Development of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium) Chloride-Modified Activated Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Methyl Red in Aqueous Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of PDADMAC-AC
2.3. Characterization and Analytical Methods
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests (RSSCTs)
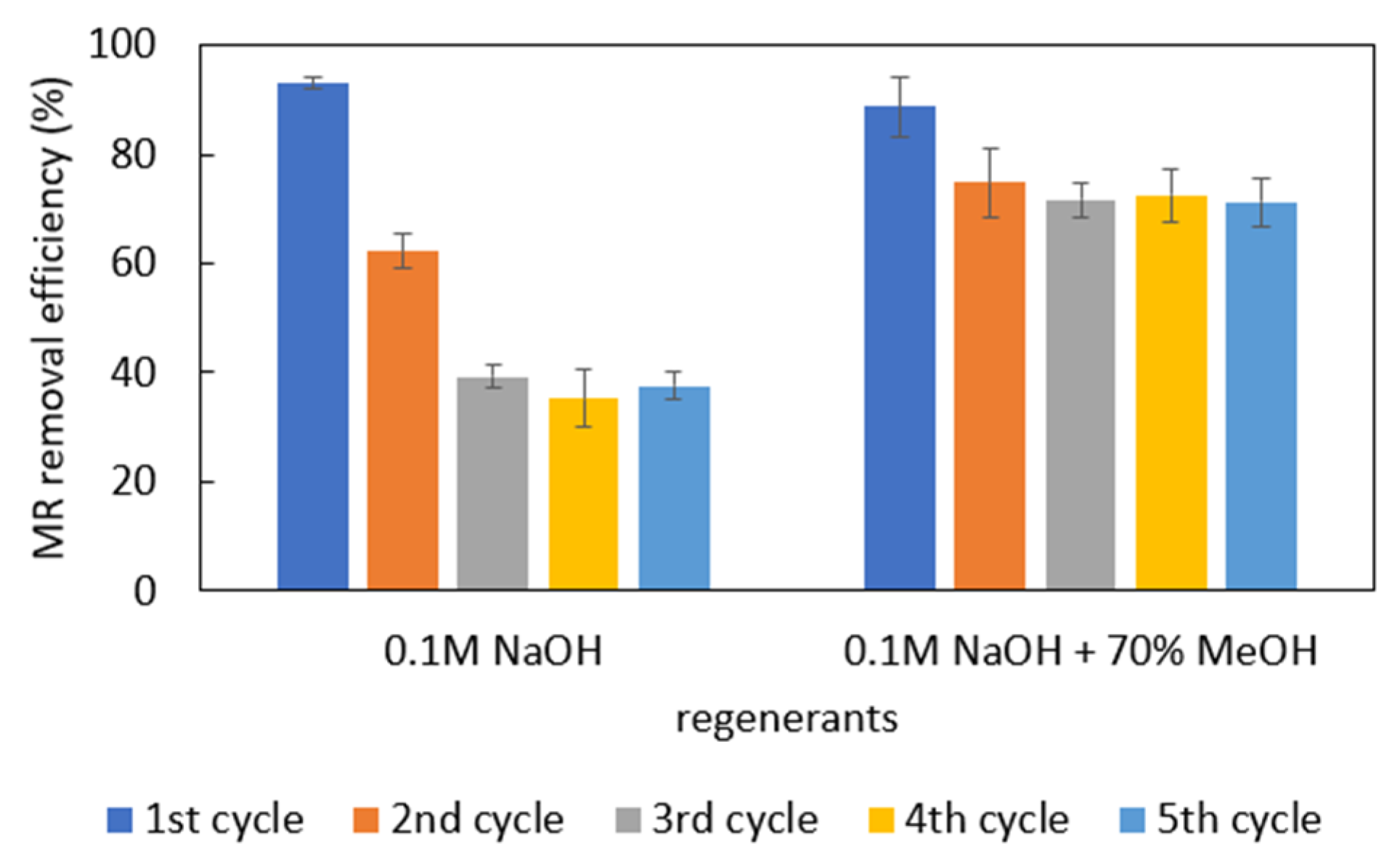
2.6. Regeneration Tests
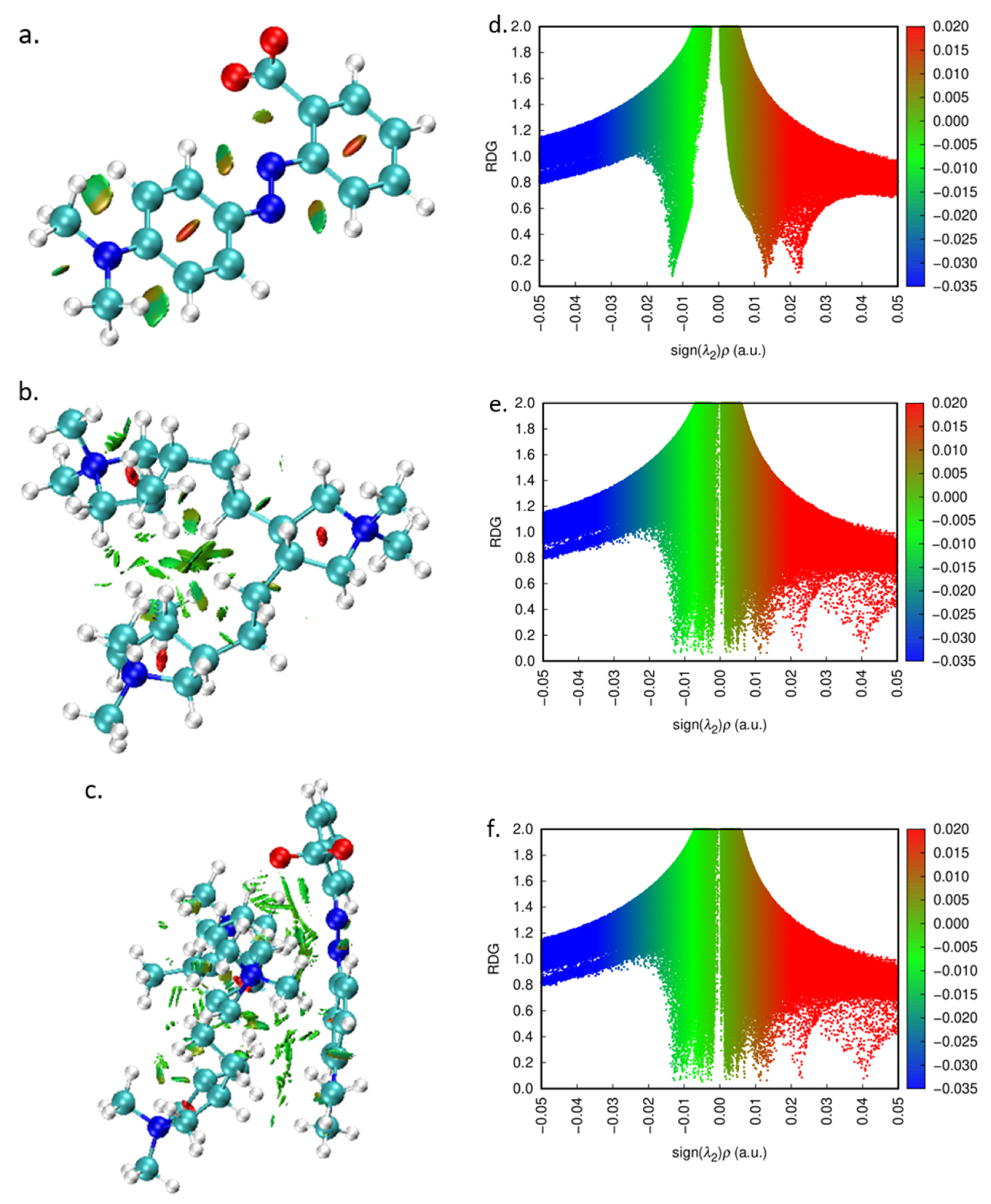
2.7. Quantum Chemical Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of PDADMAC Concentration
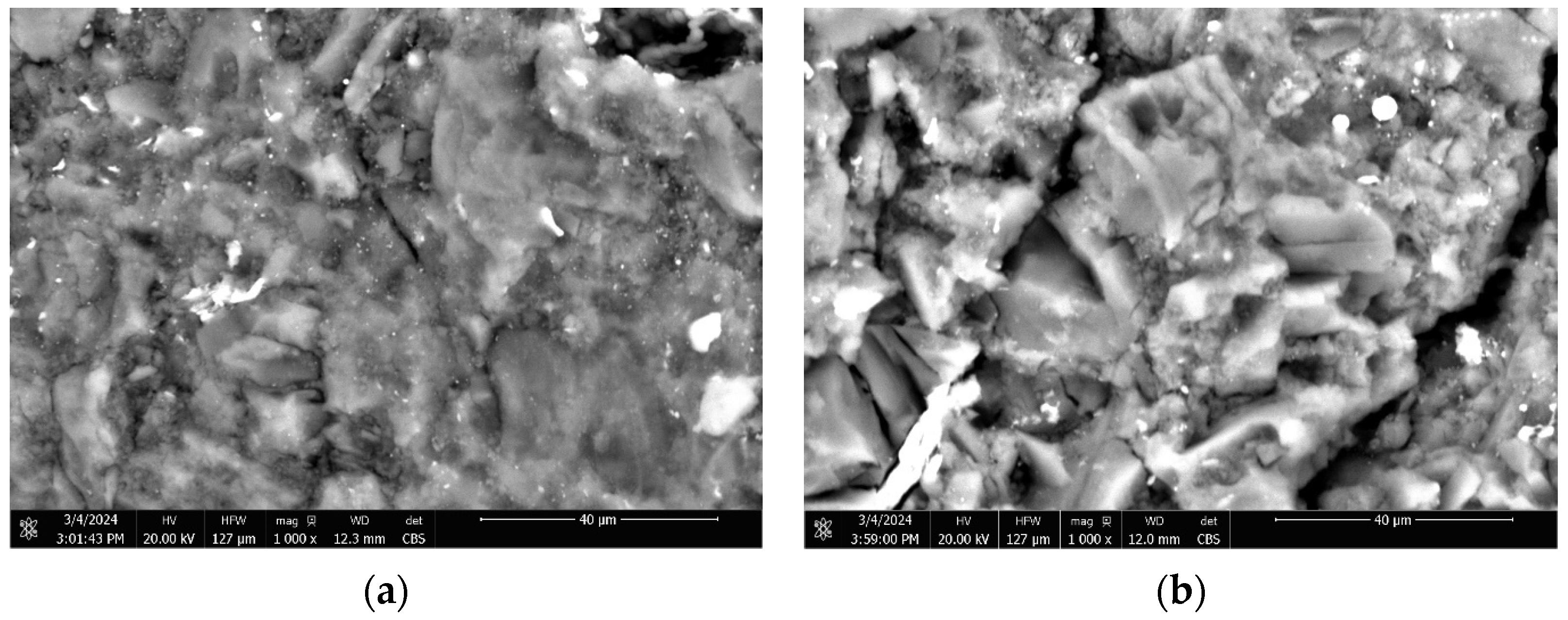
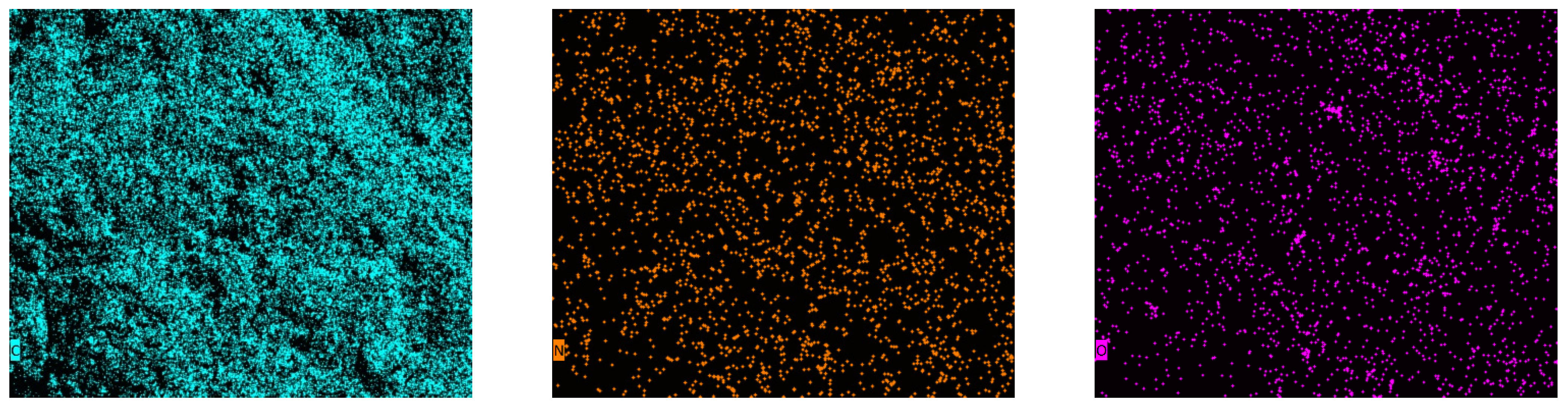
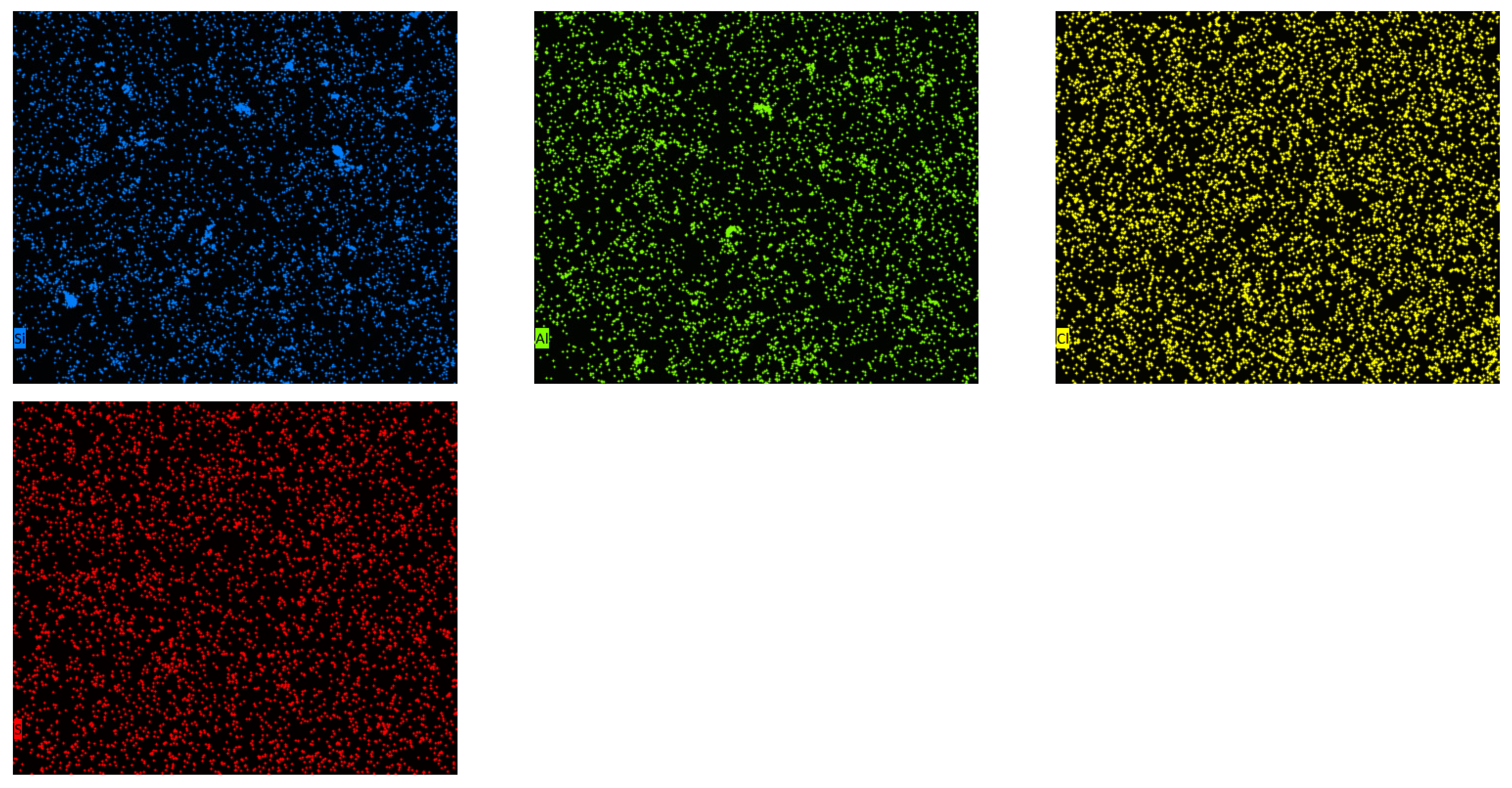
3.2. Characterization of Adsorbents
3.3. Batch Adsorption Results
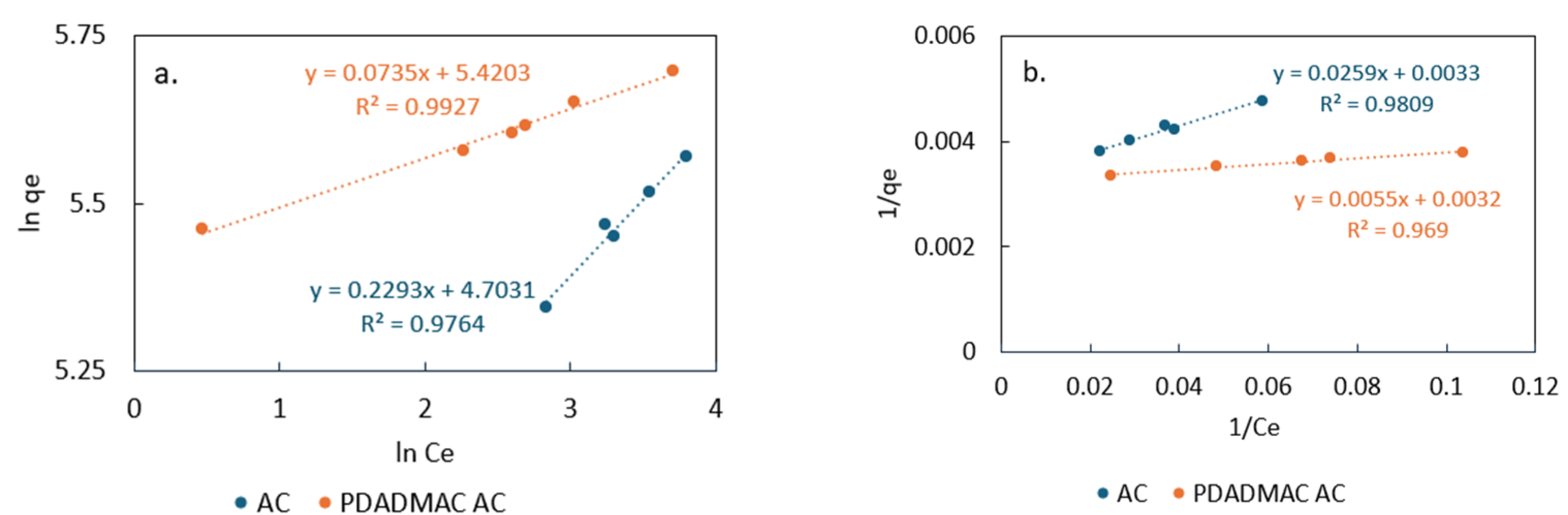
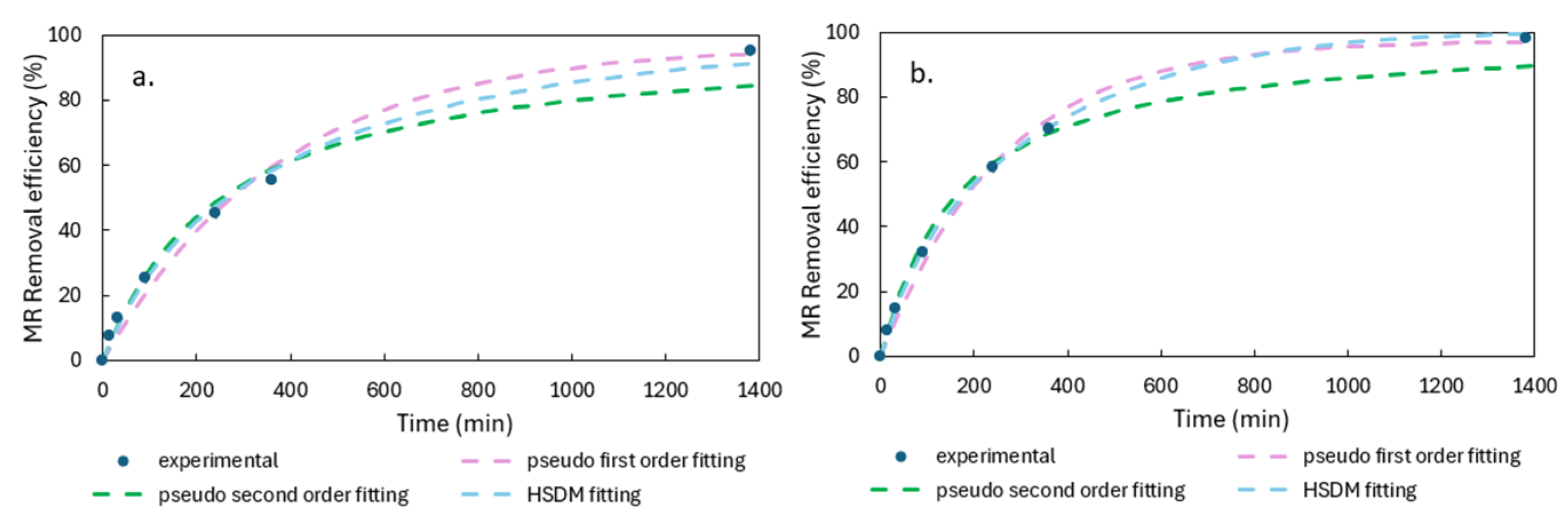
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
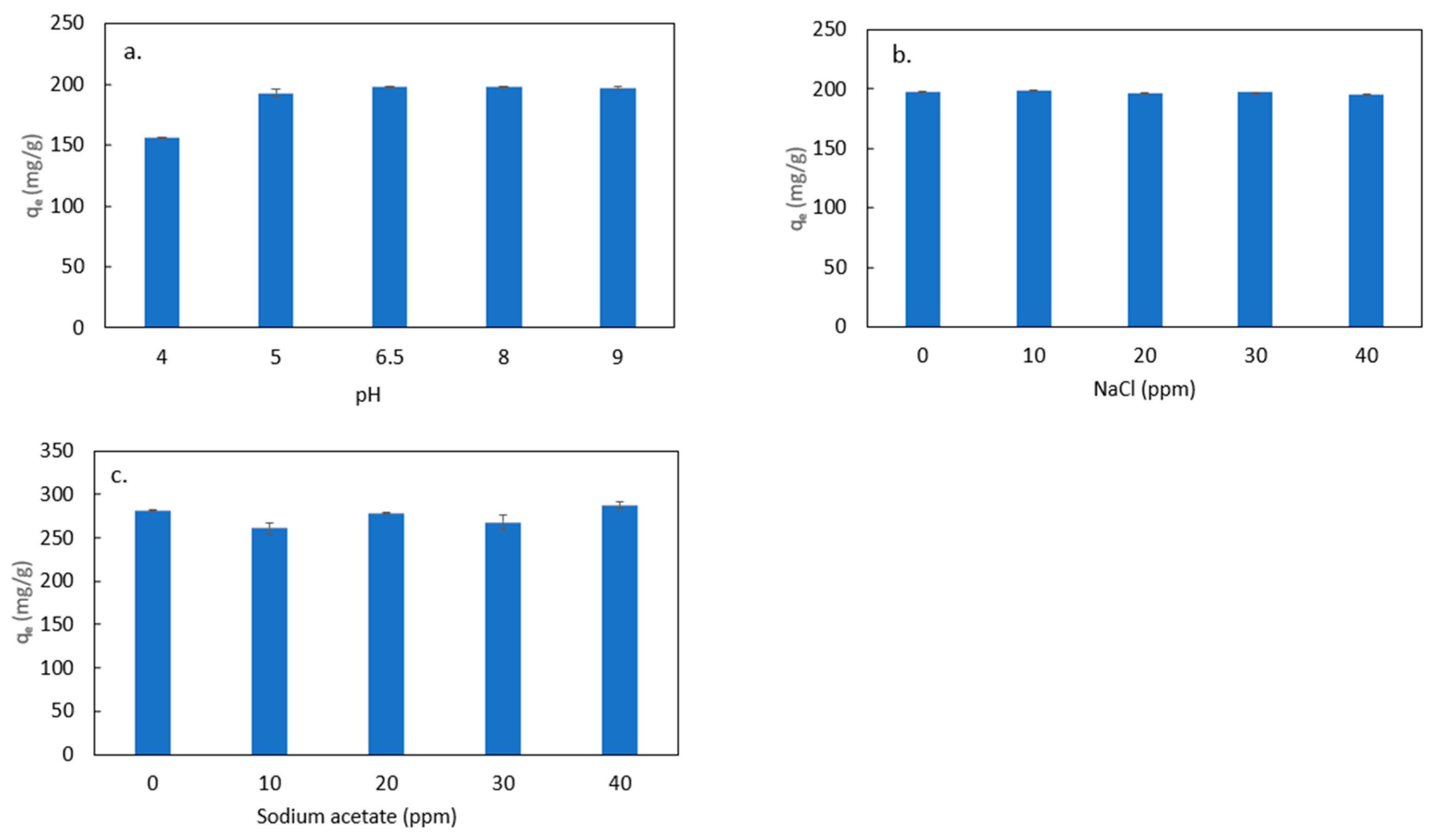
3.3.2. Effects of Water Matrix
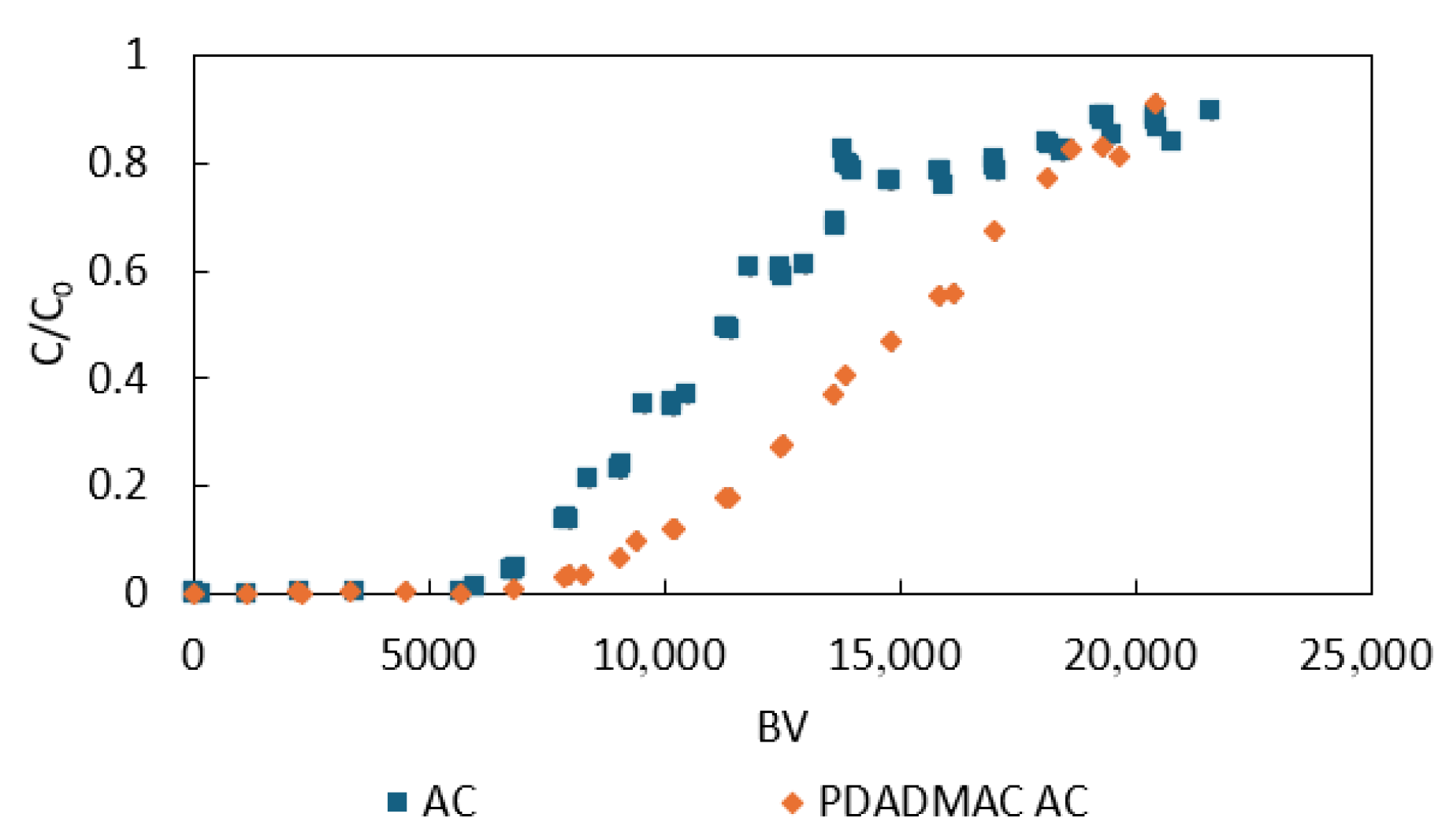
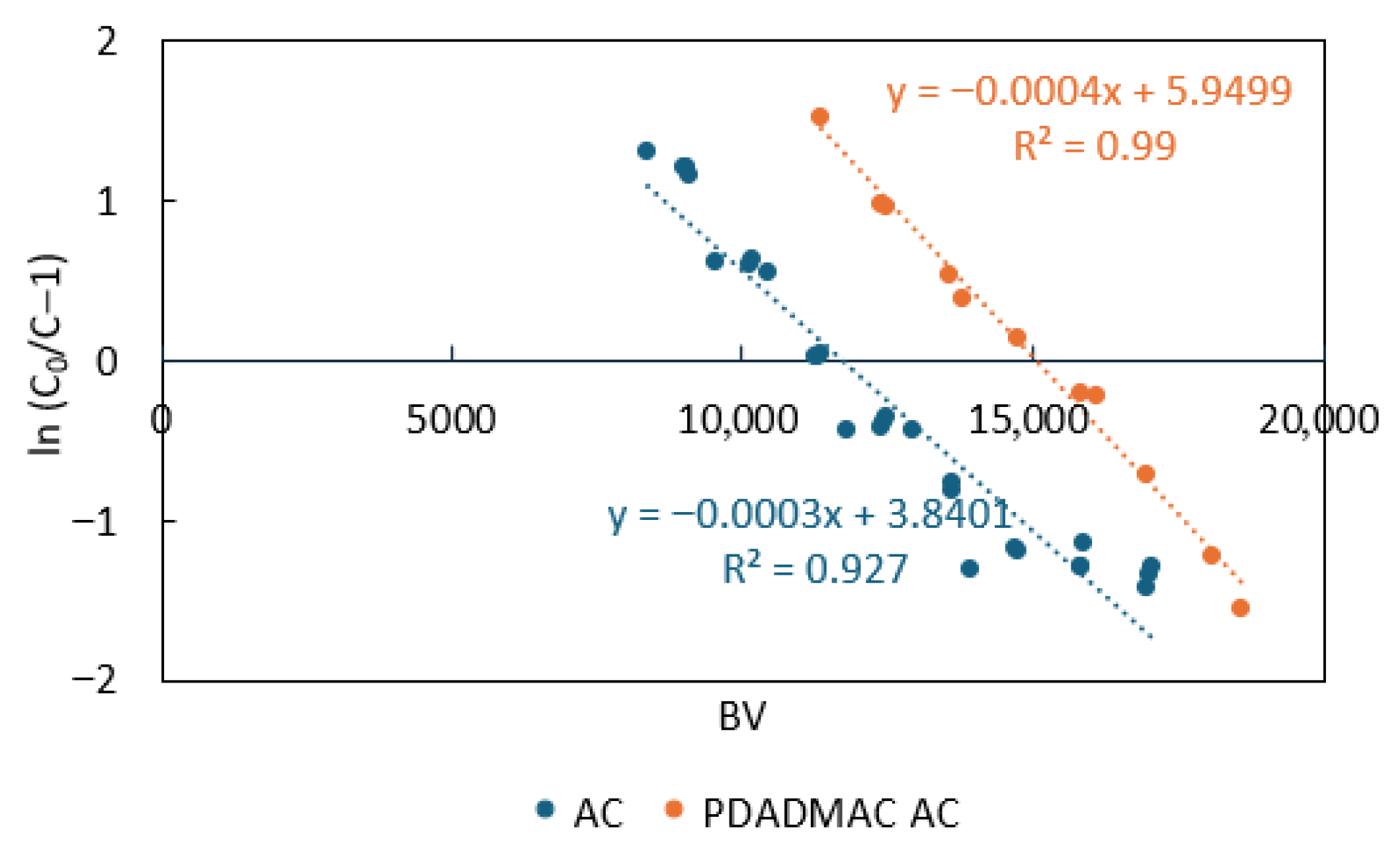
3.4. Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests
3.5. Regeneration of Adsorbents
3.6. Quantum Chemical Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, R.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Padhye, L.P. Conducting Polymers-Based Photocatalysis for Treatment of Organic Contaminants in Water. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 4, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpongwana, N.; Rathilal, S. A Review of the Techno-Economic Feasibility of Nanoparticle Application for Wastewater Treatment. Water 2022, 14, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, S.; Horcajada, P. Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants in Water. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8378–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Adhikary, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Roy, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, A.; Nanda, S.; Rajak, P. Contamination of Textile Dyes in Aquatic Environment: Adverse Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystem and Human Health, and Its Management Using Bioremediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila-Leal, L.D.; Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Quevedo-Hidalgo, B.E. A Brief History of Colour, the Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dyes and Removal by Using Laccases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Ahmed, N.B.; Adegoke, K.A.; Bello, O.S. Sorption Studies of Methyl Red Dye Removal Using Lemon Grass (Cymbopogon citratus). Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 22, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Kavitha, D. Removal of Congo Red from Water by Adsorption onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Coir Pith, an Agricultural Solid Waste. Dyes Pigment. 2002, 54, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.K. Use of Activated Carbons Prepared from Sawdust and Rice-Husk for Adsorption of Acid Dyes: A Case Study of Acid Yellow 36. Dyes Pigment. 2003, 56, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Xia, H.; Peng, J.; Shu, J.; Li, C. Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Fe-Activated Carbon as an Effective Low-Cost Adsorbent for Dyes Wastewater Treatment. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78936–78946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and Mechanism of Removal of Methylene Blue by Adsorption on Various Carbons—A Comparative Study. Dyes Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezohegyi, G.; van der Zee, F.P.; Font, J.; Fortuny, A.; Fabregat, A. Towards Advanced Aqueous Dye Removal Processes: A Short Review on the Versatile Role of Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.; Rownok, M.H.; Sabrin, M.; Rahaman, M.H.; Alam, S.M.N. A Review on Experimental Chemically Modified Activated Carbon to Enhance Dye and Heavy Metals Adsorption. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, B.; Lin, L.; Ndagijimana, P.; Wang, Y. N-Nitrosodimethylamine Removal by a Novel Silver/Sulfur-Coated Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron/Activated Carbon Composite: Adsorption Kinetics, Mechanisms, and Degradation Pathways. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Liu, X.; Ilyas, H.N.; Hanphaiboon, P.; Wang, W.; Noman, M.; Pan, B.; Wang, Y. One-Step Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Activated Carbon Composite for Efficient Removal of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water: Adsorption Mechanisms and DFT Study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 367, 132797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.S.; Pignatello, J.J. Modified Carbons for Enhanced Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Adsorbed Methyl Bromide. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 233, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Cannon, F.S.; Brown, N.R.; Byrne, T.; Gu, X.; Delgado, C.N. Granular Activated Carbon Anchored with Quaternary Ammonium/Epoxide-Forming Compounds to Enhance Perchlorate Removal from Groundwater. Carbon 2013, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudov, R.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.P. Functionalized Activated Carbon for the Adsorptive Removal of Perchlorate from Water Solutions. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.Y.; Aroua, M.K.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Review of Modifications of Activated Carbon for Enhancing Contaminant Uptakes from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 52, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.Y. Adsorption of Bromate and Competition from Oxyanions on Cationic Surfactant-Modified Granular Activated Carbon (GAC). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.W.; Chon, C.M.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, B.H.; Schwartz, F.W.; Lee, E.S.; Song, H. Adsorption of Nitrate and Cr(VI) by Cationic Polymer-Modified Granular Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 175, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radian, A.; Mishael, Y. Effect of Humic Acid on Pyrene Removal from Water by Polycation-Clay Mineral Composites and Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6228–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radian, A.; Mishael, Y.G. Characterizing and Designing Polycation—Clay Nanocomposites as a Basis for Imazapyr Controlled Release Formulations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Su, C.; Wang, Z. Surface Modified TiO2 Floating Photocatalyst with PDDA for Efficient Adsorption and Photocatalytic Inactivation of Microcystis Aeruginosa. Water Res. 2018, 131, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalwagy, M.E.; Elsherbiny, A.S.; Gemeay, A.H. Amine-Rich Polymers for Water Purification Applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 27, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Mohammadkhani, R.; Ahmadipouya, S.; Shokrgozar, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Molavi, H.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Arjmand, M. Superior Chemical Stability of UiO-66 Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for Selective Dye Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, F.; Hnát, J.; Paidar, M.; Schauer, J.; Bouzek, K. Determination of the Ion-Exchange Capacity of Anion-Selective Membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, E.F.; Lin, Z.W.; Cifuentes, E.S.; Barajas-Rodriguez, F.J.; Gwinn, R.; Dichtel, W.R.; Packman, A.I. Removal of PFAS and Pharmaceuticals from Municipal Wastewater Using a Novel β-Cyclodextrin Adsorbent over Distinct Contact Times. Water Res. 2025, 282, 123631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavian, S.; Hooper, J.; Abusallout, I.; Hofmann, R. Granular Activated Carbon for PFAS Removal in Municipal Wastewater: A Rapid Small-Scale Column Test Study. ACS ES T Water 2025, 5, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, T.G.; Ersan, M.S.