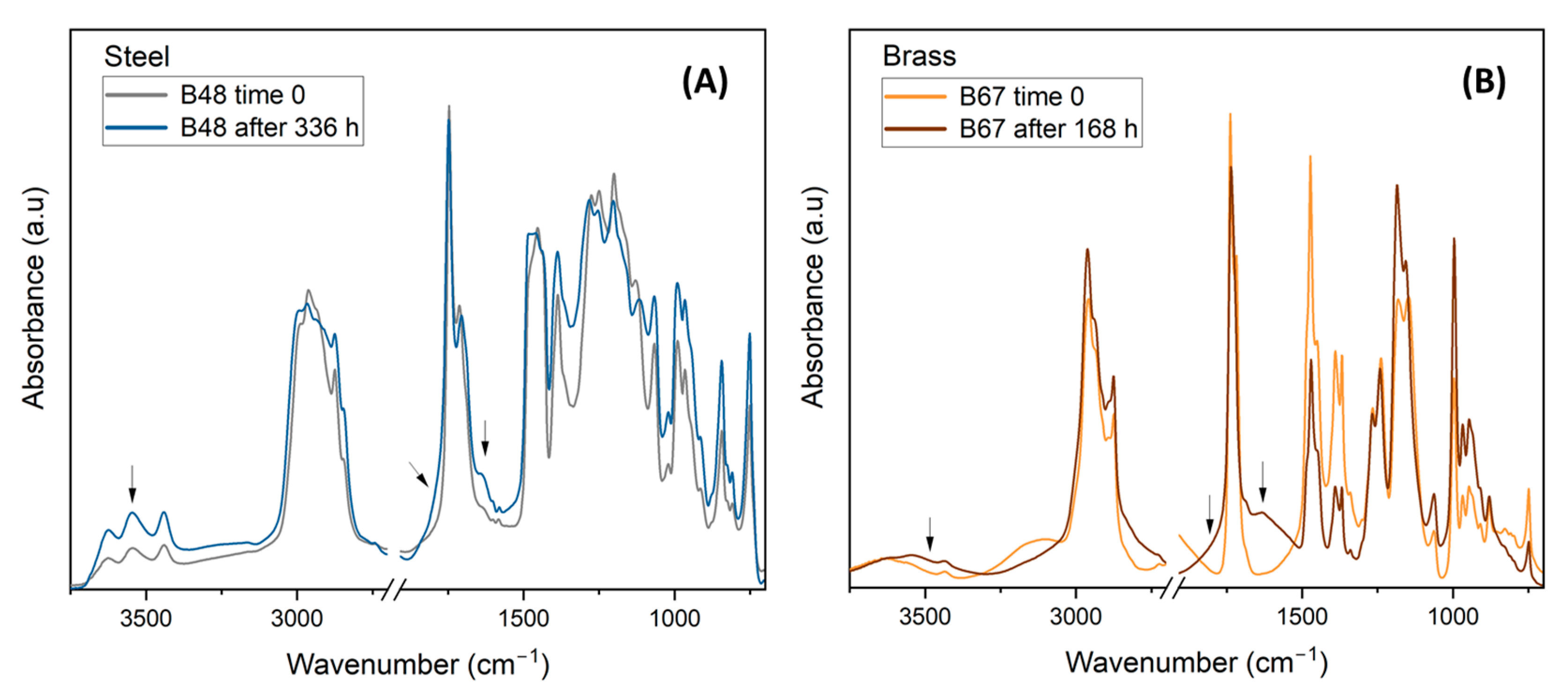
3.2.5. FTIR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreno-Gómez, E. Instrumentos de La Ciencia Española: Los Aparatos Históricos Del CSIC; Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas, Ed.; Catarata: Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Newey, H. Conservation and the preservation of scientific and industrial collections. Stud. Conserv. 2000, 45, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.; Tissot, I. Reflections on the conservation challenges of scientific and technological objects. Conserv. Patrim. 2020, 33, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, A. The importance of movement and operation as preventive conservation strategies for heritage machinery. JAIC 2017, 56, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, E. Challenges of conservation: Working objects. Sci. Museum Group J. 2022, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Cortés, A.; Barat, B.R.; Leal, J.; Llorente, I.; del Egido, M.; Cano, E. Diagnosis of the condition of scientific and technical collections: Historical extinguishers of the MUNCYT. Ge-Conservacion 2020, 18, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Lafuente, D. Corrosion Inhibitors for the Preservation of Metallic Heritage Artefacts. In Corrosion and Conservation of Cultural Heritage Metallic Artefacts; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; Volume 594, pp. 570–594. [Google Scholar]
- Otieno-Alego, V.; Hallam, D.; Viduka, A.; Heath, G.; Creagh, D. Electrochemical impedance studies of the corrosion resistance of wax coatings on artificially patinated bronze. In Proceedings of the METAL 98: Proceedings of the International Conference on Metals Conservation, Draguignan-Figanières, France, 27–29 May 1998; Mourey, W., Robbiola, L., Eds.; James and James: London, UK, 1998; pp. 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Web MUNCYT. Available online: https://www.muncyt.es/ (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Molina, M.T.; Ramirez Barat, B.; Díaz, I.; Cano, E. Estrategias Innovadoras para la conservación preventiva de Los objetos metálicos en colecciones de museos. In Proceedings of the MetalEspaña 2020/2021 III Congreso de Conservación y Restauración del Patrimonio Metálico; Barrio Martín, J., Buendía Ortuño, M., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 2022; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Karydas, A.G. Application of a portable XRF spectrometer for the non-invasive analysis of museum metal artefacts. Ann. Chim. 2007, 97, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguregui, M.; Morillas, H.; Marcaida, I.; García-Florentino, C.; de Errazti, I.O.; Aransay, C.; Madariaga, J.M. A non-invasive in situ methodology to characterise the lacquers and metals from the edo period Japanese armour. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, J.; Michel, A.; Mirabaud, S.; Bellot-Gurlet, L.; Paris, C.; Brambilla, L. Transparent varnishes on copper alloys dating from the 19th century: Characterization and identification strategies. In Proceedings of the Metal 2019: Interim Meeting of the ICOM-CC Metals Working Group, Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 2–6 September 2019; Chemello, C., Brambilla, L., Joseph, E., Eds.; Haute Ecole Arc: Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4892-3; Plastics–Methods of Exposure to Laboratory Light Sources—Part 3: Fluorescent UV Lamps. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Ramírez Barat, B.; Cano, E.; Letardi, P. Advances in the Design of a Gel-Cell Electrochemical Sensor for Corrosion Measurements on Metallic Cultural Heritage. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, E.; Crespo, A.; Lafuente, D.; Ramirez Barat, B. A novel gel polymer electrolyte cell for In-Situ application of corrosion electrochemical techniques. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 41, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywacz, C.M. Monitoring for Gaseous Pollutants in Museum Environments; The Getty: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-89236-851-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tétreault, J. Airborne Pollutants in Museums, Galleries and Archives: Risk Assessment, Control Strategies and Preservation Management; Canadian Conservation Institute: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tétreault, J.; Cano, E.; Van Bommel, M.; Scott, D.; Dennis, M.; Barthés-Labrousse, M.G.; Minel, L.; Robbiola, L. Corrosion of copper and lead by formaldehyde, formic and acetic acid vapours. Stud. Conserv. 2003, 48, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Barat, B.; Cano, E. Agar versus Agarose Gelled Electrolyte for In Situ Corrosion Studies on Metallic Cultural Heritage. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanterna, G.; Giatti, A. Caratterizzazione non invasiva delle vernici da ottone degli strumenti scientifici: Ricette storiche, realizzazione di provini verniciati, ricerca analitica e applicazioni “In Situ” su strumenti storici. OPD Restauro 2014, 26, 165–180. [Google Scholar]
- Argyropoulos, V.; Giannoulaki, M.; Michalakakos, G.P.; Siatou, A. A Survey of the Type of Corrosion Inhibitors and Protective Coatings Used for the Conservation of Metal Objects from Museum Collections in the Mediterranean Basin. In Proceedings of the Strategies for Saving Our Cultural Heritage, Cairo, Egypt, 26–28 February 2007; Argyropoulos, V., Hein, A., Harith, M.A., Eds.; T.E.I. of Athens: Greece, Athens; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, J.; Grayburn, R.; Khanjian, H.; Heginbotham, A.; Phenix, A. Deconstructing incralac: A formulation study of acrylic coatings for the protection of outdoor bronze sculpture. In Proceedings of the ICOM-CC 18th Triennial Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2017; Brigland, J., Ed.; International Council of Museums: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watkinson, D. Preservation of metallic cultural heritage. In Shreir’s Corrosion; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 3307–3340. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfram, J.; Brüggerhoff, S.; Eggert, G. Better than Paraloid B-72? Testing Poligen® Waxes as Coatings for Metal Objects. In Proceedings of the Metal 2010: Interim Meeting of the ICOM-CC Metal Working Group, Charleston, SC, USA, 11–15 October 2010; Mardikian, P., Chemello, C., Watters, C., Hull, P., Eds.; Clemson University: Clemson, SC, USA, 2011; pp. 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff, L.B. Coating Strategies for the Protection of Outdoor Bronze Art and Ornamentation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Švadlena, J.; Stoulil, J. Evaluation of protective properties of acrylate varnishes used for conservation of historical metal artefacts. Koroze Ochr. Mater. 