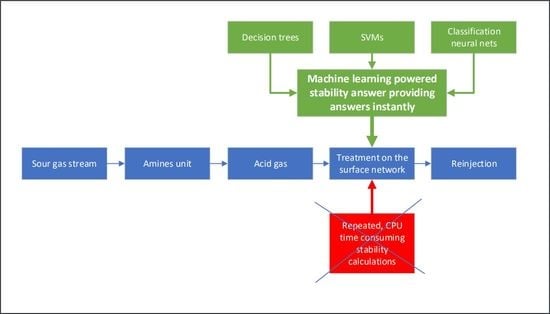
Acid Gas Re-Injection System Design Using Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
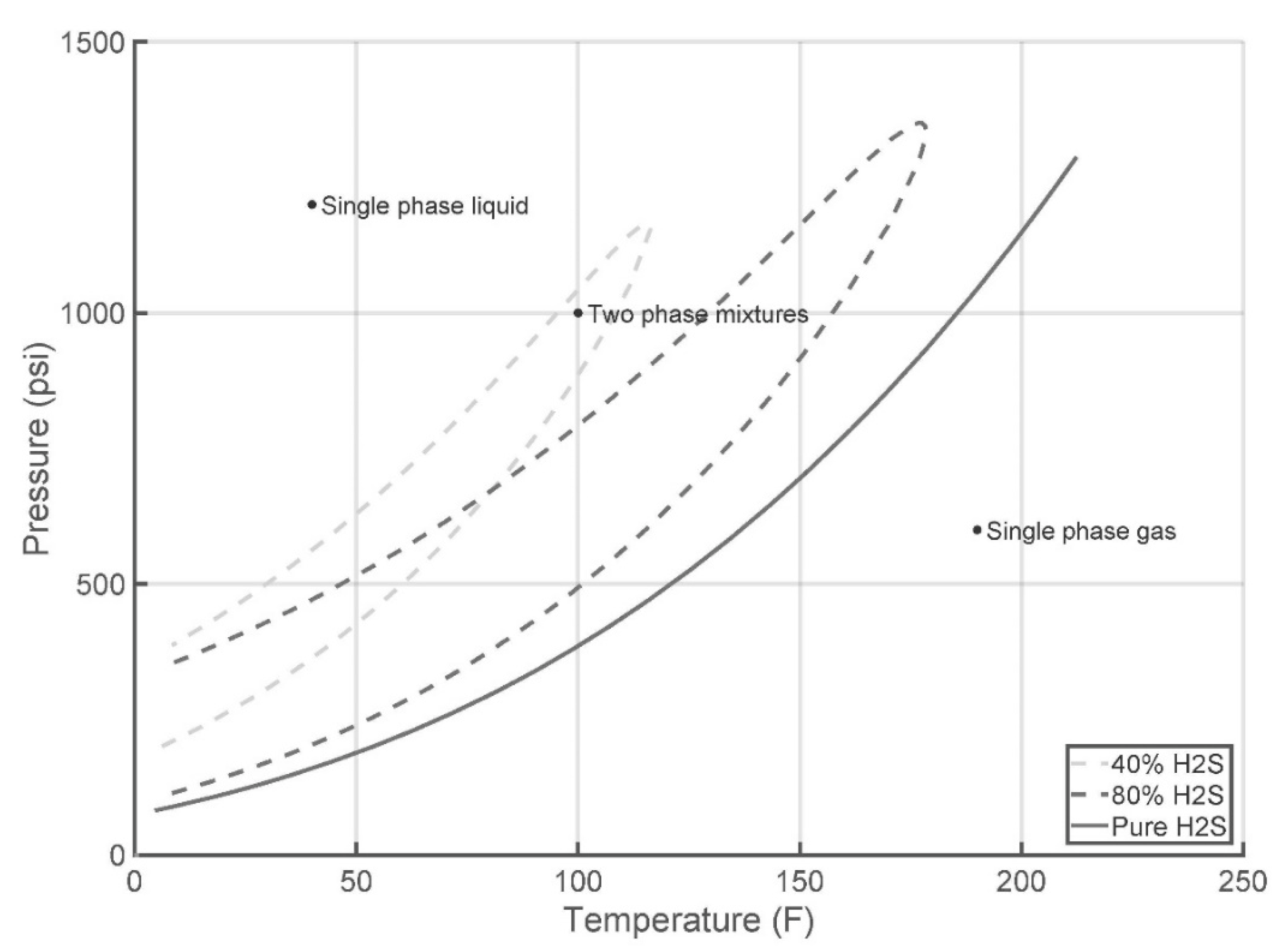
2.1. Conventional Stability Calculations
2.2. Stability Calculations in the Classification Framework
2.3. Classification Models Considered
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Generation of the Training Data
- Acid gas is explicitly stable at temperatures above the highest cricodentherm and at pressures above the highest cricodenbar, 1500 psi and 220 °F, respectively;
- Acid gas is explicitly stable if current conditions lie above the upper boundary line;
- Acid gas is explicitly stable if current conditions lie below the lower boundary line;
- Otherwise, the classifier needs to be invoked to identify the number of phases present at current operating conditions.
