Abstract
Deep eutectic solvents (DES) are compounds of a hydrogen bond donor (HBD) and a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) that contain a depressed melting point compared to their individual constituents. DES have been studied for their use as carbon capture media and biogas upgrading. However, contaminants’ presence in biogas might affect the carbon capture by DES. In this study, conductor-like screening model for real solvents (COSMO-RS) was used to determine the effect of temperature, pressure, and selective contaminants on five DES’ namely, choline chloride-urea, choline chloride-ethylene glycol, tetra butyl ammonium chloride-ethylene glycol, tetra butyl ammonium bromide-decanoic acid, and tetra octyl ammonium chloride-decanoic acid. Impurities studied in this paper are hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, water, nitrogen, octamethyltrisiloxane, and decamethylcyclopentasiloxane. At infinite dilution, CO2 solubility dependence upon temperature in each DES was examined by means of Henry’s Law constants. Next, the systems were modeled from infinite dilution to equilibrium using the modified Raoults’ Law, where CO2 solubility dependence upon pressure was examined. Finally, solubility of CO2 and CH4 in the various DES were explored with the presence of varying mole percent of selective contaminants. Among the parameters studied, it was found that the HBD of the solvent is the most determinant factor for the effectiveness of CO2 solubility. Other factors affecting the solubility are alkyl chain length of the HBA, the associated halogen, and the resulting polarity of the DES. It was also found that choline chloride-urea is the most selective to CO2, but has the lowest CO2 solubility, and is the most polar among other solvents. On the other hand, tetraoctylammonium chloride-decanoic acid is the least selective, has the highest maximum CO2 solubility, is the least polar, and is the least affected by its environment.
Keywords:
biogas; carbon capture; deep eutectic solvents; Henry’s Law; Raoult’s Law; selectivity; solubility 1. Introduction
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is the process of breaking down organic substances in anoxic conditions by bacteria [1]. Organic macro-molecules such as fats, carbohydrates, and proteins are digested into micro-molecules during AD, which results in a nutrient-rich solid for plants (fertilizer) and biogas [2]. This process occurs naturally in landfills, but also in a controlled environment in equipment called anaerobic digestors. The feedstock for AD are materials that are otherwise considered waste, such as agricultural waste, manure, organic waste from animal processing plants, food waste, and many others [3,4]. The growing adoption of AD offers a new approach to these waste streams which supports a recycle economy that increases market efficiency and bolsters the renewable energy industry as the globe shifts towards green fuel.
During AD, several reactions occur, but the process can be categorized into four stages: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis. During hydrolysis, long-chain polymers like cellulose are hydrolyzed into fermentable forms like glucose. Acidogenesis and acetogenesis are characterized by the generation of hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide from monomers and glucose. The final stage, methanogenesis, is the stage where most of the methane is produced. Apart from CH4 and CO2, several other impurities are formed dependent upon the feed, such as ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, water, nitrogen, and siloxanes. The presence of CO2 and the impurities lower the overall energy content of the biogas and can cause premature failure of point-of-use equipment [5]. For these reasons, carbon capture and biogas upgrading are often required prior to biogas application. Currently, biogas upgrading is conventionally performed through amine-based ionic liquid absorption or water scrubbing [6]. Ionic liquid (IL) amine-based absorption is desirable due to the solvents having a high selectivity for CO2 over CH4, which can achieve ~99% CH4 purity [6,7,8,9]. However, the high viscosity, high cost, and toxicity of these solvents suggest the need for an alternative [9,10,11]. Water scrubbing has a high efficiency (~97% CH4 purity achieved), but it has been associated with bacterial growth issues, massive water consumption, and its necessity for additional processes in series to remove feed impurities [6,9]. Other processes have also been developed for CO2 removal, such as solid sorbents. These solid-based sorbents are found to have a large range of CO2 capacity that reach up to 80 weight percent but have high operating temperatures that exceed 500 °C [12,13]. However, due to the low combustive properties of some impurities, low-temperature solid adsorbents like zeolites are the only feasible option, which have significantly lower capacities [14,15].