2017, 61, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, M.; Chiantore, O. Thermal-ageing of paraloid acrylic protective polymers. Polymer 2000, 41, 6447–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki, W.; Tatol, M. Color difference delta E-A survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, G. Unstable thin polymer films: Rupture and dewetting processes. Langmuir 1993, 9, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Sharma, A. Instability, self-organization and pattern formation in thin soft films. Soft Matter. 2015, 11, 8717–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, J.A.; Dalnoki-Veress, K. The Glass Transition in Thin Polymer Films. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 94, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinçotte, A.; Beauvoit, E.; Boyard, N.; Guilminot, E. Effect of Solvent on PARALOID® B72 and B44 Acrylic Resins Used as Adhesives in Conservation. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tsavalas, J.G.; Sundberg, D.C. Water whitening of polymer films: Mechanistic studies and comparisons between water and solvent borne films. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 105, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsavalas, J.G.; Sundberg, D.C. Hydroplasticization of polymers: Model predictions and application to emulsion polymers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6960–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingson, L.A.; Brostoff, L.B.; Shedlosky, T.J.; Bierwagen, G.P.; De la Rie, E.R. The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in the evaluation of coatings for outdoor bronze. Stud. Conserv. 2004, 49, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Barat, B.; Crespo, A.; García, E.; Díaz, S.; Cano, E. An EIS Study of the Conservation Treatment of the Bronze Sphinxes at the Museo Arqueológico Nacional (Madrid). J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 24, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letardi, P. Laboratory and field tests on patinas and protective coating systems for outdoor bronze monuments. In Proceedings of the Metal 04: Interim Meeting of the ICOM-CC Metals Working Group, Camberra, Australia, 4–8 October 2004; Hallam, D., John, A., Eds.; National Museum of Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2004; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, E.; Lafuente, D.; Bastidas, D.M. Use of EIS for the evaluation of the protective properties of coatings for metallic cultural heritage: A review. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 14, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, N.; Clare, T.L. On the protective nature of wax coatings for culturally significant outdoor metalworks: Microstructural flaws, oxidative changes, and barrier properties. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 2015, 54, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantore, O.; Trossarelli, L.; Lazzari, M. Photooxidative degradation of acrylic and methacrylic polymers. Polymer 2000, 41, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantore, O.; Lazzari, M. Photo-oxidative stability of paraloid acrylic protective polymers. Polymer 2001, 42, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Thicknesses on Steel (µm) | Thicknesses on Brass (µm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coupon 1 | Coupon 2 | Coupon 3 | Coupon 1 | Coupon 2 | Coupon 3 | |
| B44 | 7.8 ± 1.3 | 13.8 ± 4.7 | 10.2 ± 2.4 | 5.8 ± 2.1 | 7.7 ± 3.3 | 5.7 ± 3.5 |
| B48 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 1.7 | 9.6 ± 2.4 | 6.4 ± 3.6 | 7 ± 3.1 | 10 ± 3.9 |
| B67 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 4 ± 0.6 | 5.1 ± 1.9 | 1.6 ± 1 | 3.1 ± 2.3 | 4.5 ± 5.2 |