3.2. Classifiers Training
3.2.1. Decision Trees
3.2.2. Support Vector Machines
3.2.3. Neural Networks
3.3. Further Calculations Speed-Up
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smil, V. Natural Gas: Fuel for the 21st Century; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-119-01286-3. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, E.; Doukas, A.; Shaw, K. Greenwashing gas: Might a ‘transition fuel’ label legitimize carbon-intensive natural gas development? Energy Policy 2012, 46, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council. Paris Agreement on Climate Change. Available online: http://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/policies/climate-change/timeline/ (accessed on 3 September 2019).
- Eylander, J.G.R.; Holtman, H.A.; Salma, T.; Yuan, M.; Callaway, M.; Johnstone, J.R. The Development of Low-Sour Gas Reserves Utilizing Direct-Injection Liquid Hydrogen Sulphide Scavengers. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 September–3 October 2001; p. SPE-71541-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Luqman, A.; Moosavi, A. The Impact of CO2 Injection for EOR & its Breakthrough on Corrosion and Integrity of New and Existing Facilities. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–10 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.R.; Hawkins, E.; Jones, P.D. CO2, the greenhouse effect and global warming: From the pioneering work of Arrhenius and Callendar to today’s Earth System Models. Endeavour 2016, 40, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohl, A.L.; Nielsen, R.B. Gas Purification, 5th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 1997; pp. 670–730. ISBN 9780884152200. [Google Scholar]
- Kokal, S.L.; Abdulwahid, A. Sulfur Disposal by Acid Gas Injection: A Road Map and A Feasibility Study. In Proceedings of the SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, Al Manama, Bahrain, 12–15 March 2005; p. SPE-93387-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Goar, B. Sulfur Recovery Technology. Energy Progress 1986, 6, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, B.; (Bruce Scott, Inc., San Rafael, CA, USA); Hendricks, D.; (Pacific Environmental Services, Inc., Research Triangle Park, NC, USA). Personal communication, 28 February 1992.
- Bachu, S.; Adams, J.J.; Michael, K.; Buschkuehle, B.E. Acid Gas Injection in the Alberta Basin: A Commercial-Scale Analogue for CO2 Geological Sequestration in Sedimentary Basins. In Proceedings of the Second Annual Conference on Carbon Dioxide Sequestration, Alexandria, VA, USA, 5–8 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.A.; Svrcek, W.Y.; Monnery, W.O.; Jamaluddin, A.K.M.; Bennion, D.B.; Thomas, F.B.; Wichert, E.; Reed, A.E.; Johnson, D.J. Designing and Optimized Injection Strategy for Acid Gas Disposal without Dehydration. In Proceedings of the 77th Annual Convention of the Gas Processors Association, Dallas, TX, USA, 16–18 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.J.; Maddocks, J.R. Design considerations for acid gas injection. In Proceedings of the 49th Laurance Reid Gas Conditioning Conference, Norman, OK, USA, 21–24 February 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, M.L. New Perspective on Oil and Gas Separator Performance. SPE Prod. Facil. 1993, 8, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitani, A.M. Sour Natural Gas Drying. Hydrocarbon Process. 1993, 72, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, J.G. Oil and Gas Corrosion Prevention, 1st ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2014; pp. 3–37. ISBN 9780128004159. [Google Scholar]
- Weiland, R.H.; Sivasubramanian, M.S.; Dingman, J.C. Effective Amine Technology: Controlling Selectivity, Increasing Slip, and Reducing Sulfur. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Laurance Reid Gas Conditioning Conference, Norman, OK, USA, 24 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lens, P.; Hulshoff, P.L.W. Environmental Technologies to Treat Sulfur Pollution: Principles and Engineering, 1st ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2000; pp. 238–239. ISBN 13: 9781900222099. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, C.F.; Apps, J.A. Underground Injection Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; p. 624. ISBN 9780080457901. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, H.; Carroll, J.J.; Maddocks, J. Impact of Thermophysical Properties Research on Acid Gas Injection Process Design. In Proceedings of the 78th Annual GPA Convention, Nashville, TN, USA, 1–3 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bierlein, J.A.; Kay, W.B. Phase-Equilibrium Properties of System Carbon Dioxide-Hydrogen Sulfide. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1953, 45, 618–624. [Google Scholar]
- Kellerman, S.; Stouffer, C.; Eubank, P.; Holste, J.; Hall, K.; Gammon, B.; Marsh, K. Thermodynamic Properties of CO2 + H2S Mixtures; Gas Processors Association: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1995; OCLC: 37647473. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, D.; Thomas, F.; Schulmeister, B.; Imer, D.; Shtepani, E. The Phase Behavior of Acid Disposal Gases and the Potential Adverse Impact on Injection or Disposal Operations. In Proceedings of the Petroleum Society’s Canadian International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 11–13 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Commodore, J.A.; Deering, C.E.; Bernard, F.; Marriott, R.A. High-Pressure Densities and Excess Molar Volumes for the Binary Mixture of Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen Sulfide at T = 343–397 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 4236–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T. Reservoir Engineering Handbook, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 9780080966670. [Google Scholar]