Deep eutectic solvents (DES) are a relatively new material that is being studied as a carbon capture media [16,17,18]. DES are made from a hydrogen bond donor (HBD) and a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) [16,19]. The melting point of DES is decreased significantly compared to individual HBA and HBD due to charge delocalization from hydrogen bonding [20,21,22]. Studies have proven DES to exhibit desirable traits for use as a CO2 absorbent, such as thermal stability, tunability, reversibility, and reasonable CO2 solubility [14,17,23], with Zhang et al. [15] reporting a 1:1 mol CO2 per mol solvent solubility ratio [24], Bi et al. [25] reporting a 0.25 g/g of CO2 per solvent solubility, and Ren et al. [25] reporting 0.4 mol CO2 per mol solvent solubility. The literature often uses experimental methods to develop CO2 capture on DES. However, the use of computational software with highly accurate determinations may make the down-selection of DES easier. Therefore, conductor-like screening model for real solvents (COSMO-RS), which is a thermodynamic property prediction software that relies on the generation of sigma profiles rather than databases of functional group interactions, was used in this study. COSMO has been used by several authors to model CO2 capture, such as Song et al. [26], who was able to screen a database containing thousands of HBD and HBA combinations for potential CO2-capturing solvents. Of the various DES, quaternary ammonium salts have garnered a significant amount of attention for their ability to solvate CO2 [18,27]. The accuracy of COSMO was also studied by Liu et al. [28] by testing hundreds of DES for CO2 absorption, and they found a maximum of 10.3% error after tuning the program across the studied samples. Several studies have been performed on the solubility of CO2 in DES [22,29], however, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, none was conducted on understanding how various impurities in biogas affect the carbon capture by DES. This knowledge is essential to design an absorption system for biogas upgrading since solubility and selectivity of a solvent can be adversely affected by contaminants, especially when accounting for accumulation during repeated use.
This study focuses on evaluating the affinity various DES have for selected contaminants and how their presence in various amounts affects the affinity for CO2 in these solvents. This will be performed using COSMO by first modeling the DES and contaminants not found in the software library, then generating thermophysical properties of Henry’s Law constants and activity. Selectivity of CO2 over CH4 and solubility of CO2 changes in a selected group of DES were studied here for both infinite dilution and partial pressure at various temperature ranges. Finally, effects of impurities ranging from 0 to 5 mole % on CO2 solubility in various DES were evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composition of Biogas
The standard percent ranges of biogas composition used in this study have been listed in Table 1. The variance of the composition depends upon several factors surrounding the AD process, such as temperature, retention time, kinetics, and feed stock composition [30]. Table 1 shows the components studied with their respective abbreviations for the investigation and their industrial compositions.

Table 1.
Pre-treatment biogas components and composition for studied molecules.
2.2. Deep Eutectic Solvents
Table 2 lists the five common DES considered for this study, including choline chloride-urea, choline chloride-ethylene glycol, tetra butyl ammonium chloride-ethylene glycol, tetra butyl ammonium bromide-decanoic acid, and tetra octyl ammonium chloride-decanoic acid, along with their components and component mixing ratios. The solvents studied are termed quaternary ammonium salts due to the structure of the HBD. The quaternary ammonium salts are relatively cheap, safe for the environment, and naturally derived [16,36,37]. The specific solvents were chosen as an attempt to represent a large range of their class by means of carbon chain length of the quaternary ammonium salts and commonly paired HBDs.

Table 2.
Selected deep eutectic solvents for biogas upgrading and their abbreviations.
2.3. COSMO Simulation
COSMO is a quantum modeling software that determines thermodynamic properties using density functional theory (DFT). To determine the thermodynamic properties, the HBAs and HBDs are modeled using TurboMoleX software. The impurities are selected from the COSMO library. HBAs and HBDs are then mathematically evaluated for their natural geometrical lowest energy state and conformers. COSMO was then used for all thermophysical property calculations. TurboMoleX® was used to generate all molecular sigma profiles, conformers, and data not already found in the included database. TZVP (tri-zeta-valence-polarized) settings were used with default numerical grid of m3 and BP86 functions. COSMOThermX® was used for all thermodynamic property calculations. These properties were used to calculate sigma profile of the molecules, where charge density is plotted with charge of the molecule. Here, the molecule is differentiated into charge density segments, with each segment representing areas with charge density ranging from −0.3 to +0.3 e/Å2. The charge density segments are plotted to form the sigma profiles. The data from the sigma profiles are used to model microscopic molecular surface charge interactions between analytes, then a statistical thermodynamic procedure is carried out to derive macroscopic thermodynamic properties from the generated information [38]. The base values generated are chemical potentials of the systems’ constituents, these are then applied to thermodynamic calculations of Henry’s Law coefficient and activity coefficients. Determination of the solubility and selectivity of the systems was carried out by COSMO-RS, whose results are based upon the chemical potential generated by COSMO-RS.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sigma Profiles of DES’s, Polar, and Non-Polar Molecules
A sigma profile is a distribution function that relates the surface area of a molecule to the charge density of the surface [39]. In this study, sigma profiles are used to understand the electrostatic interactions between DES and selected polar and nonpolar molecules. The sigma profiles explain the trends of solubility and selectivity for a DES-based extraction. To generate these profiles, COSMO creates incremental segments of the studied molecule, which are then organized based upon surface charge density. The area under these sigma profile curves gives the total surface area of the studied molecule. Peaks between ±0.0082 e/Å2 charge density indicate that the molecule readily undergoes van der Waals interactions [39,40]. Peaks outside of this range indicate hydrogen bonding as the preferred interaction due to polarity [40].
