Evaluation of the Irradiation Treatment Effects on Ancient Parchment Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial and Fungal Strains Identification
2.2. The Disinfection by Irradiation
2.3. LTA
2.4. FORS
2.5. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy
2.6. UV Resonant Raman Spectroscopy
2.7. Atomic Force Microscopy Nano-Indentation Measurements
3. Results
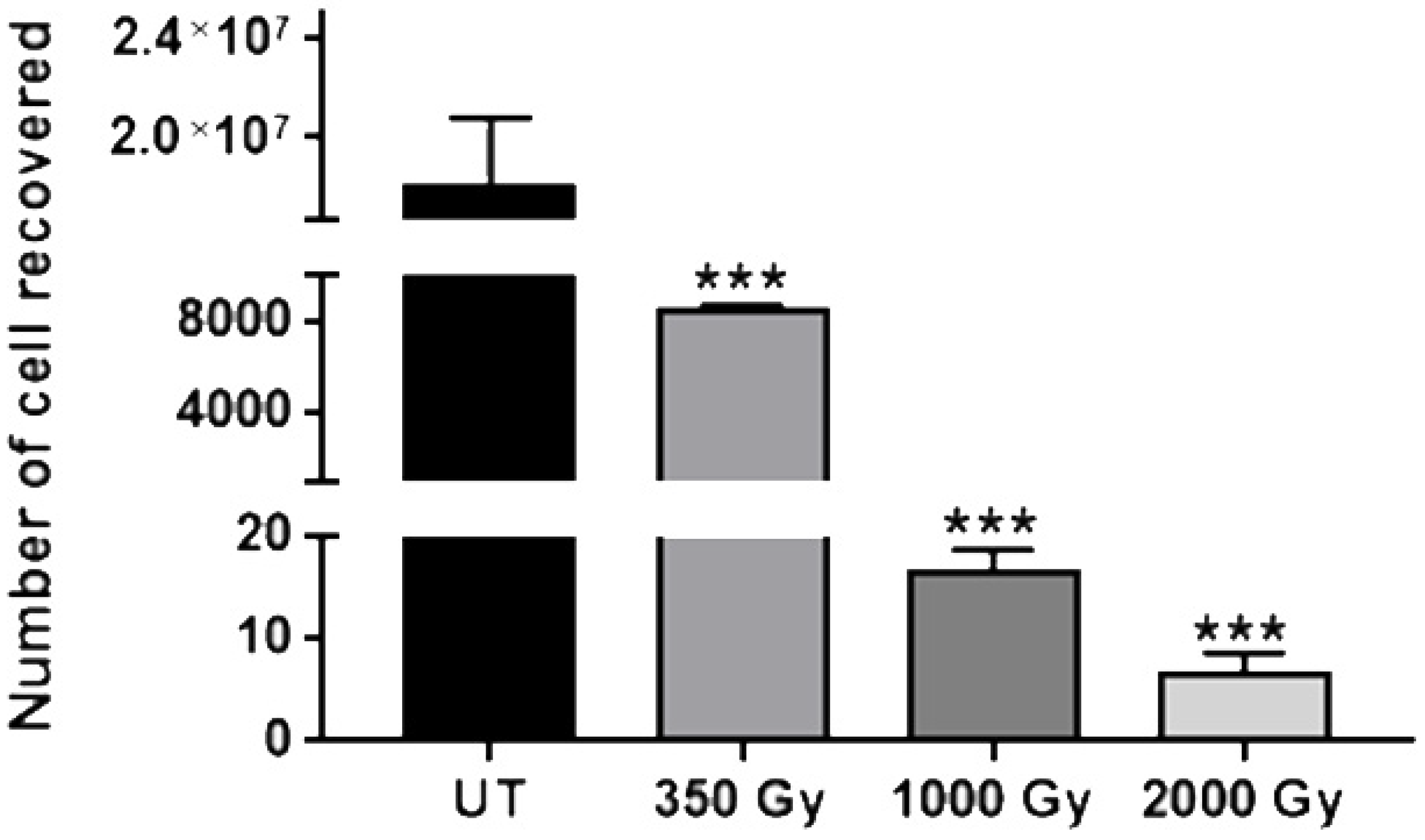
3.1. Identification of Bacterial and Fungal Colonies and Cell Viability Test
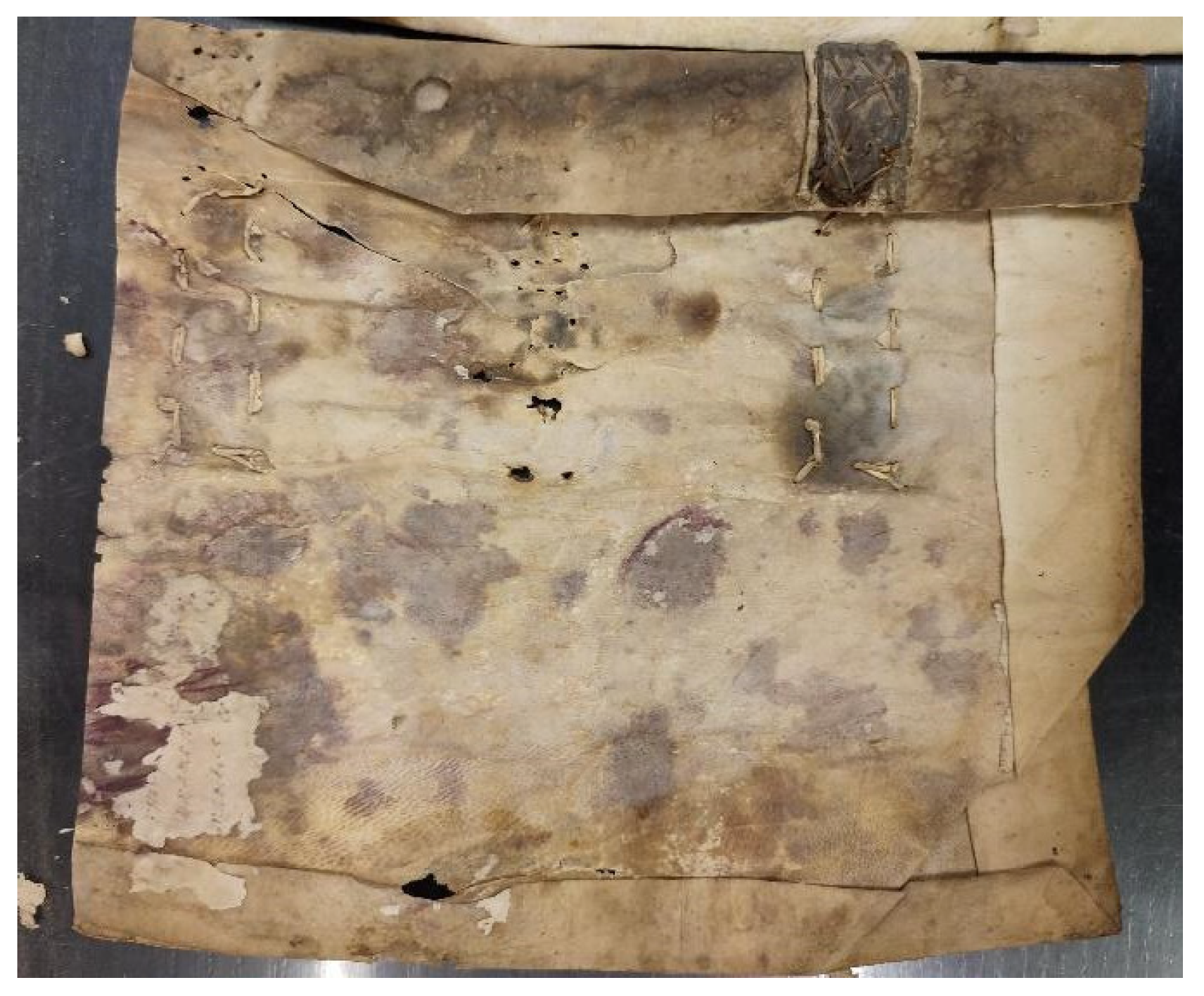
3.2. Characterization of the Parchment Deterioration
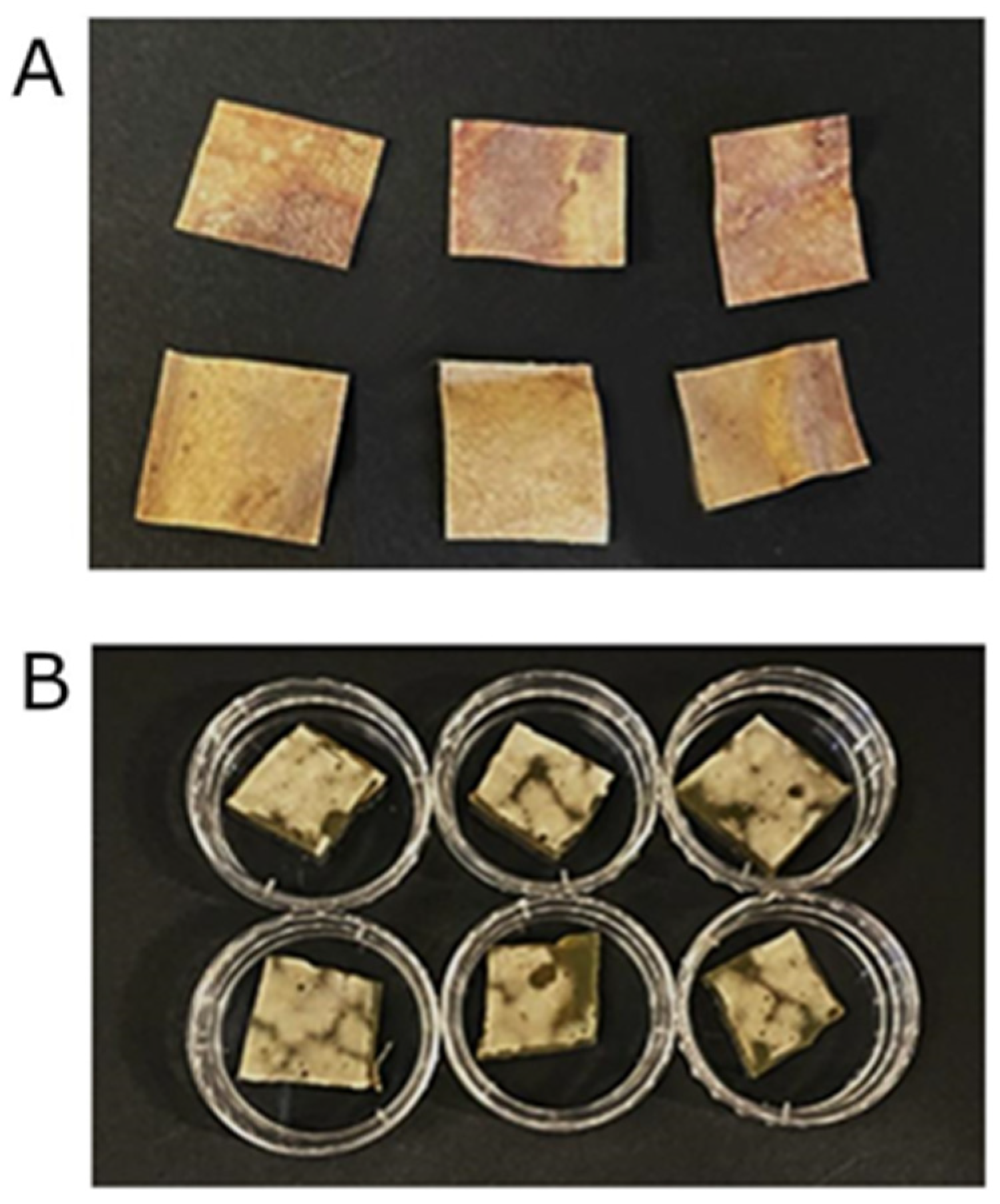
3.2.1. LTA
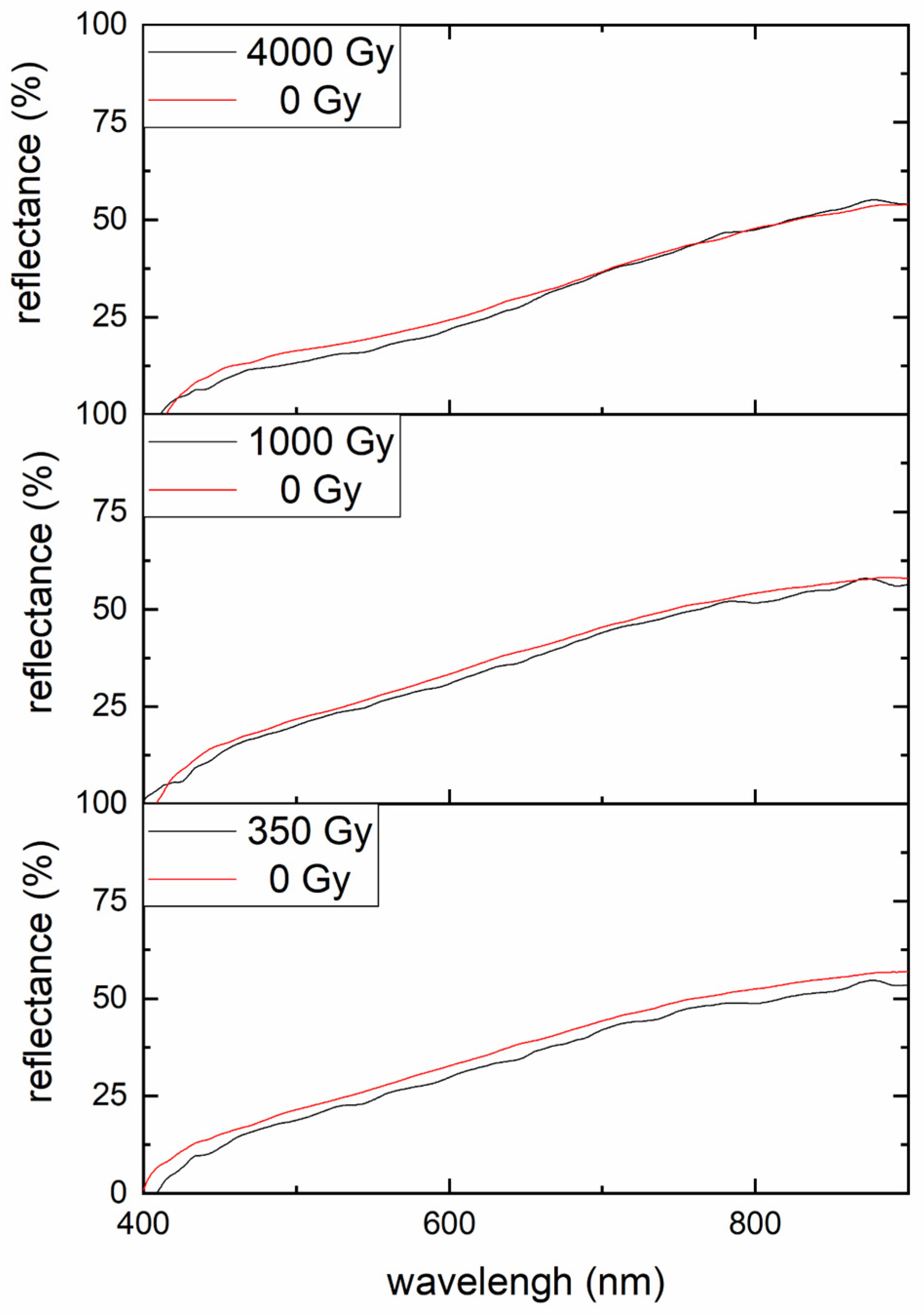
3.2.2. FORS
3.2.3. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy Results
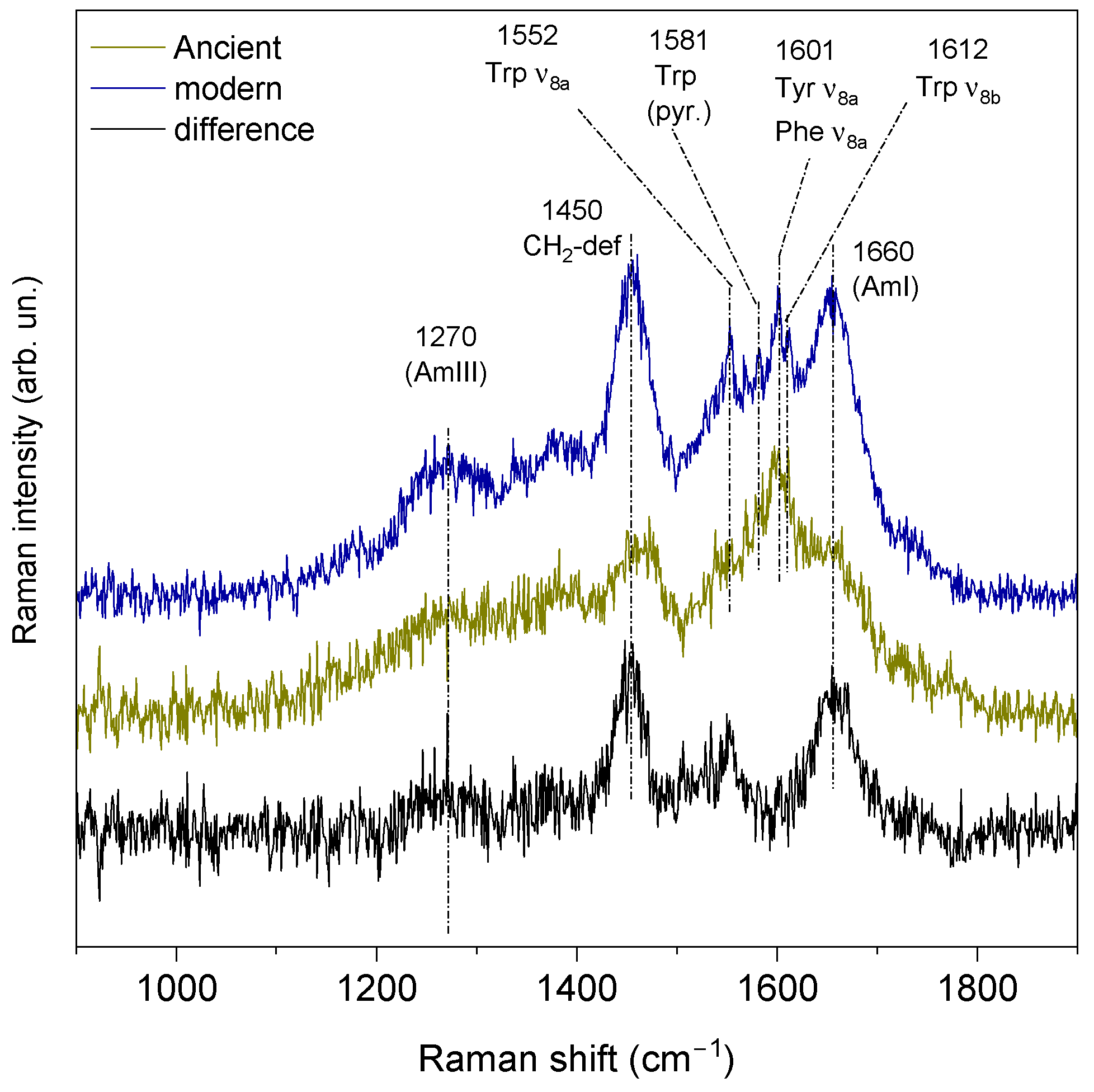
3.2.4. UV Resonant Raman Spectroscopy
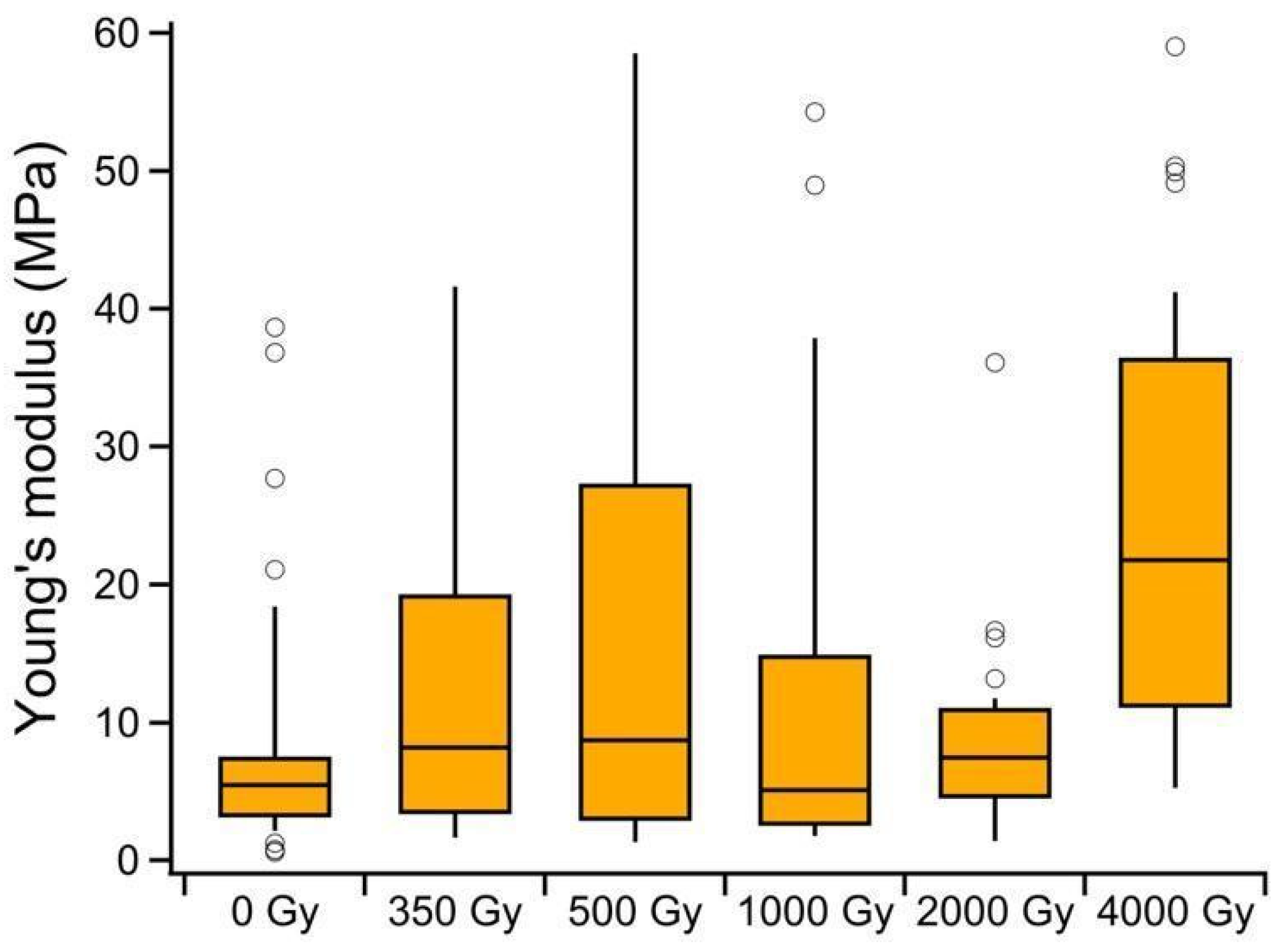
3.2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy Mechanical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agati, M. The Manuscript Book, a Compendium of Codicology, 1st ed.; L’Erma di Bretschneider: Roma, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.J.; Wess, T.J. The Structure of Collagen within Parchment—A Review. Restaurator 2003, 24, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kite, M.; Thomson, R. Conservation of Leather and Related Materials, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, E.F.; Lee, S.N.; Sobel, H. The Effects of Relative Humidity on Some Physical Properties of Modern Vellum: Implications for the Optimum Relative Humidity for the Display and Storage of Parchment. JAIC 1992, 31, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowska-Berent, J.; Górny, R.L.; Strzelczyk, A.B.; Wlazło, A. Airborne and dust borne microorganisms in selected Polish libraries and archives. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñar, G.; Sterflinger, K.; Ettenauer, J.; Quandt, A.; Pinzari, F. A Combined Approach to Assess the Microbial Contamination of the Archimedes Palimpsest. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, C.; Pinzari, F.; Mercuri, F. 18th Century knowledge on microbial attacks on parchment: Analytical and historical evidence. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 134, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Thaller, M.C.; Vendittozzi, G.; Mejia, A.Y.; Mercuri, F.; Orlanducci, S.; Rubechini, A. Purple spot damage dynamics investigated by an integrated approach on a 1244 A.D. parchment roll from the Secret Vatican Archive. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Perini, N.; Mercuri, F.; Orlanducci, S.; Rubechini, A.; Thaller, M.C. Three ancient documents solve the jigsaw of the parchment purple spot deterioration and validate the microbial succession model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R. Alternative approaches to the treatment of mould biodeterioration—An international problem. Pap. Conserv. 1986, 10, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, S.; Cabrita, E.J.; Macedo, M.F. Antifungals on paper conservation: An overview. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 74, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, A.; Pinzari, F.; Barbabietola, N.; Piñar, G. Monitoring the effects of different conservation treatments on paper-infecting fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 84, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfendler, S.; Borderie, F.; Bousta, F.; Alaoui-Sosse, L.; Alaoui-Sosse, B.; Aleya, L. Comparison of biocides, allelopathic substances and UV-C as treatments for biofilm proliferation on heritage monuments. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 33, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, A.M.; Giovannotti, M.; Magaudda, G.; PLoSsi Zappalà, M.; Rocchetti, F.; Rossi, G. Effect of Gamma Rays on Pure Cellulose Paper as a Model for the Study of a Treatment of “Biological Recovery” of Biodeteriorated Books. Restaurator 1998, 19, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, M.; Brizzi, M.; Magaudda, G.; Martinelli, G.; PLoSsi-Zappalà, M.; Rocchetti, F.; Savagnone, F. Gamma Radiation Treatment of Paper in Different Environmental Conditions: Chemical, Physical and Microbiological Analysis. Restaurator 2001, 22, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaudda, G. The recovery of biodeteriorated books and archive documents through gamma radiation: Some considerations on the results achieved. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero D’Almeida, M.L.; de Souza Medeiros Barbosa, P.; Guerra Boaratti, M.F.; Borrely, S.Y. Radiation effects on the integrity of paper. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, K.; Otlewska, A.; Danielewicz, D.; Dybka, K.; Pangallo, D.; Kraková, L.; Puškárová, A.; Bučková, M.; Scholtz, V.; Ďurovič, M.; et al. Disinfection of archival documents using thyme essential oil, silver nanoparticles misting and low temperature plasma. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 24, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo-Arantes, S.; Piçarra, A.; Caldeira, A.T.; Candeias, A.E.; Martins, M.R. Essential oils of Portuguese flavouring plants: Potential as green biocides in cultural heritage. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, S.; Omar, A.; Maher, M. Comparative Inhibition Study by Nanomaterial, Plant Extract and Chemical Microcide on the Screaming Mummy in Egyptian Museum Store. Heritage 2021, 4, 2481–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueidão, M.; Vieira, E.; Bordalo, R.; Moreira, P. Available green conservation methodologies for the cleaning of cultural heritage: An overview. Estud. Conserv. E Restauro 2021, 12, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Borgognoni, F.; Cicero, C.; Perini, N.; Migliore, L.; Mercuri, F.; Orazi, N.; Rubechini, A. Parchment processing and analysis: Ionizing radiation treatment by the REX source and multidisciplinary approach characterization. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 149, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; De Bellis, G.; Mazzuca, C.; Mercuri, F.; Borgognoni, F.; Schifano, E.; Uccelletti, D.; Cicero, C. Effects of the Ionizing Radiation Disinfection Treatment on Historical Leather. Front. Mater. 2020, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlay, J.A.; Linn, S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science 1988, 240, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Delatour, T.; Douki, T.; Gasparutto, D.; Pouget, J.P.; Ravanat, J.L.; Sauvaigo, S. Hydroxyl radicals and DNA base damage. Mutat Res. 1999, 424, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilquin, B. Actions Biologique et Chimique des Rayonnements Ionisants; Nauwelaerts: Paris, France, 2001; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Borrely, S.I.; Cruz, A.C.; Del