Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by a novel and rapidly mutating coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Although several drugs are already in clinical use or under emergency authorization, there is still an urgent need to develop new drugs. Through the mining and analysis of 2776 genomes of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, we identified papain-like protease (PLpro), which is a critical enzyme required for coronavirus to generate a functional replicase complex and manipulate post-translational modifications on host proteins for evasion against host antiviral immune responses, as a conserved molecular target for the development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapy. We then made an infection model using the NCI-H1299 cell line stably expressing SARS-CoV-2 PLpro protein (NCI-H1299/PLpro). To investigate the effect of targeting and degrading PLpro mRNA, a compact CRISPR-Cas13 system targeting PLpro mRNA was developed and validated, which was then delivered to the aforementioned NCI-H1299/PLpro cells. The results showed that CRISPR-Cas13 mediated mRNA degradation successfully reduced the expression of viral PLpro protein. By combining the power of AAV and CRISPR-Cas13 technologies, we aim to explore the potential of attenuating viral infection by targeted degradation of important viral mRNAs via safe and efficient delivery of AAV carrying the CRISPR-Cas13 system. This study demonstrated a virus-against-virus gene therapy strategy for COVID-19 and provided evidence for the future development of therapies against SARS-CoV-2 and other RNA viral infections.
1. Introduction
The COrona VIrus Disease 19 pandemic (COVID-19) has exploded since cases were first reported in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Later, a novel coronavirus was isolated from patients’ respiratory samples, and genome analysis showed that the virus is closely related to prototype severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus; therefore, the virus was renamed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [1]. The first published study reporting the clinical features of 41 patients admitted to Jin Yin-tan Hospital has shown that the SARS-CoV-2 virus causes severe pneumonia with a ventilatory support rate of 9.8% and a fatality rate of 2.9% [2]. The study provided first-hand data regarding the severity of the SARS-CoV-2 infections. By 29 June 2022, the total number of global reported cases of COVID-19 had approached 545 million, resulting in 6.3 million deaths [3]. Many vaccines and therapies have been developed. The current treatment guidelines include antiviral agents (e.g., remdesivir, molnupiravir, and paxlovid), monoclonal antibodies (e.g., bebtelovimab), and immunomodulators (e.g., corticosteroids, interferons, and colchicine) [4]. Paxlovid and certain anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies received emergency use authorizations from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of COVID-19. Remdesivir, which targets the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of coronaviruses, is currently the only drug that is approved by the FDA for COVID-19.
Due to the inherent features of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, SARS-CoV-2 has a very high mutation rate compared with other viruses and is more prone to mutation accumulation [5,6,7,8]. The viral evolution, especially the structural protein spike mutations, may decrease the efficacy of the current treatments and vaccines, especially monoclonal antibodies and vaccines designed against existing spike proteins [8,9]. To combat this challenge, new approaches are needed to provide alternative therapeutic options. A promising therapeutic target of SARS-CoV-2 is nonstructural proteins, which are essential for viral maturation, replication, and invasion. The disruption of their functions should be able to significantly interfere with the virus’s infection and replication cycle. Papain-like protease (PLpro) is one of the two nonstructural proteases encoded by SARS-CoV-2 [9,10]. In addition to the primary function of processing viral polyprotein, PLpro is also involved in stripping ubiquitin and interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) to assist the viral evasion of the host innate immune responses [11,12]. Therefore, targeting PLpro provides dual benefits by inhibiting viral replications and fixing the dysregulated signal cascades of the infected cell.
Recently, Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) gene editing tools have been developed for therapeutic applications in many research fields. Similar to the CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) protein complex system, CRISPR-associated protein 13 (Cas13) uses a short crRNA sequence to guide programmable RNase activity. The recent discovery of compact Cas13 [13] subcategories (Cas13d and Cas13bt) has made it possible to meet the packaging capacity of adeno-associated virus (AAV), which has been a safe, efficient, and commonly used vehicle for gene therapy [14]. In combination with the AAV delivery system, CRISPR-Cas13 provides us with a versatile tool for diagnostic and therapeutic applications to combat virus infections [15,16,17,18,19]. In the present study, we reported the application of AAV-mediated CRISPR-Cas13 knockdown of SARS-CoV-2-PLpro and the subsequent disruption of the production and function of the corresponding viral protein in the NCI-H1299/PLpro mammalian cells. This research validated PLpro as a potential therapeutic target against SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses. Furthermore, we are the first to apply Cas13 for the development of therapeutic strategies for SARS-CoV-2 virus infection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SARS-CoV-2 Genome Bioinformatics Study
The relative amount of genetic diversity across the SARS-CoV-2 genomes was examined using a total of 2776 genomes sampled between December 2019 and October 2022 obtained from the Nextstrain platform database [19].
2.2. Cell Culture
NCI-H1299 (ATCC: CRL-5803™) and HEK-293T (ATCC: CRL-3216™) cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) (ATCC: 30-2002™) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were maintained at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
2.3. Construction of PLpro Stable Cell Line
According to the amino acid sequence of PLpro, the encoded cDNA sequence was obtained and codon-optimized for mammalian cell expression (see Table S1 for cDNA sequence). After the cDNA sequence was synthesized (Gene Universal Inc., Newark, DE, USA), it was ligated into the pLVX-EF1alpha-IRES-Puro expression vector treated with restriction enzymes (EcoRI and BamHI). As there was no commercial antibody available for PLpro at the time of designing the experiments (June 2020), a Flag tag (N-terminal) was added for PLpro detection. The constructed expression plasmid was transfected into NCI-H1299 cells via lipofectamine™ 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and the stable NCI-H1299/PLpro cell line was selected by puromycin and maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) (ATCC: 30-2002™) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin/puromycin. (Scheme S1).
2.4. RNA Secondary Structures and Design of crRNA for CRISPR-Cas13 Systems
The RNA secondary structures of this study were predicted using UFold Webserver v1.2 (https://bio.tools/ufold accessed on 6 June 2020). The mRNA sequence of PLpro was conversated from the cDNA sequence (Table S1 #10). cas13design (https://cas13design.nygenome.org/ accessed on 5 September 2024), an online platform, was used to design the Cas13d guide RNA sequences targeting the selected sites of PLpro mRNA [20]. Three crRNA sequences were selected in the middle and near the end of the PLpro mRNA sequences targeting different regions based on the predicted PLpro mRNA structure.
