1. Introduction
One quarter of the way through the 21st century, we earthlings find ourselves deep in the throes of the Anthropocene, the geological epoch characterized by human activity. The earliest date for the start of this epoch has been identified as 1610, when global maritime expansion by European imperial conquistadors, crusaders, missionaries, and settlers resulted in the deaths of so many people in the Western Hemisphere that global carbon dioxide emissions plummeted, leaving an indelible anthropogenic mark on Earth’s crust [
1,
2]. The sudden global spread of floral and faunal species following the ‘Age of European Discovery’, and the biotic homogenization that we see now, will leave another anthropogenic mark in the fossil record [
2] (pp. 273–274). The Anthropocene and colonialism are inextricably entwined; in other words, what began as continental genocide has erupted over the last few centuries into global ecocide.
Continuing the fallout of the Columbian Exchange, anthropogenic geological markers have become more frequent: layers of plastics, layers of chicken bones, the sixth mass extinction, radiation from nuclear bombs testing, CO
2 spikes from burning fossil fuels, methane spikes from fossil fuels and corporate agriculture, etc. For these reasons, the Anthropocene Working Group has pinned the date of 1950 as the Anthropocene’s official start. However, the groundwork for the Great Acceleration, with its globalization and industrialization, was already set in stone in 1610; in other words, the documented geological features of neocolonialism require the
a priori onset of colonialism [
3]. Therefore, the 1610 start date of this new epoch is more comprehensive, lest we forget that the Anthropocene is the mere ‘
extension and enactment of colonial logic’, as Indigenous and other scholars have argued [
4] (p. 769, original emphasis) [
3,
5].
Over the last 400 years, the intensified deposition of anthropogenic strata and the proliferation of ‘material culture’ into nearly every feature of the planet support Shanks’ observation that all scientific research is archaeology [
6]. With thousands of man-made chemicals polluting rivers, lakes, and streams, and microplastics in polar ice, tap water, beer, and blood, even phlebotomy is archaeology. Shanks’ observation, which a decade later seems grimmer than when first written, was forecast by Flatman and Staniworth, who observed that in the postcolonial era, nearly all historical archaeology is maritime, contingent as material culture of this age is upon the transoceanic movement of people, things, and ideas [
7]. In these ways, material culture from the last four centuries, even the dirtiest polluting bits we archaeologists often ignore, falls under the remit of maritime archaeology. The peculiarities and predicaments of the Anthropocene also raise the question of what archaeology, and maritime archaeology in particular, might consist of in the future [
8]. Anthropocene reality awakens the importance of inclusive studies of ‘maritime cultural heritage’ that account for, not only the beautiful and inspiring, but the revolting and the shameful. But how can we begin to acknowledge these more ‘unruly’ kinds of maritime heritage [
9]? We argue that because the Anthropocene is an effect of colonialism, an Anthropocene archaeology—which is fundamentally maritime in nature—is most effectively and responsibly situated from the premise of anti-colonialism.
Therefore, this paper seeks to provoke introspection into what an anti-colonial maritime archaeology might be or become. Although terrestrial archaeology has long grappled with the discipline’s colonial legacy, its maritime counterpart lags behind in discussions of how power relations influence interpretation and management of underwater cultural heritage [
10,
11]. This reluctance to address colonialism continues despite the 25 years that have passed since Fred McGhee first published his provocation, ‘
Toward a Postcolonial Nautical Archaeology’ [
12]. Because not much has changed in these 25 years, we aim to pick up the torch here. In so doing, we attempt to present our ideas forcefully (because we believe in them) but with humility (knowing that we might get some things wrong) and from our own perspectives (a woman of mixed ancestry settled on unceded Waccamaw land, the Vice Chief of the Waccamaw Indian People, and an African-American man residing on the unceded territories of the Susquehannock and Piscataway Nations). Our question, and the case presented here, comes from a place of concern for how best to care for antiquities with integrity, and from a place of respect for the discipline of maritime archaeology and its
im-material cultures.
McGhee’s paper dedicates one section each to postcolonial views on the conspicuous absences of the African diaspora and Indigenous America in nautical archaeology. Our paper’s structure is similar but starts with the case of Indigenous American material culture and finishes with the case of a slave ship and the African diaspora. Our argument, that conforming to ‘industry standards’ of artifact preservation and conservation may conflict with the aims of anti-colonialism, is made by first presenting two new theoretical angles into the inquiry of anti-colonial maritime archaeology. We then think with these new frameworks to consider the fate of a late Archaic dugout canoe from the American Southeast. Finally, we conclude by presenting a second case from the American Southeast, that of the last slave ship to the United States, Clotilda. Bringing an ancient, fragmented canoe and a historic wrecked schooner into direct conversation may seem a bridge too far, but with this concluding discussion, we hope to provide a proof of concept and demonstrate what we believe to be the broader implications of the paper’s findings.
2. Thinking with Theory
French philosopher Paul Virilio famously stated (twice) that the invention of the ship was the invention of the shipwreck [
13,
14]. His sensible warning to consider the eventual and inevitable failure of our technologies has, of course, not been heeded, and the result is widespread ecological ruination. Oil spills, burst pipelines, and nuclear radiation disasters are a few examples of technologies whose inevitable failure was inadequately anticipated. Waterways often bear the brunt of ruined technologies in the form of runoff and spillage, but shipwrecks also frequently contain and comprise toxic and pollutive materials that damage marine, lacustrine, and riverine ecosystems [
15].
