Abstract
Despite the growing attention to Underwater Cultural Heritage (UCH) in Europe and worldwide, the efforts in wholly enjoying underwater archaeological assets and sites are still remarkable; hence, the need for innovative research and solutions that are suitable for raising knowledge on the subject. In this way, this paper wants to be a review for highlighting all of the developments, potentials, and results achieved in the last decade to reach a good protection of UCHs related to the study of stone materials, degradation processes, and the new methods for protection/consolidation directly in situ. The present work is focused on the analysis of the main results obtained from several studies conducted to date, providing additional guidelines for operators in the UCH sector (i.e., restorers, archaeologists, conservation scientists, geologists, etc.). Such guidelines will be a very useful key factor in enhancing knowledge, management, protection, and promotion of underwater sites. In particular, the purpose of this paper is to provide an analysis of the state of the art on both consolidated techniques for studying materials coming from seawater and innovations in the field of protection and consolidation of UCH against biofouling, the main cause of damage in underwater environments.
1. Introduction
For the last several decades, and after the adopted UNESCO Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage (UCH) [1], the safeguarding of materials from underwater environments has represented an ongoing challenge in the field of conservation of UCH [1]. Conservation of UCH is essential to preserve humankind’s history and ancient traditions, safeguarding tangible evidence of past human life while ensuring its accessibility and knowledge to future generations. A great cultural heritage lies beneath the worldwide sea, counting the archaeological remains of more than three million vessels, as well as historic/archaeological monuments and whole cities [1]. In terms of conservation, and even before the adoption of the UNESCO convention, there have been significant contributions to the study and treatment of waterlogged and decayed materials, such as the research carried out by Cronyn [2] and Hamilton [3]. Special attention was given, as it is still today, to preventive conservation in situ, including all actions and solutions to reduce the deterioration and loss of historical/archaeological sites and ancient material remains. Underwater archaeological sites worldwide, particularly in coastal areas, are often tourism-based economies with the potential to include important UCH assets, but, due to their geomorphic features, they are also vulnerable to the effects of climate changes and the various and changing parameters that affect the environmental conditions in marine ecosystems [4,5,6,7].
From the beginning of modern underwater archaeology, more or less starting from the 1930s, scientists and researchers working on such specific and innovative subjects faced common and considerable challenges mainly linked to: (a) The lack of techniques, methods, tools, and resources tailored for the preservation of UCH, also in situ; (b) insufficient measures to tackle the effects of climate changes or the damages that materials suffered in underwater environments. Moving from these difficulties, scientific and international Cultural Heritage protection organizations agreed on promotion, protection, and, where possible, in situ preservation of underwater archaeological and historical Heritage (i.e., [1,8]). Specifically, the UNESCO Convention [1] provided a detailed States-cooperation system and set out the basic principles for the protection of UCH. To date, the Convention has been ratified by 63 countries. One of the main goals of that Convention states that the in situ preservation of UCH should be considered as the first option before engaging in any further actions. Following these principles and recommendations, in the last twenty years, many research works were focused on developing and testing new techniques and tools to support the protection and in situ conservation of underwater archaeological remains/structures [9,10,11,12,13].
Starting from these considerations and with the goals of this work, there is the need to show to the general public and experts in the field the integrated approach for the protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage pursued by several researches to date through the transferring of the main outputs and outcomes [14,15,16,17].
Based on the results achieved and research conducted, an overview is reported on how to guarantee and deal with the correct management of UCH, highlighting which are the best practices and techniques adopted to date. In particular, through the years, different analytical techniques have been adopted and implemented to study stone materials and their interaction with the aquatic environment (considering parameters such as salinity, pH, sea level, currents, waves, depth, biological activity, etc.) [18,19,20]. In the present work, a special focus is paid to studying the damage caused to stone materials due to biological activity through validated analytical techniques; also, a brief overview of the latest challenges and the experimentation with some eco-sustainable methods, techniques, and products to be applied in situ is presented.
2. Stone Materials’ Damage Underwater
Historical stone materials lying on the seabed may exhibit different deterioration forms and conservative conditions regardless of the discovery areas and epochs of belonging. Decay processes are mainly linked to the different and changing exposure conditions and are also related to the properties of the constitutive materials [4,5,6,7,21,22,23]. The existing relationship between “Cultural Heritage—Environment” has a key role in the study of degradation processes of underwater resources; it is supported by experts in the field to such an extent that the assessment of the environmental parameters and their interactions with the minero-petrographic material’s properties is necessary in planning a diagnosis and to undertake conservation strategies aimed at protecting the UCH.