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Ersan, G. Predicting Full-Scale Performance of Adsorbents for per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Adsorption: The Role of Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 974, 178944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, I.; Gallagher, B.; Vishwanath, N.; Blute, N.; Gorzalski, A.; Feffer, A.; Richardson, S. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Removal with Granular Activated Carbon and a Specialty Adsorbent: A Case Study. AWWA Water Sci. 2021, 3, e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, E. Adsorption Technology in Water Treatment: Fundamentals, Processes, and Modeling; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrigan, J.K., Jr. Scale-Up of Rapid Small-Scale Adsorption Tests to Field-Scale Adsorbers: Theoretical and Experimental Basis; Michigan Technological University: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1985; ISBN 1083381903. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.F.; Ng, K.M. Flow in Packed Tubes with a Small Tube to Particle Diameter Ratio. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Malekshah, R.E.; Heidari, Z.; Pelalak, R.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. Molecular Dynamic Simulations and Quantum Chemical Calculations of Adsorption Process Using Amino-Functionalized Silica. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 330, 115544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, A.L.; Rowley, C.N. Benchmarking Quantum Chemical Methods for the Calculation of Molecular Dipole Moments and Polarizabilities. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mageed, H.R.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.A. Elucidating the Adsorption and Detection of Amphetamine Drug by Pure and Doped Al12N12, and Al12P12nano-Cages, a DFT Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Muddana, H.S.; Gilson, M.K. Quantum Mechanical Calculation of Noncovalent Interactions: A Large-Scale Evaluation of PMx, DFT, and SAPT Approaches. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. Software Update: The ORCA Program System—Version 5.0. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2022, 12, e1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ratés, M.; Neese, F. Effect of the Solute Cavity on the Solvation Energy and Its Derivatives within the Framework of the Gaussian Charge Scheme. J. Comput. Chem. 2020, 41, 922–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. An Improvement of the Resolution of the Identity Approximation for the Formation of the Coulomb Matrix. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A Consistent and Accurate Ab Initio Parametrization of Density Functional Dispersion Correction (DFT-D) for the 94 Elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A Multifunctional Wavefunction Analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T. A Comprehensive Electron Wavefunction Analysis Toolbox for Chemists, Multiwfn. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 082503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bakshi, S.; Li, C.; Parikh, S.J.; Hsieh, H.S.; Pignatello, J.J. Modification of Pyrogenic Carbons for Phosphate Sorption through Binding of a Cationic Polymer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 579, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoriya, S.; Saharan, V.K.; Pundir, A.S.; Nigam, M.; Roy, K. Adsorption of Methyl Red Dye from Aqueous Solution onto Eggshell Waste Material: Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamic Studies. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-khuder, Z.H.A.; Karam, F.F. Synthesis and Characterization of a Quaternary Composite Based on RGO/MWCNTs/Choline Chloride + Malonic Acid for Methyl Orange Dye Adsorption. Results Chem. 2025, 15, 102133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouda, I.; Ben Seddik, N.; El Boumlasy, S.; Achache, M.; Hadri, M.; El Midaoui, A.; Draoui, K. Enhanced Cationic Dyes Adsorption: Experimental and Theoretical Insights into Moroccan Clays vs. Commercial Montmorillonite. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 59, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhala, A.; Sethi, S.; Singh, B.G.; Pal, S. Equilibrium, Kinetics and Mechanistic Study of PM567 Laser Dye Adsorption from Ethanol. Indian Chem. Eng. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Alkaim, A.F.; Alsultany, F.H.; Issa, S.K. Highly Reusable Nano Adsorbent Based on Clay-Incorporated Hydrogel Nanocomposite for Cationic Dye Adsorption. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 35, 1165–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Fajardo, C.A.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Pirajan, J.C. Isotherm, Thermodynamic, and Kinetic Studies of Dye Adsorption on Graphene Oxides with Varying Oxidation Degrees. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Yi, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, S.; Ding, P.; Chen, C.; Pan, H. Optimization on Preparation of Fe3O4/Chitosan as Potential Matrix Material for the Removal of Microcystin-LR and Its Evaluation of Adsorption Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, E.A.; Shahjahan; Khan, T.A. Adsorption of Methyl Red on Activated Carbon Derived from Custard Apple (Annona squamosa) Fruit Shell: Equilibrium Isotherm and Kinetic Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukkumaran, A.; Aravamudan, K. Combined Homogeneous Surface Diffusion Model—Design of Experiments Approach to Optimize Dye Adsorption Considering Both Equilibrium and Kinetic Aspects. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, R.M.C.; Campinas, M.; Costa, H.; Rosa, M.J. How Do the HSDM and Boyd’s Model Compare for Estimating Intraparticle Diffusion Coefficients in Adsorption Processes. Adsorption 2014, 20, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, H.P. Determination of PKa of Dyes by Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2008, 88, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouni, A.; Fersi, C.; Cuartas-Uribe, B.; Bes-Pía, A.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I.; Dhahbi, M. Reactive Dyes Rejection and Textile Effluent Treatment Study Using Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration Processes. Desalination 2012, 297, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muda, K.; Aris, A.; Salim, M.R.; Ibrahim, Z.; Yahya, A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ahmad, A.; Nawahwi, M.Z. Development of Granular Sludge for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4341–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.A.; Uchiyama, K.; Inadama, D.; Ishida, Y.; Yamagiwa, K. Treatment of Azo Dye Acid Orange 7 Containing Wastewater Using Up-Flow Constructed Wetland with and without Supplementary Aeration. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9049–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panswad, T.; Iamsamer, K.; Anotai, J. Decolorization of Azo-Reactive Dye by Polyphosphate- and Glycogen-Accumulating Organisms in an Anaerobic–Aerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary Lissy, P.N.; Madhu, G.; Thomas, R.M. Numerical Modelling of a Fixed Bed Column for the Cr(VI) Adsorption Using Pyrrole Coated Nanocomposite. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2025, 102, 101568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.H.; Tlaiaa, Y.S.; Naser, Z.A.; Al-Sharify, Z.T. Simulation of Heavy Metals Removal in Fixed Bed Coloumn by Adams-Bohart, Thomas, Yoon-Nelson and Wolborska Models. AIP Conf. Proc. 2025, 3169, 040029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabichi, I.; Ezzahi, K.; Yaacoubi, F.E.; Izghri, Z.; Ennaciri, K.; Ounas, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Baçaoui, A.; Hafidi, M.; El Fels, L. Evaluating the Fixed-Bed Column Adsorption Capacity of Olive Pomace Biochar Activated with KOH and H3PO4 for Olive Mill Wastewater Treatment: Insights from TOC and HPLC Analysis. Chemosphere 2025, 377, 144356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zusman, O.B.; Kummel, M.L.; De la Rosa, J.M.; Mishael, Y.G. Dissolved Organic Matter Adsorption from Surface Waters by Granular Composites versus Granular Activated Carbon Columns: An Applicable Approach. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Du, E. The Effects of Thermal Regeneration Conditions and Inorganic Compounds on the Characteristics of Activated Carbon Used in Power Plant. Energy Procedia 2012, 17, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Junior, O.P.; Vargas, A.M.M.; Da Silva, A.P.; Zou, X.; Asefa, T.; Almeida, V.C. Thermal Regeneration Study of High Surface Area Activated Carbon Obtained from Coconut Shell: Characterization and Application of Response Surface Methodology. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, D.; Bazan-Wozniak, A.; Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Pietrzak, R. Removal of Methylene Blue and Methyl Red from Aqueous Solutions Using Activated Carbons Obtained by Chemical Activation of Caraway Seed. Molecules 2023, 28, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, T.; Grich, A.; Naboulsi, A.; Regti, A.; Alaoui Tahiri, A.; El Himri, M.; El Haddad, M. Adsorption of Methyl Red on Porous Activated Carbon from Agriculture Waste: Characterization and Response Surface Methodology Optimization. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 158, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahirah, M.A.; Jidin, M.; Jani, M.; Fauzi, N.M.; Subki, N.S. Removal of Methyl Red in Wastewater by Activated Carbon Derived from Rice Husk. J. Trop. Resour. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 8, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, A.; Bouchareb, E.M.; Derbal, K.; Boukhaloua, S.; Chahbouni, B.; Bouchareb, R. Uptake of Methyl Red Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Activated Carbons Prepared from Moringa Oleifera Shells. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 4, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, N.S.M.; Ahmed, A.S.A.; Abdallah, M.H.; Gouda, G.A. ZnO@ Activated Carbon Derived from Wood Sawdust as Adsorbent for Removal of Methyl Red and Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solutions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafidah, H.S.; Prasetia, H.; Saefumillah, A. Adsorption Study of Methylene Blue and Methyl Red on Activated Carbon from Silver Composite Using the Extract of Spent Coffee Grounds. J. Sains Mater. Indones. 2024, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Isotherm | Parameters | AC | PDADMAC-AC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | Kf (mg/g) (L/mg)1/n | 110.3 ± 17.6 | 225.9 ± 4.4 |