Sigma profiles are useful for determining how molecules will interact in a solvent-solute system. From a range of sigma profiles, appropriate solvents may be identified for a given molecule based on how the charge densities between the two profiles align. A highly polar solvent that has significant charge density in the HBA region (−0.0082 e/Å2) could be expected to have a high affinity for a solute that shows a significant charge density in the HBD region (+0.0082 e/Å2). The same is true for two molecules that have significant charge densities in the non-polar region of the sigma profile (±0.0082 e/Å2). This logic can be used to determine if an impurity will have a lesser or higher affinity than a solute, giving rise to competition for the solvents’ binding sites.
In Figure 1, the sigma profiles of each DES are displayed. The order of the solvents from the most to the least polar and, therefore, most available for hydrogen bonding to least available, are as follows: ChCl:U > ChCl:EG > N4Cl:EG > N4Br:DA > N8Br:DA. The peaks between 0.015 and 0.002 e/Å2 are from the halogens associated with each solvent. It is observed that by changing the HBD groups as with the tetrabutylammonium variants, the sigma structure is significantly altered, which lends to the notion of DES properties being highly tunable [16,41].
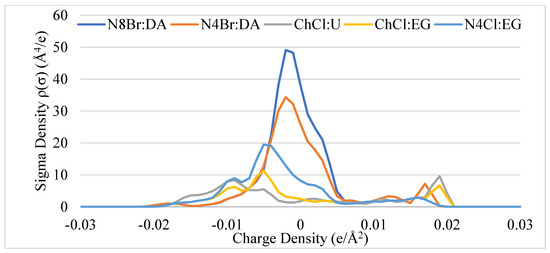
Figure 1.
Sigma potential profiles of DES with respect to charge density.
Sigma profiles of non-polar gases can be seen in Figure 2. For the non-polar gases, the key difference in the sigma profiles of the molecules is the charge density distribution of CO2 vs. N2 vs. CH4. N2 and CH4 have most of their area concentrated around the zero-x-axis compared to CO2. CO2 is considered a non-polar gas, since the distribution of the charges for CO2 are weighted between ±0.0082 e/Å2. However, CO2 can be influenced by its environment to make it behave more like a polar molecule and participate in hydrogen bonding or behave more like a non-polar molecule and participate in van der Waals interactions. The potential for this behavior can be seen in the sigma profile as the charge density is concentrated closely to the ±0.0082 e/Å2 boundary. It is also understood that CO2 contains two polar bonds, but the linear structure of the molecule creates a net-zero dipole moment. However, in a polar environment such as CO2 in water, it behaves as an acid gas.
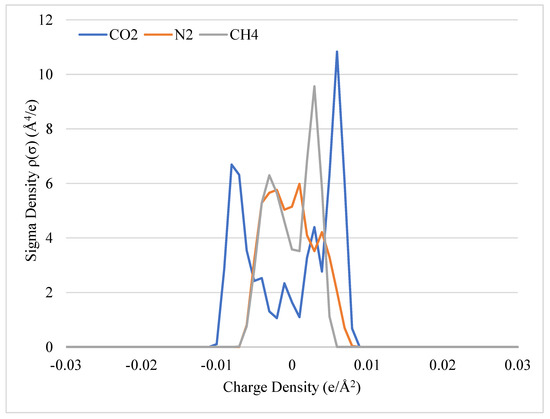
Figure 2.
Sigma potential profiles of non-polar molecules with respect to charge density.
Regarding polar gases, only gases reported as impurities of biogas are selected for this study. There exist large variations in profiles among this group, as seen in Figure 3. The most notable impurity is water, which reaches the farthest among the other gases on the charge density and is relatively symmetric, which concludes its adaptability in assuming the roles as a Lewis acid or base. Acetone has a large peak near the 0 e/Å2 yet behaves as a Lewis base due to the considerable peak beyond 0.01 e/Å2. H2S is relatively evenly dispersed along the x-axis, suggesting it can participate in both van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonding depending upon its environment. SO2 is heavily concentrated around the boundaries of ±0.0082 e/Å2, and as such, would be expected to have lower solubility among the less polar DES. Ammonia is a weak base, and this is indicated in the large peaks near the HBA region (−0.0082 e/Å2) but is capable of hydrogen donating interactions, as seen in the trailing area in the positive region of the plot as it extends to nearly 0.03 e/Å2.
