The Impact of Penalty Function and Equivalence Factor on the Performance of ECMS Controller in Range Extended Electric Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (a)
- ≥ 0, battery discharging mode:
- (b)
- < 0, battery charging mode:where and are the equivalence factors for battery charging and discharging operations, respectively ; is the low heating value of fuel, .
2.1. The Analysis of Equivalence Factor
2.1.1. Constant Equivalence Factors
2.1.2. Variable Equivalence Factor
2.2. The Analysis of Different Penalty Functions
2.2.1. Proportional Penalty Function
2.2.2. Exponential Penalty Function
2.2.3. PI—Controlled Penalty Function
3. Results
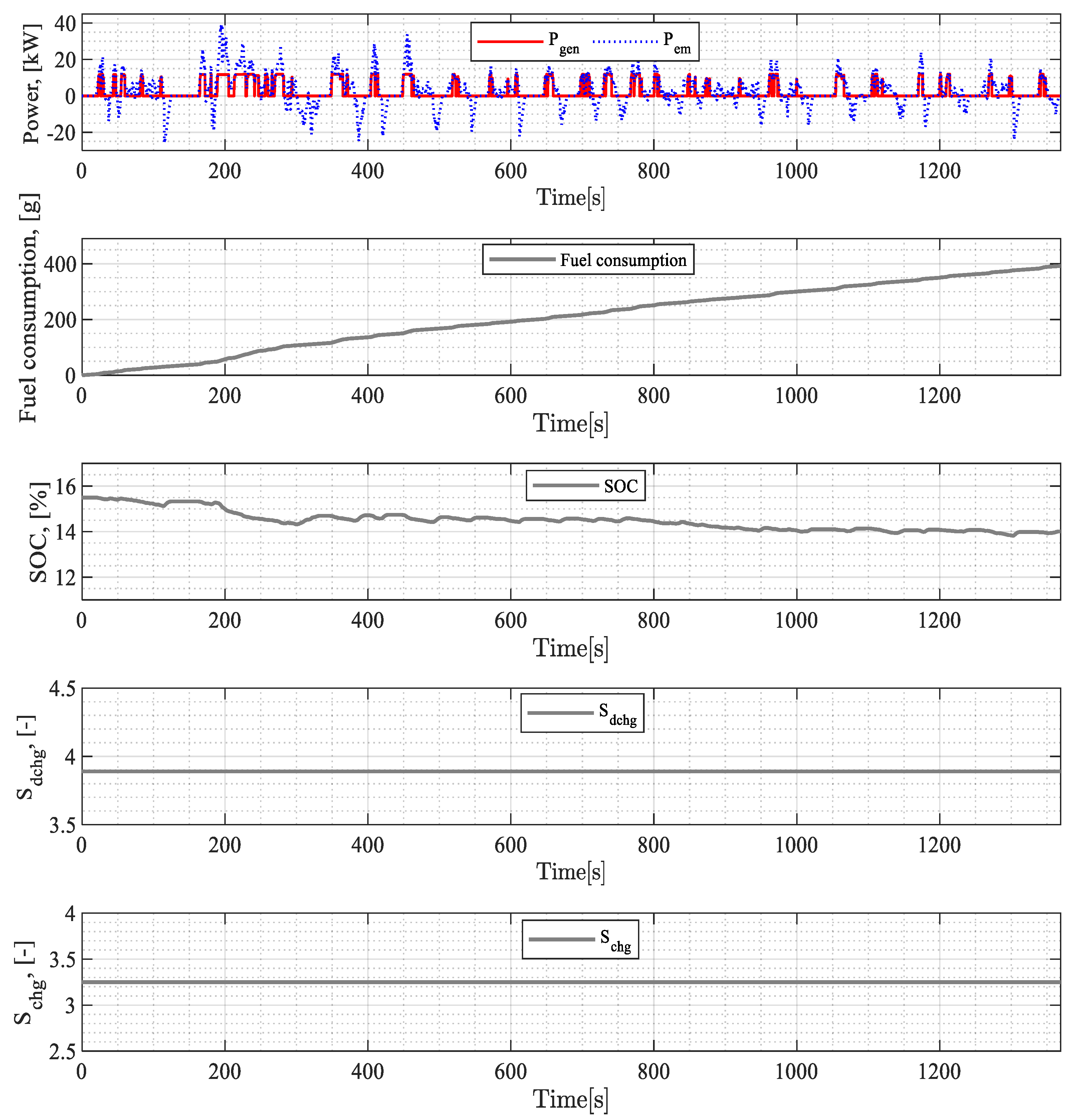
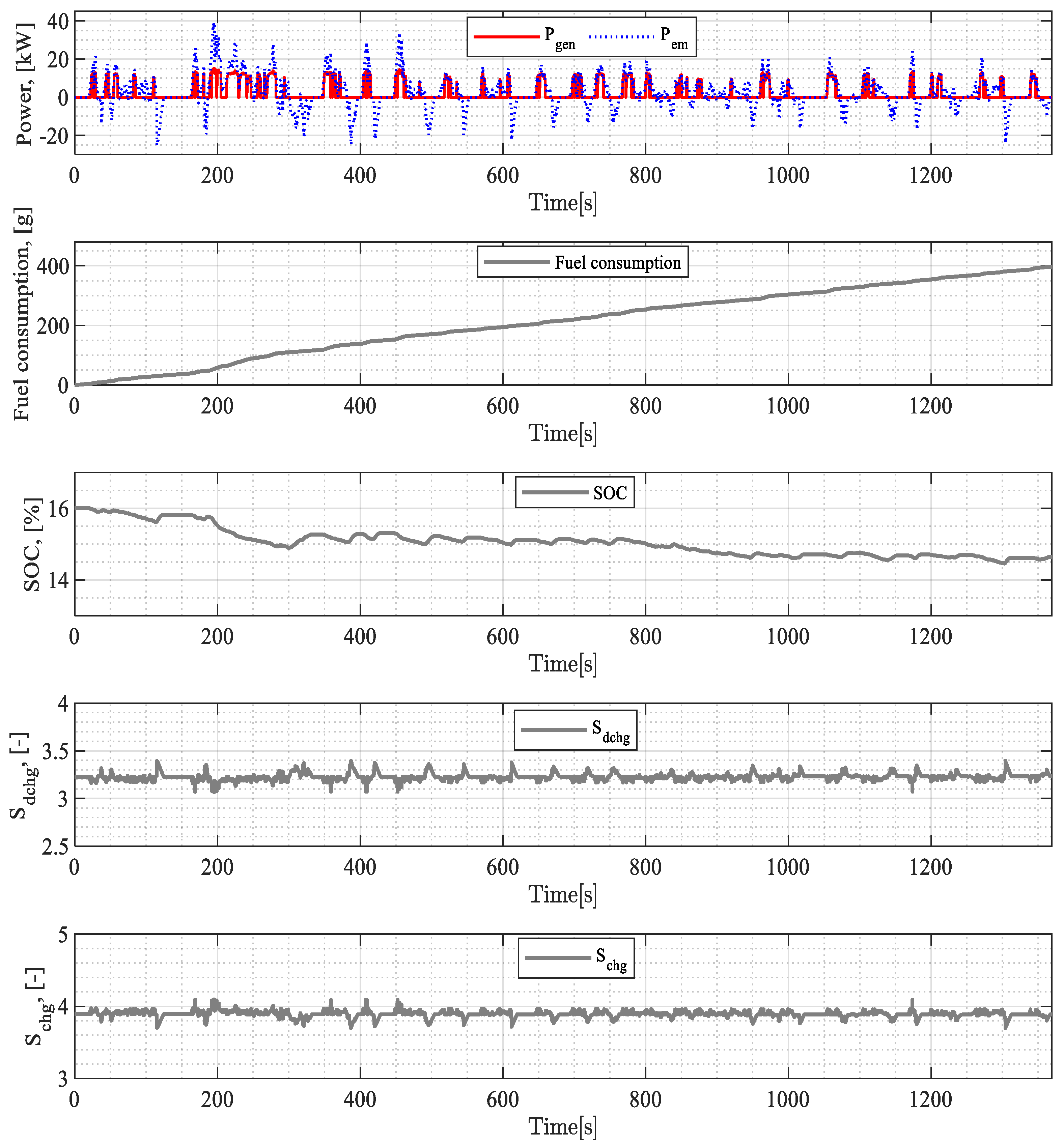
3.1. Equivalence Factor Results
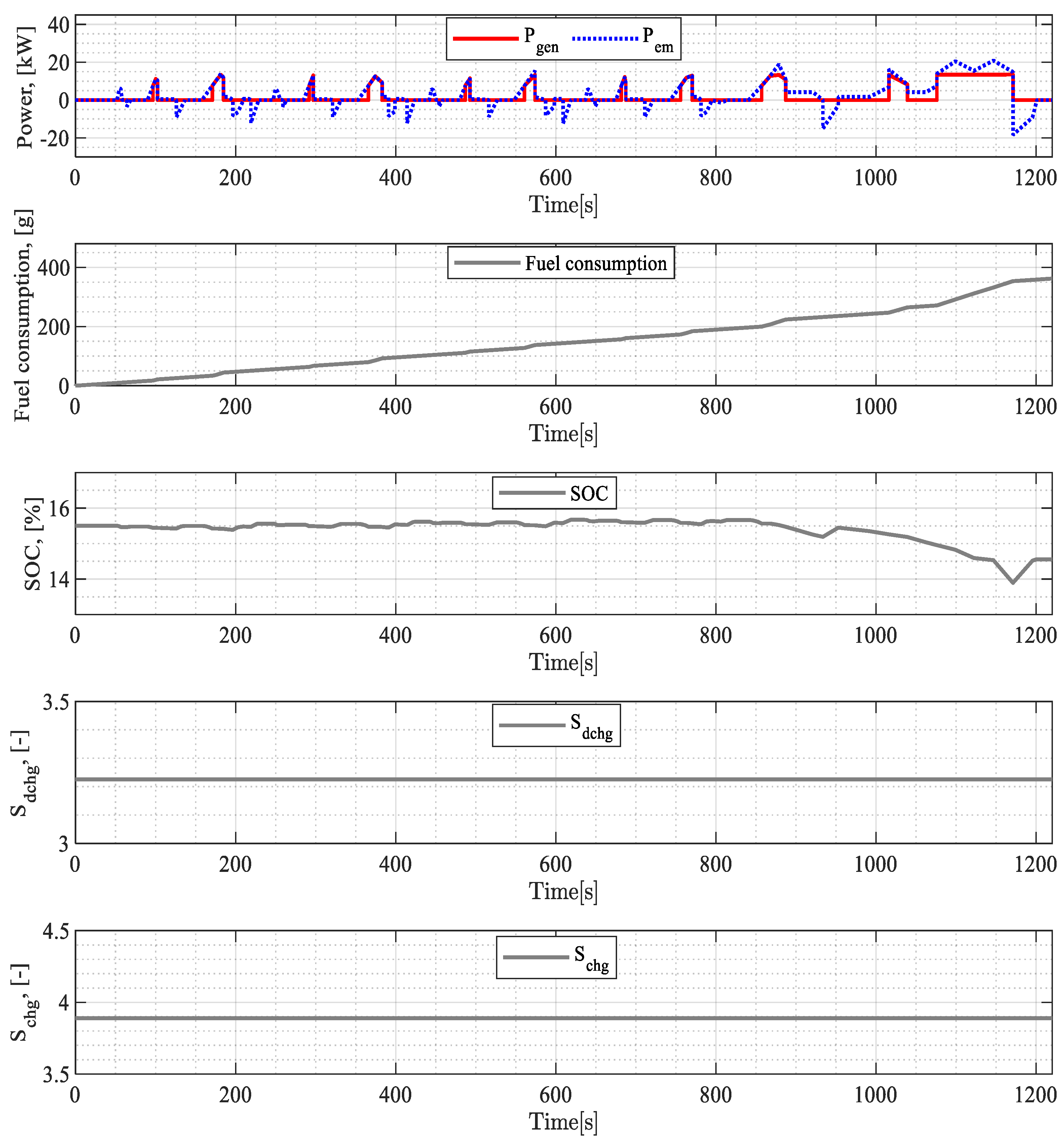
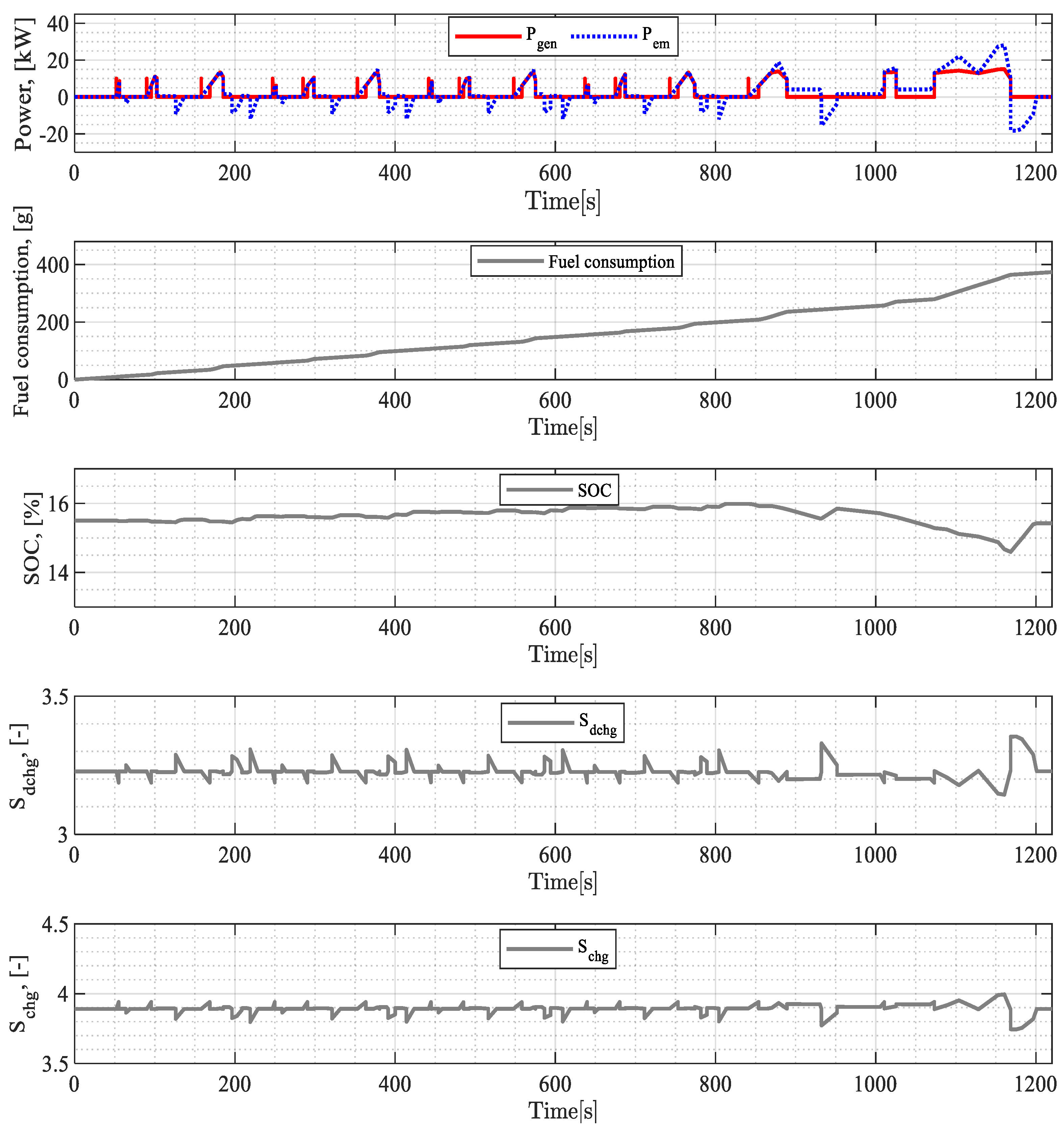
3.2. Penalty Function Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APU | Auxiliary Power Unit |
| BSFC | Brake Specific Fuel Consumption |
| CS | Charge Sustaining |
| ECMS | Energy Consumption Minimization Strategy |
| EMS | Energy Management Strategy |
| HWFET | Highway Fuel Economy Test |
| INL | Idaho National Laboratory |
| LHV | Low Heating Value |
| NEDC | New European Driving Cycle |
| PI | Proportional Integral |
