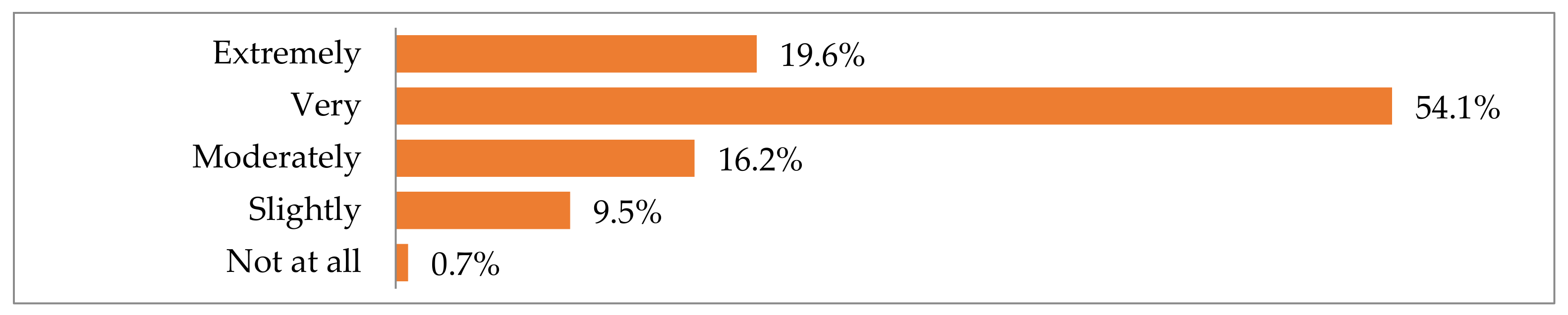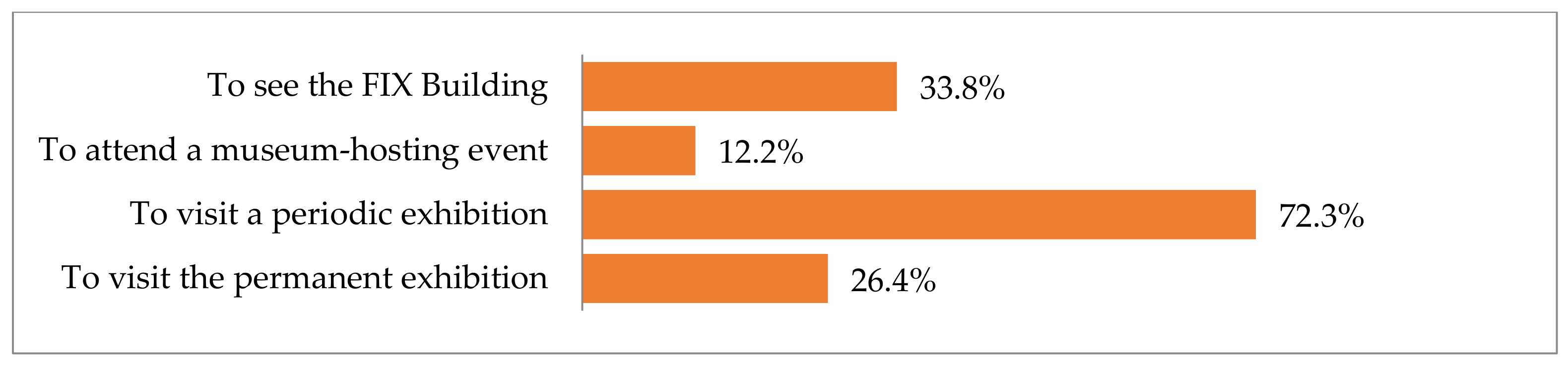Abstract
Adaptive reuse is a rapidly expanding frontier study area across the world. Adaptive reuse can have a significant influence in relation to contemporary trends in (peri-)urban sustainability, especially considering the past decades of the human-caused depletion of natural resources and environmental pollution. Adaptive reuse developments, which manage to incorporate a (scientifically) predefined set of conceptual theories, policy principles, and practical tools, as all the available data suggest, can achieve a good balance between invested capital, ecological conservation, the preservation of the cultural heritage, and sustainable urban regenerative renewal. This study focused on the recent FIX Brewery adaptive reuse project in Athens, Greece, as a means to establish the key public perception determinants of the adaptive reuse practice impacts on (peri-)urban sustainable development. Evidence for the relationships among five factors was provided through multiple linear regression analysis. The new empirical findings are likely to encourage concerned parties and stakeholders, and particularly regulatory entities, to pursue essential actions to set adaptive reuse at the core of urban and spatial masterplans, paving the way toward sustainable and circular cities.
1. Introduction
Numerous underutilized and abandoned assets have resulted from deindustrialization in Europe [1]. Many factories have been shut down, and many industrial sites have been deserted [2]. This tendency has also formed the commonly known “black holes” in the urban morphology of cities, packed with underutilized and vacant installations waiting to be reborn [3]. These abandoned industries are actually untapped sources that can help make cities more desirable places to live in from the perspectives of the environment, the economy, the sociocultural context, architecture, and tourism [4,5,6,7]. Industrial institutions served as the main driving force behind social economic growth at the start of the nineteenth century, acting as representations of neoliberalism and power [8,9]. A number of these industrial units have now been reduced to bare monuments, disrupting the city’s continuity and symbolizing abandonment and degradation [10,11].
The pressing issue of unplanned and unsustainable urban expansion and growth [12,13,14,15] has sparked attempts to revitalize these no-longer-in-use developments [16]. Protecting, preserving, and reusing past industrial installations contributes to the development of an increasingly condensed and functionally organized community system [17], in addition to supporting (peri-)urban regenerative initiatives [18]. The concept of urban renewal encompasses a wide range of interconnected perspectives, such as social, cultural, ethical, legal, technical, and environmental [19,20,21,22,23].
Therefore, it is not surprising that professionals and government officials have shown a keen interest in recent years in creating strategies for the adaptive reuse of the available stock of abandoned architecture, especially culturally significant industrial complexes [21,24,25,26]. In order to preserve historic industrial setups, both national and international organizations stress the importance of establishing intervention targets and intermutual functional, conversion, and reuse opportunities; mechanisms; and assessment criteria [27,28].
In terms of functional changes, adaptive reuse includes a variety of options, from residential to non-residential. In particular, properties that have been successfully converted into non-residential public-use premises in the cultural context, namely museums, libraries, and similar institutions, are recognized as a means of sustainable urban renewal. Beyond the extension of the structure’s lifecycle, the waste reduction, the reuse of energy, etc., significant direct and indirect economic and sociocultural benefits are brought to the community. This functional option helps preserve the character and legacy of certain eras; the city’s identity [29,30], history, and culture [31,32]; and the community’s ethos [33,34], so that they can be experienced and appreciated by both the present generation and the generations to come, whether as part of the community or just as visitors.
As long as it involves changing the functions of old and neglected developments to counterbalance sustainability concerns in terms beyond just the perceptions of the purpose and lifecycle of buildings (from design to demolition), the adaptive reuse of industrial properties of cultural significance—hereafter simply referred to as “adaptive reuse”—is a crucial enterprise. This work complies with Vardopoulos’s definition of adaptive reuse [35], namely the process of adapting an existing property to a new use, preserving as many aspects as feasible of the initial construction development while modernizing its efficiency to reflect present-day norms. Currently, few research studies have examined how visitors’ expectations and views of adaptive reuse projects are affected by new uses. Within this frame of reference, the scope of the current study was to identify the key determinants of public perceptions regarding the effects of adaptive reuse on (peri-)urban sustainability.
2. Review of the Adaptive Reuse Literature
One of the biggest resource consumers in the world is often considered to be the building industry [36,37]. Thus, efforts to improve its sustainability have arisen and are still growing through the adaptive reuse of existing properties [38]. As a consequence of the extensive and diverse solutions offered by the sustainability branch of the circular economy core concept [39,40], the notion of adaptive reuse has managed to garner a lot of attention [40]. The circular economy concept is described by a number of scientific publications (see [11,39,41,42,43,44,45,46]) deriving from the European Union’s Horizon 2020-funded CLIC Project (www.clicproject.eu) as a way to circularize the flow of energy, raw resources, cultural capital, and social capital.
According to the results of recent investigations, the number of both funded research projects (see OpenHeritage [47,48], ReMIND [49], and ROCK [50,51,52,53]) and scientific papers devoted to adaptive reuse research has advanced significantly in recent years, and more advancements are anticipated in the future [54].
In an early adaptive reuse study, Bullen (2007) [55] argued that there has been increasing recognition of adaptive reuse projects’ contribution to key aspects of sustainable development, with most owners of existing structures viewing adaptive reuse practices as a realistic and viable alternative to demolition. Four years later, Plevoets and Van Cleempoel (2011) [56] presented what was likely the very first comprehensive examination of adaptive reuse theoretical perspectives and practical techniques. They also discussed the complexities of adaptively reusing an architectural structure, namely the genius loci (see also [57]), and ultimately suggested that by placing emphasis and solely relying on the building’s economic efficacy—particularly in the case of properties not listed as monuments under protection—other factors, such as the social, cultural, historical, and architectural value, which support broader urban sustainable development concerns, are left unaddressed. Bullen and Love (2009) [58] evaluated a strategic plan and the consequential laws enacted to promote adaptive reuse practices and found that providing incentives is essential for the successful implementation of these kinds of urban community transformational redevelopment projects. This is further supported by other studies showing that compliance with policy and regulatory requirements, as well as state-of-the-art design principles and standards, are considered significant constraints associated with the successful development of adaptive reuse projects. As a result, efforts towards creating future regulations and government-led urban regeneration projects are required [59,60]. In a more recent analysis, Mohamed et al. (2017) [61] employed the so-called “three Es of Sustainable Development” to describe adaptive reuse practices. They also suggested that in adaptive reuse policy, intervening actions have become a necessity for addressing the “Equity” pillar. From a design point of view, Eyüce and Eyüce (2010) [62] observed that adaptive reuse project development fails to capture and provide an explicitly expressed design process as well as recognized and established methodologies that may serve as a fiducial mark; instead, they seem to be case-specific and require a special approach. This explains the profusion of case-study-based research methodologies [63,64,65,66,67,68]. Following this, Plevoets and Van Cleempoel (2014) [69] investigated adaptive reuse from the unique perspective of the interior architecture (see also [70]), considering how the interior design is anchored within the inner world of every building. On the other hand, in order to sway public perceptions towards forging a bond with the city and its past, Tsilika and Vardopoulos (2022) [8] emphasized the significance of the external faces of a building and the reasons for which an adaptive reuse strategy calls for their protection and preservation.
There is a considerable collection of research publications illuminating ways to create and/or apply adaptive reuse methodologies and structured conceptual systems, inter alia the adaptive reuse potential model [71], the design framework for adaptable buildings [72], adapSTAR [73], iconCUR [74], causal loop diagrams [75], the preliminary evaluation adaptability adaptation template [76], the triple-bottom-line model for optimizing retrofit practices [77], the learning buildings platform [78], and Maslow’s hierarchy of needs assessment framework [79]. Interestingly, there seems to be evidence of a strong positive connection between these strategies. [80,81]. Additionally, a rising number of scholarly journal articles on adaptive reuse adopting decision-making strategies based on various and complex sets of criteria (see [82,83]) are also available [84], such as the DELPHI model [85], the ANN-based method [86], the TOPSIS applications [87], the Macbeth methodology [88], the AHP technique [89], the DEMATEL approach [90], fuzzy sets [90,91], and combinations of the above [92].