The list of ecological horrors is ever increasing as climate scientists warn of apocalypse looming ever larger on the horizon. These warnings are secular variations on Christian eschatology and prophecies of Armageddon or the Rapture; the fall of current civilization is always in the future, the dates changing with new interpretations of scriptures or data. Whenever it comes, the apocalypse will be painful but unstoppable. However, from an Indigenous perspective, the apocalypse has been underway since 1492, ever since Columbus’
nau (or carrack),
Santa María, wrecked on the shores of Ayiti, and he claimed the island and its people for Spain and the Christian god. While all shipwrecks are catastrophic, this particular wrecking event launched the ‘ancestral catastrophe’ of genocide and ecocide that continues to unfold, and which is now beginning to ripple into the lives of settlers too [
5,
16,
17]. Survivors of Indigenous genocides and the Middle Passage know well that apocalypse is not on the horizon; it has been here since 1492 and the Columbian Exchange, since 1610 and the start of the Anthropocene [
1,
2], since 1619 with the arrival of the first African slaves to America [
18,
19]. Many settlers, however, especially those who have benefited from ancestral catastrophe, have been able to ignore its effects until now.
But now, the reach of the colonial apocalypse is everywhere: in the water we drink, in the blood coursing through our veins, in the placentas feeding our unborn children. As Métis environmental scientist Max Liboiron has deftly argued, pollution is colonialism [
20]. To be clear, the Anthropocene is not wholly defined by pollution, as it includes other facets of
Homo sapiens’ capacity to act as a geophysical force that leaves permanent records in Earth’s crust. That said, Liboiron argues, pollution is not merely an effect of colonialism, the way that the Anthropocene is its effect. Instead, the act of polluting is a colonial act. We might define the relationship like this, noting how it folds in on itself, as an ouroboros:
As Liboiron explains, in the process of polluting, there are baseline assumptions made about access to and rights over
land (a synecdoche that includes the air and waters that flow in and around land), and about the passivity of land as a mere surface to traverse, a ground to build upon, or as a receptacle for waste. Put simply, ‘pollution is best understood as the violence of colonial Land relations’ [
20] (pp. 6–7), a violence that is epistemic, ontological, and cosmological [
21]. Colonialism is when land, and all that it encompasses, is conceptualized as a
resource for profit; along the same lines, pollution defines land as both
resource and receptacle (or sink) to further the colonial agenda of extraction and exploitation, commodification, and appropriation [
15,
20,
21]. In this way, Liboiron reiterates, pollution is colonialism.
Because of this equation, one could further argue that the role of the anti-colonial maritime archaeologist in the Anthropocene is to reframe research questions so that focus is directed toward deleterious interactions between the marine and the maritime.
Marine is often defined by ‘nonhuman’ activities such as ocean currents, organisms and habitats, and geological processes, whereas
maritime most often applies to things that directly involve humans, like wrecks, ports, and submerged prehistoric sites. But again, in the Anthropocene, when the human reach is everywhere, it becomes ever more apparent that the distinction between these two concepts of marine and maritime, just as the distinction between ‘nature’ and ‘society’, has always been arbitrary if not insidiously destructive [
15,
22,
23]. With the equation of pollution and colonialism in mind, questions like these below become more relevant to our discipline, and more pressing:
Given the increasing amount of satellite and rocket debris that re-enters Earth and crashes into oceans, what can maritime archaeologists contribute to the study of its effects on marine habitats?
As those who study death by drowning (shipwrecks and submerged coastal settlements) in the midst of global cataclysm, how can maritime and nautical archaeologists significantly contribute to conversations about and actions against global sea-level rise?
What can nautical archaeologists offer to mitigation efforts of polluting Industrial-era and contemporary shipwreck sites?
In what ways can maritime archaeologists convert their knowledge of waterways into concrete changes to public policy on nuclear waste disposal, fossil-fuel pollution, sea- and airborne pandemics, microplastics pervasion, wastewater and runoff?
With the understanding that ships were the mechanisms of European colonialism, how can maritime archaeology contribute to post- and anti-colonial narratives, instead of reiterating that of the seafaring colonizer as ‘Great Man’?
This paper attempts to offer new perspectives into some of these provocations: namely, the potential ways that nautical archaeology might start mitigating pollution as one way of
refusing its larger twin, colonialism [
25].
Lynn Meskell makes a strong case that UNESCO’s approach to
global world heritage could be perceived by some as an extension of the colonial project, traveling to, knowing and mapping territories outside one’s own national boundaries. The language of the UNESCO conventions reinforces Western notions of value and rights, while the ownership and maintenance of the past is suffused with the concepts surrounding property
[
26] (original emphasis).
Meskell’s concerns extend to ‘property’ on the seafloor too. Several problems emerge from UNESCO’s protocols for underwater cultural heritage, but one general aspect of maritime archaeology that relies on colonial land relations has been termed the ‘resurrection model’ [
11]. This model places the
scholar in the position of
savior by construing the wreck as a dead ship and commencing to resurrect the ship from the wreck. The resurrection, or savior-scholar, model has dominated nautical archaeology from the discipline’s outset, and can be seen in famous examples, like the
Mary Rose and the
Vasa, whose corpses have been scientifically exhumed from their watery graves and placed on display in the utopian space of a museum. Originating in the West, the resurrection model quickly became the dominant protocol on a global scale (e.g., Nanhai no. 1 in China, Kyrenia in Cyprus,
Batavia in Australia, and the Kinnaret and Ma’agan Michael in Israel). The model rests on the assumption that the wreck is a passive entity, despite its active presence in composing underwater habitats, a presence that in the vast majority of cases has persisted far longer than the ship ever functioned on the surface of the water.
