1. Introduction
The origin of Tibetan Dzi beads, also known as “tian zhu” (heaven’s pearl) or commonly accepted as Tibetan beads, has always been a mystery. They first appeared between 2000 and 1000 BC in countries surrounding the Himalayas. Authentic Dzi beads are found primarily in Tibet, according to Bolin [
1]. There are many legends about how these beads came to be. This is because the Tibetan people believe the beads are of supernatural origin [
2]. One story tells of semigods owning them as ornaments. It is said that the beads would be thrown away if they became imperfect in any way. This story explains why Dzi beads are never found in perfect condition [
1,
2]. Another story is perhaps more well-known and widespread, describing the Dzi beads to be insects. The story tells of a man in the mountains who supposedly threw his hat over such an insect, petrifying it. This petrified insect is said to have been a Dzi bead [
1,
2]. There are a multitude of other stories that have been told, including the Dzi bead being found in the horns of slaughtered animals as well as in dung [
1,
2,
3]. The people of Tibet hold these beads in high regard and consider them heritage gems; they are reluctant to sell them for low sums, especially to those in the Western world. Therefore, there has been very little scientific research conducted on them. It is generally accepted, however, that Dzi beads are made from agate, a form of chalcedony quartz with a chemical composition of SiO
2 [
1,
2,
3].
It is said that the owner or wearer of a Dzi bead is protected from catastrophe. The Dzi bead supposedly wards off evil spirits that might have ill effects on the wearer [
1,
2]. While being worn, if the bead breaks or chips, it is thought to have served its purpose and has absorbed the energy of a catastrophic event that was intended for the wearer. Thus, the effects of the bead are rendered useless, as it is no longer regarded as “pure” [
1,
2]. The only time a Dzi is deliberately broken is for medicinal purposes. Doctors in Tibet use powder from the beads mixed with herbs to treat ailments such as epilepsy [
1,
2].
In Ebbinghouse and Winsten’s article, they mention three techniques that have been recorded for creating Dzi beads [
2]. The first technique for creating a white pattern on a natural stone background involves the painting of an alkali substance onto the surface of the bead and then firing the whole bead [
3,
4,
5]. The area that has been painted then turns white, and this continues through the surface into the Dzi bead interior [
6,
7]. The second technique creates a black design on a whitened background. The whitening is done with the aforementioned technique on the entire bead, and then the dark pattern is painted with a chemical such as copper nitrate [
8]. Using similar techniques, the third type of Dzi is a black design on a natural stone background [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. It should also be noted that drill bits made of reed in the old days and then copper were used to drill holes in the crafting process. Bolin’s book (p. 29) also describes similar treatments in the craft, including darkening with plant sugar and heat, beaching and white line etching with natron (a naturally occurring mixture of sodium carbonate decahydrate, Na
2CO
3·10H
2O, and sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO
3, along with small amounts of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate) and protecting the desired areas with grease, clay, etc. [
1].
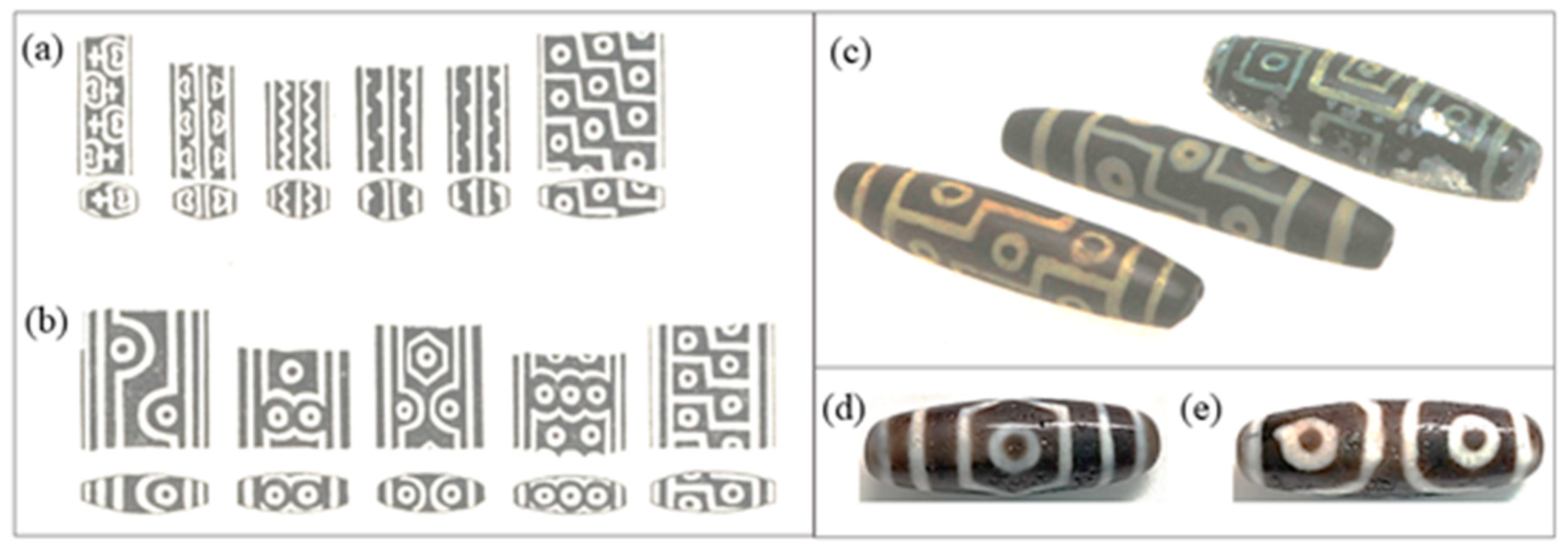
