Exploring Protist Communities in the Rhizosphere of Cultivated and Wild Date Palms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Soil Sampling
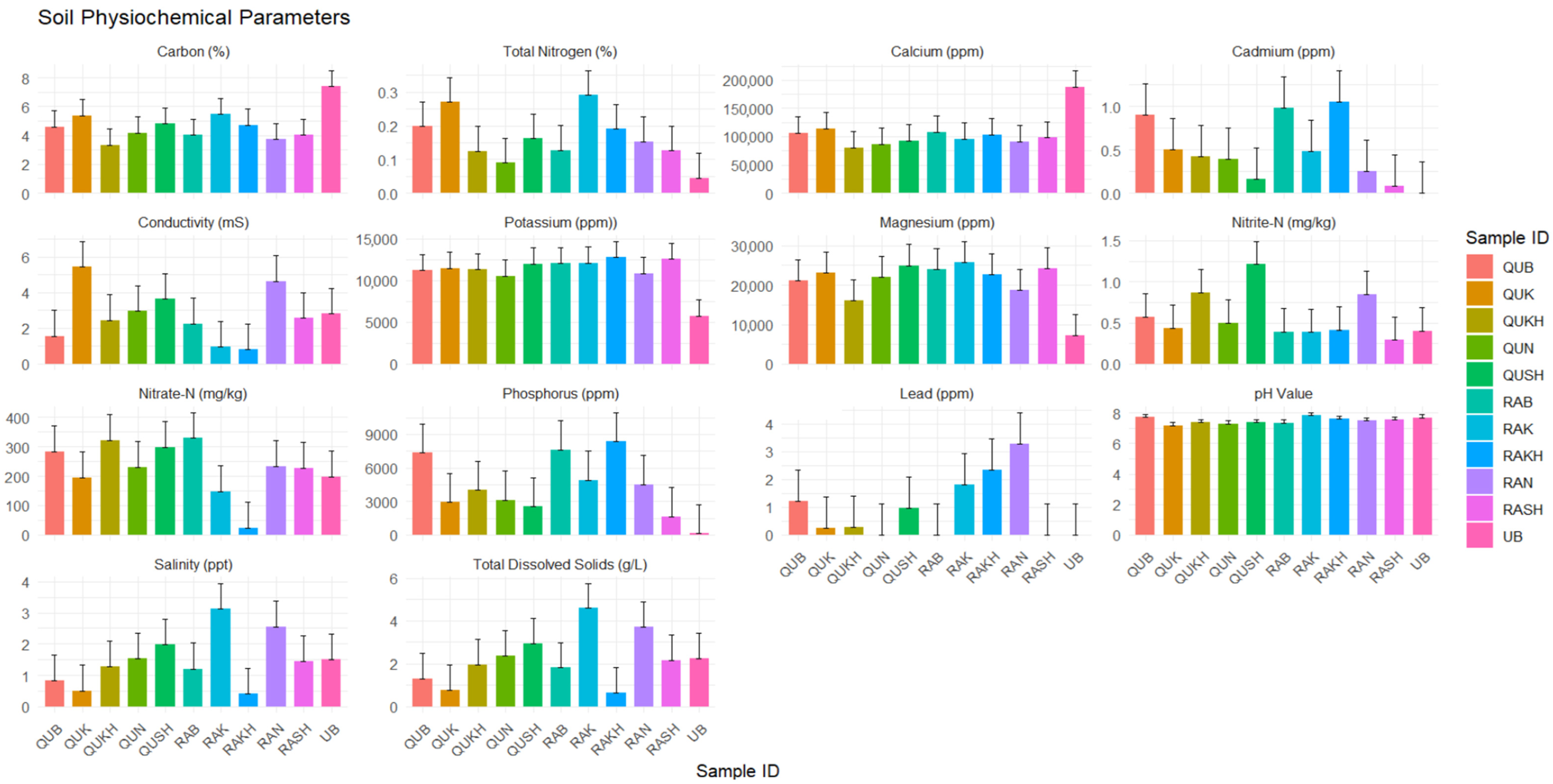
2.2. Soil Physiochemical Characteristics
2.3. DNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Illumina Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
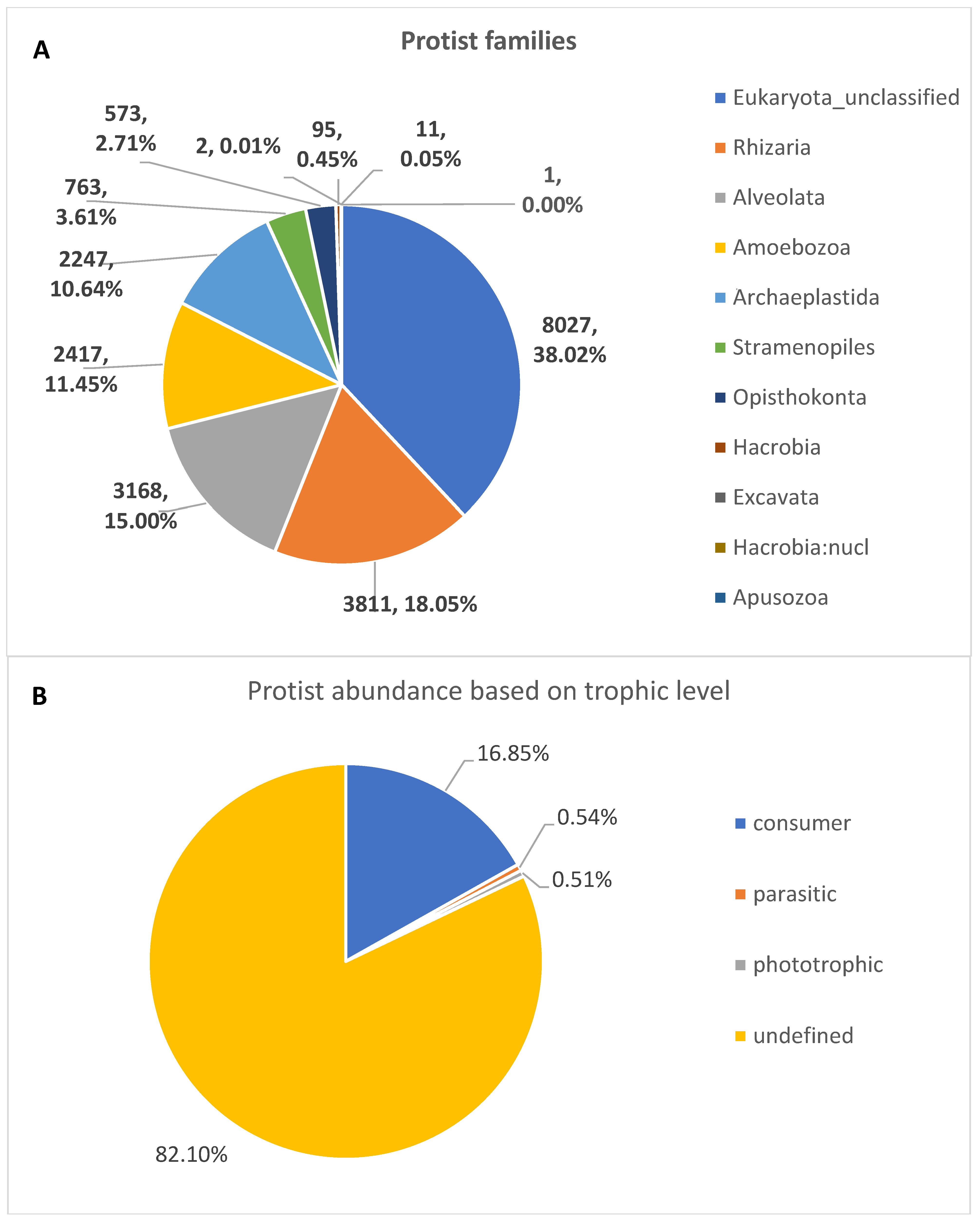
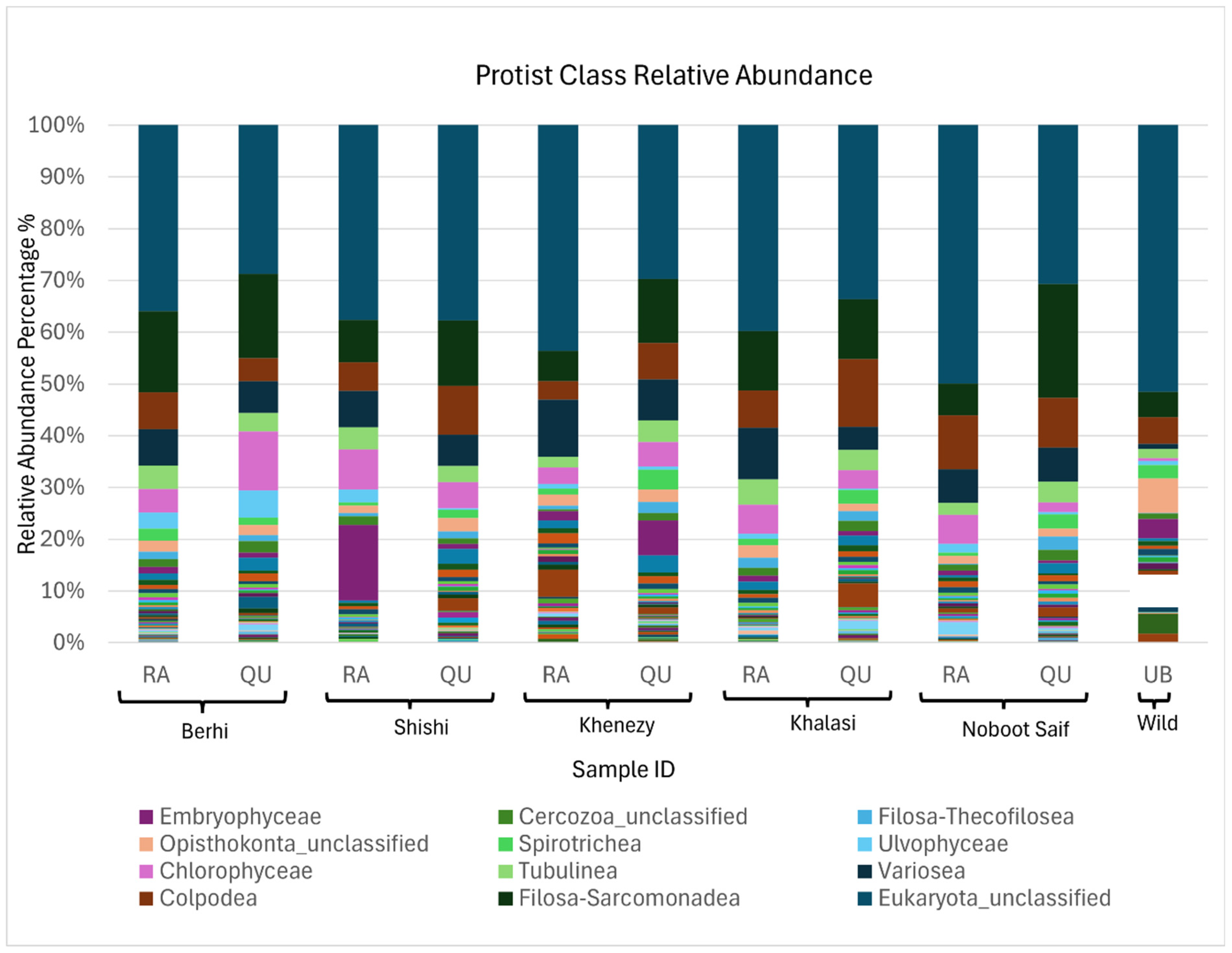
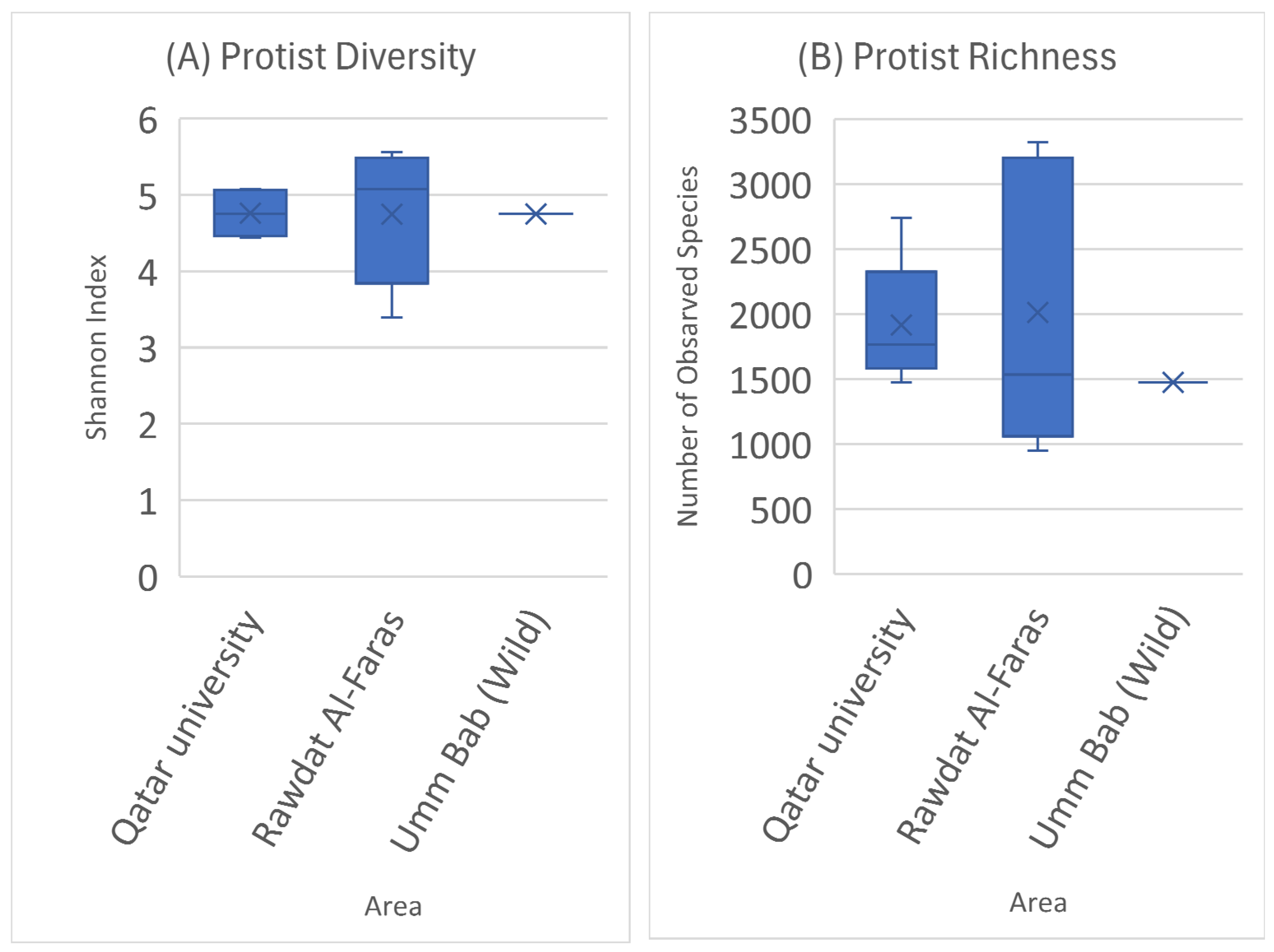
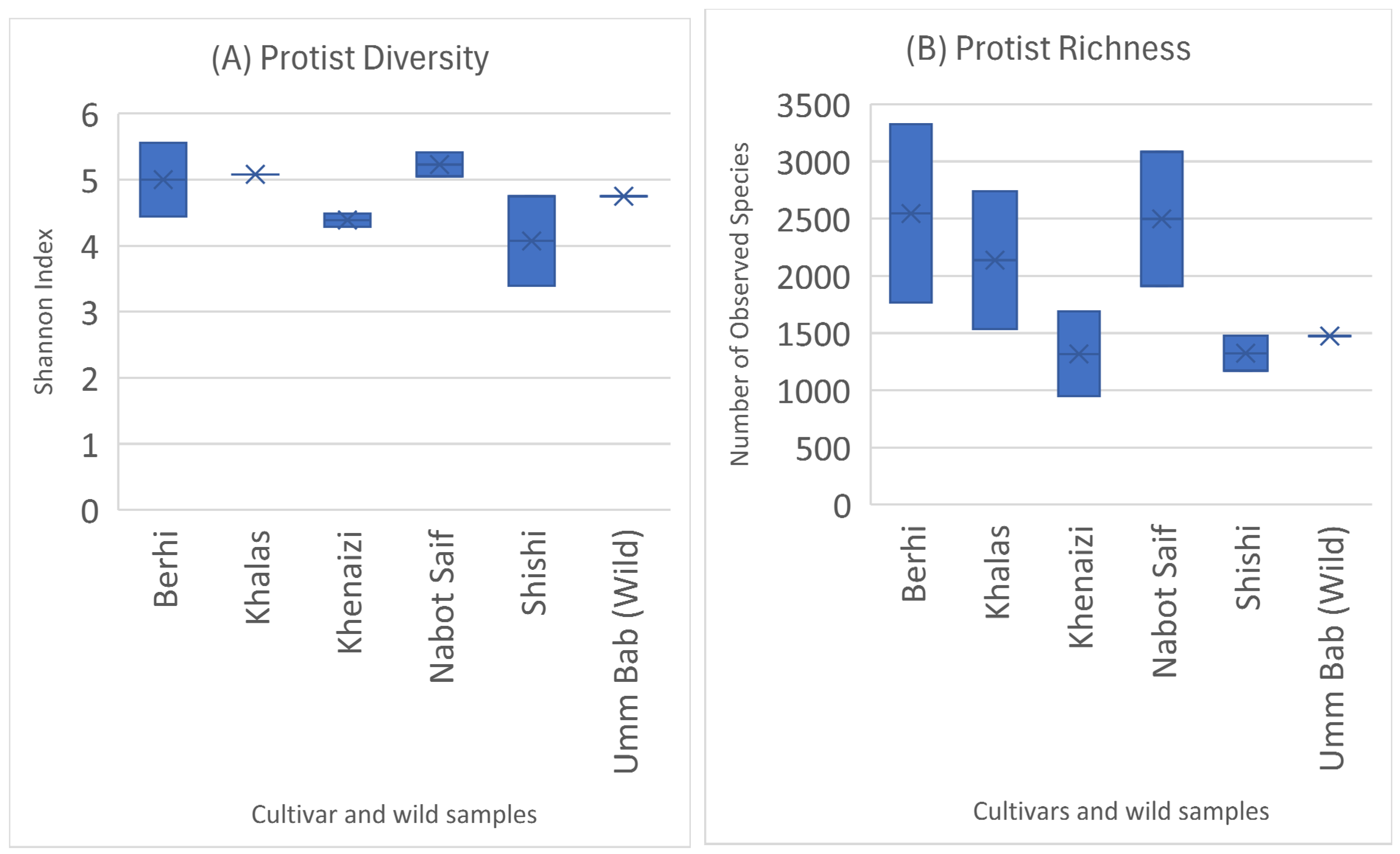
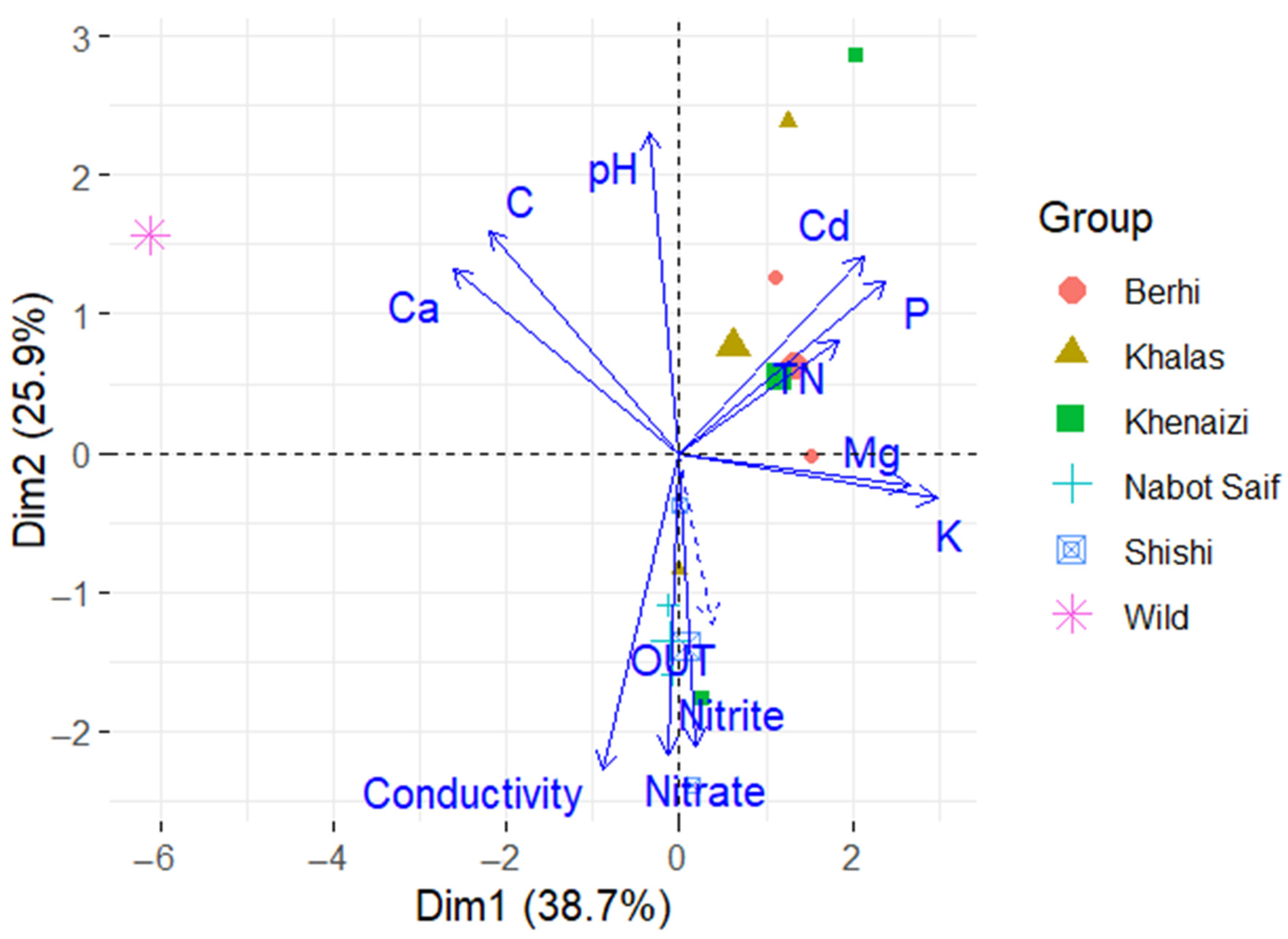
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jousset, A. Application of Protists to Improve Plant Growth in Sustainable Agriculture. In Rhizotrophs: Plant Growth Promotion to Bioremediation; Mehnaz, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlinches de Gea, A.; Li, G.; Chen, J.O.; Wu, W.; Kohra, A.; Aslan, S.K.; Geisen, S. Increasing Soil Protist Diversity Alters Tomato Plant Biomass in a Stress-Dependent Manner. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 186, 109179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, S.; Hu, S.; dela Cruz, T.E.E.; Veen, G.F. Protists as Catalyzers of Microbial Litter Breakdown and Carbon Cycling at Different Temperature Regimes. ISME J. 2021, 15, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Karlsson, I.; Geisen, S.; Kowalchuk, G.; Jousset, A. Protists: Puppet Masters of the Rhizosphere Microbiome. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisen, S.; Mitchell, E.A.D.; Adl, S.; Bonkowski, M.; Dunthorn, M.; Ekelund, F.; Fernández, L.D.; Jousset, A.; Krashevska, V.; Singer, D.; et al. Soil Protists: A Fertile Frontier in Soil Biology Research. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 293–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore-Donno, A.M.; Weinert, J.; Wubet, T.; Bonkowski, M. Metacommunity Analysis of Amoeboid Protists in Grassland Soils. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, J. Quest of Soil Protists in a New Era. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Torruella, G.; Moreira, D.; López-García, P. Phylogenetic and Ecological Diversity of Apusomonads, a Lineage of Deep-Branching Eukaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.; Gregorich, E.; Adl, S.; Acosta-Mercado, D.; Anderson, T.; Lynn, D. Methods in Soil Protozoa. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Chao, Y.; Shu, L.; Qiu, R. Interactions between Soil Protists and Pollutants: An Unsolved Puzzle. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foissner, W. Protist Diversity: Estimates of the Near-Imponderable. Protist 1999, 150, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahé, F.; de Vargas, C.; Bass, D.; Czech, L.; Stamatakis, A.; Lara, E.; Singer, D.; Mayor, J.; Bunge, J.; Sernaker, S.; et al. Parasites Dominate Hyperdiverse Soil Protist Communities in Neotropical Rainforests. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.S.; Schöler, A.; Nielsen, T.K.; Hansen, L.H.; Schloter, M.; Winding, A. Land Use as a Driver for Protist Community Structure in Soils under Agricultural Use across Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliverio, A.M.; Geisen, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Turner, B.L.; Fierer, N. The Global-Scale Distributions of Soil Protists and Their Contributions to Belowground Systems. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, L.; Jensen, M.; Pandey, R.V.; Jost, S.; Bass, D.; Psenner, R.; Boenigk, J. Molecular Investigation of Protistan Diversity along an Elevation Transect of Alpine Lakes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 78, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiloglu, R.; Shiroishi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Turgay, O.C.; Harada, N. Soil Properties Have More Significant Effects on the Community Composition of Protists than the Rhizosphere Effect of Rice Plants in Alkaline Paddy Field Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 108397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.-A.T.; Chen, Q.-L.; Yan, Z.-Z.; Li, C.; He, J.-Z.; Hu, H.-W. Distinct Factors Drive the Diversity and Composition of Protistan Consumers and Phototrophs in Natural Soil Ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Jousset, A.; Guo, S.; Karlsson, I.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, H.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Shen, Q.; Li, R.; Geisen, S. Soil Protist Communities Form a Dynamic Hub in the Soil Microbiome. ISME J. 2018, 12, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abumaali, D.; Al-Hadidi, S.; Ahmed, T.; Al-khis, A.; Al-Malki, S.; Yaish, M.; Hassan, H.; Al-Thani, R.; Alatalo, J. Bacterial Community Structure and Predicted Function in the Rhizosphere of Wild and Cultivated Date Palms: Effects of Fertilizers on Composition and Functionality. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2023, 29, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hadidi, S.; Abumaali, D.; Ahmed, T.; Al-khis, A.; Al-Malki, S.; Yaish, M.; Rahim, H.; Khalid, M.; Hassan, H.; Alatalo, J. The Effect of Type and Combination of Fertilizers on Eukaryotic Microbiome of Date Palm Rhizosphere. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 103, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodur, S.O.; Samuel, S.O.; Suzuki, K.; Harada, N.; Asiloglu, R. Nitrogen-Based Fertilizers Differentially Affect Protist Community Composition in Paddy Field Soils. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2024, 6, 230221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliola, M.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S.; Crecchio, C.; Pii, Y. Bioinoculants as Promising Complement of Chemical Fertilizers for a More Sustainable Agricultural Practice. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 4, 622169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-B.; He, J.-Z.; Quan, Z.; Wu, C.-F.; Sheng, R.; Zhang, L.-M.; Geisen, S. Fertilization Changes Soil Microbiome Functioning, Especially Phagotrophic Protists. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jaramillo, J.E.; Carrión, V.J.; de Hollander, M.; Raaijmakers, J.M. The Wild Side of Plant Microbiomes. Microbiome 2018, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Chang, J.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Ji, L.; Li, X.; Tian, C. Comparative Analysis of the Rhizomicrobiome of the Wild versus Cultivated Crop: Insights from Rice and Soybean. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenan, S.; Oja, J.; Alatalo, J.M.; Shraim, A.M.; Alsafran, M.; Tedersoo, L.; Zobel, M.; Ahmed, T. Diversity of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Its Chemical Drivers across Dryland Habitats. Mycorrhiza 2021, 31, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaish, M.W.; Al-Harrasi, I.; Alansari, A.S.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Glick, B.R. The Use of High Throughput DNA Sequence Analysis to Assess the Endophytic Microbiome of Date Palm Roots Grown under Different Levels of Salt Stress. Int. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, N.H.; Ahmed, O.E.; Ahmed, T.A.; Al-Yafai, M.S. Date palm status and perspective in Qatar. In Date Palm Genetic Resources and Utilization: Volume 2: Asia and Europe; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 323–351. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.I.; Farooq, M.; Syed, Q.A. Nutritional and biological characteristics of the date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.)—A review. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, S. Thorough High-throughput Sequencing Analyses Unravels Huge Diversities of Soil Parasitic Protists. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly Accurate OTU Sequences from Microbial Amplicon Reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference Database (PR2): A Catalog of Unicellular Eukaryote Small Sub-Unit rRNA Sequences with Curated Taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, D.; Seppey, C.V.W.; Lentendu, G.; Dunthorn, M.; Bass, D.; Belbahri, L.; Blandenier, Q.; Debroas, D.; de Groot, G.A.; de Vargas, C.; et al. Protist Taxonomic and Functional Diversity in Soil, Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A Free Online Platform for Data Visualization and Graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, F.; Keeling, P.J. Rhizaria. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R103–R107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Queller, D.C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Q.; He, Z.; He, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Shu, L. The Ecology and Evolution of Amoeba-Bacterium Interactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e01866-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Sun, A.; Lu, C.; Su, J.-Q.; Chen, Q.-L. Protists and Fungi: Reinforcing Urban Soil Ecological Functions against Flash Droughts. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Adhikari, M.; Jeong, S.S.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, G.S.; Park, D.H.; Kim, H.; Yang, J.E. Microbial Diversity of Soils under Different Land Use and Chemical Conditions. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogola, H.J.O.; Ijoma, G.N.; Edokpayi, J.N. Exploring the Dichotomy: Shotgun Metagenomics Reveals Diversity of Beneficial and Pathogenic Protist Community in Arid Wetlands of Northeastern South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichman, Y.; Mittler, R. Integration