Additional to the resurrection model’s roots in Christian theology and its imperialism, it clearly replicates extractive colonial land relations, even if—or especially because—the land in question is below a body of water—a body that is often conceptualized as feminine [
11]. In this way, an anti-colonial maritime archaeology ought to at least be deeply suspicious of the resurrection model of ‘saving’ artifacts and entire ships who ‘have fallen victim to Earth’s watery depths’ [
27] (p. 10). Suspicion might further pique when wrecks are labeled as cultural heritage
resources—things to profit from, things to exploit, things to commodify—rather than ‘as
sources—of community, of biodiversity, of nutrients, of toxicity, of hazardous waste, of contemplation, of knowledge’ [
15]. By acknowledging fundamental conceptual differences between
source and
resource, nautical archaeologists might be placed in a better position to intervene where it is most needed, rather than assuming, like deep-sea miners, a passive underwater landscape for the plucking [
28]. Indeed, it is odd that Earth’s oceans and seas are often regarded as the world’s largest museum, yet when we excavate (for science or for profit), it is not regarded as museum theft [
10,
29,
30].
Another aspect of the resurrection model, relevant for our purposes here, is its emphasis on immortality. In the case of wrecks, immortality may be achieved by physical resurrection to a museum space or digital resurrection to the even more utopian space of virtuality [
11,
29]. Sara Rich explains that this practice is an inheritance of Christian theology and its influence on science in the Early Modern era; in this respect, scientific resurrection of ships from wrecks assumes that the wrecked ship’s rightful place is a heavenly zone of immortality, preserved eternally with pixels or conserved eternally with polyethylene glycol (PEG) [
11].
1UNESCO’s first recommendation for in situ preservation of underwater cultural heritage is in some respects progressive, and it would seem to mitigate these concerns about the resurrection of ships from wrecks. However, the protocol is at least partially in place due to the limitations of excavation technologies, budgets, and museum spaces [
31,
32]. The cases of the
Mary Rose and the
Vasa have suggested that ‘ultimately such recovery would be the appropriate practice in underwater archaeology’ but because of present limitations, as many wreck sites as reasonably possible ought to be managed and ‘preserved for future generations, including future generations of researchers’ [
31] (pp. 24–25) [
33] (p. 109). While future generations of fish, corals, or cephalopods might also benefit from a wreck’s in situ preservation, as it forms an artificial reef, these benefits are ancillary to the strictly anthropocentric intention of the passage. The preference for preserving wrecks in situ is concerned with increasing the longevity of the wreckage so that it might again benefit (some) humans in the (near or distant) future. The archaeological fixation on preservation for the sakes of heritage and the archaeological record is apparent here, despite the philosophical shortcomings of both arguments [
34,
35].
Another part of our concern with the archaeological imposition of immortality onto shipwrecks is that the preservationist agenda assumes a predictable future with a linear, pseudo-evolutionary, trajectory from the simplicity and imperfection of the present toward the complexity and perfection of the future. Preservationism rests on the belief that excavation methods and archaeometric analyses will inevitably improve over time, that more knowledge can be gained from the wreckage then, that we will have better ways to present underwater cultural heritage to the public, and that the public will care more—or at all—about underwater cultural heritage [
31]. In other words, deferring to the future (despite the impossibility of its arrival in the now) assumes that our technologies will be improved such that resurrecting entire wrecks from their watery graves will become more plausible and more desirable. However, as it looks from the Anthropocene crow’s nest (
Figure 1) [
36] (fig. 1), none of these assumptions about the future is safe, let alone certain [
37].
Furthermore, the immortalization of the wreck for human posterity denies the wreck the possibility of decaying into the food chain, or otherwise returning to the muddy waters from whence all things came [
38]. In psychological terms, because there is a transference of the human body onto the form of the ship, we tend to project our own anxieties of decay and death onto the form of the wrecked ship [
11,
38]. However, this outlook is specific to Western thought, with its roots in a Christian theology that valorizes eternal salvation, bodily resurrection, and heavenly utopia over aging, death, and disintegration. Given that European scientific development and its corresponding colonialism was a theological project [
39], it is not surprising that archaeologists notoriously have a hard time ‘letting go’ [
40,
41]. It is as if the colonial project has known all along that its powers would burn hot and fast, with the preservation fetish emerging as an attempt to preempt the ruins of settler states [
42,
43]. In short, we echo the claim that preservationist agendas for underwater cultural heritage are ‘a continuation of the same anthropocentric logic underlying quests for utopia and immortality that first sent colonizing crusaders across the Atlantic in 1492′ [
11] (p. 25). Therefore, in advocating for a more earthbound, anti-colonial, maritime archaeology that places decay in the context of recurring cycles of existence and entropy, we are also advocating for something of an existentialist maritime archaeology that embraces the finitude of all objects, physical and metaphysical [
35,
37,
38].