According to the latest research [4,5,6,7,10,12,13,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23], in the framework of conservation of the UCH, two main steps should be pursued by scientists. The first one focuses on the study of the state of conservation, while the second one implies the study and testing of preventive and conservative methods to reduce the damage by developing new conservation strategies. Concerning the study of the complex processes and mechanisms of stone decay (step I), there is awareness of a knowledge of the marine habitat, where the materials (i.e., UCH) find a new lying site, becoming substrates for the growth of diversified biotic communities. Generally, they are benthic forms growing in close association with hard substrates, enclosing the communities of both plants and animals. The growth of benthic organisms determines the formation of biofouling, nothing more than an encrustation, more or less thick and layered, on the surface of the materials. The development and growth of biofouling, also considering its classification as macrofouling, microfouling, and biofilm, vary temporally according to the different biological, physical–chemical, and environmental factors, and are a well-known phenomenon widely described by various experts in the field [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31].
The study of the benthic community may represent a precious tool for giving insights about the growth of the marine organisms and the preference of one substrate rather than another, as well as for deepening the knowledge on the marine life and bioreceptivity of the investigated areas [5]. The life cycle of some of these organisms (i.e., biodeteriogens) is among the main causes that contribute to the deterioration of stone assets located on the seabed. Anyway, in limited proportions and certain conditions, the phenomenon is not unequivocally harmful. In addition, there are cases in which such marine organisms become key elements for the occurring of the damages, sometimes causing extensive and irreversible losses (bioerosion phenomenon) [5,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. The latter phenomenon is among the most aggressive and occurs mainly on calcareous substrates, also considering rocks, shells, etc. [38,39]. It is a destruction process of substrates, activated by various marine organisms through several mechanisms, such as excavation, perforation, abrasion, etc. [31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
Bioerosion and Calcareous Materials
The organisms causing bioerosion phenomena include both micro-perforating organisms (such as algae, bacteria, and fungi) and macro-perforating ones (such as bivalves and sponges). This phenomenon primarily affects carbonate materials and can occur superficially or push deeply inside the substrate, producing internal cavities.
The external phenomenon is mainly generated by the activity of grazers, herbivorous organisms such as echinoderms, gastropod mollusks, and some fish that graze on the substrate, removing significant portions. In depth, the substrate can instead be destroyed by the action of endolithic perforators, such as porifera and mollusks. Strong evidence on this phenomenon can be found in the studies of the Croatian biologist Stjepko Golubic [40], among the first pioneers to detect and study bioerosion phenomena on carbonate surfaces from underwater environments.
His studies show that organisms, particularly those that carry out the endolithic activity, penetrate the rock by digging cavities and/or tunnels through chemical–physical and biological processes, where they lie and reproduce. These processes, which similarly occur on the biogenic substrates of carbonate nature (such as Posidonia oceanica, Maerl beds, coralligenous, tegnùe, deep corals, etc.) and natural calcareous rocky seabed [31,32,33,34,35,36,37], suggest that bioerosion is among the most aggressive and devastating decay processes affecting submerged calcareous stone materials [5,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. The growth of benthic forms on calcareous materials may cause damage attributable to three distinct classes: Structural, functional, and aesthetic damage. Generally, but not always, the types of damage occur simultaneously despite the prevalence of one over the other. This variability could be related to the diversified and changing environmental parameters (light, temperature, depth, topography of the seabed, water, salinity, etc.), which may or may not affect the growth of certain marine organisms. So, individual species may exhibit more or less wide tolerance spectra of growth depending on the surrounding environment.
The most appropriate methodological approach is therefore represented by a systematic ecological study of the marine habitat, looking to study the causes that may have favored the development of a particular species rather than another on that material [36,37,38,39,41]. Moving from these considerations, it is clear that to investigate the bioerosion phenomena in underwater environments, the relationships that organisms establish with submerged materials, evaluating their close connections, must necessarily be investigated.
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods Applied in Geosciences to Study UCH
A preliminary investigation method for the study of degradation products affecting underwater materials, a macroscopic mapping of the item, is needed, possibly in situ. This stage allows an overview of marine organisms’ distribution and rate to detect environmental parameters of the site and the lying conditions of the cultural resources (burial, exposure, etc.), as well as the definition of danger levels and indices. Detailed mapping systems are used for data collection, specially processed by the ICR (Central Institute for Restoration, Rome) for the definition of the state of conservation of submerged artefacts; in particular, through the SAMAS and SAMAS BIO I and II level filing system [42]. This data collection system implies a reference to both materials of biological interest and historical/archaeological ones.
The in situ data collection is followed by sampling activities intended for analytical laboratory investigations, which are useful for the recognition of marine organisms causing decay (biodeteriogens) and the study of the colonized lithotypes and related damage forms through physical and geochemical methods. In the laboratory, after appropriate sample conservation treatments, the usual procedure implies observing the samples using microscopic techniques.
