Blending Potassium Rocks with KCl Fertilizer to Enhance Crop Biomass and Reduce K Leaching in Sandy Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Greenhouse Column Experiment
2.2. Biomass, Nutrient Uptake, Soil K Content, and Leaching Analyses
3. Results
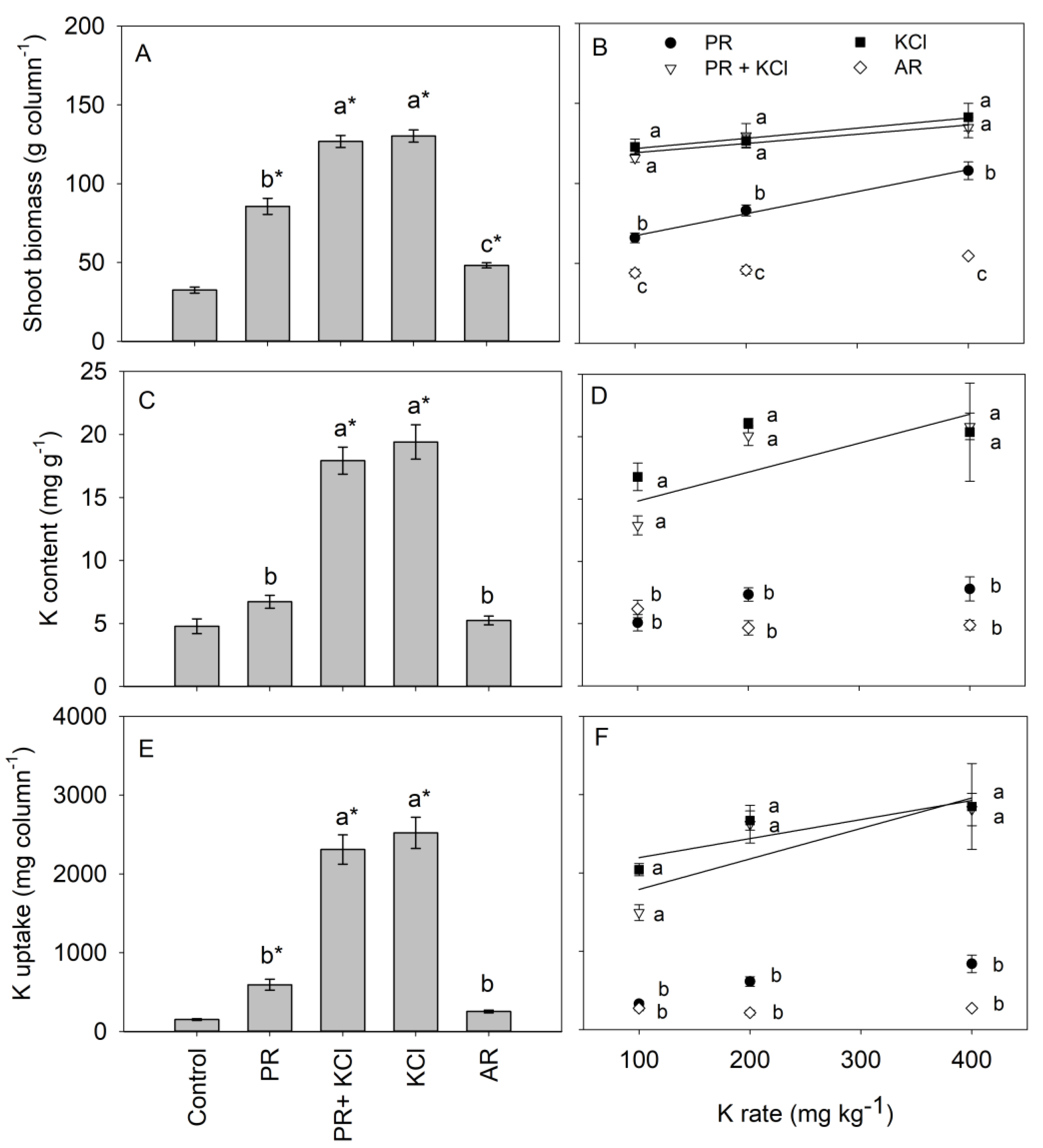
3.1. Maize Biomass and K Uptake
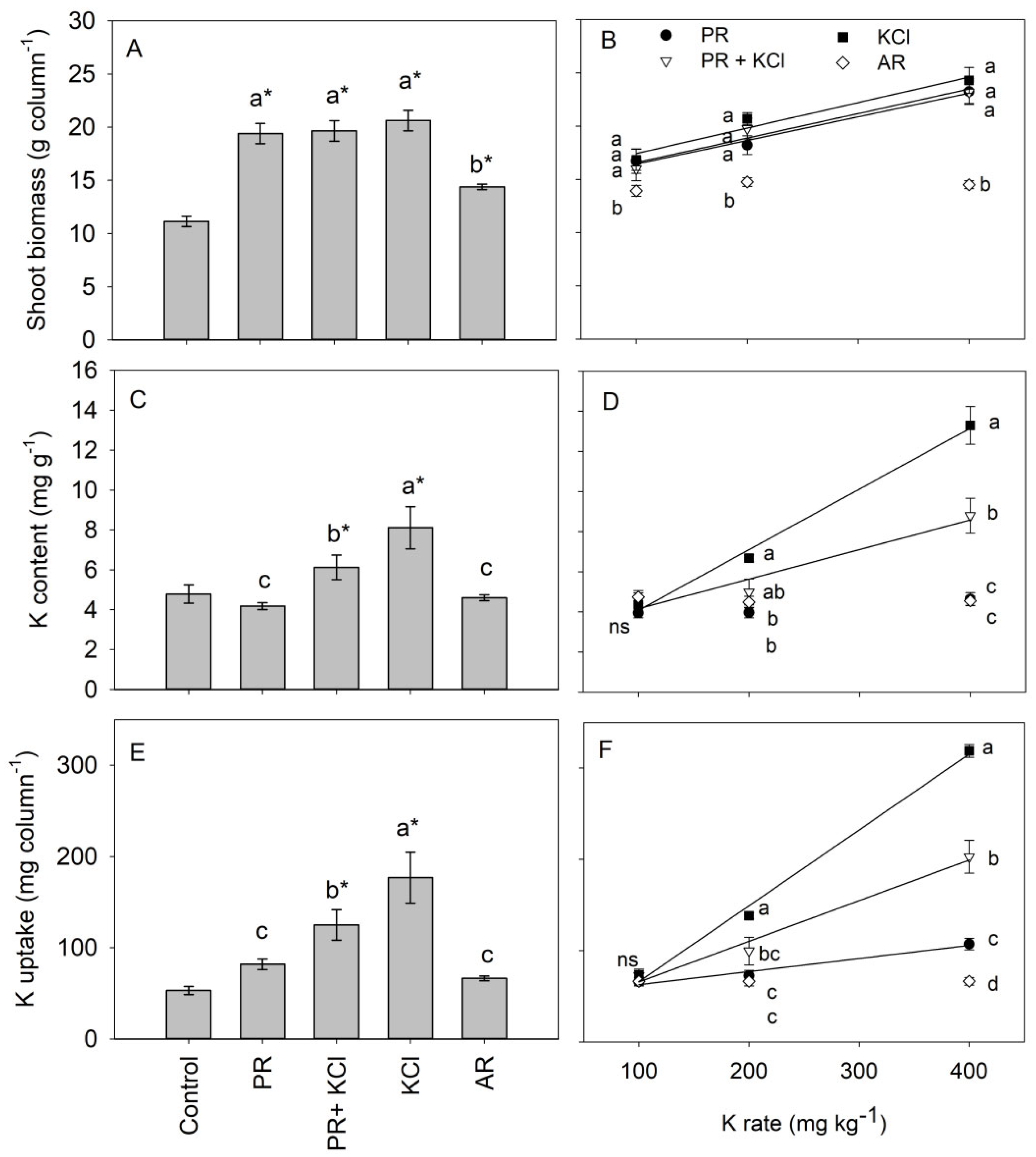
3.2. Rice Biomass and K Uptake
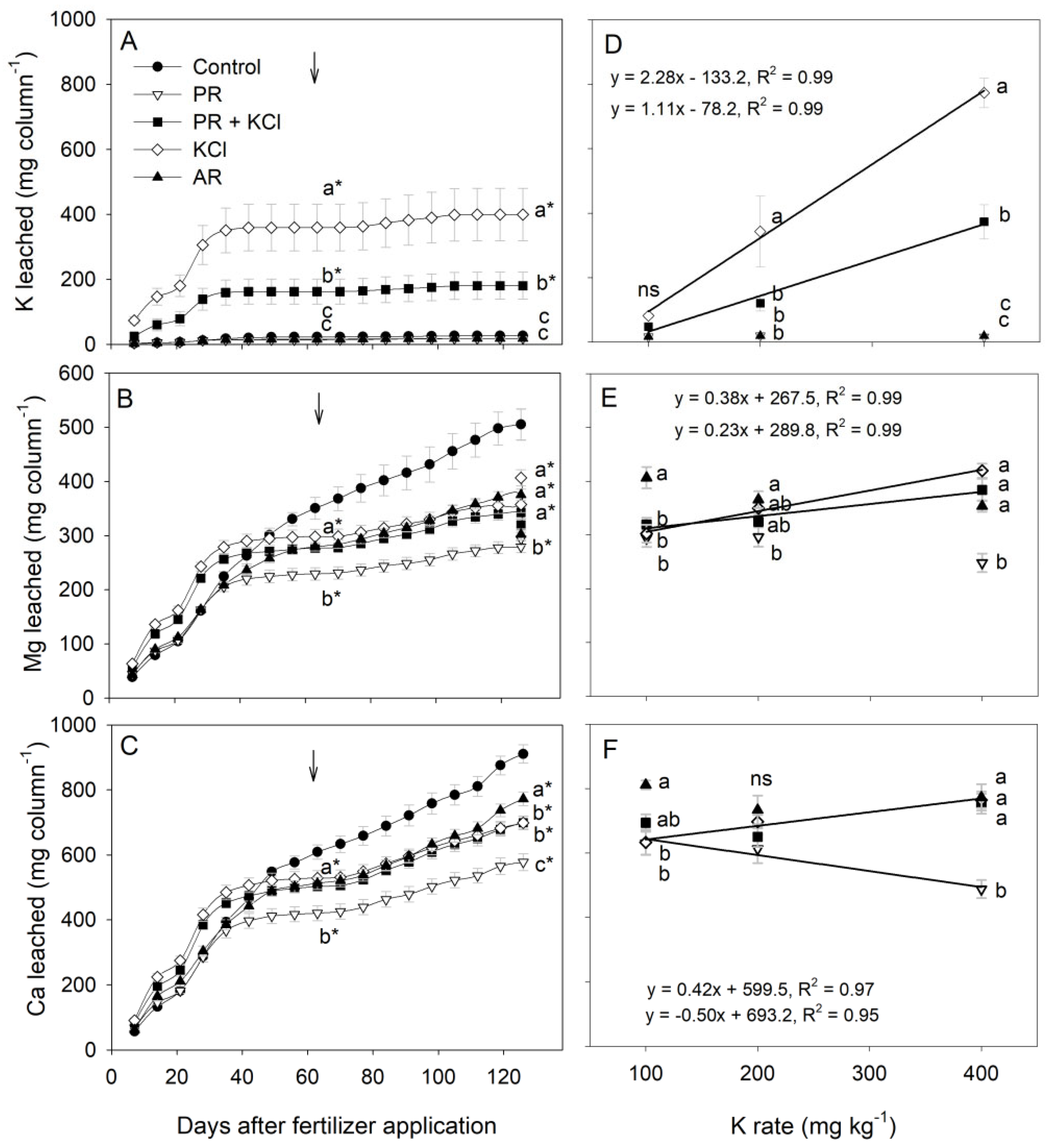
3.3. K, Ca, and Mg Leaching and Soil K Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marschner, P. (Ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-12-384905-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zörb, C.; Senbayram, M.; Peiter, E. Potassium in Agriculture—Status and Perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulding, K.W.T.; Loveland, P.J. The Classification and Mapping of Potassium Reserves in Soils of England and Wales. J. Soil Sci. 1986, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANDA. Anuário Estatístico Setor de Fertilizantes; ANDA (Associação Nacional para a Difusão de Adubos): São Paulo, Brazil, 2021. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- IFA. Public Summary Short-Term Outlook 2023–2024—IFA (International Fertilizer Association). Available online: https://www.ifastat.org/market-outlooks (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A.; Mattos, D.; Boaretto, R.M.; van Raij, B. Boletim 100: Recomendações de Adubação e Calagem Para o Estado de São Paulo; Instituto Agronômico: Campinas, Brazil, 2022; ISBN 978-65-88414-09-5. (In Portuguese)
- Rosolem, C.A.; Steiner, F. Effects of Soil Texture and Rates of K Input on Potassium Balance in Tropical Soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirale, A.O.; Meena, B.P.; Gurav, P.P.; Srivastava, S.; Biswas, A.K.; Thakur, J.K.; Somasundaram, J.; Patra, A.K.; Rao, A.S. Prospects and Challenges in Utilization of Indigenous Rocks and Minerals as Source of Potassium in Farming. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2682–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Sarkar, B.; Maity, A.; Chari, M.S.; Banerjee, A.; Biswas, D.R. Low-Grade Silicate Minerals as Value-Added Natural Potash Fertilizer in Deeply Weathered Tropical Soil. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusciol, C.A.C.; Soratto, R.P.; Gilabel, A.P.; Costa, C.H.M.d.; Campos, M.d.; Castro, G.S.A.; Ferrari Neto, J. Broadcast Application of Ground Silicate Rocks as Potassium Sources for Grain Crops. Pesqui. Agropecuária Bras. 2022, 57, e02443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, D.A.C.; Baptista, J.; Sanchez Limon, M.; Brandt, K. Testing the Ability of Plants to Access Potassium from Framework Silicate Minerals. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyono, J.; Gilkes, R.J. High-Energy Milling Improves the Effectiveness of Silicate Rock Fertilizers: A Glasshouse Assessment. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soratto, R.P.; Crusciol, C.A.C.; Campos, M.D.; Costa, C.H.M.D.; Gilabel, A.P.; Castro, G.S.A.; Ferrari Neto, J. Silicate Rocks as an Alternative Potassium Fertilizer for Upland Rice and Common Bean Crops. Pesqui. Agropecuária Bras. 2021, 56, e01411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, S.; Lu, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Can Potassium Silicate Mineral Products Replace Conventional Potassium Fertilizers in Rice–Wheat Rotation? Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.A.C.D.; Orioli Júnior, V.; Bernardes, J.V.S.; Sargentim, M.M.; Silva, G.A.; Kochenborger, A.C.D. Efficiency of Phonolite as a Potassium Source for Paiaguás Palisadegrass. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 2021, 51, e67857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchese, A.V.; de Castro Leite, I.J.G.; Alves, M.L.; dos Santos Vieceli, J.P.; Pivetta, L.A.; Missio, R.F. Can Basalt Rock Powder Be Used as an Alternative Nutrient Source for Soybeans and Corn? J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4044–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, T.A.R.; Miranda, B.G.; Jalal, A.; Lessa, L.G.F.; Filho, M.C.M.T.; Marcante, N.C.; Abreu-Junior, C.H.; Jani, A.D.; Capra, G.F.; Moreira, A.; et al. Nepheline Syenite and Phonolite as Alternative Potassium Sources for Maize. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Sarkar, B.; Sanderson, P.; Naidu, R. Waste Mineral Powder Supplies Plant Available Potassium: Evaluation of Chemical and Biological Interventions. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bauwhede, R.; Muys, B.; Vancampenhout, K.; Smolders, E. Accelerated Weathering of Silicate Rock Dusts Predicts the Slow-Release Liming in Soils Depending on Rock Mineralogy, Soil Acidity, and Test Methodology. Geoderma 2024, 441, 116734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oze, C.; Smaill, J.B.; Reid, C.M.; Palin, M. Potassium and Metal Release Related to Glaucony Dissolution in Soils. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBRAPA. Brazilian Soil Classification System, 5th ed.; Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (EMBRAPA): Brasília, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook; Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- van Raij, B.; Andrade, J.C.; Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A. Análise Química Para Avaliação Da Fertilidade de Solos Tropicais; Instituto Agronômico: Campinas, Brazil, 2001. (In Portuguese)
- Blake, G.R.; Hartge, K.H. Bulk Density. In Methods of Soil Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; pp. 363–375. ISBN 978-0-89118-864-3. [Google Scholar]
- MAPA. Ministério Da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento (MAPA). Manual de Métodos Analíticos Oficiais Para Fertilizantes e Corretivos; Secretaria de Defesa Agropecuária: Brasilia, Brazil, 2017. (In Portuguese)
- Malavolta, E. Elementos de Nutrição Mineral de Plantas; Editora Agronômica Ceres: São Paulo, Brazil, 1980. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- van Raij, B. Fertilidade do Solo e Manejo de Nutrientes; IPNI: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2011; ISBN 978-85-98519-07-4. [Google Scholar]
- Malavolta, E.; Vitti, G.C.; Oliveira, S.A. Avaliação do Estado Nutricional de Plantas; Associação Brasileira para Pesquisa da Potassa e do Fosfato: Piracicaba, Brazil, 1997. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Ferreira, E.B.; Cavalcanti, P.P.; Nogueira, D.A. ExpDes: Experimental Designs Package. R Package Version 1.2.1. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ExpDes.pt/index.html (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Lumley, T.; Johnson, R.C. Contributions from Randall C. Johnson Are Copyright SAIC-Frederick, Inc. Funded by the Intramural Research Program, of the NIH, National Cancer Institute and Center for Cancer Research Under NCI Contract NO1-CO-12400. (2018). Gmodels: Various R Programming Tools for Model Fitting. R Package Version 2.18.1. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=gmodels (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Systat Software (SSI). Sigmaplot for Windows, Version 12.5; Systat Software: San Jose, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, T.A.; Blackmer, T.M.; Francis, D.D.; Schepers, J.S. G93-1171 Using a Chlorophyll Meter to Improve N Management. Historical Materials from University of Nebraska-Lincoln Extension 1353. 1993. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/extensionhist/1353 (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Anjanadevi, I.P.; John, N.S.; John, K.S.; Jeeva, M.L.; Misra, R.S. Rock Inhabiting Potassium Solubilizing Bacteria from Kerala, India: Characterization and Possibility in Chemical K Fertilizer Substitution. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, B.B.; Maity, A.; Ray, P.; Biswas, D.R.; Roy, S. Potassium Supply in Agriculture through Biological Potassium Fertilizer: A Promising and Sustainable Option for Developing Countries. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, L.A.; Klaic, R.; Bortoletto-Santos, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Farinas, C.S. Unveiling the Solubilization of Potassium Mineral Rocks in Organic Acids for Application as K-Fertilizer. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2431–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schueler, T.A.; Dourado, M.L.; Videira, S.S.; da Cunha, C.D.; Rizzo, A.C.L. Biosolubilization of Verdete: An Alternative Potassium Source for Agriculture Fertilizer. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 102031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supanjani; Han, H.S.; Jung, J.S.; Lee, K.D. Rock Phosphate-Potassium and Rock-Solubilising Bacteria as Alternative, Sustainable Fertilisers. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2006, 26, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Sarkar, B.; Naidu, R. Environmentally Safe Release of Plant Available Potassium and Micronutrients from Organically Amended Rock Mineral Powder. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3273–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.G.; Dalmora, A.C.; Kautzmann, R.M.; Hower, J.; Dotto, G.L.; Oliveira, L.F.S. Sustainable Release of Macronutrients to Black Oat and Maize Crops from Organically-Altered Dacite Rock Powder. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saritha, M.; Kumar, P.; Panwar, N.R.; Burman, U. Plant Response to Novel Organo-Mineral Fertilizers Based on Selective Enrichment of P- and K-Solubilizing Microorganisms in Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirale, A.O.; Meena, B.P.; Biswas, A.K.; Gurav, P.P.; Srivastava, S.; Das, H.; Thakur, J.K.; Patra, A.K.; Rao, A.S. Characterization and K Release Pattern of Glauconite in Contrasting Soils of India. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4632–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.S.; Biswas, D.R.; Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, A. Oxalic-Acid-Treated Waste Mica, a Potent Natural Supplement to K Fertilizers for Growing Wheat and Rice in Inceptisol. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbissik, A.; Khiari, L.; Raji, O.; Elghali, A.; Lajili, A.; Ouabid, M.; Jemo, M.; Bodinier, J.-L. Potassium Fertilizer Value of Raw and Hydrothermally Treated Igneous Rocks. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1030–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.O.; Mattiello, E.M.; Vergutz, L.; Costa, R.F. Production and Evaluation of Potassium Fertilizers from Silicate Rock. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2016, 179, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folego, T. O Brasil tem um Fertilizante de Baixo Carbono. Mas Precisa Desbravar o Mercado. Available online: https://capitalreset.uol.com.br/agronegocio/o-brasil-tem-um-fertilizante-de-baixo-carbono-mas-precisa-desbravar-o-mercado/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). (In Portuguese).