| REEV | Range Extended Electric Vehicle |
| SHEV | Series Hybrid Electric Vehicle |
| SOC | State Of Charge |
| UDDS | Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule |
| WLTP | Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Testing Procedure |
References
- Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.; Han, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C. Energy Management Strategies for Extended-Range Electric Vehicles with Real Driving Emission Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, X.; Teng, T.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Lv, Q. A Comprehensive Review on Classification, Energy Management Strategy, and Control Algorithm for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Kong, Y.; Chu, L.; Ju, H.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z. Towards a Smarter Energy Management System for Hybrid Vehicles: A Comprehensive Review of Control Strategies. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, W.; Lin, W.; Ma, T. Comparison of Two Energy Management Strategies Considering Power System Durability for PEMFC-LIB Hybrid Logistics Vehicle. Energies 2021, 14, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Gao, Y.; Gay, S.E.; Emadi, A. Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-P.; Zhu, G.-M.G.; Strangas, E.G.; Sun, F.-C. Equivalent fuel consumption optimal control of a series hybrid electric vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2009, 223, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch, T.; Cerofolini, A.; Mancini, G.; Cavina, N.; Onder, C.; Guzzella, L. Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for the Control of Real Driving NOx Emissions of a Diesel Hybrid Electric Vehicle. Energies 2014, 7, 3148–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, S.; Serrao, L.; Rizzoni, G. Hybrid Electric Vehicles. In SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering; Springer: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musardo, C.; Rizzoni, G.; Guezennec, Y.; Staccia, B. A-ECMS: An Adaptive Algorithm for Hybrid Electric Vehicle Energy Management. Eur. J. Control 2005, 11, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Liu, H. Energy Management of Hybrid Engineering Vehicles Based on Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Lu, X.; Chao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, F. Adaptive Equivalent Fuel Consumption Minimization Based Energy Management Strategy for Extended-Range Electric Vehicle. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, D.; Li, G.; Chen, Z. Research on equivalent factor boundary of equivalent consumption minimization strategy for PHEVs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 6011–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y. A new real-time optimal energy management strategy for range extended electric vehicles considering battery degradation and engine start-up. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2024, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, D.; Wang, S. Minimum Energy Management Strategy of Equivalent Fuel Consumption of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on Improved Global Optimization Equivalent Factor. Energies 2019, 12, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lei, N.; Chen, B.; Li, B.; Li, R.; Wang, Z. Modeling and control system optimization for electrified vehicles: A data-driven approach. Energy 2024, 310, 133196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lei, N.; Peng, W.; Li, B.; Lv, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z. Bi-Level Transfer Learning for Lifelong-Intelligent Energy Management of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 16174–16187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puma-Benavides, D.S.; Izquierdo-Reyes, J.; Calderon-Najera, J.d.D.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A. A Systematic Review of Technologies, Control Methods, and Optimization for Extended-Range Electric Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzella, L.; Sciarretta, A. Vehicle Propulsion Systems, Introduction to Modeling and Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; ETH: Zurich, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- QSS Toolbox. Available online: https://idsc.ethz.ch/research-guzzella-onder/downloads.html (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Technical Specifications. BMW i3 94 Ah. Available online: https://www.press.bmwgroup.com/global/article/attachment/T0259598EN/359587 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Available online: https://www.anl.gov/taps/d3-2014-bmw-i3rex (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Keldiyarova, M.; Ruzimov, S.; Bonfitto, A.; Mukhitdinov, A. Comparison of two control strategies for range extender hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Electromobility (ISEM), Puebla, Mexico, 17–19 October 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsson, M.; Sundström, C.; Eriksson, L. Adaptive Control of a Hybrid Powertrain with Map-based ECMS. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 2949–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; Propp, K.; Longo, S.; Wild, M. A review on electric vehicle battery modelling: From Lithium-ion toward Lithium–Sulphur. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battery Pack Laboratory Testing Results–2014 BMW i3 REX–VIN 3436. Available online: https://avt.inl.gov/sites/default/files/pdf/phev/batteryi3436.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Curve Fitting Toolbox. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/curvefitting.html (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Serrao, L.; Sciarretta, A.; Grondin, O.; Chasse, A.; Creff, Y.; Di Domenico, D.; Pognant-Gros, P.; Querel, C.; Thibault, L. Open Issues in Supervisory Control of Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Unified Approach Using Optimal Control Methods. Oil Gas Sci. Technol.–Rev. IFP Energ. Nouv. 2013, 68, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Coskun, S.; Pang, H.; Cui, Y.; Xi, J. Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Review, Classification, Comparison, and Outlook. Energies 2020, 13, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

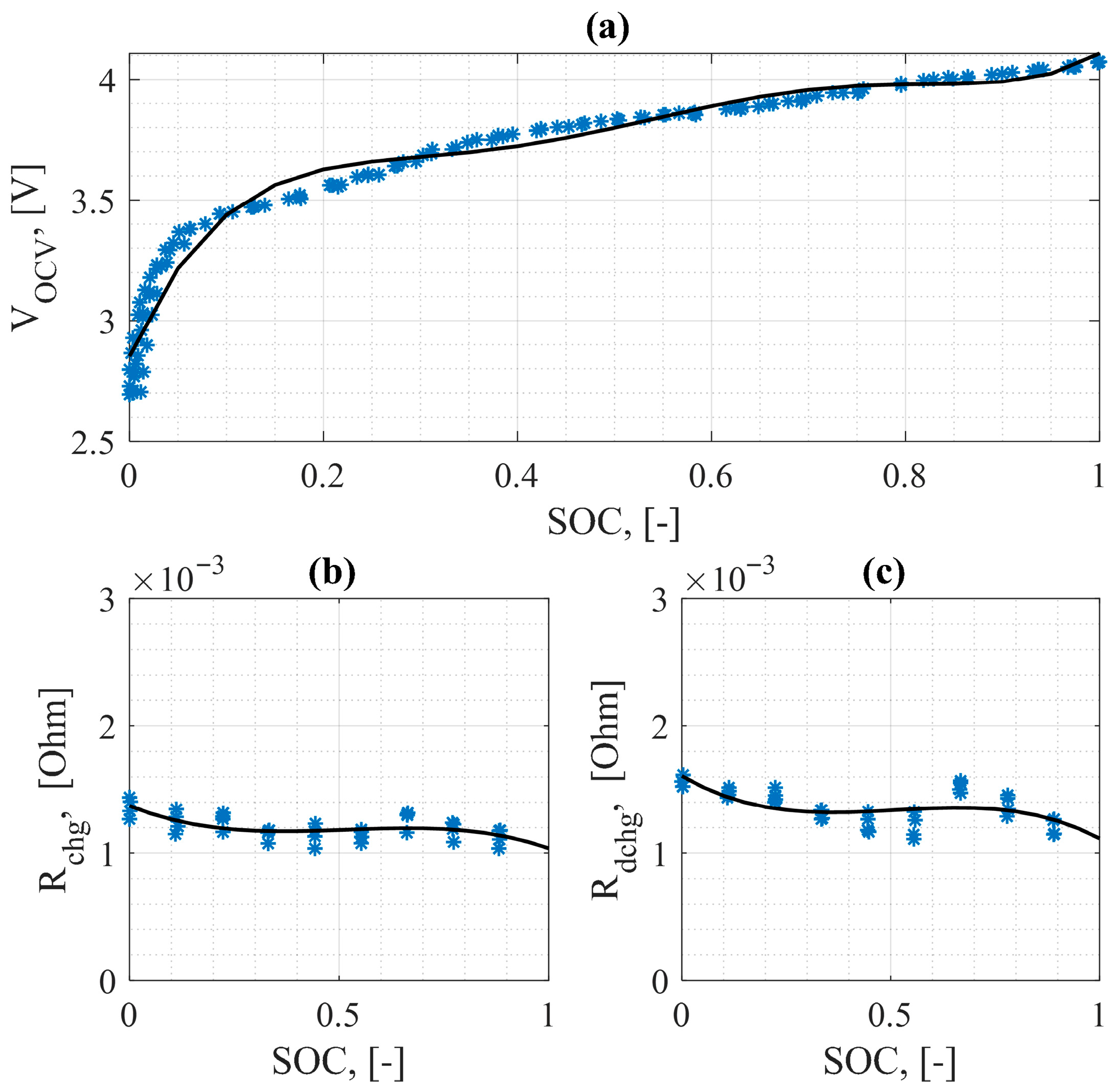
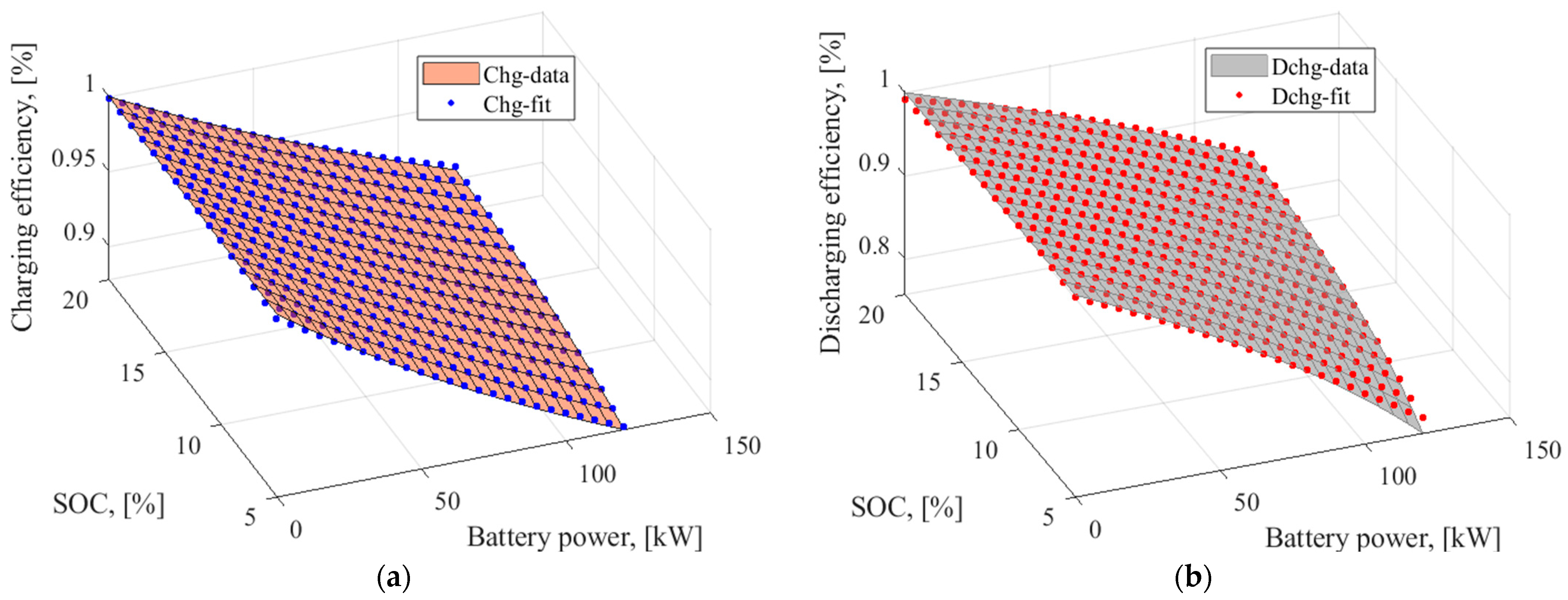
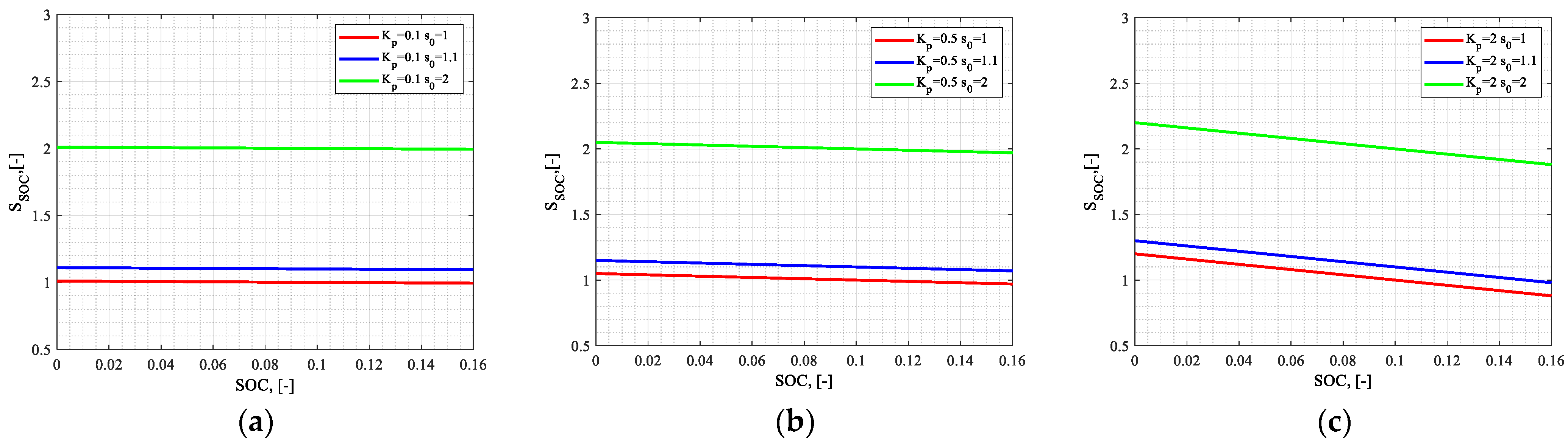