3. The Late Archaic Canoe
Normative claims such as those made above tend to be universalizing, but our intention here is merely to introduce a healthy sense of skepticism into the long-established norms that govern our treatment of underwater wreckage. Because each site is situated locally, comes with various sets of peculiars and particulars, and (mis)behaves differently within its ecosystem, each deserves its own set of considerations for how, when, or if humans ought to intervene. As Liboiron summarizes, ‘The universal is never universal, but rather an argument to imperialistically expand a particular worldview as
the worldview,’ so even—or especially—anti-colonial claims are best weighed on a case-by-case basis to allow for local nuance [
20] (p. 52, original emphasis) [
44]. Here we consider a late Archaic dugout canoe from the waterway now known as the Cooper River, in the region now known as South Carolina (USA). This case represents an apparent clash of universalizing and local value systems, and a considerable amount of nuance.
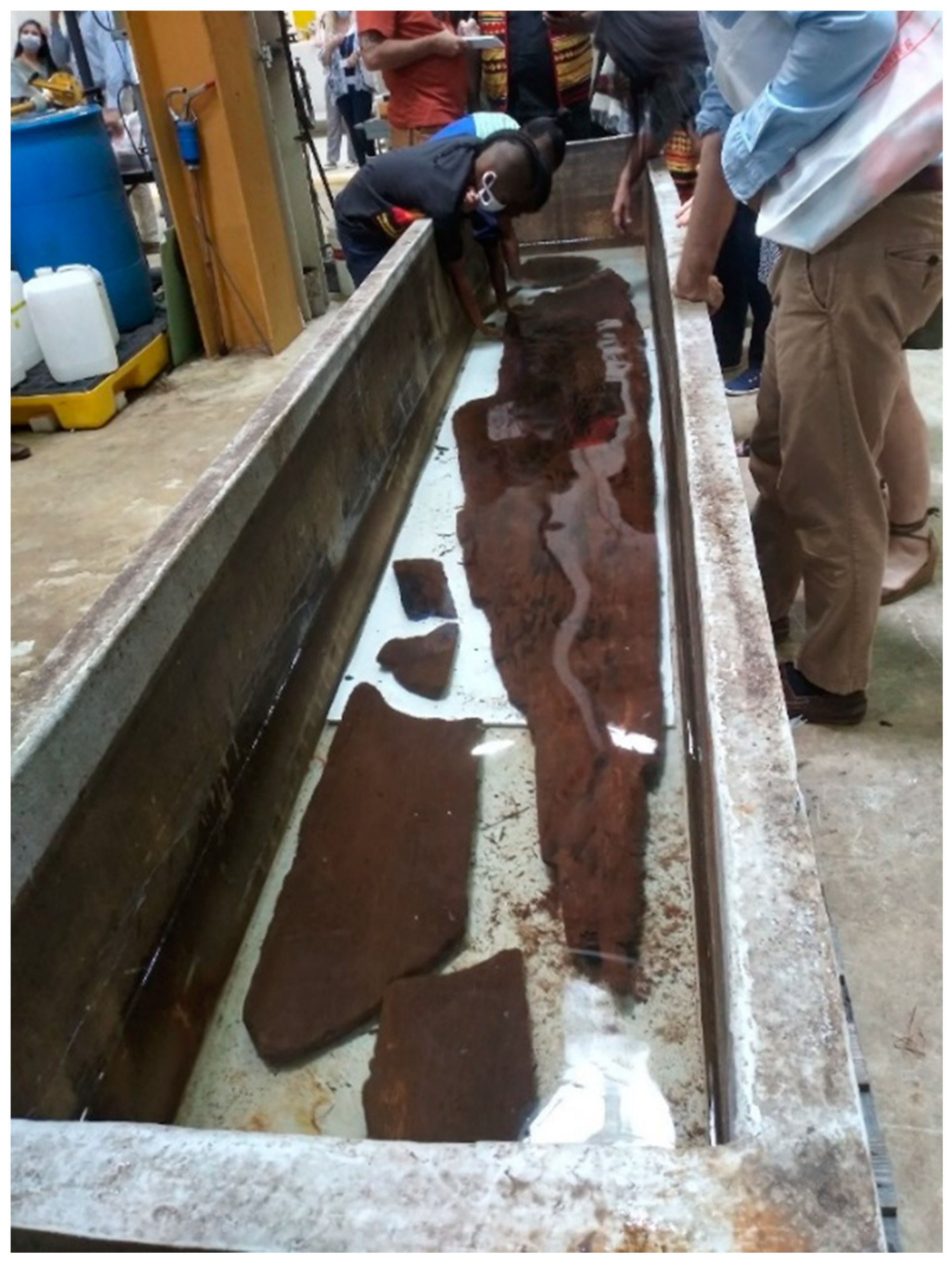
In 1987, the remains of the late Archaic canoe were illegally excavated from the Cooper River near Charleston, South Carolina. Although the canoe’s exact findspot was never divulged to authorities, the river and its environs are home to various historical Indigenous communities, many of the descendants of whom still live in the region. Later that year, the canoe was surrendered to the South Carolina Institute for Archaeology and Anthropology (SCIAA), at which point it was radiocarbon dated and determined to be the oldest-known watercraft in the state, having been fashioned from the trunk of a single cypress tree (
Taxodium distichum) in the late Archaic period, 4170 +/− 70 yBP. Without funds for conservation, the canoe remained in a tank of water outside the SCIAA office in Fort Johnson until 2020 when it was moved back to the Charleston area, where it currently resides at Clemson University’s Warren Lasch Conservation Center (
Figure 2) [
45].