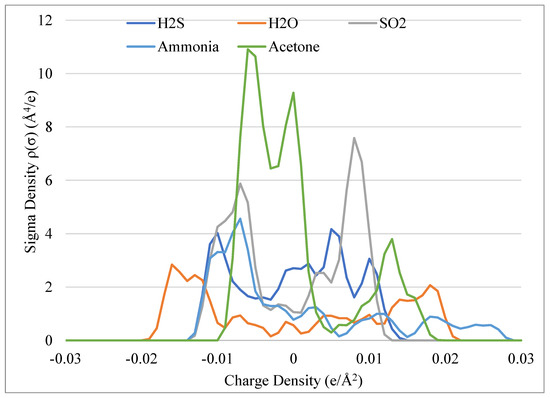
Figure 3.
Sigma potential profiles of polar molecules with respect to charge density.
As discussed previously, CO2 can be influenced by its environment to partake in hydrogen bonding or van der Waals interactions. Due to this and the generated sigma profiles, it stands to reason that a DES containing significant amounts of a polar or non-polar contaminant may change the level of solubility of CO2 within that system. For example, when considering the relatively polar profile of ChCl:U, it could be reasoned that if it were to accumulate strong polar molecules like water then the effect of hydrogen bond affinity for CO2 would be enhanced. Thus, resulting in a higher selectivity for CO2 than CH4 in this particular solvent.
3.2. Selectivity for CO2 over CH4 by DES in Infinite Dilution
Considering the valuable product of biogas upgrading is methane, the selectivity of a solvent to solvate is of significant importance. The selectivity of CO2 over CH4 was first studied for various DES at infinite dilution by Henry’s Law calculations and presented in Figure 4. Henry’s Law constants are used to study the solubility of CO2 vs. CH4 for a pure DES regarding the first molecules of gas and how they selectively enter the DES and are only valid at low concentrations of gases in the DES. At room temperature and at infinite dilution, the largest selectivity of 4.7 can be observed in ChCl:U. Here, approximately 4.7 moles of CO2 are expected to be absorbed per mole of CH4. The least selective solvent in this model is N8Br:DA at approximately 1.75. The remaining solvents show a slight trend up from N8Br:DA. The data follows a rational trend of selectivity to size, with the smallest DES molecular constituents displaying the highest selectivity. However, this does not explain the dramatic increase in selectivity between ChCl:EG and ChCl:U, considering they are nearly the same mass (Table 2) and considering the selectivity is molar-based. This behavior could be explained from sigma profiles. Figure 1 shows ChCl:U as being the most likely to participate in hydrogen bonding of the five solvents and N8Br:DA as most likely to participate in van der Waals interactions. As previously mentioned, CO2 can become polarized in a polar environment, which makes it much more likely to bind with ChCl:U than methane. In a relatively non-polar environment like N8Br:DA, both molecules will behave non-polar and bind closer to a 1:1 ratio. The values for simulated vs. experimental solubilities of CO2 in ChCl:U at 5.6 MPa and 303.15 K are reported as 5.7 and 3.56 (mol/kg), respectively. The difference was reported to be caused by poorly optimized DES structures [42]. Xie et al. and Ji et al. report experimental solubilities of CO2 in ChCl:U at 308.2 K and 0.651 and 0.678 p/MPa respectively, as 0.05 and 0.045 mole fraction, respectively. The solubility parameters were studied in this paper at a highest-pressure condition of 0.6 MPa and 25 °C, and for ChCl:U, the solubility of CO2 at these conditions is 0.074. The discrepancies between experimental and calculated values could be attributed by the limitations of COSMO to fully model all solvation phenomena that occur, such as hole theory, induced polarity of solutes, and induced conformers of analytes. The selectivity appears to be mostly influenced by the polarity of the DES at room temperature. Similar observation was found in the literature, where Slupek et al. [10] compared the sigma profiles of their studied DES with solutes and determined that the overlapping regions between the two plots suggested interaction compatibility.
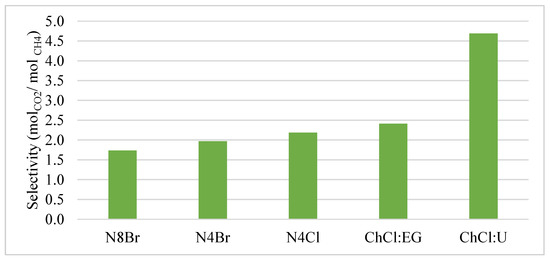
Figure 4.
Selectivity of CO2 vs. CH4 at STP and infinite dilution calculated from Henry’s Law coefficients for each DES.