2.5. Compact CRISPR-Cas13 Plasmid Construction
The Cas13bt sequence was synthesized by GenScript according to the published sequence from the literature [16], and the fragment was amplified by PCR using 13bt-NONLS-F and 13bt-NONLS-R primers (see Table S1 for details). The Cas13d fragment was amplified from plasmid pM124: pAAV-EFS-CasRx-VEGFA presgRNA [21] (addgene: #166872) using 13d-NONLS-F and 13d-NONLS-R primers. Plasmid pM125: pAAV-EFS-CasRx-VEGFA array presgRNA [22] (addgene #166873) was used as the backbone to construct the AAV-Cas13d and Cas13bt plasmids. The fragments and pM125 plasmid were treated with restriction enzymes (Xba I and Sal I), and then the Cas13bt and Cas13d fragments and linearized pM125 backbone were assembled using NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Cloning Kit (Ipswich, MA, USA) to construct AAV-Cas13bt and AAV-Cas13d plasmids. Five guide crRNA fragments, including the three guide sequences of crRNA, were directly synthesized from Sigma Aldrich (Table S1 #5–9, St. Louis, MO, USA). The guide fragments were assembled to linearize AAV-Cas13bt and AAV-Cas13d (Hind III and Ned I) plasmids using the ssDNA bridging assembly method [23]. The correct clones were verified with restriction enzyme cleavages and DNA electrophoresis between each step, and the final constructed plasmids were sequenced by Eurofins Genomics LLC (Louisville, KY, USA). Plasmid mappings are shown in Figures S1 and S2.
2.6. Recombined Adeno-Associated Virus (rAAV) Production and Titration
rAAV-Cas13 plasmids were prepared using the AAV-2 Helper Free Packaging System (Cell Biolabs: VPK-402, San Diego, CA, USA). HEK-293T cells were seeded at a density of 500,000 cells/well in 6-well plates. After overnight incubation, cells were cotransfected with 300 ng pAAV-Cas13 expression vectors (pAAV-Cas13d-1, Cas13d-2, Cas13d-3, Cas13d-array, and Cas13bt-array), 300 ng pAAV-RC2, and 300 ng pHelper. All transfections were performed in duplicate using PolyJet™ In Vitro DNA Transfection Reagent (Signagen: SL100688, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). At 48 h after the transfection, the cells were harvested and centrifuged to remove the supernatant. The cell pellets were resuspended in 1 mL Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS), then frozen and thawed repeatedly in a dry ice/ethanol bath and 37 °C water bath. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 12,000× g for 10 min and the supernatants were collected as rAAV crude lysate. The titer of rAAVs was measured with QuickTiter™ AAV Quantitation Kit (Cell Biolabs: VPK-145).
2.7. rAAV Infection and Western Blotting
NCI-H1299/PLpro cells were seeded at a density of 300,000 cells/well in 6-well plates and incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for one hour. Then, rAAV-Cas13 was added to the cell cultures at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) 10,000 viral genome (vg)/cell. The infected cells were collected after 24 h of incubation and the cells were lysed with 1× RIPA buffer with 1× cOmplete™ EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche: 04693159001, Basel, Switzerland) and 1× PhosSTOP™ phosphatase inhibitors (Roche: PHOSS-RO) for Western blotting. Cells were lysed at 4 °C for 20 min and lysates were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C. Supernatants were collected and protein concentrations were quantified using Pierce BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific™: 23227). A total of 50 μg of the total protein was loaded to 8% SDS-PAGE Tris-glycine gel electrophoresis and ran for 60–90 min at 30 V, then 30 min at 200 V. The gel was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Thermo Scientific™: PI88018) for 1 h at 110 V on ice and then blocked with 5% milk in 1× PBS-T for 1 h at room temperature. The Western blots were incubated at 4 °C with corresponding primary antibodies overnight: (1) mouse-anti-Flag (Sigma-Aldrich: F1804) at 1:1000 dilution in 5% milk in TBS-T and (2) rabbit-anti-beta-tubulin (polyclonal IgG, H-235, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) at 1:1000 dilution in 5% milk in TBS-T. The blots were washed with TBS-T 3–6 times and incubated with a secondary antibody, mouse-anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (sc-2357, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), m-IgGk BP-HRP (sc-516102, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), at 1:2000 dilution in 5% milk in TBS-T at room temperature for 1 h. After 3–6 times washing with 1× TBS-T, the Western blots were developed with Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Thermo Scientific™: 32109). The acquisition and analysis of the blots were performed on the Odyssey® XF Imaging System (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA).
2.8. Total RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR)
Total RNA extraction was conducted using TRIzol reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Invitrogen). Cells were collected and centrifuged for 5 min at 500× g; then, 1 mL of TRIzol reagent was added to the pellet and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. A total of 0.25 mL of chloroform was added to the sample, mixed thoroughly by vortex, and incubated at room temperature for 20 min. Followed by centrifugation at 12,000× g for 15 min at 4 °C, the RNA containing the aqueous phase was transferred to a new tube and 0.5 mL isopropanol was added to precipitate the RNA. Followed by centrifugation at 12,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C, the RNA precipitation formed a white gel-like pellet. Then, the RNA pellet was washed with 1 mL 75% ethanol at least once, then air-dried and redissolved in DEPC-treated water. RNA concentration was measured using NanoDrop™ 2000/2000c spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific™: ND-2000). Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg total RNA using the Maxima H Minus Double-Stranded cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific: K2561) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.9. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
qPCR was performed using PowerTrack SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Scientific ™: A46109). The PLpro, GAPDH, and beta-actin primers were designed using the qPCR assay design tool from Eurofins Genomics [24]. The targets’ primer sequences (from Sigma Aldrich) were listed in Table S1. The qPCR was carried out on StepOne™ Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems™, Waltham, MA, USA) with the following protocol: 50 °C for 2 min, 95 °C for 2 min; 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s. The melting curve analysis was conducted at the end of each qPCR cycle to check the quality of the PCR reactions. PLpro data were analyzed using the relative expression ratio method [21].