The Tibetan people only regard certain Dzi beads as real or “pure”. Dzi beads come in a varied array of patterns, shapes and sizes. A set of patterns that are universally recognized as “pure” are the “eye” patterns, as shown in
Figure 1a,b together with representative fakes (
Figure 1c) and the three-eye specimen we used in this investigation,
Figure 1d,e. Every pattern holds a different meaning and benefit to the wearer [
1,
2,
3]. The most highly coveted Dzi bead is the nine-eye bead. This bead symbolizes the nine planets, holds the activity of the entire universe and possesses the wisdom of humanity [
1,
2], and it is said to assist the owner in gaining wealth, good health, success, power, compassion and glory [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8].
Tibetans have created criteria for what makes a Dzi bead valuable. As mentioned, the bead must have a desirable pattern that is considered “pure”. A Dzi bead must possess a round cross-sectional shape and not appear thin [
1,
2]. As noted above, the Dzi bead must not be broken or chipped, as this is said to reflect the fact that it has already served its purpose. When held up to the sun, the bead should be translucent or reveal any internal flaws with the pattern, although there are exceptions [
1,
2]. Tibetans know how to identify a genuine Dzi bead from a fake; however, imitations have been created because these beads are so valuable.
The demand for Dzi beads in Asian regions has increased and spurred the production of replicas. Some replicas have such minute details that they must be observed more closely under a microscope or cut open to reveal if they are fake. In most cases, it has been identified that a replica weighs less than the original [
4]. Other replicas are fitted with a metal center to imitate the weight of the real beads. Dzi bead replicas are usually made of plastic, glass or a light metal such as aluminum; examples are shown in
Figure 1c [
4].
The objective of this work is to investigate the pattern, the elemental and chemical composition as well as the structure of a three-eye Dzi bead using conventional laboratory techniques, such as optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and advanced X-ray techniques from a synchrotron source. X-ray diffraction (XRD) reveals the crystal structure and, hence, mineral formation of the bead; X-ray fluorescence (XRF) reveals its elemental composition; and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) reveals the local structure of a selected element of interest. Using a micro-X-ray beam, we can conduct microscopy and microanalysis of the different patterns of the specimen. We have gained considerable experience over the years in the research and development of these techniques [
9] and are encouraged by our recent success in retrieving high-resolution images from badly tarnished daguerreotypes [
10,
11,
12], the first public photographs in human history. The applications of X-rays from synchrotrons in art and archaeology have also been reviewed recently [
13]. Based on these techniques, we will attempt to investigate if the specimen is genuine or fake, if the pattern is natural or man-made and if there is any evidence for the crafting methods we noted above, as described by Bolin and Ebbinghouse and Winsten [
1,
2]. We show below that we can provide some positive answers for these questions in this preliminary study using synchrotron radiation.
4. Discussion
We have presented and analyzed all data from XRD, XRF imaging and micro-XANES of selected regions of the Dzi bead. We now attempt to understand what these results mean in connection with the questions we set out to explore: (1) what is this three-eye Dzi bead made of, (2) is it genuine or fake and (3) how was the crafting done?