At that point in 2020, plans were made to invite leaders from the state’s fourteen recognized tribal entities and two tribal non-profits into consultation with archaeologists and conservators to discuss how to proceed with the canoe’s remains. Invitations such as these are uncommon and usually reserved for human remains or other items or places considered explicitly ‘sacred’. The event organizers are to be commended for initiating consultation with Native partners in this case of a cultural object allegedly outside this ill-defined category [
45] (but see [
46]). Given the novelty of the opportunity to consult with scientific experts on this matter, the invitation was accepted by eight tribal leaders located across the state (Wassamasaw; Edisto Natchez-Kusso; Waccamaw; Catawba; Yemassee; PAIA Lower Eastern Cherokee; Pine Hill; and the Eastern Cherokee, Southern Iroquois, and United Tribes of South Carolina). As welcome as the consultation event was for all in attendance, we need not become complacent once a precedent is established; rather, we ought to strive to improve upon those precedents and to do the work of redressing colonialism in all its forms.
Over the course of the day-long consultation event, Native partners conceded that the canoe, consisting of one large hull section that preserves part of the curve of either bow or stern along with several smaller fragmentary hull pieces, would be conserved with PEG and then placed on display in a public museum. At first glance, this outcome seems to be a rare case of rapid consensus between multiple stakeholders, and at the same time, a rare case in which the resurrection model works in the service of anti-colonialism, rather than in celebration of imperial or dominant-culture prowess. However, thinking with theory about the implications of this decision, and the immediate and broader contexts in which it was made, may lead us toward new processes for future consultations, and toward a better understanding of the subtler impacts of colonization.
The consultation event was a unique opportunity for leaders of multiple South Carolina tribal entities to come together, in the first place, and in the second, to offer views on how their own material culture ought to be managed. Because of the canoe’s extraordinary antiquity, ownership cannot legitimately be claimed by any one contemporary tribal group, so the consultation presented an opportunity for diverse descendant communities to unite in a decision that would potentially affect everyone. With this in mind, the consultation was primarily to inform Indigenous partners of the lengthy process for conservation of the canoe with PEG, to gauge interest in a website and determine who would host it, and to raise possibilities for eventual museum display and other outreach initiatives.
An unexpected discussion of the presumed conservation method nearly derailed the agenda. Present at the consultation by invitation of the Waccamaw Indian People, the first author of this paper drew on niche archaeological knowledge of waterlogged wood conservation to raise the point that conservation with PEG would fundamentally alter the nature of the canoe, as the process infuses the cellular structure of waterlogged wood with a petroleum-derived liquid plastic. The process would irreversibly change the canoe from wet to dry and from organic to inorganic. The second author of this paper, the Vice Chief of the Waccamaw Indian People and an expert in industrial pollutants, along with Chief Michelle Mitchum (Pine Hill), seconded and thirded the concern that this method of conservation presented a conflict with Native interests: in particular, the way that some Native peoples understand their material culture as borrowed from the earth, and just as importantly, that pollution is colonialism. This issue sparked considerable conversation between Native and non-Native consultation partners [
47].
Chief Se’khu Gentle Hadjo (Yemassee) explained first that the spirit or soul of the cypress tree persists, even as it was transformed into a canoe, and that canoe was transformed into a ruined or fragmented state in the riverbed; in other words, the tree-canoe is best thought of as a living thing (on life and non-life in Indigenous thought, see [
48]). The tree-canoe may not be an ancestor per se, but it is a relation, and we have certain obligations to our relations [
20,
46,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53]. Chief Hadjo went on to explain that the ancestors brought forth these ruins at this particular moment for a particular reason: namely, to unify and empower the tribal communities and future generations of Indigenous South Carolinians. This point was rendered all the more salient given that his own young children were in attendance for the consultation (
Figure 2).
With the first part of Chief Hadjo’s commentary, it became apparent that the Yemassee, with concurrence from other Native leaders present, believe that change, including disintegration, is an integral part of the sacred life cycle. All living things, including those altered by human hands, must perish and return to the earth. His sentiment recalled the famous mantra, ‘keep it in the ground’, of the Water Protectors who fight against fossil fuel infrastructure and its encroachment on and pollution of Native lands and waterways. Living things gone back to the earth, including oil, are best kept in the ground [
49]. Of course, there was no way to prevent or undo the canoe’s illegal excavation, or rather, its theft. Yet the option to return the canoe to the river was weighed only briefly among other alternatives (freeze-drying, in-water retainment, sugar–alcohol impregnation [
54,
55]) before reaching the consensus to conform with ‘industry standards’ and plasticize the tree-canoe [
45,
47].
On one hand, it may seem that the consensus of Indigenous partners was an expression of self-governance, autonomy, and sovereignty, and certainly this consultation event was a step in that direction (but see [
12]). However, there were some barriers to leveling the uneven playing field: the highly consequential decision of the canoe’s fate needed to be made that day; some consulting scientists seemed insistent that PEG impregnation was the right or even only rational choice; and the pressure to rapidly make the ‘right’ decision inhibited partners from gaining sufficient contextual knowledge. Some might even point to the hierarchical if not confrontational arrangement of speakers versus sitters, at odds with the ‘talking circle’ where all partners are equally seen and heard [
52]. Some tribal leaders expressed feeling that they were students being instructed rather than consulted as experts and equals.
