The Crystallization Effect of Sodium Sulfate on Some Italian Marbles, Calcarenites and Sandstones
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
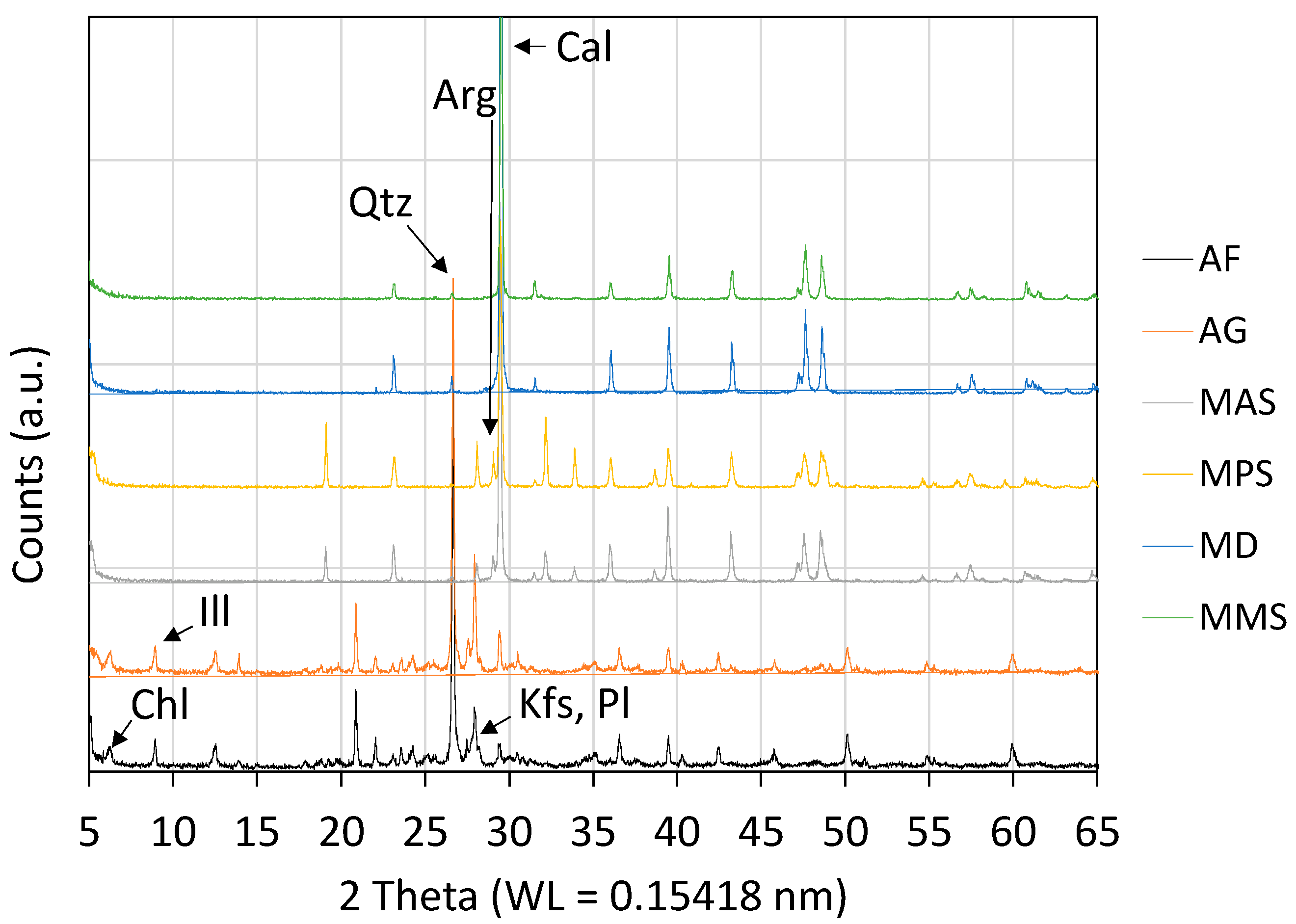
3.1. Chemical, Mineralogical, Petrographic Characteristics, and Physical Properties
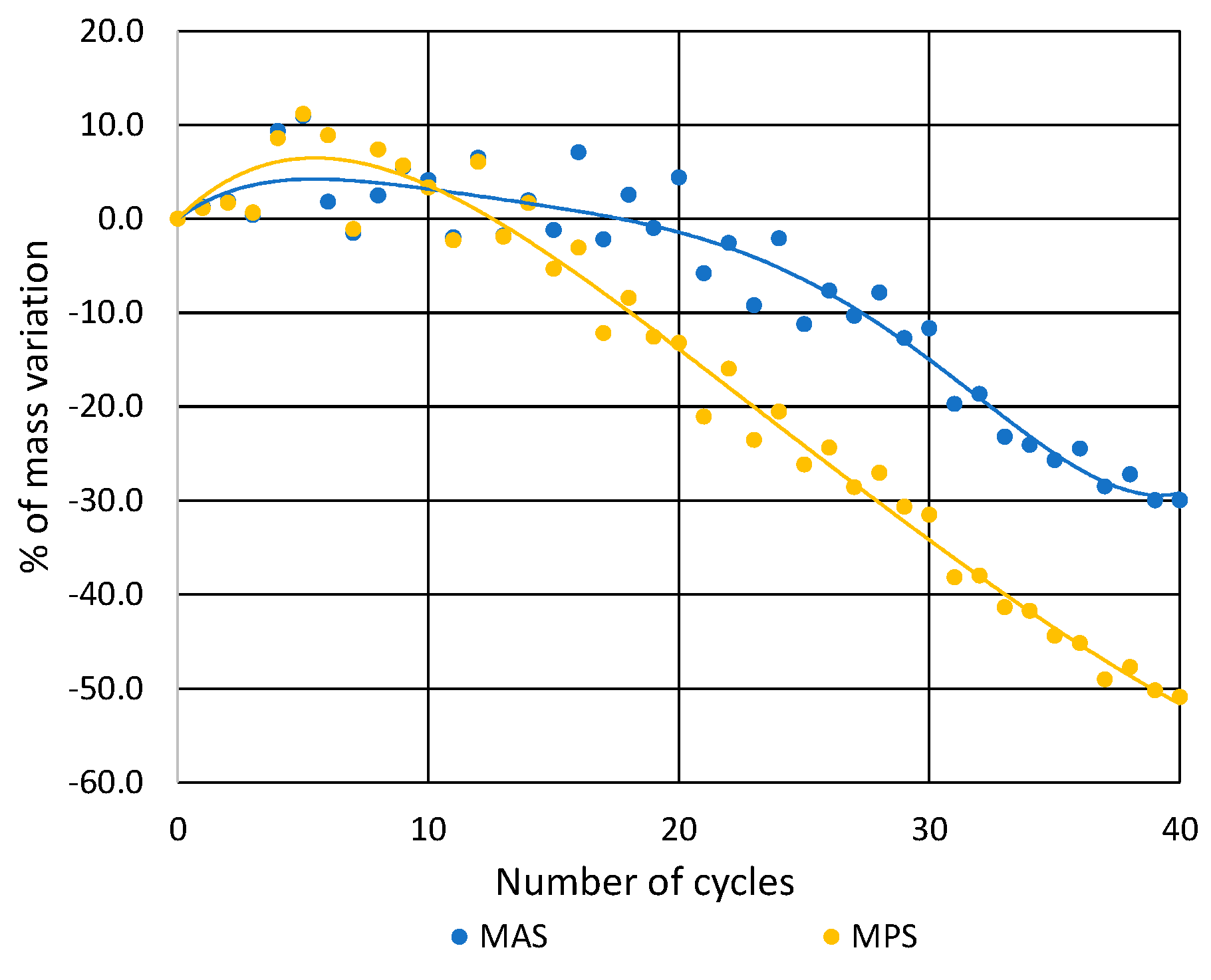
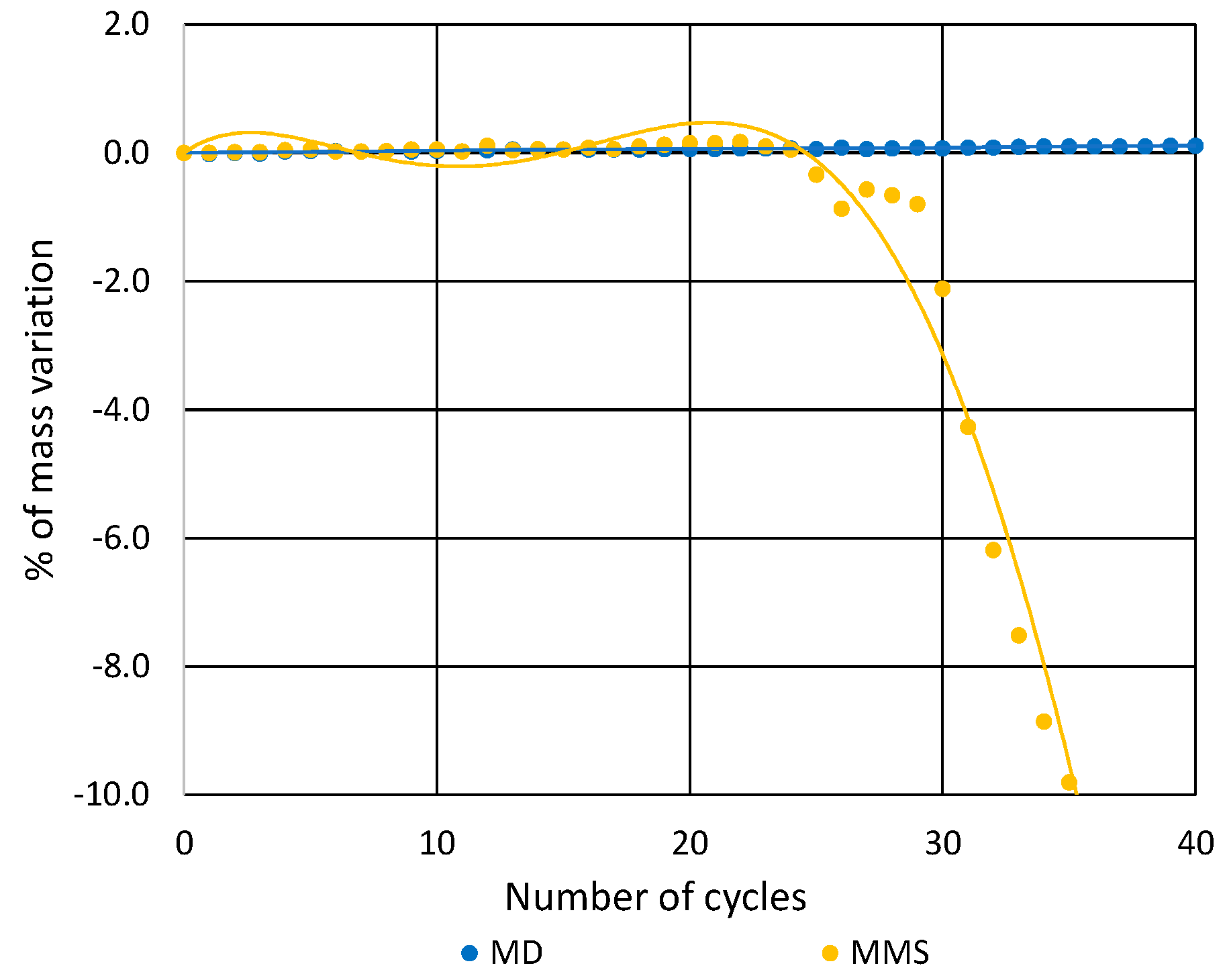
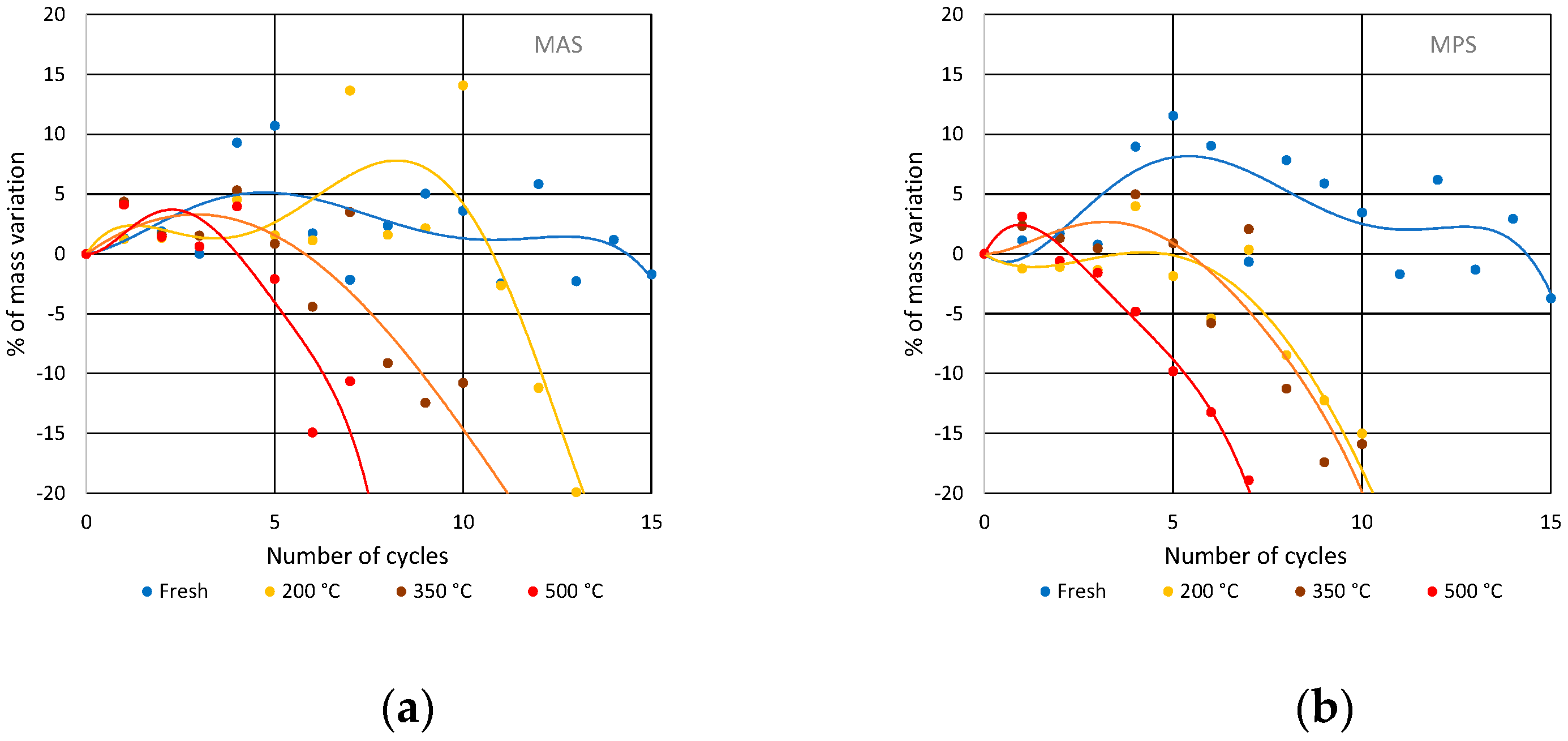
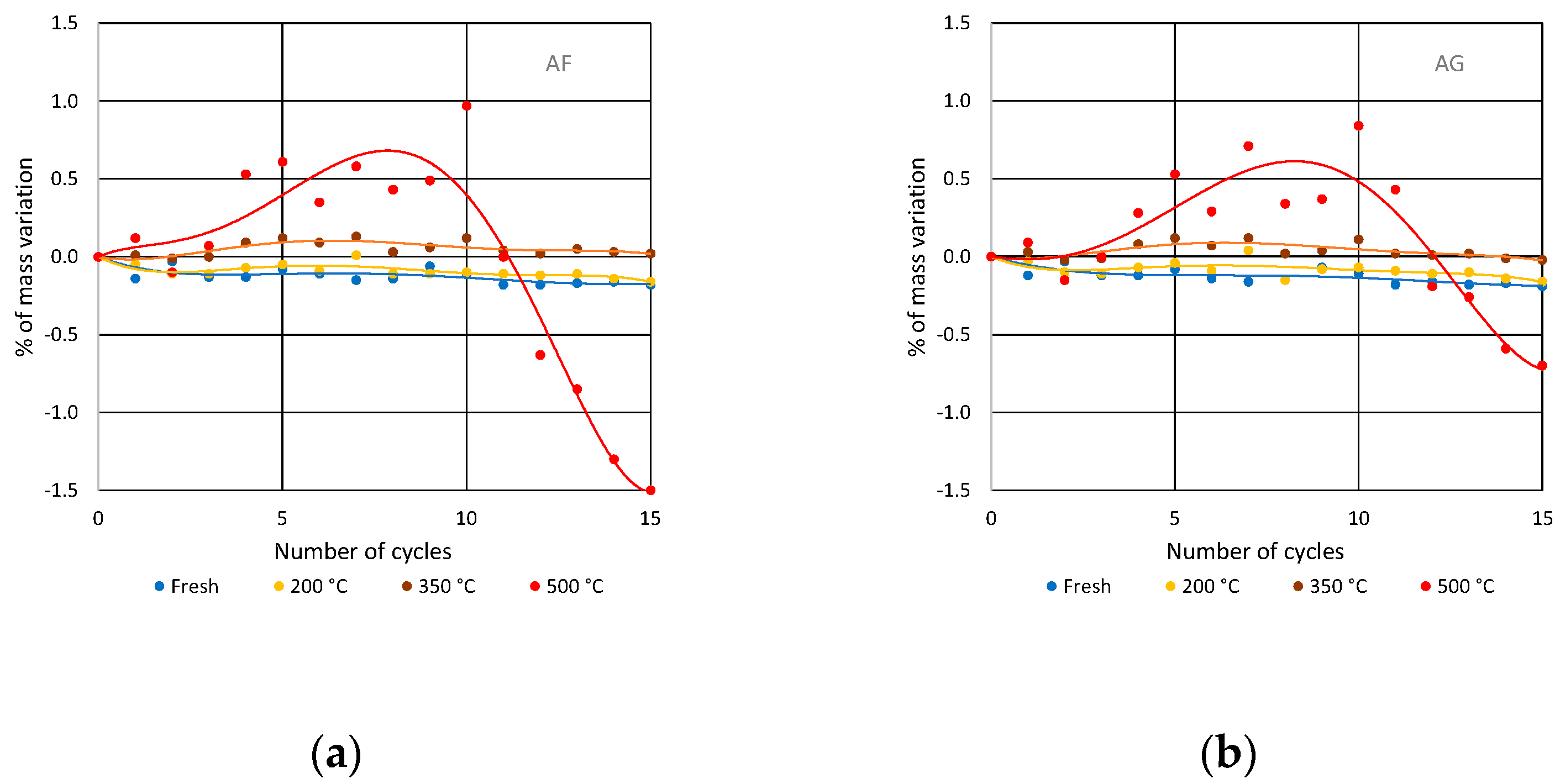
3.2. Soluble-Salt Crystallization
3.3. Salt Crystallization in Degraded Stones
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lubelli, B.; Cnudde, V.; Diaz-Goncalves, T.; Franzoni, E.; Van Hees, R.P.J.; Ioannou, I.; Menéndez, B.; Nunes, C.; Siedel, H.; Stefanidou, M.; et al. Towards a more effective and reliable salt crystallization test for porous building materials: State of the art. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2018, 51, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; Zehnder, K. Monitoring wall paintings affected by soluble salts. In The Conservation of Wall Paintings, Proceedings of a Symposium Organized by the Courtauld Institute of Art and the Getty Conservation Institute, London, UK, 13–16 July 1987; Getty Conservation Institute: Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 1991; pp. 103–135. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, C.; Silva, Z.; Simão, J. Evaluation of Portuguese limestones’ susceptibility to salt mist through laboratory testing. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D.; del Cura, M.A.G.; Fort, R.; Ordónez, S. Durability estimation of porous building stones from pore structure and strength. Eng. Geol. 2004, 74, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.A. Testing porous building stone. Archit. J. 1975, 162, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Benavente, D.; Garcıa del Cura, M.A.; Bernabeu, A.; Ordonez, S. Quantification of salt weathering in porous stones using an experimental continuous partial immersion method. Eng. Geol. 2001, 59, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.; Mas, Á.; Lerma, C.; Vercher, J. Exposure Factors Influence Stone Deterioration by Crystallization of Soluble Salts. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 348195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunagawa, I. Characteristics of crystal growth in nature as seen from the morphology of mineral crystals. Bull. Mineral. 1981, 104, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Arce, P.; Eric, D. Kinetics of sodium sulfate efflorescence as observed by humidity cycling with ESEM. In Heritage, Weathering & Conservation, Proceedings of the International Heritage, Weathering and Conservation Conference (HWC-2006), Madrid, Spain, 21–24 June 2006; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, N.; Flatt, R.J.; Scherer, G.W. Crystallization damage by sodium sulfate. J. Cult. Herit. 2003, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derluyn, H.; Vontobel, P.; Mannes, D.; Derome, D.; Lehmann, E.; Carmeliet, J. Saline Water Evaporation and Crystallization-Induced Deformations in Building Stone: Insights from High-Resolution Neutron Radiography. Transp. Porous Media 2019, 128, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, E. Salts. In ARC Laboratory Handbook; ICCROM—International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property: Rome, Italy, 1999; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Genkinger, S.; Putnis, A. Crystallisation of sodium sulfate: Supersaturation and metastable phases. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J. Salt damage in porous materials: How high supersaturations are generated. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 242, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussy, O. Deformation and stress from in-pore drying-induced crystallization of salt. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2006, 54, 1517–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.; Viles, H.A. Salt Weathering Hazard; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- D’Altri, A.M.; de Miranda, S.; Beck, K.; De Kock, T.; Derluyn, H. Towards a more effective and reliable salt crystallisation test for porous building materials: Predictive modelling of sodium chloride salt distribution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D.; Cueto, N.; Martínez-Martínez, J.; García del Cura, M.A.; Cañaveras, J.C. The influence of petrophysical properties on the salt weathering of porous building rocks. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, G.G.; Fasina, V. Stone Decay and Conservation. Atmospheric Pollution, Cleaning, Consolidation and Protection; Elsevier Science Pub.: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, L.; Siegesmund, S.; Wedekind, W. Salt weathering in granitoids: An overview on the controlling factors. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, W. Combined effects of salts and wetting–drying cycles on granite weathering. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Arce, P.; Varas-Muriel, M.J.; Fernández-Revuelta, B.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; Fort, R.; Pérez-Soba, C. Artificial weathering of Spanish granites subjected to salt crystallization tests: Surface roughness quantification. Catena 2010, 83, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardell, C.; Benavente, D.J. Rodríguez-Gordillo, Weathering of limestone building material by mixed sulfate solutions. Characterization of stone microstructure, reaction products and decay forms. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardell, C.; Delalieux, F.; Roumpopoulos, K.; Moropoulou, A.; Auger, F.; Van Grieken, R. Salt-induced decay in calcareous stone monuments and buildings in a marine environment in SW France. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Belfiore, C.M.; Aloise, P.; Randazzo, L.; Rovella, N.; Pezzino, A.; Montana, G. Study of the effects of salt crystallization on degradation of limestone rocks. Period. Mineral. 2013, 82, 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Viles, H.; Desarnaud, J.; Yang, S.; Guo, Q. Laboratory simulation of salt weathering under moderate ageing conditions: Implications for the deterioration of sandstone heritage in temperate climates. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desarnaud, J.; Kiriyama, K.; Bicer Simsir, B.; Wilhelm, K.; Viles, H. A laboratory study of Equotip surface hardness measurements on a range of sandstones: What influences the values and what do they mean? Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.Y.; İbrahimoglu, A. Characterization of travertine stones from Turkey and assessment of their durability to salt crystallization. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Figueiredo, C.A.M.; Sanjurjo-Sánchez, J.; Hernández, A.C. Salt weathering of natural stone: A review of comparative laboratory studies. Heritage 2021, 4, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedel, H.; Siegesmund, S. Characterization of Stone Deterioration on Buildings. In Stone in Architecture. Properties, Durability; Siegesmund, S., Snethlage, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 349–414. [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi, C.T.; Yu, S. A review of theoretical salt weathering studies for stone heritage. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivano, S.; Gaggero, L. An experimental investigation into the salt-weathering susceptibility of building limestones. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 5329–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Williams, R.B.G. Experimental weathering of sandstone by combination of salts. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2000, 25, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Torabi-Kaveh, M.; Mohseni, H. Assessment of the Effects of Freeze–Thaw and Salt Crystallization Ageing Tests on Anahita Temple Stone, Kangavar, West of Iran. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnow, K.; Zeunert, A.; Steiger, M. Investigation of sodium sulfate phase transitions in a porous material using humidity- and temperature-controlled x-ray diffraction. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4683–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Taboada, N.; Fdez-Ortiz de Vallejuelo, S.; Veneranda, M.; Marcaida, I.; Morillas, H.; Maguregui, M.; Castro, K.; De Carolis, E.; Osanna, M.; Madariaga, J.M. Study of the soluble salts formation in a recently restored house of Pompeii by in-situ Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Doehne, E.; Sebastian, E. How does sodium sulfate crystallize? Implications for the decay and testing of building materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiro, M.; Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Rodriguez-Navarro, C. Damage mechanisms of porous materials due to in-pore salt crystallization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 265503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, K.; Arnold, A. Crystal growth in salt efflorescence. J. Cryst. Growth 1989, 97, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Ellsmore, D. Salt Attack and Rising Damp. A Guide to Salt Damp in Historic and Older Buildings; Heritage Council of NSW: Parramatta, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Angeli, M.; Bigas, J.P.; Benavente, D.; Menéndez, B.; Hébert, R.; David, C. Salt crystallization in pores: Quantification and estimation of damage. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, J.; Guimarães, A.S.; De Freitas, V.P.; Antepara, I.; Kočí, V.; Černý, R. Salt damage and rising damp treatment in building structures. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1280894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vavouraki, A.I.; Koutsoukos, P.G. Kinetics of crystal growth of mirabilite in aqueous supersaturated solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 338, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, M.; Asmussen, S. Crystallization of sodium sulfate phases in porous materials: The phase diagram Na2SO4–H2O and the generation of stress. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4291–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzerini, M.; Di Battistini, G.; Zucchi, D.; Miriello, D. Provenance and compositional analysis of marbles from the medieval Abbey of San Caprasio, Aulla (Tuscany, Italy). Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2012, 108, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, A.E.; Lezzerini, M.; Prosser, G.; Munnecke, A.; Koch, R.; Rizzo, G. Matera building stones: Chemical, mineralogical and petrophysical characterization of the calcarenite di Gravina formation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IMEKO TC-4 International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, Florence, Italy, 4–6 December 2019; pp. 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Lezzerini, M.; Franzini, M.; Di Battistini, G.; Zucchi, D. The «Macigno» sandstone from Matraia and Pian di Lanzola quarries (north-western Tuscany, Italy). A comparison of physical and mechanical properties. Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. A 2008, 113, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Franzini, M.; Leoni, L. A full matrix correction in X-ray fluorescence analysis of rock samples. Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. A 1972, 79, 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lezzerini, M.; Tamponi, M.; Bertoli, M. Reproducibility, precision and trueness of X-ray fluorescence data for mineralogical and/or petrographic purposes. Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. A 2013, 120, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzerini, M.; Tamponi, M.; Bertoli, M. Calibration of XRF data on silicate rocks using chemicals as in-house standards. Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Ser. A 2014, 121, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzini, M.; Lezzerini, M. A mercury-displacement method for stone bulk-density determinations. Eur. J. Mineral. 2003, 15, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1015-10; Methods of Test for Mortar for Masonry—Part 10: Determination of Dry Bulk Density of Hardened Mortar. Comité Européen de Normalisation: Bruxelles, Belgium, 1999.
- EN 12370; Natural Stone Test Methods—Determination of Resistance to Salt Crystallization. Comité Européen de Normalisation: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2020.
- EN 13755; Natural Stone Test Methods—Determination of Water Absorption at Atmospheric Pressure. Comité Européen de Normalisation: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2008.