The selectivity thus far has been discussed at 25 °C, however, temperature of the biogas could be as high as 55 °C depending on mesophilic or thermophilic microorganisms. Therefore, the effect of temperature on selectivity at infinite dilution is of practical interest. Figure 5 has shown the effect of temperature on Henry’s Law constant, which is analogous to selectivity. Due to the unit of the Henry constant, the lower values are associated with higher solubility. With the increase of temperature, the Henry’s Law constant increases. Interestingly, for the same HBA (e.g., ChCl), exceptional deviations in Henry’s Law constant can be found for different HBD (e.g., urea versus ethylene glycol). This is probably due to the smaller HBA chain lengths that might have a naturally smaller affinity for CO2 [41]. However, the induced polarity phenomena have a stronger impact on the solubility outcome. This is due to CO2 being naturally non-polar, as seen in Figure 2. Thus, the magnitude of the dipole moment of a solvent will determine the affinity CO2 will have for it.
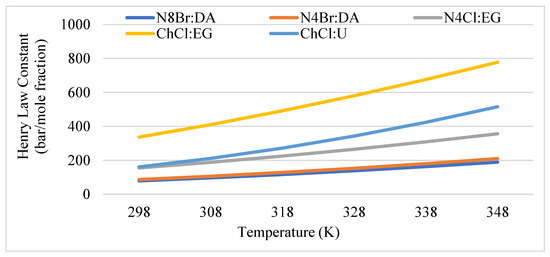
Figure 5.
Effect of temperature on solubility of CO2 at infinite dilution calculated with Henry’s Law coefficients for each DES.
3.3. Effect of Pressure on Selectivity and Solubility of CO2 in Various DES
Selectivity of CO2 over CH4 in various DES at infinite dilution provides valuable information on how polarity of DES and solute affect the selectivity. However, Henry’s Law is only valid for infinite dilution, which might be misleading for carbon capture from biogas, as CO2 concentration in biogas is often high. Therefore, Raoult’s Law might provide more accurate information of the solubility and selectivity. In this study, modified Raoult’s Law calculations are used to determine the maximum solubilities for a pure solvent by studying the last molecules to enter the system at any concentration. Understanding the effect pressure has on a system and how its constituents behave away from ideality is crucial to its design parameters. Figure 6 investigates the last molecules entering the system at equilibrium. It provides total saturation values for CO2 on the left axis and selectivity of CO2 vs. CH4 on the right axis at varying partial pressures in 40% increments, since this falls within the composition range for both CO2 and CH4, as shown in Table 1. The first observation in this Figure 6 is the increase in solubility of CO2 with increased pressure, regardless of solvent. The next is the same trend being seen in Figure 4 with respect to the solvent ordering of selectivity. This trend becomes significantly more pronounced when the system is closer to saturation. For example, the selectivity of ChCl:U at 1 bar is nearly 25 in Figure 6 compared to the Henry’s Law calculations which were 4.7 in Figure 4. A possible explanation for this could be due to the solvent matrix becoming more of a polar environment as the holes fill with CO2 and CH4 has to squeeze into the smaller polarized spaces in order to occupy the solvent, which is not energetically favorable. The negative slopes of the selectivity analysis are due to the increase in pressure, as the molecules are forced into solvent, they become less selective. The more drastic change occurs within ChCl:U as the influence of polarity is overcome by the force of pressure, resulting in a non-linear relationship unlike the other less acidic solvents. The total capacity for CO2 varies significantly between pressures, and the resulting trends of the bars suggest that the effect on the solvents also vary significantly. As discussed previously, the order of solvents in their ability to solvate CO2 and the gaps in capacities are explained through alkyl-chain lengths [16], HBD selection, and the resulting polarity of these combinations with little effect from the halogens. The results here further confirm this by segregating the solvents into 3 visible groupings regarding solubility of CO2 of N8Br:DA and N4Br:DA, N4Cl:EG and ChCl:U, and ChCl:EG. The most significant finding from this grouping is the relative effects on solubility between HBA chain length and associated HBD. N4Br:DA and N8Br:DA have relatively similar capacities for CO2 that are significantly higher compared to N4Cl:EG. N4Br:DA finds a maximum ratio of approximately 1.9 over the CO2 solubility of N4Cl:EG, where the alkyl chain lengths are the same but the HBD are different. However, N8Br:DA only finds a maximum approximate ratio of 1.08 over the CO2 solubility of N4Br:DA, which displays a difference in alkyl chain length but the same HBD.