There is more to respecting sovereignty than simply recognizing the peoples’ authority to make decisions on their own behalf. Due to centuries of unequal power relations, sovereignty demands respect along with reciprocity and responsibility [
52], where ‘partners’ are truly understood as equals, with all the relevant information shared bilaterally. For example, while Native partners were informed of some of the risks of PEG conservation, they were not informed that PEG-infused
Vasa is deteriorating faster now than when it was underwater [
56]. They were not made aware of the possibility that the canoe had been an ancestor’s coffin [
57,
58,
59]). Nor were they privy to how others have resolved the question of what to do with an old canoe, which is often—though not always [
60,
61,
62]—to rebury it [
45,
63,
64,
65]. But at the end of the day, the ‘conservation paradigm’ of loss aversion [
66] with its managerial ontology [
20] was agreed upon. To further understand why, we will provide some political context and explore additional underlying factors that may have contributed to the consensus.
Five centuries of attempting to render Indigenous peoples extinct have resulted in death-defying acts of resilience. Sometimes just to exist is to resist, as in the numerous accounts of children having been told by teachers in South Carolina that they cannot be of the tribe they say they are because Indians only exist on reservations out West or, worse yet, ‘that tribe is extinct’. Most children’s textbooks in South Carolina mention only three tribes (Catawba, Cherokee, and Yemassee) of the sixteen or more still present, and those three are written about in the past tense. With this context in mind, the canoe was rapidly embraced as a symbol of Indigenous resistance and perseverance [
47], qualities shared by all contemporary tribal communities in the American Southeast and worldwide. It is often said that history is written by the victor, but material objects can offer powerful alternatives to received narratives, challenging and subverting those stories to offer a direct link to the past itself, as opposed to the stories told about it.
But this particular symbolic attachment to the canoe raises a series of questions: If its main purpose now is to parallel Indigenous survival against all odds, how does this reductionist metaphor affect its autonomy as an animate, lively being? Has the tree-canoe now become subservient to its symbolism? If so, are there any dangers associated with an object’s symbolic content overpowering the thing in itself? And do the ends (museum artifact to showcase Native perseverance) justify the means (the tree-canoe’s eternal preservation in plastic)?
Ultimately, the canoe as symbol of survival renders it entwined with political goals of a unified voice, federal recognition as sovereign nations, and legal rights to artistic and religious freedoms and protections that are not afforded tribes without federal recognition. To place these aims in context, of the sixteen or more existing tribal entities in South Carolina, only one (Catawba) is federally recognized, and only nine others have state recognition [
67]. The radically conservative nature of South Carolina politics places a higher price on the goal of legal recognition than in other areas where that status is easier to attain [
62,
68]. Because of these circumstances, the canoe’s political symbolism has overwhelmed its spiritual (or ontological-epistemological) reality, despite the absence in traditional thinking of a division between the political and spiritual, or the scientific and spiritual [
17,
46,
51,
52,
53]. Hence, the desire to preserve and display the canoe as a perpetual symbol of intertribal unity and shared struggles won out against concerns surrounding the tree-canoe’s own life, spirit, and autonomy—and it won out against concerns of the pollutive plasticization process of PEG that renders the ensouled organic into a desouled inorganic, its substance and essence as indelibly altered as Earth’s crust since 1610.
And yet, there may be still other contributing factors behind the consensus to immortalize the tree-canoe, and to concede ancient spirit to modern symbolism in what Native stakeholders were several times reassured is ‘industry standard’ for conservation. It is possible that Western ideals have so permeated Indigenous thought that resurrection and immortality are now Indigenous values too. Tribal communities living along the mid-Atlantic coastlines were among the first to be impacted by colonization, so the forces of assimilation have been at work for some 500 years in this area. It took only two generations following first contact for Native peoples in the Southeast to substitute guns for bows. Following still more generations of assimilation, much of it forced, many if not most Indigenous South Carolinians are Christian, so the archaeological fixation on resurrection and immortality may after all be perfectly aligned with tribal members’ own political and spiritual values.
On the other hand, and most concerning, is that the consensus among Native partners may also represent an acceptance of a Western paradigm of immortality in order to affirm their own Indigeneity. In other words, over the course of centuries of settler colonialism, Native identity in South Carolina may have become defined more by survival than other (pre-contact) shared values, such as land stewardship, kinship ties, cosmologies, epistemologies, and ontologies [
52].
2 Echoing Liboiron, colonialism is sneaky like that [
20].
To summarize, we find that the ensouled tree-canoe has become subservient to its post-colonial symbolism of Indigenous unity, resilience, and resistance, but ironically, by subscribing to the colonial ‘resurrection model’ of maritime archaeology and the pollution that it entails, the immortalized canoe may not be the anti-colonial statement that was intended by its conservation. This case serves as a potent reminder that post-colonial and anti-colonial are not synonyms [
20]. But it is also a reminder of how powerful metaphors are, and the care that we must take when constructing them, especially in the context of settler colonialism [
21].