- Ezekwe, N. Petroleum Reservoir Engineering Practice; Pearson Education: Westford, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780132485210. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, L.E.; Pierce, A.C.; Luks, K.D. Gibbs Energy Analysis of Phase Equilibria. SPE J. 1982, 22, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, M.L. The isothermal flash problem: Part I. Stability. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1982, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, M.L. The isothermal flash problem. Part II. Phase-split calculation. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1982, 9, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgis, G.M.; Voutsas, E.; Yakoumis, I.; Tassios, D.P. An equation of state for associating fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 4310–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivintzelis, I.; Kontogeorgis, G.; Michelsen, M.; Stenby, E. Modeling phase equilibria for acid gas mixtures using the CPA equation of state. Part II: Binary mixtures with CO2. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2011, 306, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaganis, V.; Varotsis, N. Machine learning methods to speed up compositional reservoir simulation. In Proceedings of the SPE Europec/EAGE Annual Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–7 June 2012; p. SPE-154505-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Nichita, D.V.; Petitfrere, M. Phase stability analysis using a reduction method. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2013, 358, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S. Acceleration of the NVT-flash calculation for multicomponent mixtures using deep neural network models. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 12312–12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 10: 978-0-387-31073-2. [Google Scholar]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Mikosch, T.V., Robinson, S.M., Resnick, S.I., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-387-30303-0. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-7139-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gaganis, V. Rapid phase stability calculations in fluid flow simulation using simple discriminating functions. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 108, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, M.; Ghahfarokhi, A.; Wui, C.; Zeraibi, N. Optimization of WAG in real geological field using rigorous soft computing techniques and nature-inspired algorithms. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, M.; Zeraibi, N.; Redouane, K. Optimization of WAG Process Using Dynamic Proxy, Genetic Algorithm and Ant Colony Optimization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 6399–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Zendehboudi, S.; James, L. Developing a robust proxy model of CO2 injection: Coupling Box–Behnken design and a connectionist method. Fuel 2018, 215, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Mohaghegh, S. Application of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Proxy Modeling for Fluid Flow in Porous Media. Fluids 2019, 4, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahkarami, A.; Mohaghegh, S. Applications of smart proxies for subsurface modelling. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, H.; Kamin, M.; Khare, P. Design Space Exploration of Turbulent Multiphase Flows Using Machine Learning-Based Surrogate Model. Energies 2020, 13, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samnioti, A.; Anastasiadou, V.; Gaganis, V. Application of Machine Learning to Accelerate Gas Condensate Reservoir Simulation. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usama, A.; Daegeun, H.; Jinjoo, A.; Umer, Z.; Chonghun, H. Fault propagation path estimation in NGL fractionation process using principal component analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 162, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Petitfrere, M. EOS Based Simulations of Thermal and Compositional Flows in Porous Media. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pau and Pays de l’Adour, Pau, France, 12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, C.M.; Floudas, C.A. Global optimization for the phase stability problem. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 1798–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S.T.; Floudas, C.A. Phase stability with cubic equations of state: A global optimization approach. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 1422–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.Z.; Brennecke, J.F.; Stadtherr, M.A. Reliable prediction of phase stability using an interval Newton method. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1996, 116, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, J.Z.; Brennecke, J.F.; Stadtherr, M.A. Reliable computation of phase stability using interval analysis: Cubic equation of state models. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1998, 22, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitson, C.; Brule, M. Phase Behavior, SPE Monograph; Henry, L., Ed.; Doherty Memorial Fund of AIME, Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Michelsen, M.L. Simplified flash calculations for cubic equations of state. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1986, 25, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, E.M.; Van Bergen, A.R.D. Application of a reduction method to phase equilibria calculations. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1992, 74, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozabadi, A.; Pan, H. Fast and robust algorithm for the compositional modeling: Part I. Stability analysis testing. SPE J. 2002, 7, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Firoozabadi, A. Fast and robust algorithm for compositional modeling: Part II—Two-phase flash computations. SPE J. 2003, 8, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaganis, V.; Varotsis, N. Non-iterative phase stability calculations for process simulation using discriminating functions. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2011, 314, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaganis, V.; Varotsis, N. An integrated approach for rapid phase behavior calculations in compositional modeling. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2014, 118, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichita, D.V.; Broseta, D.; Montel, F. Calculation of convergence pressure/temperature and stability test limit loci of mixtures with cubic equations of state. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2007, 261, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 10: 0387952845. [Google Scholar]
- Burges, C. A tutorial on Support Vector Machines for pattern recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 121–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J.C. Fast training of support vector machines using Sequential Minimum Optimization, advances in kernel methods. In Support Vector Machines; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 185–208. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-19-853864-6. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.J. Phase Equilibria Relevant to Acid Gas Injection, Part 1-Non-Aqueous Phase Behavior. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2002, 41, PETSOC-02-06-02. [Google Scholar]
- Burges, C. Simplified support vector decision rules. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Machine Learning, Bari, Italy, 3–6 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, V.S.; Crouson, J. Self-Splitting Modular Neural Network—Domain Partitioning at Boundaries of Trained Regions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Hong Kong, China, 1–8 June 2008. [Google Scholar]









| Component | Range (mol%) |
|---|---|
| CO2 | 1–99% |
| H2S | 1–99% |
| C1 | 0–5% |
| C2 | 0–3% |
| Training Data | Testing Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True labels | True labels | ||||||
| Stable | Unstable | Stable | Unstable | ||||
| Classifier labels | Stable | 20.52% | 1.19% | Classifier labels | Stable | 28.90% | 1.40% |
| Unstable | 1.93% | 76.36% | Unstable | 2.46% | 67.24% | ||
| Training Data | Testing Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True labels | True labels | ||||||
| Stable | Unstable | Stable | Unstable | ||||
| Classifier labels | Stable | 31.16% | 0.92% | Classifier labels | Stable | 30.32% | 0.96% |
| Unstable | 1.72% | 66.20% | Unstable | 0.56% | 68.16% | ||
| Training Data | Testing Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True labels | True labels | ||||||
| Stable | Unstable | Stable | Unstable | ||||
| Classifier labels | Stable | 28.09% | 0.85% | Classifier labels | Stable | 14.62% | 0.22% |
| Unstable | 0.85% | 70.21% | Unstable | 0.12% | 85.04% | ||
| P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (1) | Medium (2) | High (3) | ||
| T | Low (1) | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Medium (2) | 7 | 7 | 6 | |
| High (3) | - | 6 | 6 | |
| Classification Model | Training Datapoints | Validation Datapoints |
|---|---|---|
| Decision trees | 5,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Support Vector Machines | 5000 | 5000 |
| Neural networks | 5000 | 5000 |
| 3 × 3 split neural networks | 5000 | 5000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anastasiadou, V.; Samnioti, A.; Kanakaki, R.; Gaganis, V. Acid Gas Re-Injection System Design Using Machine Learning. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 1001-1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4040062
Anastasiadou V, Samnioti A, Kanakaki R, Gaganis V. Acid Gas Re-Injection System Design Using Machine Learning. Clean Technologies. 2022; 4(4):1001-1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4040062
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnastasiadou, Vassiliki, Anna Samnioti, Renata Kanakaki, and Vassilis Gaganis. 2022. "Acid Gas Re-Injection System Design Using Machine Learning" Clean Technologies 4, no. 4: 1001-1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4040062
APA StyleAnastasiadou, V., Samnioti, A., Kanakaki, R., & Gaganis, V. (2022). Acid Gas Re-Injection System Design Using Machine Learning. Clean Technologies, 4(4), 1001-1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4040062