Precision Fertilization Strategies Modulate Growth, Physiological Performance, and Soil–Plant Nutrient Dynamics in Sabal palmetto
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Plant Material
2.2. Experimental Design and Fertilizer Application
2.3. Morphological and Physiological Measurements
2.4. Leachate and Salinity Monitoring
2.5. Carbon and Nitrogen Analysis in Tissue and Substrate
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
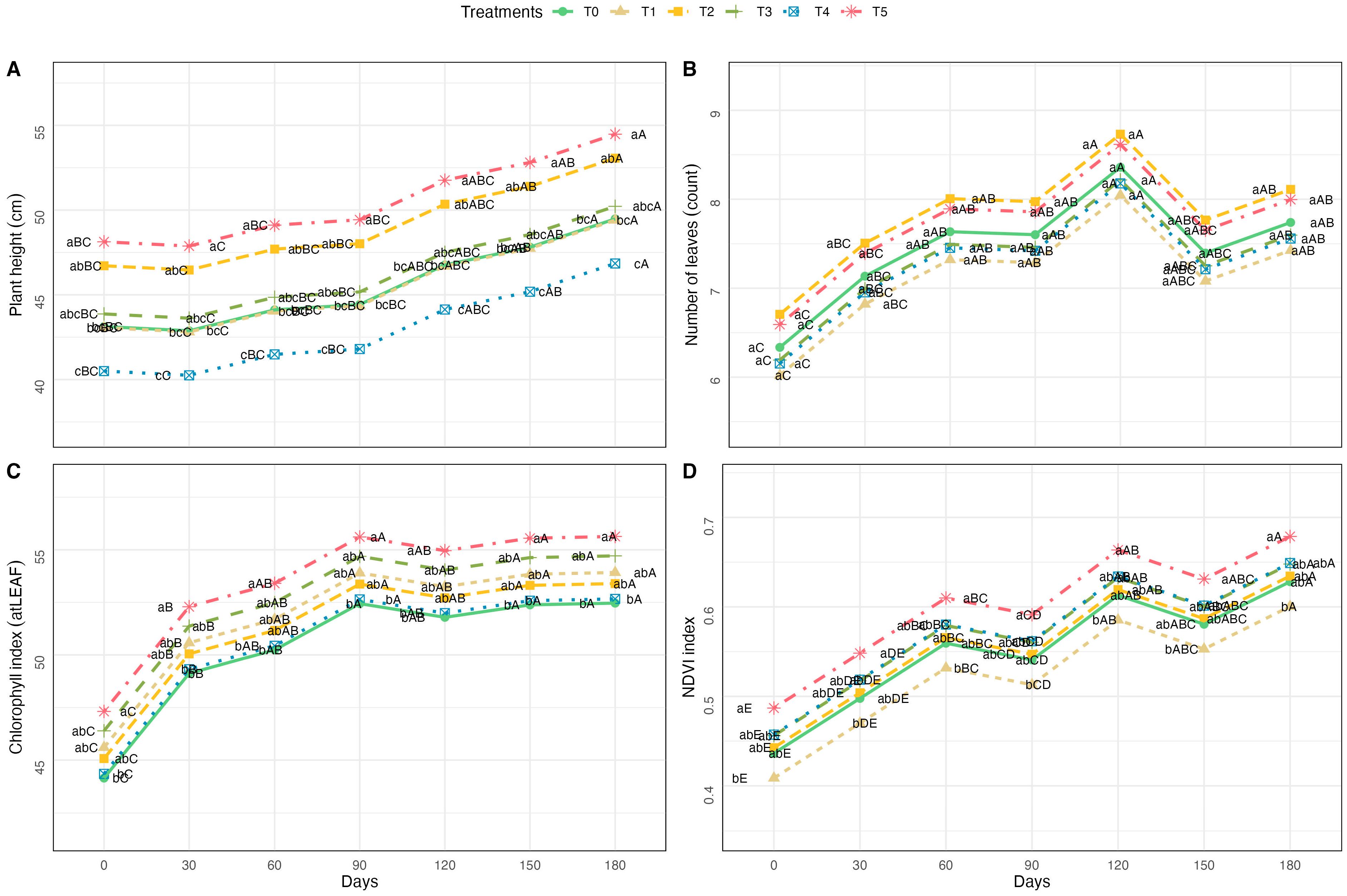
3.1. Morphological and Physiological Responses to Fertilization Treatments
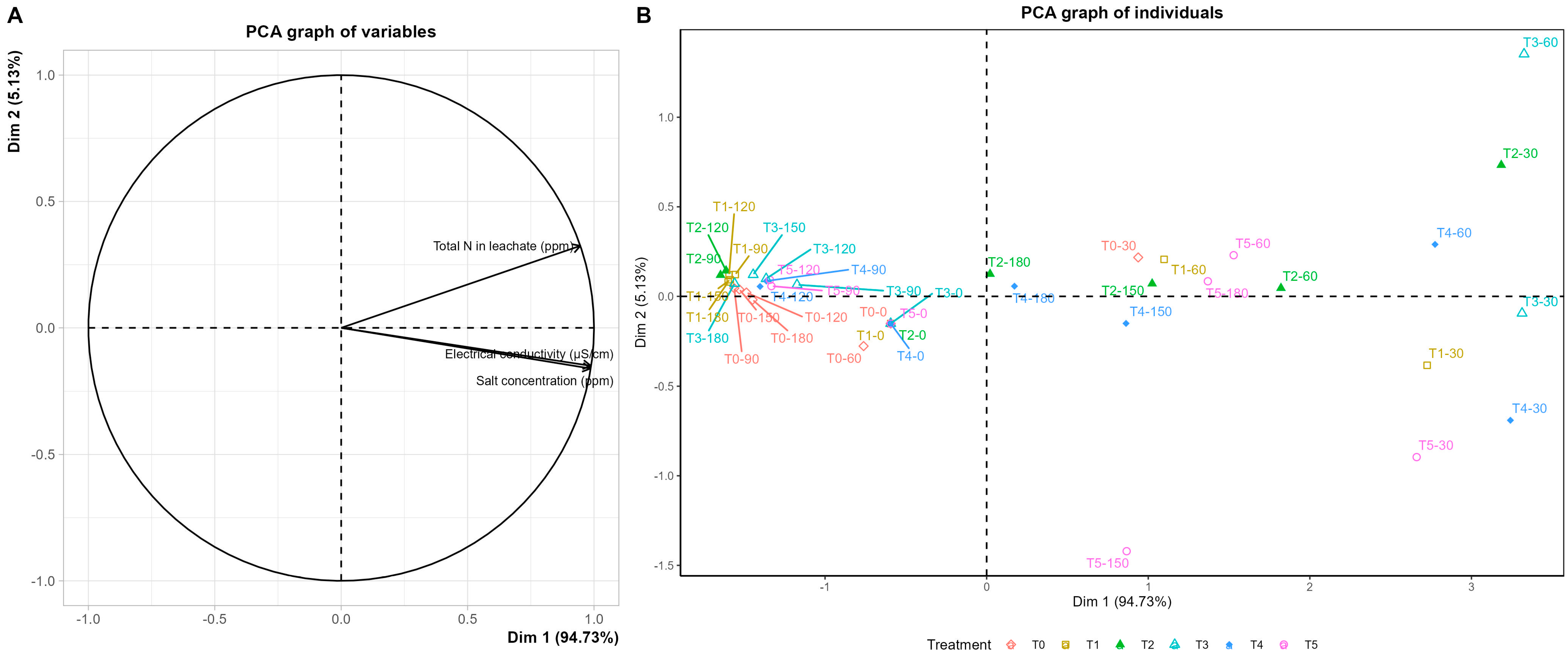
3.2. Substrate Chemical Properties and Leachate Dynamics
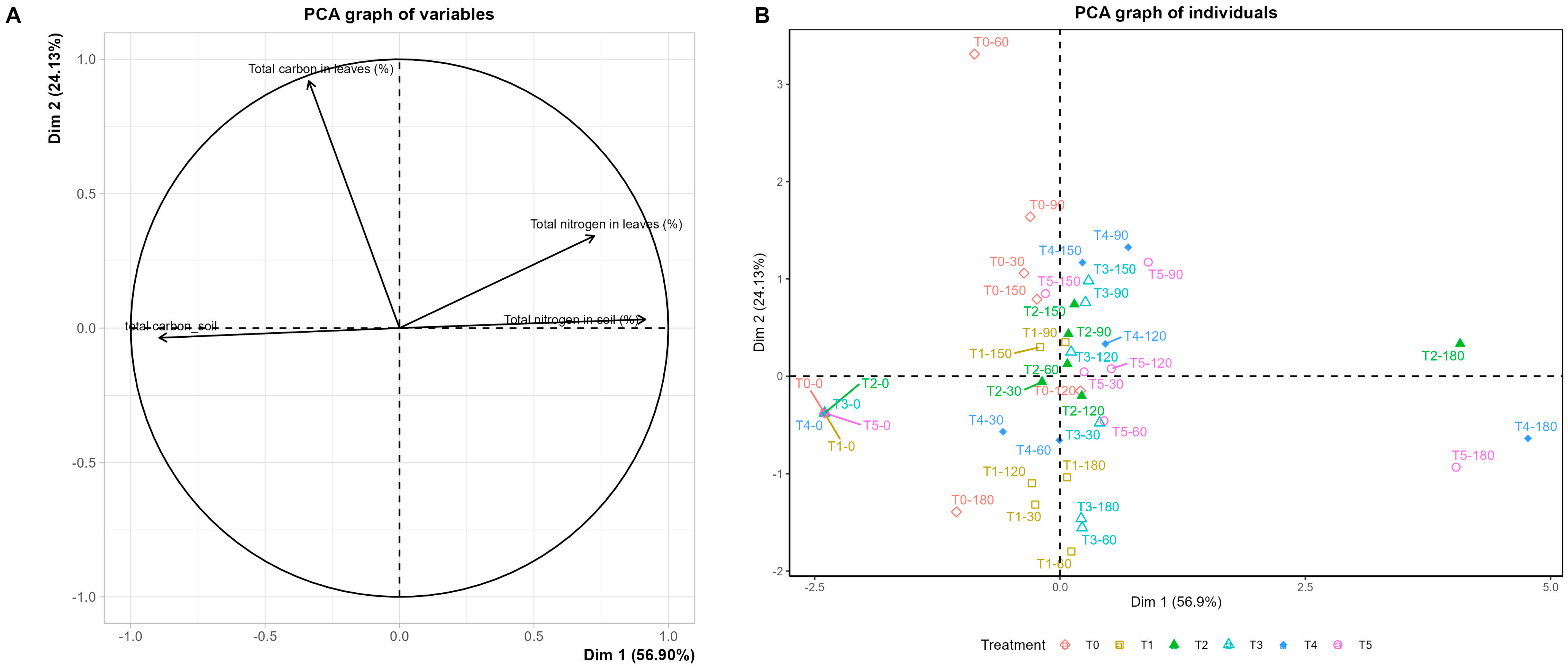
3.3. Foliar Nitrogen Partitioning and Substrate Nutrient Availability
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Input Influenced Vegetative Performance
4.2. Balance Between Growth Promotion and Reduced Nutrient Losses
4.3. Monitoring Nutrient Status Under Non-Destructive Diagnostics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dincă, L.C.; Grenni, P.; Onet, C.; Onet, A. Fertilization and Soil Microbial Community: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervash, M.A.; Yousuf, A.; Bhat, M.A.; Ozturk, M. Soil Stress Ecology: Concept, Impacts, and Management Strategies. In Soil Organisms; SpringerBriefs in Microbiology; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 25–38. ISBN 978-3-031-66292-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Isla, F.; Campos, M.L.O.; Endres, L.; Bezerra-Neto, E.; Pompelli, M.F. Effects of Seed Storage Time and Salt Stress on the Germination of Jatropha curcas L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Watson, O.; Samarakoon, U.C.; Altland, J.E.; Moine, J. Evaluation of Liquid Organic Fertilizers for Containerized Production under Controlled Environment. HortScience 2025, 60, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoddamzadeh, A.A.; Dunn, B.L. Application of Optical Sensors for Nitrogen Management in Chrysanthemum. HortScience 2016, 51, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidenreich, A.; Barraza, G.; Jayachandran, K.; Khoddamzadeh, A.A. Precision Agriculture Application for Sustainable Nitrogen Management of Justicia Brandegeana Using Optical Sensor Technology. Agriculture 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianpoor Kalkhajeh, Y.; Huang, B.; Hu, W.; Ma, C.; Gao, H.; Thompson, M.L.; Bruun Hansen, H.C. Environmental Soil Quality and Vegetable Safety under Current Greenhouse Vegetable Production Management in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 307, 107230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, K.; Henny, R.J.; Chen, J.; Mellich, T.A. Effect of Light Intensity and Nutrition Level on Growth and Flowering of Adenium obesum ‘Red’ and ‘Ice Pink’. HortScience 2014, 49, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, F.M.; Gallardo, M.; Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; De Souza, R.; Thompson, R.B. Proximal Optical Sensors for Nitrogen Management of Vegetable Crops: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, S.; Vellingiri, G.; Sellaperumal, P.; Pandian, K.; Sivasankar, A.; Sangchul, H. Real-Time Nitrogen Monitoring and Management to Augment N Use Efficiency and Ecosystem Sustainability–A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Poudyal, S.; Kopp, K.; Zhang, Y. Response of Ornamental Plants to Salinity: Impact on Species-Specific Growth, Visual Quality, Photosynthetic Parameters, and Ion Uptake. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1611767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argento, F.; Merz, Q.; Perich, G.; Anken, T.; Walter, A.; Liebisch, F. A Comparison of Proximal and Remote Optical Sensor Platforms for N Status Estimation in Winter Wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Singha, P.; Roy Chowdhury, A.; Sinha, A.K.; Skalicky, M.; Laing, A.M.; Alamri, S.; Hossain, A. Optical Sensor-Based Nitrogen Management: An Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Approach for Sustainable Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Production on Eastern Plains of India. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1153575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, M. Hand-Held Optical Sensors for Optimizing Nitrogen Application and Improving Nutrient Use Efficiency. Int. J. Bioresour. Sci. 2023, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Qin, K. Exploring a Cost-Effective Way for Nutrient Management with Machine Learning for Container Plants. Technol. Hortic. 2025, 5, e012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoddamzadeh, A.A.; Souza Costa, B.N. Best Nitrogen Management Practices Using Sensor-Based Smart Agriculture in Nursery Production of Cacao. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, E.F.; Watson, D.G. Sabal palmetto. Cabbage Palm. In Fact Sheet ST-575; Environmental Horticulture Department, Florida Cooperative Extension Service, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, L.; Williams, K. Effects of Salinity and Flooding on Seedlings of Cabbage Palm (Sabal palmetto.). Oecologia 1996, 105, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoddamzadeh, A.A.; Flores, J.; Griffith, M.P.; Nogueira Souza Costa, B. Saltwater Intrusion Ecophysiological Effects on Pseudophoenix sargentii, Roystonea regia, Sabal palmetto “Lisa,” and Thrinax radiata in South Florida. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1127679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.D.; Tucker, D.A.; Nageswara-Rao, M.; Griffith, M.P.; Balaji Baskar, M.S.; Ross, M.; Khoddamzadeh, A.A. Enhancing Cabbage Palm Resilience to Saltwater Stress through Silicon Applications. HortScience 2025, 60, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broschat, T.K. Fertilization of Field-Grown and Landscape Palms in Florida. EDIS 2006, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broschat, T.K. Nutrient Deficiencies of Landscape and Field-Grown Palms in Florida: ENH1018/EP273. EDIS 2006, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.V.; Godoy, L.J.G.D.; Stucchi, G.; Reis, A.G.P.D.; Pacheco, M.A.A. Controlled Release, Organic or Organomineral Fertilizers for Areca Palm Production. Ornam. Hortic. 2022, 28, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, M.E.; Mullahey, J.J.; Krewer, G.; Boland, B.; Affolter, J. Saw Palmetto (Serenoa repens): An Emerging Forest Resource in the Southeastern United States. South. J. Appl. For. 2000, 24, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, K.; Patel, G.; Sindha, M.; Chaudhari, V.; Shivaswamy, C. Palm: Versatile Group of Plant Material for Landscape Gardening. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2023, 7, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida Climate Center Precipitation. Available online: https://climatecenter.fsu.edu/products-services/data/statewide-averages/precipitation (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Sharma, R.; Singh, S.; Pant, K.; Mashiana, H.K.; Dubey, R.K. Protected Cultivation of Floriculture Crops: Innovative Technologies and Future Challenges. In Ornamental Horticulture: Latest Cultivation Practices and Breeding Technologies; Bhargava, B., Kumar, P., Verma, V., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 15–43. ISBN 978-981-97-4027-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mirbolook, A.; Sadaghiani, M.R.; Keshavarz, P.; Alikhani, M. New Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer Fortified with Zinc for Improving Zinc Availability and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Maize. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 45715–45728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Isla, F.; Farfan-Vignolo, E.R.; Gutierrez, R.; Blas, R.; Awais, K. Harvest Index Is a Key Trait for Screening Drought-Tolerant Potato Genotypes (Solanum tuberosum). J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 27, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira Souza Costa, B.; Khoddamzadeh, A.A. Data-Driven Nitrogen Application for Satinleaf: Leveraging Optical Sensors in Urban Landscape Management. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1522662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, K.; Witcher, A.; Baysal-Gurel, F. Evaluation of Physiological Changes in Flowering Dogwood under Drought Conditions in a Container Production System. HortScience 2023, 58, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira Souza Costa, B.; Tucker, D.A.; Khoddamzadeh, A.A. Precision Horticulture: Application of Optical Sensor Technology for Nitrogen Monitoring Status in Cocoplum, a Native Landscaping Plant. Plants 2023, 12, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBude, A.; Bilderback, T.E. The Pour-through Extraction Procedure: A Nutrient Management Tool for Nursery Crops; North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Landaverde, A.C.; Shreckhise, J.H.; Altland, J.E. Storage Procedures Affect pH, Electrical Conductivity, and Nutrient Concentrations of Pour-through Leachate from Pine Bark and Peat-Based Substrates. HortScience 2020, 55, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriam, J.; McDowell, W.H.; Currie, W.S. A High-Temperature Catalytic Oxidation Technique for Determining Total Dissolved Nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C. Reference Sufficiency Ranges for Plant Analysis in the Southern Region of the United States; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin: Athens, GA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, M.; Zebarth, B.J.; Miller, J.J.; Burton, D.L.; Grant, C.A. Soil Nitrogen Mineralization in a Soil with Long-Term History of Fresh and Composted Manure Containing Straw or Wood-Chip Bedding. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 99, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2025; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A Protocol for Data Exploration to Avoid Common Statistical Problems: Data Exploration. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Isla, F. Inti: Tools and Statistical Procedures in Plant Science 2025, 0.6.9. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/inti/index.html (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Kozak, M.; Piepho, H. -P. What’s Normal Anyway? Residual Plots Are More Telling than Significance Tests When Checking ANOVA Assumptions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2018, 204, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using “Eigen” and S4 2003, 1.1-37. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lme4/lme4.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S.; Price, B. Car: Companion to Applied Regression 2001, 3.1-3. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/car/car.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Lenth, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means 2017, 1.11.2. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/emmeans.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Multcomp: Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models 2002, 1.4-28. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/multcomp/vignettes/generalsiminf.