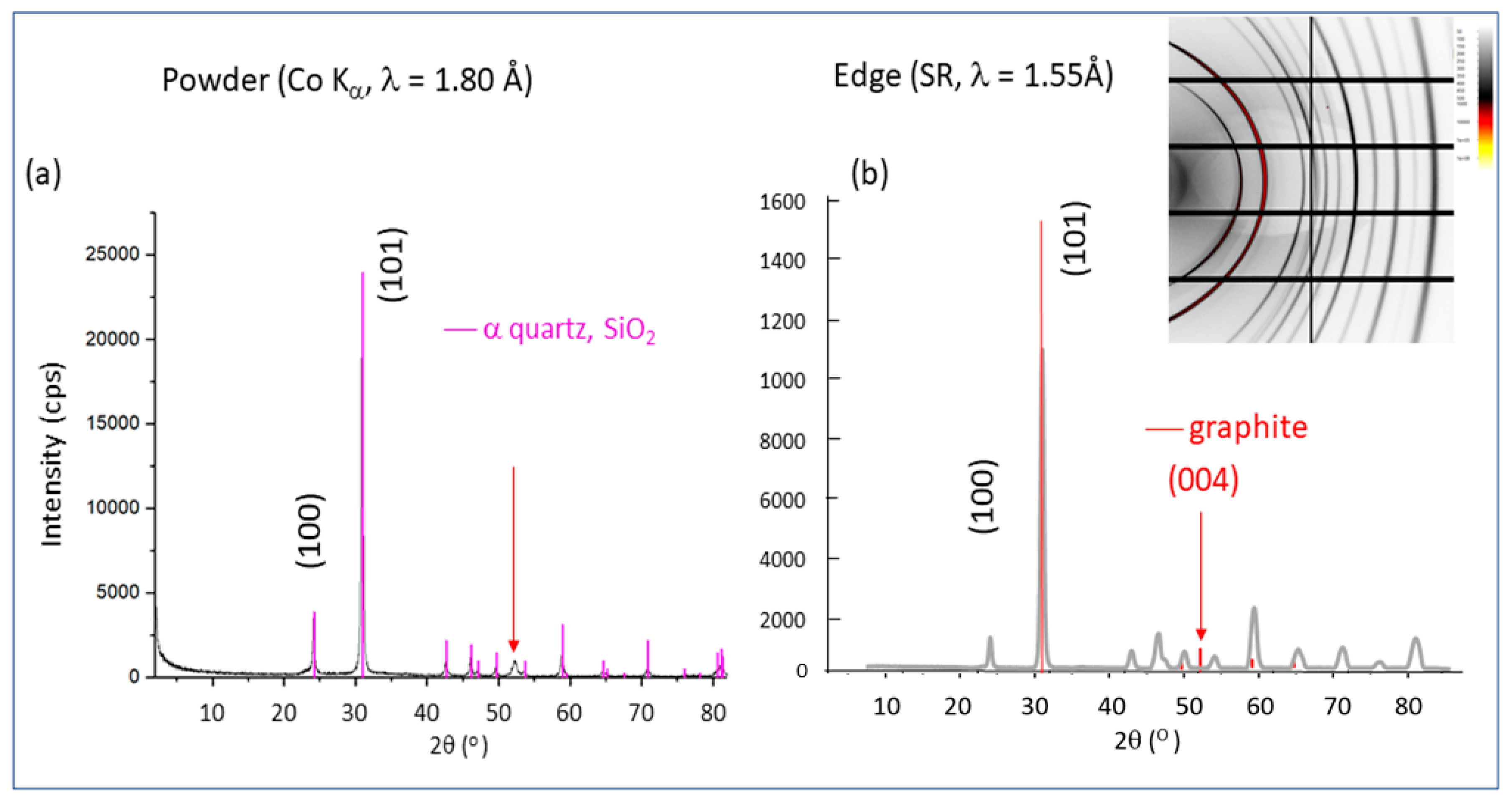
We begin with the first question. Based on the XRD, XRF mapping and XANES, there is absolutely no doubt that this sample was made of SiO
2 (quartz) consistent with an agate origin. For the second question, since it is generally agreed by Dzi bead collectors and traders that Dzi beads are made of agate, our observations clearly show that it was made of SiO
2 (quartz), which eliminates all the fake possibilities illustrated in
Figure 2c (plastic with metal core, polymer clay and painted aluminum).
The third question is perhaps the most interesting yet challenging and is most relevant to our analysis. Based on the descriptions of Bolin [
1] and Ebbinghouse and Winsten [
2], there are many ways to inspect Dzi beads and how they are crafted. We will focus on the surface-etched rings; the dark and light pattern; and how the XRF map, especially the Cu pattern we found in this analysis, may reveal how this three-eye Dzi bead was crafted.
