Nondestructive Analysis of Wall Paintings at Ostia Antica
Abstract
:- NMR depth profiles reveal the mortar-layer signature of hidden wall paintings
- NMR suggests a doubling of the top mortar layer in high-quality wall paintings
- The mortar-layer stratigraphy is destroyed when detaching wall paintings from the wall for preservation
- VIL suggests that Egyptian blue was used mostly in earlier and higher quality wall paintings
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
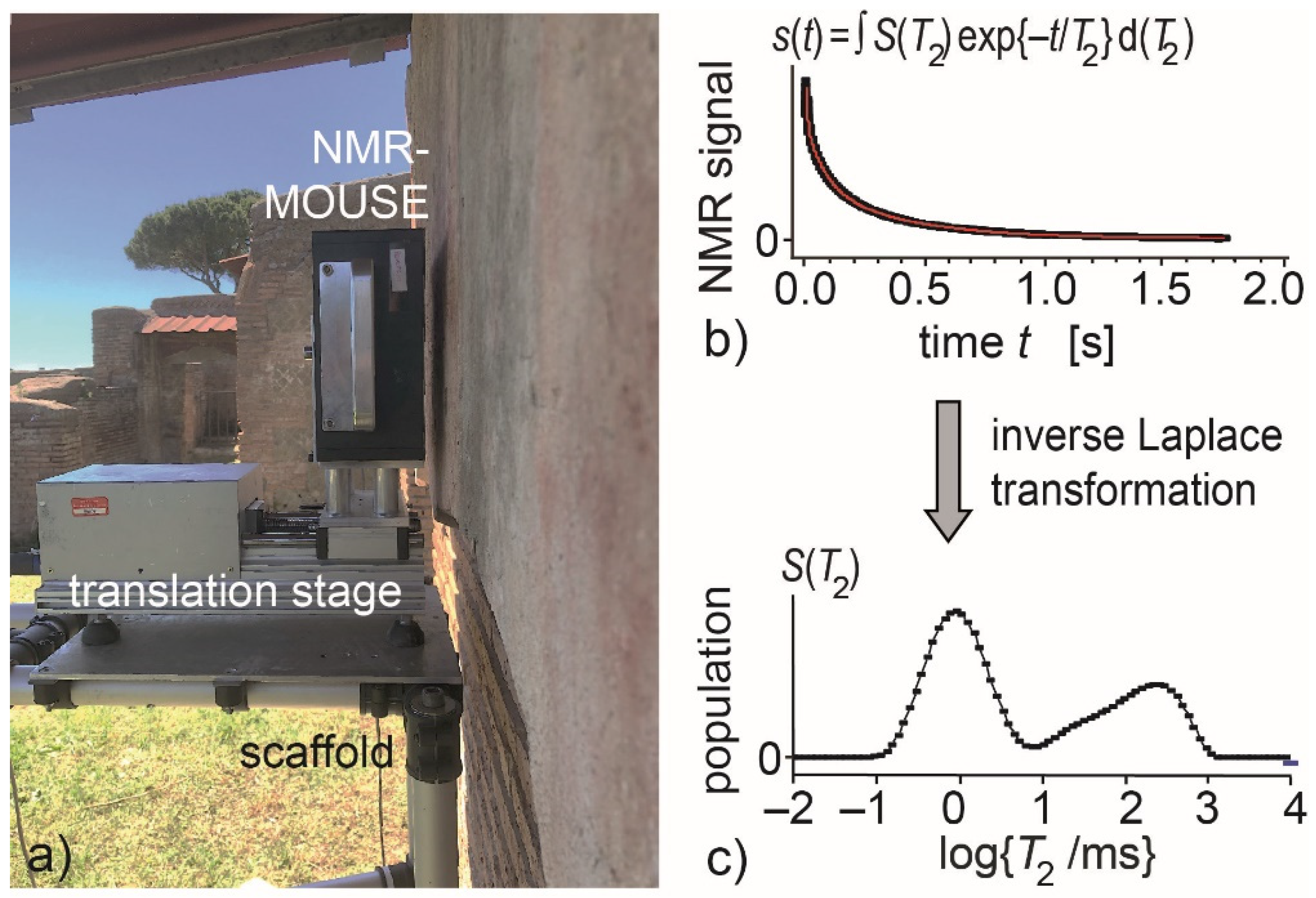
2.2. NMR Depth Profiles
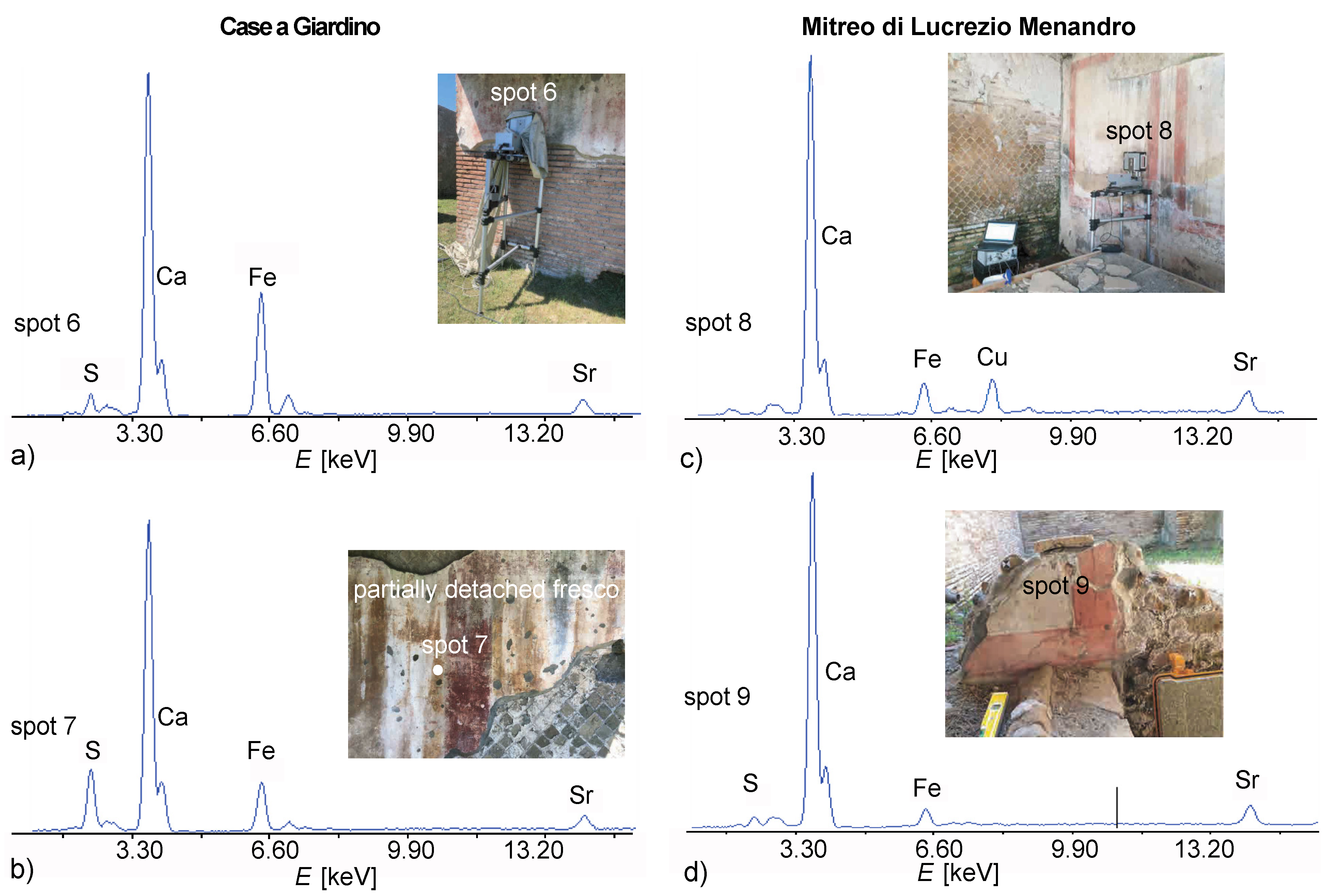
2.3. Portable X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
2.4. Visible Induced Luminescence (VIL)
3. Results
3.1. Hidden Wall Paintings
3.2. Stratigraphy of the Top Mortar Layers in Wall Paintings of High Quality
3.3. NMR Depth Profiles of Wall Paintings in Different Conditions of Preservation and Conservation
3.4. XRF and VIL Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinna, D.; Galeotti, M.; Mazzeo, R. (Eds.) Scientific Examination of Paintings. Handbook for Conservator-Restorers; Centro Di: Florence, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Casanova, F.; Wache, W.; Segre, A.; Blümich, B. Analysis of historical porous building materials by the NMR-MOUSE®. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2003, 21, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, N.; Capitani, D.; Rossi, E.; Cozzolino, S.; Segre, A.L. Unilateral NMR study of a XVI century wall painted. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 186, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümich, B.; Casanova, F.; Perlo, J.; Presciutti, F.; Anselmi, C.; Doherty, B. Noninvasive testing of art and cultural heritage by mobile NMR. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, D.; Di Tullio, V.; Proietti, N. Nuclear magnetic resonance to characterize and monitor cultural heritage. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectr. 2012, 64, 29–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baias, M. Mobile NMR: An essential tool for protecting our cultural heritage. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2017, 55, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baias, M.; Blümich, B. Nondestructive testing of objects from cultural heritage with NMR. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Webb, G., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Rehorn, C.; Blümich, B. Cultural heritage studies with mobile NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7304–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümich, B.; Perlo, J.; Casanova, F. Mobile single-sided NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectr. 2008, 52, 197–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Perlo, J. Single-Sided NMR, 1st ed.; Blümich, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Blümich, B. Essential NMR, 2nd ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Blümich, B.; Haber-Pohlmeier, S.; Zia, W. Compact NMR; de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Casieri, C.; Senni, L.; Romagnoli, M.; de Luca, F.; Santamaria, U. Determination of moisture fraction in wood by mobile NMR device. J. Magn. Reson. 2004, 171, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizi, L.; Camaiti, M.; Bortolotti, V.; Fantazzini, P.; Blümich, B.; Haber-Pohlmeier, S. One and two-dimensional NMR to evaluate the performance of consolidants in porous media with a wide range of pore sizes: Applications to cultural heritage. Micro. Meso. Mat. 2018, 269, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaschtschuk, D. Advances in Low-Field NMR Relaxometry. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Perlo, J.; Casanova, F.; Blümich, B. Profiles with microscopic resolution by single-sided NMR. J. Magn. Reson. 2005, 176, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shugar, A.; Mass, J. Handheld XRF in Art and Archeology; Leuven University Press: Leuven, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Accorsi, G.; Verri, G.; Bolognesi, M.; Armaroli, N.; Clementi, C.; Miliani, C.; Romani, A. The exceptional near-infrared luminescence properties of cuprorivaite (Egyptian blue). Chem. Commun. 2009, 23, 3392–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verri, G. The spatially resolved characterization of Egyptian blue, Han blue and Han purple by photo-induced luminescence digital imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verri, G.; Saunders, D.; Ambers, J.; Sweek, T. Digital mapping of Egyptian blue: Conservation implications. Stud. Conserv. 2010, 55, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, G.; Saunders, D. Xenon flash for reflectance and luminescence (multispectral) imaging in cultural heritage applications. Br. Mus. Tech. Bull. 2014, 8, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Blümich, B.; Haber, A.; Casanova, F.; Del Federico, E.; Boardman, V.; Wahl, G.; Stilliano, A.; Isolani, L. Noninvasive depth profiling of walls by portable nuclear magnetic resonance. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3117–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, A.; Blümich, B.; Souvorova, D.; Del Federico, E. Ancient Roman wall paintings mapped nondestructively by portable NMR. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehorn, C.; Kehlet, C.; Del Federico, E.; Zia, W.; Meldrum, T.; Blümich, B. Automatizing the comparison of NMR depth profiles. Strain 2018, 54, e12254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehorn, C.W.G. Studies of Tangible Cultural Heritage with Portable Stray-Field NMR. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baccini Leotardi, P. Pitture con Decorazioni Vegetali dalle Terme, Monumenti della Pittura Antica Scoperti in Italia III, 5; Polygraphic Institute and State Mint-State Archives: Rome, Italy, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Falzone, S.; Zimmermann, N. Stratigrafia orizzontale delle pitture delle Case a Giardino. Modello della fase originaria dei blocchi centrali del complesso ostiense. AnzWien 2010, 145, 107–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oome, N. The caseggiato del mitreo di lucrezio menandro (I iii 5). A Case-study of wall painting in Ostia 1. BABesch 2007, 82, 232–246. [Google Scholar]
- Blümich, B.; Anferova, S.; Kremer, K.; Sharma, S.; Herrmann, V.; Segre, A. Unilateral NMR for quality control: The NMR-MOUSE®. Spectroscopy 2003, 18, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Vitruvius, M.P. Ten Books on Architecture (De architectura libri decem); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Varone, A. L’organizzazione del lavoro di una bottega di decoratori: Le evidenze dal recente scavo pompeiano lungo via dell’Abbondanza. Meded. Van Het Ned. Inst. Rome 1995, 24, 124–136. [Google Scholar]
- Varone, A.; Béarat, H. Pittori romani al lavoro. Materiali, strumenti, tecniche: Evidenze archeologiche e dati analitici di un recente scavo pompeiano lungo Via dell’Abbondanza (Reg. IX Ins.12). In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Roman Wall Paiinting, Fribourg, Switzerland, 7–9 March 1996; pp. 199–214. [Google Scholar]
- Beeston, R.F.; Becker, H. Investigation of ancient Roman pigments by portable x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and polarized light microscopy. ACS Symp. Ser. 2013, 1147, 19–41. [Google Scholar]
- Aliatis, I.; Bersani, D.; Campani, E.; Casoli, A.; Lottici, P.; Mantovana, S.; Marino, I. Pigments used in Roman wall paintings in the Vesuvian area. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadori, M.L.; Barcelli, S.; Poldi, G.; Ferrucci, F.; Andreotti, A.; Baraldi, P.; Colombini, M.P. Invasive and non-invasive analyses for knowledge and conservation of Roman wall paintings of the Villa of the Papyri in Herculaneum. Microchem. J. 2015, 118, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, C.; Ciocan, V.; Vagnini, M.; Doherty, B.; Tabasso, M.L.; Conti, C.; Brunetti, B.G.; Miliani, C. Non-invasive and micro-destructive investigation of the Domus Aurea wall painting decorations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Galli, G.; La Russa, M.F.; Longo, F.; Maisano, G.; Majolino, D.; Malagodi, M.; Pezzino, A.; Ricca, M.; Rossi, B.; et al. Multi-technique investigation of Roman decorated plasters from Villa dei Quintili (Rome, Italy). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Fovo, A.; Mazzinghi, A.; Omarini, S.; Pampaloni, E.; Ruberto, C.; Striova, J.; Fontana, R. Non-invasive mapping methods for pigments analysis of Roman mural paintings. J. Cult. Herit. 2015, 43, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.; Jimenez de Haro, M.C.; Perez-Rodriguez, J.L.; Franquelo, M.L.; Herrera, L.K.; Justo, A. Determination of pigments and binders in Pompeian wall paintings using synchrotron radiation—high-resolution x-ray powder diffraction and conventional spectroscopy—chromatography. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 286–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, V.; Comite, V.; Andreoli, M.; Dematin, F.; Lombardi, C.A.; Fermo, P. Pigments on Roman wall painting and stucco fragments from the Monte d’Oro Area (Rome): A multi-technique approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradisi, A.; Sodo, A.; Artioli, D.; Botti, A.; Cavezzali, D.; Giovagnoli, A.; Polidoro, C.; Ricci, M.A. Domus aurea, the ‘Sala delle Maschere’: Chemical and spectroscopic investigations on the fresco paintings. Archaeometry 2012, 4, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, R.; Siddall, R.; Mazzoli, C.; Nodari, L. The temple of Venus (Pompeii): A study of the pigments and painting techniques. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbroscia, M.; Cestelli-Guidi, M.; Colao, F.; Falzone, S.; Gioia, C.; Gioia, P.; Marconif, C.; Mirabil Gattia, D.; Loreti, E.M.; Marinelli, M.; et al. Multi-analytical nondestructive investigation of pictorial apparatuses of “Villa della Piscina” in Rome. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarquini, O.; Pronti, L.; Lorenzetti, E.G.; Felici, A.C. Pigment identification on campana reliefs from the palatine hill and colosseum valley in Rome. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 43, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrucci, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Sorrentino, B.; Falzone, S.; Gioia, C.; Gioia, P.; Loreti, E.M.; Chiari, M. Characterisation of ancient Roman wall-painting fragments using non-destructive IBA and MA-XRF techniques. X-ray Spectrom. 