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Husson, F.; Josse, J.; Le, S.; Mazet, J. FactoMineR: Multivariate Exploratory Data Analysis and Data Mining 2006, 2.12. Available online: https://husson.r-universe.dev/FactoMineR (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research 2007, 2.5.6. Available online: https://personality-project.org/r/psych/psych-manual.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D.; Van Den Brand, T. Ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics 2007, 3.5.2. Available online: https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/cran/web/packages/ggplot2/ggplot2.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Wilke, C.O. Cowplot: Streamlined Plot Theme and Plot Annotations for “Ggplot2” 2015, 1.2.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cowplot/index.html (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Abrahamson, W.G.; Abrahamson, C.R. Life in the Slow Lane: Palmetto Seedlings Exhibit Remarkable Survival but Slow Growth in Florida’s Nutrient-Poor Uplands. Castanea 2009, 74, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broschat, T.K. Sabal palmetto: Sabal or Cabbage Palm: (ENH-733/ST575). EDIS 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.J.; Larson, M. Climate Change Winners and Losers: The Effects of Climate Change on Five Palm Species in the Southeastern United States. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 10408–10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novichonok, E.V.; Novichonok, A.O.; Kurbatova, J.A.; Markovskaya, E.F. Use of the atLEAF+ Chlorophyll Meter for a Nondestructive Estimate of Chlorophyll Content. Photosyntetica. 2016, 54, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrenkott, B.A.; Craig, J.L.; McVey, G.R. A Leach Collection System to Track the Release of Nitrogen from Controlled-Release Fertilizers in Container Ornamentals. HortScience 2005, 40, 1887–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, M.P.N.; Elmer, W.H.; Macherla, K.; McAvoy, R.J. Effects of Salinity and Irrigation Management on Growth and Nutrient Concentrations in Poinsettia. HortScience 2016, 51, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palms, A. Palmetto. Q. J. Fla. Nativ. Plant Soc. 2016, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli, M.; Rouphael, Y.; Muntean, D.; Colla, G. Growth, Quality Index, and Mineral Composition of Five Ornamental Cabbage Cultivars Grown Under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Rates. HortScience 2015, 50, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majsztrik, J.C.; Ristvey, A.G.; Lea-Cox, J.D. Water and Nutrient Management in the Production of Container-Grown Ornamentals. In Horticultural Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 253–297. ISBN 978-0-470-64470-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zondag, R.H.; Merrick, J.; Demaline, T.; Krause, C.R. Nutrient Leaching from Container-Grown Ornamental Tree Production. J. Environ. Hortic. 