Mastro, N.L.; Sampa, M.H.O.; Somessari, E.S. Radiation processing of sewage and sludge: A review. Prog. Nucl. Energy 1998, 33, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condón-Abanto, S.; Pedrós-Garrido, S.; Cebrián, G.; Raso, J.; Condón, S.; Lyng, J.G.; Álvarez, I. Crab-meat-isolated psychrophilic spore forming bacteria inactivation by electron beam ionizing radiation. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Cicero, C.; Parisse, P.; Casalis, L.; De Bellis, G. Surface evaluation of the effect of X-rays irradiation on parchment artefacts through AFM and SEM. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 513, 145881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Cicero, C.; Mazzuca, C.; Mercuri, F.; Missori, M.; Orazi, N.; Severini, L.; Zammit, U. Effect of X-ray and artificial aging on parchment. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K.; Pinzari, F. The revenge of time: Fungal deterioration of cultural heritage with particular reference to books, paper and parchment. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñar, G.; Tafer, H.; Schreiner, M.; Miklas, H.; Sterflinger, K. Decoding the biological information contained in two ancient Slavonic parchment codices: An added historical value. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3218–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, C.; Mercuri, F.; Paoloni, S.; Orazi, N.; Zammit, U.; Glorieux, C.; Thoen, J. Integrated adiabatic scanning calorimetry, light transmission and imaging analysis of collagen deterioration in parchment. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 676, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, E.; Cicero, C.; Orazi, N.; Mercuri, F.; Zammit, U.; Mazzuca, C.; Orlanducci, S. Nanodiamond composites: A new material for the preservation of parchment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, E.; Pauli, H.K.A. Whiteness and tint formulas of the Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage: Approximations in the L*a*b* color space. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2998–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleari, C. Misurare il Colore, 1st ed.; Hoepli: Milano, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- De Campos Vidal, B.; Mello, M.L.S. Collagen type I amide I band infrared spectroscopy. Micron 2011, 42, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwing, K.; Gerhards, M. Investigations on isolated peptides by combined IR/UV spectroscopy in a molecular beam—Structure, aggregation, solvation and molecular recognition. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2016, 35, 569–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A.; Ludwig, M.; Johnson, C.R. UV resonance Raman excitation profiles of the aromatic amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 3186–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, E.; Cavallini, D.; De Bellis, G.; Bracciale, M.P.; Felici, A.C.; Santarelli, M.L.; Sarto, M.S.; Uccelletti, D. Antibacterial Effect of Zinc Oxide-Based Nanomaterials on Environmental Biodeteriogens Affecting Historical Buildings. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Mugunthan, M. Evaluation of three DNA extraction methods from fungal cultures. Med. J. Armed. Forces India 2018, 4, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Ferrari, P.; Borgognoni, F.; Campani, L. The REX irradiation facility and its applications. Nucl. Instrum. 2019, 930, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebojsa, P.; Nils, K.A.; Ragni, O.; Achim, K. Monitoring Protein Structural Changes and Hydration in Bovine Meat Tissue Due to Salt Substitutes by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Microspectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10052–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivu, B.; Seshadri, S.; Li, J.; Oberg, K.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Distinct β-Sheet Structure in Protein Aggregates Determined by ATR–FTIR Spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5176–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavan, V.; Giurginca, M.; Budrugeac, P.; Vilsan, M.; Miu, L. Evaluation of the physico-chemical characteristics of leather samples of some historical objects from kiev. Rev. Chim. 2010, 61, 627–631. [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico, F.; Saito, M.; Bencivenga, F.; Marsi, M.; Gessini, A.; Camisasca, G.; Principi, E.; Cucini, R.; Di Fonzo, S.; Battistoni, A.; et al. UV resonant Raman scattering facility at Elettra. Nucl. Instrum. 