2020, 49, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, R.; Crupi, R.; Frontoni, R.; Galli, C.; La Russa, M.F.; Licchelli, M.; Majolino, D.; Malagodi, M.; Rossi, B.; Ruffolo, S.A.; et al. Handheld XRF and Raman equipment for the investigation of Roman finds in the Villa deil Quintili (Rome, Italy). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofano, I.; Perez-Rodriguez, J.L.; Robador, M.D.; Duran, A. An innovative combination of non-invasive UV–Visible-FORS, XRD and XRF techniques to study Roman wall paintings from Seville, Spain. J. Cult. Her. 2016, 22, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracci, S.E.; Cantisani, S.; Falzone, M.M.; Tomassini, P. Archaeometry and Roman painting: The case of pre-hadrianic paintings in Ostia Antica. In La peinture Murale Antique, Méthodes Apports d’une Approche Technique, Actes du Colloque International de Louvain-la-Neuve, 21 Avril 2017 (AIRPA); Cavalieri, M., Tomassini, P., Eds.; Edizioni QUASAR: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Falzone, S.; Marano, M.; Tomassini, P. Decorating the harbour of Rome: Dynamics of production and craftsmanship in Ostian wall paintings. In Local Styles or Common Pattern Books in Roman Wall Painting and Mosaics, Proceedings of the Panel 3.22; Thomas, R., Ed.; Proceedings of the XIXth Congress of the Associazione Internazionale di Archeologia Classica (AIAC) 49–64; Propylaeum: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Terrapon, N. Les enduits peints du péristyle et de l’œcus 101 de la Domus aux Bucranes: Observations techniques. In Villas, Maisons, Sanctuaires et Tombeaux Tardo-Républicains: Découvertes et Relectures Récentes, Actes du Colloque International de Saint-Romain-en-Gal en L’honneur d’Anna Gallina Zevi (Vienne-Saint-Romain-en-Gal, 8–10 Février 2007); Perrier, B., Ed.; Edizioni Quasar: Rome, Italy, 2007; pp. 81–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bracci, S.; Cantisani, E.; Cantisani, E.; Conti, C.; Tomassini, P.; Martinad, M. Enriching the knowledge of Ostia Antica painted fragments: A multi-methodological approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 265, 120260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliny the Elder. Natural History, Book 35; Jones, W.H.S., Translator; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956; pp. 1–100. [Google Scholar]
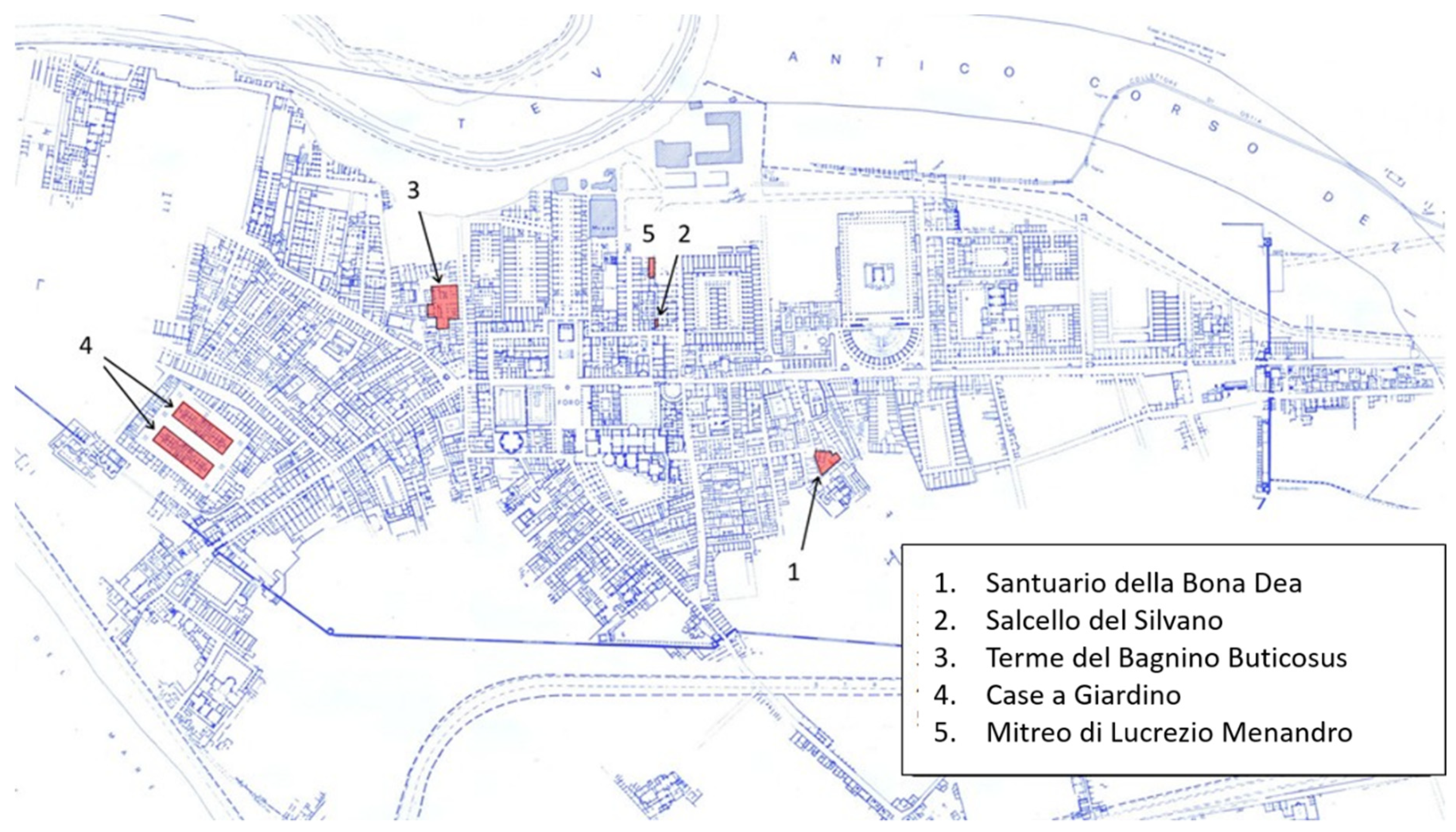