2015, 33, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, A. Advances in Controlled-Release Fertilizers. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 71, pp. 1–49. ISBN 978-0-12-000770-7. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity Induced Physiological and Biochemical Changes in Plants: An Omic Approach towards Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assouline, S.; Russo, D.; Silber, A.; Or, D. Balancing Water Scarcity and Quality for Sustainable Irrigated Agriculture. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3419–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-Term Effects of Organic Amendments on Soil Fertility. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broschat, T.K.; Moore, K.K. Release Rates of Ammonium-Nitrogen, Nitrate-Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Magnesium, Iron, and Manganese from Seven Controlled-Release Fertilizers. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2007, 38, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, T.; Gardner, T.; Nyhuis, K. Nutrient Loading from Initial Watering of Container Plants. Acta Hortic. 2018, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.O.; Hochmuth, G.J.; Martinez, C.J.; Boyer, T.H.; Dukes, M.D.; Toor, G.S.; Cisar, J.L. Evaluating Nutrient Impacts in Urban Watersheds: Challenges and Research Opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira Souza Costa, B.; Munoz-Salas, M.N.; Gil, K.; Khoddamzadeh, A.A. Effect of Silicon Amendment on Growth and Nitrogen Status of Common Landscaping Plants. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangpan, S.; Tongchu, Y.; Hussain, T.; Eksomtramage, T.; Onthong, J. Beneficial Effects of Silicon Fertilizer on Growth and Physiological Responses in Oil Palm. Agronomy 2022, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayzaitul-Azwa, N.J.; Shuhada, N.M.T.; Hanafi, M.M.; Huda, N. Impact of Silicon-Enriched Fertilizer on Basal Stem Rot Disease in Palm Species Caused by Ganoderma boninense. J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2025, 48, 973–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samborski, S.M.; Tremblay, N.; Fallon, E. Strategies to Make Use of Plant Sensors-Based Diagnostic Information for Nitrogen Recommendations. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 800–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, J.; Osterman, J.C.; Mitchell, J.L. Calibration of the Minolta SPAD-502 Leaf Chlorophyll Meter. Photosynth. Res. 1995, 46, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tremblay, N.; Liang, Y. Comparing SPAD and atLEAF Values for Chlorophyll Assessment in Crop Species. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2012, 92, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracke, J.; Elsen, A.; Adriaenssens, S.; Schoeters, L.; Vandendriessche, H.; Van Labeke, M.