- Sanches, G.M.; Magalhães, P.S.G.; Kolln, O.T.; Otto, R.; Rodrigues, F.; Cardoso, T.F.; Chagas, M.F.; Franco, H.C.J. Agronomic, Economic, and Environmental Assessment of Site-Specific Fertilizer Management of Brazilian Sugarcane Fields. Geoderma Reg. 2021, 24, e00360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Geisseler, D.J.; Brown, P.H.; Khalsa, S.D.S. Distribution of Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium Ions from Potassium Fertilizers in Columns of Orchard Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2023, 87, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Depth | pH | OM | P | K | Ca | Mg | H + Al | CEC | BS | Sand | Silt | Clay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | - | g dm−3 | mg dm−3 | mmolc dm−3 | % | g kg−1 | ||||||
| 0–20 | 4.9 | 15 | 9 | 1.2 | 10 | 6 | 18 | 35.2 | 49 | 817 | 19 | 163 |
| 20–40 | 4.7 | 10 | 6 | 0.7 | 10 | 5 | 18 | 33.7 | 47 | 811 | 14 | 175 |
| K Source | Potassium Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total * | Citric Acid 2% † | Water ‡ | |
| K2O Content (% of Total K2O) | |||
| Phonolite rock (PR) | 7.59 | 0.79 (10%) | 0.06 (0.8%) |
| PR + KCl | 15.60 | 11.44 (73%) | 10.41 (67%) |
| Alkaline rock (AR) | 12.40 | 0.22 (1.8%) | 0.20 (1.6%) |
| KCl | 60.15 | 60.15 (100%) | 60.10 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silveira, C.P.; Soares, J.R.; Montes, R.M.; Savieto, J.; Otto, R. Blending Potassium Rocks with KCl Fertilizer to Enhance Crop Biomass and Reduce K Leaching in Sandy Soil. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030083
Silveira CP, Soares JR, Montes RM, Savieto J, Otto R. Blending Potassium Rocks with KCl Fertilizer to Enhance Crop Biomass and Reduce K Leaching in Sandy Soil. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilveira, Cristiane Prezotto, Johnny Rodrigues Soares, Rafael Marangoni Montes, Julia Savieto, and Rafael Otto. 2025. "Blending Potassium Rocks with KCl Fertilizer to Enhance Crop Biomass and Reduce K Leaching in Sandy Soil" Soil Systems 9, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030083
APA StyleSilveira, C. P., Soares, J. R., Montes, R. M., Savieto, J., & Otto, R. (2025). Blending Potassium Rocks with KCl Fertilizer to Enhance Crop Biomass and Reduce K Leaching in Sandy Soil. Soil Systems, 9(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030083