| Location | Description | Spot Number | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Santuario della Bona Dea | detached wall painting | 1, 2 |  |
| Santuario della Bona Dea | wall section | 3 |  |
| Terme del Bagnino Buticosus | wall sections | 4, 5 |  |
| Case a Giardino | wall sections front and side | 6, 7 |  |
| Mitreo di Lucrezio Menandro | wall sections | 8, 9 |  |
| Nuovi Depositi | fragments | 10, 11, 12 |  |
| Building/Fragment | Spot | Date | Area studied | Elements Present | Pigments by XRF/VIL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Santuario della Bona Dea | 1 | 1st c C.E. |  | Ca, Fe, Sr (S) | Iron-based red |
| 2 | 1st c C.E. |  | Ca, Fe, Mn, Sr (S) | Iron-Manganese based black | |
| 3 | 1st c B.C.E. |  | Si, Ca, Fe, Cu, (Pb) | Iron-based yellow, red and green, pigments, Egyptian Blue (C black) | |
| Terme del Bagnino Botiscus | 4 | 3rd c C.E. |  | Ca, Fe, (Pb) | Iron-based red |
| 5 | 3rd c C.E. |  | Ca, Fe | Iron-based red | |
| Case a giardino | 6 | 2nd c C.E. |  | S, Ca, Fe, Sr | Iron -based yellow |
| 7 | 2nd c C.E. |  | S, Ca, Fe, Sr | Iron-based red | |
| Mitreo di Lucrezio Menandro | 8 | 1st c C.E. |  | (Si), Ca, Fe, Cu, Sr | Iron-based red, green and yellows, Egyptian Blue, Calcium-based white |
| 9 | 2nd c C.E. |  | Ca, Fe, Sr | Calcium-based white | |
| Fragments | 12 | 1st c B.C.E. |  | S, Ca, Fe, Hg, Sr | Cinnabar (HgS) |
| Salcello del Silvano | 13 | 3rd c C.E. |  | S, Ca, Fe, Pb, (Cu), (Zn), Sr | Iron and Lead-based pigments |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blümich, B.; Del Federico, E.; Jaschtschuk, D.; Küppers, M.; Fallon, K.; Steinfeld, A.; Tomassini, P. Nondestructive Analysis of Wall Paintings at Ostia Antica. Heritage 2021, 4, 4421-4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040244
Blümich B, Del Federico E, Jaschtschuk D, Küppers M, Fallon K, Steinfeld A, Tomassini P. Nondestructive Analysis of Wall Paintings at Ostia Antica. Heritage. 2021; 4(4):4421-4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040244
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlümich, Bernhard, Eleonora Del Federico, Denis Jaschtschuk, Markus Küppers, Katelin Fallon, Adelaide Steinfeld, and Paolo Tomassini. 2021. "Nondestructive Analysis of Wall Paintings at Ostia Antica" Heritage 4, no. 4: 4421-4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040244
APA StyleBlümich, B., Del Federico, E., Jaschtschuk, D., Küppers, M., Fallon, K., Steinfeld, A., & Tomassini, P. (2021). Nondestructive Analysis of Wall Paintings at Ostia Antica. Heritage, 4(4), 4421-4438. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4040244