Currently, published works have focused on modeling the deconstruction process and planning material reuse [93,94,95,96,97], constructing models of buildings’ lifecycle expectancy [98,99,100], rating the environmentally friendly characteristics of adaptive reuse developments [101,102], assessing infrastructure resilience [103,104], interface management [105], developing theories and applications for smart-city infrastructure and the internet of cultural things [19,106], measuring building stock vacancies [107], and establishing facility asset management kits [108]. The broader body of scientific literature also contains studies largely concerned with energy savings, thermal comfort, and modernization [109,110,111,112].
Other studies have focused on the key factors affecting the success of adaptive reuse developments [113], not to mention the suitability of the new use’s additional features and functions [114]. Previous research has also discussed the parties involved in adaptive reuse initiatives and how well they operate together [115].
Adaptive reuse conducted and supported by the community develops social networks while preserving a unique way of life, according to Yung Chan et al. (2014) [116]. Others emphasize the value of humanitarian adaptive reuse developments [43]. Glumac and Islam (2020) [117], for example, concurred that performance-based frameworks promoting adaptive reuse are enhanced by an end-user perspective. Others have illustrated the social supportive role that adaptive reuse may play in promoting individual well-being and quality of life [118,119], as described by Cortesi et al. [120] and others [121]. By examining the visitor perceptions and expectations, Md Ali et al. (2019) [122] considered the effects on the quality of the museum services after the adaptive reuse development of a culturally significant property into a museum. Other studies have examined how tourists (for research on memorable tourism experiences, see [123]) perceive adaptive reuse with reference to satisfaction and, hence, destination competitiveness [124,125,126]. Still, the critical aspect of visitor perceptions related to the actual usability of the property, in connection with the choice of use and the achievement of local sustainable development, appears to be an overlooked topic in the lively international discussion on adaptive reuse. Thus, the purpose of this research was to fill this gap by exploring and establishing key determining factors for public perceptions regarding the impacts of adaptive reuse developments on the sustainable development of local (peri-)urban settings.
3. Materials and Methods
Building upon the heretofore-reported literature overview, this study conducted an empirical analysis, commonly regarded as appropriate for conceptualizing and understanding contemporary phenomena [127,128]. Therefore, a case-specific survey was developed and conducted to determine the elements influencing visitor views with regards to the impact of the adaptive reuse development of a culturally significant metropolitan industrial facility on the overall (re-)development of the (peri-)urban context.
3.1. The Iconic FIX Brewery Building Case as a Point of Reference
In an attempt to offer a comprehensive and in-depth perspective on the variables involved in influencing visitor views of the impacts of adaptive reuse, the present research project laid emphasis on the recent adaptive reuse development of the long-unused FIX Brewery building in Athens, providing a space for the recently introduced Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art.
Johann Karl Fix established the brewing business bearing the well-known brand name “FIX” in Athens in 1865, and it quickly rose to prominence as one of the country’s leading breweries. Due to the rising demand, the brewing industry premises were moved close to the southeast Athenian neighborhood known as Koukaki, which at the time showed no signs of development. In the middle of the 1950s, the management of the FIX Brewery made the decision to completely renovate the industrial facility after taking into account the opportunities provided by Greece’s industrial restructuring.
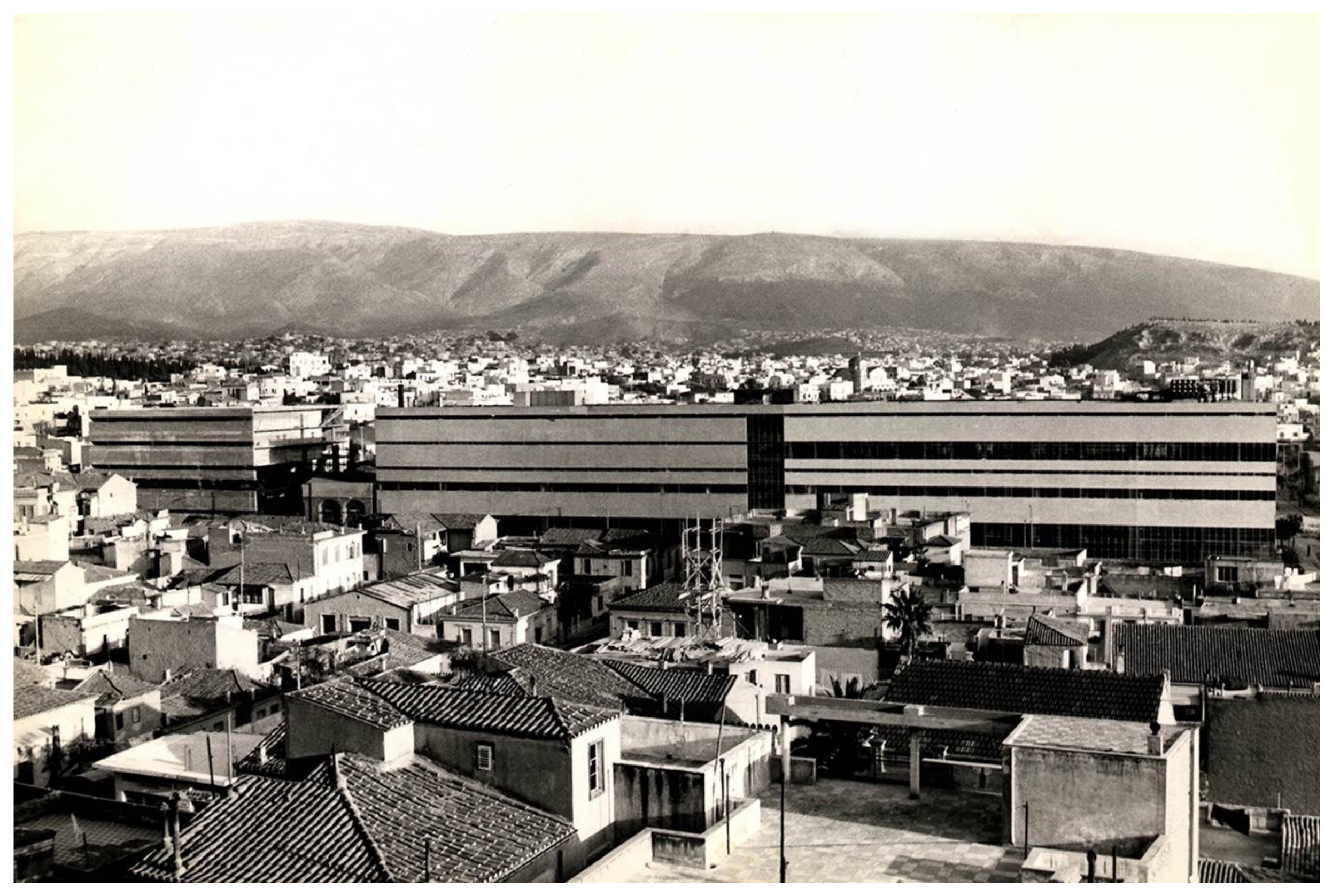
Takis Zenetos and Margaritis Apostolidis, two well-known modernist architects [129], were assigned the task. During their prolific endeavor to provide shelter for a complex and evolving manufacturing line, ensuring adaptability and flexibility to meet future needs (even beyond the merely industrial), their ground-breaking overall architectural design represented the fundamental ideas of the modernist movement [130]. It did not take long after their work was completed in 1961 for the building to emerge as an illustrious monument of modern architecture, in addition to a symbol of the advanced growth and development of the modern era (Figure 1). However, soon afterwards, the brewery had to relocate out of the heart of the city, and the famous structure was regrettably left empty.

Figure 1.
Complete overview of the Fix Brewery premises on Sygrou Avenue, Athens, circa 1960, architecturally designed by Zenetos and Apostolidis. Source: [131].
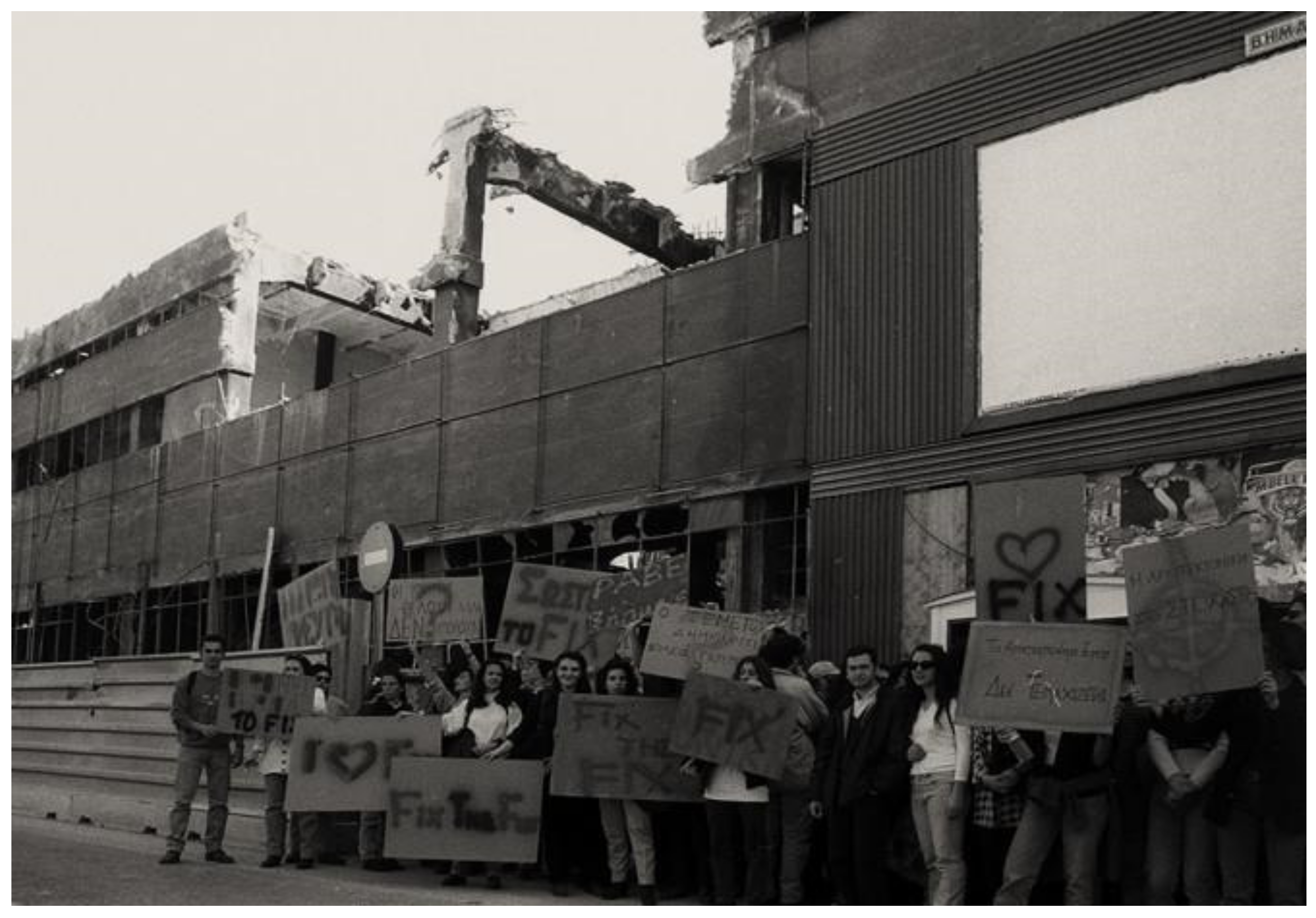
In 1994, a sizable portion of the northern section of the highly praised edifice was destroyed (Figure 2), amid harsh and intensifying criticism and denunciation [132].

Figure 2.