| B72 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 6.2 ± 1.8 | 7.2 ± 1.7 | 5.5 ± 2.5 | 4.9 ± 3.2 | 7.2 ± 2.7 |
| B72 + H80 | 6.1 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 2.2 | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 6.3 ± 2.4 | 10 ± 3.9 | 6.1 ± 3.2 |
| H80 | 4.6 ±1.4 | 4.2 ± 1.9 | 4.5 ± 1.9 | 12.9 ± 2.8 | 10.9 ± 4.3 | 13.3 ± 3.5 |
| Incralac | 8.6 ±2.7 | 11.9 ± 2.9 | 10.9 ± 3.8 | 12.2 ± 2.9 | 11.5 ± 3.6 | 8 ± 2.2 |
| Shellac | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 6.2 ± 0.8 | 9.2 ± 1.4 | 6.3 ± 1.7 | 7.3 ± 3.1 | 6.4 ± 1.4 |
| Object | Name (Date) | XRF Elemental Quantification (% in Mass) | Assignation |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Reflector Telescope (1755) | 69.52% Cu, 32.08% Zn, 2.95% Pb, 0.29% Fe, 0.32% Sn, 0.05% Sb, 0.03% Ni | Brass |
 | Tellurium (1789) | 74.47% Cu, 18.91% Zn, 2.63% Pb, 0.53% Sn, 0.37% Fe, 0.05% Sb, 0.04% Ni | Brass |
 | Mammoth Gramophone (1907–1914) | (Horn): 64.13% Cu, 35.34% Zn, 0.3.6% Pb, 0.06% Fe, 0.04% Cd, 0.02% Sn | Brass |
| (Arm): 49.55% Ni, 49.41% Fe, 0.29% Co, 0.30% Mn, 0.20% Zn, 0.05% Ti, 0.02% Pb | Nickel-plated steel | ||
 | Artillery compass (1584) | 47.81% Au, 41.94% Cu, 8.09% Zn, 0.81% Pb, 0.25% Fe, 0.20% Ni, 0.21% Sn, 0.06% Sb, 0.22% Ag + (123,331.80 ppm of Hg) | Gold plated copper (Ormolu) |
 | Gramophone PathéPost (1908) | (Box): 64.14% Fe, 25.41% Pb, 1.74% Ti, 0.90% V, 0.67% Mn, 0.40% S, 0.26% Co, 0.23% Cu, 0.17% Cr, 0.07% Zn | Minium painted steel |
 | Buttocks exvoto (XIX century) | 66.93% Ag, 30.08% Cu, 1.53% Zn, 1.11% Ni, 0.33% Pb | Silver and copper alloy |
 | Trepanning set (1820–1840) | (Tools): 98.55% Fe, 0.41% Mn, 0.20% Ni, 0.09% Cu, 0.06% Cr | Steel |
| (Tool handles): 91.32% Ag, 5.58% Cu, 2.06% Fe, 0.44% Cr, 0.23% Pb, 0.20% Au, 0.14% Zn | Sterling silver |
| Colour Differences (ΔE*) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare | B44 | B48 | B67 | B72 | B72 + H80 | INC | H80 | Shellac | |
| Steel | 13.9 | 2.9 | 4.1 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 18.6 |
| Brass | 64.3 | 9.3 | 19.9 | 7.9 | 10.3 | 14.0 | 7.9 | 10.5 | 19.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molina, M.T.; Cano, E.; Leal, J.; Fort, R.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; Ramírez-Barat, B. Protective Coatings for Metals in Scientific—Technical Heritage: The Collection of the Spanish National Museum of Science and Technology (MUNCYT). Heritage 2023, 6, 2473-2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6030130
Molina MT, Cano E, Leal J, Fort R, Álvarez de Buergo M, Ramírez-Barat B. Protective Coatings for Metals in Scientific—Technical Heritage: The Collection of the Spanish National Museum of Science and Technology (MUNCYT). Heritage. 2023; 6(3):2473-2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6030130
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolina, María Teresa, Emilio Cano, Joaquina Leal, Rafael Fort, Mónica Álvarez de Buergo, and Blanca Ramírez-Barat. 2023. "Protective Coatings for Metals in Scientific—Technical Heritage: The Collection of the Spanish National Museum of Science and Technology (MUNCYT)" Heritage 6, no. 3: 2473-2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6030130
APA StyleMolina, M. T., Cano, E., Leal, J., Fort, R., Álvarez de Buergo, M., & Ramírez-Barat, B. (2023). Protective Coatings for Metals in Scientific—Technical Heritage: The Collection of the Spanish National Museum of Science and Technology (MUNCYT). Heritage, 6(3), 2473-2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6030130