2.10. Immunofluorescence (IF) Imaging
NCI-H1299/PLpro cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min after being fixed with 3.6% formaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature. Following this, cells were blocked for 1 h with the blocking solution (2 mg/mL BSA in PBS) and then incubated with mouse-anti-Flag (Sigma-Aldrich: F1804) at 4 °C overnight. Next, cells were washed three times with DPBS and then mounted with ProLong Gold antifade reagent and DAPI after being treated for 1 h with a fluorescein-conjugated horse anti-mouse antibody (DI-2488, Vector Laboratories, Newark, CA, USA) (P36931, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Images were captured with a ZEISS Axio Observer imaging system (ZEISS, Jena, Germany) with an exposure time of 950 ms using default autoexposure parameters. The IF images were subsequently examined using Image J software version 1.53 t. Three fields of each group were randomly selected for quantificational analysis.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was repeated at least three times with three replicates. Bar plots are expressed as the geometric mean values ± S.E. The significance of the differences between mean values was assessed using one-way ANOVA. Post hoc tests were conducted if the ANOVA showed significant differences. p-values lower than 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Target Genome Mining
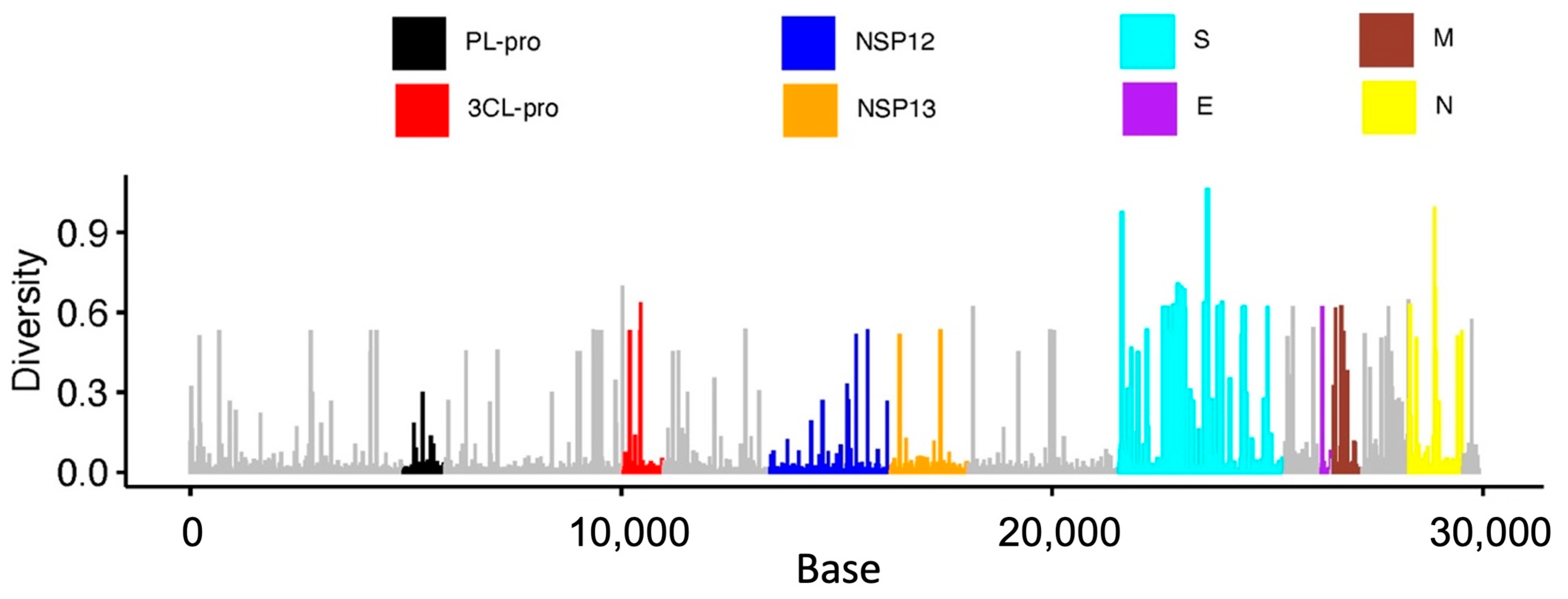
The whole-genome variation obtained from Nextstrain shows the low genetic diversity of the PLpro region with respect to other nonstructural and structural regions (Figure 1). Meanwhile, the compact size of the PLpro protease (35.6 kDa) makes it easier to establish the expression system in mammalian cells compared to the spike protein (180–200 kDa). Furthermore, PLpro, with no human homolog, has a dual function in the suppression of innate immune sensing and viral replication [25]. Thus, PLpro serves as an attractive target for SARS-CoV-2 antiviral therapeutic design.
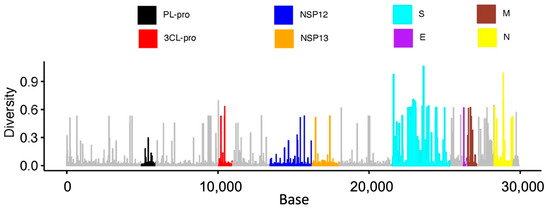
Figure 1.
Bar plot showing the relative amount of genetic diversity across SARS-CoV-2 based on 2776 genomes. Selected nonstructural proteins (Papain-like protease PLpro; 3C-like proteinase, 3CL-pro; RdRp RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, NSP12; helicase, NSP13) and structural proteins (spike, S; envelope, E; membrane, M; and nucleocapsid, N) are shown to highlight their overall variation.