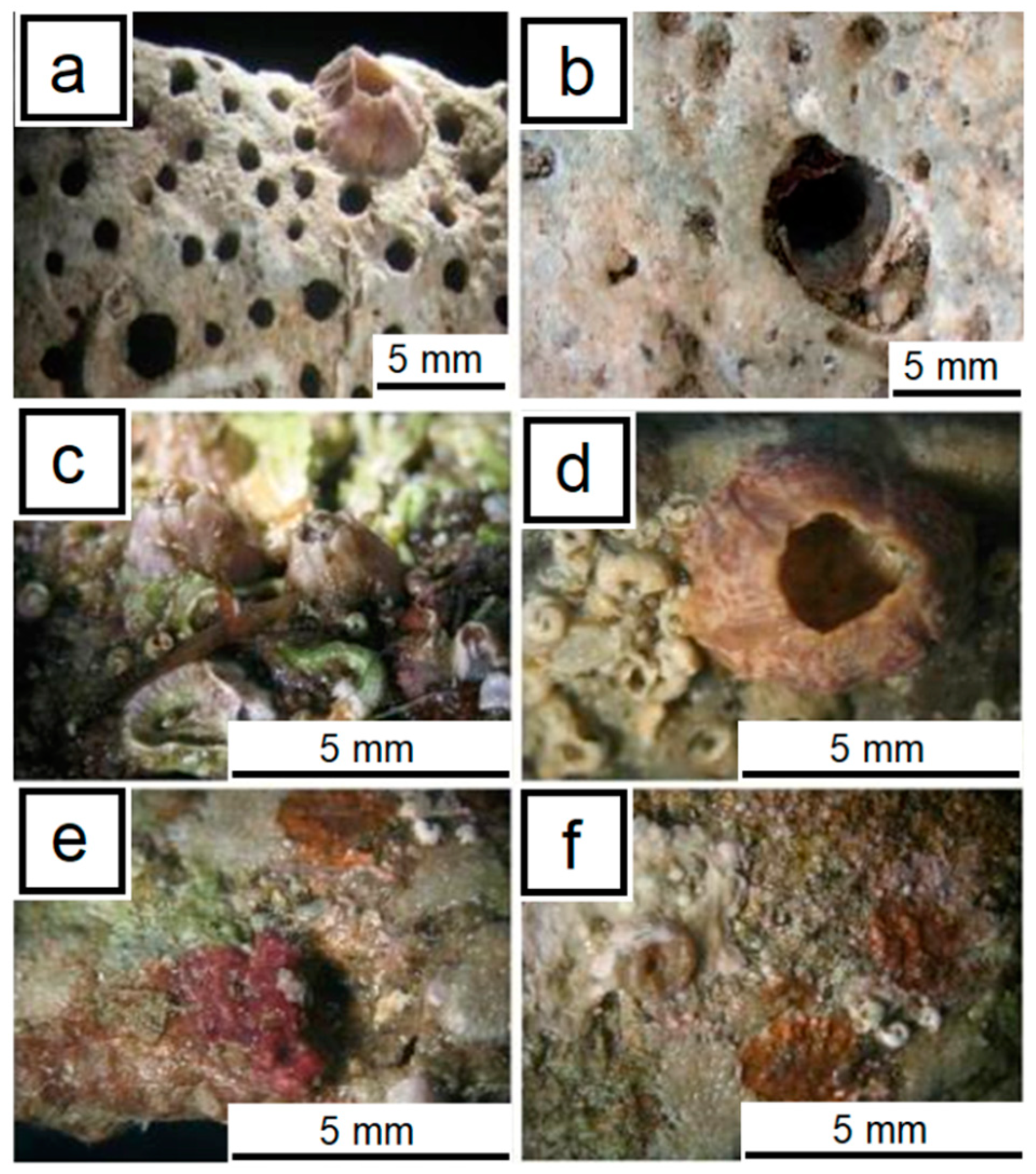
The stereomicroscope allows recognition and inspection of the more superficial morphological features, focusing on the patinas, sediments, and encrustations (e.g., surface layers, also multiple, characterized by concretions and patinas due to skeletal remains of benthic forms or sediments) and on approximately quantifying the extent of irreversible damage (e.g., perforations, boring, loss of material) (Figure 1), which is often visible even with the naked eye.
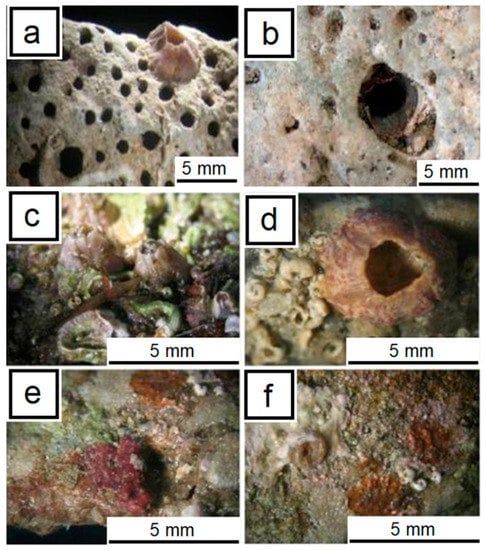
Figure 1.