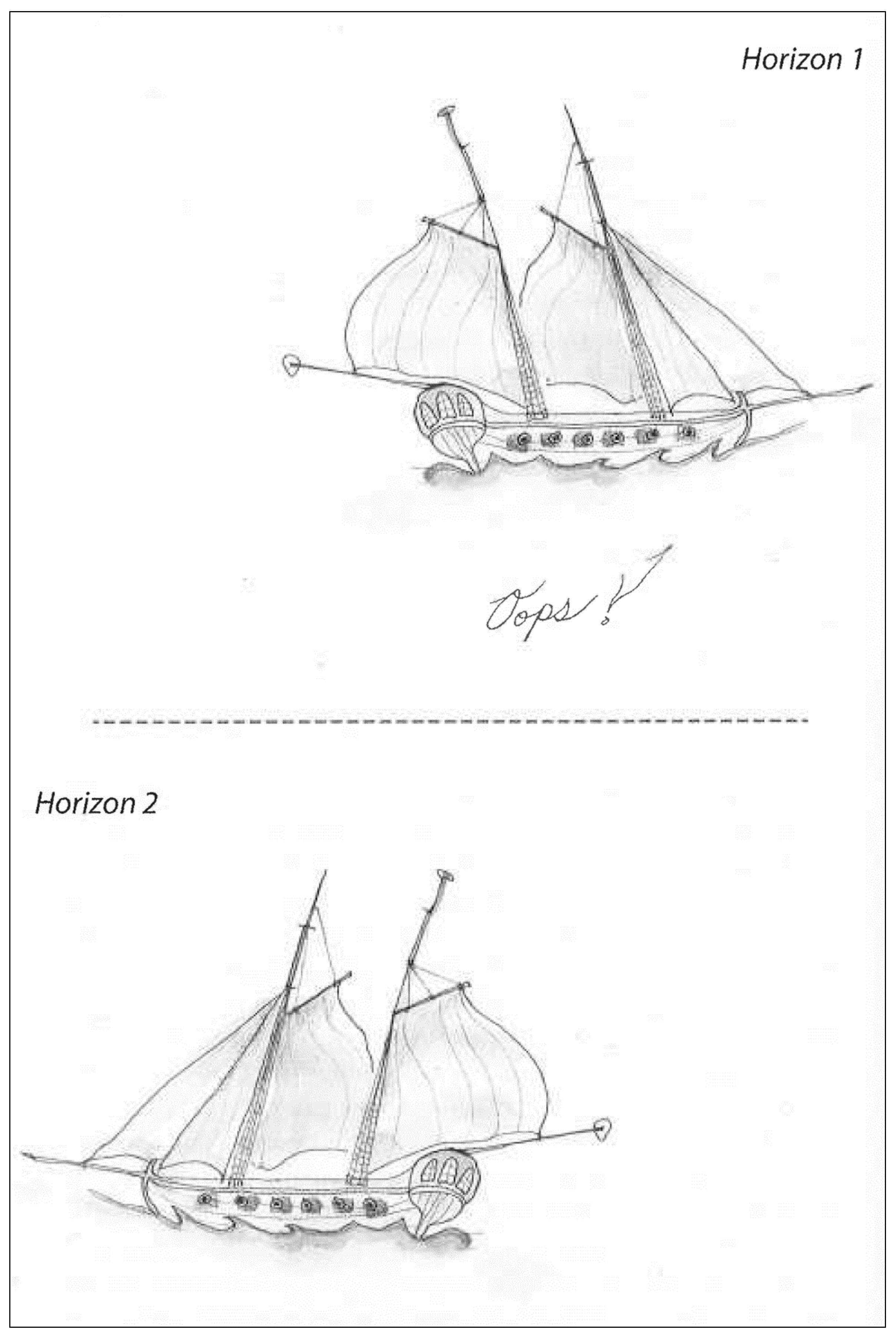
In 1984, three years before the canoe was stolen from the Cooper River, Audre Lorde published a now-famous essay explaining how the structures of colonial patriarchy cannot be disbanded by rebranding those same structures and harnessing them into a new one [
69]. That method (dismantling the master’s house using the master’s tools, in her words) can only ever replicate the selfsame dysfunctional structures that need tearing down. Elizabeth Povinelli seems to have a similar metaphor in mind with her illustration of a Spanish ship (galleon, carrack, or
nau): in the upper panel, it heads toward ‘Horizon 1′, realizes it made a mistake (‘oops!’ is scrawled in the negative space), and reroutes toward ‘Horizon 2′ in the lower panel (
Figure 3) [
16] (fig. 2.1). The problem is that the horizon is the same, regardless of the direction taken to reach it. In other words, it is the horizon that needs radical reconfiguration, not the compass. We might expand on this metaphor by suggesting that the galleon—that symbol of European conquest, that forest turned floating war machine—might also be scrapped to build a new means for new ends. Following Lorde and Povinelli, we see a similar scenario playing out in this context and suggest that an anti-colonial maritime archaeology cannot hope to dismantle the master’s
nau using the master’s tools; or, we cannot hope to reach the horizon of a different, less catastrophic, future by relying on the same old neoliberal methods of the present. An anti-colonial maritime archaeology does not need to subscribe to the same ‘industry standards’ as archaeology practiced elsewhere, especially when there are good reasons for questioning the continuation of those practices in the first place.
In time, when the immortalized tree-canoe goes on public museum display, we hope that it is presented in a way that intentionally generates dialogue among audience members as to the treatment of cultural heritage in a world being slowly but assuredly decolonized [
17]. As Natali Pearson writes, ‘Orphaned [looted or otherwise decontextualized] underwater objects are the ideal starting point for examining these legacies, because they force museums to question their very reason for being’ [
10] (p. 137). If that reason truly is for education, then surely part of the museum’s charge will be to open conversation—debates, even—about the theft of the canoe from the river, but also—and just as importantly—about how and why the conservation method and the museum context have irreversibly changed this object, and whether the ends justify the means.