The historic FIX Brewery’s northern section demolished in March 1995 despite resistance demonstrations.
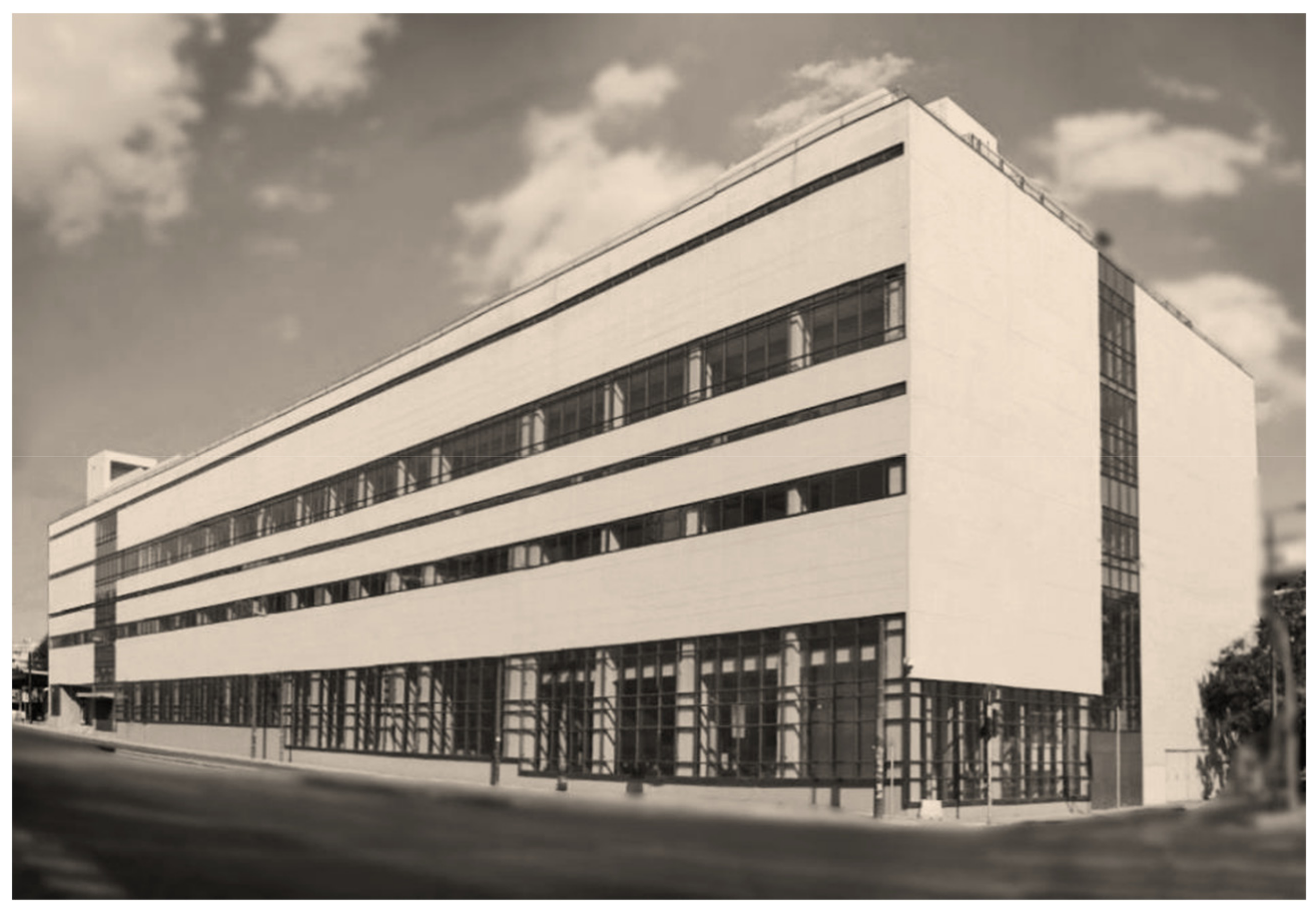
After a protracted period of primarily ministerial meetings and deliberations, it was ultimately decided to utilize the “amputated” and neglected structure to provide a space for the recently established Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art. The partnership formed by Mouzakis Architects and 3SK Architects was assigned the reuse project. The Hellenic-Government-sponsored project was finished in 2014 (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
World-famous FIX Brewery building as it currently stands, having been transformed to shelter the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art; present exterior core perspective on Sygrou Avenue side.
3.2. Survey
A two-part questionnaire was created for the purpose of the survey. The survey form was subdivided into two core parts: one to determine the respondents’ demographic characteristics, and the other to gather data on how the visitors perceived the impact of the adaptive reuse project on the nearby metropolitan environment, along with the contributing factors. Only closed-ended questions were posed to those who participated in the survey.
Unfortunately, the museum was closed during the investigation, since installation work for a permanent show was taking place. However, it was crucial for the study to consider the views of people whose visits (up until then) to the museum were verified as having taken place. The sample for this research project thus consisted of visitors who used ‘Instagram’ to publish a location-tagged picture (or picture set) from and of the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art, counted as evidence of a visit (during the period of time when the premises were safe to accept visitors). This approach turned the aforementioned obstacle into an opportunity. Owing to the fact that the ‘Instagram’ social networking service has security precautions that prohibit large-scale mail-outs, it is important to note that mass-messaging Instagram subscribers was incredibly difficult and time-consuming in this context. Although this research design of effectively utilizing the ‘Instagram’ app to assemble a set of data might be applicable across various research disciplines [133,134], to the author’s knowledge, no analysis has so far been published attempting to address the research gap identified herein.
As a pilot test, the survey was initially sent to just a few ‘Instagram’ app visitors (n = 21) prior to the full distribution (see [135,136]). The pilot resulted in a few modest alterations and revisions. The survey received a sum of N = 148 accountable responses over the course of its 7 subsequent months of operation. It is widely supported [19,137,138] that because the sample was thought to be typical of the visitors to the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art, it provided a solid foundation for examining the stated hypothesis. With a view to obtaining both descriptive and inferential statistics, data were analyzed statistically using SPSS (see also [139,140]).
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis
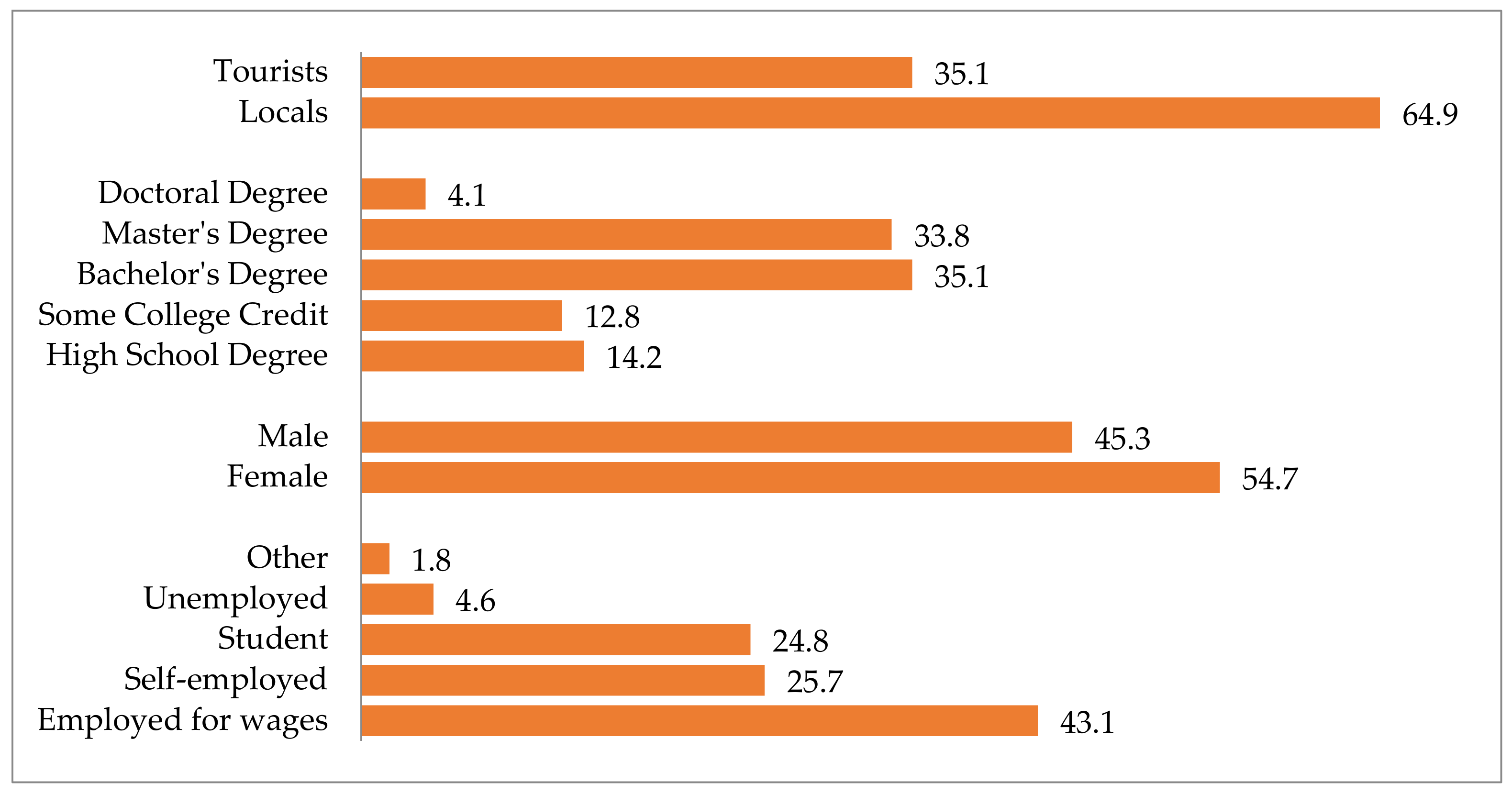
The sample predominantly contained young(er) graduates, which generally adheres to the representativeness of online surveys [141]. Of the 148 survey respondents, 54.7% were female. The sample included both tourists and locals (64.9%). The average age of the respondents was 31 years (minimum 18; median 30; maximum 62). The vast majority were university (post)graduate degree holders (73%). Regarding employment status, 66.9% had a paying job, 23.6% were students, and 5.4% were out of work (Figure 4). The respondents to the survey reported average monthly earnings of EUR 1191.8 (minimum 100; median 900; maximum 5000). The sample demographic profile analysis was supported by previous evidence from both official statistics as well as a vast body of published research [141,142].
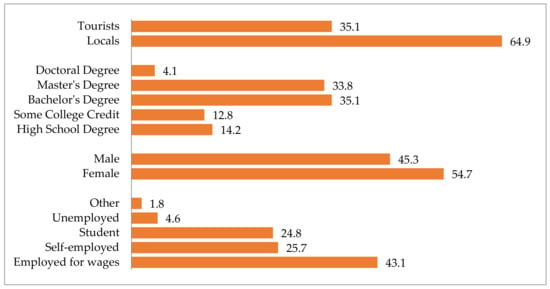
Figure 4.
Sample demographics.
In addition to being asked about their socioeconomic backgrounds, the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art visitors were asked about: (1) the museum, concerning the reason(s) for and impressions of their visit, their activities before and after the visit, etc.; and (2) their opinions on adaptive reuse and their familiarity with the FIX Brewery building, among other things. First, almost everyone who responded believed that museums are tourist attractions (Figure 5).
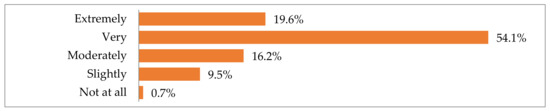
Figure 5.