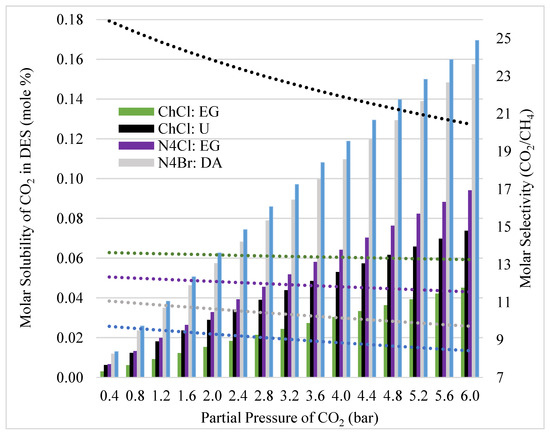
Figure 6.
Effect of pressure on selectivity of CO2 vs. CH4 and solubility of CO2 at equilibrium and 25 °C for each DES. Y-axis 1 is the solubility and y-axis 2 is the selectivity. The dotted lines coincide with y-axis 2 and the bars coincide with y-axis 1. The partial pressure is the same for CO2 and CH4.
3.4. Effect of Impurities on CO2 Solubility in Various DES
Effect of selected impurities on CO2 solubility of various DES at different temperatures under 3.6 bar pressure conditions are studied by solubilities. Analysis was performed on each DES to determine how the presence of contaminants within the feed gas, captured by the solvent, would affect the absorptive capacity for CH4 and CO2. This was performed on a wide range of contaminants found in Table 1 over three temperatures (25, 37, and 55 °C) at ambient pressure and three mole fractions of contaminant within the solvent (1, 3, and 5 mol%). The solubilties were normalized to show the deviation from the maximum solubility of CO2 and CH4 at DES, with no contaminants.
Of the five DES, ChCl:U is the most affected to the presence of all the impurities within biogas, as can be seen in Table 3. With the increase of ammonia in biogas, the maximum solubility of CO2 and CH4 increase in ChCl:U. For instance, the values for CO2 at 37 °C are 1.01 and 1.03 for ammonia in ChCl:U at 1 and 5 mol%, respectively. However, the presence of all other contaminants decrease the maximum solubility of both CO2 and CH4 in ChCl:U. All contaminants produce a change greater than 5% from the base case, with the octa and deca siloxane compounds inciting the greatest changes. This finding is significant, as Jiang et al. [43] report an average concentration of siloxanes in untreated biogas reaching up to 2000 . It is observed that change in temperature produces minimal effect on how the impurities in ChCl:U alter the maximum solubility of CO2. Although, there is a significant change on the solubility of CO2. For example, the presence of propanone at 5 mole percent in CH4 shows a deviation from the baseline of 1 as the values 0.89 and 0.92 for temperatures of 25 and 55 °C respectively, while the same conditions provide a range of 0.93 to 0.94 for CO2.

Table 3.
Normalized values for solubility of CO2 at various mole percentages in ChCl:U and at varying temperatures. The values are normalized to fresh solvent solubilities of respective CO2 and CH4.
The solvents with the HBD of ethylene glycol (in Supplementary Information Tables S1 and S2) show a positive effect from every contaminant except H2O, H2S, and SO2. The other contaminants show asymmetry with a weighted area around the HBA region, whereas H2O, H2S, and SO2 are significantly more symmetrical regarding sigma profiles. A notable difference between the two DES with these HBD groups is the response to the contaminants at varying concentrations. At lower concentrations of the contaminants (1 mol%), N4Cl:EG is much more affected in terms of maximum CO2 and CH4 solubility compared to its ChCl:EG counterpart, but the opposite is true at higher concentrations. For example, at 25 °C, the CO2 maximum solubility increases by 4% when octa makes up 1 mole percent of N4Cl:EG, however there is virtually no change when these same conditions are met for ChCl:EG as a value of 1 is reported. The trend found in ChCl:U between the temperature change and solubility change is not present in either of these DES.
The solvents with the HBD decanoic acid (N4Br:DA and N8Br:DA, Tables S3 and S4, respectively) show negative effects from all contaminants except siloxanes. Here, CH4 solubility increases with the presence of octa and deca but CO2 decreases with their presence. For these two DES, another similar trend follows regarding CO2 and CH4 solubility. The solubility varies little with contaminant mole percent, with nearly all changes being within 2%, with the exception of H2O and ammonia for N8Br:DA and H2O, ammonia, deca, and octa for N4Br:DA. At 1% contamination presence, the solubility of CO2 in both DES start above 1 with higher solubility and decrease with increasing percentages of contaminant. Another trend to note is the slightly less negative effect the contaminants have upon N4Br:DA than N8Br:DA, whose main difference is their alkyl chain length.