2013, 703, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, J.R.; Nakamoto, K.; Brown, C.W. Introductory Raman Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lech, T. Evaluation of a Parchment Document, the 13th Century Incorporation Charter for the City of Krakow, Poland, for Microbial Hazards. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2620–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, N.; Portugal, A.; Videira, S.; Rodríguez-Echeverría, S.; Bandeira, A.M.L.; Santos, M.J.A.; Freitas, H. Fungal diversity in ancient documents. A case study on the Archive of the University of Coimbra. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyskočilová, G.; Ebersbach, M.; Kopecká, R.; Prokeš, L.; Príhoda, J. Model study of the leather degradation by oxidation and hydrolysis. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichi, A.; Eliazyan, G.; Kazarian, S.G. Study of the Degradation and Conservation of Historical Leather Book Covers with Macro Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Imaging. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7150–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachetti, M.; D’Amico, F.; Pascolo, L.; Pucciarelli, S.; Gessini, A.; Parisse, P.; Vaccari, L.; Masciovecchio, C. UV Resonance Raman explores protein structural modification upon fibrillation and ligand interaction. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 4575–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A.; Johnson, C.R. Raman Spectroscopy of a Coal Liquid Shows That Fluorescence Interference Is Minimized with Ultraviolet Excitation. Science 1984, 225, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullekson, C.; Lucas, L.; Hewitt, K.; Kreplak, L. Surface-sensitive Raman spectroscopy of collagen I fibrils. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A.; Ianoul, A.; Mix, G.R.; Boyden, M.N.; Karnoup, A.S.; Diem, M.; Schweitzer-Stenner, R. Dihedral psi angle dependence of the amide III vibration: A uniquely sensitive UV resonance Raman secondary structural probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11775–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A.; Mikhonin, A.V.; Bykov, S. UV Raman Demonstrates that α-Helical Polyalanine Peptides Melt to Polyproline II Conformations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8433–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieridou, G.K.; Hayes, S.C. UV resonance Raman spectroscopy of TTR(105–115): Determination of the pKa of tyrosine. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 5302–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, B.; Pflüger, F.; Kruglik, S.G.; Ghomi, M. Characteristic Raman lines of phenylalanine analyzed by a multiconformational approach. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, D.; Singh, A. Radiation sterilization of tissue allografts: A review. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.T. Application of Gamma Radiations and X-rays for Disinfection of Fungi in Historical Archives. Ph.D. Thesis, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Japan, 2020. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Application-of-gamma-radiations-and-X-rays-for-of-Linh/a37c2acaa4f1eec02b1f623bbea5596b667c553a (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Cleland, M.R. X-ray processing: A review of the status and prospects. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1993, 42, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehisa, M.; Saito, T.; Takahashi, T.; Sato, Y.; Sato, T. Characteristics of a contract electron beam and bremsstrahlung (X-ray) irradiation facility of Radia Industry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1993, 42, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Kashiwagi, M.; Mizusawa, K.; Sakamoto, I.; Hoshi, Y.; Tomita, K. A 5 MV 30 mA EB/X-ray processing system. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1993, 42, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusawa, K.; Kashiwagi, M.; Hoshi, Y. 5 MeV electron beam facilities in Japan. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1998, 52, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stichelbaut, F.; Bol, J.-L.; Cleland, M.R.; Grégoire, O.; Herer, A.S.; Jongen, Y.; Mullier, B. The Palletron™: A high-dose uniformity pallet irradiator with X-rays. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, O.; Cleland, M.R.; Mittendorfer, J.; Vander Donckt, M.; Meissner, J. Radiological safety of medical devices sterilized with X-rays at 7.5 MeV. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2003, 67, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, J.; Abs, M.; Cleland, M.R.; Herer, A.S.; Jongen, Y.; Kuntz, F.; Strasser, A. X-ray treatment at 5 MeV and above. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2000, 57, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongen, Y.; Abs, M.; Bol, J.-L.; Mullier, B.; Poncelet, E.; Rose, G.; Stichelbaut, F. Advances in sterilization with X rays, using a very high power Rhodotron and a very low DUR pallet irradiator. In Proceedings of the Technical Meeting on Emerging Applications of Radiation Processing, Vienna, Austria, 28–30 April 2003. [Google Scholar]


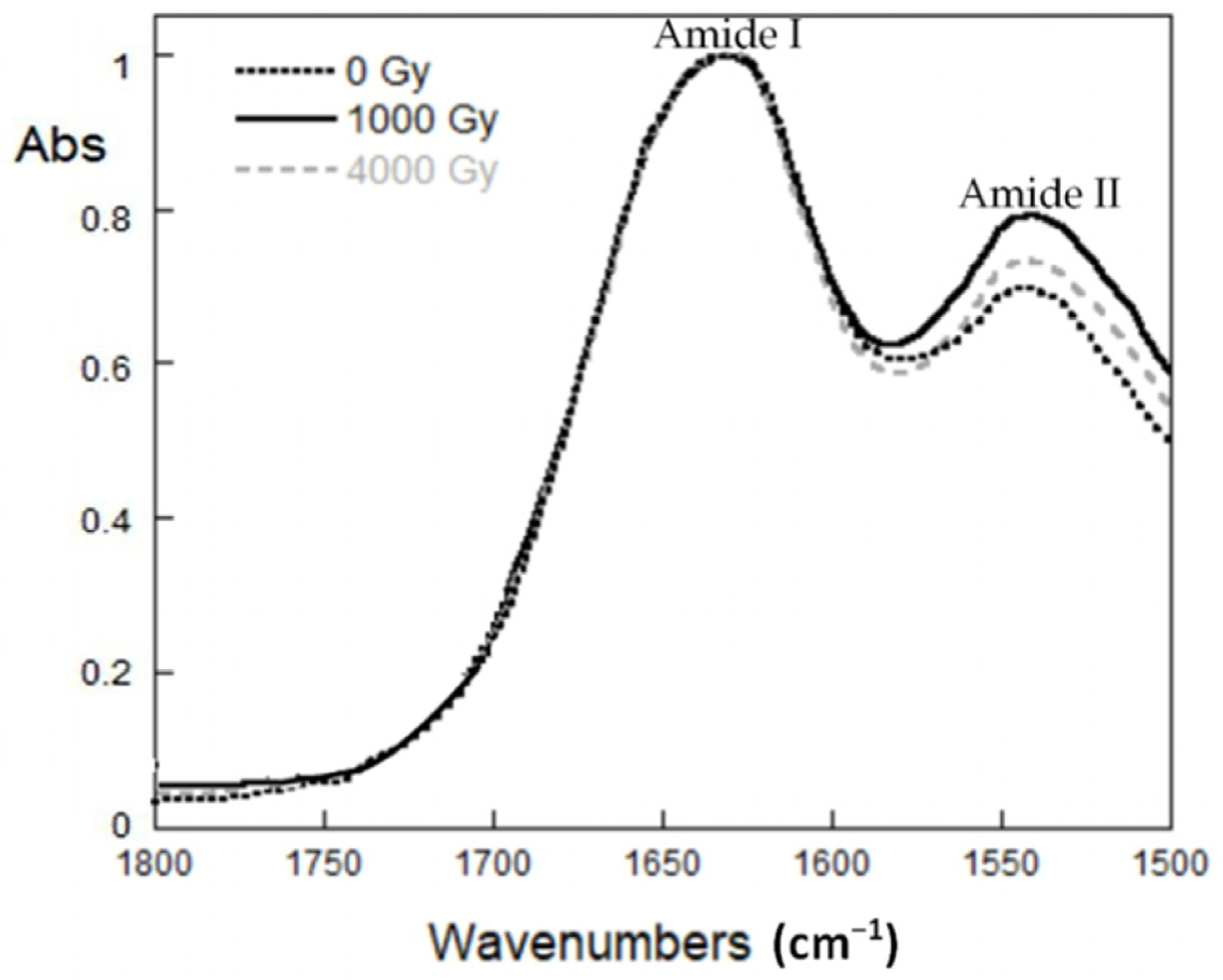
| X-rays Dose (Gy) | IAmideI/IAmideII |
|---|---|
| Non-irradiated (0 Gy) | 3.0 ± 0.1 |
| 350 | 2.8 ± 0.4 |
| 500 | 2.1 ± 0.3 |
| 1000 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| 2000 | 1.9 ± 0.4 |
| 4000 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vadrucci, M.; Cicero, C.; Mazzuca, C.; Severini, L.; Uccelletti, D.; Schifano, E.; Mercuri, F.; Zammit, U.; Orazi, N.; D’Amico, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Irradiation Treatment Effects on Ancient Parchment Samples. Heritage 2023, 6, 1308-1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6020072
Vadrucci M, Cicero C, Mazzuca C, Severini L, Uccelletti D, Schifano E, Mercuri F, Zammit U, Orazi N, D’Amico F, et al. Evaluation of the Irradiation Treatment Effects on Ancient Parchment Samples. Heritage. 2023; 6(2):1308-1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6020072
Chicago/Turabian StyleVadrucci, Monia, Cristina Cicero, Claudia Mazzuca, Leonardo Severini, Daniela Uccelletti, Emily Schifano, Fulvio Mercuri, Ugo Zammit, Noemi Orazi, Francesco D’Amico, and et al. 2023. "Evaluation of the Irradiation Treatment Effects on Ancient Parchment Samples" Heritage 6, no. 2: 1308-1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6020072
APA StyleVadrucci, M., Cicero, C., Mazzuca, C., Severini, L., Uccelletti, D., Schifano, E., Mercuri, F., Zammit, U., Orazi, N., D’Amico, F., & Parisse, P. (2023). Evaluation of the Irradiation Treatment Effects on Ancient Parchment Samples. Heritage, 6(2), 1308-1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage6020072