-C. Application of Proximal Optical Sensors to Fine-Tune Nitrogen Fertilization: Opportunities for Woody Ornamentals. Agronomy 2019, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Huerta, R.; Guevara-Gonzalez, R.; Contreras-Medina, L.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Prado-Olivarez, J.; Ocampo-Velazquez, R. A Review of Methods for Sensing the Nitrogen Status in Plants: Advantages, Disadvantages and Recent Advances. Sensors 2013, 13, 10823–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, X.; Cuong, L. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on the Stability of Soil Carbon Fractions in Subtropical Castanopsis Sclerophylla Forests. Forests 2025, 16, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bi, G.; Harkess, R.L.; Denny, G.C.; Blythe, E.K.; Zhao, X. Nitrogen Rate, Irrigation Frequency, and Container Type Affect Plant Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Encore Azalea ‘Chiffon’. HortScience 2018, 53, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, N.M.; Sinclair, T.R. Water Balance in the Arborescent Palm, Sabal palmetto. II. Transpiration and Stem Water Storage. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments | FT (g) | SF (g) | November | March | Total (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| T1 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 30 |
| T2 | 15 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 45 |
| T3 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 45 |
| T4 | 30 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 60 |
| T5 | 45 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoddamzadeh, A.A.; Nogueira Souza Costa, B.; Munoz-Salas, M.N. Precision Fertilization Strategies Modulate Growth, Physiological Performance, and Soil–Plant Nutrient Dynamics in Sabal palmetto. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040121
Khoddamzadeh AA, Nogueira Souza Costa B, Munoz-Salas MN. Precision Fertilization Strategies Modulate Growth, Physiological Performance, and Soil–Plant Nutrient Dynamics in Sabal palmetto. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(4):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040121
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoddamzadeh, Amir Ali, Bárbara Nogueira Souza Costa, and Milagros Ninoska Munoz-Salas. 2025. "Precision Fertilization Strategies Modulate Growth, Physiological Performance, and Soil–Plant Nutrient Dynamics in Sabal palmetto" Soil Systems 9, no. 4: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040121
APA StyleKhoddamzadeh, A. A., Nogueira Souza Costa, B., & Munoz-Salas, M. N. (2025). Precision Fertilization Strategies Modulate Growth, Physiological Performance, and Soil–Plant Nutrient Dynamics in Sabal palmetto. Soil Systems, 9(4), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9040121