4. Conclusions
The results of this study contain important preliminary data regarding the implementation of DES in biogas upgrading systems. The fundamental understanding of the solvents and their behavior under various temperatures, pressures, and influences from contaminants show that a complex web of variables exists that must be considered when choosing a DES for any application. It has been shown that the polarity of a solvent, its size, and its constituents are factors contributing to solubility, but the main determinant is the HBD selection. The significance of the varied contaminant concentrations is providing a method to model the accumulation that occurs within recycled solvent, where not all contaminants will be purged through the regeneration process. This study is a glimpse into the potential lifetime of the solvent, and how each solvent will be suited for a specific feed gas composition. The results show that the DES are affected by these contaminants in varying degrees in order of most to least, as follows: ChCl:U, ChCl:EG, N4Cl:EG, N4Br:DA, and N8Br:DA. This trend is the same for polarity and the reverse of alkyl chain length, and also suggests the order in which the length of time the solvents will be able to operate before regeneration is necessary, from least to most. The pressure study suggests the ideal operating environment is closer to atmospheric pressure considering selectivity but not for solubility. The selectivity at ambient temperature and pressure (STP) and infinite dilution are 4.7, 2.4, 2.2, 2.0, and 1.7 mol CO2/mol CH4 for ChCl:U, ChCl:EG, N4Cl:EG, N4Br:DA, and N8Br:DA, respectively. However, the selectivity at STP and finite dilution conditions are 25.9, 13.6, 12.3, 11.1, and 9.7 mol CO2/mol CH4. For ChCl:U, the absorbance was decreased by the presence of deca at STP and 1, 3, and 5 mole % by 0.91, 0.81, and 0.74 respectively, from a normalized value of 1. The changes in the presence of CH4 at STP and 1, 3, and 5 mole % are 1.00, 0.96, and 0.92, respectively. These solvents have been shown to behave differently to each other when subjected to differing environmental factors such as temperature and pressure. All of these factors point to high tunability and complexity for these solvents.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cleantechnol3020029/s1, Table S1: Normalized values for solubility of CO2 and CH4 at various mole percentages in ChCl: EG and at varying temperatures. The values are normalized to fresh solvent solubilities of respective CO2 and CH4., Table S2: Normalized values for solubility of CO2 and CH4 at various mole percentages in N4Cl: EG and at varying temperatures. The values are normalized to fresh solvent solubilities of respective CO2 and CH4., Table S3: Normalized values for solubility of CO2 and CH4 at various mole percentages in N4Br: DA and at varying temperatures. The values are normalized to fresh solvent solubilities of respective CO2 and CH4., Table S4: Normalized values for solubility of CO2 and CH4 at various mole percentages in N8Br: DA and at varying temperatures. The values are normalized to fresh solvent solubilities of respective CO2 and CH4.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Q. and M.T.R..; methodology, T.Q.; software, T.Q.; validation, T.Q.; formal analysis, T.Q.; investigation, T.Q.; resources, M.T.R.; data curation, T.Q.: writing—original draft preparation, T.Q.; writing—review and editing, T.Q. and M.T.R.; visualization, T.Q.; supervision, M.T.R.; project administration, M.T.R.; funding acquisition M.T.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1856058 and American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund Grant No: PRF # 60342-DNI9.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We especially wish to acknowledge Kyle McGaughy for his assistance with COSMO-RS simulations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Lee, D.-J. Biogas from anaerobic digestion processes: Research updates. Renew. Energy 2016, 98, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Arshad, M.; Anjum, M.; Mahmood, T.; Dawson, L. The anaerobic digestion of solid organic waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm-Nielsen, J.; Al Seadi, T.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P. The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, R.; Moya, C.; Palomar, J. Siloxanes capture by ionic liquids: Solvent selection and process evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Biogas upgrading technologies: Energetic analysis and environmental impact assessment. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, P.; Jacquemin, J.; McCrellis, C.; Dimitriou, I.; Taylor, S.F.R.; Hardacre, C.; Allen, R.W.K. Techno-economic feasibility of selective CO2 capture processes from biogas streams using ionic liquids as physical absorbents. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5052–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Björkmalm, J.; Ma, C.; Willquist, K.; Yngvesson, J.; Wallberg, O.; Ji, X. Techno-economic evaluation of biogas upgrading using ionic liquids in comparison with industrially used technology in Scandinavian anaerobic digestion plants. Appl. Energy 2018, 227, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckebosch, E.; Drouillon, M.; Vervaeren, H. Techniques for transformation of biogas to biomethane. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słupek, E.; Makoś, P.; Gębicki, J. Theoretical and economic evaluation of low-cost deep eutectic solvents for effective biogas upgrading to bio-methane. Energies 2020, 13, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, L.K.G.; Subramanyam, S.; Chengala, M.D.; Olivera, S.; Venkatesh, K. Progress in hydrotalcite like compounds and metal-based oxides for CO2 capture: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, B.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y. Solid sorbents for in-situ CO2 removal during sorption-enhanced steam reforming process: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siongco, K.R.; Leron, R.B.; Li, M.