Representative images of stone archaeological calcareous materials from an underwater environment by stereomicroscope observations. The images (a,b) show traces of the boring activity of endolithic organisms, while (c–f) display skeletal remains of encrusting ones [5].
As for superficial encrustations, we are mainly faced with aesthetic damages, where the artefacts become unreadable and largely defaced in shape [5,7]; in this case, the damage is not always harmful, and the superficial encrustations can have a protective role on the historical/archaeological items. Conversely, regarding the loss of material mainly due to the action of perforating marine organisms, the artefacts suffer irreversible damage in terms of physical–mechanical decay [5,7]. Damage phenomena, many of which have already been widely investigated, can be attributed to systematic groups of plants and animals through the recognition of peculiar diagnostic elements, such as the structures of encrusting organisms or the morphology of some soft biocoenosis residues.
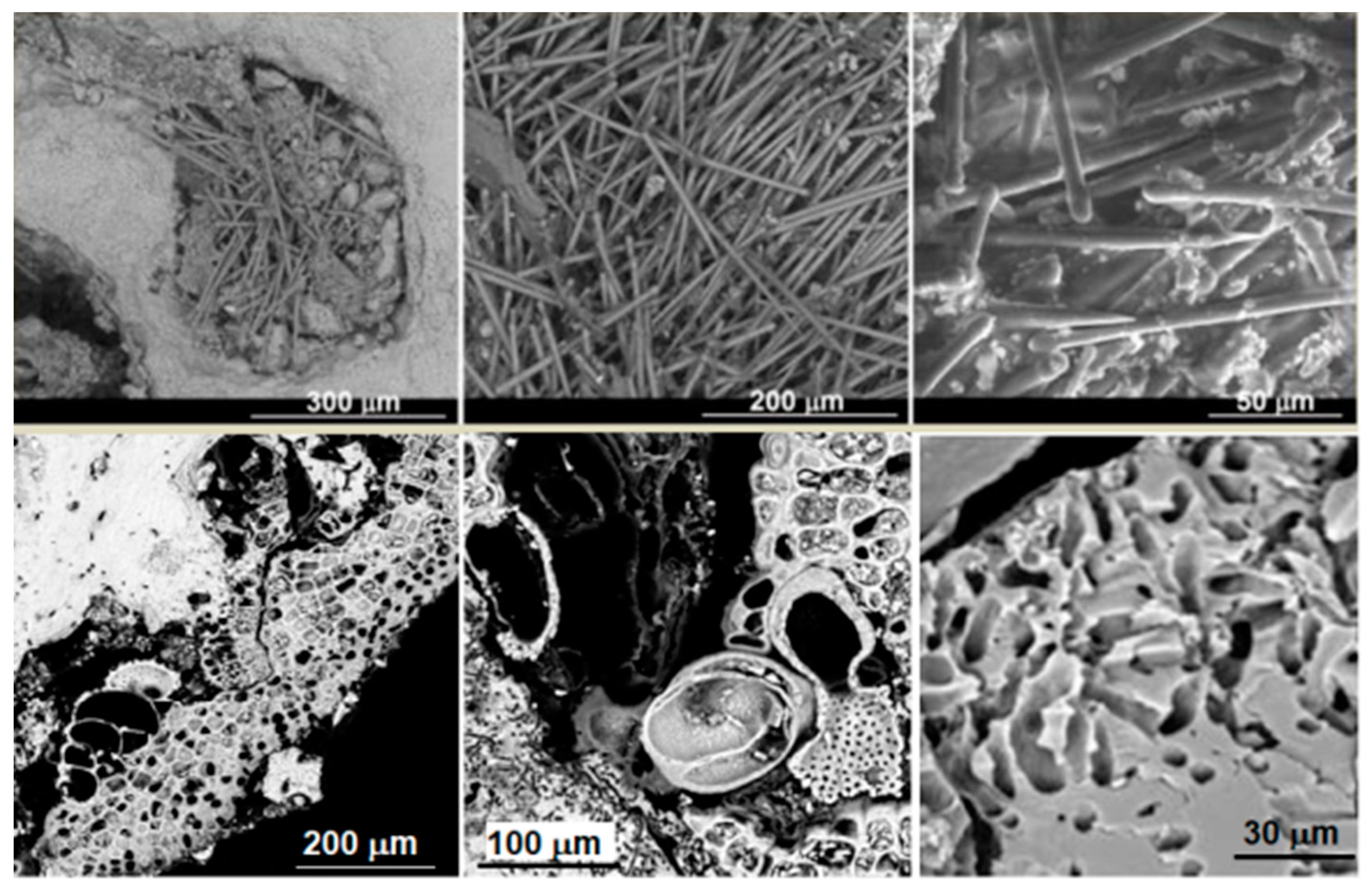
Furthermore, the presence of boring suggests the action of endolithic organisms [31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Their identification by methods applied in the geoscience disciplines is usually linked to the use of high-resolution microscopic investigation methods, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with an energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) microanalysis system [5,41,42]. Identification can also be carried out with the most common biological methods or through the most recent ones developed by the ICR and other experts in the field [43]. SEM-EDS investigations encourage a detailed morphological analysis, assessing the damage more thoroughly (Figure 2). The method is, in some cases, useful for systematic framing of benthic forms, often in conjunction with inorganic remains and characteristic traces of marine organisms. Examples are the ultrastructures of the spicules forming the sponge endoskeleton; their correct identification is possible according to the morphology (by SEM) and the chemical composition (by EDS). In addition, the cavities, micro-tunnels, and traces left inside the stone material are subject to morphological studies and encourage the identification of marine organisms.