of Electric, Calcium, Reactive Oxygen Species and Hydraulic Signals during Rapid Systemic Signaling in Plants. Plant J. 2021, 107, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, S.; Mittler, R. Plant Signaling in Biotic and Abiotic Stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1649–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, F.J.; Reineke, D.; Leventini, D.; Chen, C.C.L.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G.; Colmer, T.D.; Dodd, I.C.; Shabala, S.; Brown, P.; Bazihizina, N. Plant Responses to Heterogeneous Salinity: Agronomic Relevance and Research Priorities. Ann. Bot. 2022, 129, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, L.W.; Kuramae, E.E.; Navarrete, A.A.; van Veen, J.A.; Tsai, S.M. Taxonomical and Functional Microbial Community Selection in Soybean Rhizosphere. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfitt, R.L.; Yeates, G.W.; Ross, D.J.; Mackay, A.D.; Budding, P.J. Relationships between Soil Biota, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Availability, and Pasture Growth under Organic and Conventional Management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Wang, G. Different Long-Term Fertilization Regimes Affect Soil Protists and Their Top-down Control on Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Mollisols. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.-B.; He, J.-Z.; Geisen, S.; Han, L.-L.; Wang, J.-T.; Shen, J.-P.; Wei, W.-X.; Fang, Y.-T.; Li, P.-P.; Zhang, L.