- Lazzeri, A.; Coltelli, M.B.; Castelvetro, V.; Lezzerini, M. European Project NANO-CATHEDRAL: Nanomaterials for Conservation of European Architectural Heritage Developed by Research on Characteristic Lithotypes. In Proceedings of the 13th International Congress on the Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, Glasgow, UK, 6–10 September 2016; pp. 847–853. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomo, A.E.; Lezzerini, M.; Prosser, G.; Munnecke, A.; Koch, R.; Rizzo, G. Matera building stones: Comparison between bioclastic and lithoclastic calcarenites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 972, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, A.E.; Minervino Amodio, A.; Prosser, G.; Sileo, M.; Rizzo, G. Evaluation of soft limestone degradation in the Sassi UNESCO site (Matera, Southern Italy): Loss of material measurement and classification. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 42, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, L.; Lezzerini, M.; Battaglia, S.; Cavalcante, F. Corrensite and chlorite-rich Chl-S mixed layers in sandstones from the ‘Macigno’ Formation (northwestern Tuscany, Italy). Clay Miner. 2010, 45, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.; Pagnotta, S.; Lezzerini, M. Artificial Thermal Decay: Influence of Mineralogy and Microstructure of Sandstone, Calcarenite and Marble. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 7th World Multidisciplinary Earth Sciences Symposium (WMESS 2021), Prague, Czech Republic, 6–10 September 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkington, A.V.; Paradise, T.R. Sandstone weathering: A century of research and innovation. Geomorphology 2005, 67, 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzini, M.; Leoni, L.; Lezzerini, M.; Cardelli, R. Relationships between mineralogical composition, water absorption and hydric dilatation in the “Macigno” sandstones from Lunigiana (Massa, Tuscany). Eur. J. Mineral. 2007, 19, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Scherer, G.W. Mechanisms of damage by salt. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2010, 331, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derluyn, H.; Moonen, P.; Carmeliet, J. Deformation and damage due to drying-induced salt crystallization in porous limestone. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2014, 63, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Hattanji, T. A laboratory experiment on salt weathering by humidity change: Salt damage induced by deliquescence and hydration. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantisani, E.; Canova, R.; Fratini, F.; Del Fa, C.M.; Mazzuoli, R.; Molli, G. Relationships between microstructures and physical properties of white Apuan marbles: Inferences on weathering durability. Period. Mineral. 2000, 69, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Sitzia, E.F.; Lisci, C.; Mirão, J. Accelerate ageing on building stone materials by simulating daily, seasonal thermo-hygrometric conditions and solar radiation of Csa Mediterranean climate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
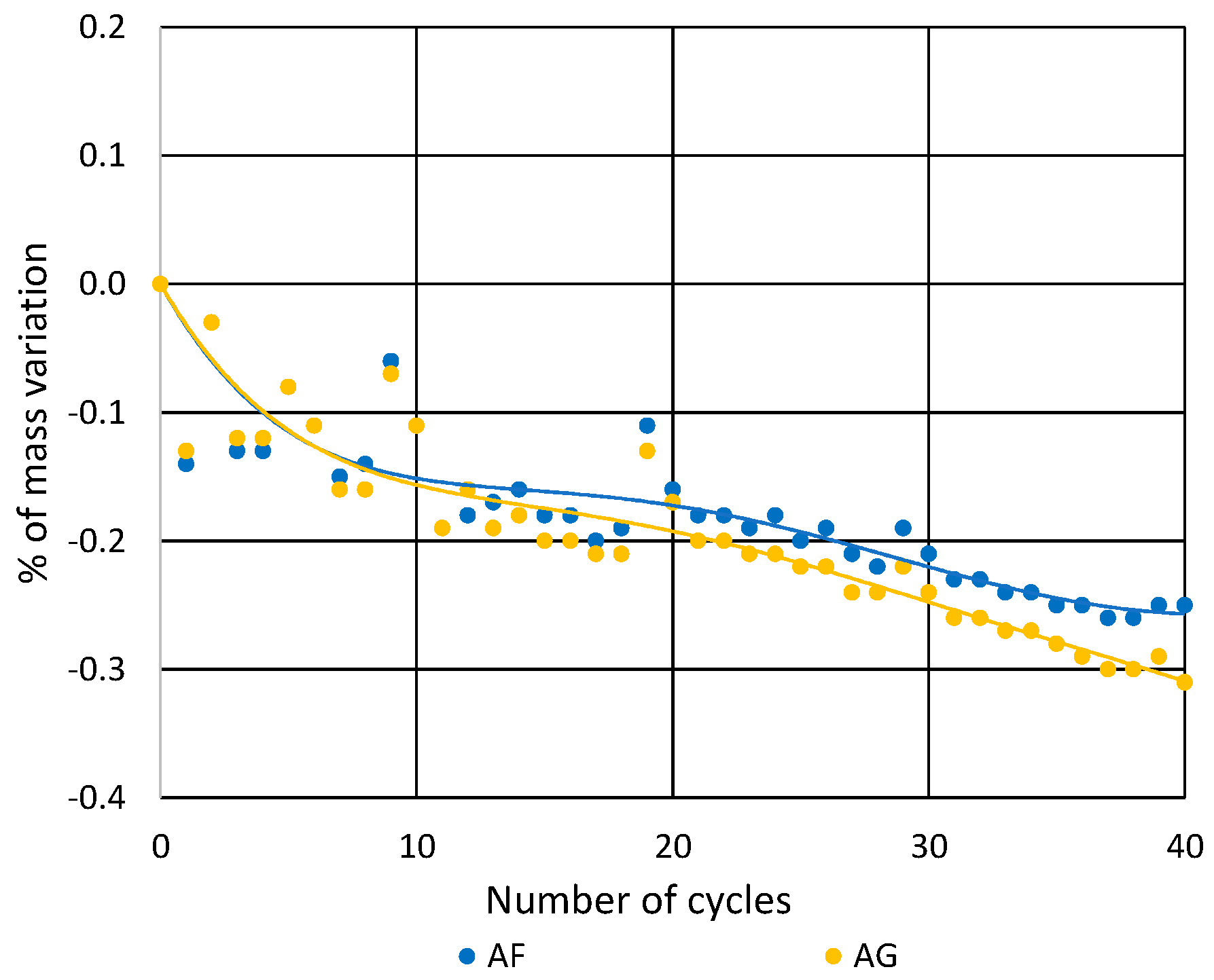

| Sample | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAS | 1.99 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 53.80 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 42.53 |
| MPS | 0.67 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 54.88 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.24 | 43.26 |
| MMS | 0.14 | <0.01 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 55.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 43.81 |
| MD | 0.09 | <0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.76 | 54.94 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.27 | 43.87 |