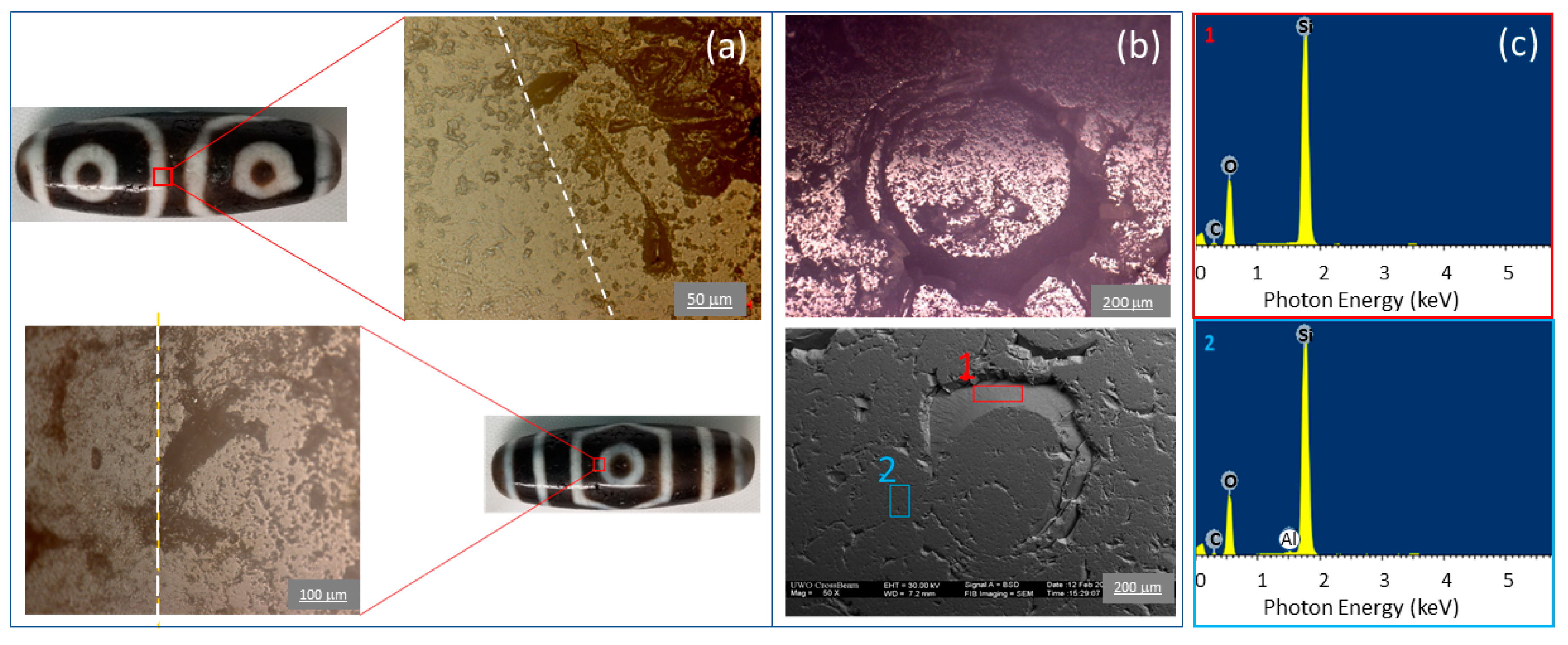
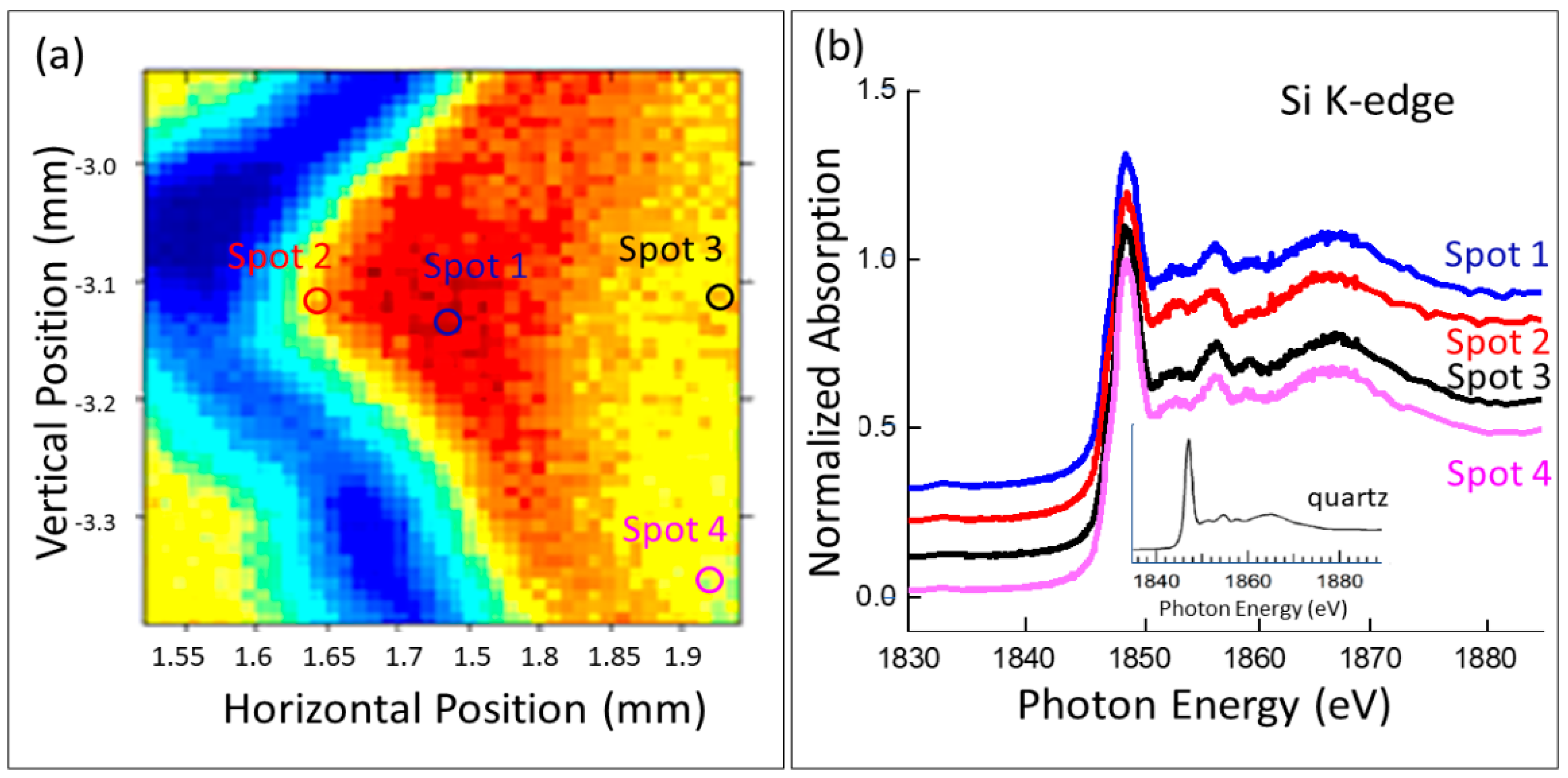
From the optical image, we see that it showed well-defined light (white) and dark patterns, and the surfaces were covered with etched rings; these are the general characteristics of Dzi beads. Upon slicing the bead in half, we could see that the piece was translucent, and the white pattern did extend considerably into the bulk, as described by Ebbinghouse and Winsten [
2]. None of the SEM, EDX, XRD and XRF mapping techniques showed any clear boundary between the light and the dark region, however. XRD of the powder showed the presence of graphite, while microdiffraction of the edge of the slice did not. It is unclear whether this is due to the sensitivity of the microbeam looking at a very small area or whether the powder was contaminated by carbon during the grinding process. This awaits future exploration. The presence of graphite may be related to light absorption in the dark region, however.