How much respondents thought of museums as tourist attractions.
A significant percentage of individuals polled indicated that their visit to the museum was for either an exhibition or a cultural event of some kind. Additionally, a sizeable percentage indicated that the purpose of their visit was to view the architecturally significant adaptive reuse of the building (Figure 6).
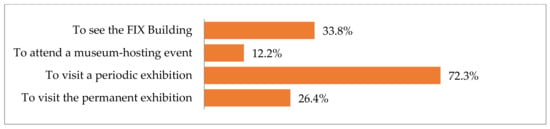
Figure 6.
Reasons for visiting the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art.
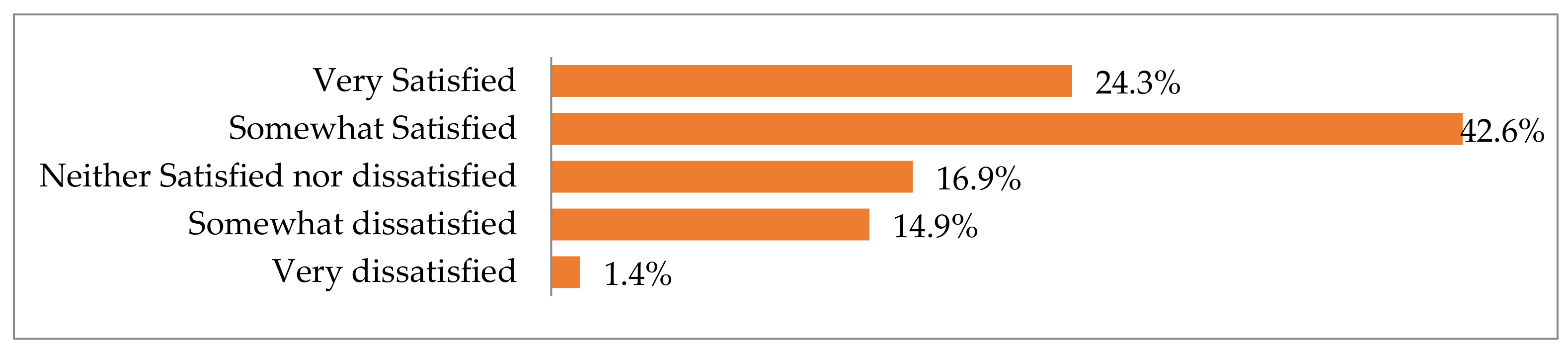
In view of the fact that the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art had only recently opened its doors to the public, it can be considered pleasantly surprising that, overall, as indicated in Figure 7, those questioned were quite satisfied with their visit to the museum’s facilities and exhibitions.
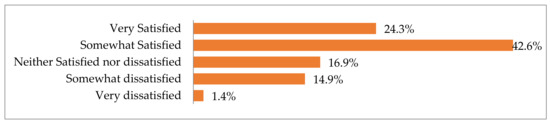
Figure 7.
How satisfied or unsatisfied museum visitors were with their visit.
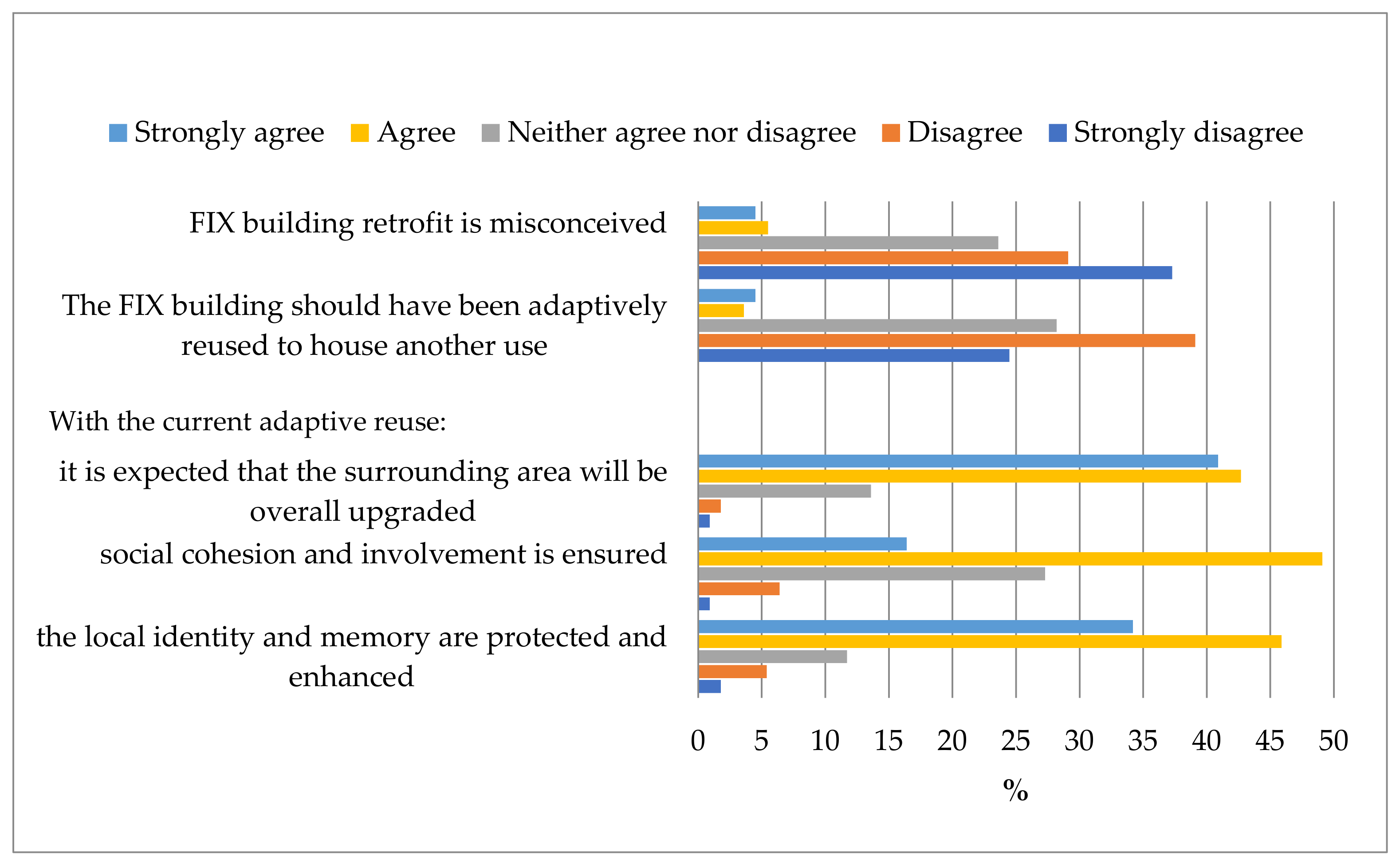
A sizable portion of Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art visitors (64.9%) said they combined their trip with a visit to a nearby cultural attraction or leisure facility. In general, respondents appeared to have some knowledge of the background of the FIX Brewery building, and several of those polled claimed that the FIX Brewery building adaptive reuse development was, to some extent, environmentally friendly and beneficial. Visitors believed that the transformation of the FIX Brewery building to make space for the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art was a good fit in terms of new use. Additionally, they favored preserving the urban character of the area and promoting social interaction (Figure 8).
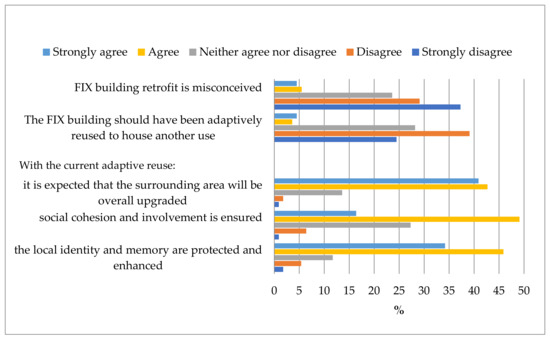
Figure 8.
Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art visitor views on the FIX Brewery transformation development.
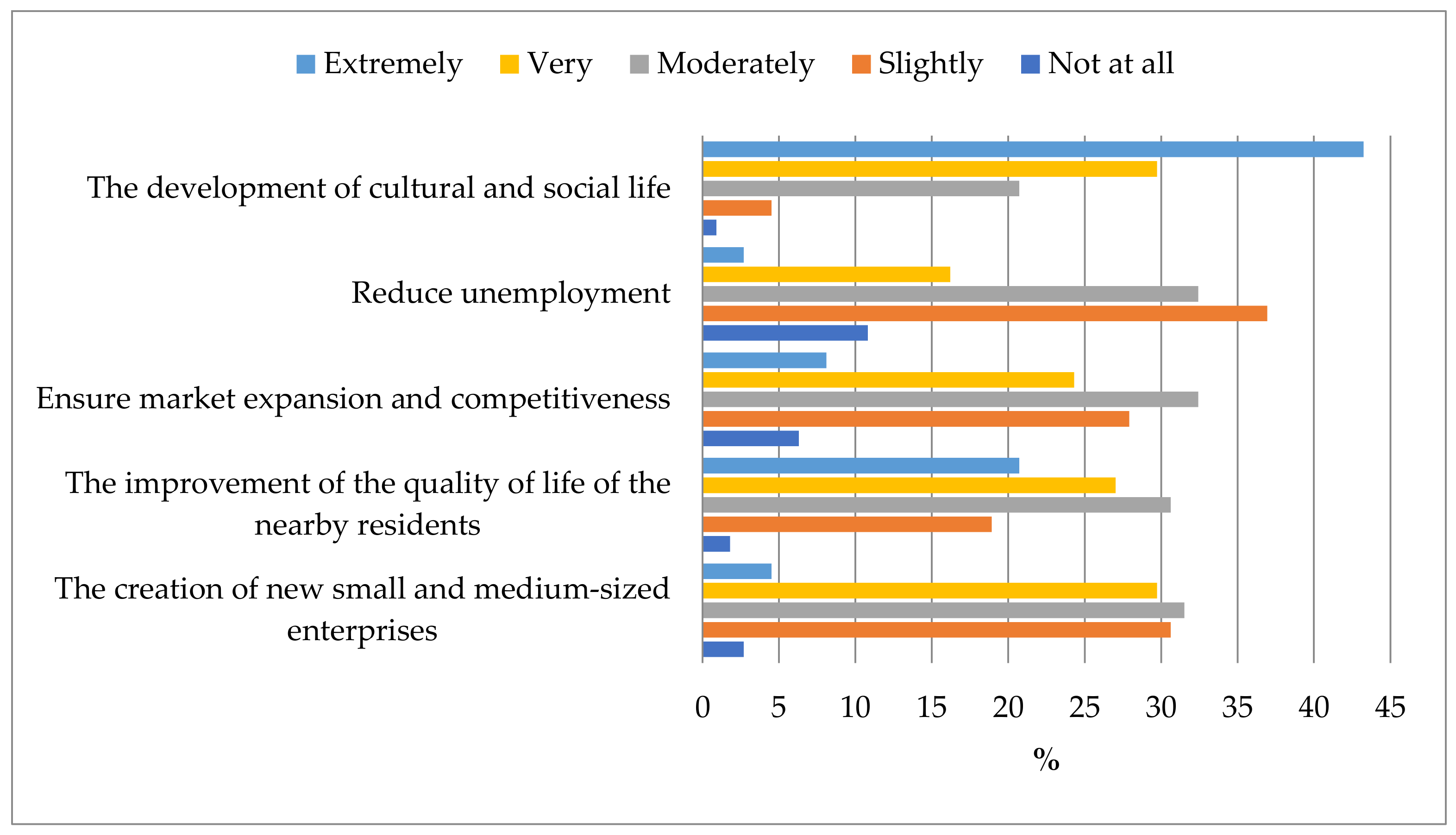
According to the respondents, the FIX Brewery building adaptive transformation development to provide shelter for the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art promoted the development of cultural and social life and improved the quality of life for locals (Figure 9).