3.2. Structure-Based Design of crRNAs Simultaneously Targeting Three Distant Sites of PLpro mRNA
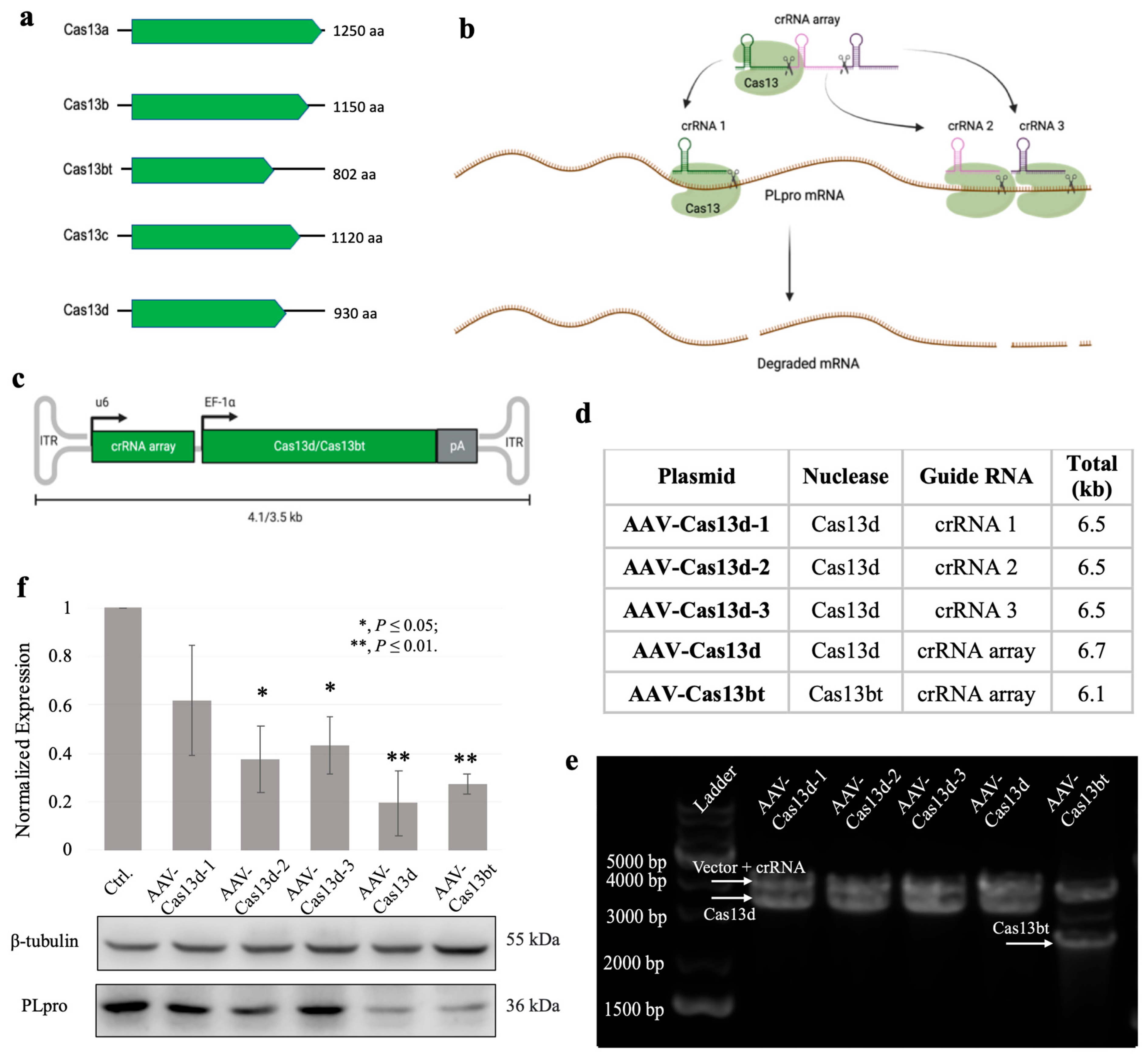
Similar to CRISPR-Cas9 DNA endonuclease systems, the CRISPR-Cas13 system requires two major components to target the specific sites of RNA, including (1) guide RNA sequences (crRNAs) and (2) the Cas13 endonuclease. There are at least four distinct subtypes of the varied Cas13 family, including Cas13a, Cas13b, Cas13c, and Cas13d (Figure 2a), initially discovered by Prof. Zhang’s lab. They first demonstrated that Cas13a could bind and cleave RNA in a program and act as a potent platform for RNA manipulation (Figure 2b) [26]. Among these subtypes of Cas13, Cas13d has the most compact size (930 aa/2.8 kb) and fits in the single adeno-associated virus (AAV) packing capacity (~4.7 kb) [27]. Recent research from the same lab discovered an ultrasmall Cas13b family protein, namely Cas13bt (802 aa/2.4 kb), that retains the programable RNases function [13]. Therefore, we decided to build the PLpro mRNA knockdown systems with two compact endonucleases, Cas13d and Cas13bt.
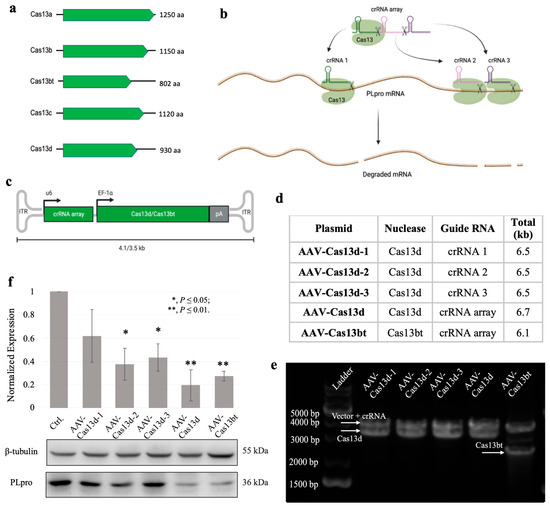
Figure 2.
Design, construction, and validation of AAV-Cas13 systems targeting PLpro. Created with BioRender. (a) Subtypes of Cas13 family endonuclease. Cas13d and Cas13bt offer a superior compact size to fit in a single AAV vehicle packing capacity. (b) Structure-based design of guide crRNAs for CRISPR-Cas13d system. (c) Recombined AAV genome carrying therapeutic genes of Cas13d/bt-crRNA system (see Figure S4 for the detailed plasmid maps). Using the compact Cas13d or Cas13bt endonuclease, the recombined AAV genome ends up being 4.1 kb or 3.5 kb, which fits a single AAV packing capacity (~4.7 kb). Inverted terminal repeats, ITR; u6 promoter, u6; EF-1α core promoter, EF-1α; poly A signal, pA. (d) Table of AAV-Cas13 plasmids constructed in this study. (e) AAV-Cas13 plasmids verification. Five constructed plasmids were linearized with Xba I and Sal I. From left to right, lane 1: DNA ladder; lane 2: AAV-Cas13d-1—DNA fragment vector + crRNA 1 (~3.7 kb) and Cas13d (~2.9 kb); lane 3: AAV-Cas13d-2—DNA fragment vector + crRNA 2 (~3.7 kb) and Cas13d (~2.9 kb); lane 4: AAV-Cas13d-3—DNA fragment vector + crRNA 3 (~3.7 kb) and Cas13d (~2.9 kb); lane 5: AAV-Cas13d—DNA fragment vector + crRNA array (~3.8 kb) and Cas13d (~2.9 kb); lane 6: AAV-Cas13bt—DNA fragment vector + crRNA array (~3.8 kb) and Cas13bt (~2.3 kb). (f) Direct lipofection of AAV-Cas13 plasmids to knockdown PLpro assay results (Ctrl.: 1.0, AAV-Cas13d-1: 0.62, AAV-Cas13d-2: 0.40, AAV-Cas13d-3: 0.45, AAV-Cas13d: 0.20, AAV-Cas13bt: 0.28). PLpro expression level is normalized with β-tubulin. The control group was NCI-H1299/PLpro cells only.