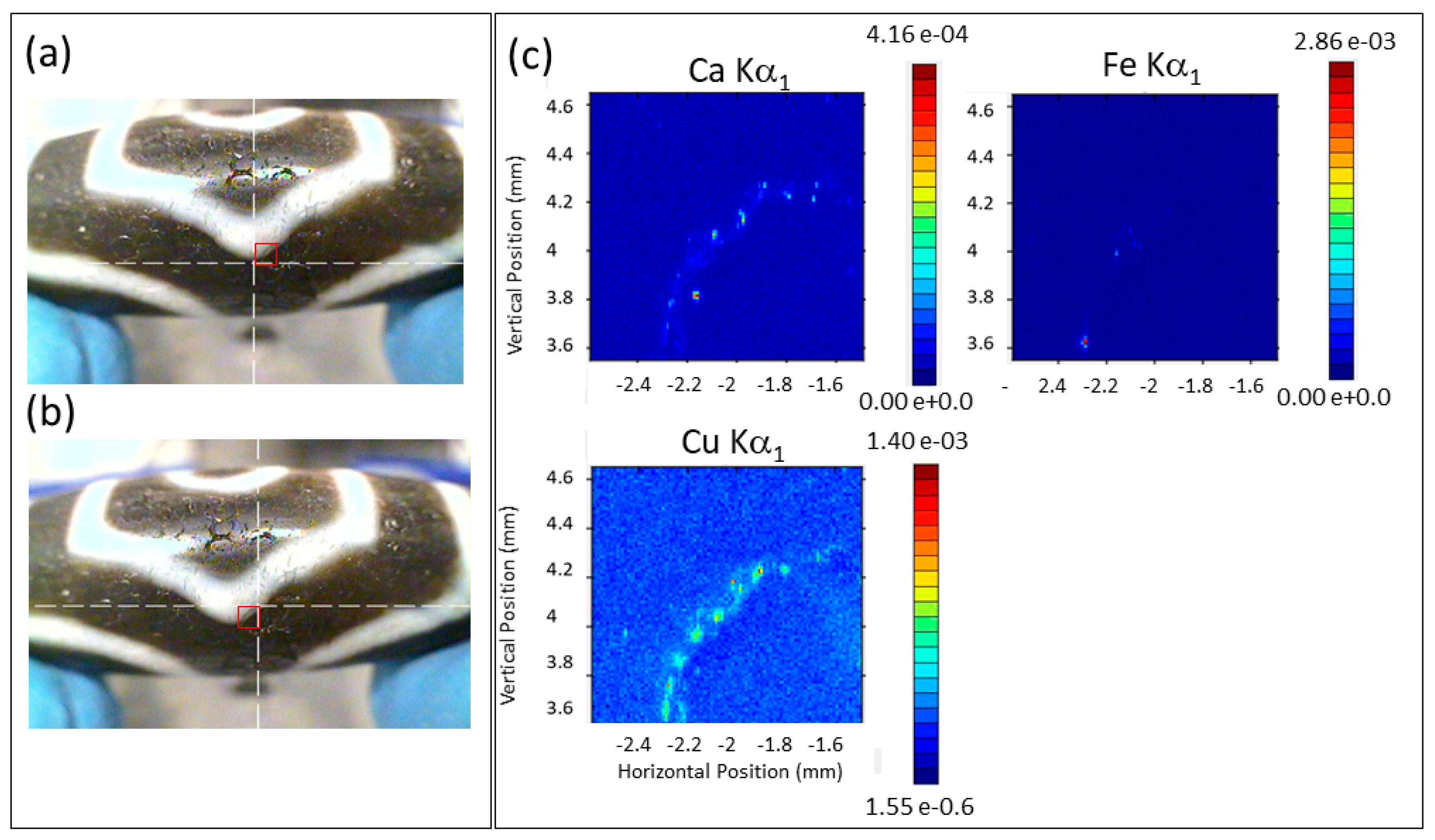
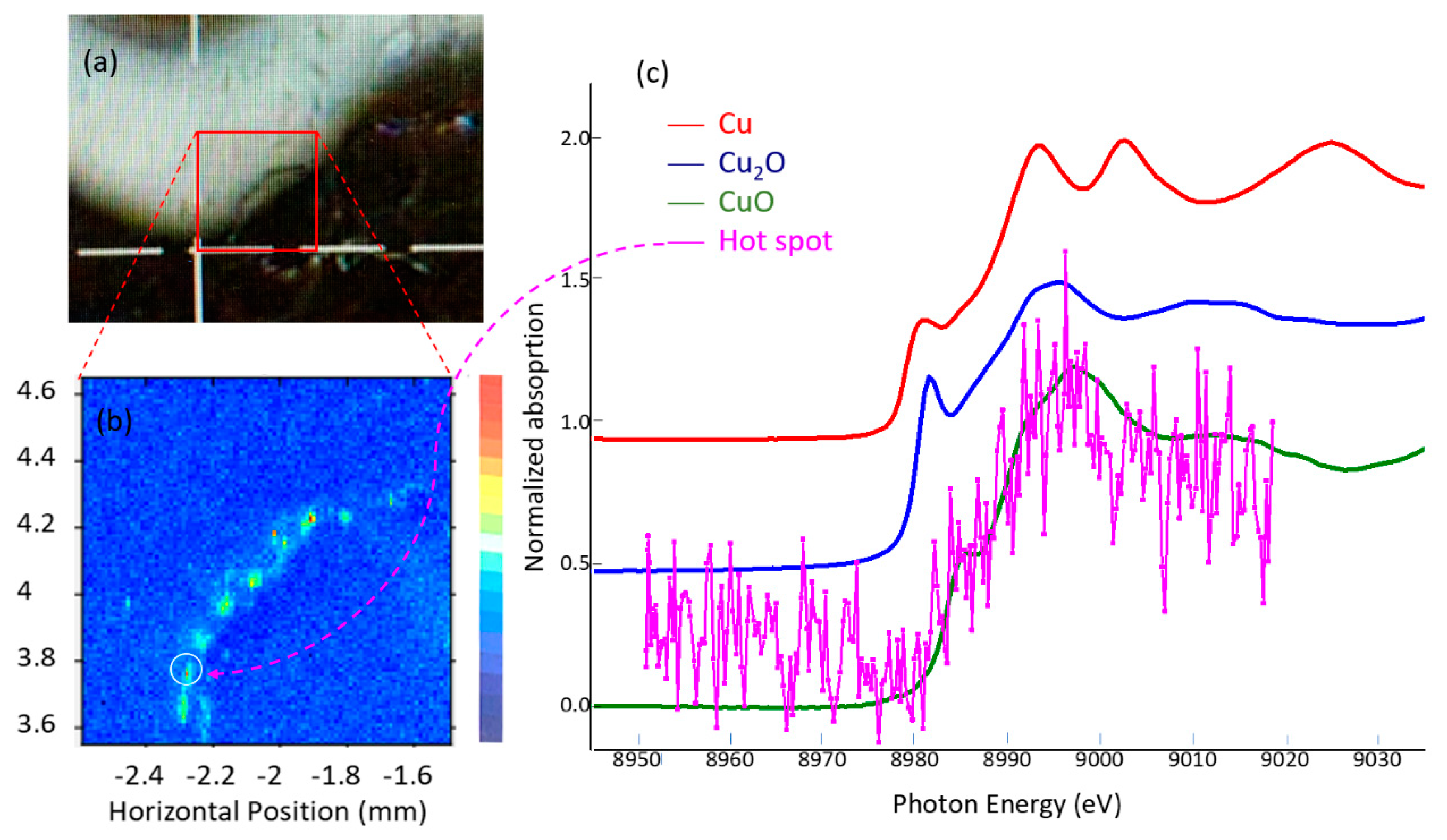
The most interesting finding was the hot spots of Cu on the circumference of the etched ring. In both Bolin’s book [
1] and the work of Ebbinghouse and Winsten [
2], drilling with small bits and the use of alkaline material and copper nitrate, Cu(NO
3)
2, were mentioned as agents put on the bead surface, followed by firing for whitening and darkening functions, respectively. The regular separation (~1 mm) of the Cu spots of ~20 µm in size could be speculated to be the tiny drill holes to facilitate diffusion of chemicals used in the pattern formation. The presence of CuO in all the Cu hot spots was likely the result of the following reaction upon firing:
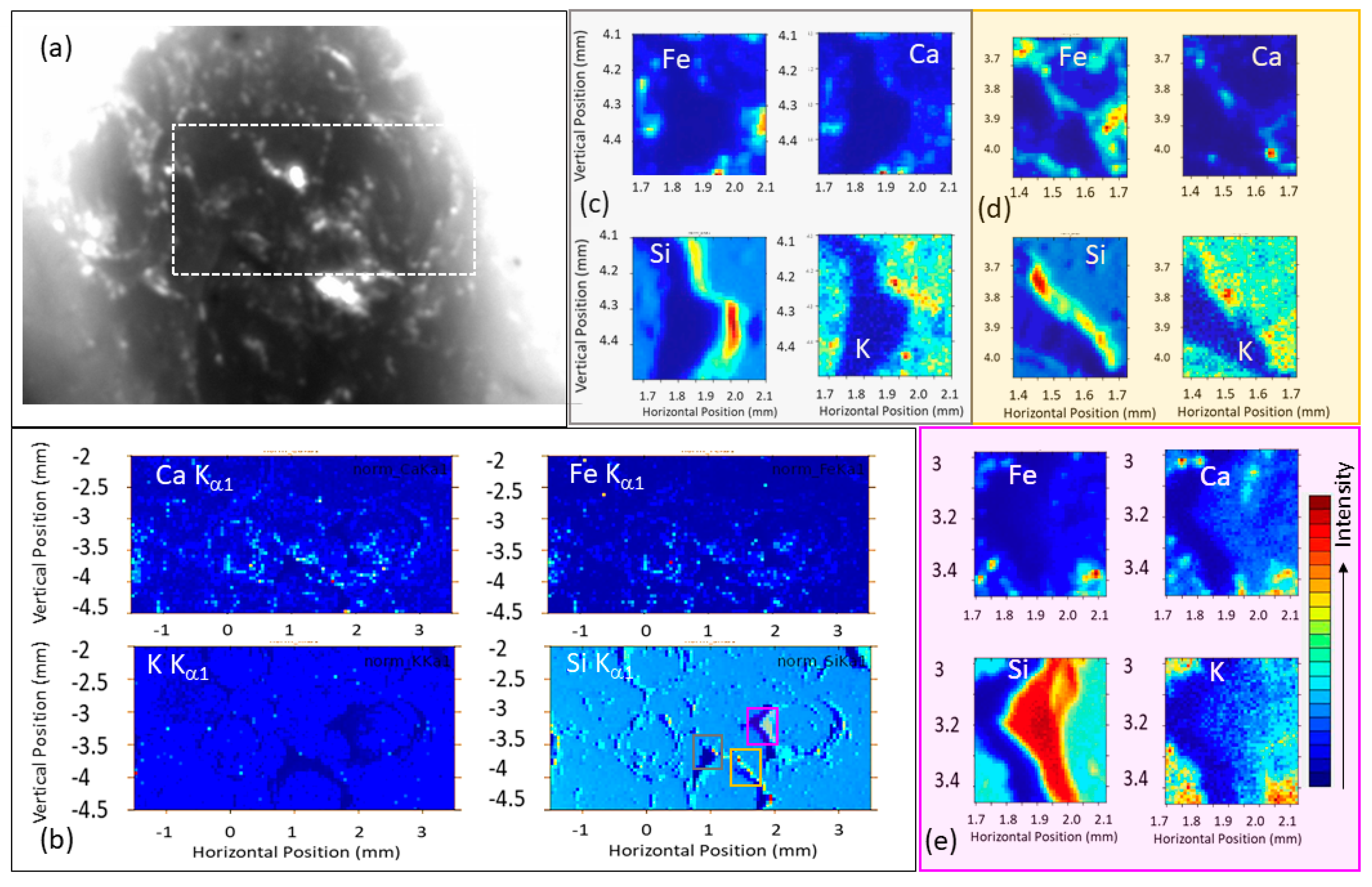
In addition to Cu, Ca and Fe were also found with both 12.0 keV (VESPERS) and 7.13 keV (SXRMB) excitation photon energy in the XRF map overlaying that of the Cu. K was also found in the tender X-ray map (not looked for in VESPERS); the origin of Ca is less clear, and Fe may have come from the tools used in crafting. It should be noted, however, that Fe is also commonly found in agate as a trace element, while Ca and K are not [
18]. Compared to the Si map, which showed extruding pilings of SiO