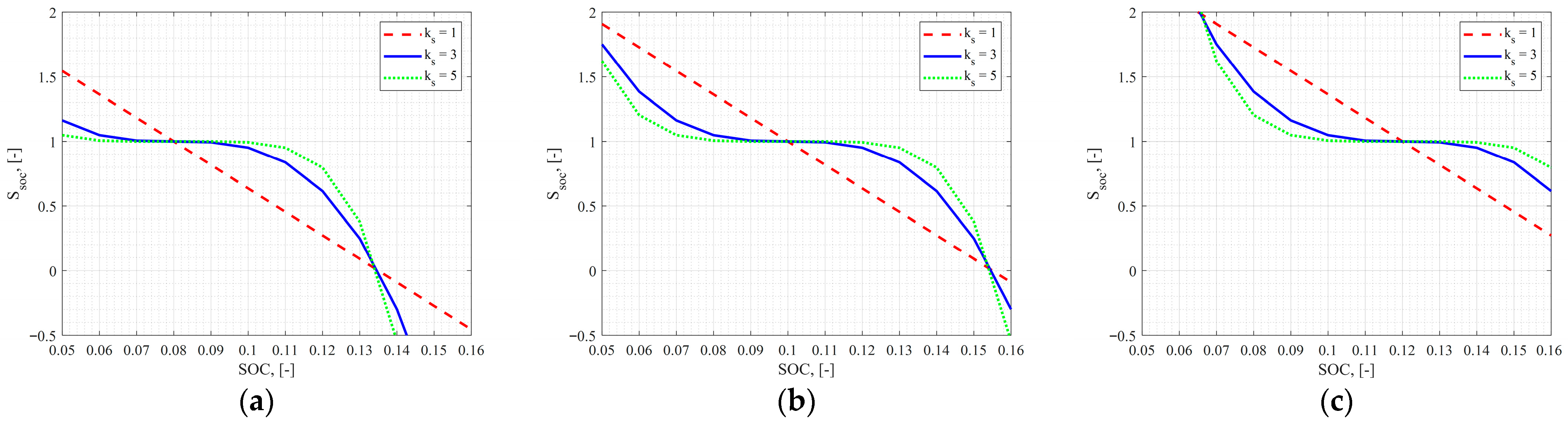
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Design curb weight | kg | 1390 |
| Electric machine | ||
| Maximum power | kW | 125 |
| Maximum torque | Nm | 250 |
| Transmission | ||
| Transmission ratio | - | 9.7:1 |
| Engine | ||
| Displacement | l | 0.647 |
| Power output | kW | 25 |
| Torque output | Nm | 55 |
| Generator | ||
| Power output | kW | 26.6 |
| Battery | ||
| Nominal cell voltage | V | 3.7 |
| Nominal system voltage | V | 355.2 |
| Rated pack capacity | Ah | 60 |
| Rated pack energy | kWh | 18.8 |
| Equivalence Factor | Drive Cycle | ∆SOC, [%] | Actual Fuel Consumption, [g] | Correction of Fuel Consumption, [g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | UDDS | −0.48 | 371 | 397.4 |
| NEDC | −0.82 | 362 | 408 | |
| WLTC | −4.1 | 573 | 798 | |
| HWFET | −2.65 | 305 | 451 | |
| Variable | UDDS | −0.2 | 376 | 386 |
| NEDC | −0.08 | 392 | 396.5 | |
| WLTC | −3.28 | 600 | 780 | |
| HWFET | −2.45 | 311 | 446 |
| Drive Cycle | Linear Penalty Function | Exponential Penalty Function | PI-Controlled Penalty Function | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| , [%] | , [%] | |||||
| UDDS | 308 | 15.2 | 22.05 | 11.11 | 228.2 | 14.13 |
| NEDC | 274.1 | 14.58 | 45.13 | 11.29 | 93.41 | 12.05 |
| WLTP | 710 | 12.58 | 368.1 | 7.5 | 125.8 | 5 |
| HWFET | 395 | 13.02 | 67.8 | 8.285 | 356 | 12.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keldiyarova, M.; Usmanov, U.; Ruzimov, S.; Mukhitdinov, A. The Impact of Penalty Function and Equivalence Factor on the Performance of ECMS Controller in Range Extended Electric Vehicles. J 2025, 8, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/j8040044
Keldiyarova M, Usmanov U, Ruzimov S, Mukhitdinov A. The Impact of Penalty Function and Equivalence Factor on the Performance of ECMS Controller in Range Extended Electric Vehicles. J. 2025; 8(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/j8040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeldiyarova, Malika, Umidjon Usmanov, Sanjarbek Ruzimov, and Akmal Mukhitdinov. 2025. "The Impact of Penalty Function and Equivalence Factor on the Performance of ECMS Controller in Range Extended Electric Vehicles" J 8, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/j8040044
APA StyleKeldiyarova, M., Usmanov, U., Ruzimov, S., & Mukhitdinov, A. (2025). The Impact of Penalty Function and Equivalence Factor on the Performance of ECMS Controller in Range Extended Electric Vehicles. J, 8(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/j8040044