Next, we designed the crRNA sequences targeting the selected sites of PLpro mRNA, according to the secondary structure of PLpro mRNA. First, the secondary structure of PLpro mRNA was generated using UFold Webserver v1.2 (https://bio.tools/ufold accessed on 6 June 2020). From the gRNA sequences generated by the online Cas13 guide RNA designing tool [20], we randomly selected three crRNA sequences targeting the middle and tail regions of the PLpro transcript (Figure 2a). We built five plasmids that contain the desired compact Cas13/crRNA systems (Figure 2c,d). The AAV-Cas13d-1 plasmid contains crRNA 1 that targets the middle region of the PLpro transcript and the endonuclease Cas13d. Computational analysis revealed the double-stranded hairpin structure of the regional PLpro mRNA. The AAV-Cas13d-2 and AAV-Cas13d-3 plasmids contain two crRNA sequences that target the tail region of PLpro transcript. Computational analysis revealed the single-stranded structure of the crRNA 2 targeting region and the double-stranded structure of the crRNA 3 targeting region (Figures S3 and S4). The AAV-Cas13d plasmid contains a crRNA array that simultaneously targets all three regions and the Cas13 endonuclease. Meanwhile, AAV-Cas13bt plasmid contains the same crRNA array but the ultrasmall Cas13bt endonuclease. All plasmids were validated to ensure they were correct (Figure 2e).
Lastly, we delivered the plasmids into the NCI-H1299/PLpro cells via lipofection to verify the knockdown functions of the compact CRISPR-Cas13 systems. The PLpro knockdown assay showed that Cas13d endonuclease prefers the single-stranded region of the local secondary structure, as the guide RNA of Cas13d-2 offers the best efficiency among the three (Figure 2f). This finding is consistent with the previous literature [28]. However, the PLpro expression knockdown differences among the three crRNA sequences individually were insignificant. Noticeably, the crRNA array targeting all three sites simultaneously has shown preeminent knockdown activity in both Cas13d and Cas13bt systems (Figure 2f and Figure S5). This finding confirmed that the Cas13bt variant’s functionality resembles the well-studied Cas13d nuclease in terms of knocking down the PLpro expression in our NCI-H1299 study model [13].
3.3. Compact CRISPR-Cas13 Knockdown PLpro with rAAV Vehicles
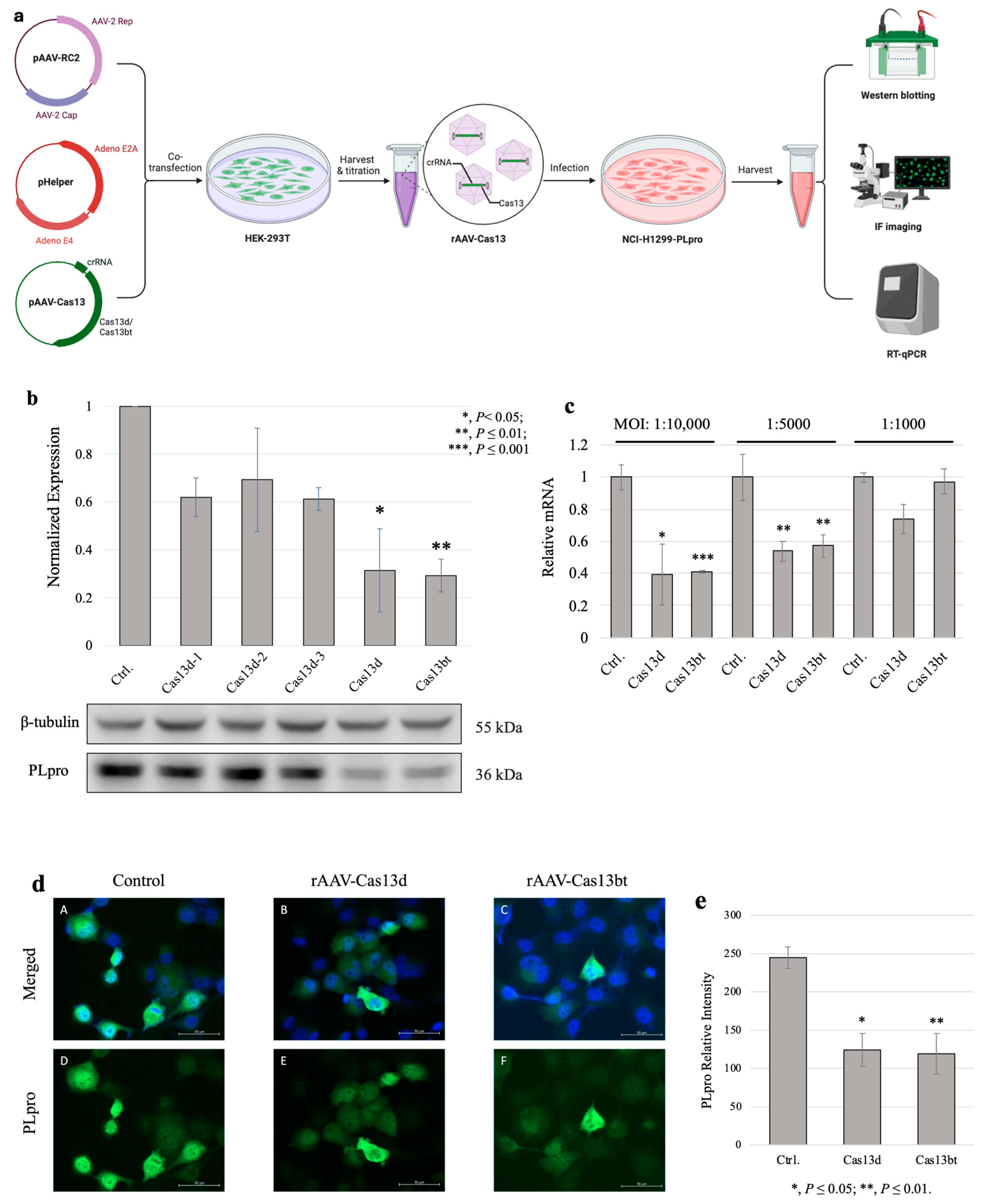
Next, we packed the compact CRISPR-Cas13 systems into AAV vehicles. The process is shown in Figure 3a. By co-infecting HEK-293T cells with AAV-RC2, Helper, and the compact AAV-Cas13 plasmids we designed and validated in 2.4, we successfully produced a recombined AAV with compact Cas13 gene therapy cargos. After infecting the NCI-H1299/PLpro cells, we examined the gene knockdown results using Western blotting, RT-qPCR, and immunofluorescence (IF) imaging. The results showed that both Cas13d and Cas13bt with triple-guiding crRNA arrays successfully knocked down PLpro at the protein levels (p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.01) (Figure 3b). Although the efficiency of the PLpro knockdown was overall lower than the Cas13 system validation results in 3.2, it is expected that the efficiency of therapeutic genes via an AAV vehicle can be lower than that of direct delivery via transfection. To determine the best time for harvesting PLpro cells after AAV infection, we conducted a time point experiment. The results showed a profound difference between the control group (NCI-H1299/PLpro cells only) and both experimental groups (rAAV-Cas13bt and rAAV-Cas13d) at 24 h considering the efficient timing of the assay (Figure S1). The subsequent AAV infection assays were all conducted for 24 h. Similar to the direct gene transfection results, we saw increased efficiency of knockdown using crRNA arrays with three distinct sequences combined (Cas13d) compared with the same three crRNA sequences guiding the Cas13 RNase activity individually (Cas13d-1, Cas13d-2, and Cas13d-3).