| n | 4.3 ± 0.9 | 13.6 ± 1.3 | |
| R2 | 0.976 | 0.993 | |
| RMSE | 1.70 | 2.69 | |
| Langmuir | qm (mg/g) | 306.6 ± 17.7 | 308.1 ± 8.5 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.59 ± 0.16 | |
| R2 | 0.981 | 0.969 | |
| RMSE | 34.68 | 2.50 |
| Pseudo First Order | Pseudo Second Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | R2 | RMSE | k2 (g/mg min) | R2 | RMSE | |
| AC | 0.0027 ± 0.0001 | 0.988 | 0.035 | 0.000039 ± 0.000001 | 0.976 | 0.050 |
| PDADMAC-AC | 0.0039 ± 0.0001 | 0.994 | 0.026 | 0.000060 ± 0.000001 | 0.986 | 0.040 |
| Ds (m2/s) | kf (m/s) | Bi | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 1.54 × 10−11 ± 3 × 10−13 | 0.00084 ± 0.00004 | 10.3 ± 0.3 | 0.993 |
| PDADMAC-AC | 1.02 × 10−11 ± 1 × 10−13 | 0.00115 ± 0.00005 | 18.9 ± 0.9 | 0.999 |
| MR | PDADMAC | MR + PDADMAC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EHOMO (eV) | –4.617 | −7.439 | −4.698 |
| ELUMO (eV) | –2.826 | −0.419 | −2.915 |
| Energy gap ∆EGAP (eV) | 1.791 | 7.020 | 1.783 |
| Ionization energy I (eV) | 4.617 | 7.439 | 4.698 |
| Electron affinity A (eV) | 2.826 | 0.419 | 2.915 |
| Global hardness η (eV) | 0.896 | 3.510 | 0.892 |
| Global softness σ (eV−1) | 1.117 | 0.285 | 1.122 |
| Chemical potential μ (eV) | −3.721 | −3.929 | −3.807 |
| Electronegativity χ (eV) | 3.721 | 3.929 | 3.807 |
| Electrophilicity index ω (eV) | 7.732 | 2.199 | 8.128 |
| Nucleophilicity index ε (eV) | 4.504 | 1.682 | 4.423 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Mohseni, M. Development of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium) Chloride-Modified Activated Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Methyl Red in Aqueous Systems. Clean Technol. 2025, 7, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030061
Li S, Mohseni M. Development of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium) Chloride-Modified Activated Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Methyl Red in Aqueous Systems. Clean Technologies. 2025; 7(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Simeng, and Madjid Mohseni. 2025. "Development of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium) Chloride-Modified Activated Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Methyl Red in Aqueous Systems" Clean Technologies 7, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030061
APA StyleLi, S., & Mohseni, M. (2025). Development of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium) Chloride-Modified Activated Carbon for Efficient Adsorption of Methyl Red in Aqueous Systems. Clean Technologies, 7(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030061