2 on the circumference of the rings, the Cu spots appeared to be more like tiny pits. The Si and Cu map were correlated (
Figure S4. It is also interesting to note that while we found CuO from the micro-XRF, it could not be detected in the XRD.
Finally, our preliminary finding was consistent with the descriptions noted in the literature [
1,
2]. Presumably, a piece of translucent agate was polished into shape and treated with alkaline solution. SiO
2 is slightly acidic, and a potash solution could do the etching (dissolving SiO
2), and the light region could come from the increased porosity. The use of pyrolytic Cu(NO
3)
2 and firing would produce CuO, which appears black. The origin of regular hot spots of CuO on the ring was possibly from drilling. The presence of graphite remains a mystery; repeated XRD measurements of various regions of the bead (not powder) revealed no crystalline carbon. The origin of carbon requires further investigation, although if plant sugar was used for darkening under heat and reed drill bits were used, it could be a source of carbon.
5. Conclusions
We have reported the preliminary results of an exploration of the mysterious Dzi beads by studying a three-eye bead using laboratory-based optical microscopy and SEM and the advanced synchrotron techniques including XRD, XRF imaging and micro-XANES. The specimen, including the surface, the edges and the interior after slicing, was inspected with an optical microscope and SEM. The crystal structure from a powder specimen, the surface and the edges of a sliced piece were subjected to XRD. They all showed the structure of quartz (SiO
2). While there appeared to be a trace of graphite in the former, it was not detected in the latter. XRF imaging also shows that the bead was made of SiO
2; in addition to SiO
2, there were regular Cu hot spots, as well as Fe, Ca and K at lower concentrations on the circumference of the etched rings. We can conclude, from the material perspective, that the three-eye bead specimen was genuine, and the patterns (dark and light as well as the etched rings), which were apparent to the naked eye, were crafted. The discovery of regular small pits containing copper oxide (CuO) on the circumference, which correlated with the SiO
2 map, and the presence of potassium were consistent with the crafting methods described in the literature [
1,
2].
Finally, while we have not fully answered the question on the origin of these beads nor expect to do so with a single specimen, in a broader context that will require further studies of representative samples from various regions and times, we are optimistic that the tools and the methodologies introduced here will play a significant role in future studies.