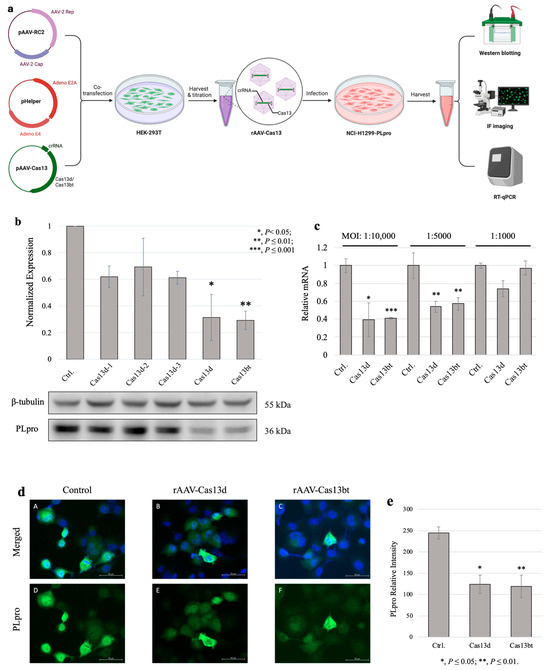
Figure 3.
Compact CRISPR-Cas13 knockdown NCI-H1299/PLpro with rAAV vehicles. (a) Schematic overview of compact CRISPR-Cas13 knockdown PLpro via recombined adeno-associated virus. Adapted from BioRender template “AAV Production by Triple Transfection”. Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates (accessed on 5 September 2024). (b) Western blotting results of recombined AAV2-Cas13 virus knockdown of PLpro assays. PLpro expression level is normalized with β-tubulin. MOI used for infection was 1:10,000, and NCI-H1299 cells were collected after 24 h of treatment. (c) RT-qPCR results of PLpro mRNA expression levels normalized with β-actin. MOI: multiplicity of infection. The ratios of NCI-H1299/PLpro cells to rAAV-Cas13 virus used in the assay were 1:10,000, 1:5000, and 1:1000. (d) IF imaging results of rAAV-Cas13d-, rAAV-Cas13bt-, or blank AAV-treated NCI-H1299-Cas13 knockdown of PLpro in NCI-H1299 cells after 24 h. Blue: DAPI; green: PLpro. Top panel: merged images with DAPI and GFP channels staining nuclei and PLpro, respectively. Bottom panel: separated channel of GFP for PLpro staining only. Left column: control of NCI-H1299/PLpro cells only. Middle column: rAAV-Cas13d-treated NCI-H1299/PLpro cells. Right column: rAAV-Cas13bt-treated NCI-H1299/PLpro cells. (e) Normalized immunofluorescence intensity of PLpro. Three visual fields were randomly selected in each group for quantitative analysis. PLpro level is measured as the intensity of GFP fluorescence normalized with the DAPI intensity of the nuclei.
To verify the successful knockdown of PLpro on gene expression levels, we conducted RT-qPCR experiments (Figure 3c). We normalized the expression levels of PLpro mRNA to two reference genes, GAPDH and β-actin, to ensure accuracy. Compared with the control group (blank AAV capsid treated), we found significantly reduced PLpro mRNA levels in the rAAV-Cas13bt- and rAAV-Cas13d-treated groups at a multiplicity of infection of 1:10,000 and 1:5000. This finding was confirmed with our Western blotting results, which showed a reduction in PLpro protein levels. To visualize PLpro expression in the cells, we also performed immunofluorescence (IF) staining and imaging on the NCI-H1299/PLpro cells (Figure 3d). After 24 h of infection, we observed a lower fluorescence intensity of PLpro, which was measured as the intensity of GFP for both AAV-Cas13 treated groups compared with the blank AAV vehicle-only group. We also randomly selected three fields of each group for quantitative analysis (Figure 3e). The normalized PLpro levels matched well with the observed IF imaging results. However, we did not find a noticeable distribution and localization of PLpro proteins within NCI-H1299 cells. Then, it can be safely assumed that the recombined AAV successfully delivered the compact CRISPR-Cas13 systems to the target cells and effectively decreased the expression of PLpro at the transcriptional level, resulting in a reduction in PLpro protein levels.
4. Discussion
The highly mutational nature of RNA viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, is a major challenge for antiviral therapies. Mutations in the virus can result in changes to its genetic code, which can alter its structure and function [29]. This can lead to the development of new virus strains resistant to existing vaccines or therapies, making it difficult to effectively control outbreaks [30]. For this reason, selecting conserved molecular targets of SARS-CoV-2 is important for the development of effective antiviral therapies. Conserved targets are those that are essential for the virus to replicate and are less likely to change due to mutations [31]. By targeting these conserved molecules, it may be possible to achieve a broad-spectrum antiviral effect that is not limited by the emergence of new strains of the virus [32].