Figure 2.
Representative images of stone archaeological calcareous materials from an underwater environment by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations. The images show traces and boring activity of endolithic organisms and skeletal remains of encrusting ones [5].
Many studies show that the dimensional heterogeneity of the perforations and their various spatial distributions may be associated with the growth stage of organisms of marine fauna and flora [5,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,43].
As mentioned above, the alteration phenomena of stone materials are also linked to the action of encrusting organisms that lead to the formation of thick and dense concretions with a predominantly calcareous nature, inducing the loss of legibility and functionality of the material [5].
To evaluate the damage from a minero-petrographic point of view, thin and stratigraphic sections with thicknesses of 30 μm are prepared for observation under a polarized light optical microscope (POM). The main goal is to evaluate how decay processes due to biological activity can vary with the structural and textural characteristics of colonized lithotypes. Recent studies carried out on marble samples have shown that damage can vary according to the grain size range and the degree of interconnection between the crystals [5,7,16,20]. The polarizing optical microscope also benefits the study of surface alteration, examining the external profile of patinas and concretions [5,7,16,20].
Finally, mineralogical and molecular studies using Fourier transform spectroscopy (FT-IR) with Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD) acquisition methods can further guide in identifying the inorganic nature of the superficial concretions [5]. Although the use of different analytical techniques is essential, the optimal and decisive identification of damage forms and biodeteriogens should be always accompanied by the comparison with data from the literature.
4. New Materials and Experimentations for the Stone Materials’ Protection in Underwater Sites
In the last decade, in the scenario of world research and technological development, innovative conservation strategies linked to UCH have thrilled researchers and experts in the field.
Different methods and products for the conservation in situ of UCH were tested as part of numerous research projects, were then patented, and became marketable products. We will discuss the protection of submerged assets against biofouling by in situ application of geotextiles [44], the experimentation with antifouling products by using nanotechnology, resins, and biocides to be applied on remains (in situ) after appropriate cleaning operations [13,17,45], or, even more, the experimentation with innovative mortars [45] for the structural enhancement of submerged resources (e.g., ancient harbors, fish ponds, etc.).
In the framework of the Italian national project COMAS, as widely described in [12], new materials and tools for improving the in situ documentation, restoration, and conservation of underwater archaeological remains were tested and then marketed after three years of in situ trials.
More specifically, regarding the products for the conservation of stone materials against biofouling, which is the most aggressive degrading agent in the underwater environment, several products with antifouling, consolidating, protective, and eco-sustainable properties have been developed [12,13,17,45]. The action of these products is often combined with that of solar radiation, favoring inhibition of alteration products, e.g., through photocatalytic action [46]. In particular, photocatalytic materials used in the cultural heritage sector, and also applied to UCH, showed great potential against biocolonization due to their antimicrobial and photocatalytic features [7,46,47]. The effectiveness of the products, as also shown by numerous studies [5,7,17], was tested through experimental campaigns and properly arranged by also taking into account the compatibility with the material to be protected and the environment.
In the specific case of the COMAS project [12], the research has been focused on the application of metal and photocatalytic oxide nanoparticles (i.e., ZnO and TiO2) on stone surfaces (mainly marbles and ignimbrites). They have been dispersed in siloxane wax in different compounds to bond the nanoparticles to the stone and to make it possible to apply the mixture directly underwater by rubbing the product on the stone surface [17]. The activity of the photocatalytics, ZnO and TiO2 [12,13,17,45,46], has been enhanced by adding small amounts of metals, specifically Ag, in the material. In particular, the Ag doping causes the slowdown of bacterial growth [17], thus reducing the biological growth on materials. After conducting a series of analytical investigations and tests, the application of different products was carried out in the laboratory on specimens, and then they were: (a) Anchored on a sample holder, (b) immersed in the pilot site, and (c) monitored over time. In all of the steps of the experimentation, untreated specimens were used to make a comparison with treated ones. After periodic and planned stays at sea, specimens were recovered and subjected to a set of laboratory investigations. In particular, microscopic investigations (see Section 3) showed a good performance of the products on specimens, highlighting that the application of all formulations on the stone surfaces leads to a slowdown of the biological colonization. After two years, there were not any traces of the protective coatings. This result was expected, since the binder itself cannot assure long-term durability. The behavior is compatible with the concepts of retractability and reversibility, fundamental parameters within the restoration guidelines. Anyway, such research represented a milestone for the development of innovative antifouling solutions for underwater restoration [17].