-H. Densities, refractive indices, and viscosities of N,N-diethylethanol ammonium chloride-glycerol or -ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvents and their aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 65, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Hu, Z.; Lin, X.; Ahmad, N.; Xu, J.; Xu, X. Efficient CO2 capture by a novel deep eutectic solvent through facile, one-pot synthesis with low energy consumption and feasible regeneration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmad, S.; Nikjoo, D.; Mikkola, J.-P. Amine functionalized deep eutectic solvent for CO2 capture: Measurements and modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, H.; Ayoub, M.; Sufian, S.; Shariff, A.M.; Hailegiorgis, S.M.; Khan, S.N. CO2 capture with the help of Phosphonium-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Li, M.-H. Solubility of carbon dioxide in a choline chloride-ethylene glycol based deep eutectic solvent. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 551, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, F.M.; Vitale, P.; Capriati, V. Deep eutectic solvents and their applications as green solvents. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 21, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids|Journal of the American Chemical Society. Available online: https://pubs-acs-org.portal.lib.fit.edu/doi/10.1021/ja048266j (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Figueroa, J.D.; Fout, T.; Plasynski, S.; McIlvried, H.; Srivastava, R.D. Advances in CO2 capture technology—The U.S. Department of Energy’s carbon sequestration program. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2008, 2, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L. Highly efficient and reversible CO2 capture by task-specific deep eutectic solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13321–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lian, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, E. Exploiting the hydrophilic role of natural deep eutectic solvents for greening CO2 capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Hu, X.; Wu, H.; Mei, M.; Linke, S.; Zhou, T.; Qi, Z.; Sundmacher, K. Systematic Screening of deep eutectic solvents as sustainable separation media exemplified by the CO2 capture process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8741–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughy, K.; Reza, M.T. Systems analysis of SO2-CO2 Co-capture from a post-combustion coal-fired power plant in deep eutectic solvents. Energies 2020, 13, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X. Screening deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture with COSMO-RS. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, I.; Abu-Zahra, M.R.; Alnashef, I. Experimental study of the solubility of CO2 in novel amine based deep eutectic solvents. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukam, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Naqvi, M.; Granström, K. A review of the chemistry of anaerobic digestion: Methods of accelerating and optimizing process efficiency. Processes 2019, 7, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, M.; Polman, E.; Jensen, J.K.; Myken, A.; Joensson, O.; Dahl, A. Adding Gas from Biomass to the Gas Grid. 2001. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/biblio/20235595 (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Al Mamun, M.R.; Torii, S. Enhancement of methane concentration by removing contaminants from biogas mixtures using combined method of absorption and adsorption. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 2017, 7906859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamukamba, P.; Mukumba, P.; Chikukwa, E.S.; Makaka, G. Biogas upgrading approaches with special focus on siloxane removal—A review. Energies 2020, 13, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yin, F.; Zhang, W.; Dong, H.; Xin, H. Characterization of Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emissions from swine manure biogas digestate storage. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Fan, J.; Zeng, G. A review on removal of siloxanes from biogas: With a special focus on volatile methylsiloxanes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30847–30862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhekenov, T.; Toksanbayev, N.; Kazakbayeva, Z.; Shah, D.; Mjalli, F.S. Formation of type III deep eutectic solvents and effect of water on their intermolecular interactions. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 441, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Leron, R.B.; Li, M.-H. Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous mixtures of (reline + monoethanolamine) at T = (313.2 to 353.2)K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 72, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, K. COSMOthermX User Guide; COSMOlogic GmbH & Co.: Leverkusen, Germany, 2019; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Palmelund, H.; Andersson, M.P.; Asgreen, C.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Rantanen, J.; Löbmann, K. Tailor-made solvents for pharmaceutical use? Experimental and computational approach for determining solubility in deep eutectic solvents (DES). Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughy, K.; Reza, M.T. Liquid—Liquid extraction of furfural from water by hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Improvement of density function theory modeling with experimental validations. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22305–22313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep eutectic solvents: Physicochemical properties and gas separation applications. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioui, O.; Benguerba, Y.; Alnashef, I.M. Investigation of the CO2-solubility in deep eutectic solvents using COSMO-RS and molecular dynamics methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhong, W.; Jafari, T.; Du, S.; He, J.; Fu, Y.-J.; Singh, P.; Suib, S.L. Siloxane D4 adsorption by mesoporous aluminosilicates. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).