PLpro has been identified as a conserved molecular target by our cross-genome bioinformatic analysis of 2776 SARS-CoV-2 genomes for structural proteins and nonstructural proteins. The structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 mainly refer to the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins [33], whereas nonstructural proteins (e.g., PLpro, 3CLpro, NSP12, and NSP13) play a role in viral survival, replication, and spread. For this reason, nonstructural proteins are less likely to change due to mutations, which was confirmed by our genome mining results. PLpro, as a protease involved in processing the viral polyprotein, is a nonstructural protein essential for the replication of the virus [25,34,35]. To create a functional replicate complex, the SARS-CoV-2 polyprotein must be processed into mature subunits by PLpro [36]. In addition, PLpro has a dual function in the suppression of host innate immune sensing. PLpro also prevents cellular proteins such as IRF3from becoming ISGylated, which results in the dysregulation of innate immune sensing [11]. Therefore, by targeting PLpro, it may be possible to effectively control the replication of SARS-CoV-2, even in the challenge of constant mutations.
The CRISPR-Cas13 technique has been successfully developed into a rapid assay, which researchers named “SHERLOCK”, to detect SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA for diagnosis, which has been translated into and validated in clinical practice [37,38]. The therapeutic use of CRISPR-Cas13 for COVID-19 is still in the early stages of research and development. The CRISPR-Cas13 system has the benefit of being flexible when it comes to generating guide RNAs, since Cas13 RNA-targeting cleavage activity is not dependent on the existence of certain neighboring sequences like the NGG motif for Cas9. This distinctive aspect of the approach satisfies the need for the fast synthesis of guide RNAs to target various viral types and may resist conventional treatments [39]. Hence, there is potential for CRISPR-Cas13 to be used as a tool for suppressing the expression of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in infected cells.
Among the Cas13 RNase family, Cas13bt and Cas13d have a smaller molecular size making them a more practical choice for gene therapy applications, as the compact size allows for easier and more efficient delivery of the Cas13 genes to cells directly or via single AAV vehicles [13,15]. Additionally, the smaller size also means that it has a lower likelihood of eliciting an immune response, which is a common challenge with larger gene-editing systems [40]. This is important for the development of safe and effective gene therapies, as an immune response can limit the effectiveness of the therapy and potentially cause adverse effects [41].
By programming compact CRISPR-Cas13 systems to recognize and cleave PLpro mRNA at three distinct sites, we demonstrated the successful knockdown of PLpro levels in NCI-H1299 cells through direct delivery of the therapeutic genes and through AAV vehicles. Furthermore, it is possible to use this approach to prevent the virus from replicating and spreading. This could reduce viral load, mitigate the severity of COVID-19 symptoms, and improve patient outcomes. However, our group does not have the necessary means to study real SARS-CoV-2 viral infections in vivo and in vitro. Another limitation is that the off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas13 systems were not investigated in this study. Off-target effects occur when the CRISPR-based gene editing system targets unintended regions of the genome or the mRNA, which can lead to unintended changes in gene expression or DNA damage [42,43]. Therefore, to develop the CRISPR-Cas13-based gene therapy against human coronaviral infections, a functional validation assay focusing on the investigation of safety and efficacy is needed in future studies. Furthermore, experiments on animal models of viral infection are needed to further validate this approach before translating it into therapeutics. In future studies, animal models will be used to further evaluate this therapeutic approach comprehensively. These studies will focus on assessing various aspects, such as the optimal dosing regimen, administration routes, and the broad-spectrum efficacy of the treatment. By systematically investigating these parameters, we aim to refine the therapeutic strategy and enhance its effectiveness across different contexts.
In addition, applying gene therapy to humans requires many ethical considerations and regulatory hurdles, especially with the use of AAV and genome-editing technologies. To minimize the possibility of non-directed genome modification, we removed a short element from the AAV vehicle sequence, that is, the nuclear localization signals (NLSs), which facilitate the protein translocation into the cell nucleus through the nuclear pore complex [44]. Theoretically, without NLS elements, the Cas13 protein would mainly be retained in the cytoplasm of the cells, which lowers the risk of unintended changes in gene expression or DNA damage.
The efficiency of AAV-Cas13-mediated knockdown of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro is closely tied to the viral entry mechanisms of AAV vectors. AAV entry initiates with binding to specific cell surface receptors, followed by internalization via receptor-mediated endocytosis, predominantly facilitated by clathrin-mediated pathways, ensuring delivery into endosomes. Subsequent endosomal escape is crucial, allowing AAV to release its genetic payload into the cytoplasm, where the unpackaging of the viral genome enables the transcription and expression of Cas13 and guide RNAs. Understanding these entry mechanisms is pivotal for optimizing vector design to enhance tissue tropism, mitigate immune responses, and ensure high Cas13 specificity. For instance, our use of AAV2, which targets the lungs, enhances its potential for respiratory disease therapy. Importantly, different AAV types can target distinct organs, further broadening the versatility and applicability of AAV-Cas13 systems across diverse therapeutic applications. Addressing these challenges will augment the therapeutic potential of AAV-Cas13 systems, not only for COVID-19 but also for a wide range of viral infections.
To sum up, it is important to note that AAV delivery of the CRISPR-Cas13 therapeutic approach is still a new and rapidly evolving field, and more research is needed to fully explore its potential for the treatment of COVID-19.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/j7030023/s1, Scheme S1: Construction of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro expression in NCI-H1299 cells; Table S1: Primers and cDNA sequences; Figure S1: AAV-Cas13d and AAV-Cas13bt plasmid maps; Figure S2: pLVX-EF1alpha-IRES-Puro-SARS-CoV-2-PLpro Map; Figure S3: Secondary Structures of crRNAs used in CRISPR-Cas13 system targeting PLpro mRNA; Figure S4: Regional and overall secondary structures of PLpro mRNA; Figure S5: rAAV-Cas13 Infection Timepoint Assay.