As for the experimentation of innovative mortars to be applied in situ and improve the stability of submerged structures, the MaTaCoS project, still in progress, has already shown promising results, as demonstrated in [45], dealing with the formulation of innovative mortars for the consolidation of archaeological structures in underwater sites. After characterizing the raw materials of mortars recovered at the pilot area [13] from a compositional and textural point of view and also identifying the various degradation processes, different experimental mortars were reproduced according to the ancient recipes and additivated with nanomaterials and other additives with antifouling action. Even in this research, mortar specimens were immersed through a sample holder at the pilot site [45]. Although the first results were promising, trials are still underway.
Lastly, another of the abovementioned preservation methods for contrasting the biological colonization consists in the use of geotextiles. Submerged ruins can be covered with geotextiles that create an unfavorable environment for the growth of most of the biological communities [44].
In particular, Terram geotextiles were successfully used by the ICR (Istituto Centrale per il Restauro) in a Baiae underwater site to cover some floors. The method has proven to be efficient in protecting findings and ruins, especially against bioerosion [44].
The results achieved in the different research show that the materials in underwater sites are particularly susceptible to degradation, especially based on their minero-petrographic features as well as their lying conditions (burial, open sea, etc.). This susceptibility leads to the need to periodically monitor the state of preservation of the underwater sites, to prevent irrecoverable damage and to plan conservative interventions, and, above all, to conduct cleaning and scheduled maintenance operations.
Regarding cleaning operations, several mechatronic tools and technologies to be used in situ have been developed, many of these within the aforementioned COMAS project [12], such as electric cleaning brushes, small electric chisels, and handheld grinding tools. These new electromechanical tools are currently making the work carried out by underwater restorers easier and faster during the cleaning operations conducted on structures and artefacts that are laying on the seabed.
5. Final Remarks
This paper provides an overview of recent challenges faced for studying materials coming from seawater and on innovations in the field of protection of UCH against biofouling as one of the main causes of damage in underwater sites.
Research conducted to date supports the hypothesis that the adoption of a multidisciplinary approach allows important data on the variability of damage forms, mainly caused by several benthic organisms that are lying on stone artefacts of historical and/or archaeological interest, to be obtained [5,12,13,43,45,48,49].
Such data are considered to be of great importance in finding a leading management plan based on suitable conservation and restoration interventions. Moreover, it is shown that the damage can vary in relation to the types of biodeteriogens, exposure conditions, and the features of the materials from a minero-petrographic and geochemical point of view.
The link between these aspects makes clear that the documentation and the diagnosis of UCH, both in situ and in the laboratory, are considered primary actions for the planning of any conservation intervention and, more generally, for a correct management, enhancement, and use of underwater areas and assets of historical and/or archaeological interest.
Only based on scientific data deriving from systematic investigations, it will be possible to define targeted interventions to be carried out on the structures and resources, allowing work to be carried out directly in situ.
Among the latest challenges in the conservation of UCH, several studies [12,17,42] show the experimentation with different materials and products for in situ conservation (geotextiles, coatings, etc.), and, although the difficulty is still significant, several obstacles have already been overcome.
The goals achieved mainly concern the methods of working in situ as well as the materials and tools used for the protection of UCH.
Future studies will certainly be able to meet the needs and difficulties still existing in the field. From the management perspective, to ensure fruition and enjoyment of UCH for future generations, these innovations (materials, coatings, tools, etc.) help to reduce the maintenance costs, thanks to the adoption of appropriate tools.