4. Conclusions: The Clotilda
We have argued that, when considering what to do with an old Indian canoe, stakeholders ought to consider what anti-colonialism means in maritime archaeology. This includes, at the very least, (a) recognizing sovereignty regardless of the object’s status as sacred or otherwise, (b) honoring equal partnerships while acknowledging unequal power relations; (c) understanding the origins in Christian imperialism of the conservation paradigm; and (d) equating colonialism and pollution, which implicates petrochemical industries and their artifact conservation materials.
Despite the specificity of the case described above, we believe that the conclusions reached here have implications for other maritime archaeological contexts too. One such example is the highly publicized 1859–1860 slave ship, Clotilda, located in the delta of the waterway now called the Mobile River in the area now called Alabama. The ship, which carried an illegal cargo of 110 enslaved Africans, was burned and scuttled after it was docked and unloaded, rendering criminal tracks covered. Documentation of the ship’s remains began in 2018, and the perennial question immediately returned of what to do with them.
In an article in
Time magazine titled ‘History Demands We Preserve the Wreck of America’s Last Slave Ship’, Ben Raines, the journalist who ‘discovered’ the vessel, forcefully argues that the
Clotilda ought to be surfaced, conserved, and reassembled for display in a new museum in Africatown, Alabama [
70], which would ‘instantly make Africatown one of the most important sites in the burgeoning Civil Rights tourism industry’ [
71]. In other words, Raines wants the resurrection model of maritime archaeology applied to a ship that was conscripted in the service of slavery, so that it may feed into a current trend in heritage tourism. He explains further, ‘To the community, having the wreck on display in a new museum is vital to both resurrecting Africatown’s declining fortunes and reconnecting the people living there to their own history’ [
71] (p. 221). Granted, it is not his decision, nor ours, to make. The
Clotilda captives’ living descendants and the people of Africatown will decide, in conjunction with the state of Alabama, whether the ship should remain in situ, where it has been for over 160 years, or if it should be ‘resurrected’ (along with the town’s fortunes).
In addition to the concerns outlined above regarding the use of petrochemicals to immortalize the ship, the
Clotilda presents an opportunity to think about what we really mean when we talk about ‘bringing history to life’ [
10,
11]. What exactly would spring to life with the ‘resurrection’ of this ship from the riverbed? When history ‘comes alive’, it’s hard to make it rest in peace again. Given that at least two enslaved passengers perished on the journey from Dahomey (modern Benin), raising
Clotilda risks severing the connection between these lost souls and the waters in which their bodies were cast. Knowing this connection between the waters and the dead,
Clotilda survivors would congregate within and around the water to perform ‘sacred community commemorative rituals. These rituals continue to the present, upheld by the descendant families’ [
72]. Many
Clotilda descendants recognize the ship and the waters in which it rests as a conveyance of lost ancestors but also as a conveyance between the Over Here and the Over There of ancestral lands [
73].
The live oaks, white oaks, and pine trees that furnished
Clotilda’s timbers [
74,
75] were likely older than the captives taken onboard. That the ship was designed to transport lumber, further connects the timbers of felled trees with the bodies of enslaved people. Although
Clotilda may not really be alive in a biological sense, neither is it really dead given the brackish and marine lives that teem within and beside those timbers now. It could be metaphorically conceived as being conscious within, if not wholly belonging to, both worlds. So exactly what good would come from the public spectacle of this exhumed body? If the only answers to this question pertain to economy and capital, let us not forget that ‘capital’ and ‘chattel’ have shared etymologies.
Further, in what ways might the decontextualized and immortalized remains of
Clotilda only serve to underscore white supremacist notions of the scientific and technological omnipotence of Euro-American shipbuilding (made public through Euro-American archaeological and museum methods of quasi-miraculous resurrection)? Even on the other side of the political spectrum, raising
Clotilda may still subject the enslaved captives and those lost at sea to a death in amber, a spectacle ironically most visible during self-interested scrutiny [
76,
77]. Along those same lines, in what ways might the slave ship’s sanitized museum remains gloss over the reality of having been chained on or to that ship, crying, screaming, bleeding, vomiting, urinating, defecating, menstruating, gestating, dying? Again, etymology is telling: museum and mausoleum both refer to the keeping of the dead, but only the former is directly positioned to commodify those holdings as a
resource.
In its current position in the Mobile River delta, the third most polluted river in the US, perhaps the symbolism of the wrecked
Clotilda is already at its most potent [
72]. Given all that the ship signifies for the descendants of its 110 enslaved passengers—grief over the violent separation from ancestors and ancestral lands, generations of oppression, the entire African diaspora, Black genocide, environmental racism, and myriad other ongoing injustices—perhaps letting the wreck gradually disintegrate into dirtied waters might open, slowly and persistently, new futures without those pollutive forces of white supremacy and colonialism that brought the ship, wrecked and burned it, and sold its human cargo.
Alternatively, if it is decided that the wreck ought to be preserved for perpetuity, perhaps the first recourse should be cutting off the streams of industrial pollutants at their sources, rather than introducing new petroleum byproducts into those same waters in efforts to immortalize Clotilda’s timbers. As McGhee writes,
For nautical archaeologists interested in studying the slave trade, it is, I think, important that the budding slave ship scholar keep several things in mind. For example, it’s one thing to say that “slavery was bad” or that “slavery is bad”. It’s another thing, however, to critically examine the conditions under which representations of slavery are produced by scholars
Keeping in mind McGhee’s call, as-yet fully unanswered, for critical examination and reflexivity, perhaps it is time to rethink the first recourse of eternal preservation and public presentation. Perhaps, again, the master’s nau cannot be dismantled with the master’s tools.