-M. Protist Communities Are More Sensitive to Nitrogen Fertilization than Other Microorganisms in Diverse Agricultural Soils. Microbiome 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuikman, P.J.; Van Veen, J.A. The Impact of Protozoa on the Availability of Bacterial Nitrogen to Plants. Biol. Fert. Soils 1989, 8, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abumaali, D.A.; Al-Hadidi, S.H.; Ahmed, T.; Ben Zineb, A.; Rasheela, A.R.P.; Al-khis, A.F.; Al-Malki, S.A.; Yaish, M.W.; Hassan, H.; Al-Thani, R.; et al. Exploring Protist Communities in the Rhizosphere of Cultivated and Wild Date Palms. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030079
Abumaali DA, Al-Hadidi SH, Ahmed T, Ben Zineb A, Rasheela ARP, Al-khis AF, Al-Malki SA, Yaish MW, Hassan H, Al-Thani R, et al. Exploring Protist Communities in the Rhizosphere of Cultivated and Wild Date Palms. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbumaali, Dana A., Sara H. Al-Hadidi, Talaat Ahmed, Ameni Ben Zineb, Abdul Rashid P. Rasheela, Amer Fayad Al-khis, Sowaid Ali Al-Malki, Mahmoud W. Yaish, Hassan Hassan, Roda Al-Thani, and et al. 2025. "Exploring Protist Communities in the Rhizosphere of Cultivated and Wild Date Palms" Soil Systems 9, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030079
APA StyleAbumaali, D. A., Al-Hadidi, S. H., Ahmed, T., Ben Zineb, A., Rasheela, A. R. P., Al-khis, A. F., Al-Malki, S. A., Yaish, M. W., Hassan, H., Al-Thani, R., & Alatalo, J. M. (2025). Exploring Protist Communities in the Rhizosphere of Cultivated and Wild Date Palms. Soil Systems, 9(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9030079