| AG | 63.63 | 0.42 | 13.38 | 3.89 | 0.05 | 5.81 | 3.67 | 2.16 | 2.57 | 0.12 | 4.30 |
| AF | 66.46 | 0.48 | 12.10 | 3.74 | 0.06 | 3.52 | 3.91 | 2.44 | 2.34 | 0.14 | 4.81 |
| Sample | Thermal Treatment (°C) | γd (g/cm3) | Abw (wt.%) | Abv (vol. %) | P (vol. %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Dev.st. | Mean | Dev.st. | Mean | Dev.st. | Mean | Dev.st. | ||
| MAS | 60 | 1.550 | 0.032 | 21.58 | 1.87 | 33.44 | 2.72 | 42.58 | 1.17 |
| 200 | 1.551 | 0.031 | 24.08 | 0.49 | 37.34 | 0.88 | 42.56 | 1.13 | |
| 350 | 1.548 | 0.021 | 26.87 | 0.90 | 41.59 | 0.82 | 42.67 | 0.78 | |
| 500 | 1.513 | 0.016 | 27.43 | 0.50 | 41.50 | 0.56 | 43.97 | 0.60 | |
| MPS | 60 | 1.535 | 0.055 | 20.65 | 3.44 | 31.65 | 5.15 | 43.16 | 2.05 |
| 200 | 1.545 | 0.103 | 21.90 | 3.51 | 33.59 | 3.38 | 42.79 | 3.81 | |
| 350 | 1.509 | 0.011 | 28.56 | 0.78 | 43.10 | 0.87 | 44.10 | 0.41 | |
| 500 | 1.483 | 0.009 | 29.18 | 0.23 | 43.29 | 0.46 | 45.06 | 0.32 | |
| MMS | 60 | 2.715 | 0.001 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0.05 |
| 200 | 2.698 | 0.001 | 0.32 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 0.01 | 1.00 | 0.05 | |
| 350 | 2.661 | 0.011 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 2.07 | 0.09 | 2.34 | 0.40 | |
| 500 | 2.562 | 0.003 | 2.30 | 0.02 | 5.89 | 0.04 | 5.98 | 0.12 | |
| MD | 60 | 2.720 | 0.004 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.15 |
| 200 | 2.713 | 0.002 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.44 | 0.07 | |
| 350 | 2.695 | 0.002 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.77 | 0.48 | 1.09 | 0.09 | |
| 500 | 2.612 | 0.047 | 1.51 | 0.72 | 3.92 | 1.81 | 4.16 | 1.73 | |
| AG | 60 | 2.684 | 0.004 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 0.13 |
| 200 | 2.682 | 0.001 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 0.02 | |
| 350 | 2.677 | 0.005 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.78 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.11 | |
| 500 | 2.634 | 0.011 | 0.74 | 0.10 | 1.93 | 0.27 | 2.43 | 0.42 | |
| AF | 60 | 2.685 | 0.002 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 0.57 | 0.06 |
| 200 | 2.682 | 0.001 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.67 | 0.04 | |
| 350 | 2.677 | 0.002 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.80 | 0.03 | 0.84 | 0.06 | |
| 500 | 2.610 | 0.006 | 1.08 | 0.06 | 2.81 | 0.16 | 3.34 | 0.23 | |
| Sample | Number of Cycles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | |
| MAS | −1 | −4 | −11 | −12 | −26 | −30 |
| MPS | −5 | −13 | −26 | −32 | −44 | −51 |
| MMS | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | −12 | −32 |
| MD | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| AG | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| AF | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lezzerini, M.; Tomei, A.; Gallello, G.; Aquino, A.; Pagnotta, S. The Crystallization Effect of Sodium Sulfate on Some Italian Marbles, Calcarenites and Sandstones. Heritage 2022, 5, 1449-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030076
Lezzerini M, Tomei A, Gallello G, Aquino A, Pagnotta S. The Crystallization Effect of Sodium Sulfate on Some Italian Marbles, Calcarenites and Sandstones. Heritage. 2022; 5(3):1449-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleLezzerini, Marco, Alessio Tomei, Gianni Gallello, Andrea Aquino, and Stefano Pagnotta. 2022. "The Crystallization Effect of Sodium Sulfate on Some Italian Marbles, Calcarenites and Sandstones" Heritage 5, no. 3: 1449-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030076
APA StyleLezzerini, M., Tomei, A., Gallello, G., Aquino, A., & Pagnotta, S. (2022). The Crystallization Effect of Sodium Sulfate on Some Italian Marbles, Calcarenites and Sandstones. Heritage, 5(3), 1449-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030076