The management of UCH, if correctly planned, encourages operators in the sector and stakeholders to properly use the innovative resources and technologies to protect the cultural heritage in the marine environment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; methodology, M.R.; validation, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; formal analysis, M.R.; investigation, M.R.; resources, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; data curation, M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R.; writing—review and editing, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; visualization, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; supervision, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; project administration, M.R. and M.F.L.R.; funding acquisition, M.R. and M.F.L.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from PON "Ricerca e Innovazione" 2014–2020—Fondo sociale europeo, Azione 1.2 "Mobilità dei Ricercatori" (AIM "Attraction and International Mobility"—LINEA 1).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from PON "Ricerca e Innovazione" 2014–2020—Fondo sociale europeo, Azione 1.2 "Mobilità dei Ricercatori" (AIM "Attraction and International Mobility"—LINEA 1), codice attività AIM1829227-3, CUP H24I19000400005, Codice Ateneo DIBEST_1_R1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- UNESCO. The entry into force of the 2001 UNESCO Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage, Paris, France, 2 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cronyn, J.M. Introducing Archaeological Conservation. In Elements of Archaeological Conservation; Routledge: London, UK, 1990; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, D.L. Basic Methods of Conserving Underwater Archaeological Material Culture; United States Department of Defense Legacy Resource Management Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Aloise, P.; Ricca, M.; Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Belfiore, C.M.; Padeletti, G.; Crisci, G.M.; La Russa, M.F. Diagnostic analysis of stone materials from underwater excavations: The case study of the Roman archaeological site of Baia (Naples, Italy). Appl. Phys. A 2013, 114, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Ricca, M.; Belfiore, C.M.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Álvarez De Buergo Ballester, M.; Crisci, G.M. The Contribution of Earth Sciences to the Preservation of Underwater Archaeological Stone Materials: An Analytical Approach. JCS 2015, 6, 335–348. [Google Scholar]
- Ricca, M.; Comite, V.; La Russa, M.F.; Barca, D. Diagnostic analysis of bricks from the underwater archaeological site of Baia (Naples, Italy): Preliminary results. Rendiconti Online della Società Geologica Italiana 2016, 38, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara, B.; De Buergo, M.Á.; Bethencourt, M.; Fernández-Montblanc, T.; La Russa, M.F.; Ricca, M.; Fort, R.; Gallego, B.C. Biodeterioration of marble in an underwater environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Convention on the Protection of the Archaeological Heritage (Revised). 1992. Available online: https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/treaty/143 (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Davidde, B. Underwater archaeological parks: A new perspective and a challenge for conservation—The Italian panorama. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2002, 31, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisci, G.M.; Russa, M.F.; Macchione, M.; Malagodi, M.; Palermo, A.M.; Ruffolo, S.A.; La Russa, M.F. Study of archaeological underwater finds: Deterioration and conservation. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 100, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirado, S.; Fortes, F.J.; Laserna, J. Elemental analysis of materials in an underwater archeological shipwreck using a novel remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system. Talanta 2015, 137, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Muzzupappa, M.; Barbieri, L.; Gallo, A.; Ritacco, G.; Lagudi, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Crisci, G.M.; Ricca, M.; et al. The CoMAS Project: New Materials and Tools for Improving the In situ Documentation, Restoration, and Conservation of Underwater Archaeological Remains. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2016, 50, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, L.; Ricca, M.; Ruffolo, S.; Aquino, M.; Petriaggi, B.D.; Enei, F.; La Russa, M.F. An Integrated Analytical Approach to Define the Compositional and Textural Features of Mortars Used in the Underwater Archaeological Site of Castrum Novum (Santa Marinella, Rome, Italy). Minerals 2019, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.; Jensen, P.; Strætkvern, K. Conservation and in situ preservation of wooden shipwrecks from marine environments. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, S139–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, C.M.; La Russa, M.F.; Barca, D.; Galli, G.; Pezzino, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Viccaro, M.; Fichera, G.V. A trace element study for the provenance attribution of ceramic artefacts: The case of Dressel 1 amphorae from a late-Republican ship. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 43, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, M.; Belfiore, C.M.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Barca, D.; De Buergo, M.A.; Crisci, G.M.; La Russa, M.F. Multi-analytical approach applied to the provenance study of marbles used as covering slabs in the archaeological submerged site of Baia (Naples, Italy): The case of the “Villa con ingresso a protiro”. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, S.A.; Ricca, M.; Macchia, A.; La Russa, M.F. Antifouling coatings for underwater archaeological stone materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 104, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Nam, B.; Park, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, C.H.; Yu, J.E. Desalination characteristics for ceramics excavated from Taean shipwreck, Korea. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Arce, P.; Zornoza-Indart, A.; Gomez-Villalba, L.S.; Perez-Monserrat, E.M.; De Buergo, M.A.; Vivar, G.; Fort, R. Archaeological ceramic amphorae from underwater marine environments: Influence of firing temperature on salt crystallization decay. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, M.; La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Davidde, B.; Barca, D.; Crisci, G.M. Mosaic marble tesserae from the underwater archaeological site of Baia (Naples, Italy): Determination of the provenance. Eur. J. Miner. 