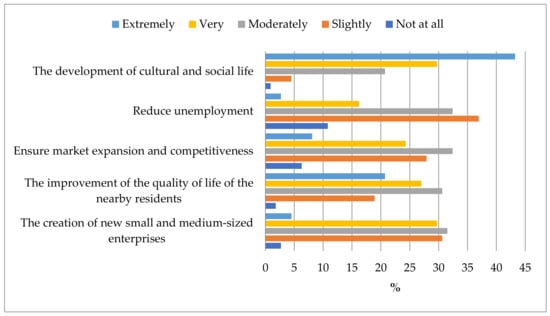
Figure 9.
Visitors’ opinions on the effects of the FIX Brewery building’s adaptive reuse as a facility for the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art on other variables.
4.2. Dependent Variable Creation
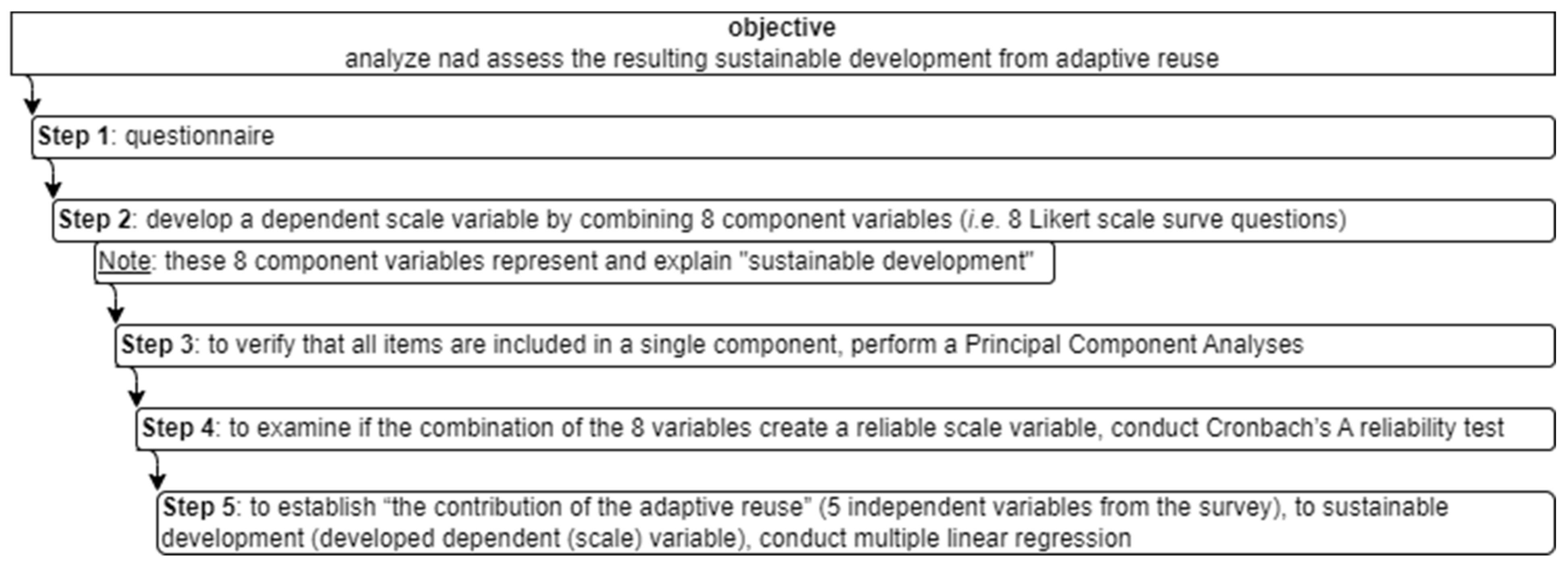
Given the lack of relevant research tools, as well as the need to analyze and assess the sustainable urban development resulting from the reuse of historic industrial buildings, the variable SDScale_MEAN, expressing respondents’ perceptions of “the contribution of the adaptive reuse of the FIX Brewery building to house the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art to sustainable development”, was developed (Figure 10) through a combination (using the mean value of each) of the eight variables presented in Table 1.

Figure 10.
Dependent scale variable creation methodological flow chart.

Table 1.
Component variables of the dependent variable.
Following the remarks of Cabrera-Nguyen [143] and of Worthington and Whittaker [144], the formulation of the questions, governed by the sustainability theory, relied mostly on relevant existing scales, indicators, and study findings, including: the place sustainability scale for measuring residents’ perceptions of the sustainability of a city by Taecharungroj et al. [145], the sustainability outlooks and the methodology of urban sustainability assessment [146], the international list of urban sustainability indicators [147], the composite indicator for sustainable local development by Salvati and Carlucci [148], the sustainable city model by Egger [149], the dimensions of the ecological city [150], the sustainability in the built environment holistic assessment kit [151], the factors affecting sustainable development [152], and the critical factors affecting local sustainable development through adapted reuse projects [90].
The answers to the questions were recorded on a five-point Likert scale (a well-established tool with international impact created by the American psychologist Rensis Likert), which was composed of specific speech expressions graded in a single direction, as follows: 1 = not at all; 2 = a little; 3 = enough; 4 = much; 5 = very much (see [120,153]).
It should be mentioned that there is intense debate about the nature of data generated by self-reported scales, a rather controversial area between ordinal and continuous variables [154,155,156,157]. Likert-type scales are usually used to measure attitude through a specific range of answers for a given question or statement [158]. Scales, in theory, belong to the ordinal type of measures, since the records are grouped into categories/orders that follow a natural or logically acceptable ascending (or descending) sequence. They lack, however, the feature of predetermined equal intervals between values. Nonetheless, contemporary scholars frequently presume that the aforementioned characteristic of equal intervals applies. Thus, although attitude and emotions cannot be measured with accuracy in either the social sciences or other scientific fields [159,160], it is generally accepted that data from self-reported scales can be considered as interval; continuous, especially when the scale takes at least five possible values [161], and can be used without reservations in parametric statistics [162,163,164].
In order to examine if the combination of the eight variables would create a reliable scale variable (i.e., the variable SDScale_MEAN), a Cronbach’s alpha reliability test was conducted. Prior to the reliability tests, a principal component analysis (PCA) [141,165] was performed in order to check that all items were included in a single component, as this is a parameter that the Cronbach’s alpha reliability test does not take into account. The PCA procedure revealed that the eight Likert items all represented the same dimension. The Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient was 0.879, although it would be lower if any of the eight elements were removed, allowing the variable SDScale_MEAN to be created.
4.3. Multiple Linear Regression
The contribution of the adaptive reuse of the FIX Brewery building to house the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art (i.e., independent variables TOURATRACTION, NEXTVISIT, SATISFA, HISTORYPERCEPTION, and NATIONALITY, see Table 2) to sustainable development (i.e., dependent variable SDScale_MEAN) was predicted using multiple linear regression. Partial regression plots and a plot of the studentized residuals against the predicted values both showed linearity. There was independence between the residuals, as assessed by the Durbin–Watson statistic of 2.126. Homoscedasticity was observed from the visual inspection of the studentized residuals versus the unstandardized predicted values, as well as from the results of a Breusch–Pagan test for heteroscedasticity. There was no evidence of multicollinearity, as assessed by tolerance values greater than 0.8. The assumption of normality was met, as assessed by a Q-Q Plot. The multiple linear regression statistically significantly predicted SDScale_MEAN, F(5.142) = 10.166, p < 0.0001, adj. R2 = 23.8%. The adj. R2 value, from an exploratory (and not explicative statistical) standpoint, was notably high (roughly 25%), showing that these results could be refined by a broader analysis, possibly searching for more variables “affecting” or “explaining” sustainable development. All five independent variables contributed statistically significantly to the prediction; regression coefficients and standard errors can be found in Table 2.

Table 2.
Multiple linear regression model.
According to Table 2, it was found that respondents who (a) considered museums in Greece to be tourist attractions, (b) combined their visit to the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art with a visit to another cultural recreational space, (c) were satisfied with their visit to the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art, (d) knew the history of the FIX Brewery building that houses the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art, and (e) had a non-Greek nationality had a more positive perception of the contribution of the adaptive reuse of the FIX Brewery building to house the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art to local sustainable development (i.e., a higher value of the dependent variable SDScale_MEAN).
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Adaptive reuse is an expanding area of frontier research around the globe. It can have a significant impact in relation to the present trends in urban sustainable development, following decades of human disdain and negligence in the form of resource depletion and environmental deterioration. Initiatives for adaptive reuse can achieve a superior balance between financial investment, environmental conservation, cultural heritage protection, and urban regeneration by incorporating specific methodologies and strategies.
This study focused on the case of the famous FIX Brewery, which was recently renovated and now houses the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art, in an effort to pinpoint the variables influencing public views of the impact of adaptive reuse on sustainable urban development. Evidence for connections between five components was provided through multiple linear regression analysis.
The majority of respondents agreed that cultural institutions such as museums throughout Greece should be viewed as tourist attractions. According to the regression model presented in Table 2, TOURATRACTION was a significant positive predictor of SDScale_MEAN in the model, at a 1% level of statistical significance. For every one-unit increase in TOURATRACTION, there was a predicted increase of 0.186 in SDScale_MEAN, with all other variables remaining constant. Or, in other words, for every increase of one point in TOURATRACTION, SDScale_MEAN was predicted to increase by 0.186 points. Therefore, the more this viewpoint is shared, the more likely it is that people will embrace the opinion that adaptive reuse creates urban opportunities. This result backs up Smith and Bugni’s [166] assertion that there are links between visitors’ perceptions, thoughts, feelings, and actions regarding architecture [124]. Additionally, this conclusion supports earlier research findings that suggested tensions between tradition and modernization within the complex relationships between tourism and cultural heritage [167].
NEXTVISIT was a significant positive predictor of SDScale_MEAN in the model, at a 10% level of statistical significance. This meant that for every one-unit increase in NEXTVISIT, there was a predicted increase of 0.229 in SDScale_MEAN, with all other variables kept constant. Since NEXTVISIT was binomially coded (0 = no, 1 = yes), the interpretation can be put more simply: for the respondents who combined their visit to the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art with a stop at a different cultural facility, the predicted SDScale_MEAN was 0.229 points higher than for those who did not combine their visit to the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art with a stop at a different cultural facility. The reason for this could be that culture serves as a flywheel for sustainability in urban areas rich in cultural resources. Furthermore, the importance of culture as a sustainable development factor has long been established, and this finding emphasizes the prospects of adaptive reuse processes for revitalizing European urban historical centers, as well as the significant implications of clustering in systems [168].
The empirical findings implied that expectations for local sustainable development resulting from the adaptive reuse process were significantly positively impacted by museum visitor pleasure. As a matter of fact, SATISFA was a positive predictor of SDScale_MEAN in the model, at a 1% level of statistical significance. Consequently, for every one-unit increase in SATISFA, there was a predicted increase of 0.242 in SDScale_MEAN, with all other variables held constant. Or, in other words, for every increase of one point on SATISFA, SDScale_MEAN was predicted to increase by 0.242 points. Several factors must be taken into account when using old urban industrial structures as museums in urban redevelopment plans. Visitor satisfaction is one of these factors. The antecedents of museum visitor experiences have not been studied by many researchers. While earlier research by Brida et al. [169] revealed no connections between the neighborhood and tourists’ satisfaction, Gao et al. [170] identified that authenticity has no major influence on visitor satisfaction. The potential links between urban destination and museum visitor satisfaction, however, have not been addressed in prior research. This study offers fresh perspectives, partially addresses the knowledge vacuum, and has significant field-wide ramifications.