Author Contributions
Design of the experiments and original draft preparation, Y.Y.; collection of experimental data, M.G.C.K.; bioinformatics data analysis and manuscript editing and review, M.R.M.-R.; immunofluorescence imaging acquisition, Y.Z.; reviewing and supervision, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Konneker Research Fund, Edison Biotechnology Institute, the Translational Biomedical Sciences program at Ohio University, and a John J. Kopchick Research Fellowship Award to Yuehan Yang.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Xianzhong Yu for his invaluable support in experimental design and manuscript editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ciotti, M.; Ciccozzi, M.; Terrinoni, A.; Jiang, W.-C.; Wang, C.-B.; Bernardini, S. The COVID-19 pandemic. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570371/ (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchene, S.; Featherstone, L.; Haritopoulou-Sinanidou, M.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G. Temporal signal and the phylodynamic threshold of SARS-CoV-2. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dorp, L.; Acman, M.; Richard, D.; Shaw, L.P.; Ford, C.E.; Ormond, L.; Owen, C.J.; Pang, J.; Tan, C.C.S.; Boshier, F.A.T.; et al. Emergence of genomic diversity and recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2020, 83, 104351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Johnson, B.A.; Xia, H.; Ku, Z.; Schindewolf, C.; Widen, S.G.; An, Z.; Weaver, S.C.; Menachery, V.D.; et al. Delta spike P681R mutation enhances SARS-CoV-2 fitness over Alpha variant. bioRxiv 2022, 39, 110829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez-Santos, Y.M.; St John, S.E.; Mesecar, A.D. The SARS-coronavirus papain-like protease: Structure, function and inhibition by designed antiviral compounds. Antivir. Res. 2015, 115, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.A.; Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, K.; Gayen, S.; Jha, T. Protease targeted COVID-19 drug discovery and its challenges: Insight into viral main protease (Mpro) and papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 115860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Mukherjee, R.; Grewe, D.; Bojkova, D.; Baek, K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Schulz, L.; Widera, M.; Mehdipour, A.R.; Tascher, G.; et al. Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity. Nature 2020, 587, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Huang, B.; Tang, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Cao, D.; et al. The complex structure of GRL0617 and SARS-CoV-2 PLpro reveals a hot spot for antiviral drug discovery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Altae-Tran, H.; Jin, X.; Madigan, V.J.; Oshiro, R.; Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V.; Zhang, F. Compact RNA editors with small Cas13 proteins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Samulski, R.J. Engineering adeno-associated virus vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudayyeh, O.O.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Essletzbichler, P.; Han, S.; Joung, J.; Belanto, J.J.; Verdine, V.; Cox, D.B.T.; Kellner, M.J.; Regev, A.; et al. RNA targeting with CRISPR–Cas13. Nature 2017, 550, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, M.; Rezaei, N. CRISPR/Cas13: A potential therapeutic option of COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Wilson, H.; Jayakumar, S.; Kulkarni, V.; Kulkarni, S. Efficient Inhibition of HIV Using CRISPR/Cas13d Nuclease System. Viruses 2021, 13, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhao, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Xu, F.; Mei, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. CRISPR-Cas13a Inhibits HIV-1 Infection. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, H.-H.; Méndez-Mancilla, A.; Guo, X.; Legut, M.; Daniloski, Z.; Sanjana, N.E. Massively parallel Cas13 screens reveal principles for guide RNA design. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.F.; Wang, P.Y.; Kumar, S.; Lama, S.; Lin, F.L.; Liu, G.S. Methods for in vitro CRISPR/CasRx-Mediated RNA Editing. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 667879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Whitford, C.M.; Blin, K.; Jørgensen, T.S.; Weber, T.; Lee, S.Y. CRISPR–Cas9, CRISPRi and CRISPR-BEST-mediated genetic manipulation in streptomycetes. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2470–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- qPCR Primer & Probe Design Tool. Available online: https://eurofinsgenomics.eu/en/ecom/tools/qpcr-assay-design/ (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- McClain, C.B.; Vabret, N. SARS-CoV-2: The many pros of targeting PLpro. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudayyeh, O.O.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Konermann, S.; Joung, J.; Slaymaker, I.M.; Cox, D.B.T.; Shmakov, S.; Makarova, K.S.; Semenova, E.; Minakhin, L.; et al. C2c2 is a single-component programmable RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector. Science 2016, 353, aaf5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flotte, T.R. Size does matter: Overcoming the adeno-associated virus packaging limit. Respir. Res. 2000, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaru, S.; Tsuji, M.H.; Shimizu, Y.; Usami, K.; Lee, S.; Takei, N.K.; Yoshitome, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Otsuki, T.; Ito, T. Structure-based design of gRNA for Cas13. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawbaa, H.M.; Osama, H.; El-Gendy, A.; Saeed, H.; Harb, H.S.; Madney, Y.M.; Abdelrahman, M.; Mohsen, M.; Ali, A.M.A.; Nicola, M.; et al. Effect of mutation and vaccination on spread, severity, and mortality of COVID-19 disease. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, M.K.; Junod, N.A.; Young, A.R.; Beachboard, D.C.; Stobart, C.C. Targeting novel structural and functional features of coronavirus protease nsp5 (3CL(pro), M(pro)) in the age of COVID-19. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, E.; van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Hilgenfeld, R. Structural and mutational analysis of the interaction between the Middle-East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) papain-like protease and human ubiquitin. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, T.; Ebert, G.; Calleja, D.J.; Allison, C.C.; Richardson, L.W.; Bernardini, J.P.; Lu, B.G.; Kuchel, N.W.; Grohmann, C.; Shibata, Y.; et al. Mechanism and inhibition of the papain-like protease, PLpro, of SARS-CoV-2. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchsung, M.; Jantarug, K.; Pattama, A.; Aphicho, K.; Suraritdechachai, S.; Meesawat, P.; Sappakhaw, K.; Leelahakorn, N.; Ruenkam, T.; Wongsatit, T.; et al. Clinical validation of a Cas13-based assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, M.J.; Koob, J.G.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Zhang, F. Sherlock: Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2986–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Zhang, Y.; Pandolfi, P.P. Virus against virus: A potential treatment for 2019-nCov (SARS-CoV-2) and other RNA viruses. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.M.; Palmer, N.; Alemán, F.; Chen, G.; Pla, A.; Jiang, N.; Leong Chew, W.; Law, M.; Mali, P. Immune-orthogonal orthologues of AAV capsids and of Cas9 circumvent the immune response to the administration of gene therapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.L.; Peter, L.; Schmueck-Henneresse, M. Cas9-directed immune tolerance in humans—A model to evaluate regulatory T cells in gene therapy? Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghwar, H.; Li, B.; Ding, X.; Hussain, A.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X.; Jin, S. CRISPR/Cas Systems in Genome Editing: Methodologies and Tools for sgRNA Design, Off-Target Evaluation, and Strategies to Mitigate Off-Target Effects. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Majeed, S.; Hoque, M.Z.; Ahmad, I. Latest Developed Strategies to Minimize the Off-Target Effects in CRISPR-Cas-Mediated Genome Editing. Cells 2020, 9, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulikas, T. Nuclear localization signals (NLS). Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1993, 3, 193–227. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, A.; Mills, R.E.; Lange, C.J.; Stewart, M.; Devine, S.E.; Corbett, A.H. Classical Nuclear Localization Signals: Definition, Function, and Interaction with Importin α. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).