2014, 26, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Ricci, S.; Davidde Petriaggi, B.; Barca, D.; Ricca, M.; Capristo, V. A Multidisciplinary approach for the study of underwater artefacts: The case of Tritone Barbato marble statue (Grotta Azzurra, Island of Capri, Naples). Period. Mineral. 2013, 82, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Belfiore, C.M.; La Russa, M.F.; Randazzo, L.; Montana, G.; Pezzino, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Aloise, P. Laboratory tests addressed to realize customized restoration procedures of underwater archaeological ceramic finds. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 114, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovella, N.; Comite, V.; Ricca, M. The Methodology of Investigation On Red- And Black-Figured Pottery of Unknown Provenance. IJCS 2016, 7, 954–964. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, M. Marine epibioses: 1 Fouling and antifouling: Some basic aspects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.N. La biocostruzione negli ecosistemi marini e la biologia marina italiana. Biologia Marina Mediterranea 2018, 8, 112–130. [Google Scholar]
- Callow, M.E.; Callow, J.A. Marine biofouling: A sticky problem. Biologist 2002, 49, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D. Carbonate production by calcareous red algae and global change. Geodiversitas 2012, 34, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, F.; Perasso, C.S.; Ricci, S.; Petriaggi, B.D. Impact of the sipunculan Aspidosiphon muelleri Diesing, 1851 on calcareous underwater Cultural Heritage. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 100, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casoli, E.; Ricci, S.; Belluscio, A.; Gravina, M.F.; Ardizzone, G. Settlement and colonization of epi-endobenthic communities on calcareous substrata in an underwater archaeological site. Mar. Ecol. 2014, 36, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidde Petriaggi, B.; Ricci, S.; Vlachogianni, E.; Antonelli, F.; Sacco Perasso, C.; Schistocheili, K. An overview of the state of conservation of the marble artefacts from the Antikythera shipwreck. Archaeol. Marit. Mediter. 2017, 14, 13–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, S.; Sanfilippo, R.; Basso, D.; Perasso, C.S.; Antonelli, F.; Rosso, A. Benthic Community Formation Processes of the Antikythera Shipwreck Statues Preserved in the National Archaeological Museum of Athens (Greece). J. Marit. Archaeol. 2018, 14, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, R.G. A stratigraphy of marine bioerosion. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2004, 228, 455–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisshak, M. High-Latitude Bioerosion: The Kosterfjord Experiment; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Wisshak, M.; Tapanila, L. Current Developments in Bioerosion; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; p. 499. [Google Scholar]
- Davidde Petriaggi, B.; Bartolini, M.; Poggi, D.; Ricci, S. Marine bioerosion of stone artefacts preserved in the Museo Archeologico dei CampiFlegrei in the Castle of Baia (Naples). Archaeol. Maritima Mediterr. 2010, 7, 1000–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, S.; Perasso, C.S.; Antonelli, F.; Petriaggi, B.D. Marine bivalves colonizing Roman artefacts recovered in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and in the Blue Grotto in Capri (Naples, Italy): Boring and nestling species. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 98, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Antonelli, F.; Perasso, C.S.; Poggi, D.; Casoli, E. Bioerosion of submerged lapideous artefacts: Role of endolithic rhizoids of Acetabularia acetabulum (Dasycladales, Chlorophyta). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 107, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.D.; Wilson, M. Palaeoecology and evolution of marine hard substrate communities. Earth Sci. Rev. 2003, 62, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, D. Excavating and endolithic sponge species (Porifera) from the Mediterranean: Species descriptions and identification key. Org. Divers. Evol. 2002, 2, 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubic, S.; Perkins, R.D.; Lukas, K.J. Boring microorganisms and microborings in carbonate substrates. In Study of Trace Fossils; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 259. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.D. The impact of the SEM in studies of living and fossil bryozoans. Syst. Assoc. Spec. 1990, 41, 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Petriaggi, R.; Davidde Petriaggi, B. Restaurare sott’acqua: Cinque anni di sperimentazione del NIAS-ICR. Boll. ICR Nuova Ser. 2007, 14, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, D.; Matthiesen, H. The 4th International Conference on Preserving Archaeological Remains In Situ (PARIS4): 23–26 May 2011, the National Museum of Denmark, Copenhagen. Conserv. Manag. Archaeol. Sites 2012, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Antonelli, F.; Sacco Perasso, C.; Davidde Petriaggi, B. Indagini Quali-Quantitative Della Colonizzazione Biologica di Geotessuti Utilizzati per la Protezione In Situ di Pavimenti Musivi Sommersi. In Proceedings of the POSTER. II Convegno Tematico di Biologia e Biotecnologie per i Beni Culturali Biologia e Archeobiologia: Dalla Conoscenza alla Conservazione Preventiva, Palermo, Italy, 19–21 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo, L.; Ricca, M.; Pellegrino, D.; La Russa, D.; Marrone, A.; Macchia, A.; Rivaroli, L.; Enei, F.; La Russa, M.F. Anti-fouling additives for the consolidation of archaeological mortars in underwater environment: Efficacy tests performed on the apsidal fishpond of Castrum Novum (Rome, Italy). IJCS 2020, 11, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C. Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Huang, M.-D.; Wu, X.-L.; Liu, A. Preparation and studies of photocatalytic silver-loaded TiO2 films by hybrid sol–gel method. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 146, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.J.; Manders, M. Best practices for locating, surveying, assessing, monitoring and preserving underwater archaeological sites. In SASMAP Guideline Manual 2; Gregory, D.J., Manders, M., Eds.; SASMAP Project: Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Davidde Petriaggi, B. Methods and strategies for the conservation and museum display in situ of underwater cultural heritage. Archaeol. Maritima Mediterr. 2004, 1, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).