Furthermore, the results of the current investigation showed that the more information a visitor had about the FIX Brewery building, the more likely it was that they believed that repurposing the FIX Brewery building to house the Hellenic National Museum of Contemporary Art improved the neighborhood in general. Old buildings, particularly unique and historic industrial buildings, i.e., lieux de mémoire (see [171]) with the characteristics of a valuable asset to be exploited, provide the opportunity for the sustainable development of a city, the preservation of local collective memory, and the transmission of local and national cultural identity to future generations through maintenance and reuse actions [64,172]. The findings of this study embrace the idea of “cultural capital” as a product of participation experiences and knowledge gained via cultural heritage traditions, customs, values, identity, and history, reflecting a community’s cultural and traditional resources, and consequently suggest that the adaptive reuse of such buildings automatically implies altering this “capital”.
Moreover, NATIONALITY was a significant negative predictor of SDScale_MEAN in the model presented in this study. For every one-unit increase in NATIONALITY, there was a predicted decrease of 0.439 in SDScale_MEAN, with all other variables held constant. Since NATIONALITY was binary coded (0 = non-Greek, 1 = Greek), the interpretation could be put more simply: for the Greek respondents, the predicted SDScale_MEAN was 0.439 points lower than for the non-Greek respondents. Adaptive reuse projects are critical factors in sustainable urban development, not only in terms of extending the lifespan of buildings, but also in terms of contributing to the transfer of cultural identity from one period to another and from one generation to the next. This transfer ultimately leads to cultural renaissance through urban regeneration [173].
Thus, if the evolution of a building from its previous use to a stage of adaptation is understood, then the reciprocal relationship is revealed, that is, buildings representing spatial landmarks of modern society’s emotional and collective memory [174] are actually part of a community’s culture and reflect the degree of culture that has been achieved at a particular point in time [175]. The longer the period between industrialization and deindustrialization, the more a building becomes a symbol and is identified with the cultural image of its community and place [176]. It is feasible for a community’s industrial building legacy to be preserved through adaptive reuse methods; however, without the transfer and/or preservation of its content in the new use, it will fail to contribute to urban cultural rebirth (see [177]).
According to earlier studies, decision-makers consider a number of variables when determining the new use of a structure. The scientific literature, it would seem, lacks a reference point for how users evaluate the final choice made once the adaptive reuse project is complete and the possibility for sustainability that has become apparent. The current study filled this gap by considering the decision-making behind the FIX Brewery building development. However, it could also help future designers and planners of adaptive reuse projects by encouraging them to add a set of decision evaluation criteria to the post-occupancy analyses and evaluations [178] and possibly even involve a creative backup plan that could be used if the evaluation were to be unsuccessful.
This study closes by suggesting that adaptive reuse developments can contribute markedly to local (peri-)urban sustainable development and directly or indirectly positively influence the local societal structure by enhancing the residents’ quality of life, empowering the cultural component, and turning the neighborhood into a well-liked tourist destination.
The promising empirical data obtained from the current research should allow the agencies responsible to take all the required actions to place adaptive reuse at the center of the city’s sustainable development plans. The findings of this study may, in general, be beneficial for important players pursuing the sustainability perspective in urban development. In addition, while the findings of the current work were based on a research methodology applied to a particular case study, a similar methodology may be used in a wider context, leading to more generally applicable findings and interpretations.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study. The survey was anonymous, gathering no sensitive data, and the participants provided consent to use their answers for research.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are contained within this manuscript for reproducibility purposes.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank all the people who directly or indirectly helped me in carrying out this study. I would specifically like to acknowledge Xanthos Pattichis for his support in advanced statistics.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Vardopoulos, I. Industrial Building Adaptive Reuse for Museum. Factors Affecting Visitors’ Perceptions of the Sustainable Urban Development Potential. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, M.; D’Alpaos, C.; Oppio, A.; D’Alpaos, C.; Oppio, A. Ranking of Adaptive Reuse Strategies for Abandoned Industrial Heritage in Vulnerable Contexts: A Multiple Criteria Decision Aiding Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzarri, C.; Sangiorgio, V.; Fatiguso, F.; Calderazzi, A. A Holistic Approach for the Adaptive Reuse Project Selection: The Case of the Former Enel Power Station in Bari. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. Applied Urban Sustainability: Mixed Methods Research on Adaptive Reuse Practices: Studying the FIX Case. Ph.D. Thesis, Harokopio University, Kallithea, Greece, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Q.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Y. Critical Success Factors for Safety Program Implementation of Regeneration of Abandoned Industrial Building Projects in China: A Fuzzy DEMATEL Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, M.; Drobnjak, B.; Kuletin Ćulafić, I. The Possibilities of Preservation, Regeneration and Presentation of Industrial Heritage: The Case of Old Mint “A.D.” on Belgrade Riverfront. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cenci, J.; Becue, V.; Koutra, S. The Overview of the Conservation and Renewal of the Industrial Belgian Heritage as a Vector for Cultural Regeneration. Information 2021, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilika, E.; Vardopoulos, I. The FIX-up Mix-up; Undue Facadism or Adaptive Reuse? Examining the Former FIX Brewery Transformation into the National Museum of Contemporary Art in Athens. ArchNet-IJAR 2022, 16, 688–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săgeată, R.; Mitrică, B.; Mocanu, I. Centralized Industrialization in the Memory of Places. Case Studies of Romanian Cities. Societies 2021, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-E.; Lee, J.-R. The Impact of Historic Building Preservation in Urban Economics: Focusing on Accommodation Prices in Jeonju Hanok Village, South Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Saleh, R. The Adaptive Reuse of Cultural Heritage in European Circular City Plans: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, S.; Vardopoulos, I.; Salvati, L. A Tale of a Shrinking City? Exploring the Complex Interplay of Socio-Demographic Dynamics in the Recent Development of Attica, Greece. Cities 2023, 132, 104089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciommi, M.; Egidi, G.; Vardopoulos, I.; Chelli, F.M.; Salvati, L. Toward a ‘Migrant Trap’? Local Development, Urban Sustainability, Sociodemographic Inequalities, and the Economic Decline in a Mediterranean Metropolis. Soc. Sci. 2022, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, L.S.; Ciommi, M.; Vardopoulos, I.; Nosova, B.; Salvati, L. The Medium-Term Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Population Dynamics: The Case of Italy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, Y.; Salvati, L.; Vardopoulos, I. Long-Term Planning and Development for Urban and Regional Inclusion, Safety, Resilience, and Sustainability. Insights from Singapore. Reg. Peripher. 2022, 14, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, K.; Papamattheakis, G.; Tryfonopoulos, S. The Fate of Unbaptized Buildings: A Theology for Preservation. In AMPS Proceedings Series 15, Proceedings of the Tangible—Intangible Heritage(s)—Design, Social and Cultural Critiques on the Past, the Present and the Future, London, UK, 13–15 June 2018; Issue 2; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sowińska-Heim, J. Adaptive Reuse of Architectural Heritage and Its Role in the Post-Disaster Reconstruction of Urban Identity: Post-Communist Łódź. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-H.; Huang, X.; Fu, G.; Chen, J.-T.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.-H.; Tzeng, G.-H. Evaluating the Sustainability of Urban Renewal Projects Based on a Model of Hybrid Multiple-Attribute Decision-Making. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Stamopoulos, C.; Chatzithanasis, G.; Michalakelis, C.; Giannouli, P.; Pastrapa, E. Considering Urban Development Paths and Processes on Account of Adaptive Reuse Projects. Buildings 2020, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, K.; Wei, S.; Ismail, M.; Kam, K. Sustainable Building Assessment of Colonial Shophouses after Adaptive Reuse in Kuala Lumpur. Buildings 2017, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medici, S.; De Toro, P.; Nocca, F. Cultural Heritage and Sustainable Development: Impact Assessment of Two Adaptive Reuse Projects in Siracusa, Sicily. Sustainability 2019, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karametou, P.; Mitoula, R.; Papavasileiou, A. The Social Impact of Ellinikon Renovation Project: The Athenians Citizen’s Perception. In Proceedings of the CHANGING CITIES V: Spatial, Design, Landscape, Heritage and Socio-Economic Dimensions, Corfu, Greece, 20–25 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Skayannis, P. Mega Infrastructure Projects in Greece after Its Accession to the EU (1981–2021). Reg. Peripher. 2021, 12, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, Q.; Guo, H.; Li, H. Quantifying the Core Driving Force for the Sustainable Redevelopment of Industrial Heritage: Implications for Urban Renewal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48097–48111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Shen, L.; Langston, C. A Fuzzy Approach for Adaptive Reuse Selection of Industrial Buildings in Hong Kong. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2014, 18, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Conservation and Adaptive Reuse of Industrial Heritage in Shanghai. Front. Archit. Civ. Eng. China 2007, 1, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ODASA Design Guidance Note: Adaptive Re-Use. Re-Using Existing Buildings for New Functions Has Many Sustainable, Cultural, Economic and Placemaking Advantages. 2014. Available online: https://cdn.environment.sa.gov.au/environment/docs/her-conservation-adaptive-reuse-guide-odasa.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Wang, M.; Yang, J. Sustainable Renewal of Historical Urban Areas: A Demand–Potential–Constraint Model for Identifying the Renewal Type of Residential Buildings. Buildings 2022, 12, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussaa, D. Urban Regeneration and the Search for Identity in Historic Cities. Sustainability 2017, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, J.; Mitoula, R. The Phenomenon of Globalization and Its Urban Expressions—Globalization and the Physiognomy of Cities. In The Identities of the New Urban Reality, Articulations Urban Forms and Social Fate; Ecole Nationale Supérieure d’Architecture de Paris La Villette, Università Degli Studi di Napoli Federico II: Naples, Italy, 2005; pp. 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanou, J.; Mitoula, R. Urban Planning in Hermoupolis—A New View on the Conservation and Enhancement of Historic Settlements. Hous. Build. Res. Cent. Int. J. 2005, 1, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Vythoulka, A.; Delegou, E.T.; Caradimas, C.; Moropoulou, A. Protection and Revealing of Traditional Settlements and Cultural Assets, as a Tool for Sustainable Development: The Case of Kythera Island in Greece. Land 2021, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, S.; De Vita, M.; De Berardinis, P.; Palmero, L.; Risdonne, A. Designing the Sustainable Adaptive Reuse of Industrial Heritage to Enhance the Local Context. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, F. Commoning Adaptive Heritage Reuse as a Driver of Social Innovation: Naples and the Scugnizzo Liberato Case Study. Sustainability 2021, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Theodoropoulou, E. Does the New ‘FIX’ Fit? Adaptive Building Reuse Affecting Local Sustainable Development: Preliminary Results. In Proceedings of the The IAFOR Conference on Heritage & the City (HCNY2018), New York, NY, USA, 7–9 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Hao, J. A Dissipative Structure Theory-Based Investigation of a Construction and Demolition Waste Minimization System in China. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 65, 514–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Webber, R.; Kalutara, P.; Browne, W.; Pienaar, J. Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: A Mini-Review. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2022, 40, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Theodoropoulou, E. Adaptive Reuse: An Essential Circular Economy Concept. Urban. Inf. 2020, 289, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ikiz Kaya, D.; Pintossi, N.; Dane, G. An Empirical Analysis of Driving Factors and Policy Enablers of Heritage Adaptive Reuse within the Circular Economy Framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marika, G.; Beatrice, M.; Francesca, A. Adaptive Reuse and Sustainability Protocols in Italy: Relationship with Circular Economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acri, M.; Dobričić, S.; Debevec, M. Regenerating the Historic Urban Landscape through Circular Bottom-Up Actions: The Urban Seeding Process in Rijeka. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosone, M.; De Toro, P.; Fusco Girard, L.; Gravagnuolo, A.; Iodice, S. Indicators for Ex-Post Evaluation of Cultural Heritage Adaptive Reuse Impacts in the Perspective of the Circular Economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco Girard, L.; Vecco, M. The “Intrinsic Value” of Cultural Heritage as Driver for Circular Human-Centered Adaptive Reuse. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravagnuolo, A.; Micheletti, S.; Bosone, M. A Participatory Approach for “Circular” Adaptive Reuse of Cultural Heritage. Building a Heritage Community in Salerno, Italy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravagnuolo, A.; Varotto, M. Terraced Landscapes Regeneration in the Perspective of the Circular Economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojev, J.; Gustafsson, C. Smart Specialisation Strategies for Elevating Integration of Cultural Heritage into Circular Economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemző, H.; Mosquera, J.; Polyák, L.; Hayes, L. Flexibility and Adaptation: Creating a Strategy for Resilience. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieg, H.A. Social Innovation in Sustainable Urban Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, F. The Adaptive Reuse of Neglected Buildings. In Contested Spaces, Concerted Projects—Designs for Vulnerable Memories; Colombo, C., Leveratto, J., Eds.; Lettera Ventidue: Siracuse, Italy, 2022; pp. 68–85. ISBN 9788862424837. [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger, S.O.M.; Longo, D.; Roversi, R. Data Evidence-Based Transformative Actions in Historic Urban Context—The Bologna University Area Case Study. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1448–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, G.; Borgers, A.; Kaya, D.I.; Feng, T. Visitor Flows at a Large-Scale Cultural Event: GPS Tracking at Dutch Design Week. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, G.; Borgers, A.; Feng, T. Subjective Immediate Experiences during Large-Scale Cultural Events in Cities: A Geotagging Experiment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijs-Perrée, M.; Dane, G.; van den Berg, P. Analyzing the Relationships between Citizens’ Emotions and Their Momentary Satisfaction in Urban Public Spaces. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owojori, O.; Okoro, C.; Chileshe, N. Current Status and Emerging Trends on the Adaptive Reuse of Buildings: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, P.A. Adaptive Reuse and Sustainability of Commercial Buildings. Facilities 2007, 25, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevoets, B.; Van Cleempoel, K. Adaptive Reuse as a Strategy towards Conservation of Cultural Heritage: A Literature Review. Struct. Repairs Maint. Herit. Archit. 2011, 118, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanchuk, A.; Gafurova, S.; Latypova, M. «Genius Loci» as a Resource for the Development of Historical Areas of the City. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 890, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, P.A.; Love, P.E.D. Residential Regeneration and Adaptive Reuse: Learning from the Experiences of Los Angeles. Struct. Surv. 2009, 27, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejos, S.; Langston, C.; Chan, E.H.W.; Chew, M.Y.L. Governance of Heritage Buildings: Australian Regulatory Barriers to Adaptive Reuse. Build. Res. Inf. 2016, 44, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, E.H.K.; Langston, C.; Chan, E.H.W. Adaptive Reuse of Traditional Chinese Shophouses in Government-Led Urban Renewal Projects in Hong Kong. Cities 2014, 39, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Boyle, R.; Yang, A.Y.; Tangari, J. Adaptive Reuse: A Review and Analysis of Its Relationship to the 3 Es of Sustainability. Facilities 2017, 35, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyüce, Ö.; Eyüce, A. Design Education for Adaptive Reuse. Archnet-IJAR 2010, 4, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Pourzargar, M. Posto-Corona Visioning for Sustainable Adaptive Reuse of Kahrzak Sugar Factory. Naqshejahan 2022, 11, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mitoula, R.; Theodoropoulou, E.; Karali, B. Sustainable Development in the City of Volos through Reuse of Industrial Buildings. Sustain. Dev. Cult. Tradit. J. 2013, 2, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamhawi, M.; Mubaideen, S.; Mahamid, B. Industrial Heritage: Towards a Sustainable Adaptive Reuse of Wheat Milling Heritage Buildings in Jordan. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Knippenberg, K.; Boonstra, B. Co-Evolutionary Heritage Reuse: A European Multiple Case Study Perspective. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorescu, I.; Dumitrică, C.; Dumitrașcu, M.; Mitrică, B.; Dumitrașcu, C. Urban Development and the (Re)Use of the Communist-Built Industrial and Agricultural Sites after 1990. The Showcase of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region. Land 2021, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misirlisoy, D.; Günçe, K. A Critical Look to the Adaptive Reuse of Traditional Urban Houses in the Walled City of Nicosia. J. Archit. Conserv. 2016, 22, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevoets, B.; Van Cleempoel, K. Aemulatio and the Interior Approach of Adaptive Reuse. Interiors 2014, 5, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celadyn, M. Interior Architectural Design for Adaptive Reuse in Application of Environmental Sustainability Principles. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, C.; Shen, L.-Y. Application of the Adaptive Reuse Potential Model in Hong Kong: A Case Study of Lui Seng Chun. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2007, 11, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahaim, F.; Alfaris, A.; Leifer, D. Towards Changeability: The Adaptable Buildings Design (ABD) Framework. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference of Arab Society for Computer Aided Architectural Design, Fès, Morocco, 19 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Conejos, S.; Langston, C.; Smith, J. AdaptSTAR Model: A Climate-Friendly Strategy to Promote Built Environment Sustainability. Habitat Int. 2013, 37, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, C.; Smith, J. Modelling Property Management Decisions Using ‘IconCUR. ’ Autom. Constr. 2012, 22, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, J.; Sassi, P.; Naim, M.; Lark, R. Adaptable Buildings: A Systems Approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2013, 7, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.J. The Preliminary Assessment of Adaptation Potential in Existing Office Buildings. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2014, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.J.; Jofeh, C.G.H. Portfolio Retrofit Evaluation: A Methodology for Optimizing a Large Number of Building Retrofits to Achieve Triple-Bottom-Line Objectives. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.E. The Learning Buildings Framework for Quantifying Building Adaptability. In Proceedings of the ASCE Architectural Engineering Institute Conference, Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 11–13 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Heath, T.; Guo, S. From Maslow to Architectural Spaces: The Assessment of Reusing Old Industrial Buildings. Buildings 2022, 12, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, C. Validation of the Adaptive Reuse Potential (ARP) Model Using IconCUR. Facilities 2012, 30, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejos, S.; Langston, C.; Smith, J. Enhancing Sustainability through Designing for Adaptive Reuse from the Outset: A Comparison of Adaptstar and Adaptive Reuse Potential (ARP) Models. Facilities 2015, 33, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. Multi-Criteria Analysis for Energy Independence from Renewable Energy Sources Case Study Zakynthos Island, Greece. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2017, 8, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorpas, A.A.; Phinikettou, V.; Voukkali, I. Proposed Rehabilitation Method of Uncontrolled Landfills in Insular Communities Through Multi-Criteria Analysis Decision Tool. In Phytoremediation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 365–383. [Google Scholar]
- Aigwi, I.E.; Egbelakin, T.; Ingham, J.; Phipps, R.; Rotimi, J.; Filippova, O. A Performance-Based Framework to Prioritise Underutilised Historical Buildings for Adaptive Reuse Interventions in New Zealand. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Chiu, Y.H.; Tsai, L. Evaluating the Adaptive Reuse of Historic Buildings through Multicriteria Decision-Making. Habitat Int. 2018, 81, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Juan, Y.-K. ANN-Based Decision Model for the Reuse of Vacant Buildings in Urban Areas. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2016, 20, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Shen, L.; Langston, C.; Liu, Y. Construction Project Selection Using Fuzzy TOPSIS Approach. J. Model. Manag. 2010, 5, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abastante, F.; Lami, I.M.; Mecca, B. How to Revitalise a Historic District: A Stakeholders-Oriented Assessment Framework of Adaptive Reuse. In Values and Functions for Future Cities. Green Energy and Technology; Mondini, G., Oppio, A., Stanghellini, S., Bottero, M., Abastante, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Della Spina, L. Cultural Heritage: A Hybrid Framework for Ranking Adaptive Reuse Strategies. Buildings 2021, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. Critical Sustainable Development Factors in the Adaptive Reuse of Urban Industrial Buildings. A Fuzzy DEMATEL Approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, D.M.; Milošević, M.R.; Simjanović, D.J. Implementation of Adjusted Fuzzy AHP Method in the Assessment for Reuse of Industrial Buildings. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Tsilika, E.; Sarantakou, E.; Zorpas, A.; Salvati, L.; Tsartas, P. An Integrated SWOT-PESTLE-AHP Model Assessing Sustainability in Adaptive Reuse Projects. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Bilal, M.; Ajayi, S.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Bello, S.A. Waste Minimisation through Deconstruction: A BIM Based Deconstructability Assessment Score (BIM-DAS). Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Rausch, C.; Haas, C. “Deconstruction Programming for Adaptive Reuse of Buildings. Autom. Constr. 2019, 107, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Rausch, C.; Haas, C.; Saari, R. A Selective Disassembly Multi-Objective Optimization Approach for Adaptive Reuse of Building Components. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Haas, C. A Novel Selective Disassembly Sequence Planning Method for Adaptive Reuse of Buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, D.; Tajani, F. Valorization of Cultural Heritage and Land Take Reduction: An Urban Compensation Model for the Replacement of Unsuitable Buildings in an Italian UNESCO Site. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 57, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksözen, M.; Hassler, U.; Rivallain, M.; Kohler, N. Mortality Analysis of an Urban Building Stock. Build. Res. Inf. 2017, 45, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erik Bradley, P.; Kohler, N. Methodology for the Survival Analysis of Urban Building Stocks. Build. Res. Inf. 2007, 35, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G. Factors Influencing the Service Lifespan of Buildings: An Improved Hedonic Model. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschmann, E.E.; Gabriel, J.N. Urban Sustainability and the LEED Rating System: Case Studies on the Role of Regional Characteristics and Adaptive Reuse in Green Building in Denver and Boulder, Colorado. Geogr. J. 2013, 179, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewiyana, E.; Ibrahim, N.; Hajar, N.H. The Green Aspects of Adaptive Reuse of Hotel Penaga. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 222, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.J.; Osmond, P. Building Resilience in Urban Settlements. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2018, 36, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, D.O.; Arslan, T.V.; Durak, S. Adaptive Reuse as a Strategy toward Urban Resilience. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 5, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eray, E.; Sanchez, B.; Haas, C. Usage of Interface Management System in Adaptive Reuse of Buildings. Buildings 2019, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, H.P. Adaptive Reuse of Cultural Heritage Elements and Fragments in Public Spaces: The Internet of Cultural Things and Applications as Infrastructures for Learning in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems (SITIS), Jaipur, India, 4–7 December 2017; pp. 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, G.; Soebarto, V.; Zuo, J. Vacancy Visual Analytics Method: Evaluating Adaptive Reuse as an Urban Regeneration Strategy through Understanding Vacancy. Cities 2021, 115, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, M.B.; Hassanain, M.A. A Framework Model for AEC/FM Knowledge in Adaptive Reuse Projects. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2022, 20, 624–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani Mehr, S.; Wilkinson, S.J. Technical Issues and Energy Efficient Adaptive Reuse of Heritage Listed City Halls in Queensland Australia. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2018, 36, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksamija, A. Regenerative Design and Adaptive Reuse of Existing Commercial Buildings for Net-Zero Energy Use. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breçani, R.; Dervishi, S. Thermal and Energy Performance Evaluation of Underground Bunkers: An Adaptive Reuse Approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, Y.S.; Shalaby, H.A.; Mohamed, M.A.A. Adaptive Reuse Decisions for Historic Buildings in Relation to Energy Efficiency and Thermal Comfort—Cairo Citadel, a Case Study from Egypt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Shuai, C.; Wang, T. Critical Success Factors (CSFs) for the Adaptive Reuse of Industrial Buildings in Hong Kong. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günçe, K.; Misirlisoy, D. Assessment of Adaptive Reuse Practices through User Experiences: Traditional Houses in Thewalled City of Nicosia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigwi, I.E.; Phipps, R.; Ingham, J.; Filippova, O. Characterisation of Adaptive Reuse Stakeholders and the Effectiveness of Collaborative Rationality towards Building Resilient Urban Areas. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2021, 34, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.W.; Xu, Y. Community-Initiated Adaptive Reuse of Historic Buildings and Sustainable Development in the Inner City of Shanghai. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2014, 140, 05014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glumac, B.; Islam, N. Housing Preferences for Adaptive Re-Use of Office and Industrial Buildings: Demand Side. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, M.S.; Kim, K.; Ramirez, G.C.; Orejuela, A.R.; Park, J. Improving Well-Being via Adaptive Reuse: Transformative Repurposed Service Organizations. Serv. Ind. J. 2021, 41, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, L.; Cassalia, G.; Calabrò, F. Economic Feasibility of a Project for the Reuse of the Old Hospital of Nicotera as a Center for Eating Disorders and for the Enhancement of the Mediterranean Diet. In Proceedings of the International Symposium New Metropolian Perspectives—Post COVID Dynamics: Green and Digital Transition, between Metropolitan and Return to Villages Perspectives, Reggio Calabria, Italy, 24–26 May 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 2347–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Cortesi, A.; Vardopoulos, I.; Salvati, L. A Partial Least Squares Analysis of the Perceived Impact of Sustainable Real Estate Design upon Wellbeing. Urban Sci. 2022, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chymis, A. Wellbeing, Productivity and Competitiveness at a Regional Level: The Role of Institutions. Reg. Peripher. 2019, 8, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Ali, Z.; Zawawi, R.; Myeda, N.E.; Mohamad, N. Adaptive Reuse of Historical Buildings. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2019, 37, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I.A.; Fayyad, S.; Ammar, S.; Abdulaziz, T.A.; Mahmoud, S.W. Adaptive Reuse of Heritage Houses and Hotel Conative Loyalty: Digital Technology as a Moderator and Memorable Tourism and Hospitality Experience as a Mediator. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I.; Theodoropoulou, E. Theoretical Considerations and Pilot Findings on the Adaptive Reuse Potential for Tourism and Sustainable Urban Development. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Scientific Conference TOURMAN 2019, Thessaloniki, Greece, 24–27 October 2019; International Hellenic University: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2019; pp. 374–376. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zang, T.; Zhou, T.; Ikebe, K. Historic Conservation and Tourism Economy: Challenges Facing Adaptive Reuse of Historic Conservation Areas in Chengdu, China. Conservation 2022, 2, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manola, M. Contribution of the Venetian Monuments of Rhodes to Cultural Tourism and the Local Development of the Island. Open J. Res. Econ. 2022, 5, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R. Case Study Research: Design and Methods; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781452242569. [Google Scholar]
- Ragazou, K.; Passas, I.; Garefalakis, A.; Zafeiriou, E.; Kyriakopoulos, G. The Determinants of the Environmental Performance of EU Financial Institutions: An Empirical Study with a GLM Model. Energies 2022, 15, 5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitonidou, M. Takis Zenetos’s Electronic Urbanism and Tele-Activities: Minimizing Transportation as Social Aspiration. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. Enduring Remnants from the Urban Industrial Past. Urban. Archit. Constr. 2021, 12, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zenetos, T.; Apostolidis, M. A Brewery in Athens. Architects: T. Ch. Zenetos—M. Ch. Apostilidis. Architektoniki 1963, Z’, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoropoulou, D. ΦΙΞFIX 120+ Years of Architecture: Takis Zenetos—Margaritis Apostolidis, a Turning Point in the History of the FIX Building; Epikentro: Athens, Greece, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gago, J.; Anastácio, P.; Gkenas, C.; Banha, F.; Ribeiro, F. Spatial Distribution Patterns of the Non-Native European Catfish, Silurus Glanis, from Multiple Online Sources—A Case Study for the River Tagus (Iberian Peninsula). Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2016, 23, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikinheimo, V.; Minin, E.D.; Tenkanen, H.; Hausmann, A.; Erkkonen, J.; Toivonen, T. User-Generated Geographic Information for Visitor Monitoring in a National Park: A Comparison of Social Media Data and Visitor Survey. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, A.N. Questionnaire Design, Interviewing, and Attitude Measurement; Bloomsbury Academic: London, UK, 1992; ISBN 0826451764. [Google Scholar]
- Arsenos, P.; Charamis, D.; Garefalakis, A. Pricing of Brand Extensions Based on Perceptions of Brand Equity. J. Gov. Regul. 2018, 7, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, A.; Zyed, Z.; Chai, W.W. Revitalising Critical Components of Urban Decay Features. J. Build. Perform. 2016, 7, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Berrens, R.; Bohara, A.; Jenkins-Smith, H.; Silva, C.; Weimer, D. The Advent of Internet Surveys for Political Research: A Comparison of Telephone and Internet Samples. Polit. Anal. 2003, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garefalakis, A.; Dimitras, A. Looking Back and Forging Ahead: The Weighting of ESG Factors. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 294, 151–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karytsas, S.; Vardopoulos, I.; Theodoropoulou, E. Factors Affecting Residents’ Attitude toward Sustainable Tourism Development. Tourismos 2019, 14, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karytsas, S.; Vardopoulos, I.; Theodoropoulou, E. Factors Affecting Sustainable Market Acceptance of Residential Microgeneration Technologies. A Two Time Period Comparative Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat Mean and Median Income by Household Type—EU-SILC and ECHP Surveys (Ilc_di04). 2020. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/data/datasets/kl0oijpz1d1aagzfj1h3fa?locale=en (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Cabrera-Nguyen, P. Author Guidelines for Reporting Scale Development and Validation Results in the Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research. J. Soc. Soc. Work Res. 2010, 1, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, R.L.; Whittaker, T.A. Scale Development Research. Couns. Psychol. 2006, 34, 806–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taecharungroj, V.; Tachapattaworakul Suksaroj, T.; Rattanapan, C. The Place Sustainability Scale: Measuring Residents’ Perceptions of the Sustainability of a Town. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2018, 11, 370–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassen, T.; Kunseler, E.; van Kessenich, L.M. The Sustainable City: An Analytical-Deliberative Approach to Assess Policy in the Context of Sustainable Urban Development. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 21, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-Y.; Jorge Ochoa, J.; Shah, M.N.; Zhang, X. The Application of Urban Sustainability Indicators—A Comparison between Various Practices. Habitat Int. 2011, 35, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Carlucci, M. A Composite Index of Sustainable Development at the Local Scale: Italy as a Case Study. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, S. Determining a Sustainable City Model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenworthy, J.R. The Eco-City: Ten Key Transport and Planning Dimensions for Sustainable City Development. Environ. Urban. 2006, 18, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. Beyond Sustainability Assessment Systems: Upgrading Topics by Enlarging The Scale of Assessment. Int. J. Sustain. Build. Technol. Urban Dev. 2011, 2, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suridechakul, W. Factors Affecting Sustainable Community Development: A Case Study of Dusit District Community. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances on Energy, Environment, Ecosystems, and Development. Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy, Environment, Ecosystems, and Development (EEED 2015), Barcelona, Spain, 7–9 April 2015; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lemonakis, C.; Garefalakis, A.; Xanthos, G.; Sialveras, N. Principle Characteristics in Firms’ Competitiveness Endeavour: Use of Managerial and Strategic Reasoning Technics for (SMEs). Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 8, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, H.N.; Boone, D.A. Analyzing Likert Data. J. Ext. 2012, 50, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS: Introducing Statistical Method, 3rd ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, S. Likert Scales: How to (Ab)Use Them. Med. Educ. 2004, 38, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnear, P.; Gray, C. SPSS 12 Made Simple; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Manion, L.; Morrison, K. Research Methods in Education; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hren, D.; Lukic, I.K.; Marusic, A.; Vodopivec, I.; Vujaklija, A.; Hrabak, M.; Marusic, M. Teaching Research Methodology in Medical Schools: Students’ Attitudes towards and Knowledge about Science. Med. Educ. 2004, 38, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santina, M.; Perez, J. Health Professionals’ Sex and Attitudes of Health Science Students to Health Claims. Med. Educ. 2003, 37, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunch, N.J. Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling Using IBM SPSS Statistics and AMOS, 2nd ed.; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 1446290573. [Google Scholar]
- Agresti, A.; Finlay, B. Statistical Methods for the Social Sciences; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using Spss, 3rd ed.; Allen and Unwin: Cros Nest, NSW, Canada, 2007; ISBN 1741762421. [Google Scholar]
- Subhash, S. Applied Multivariate Techniques; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 0471310646. [Google Scholar]
- Karytsas, S.; Choropanitis, I. Barriers against and Actions towards Renewable Energy Technologies Diffusion: A Principal Component Analysis for Residential Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Bugni, V. Symbolic Interaction Theory and Architecture. Symb. Interact. 2006, 29, 123–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuryanti, W. Heritage and Postmodern Tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 1996, 23, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, P.N.; Lazzeretti, L. Creative Cities, Cultural Clusters and Local Economic Development; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brida, J.G.; Pulina, M.; Riaño, E.M.M. Measuring Visitor Experiences at a Modern Art Museum and Linkages to the Destination Community. J. Herit. Tour. 2012, 7, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, C. Authenticity, Involvement, and Nostalgia: Understanding Visitor Satisfaction with an Adaptive Reuse Heritage Site in Urban China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2020, 15, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nora, P. Les Lieux de Mémoire; 3 Volumes; Gallimard: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Claver, J.; García-Domínguez, A.; Sevilla, L.; Sebastián, M. A Multi-Criteria Cataloging of the Immovable Items of Industrial Heritage of Andalusia. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L. Adaptive Reuse: Extending the Lives of Buildings; Birkhäuser—De Gruyter: Basel, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.F. A Life Cycle Model of Industrial Heritage Development. Ann. Tour. Res. 2015, 55, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani Mehr, S. Analysis of 19th and 20th Century Conservation Key Theories in Relation to Contemporary Adaptive Reuse of Heritage Buildings. Heritage 2019, 2, 920–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentina-Cristina, M.; George-Laurenţiu, M.; Andreea-Loreta, C.; Constantin, D.C. Conversion of Industrial Heritage as a Vector of Cultural Regeneration. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 122, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. European Actions for Sustainable Urban Development. In The Spatial Dimension of European Integration: Vonvergence or Divergence; Doukas, Y.E.L., Maravegias, N., Andreou, G., Eds.; Dionicos: Athens, Greece, 2022; pp. 171–188. ISBN 9786185665036. [Google Scholar]
- Hamida, M.B.; Hassanain, M.A. Post Occupancy Evaluation of Adaptively Reused Buildings: Case Study of an Office Building in Saudi Arabia. Archit. Civ. Eng. Environ. 2020, 13, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).