Abstract
The main problem associated with mining is the release of heavy metals into the environment, impacting the soil and overall environment. Mercury is one of the most contaminating heavy metals. It is present in soils, sediments, surface water, and groundwater. The objective of this research was to evaluate the phytoremediation carried out by the native plant Piper marginatum, in soils contaminated by mercury in an experimental lot in the municipality of Ayapel, where artisanal and small-scale gold mining is carried out. A soil phytoremediation process was carried out at a field scale using the plant species Piper marginatum in a 2.4 ha plot historically contaminated by gold mining, located in Ayapel, Colombia. A completely randomized experimental design was used with nine experimental plots, which were planted with Piper marginatum, and three controls, without planting. Through an initial soil sampling, the physicochemical characteristics and total mercury content in this matrix were determined. Piper marginatum seedlings were planted in the experimental plots and remained in the field for a period of six months. The plant biomass was collected and a final soil sampling was performed for total mercury analysis to determine the total percentage of mercury removal. The results obtained indicated mercury concentrations in soils ranging from 40.80 to 52,044.4 µg kg−1 in the experimental plots and ranged from 55.9 to 2587.4 µg kg−1 in the controls. In the plots planted with Piper marginatum, a 37.3% decrease in total mercury was achieved, while in the plots without planting there was a 23.5% increase. In plants, the average T Hg concentrations in the roots, stems, and leaves were 109.2 µg kg−1, 80.6 µg kg−1, and 122.6 µg kg−1, respectively. An average BCF < 1 and an average TF > 1 were obtained.
1. Introduction
Gold mining is considered the largest anthropogenic source of mercury (Hg) release into the environment in the world [1]. In artisanal mining, mercury is used to form an amalgam, which is to a mixture of Hg and gold in approximately equal parts. During the heating of the amalgam, part of the mercury is recovered; however, most of it evaporates and the remains are transferred to the soil and water bodies causing contamination of these [2]. Mercury is a non-essential heavy metal that bioaccumulates and biomagnifies in the environment, since it affects plants, microorganisms, and animals, and enters humans through the food chain, causing various carcinogenic effects, brain damage, central nervous system disorders, and even death [3].
Mercury (Hg) contamination from artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASM) constitutes one of the most severe environmental and health threats in the municipality of Ayapel, Córdoba (Colombia), an area located south of the Ayapel swamp and characterized by intense informal mining activity. In general, the problem of contamination and environmental degradation associated with gold mining activities using the amalgamation process has been widely documented in the departments of Córdoba. The results of these investigations report contamination with high concentrations of Hg in different environmental matrices, such as soil, air [4], water, sediments [5,6], aquatic and terrestrial plants, fish, crops, and the human population [7], with values that exceed internationally established reference thresholds [8,9,10]. Additionally, mining activity has generated deforestation, erosion, degradation, and loss of the productive capacity of the soil, degradation of water sources and watersheds in general, loss of biodiversity, among others, turning the areas of intervention into mining environmental liabilities [11,12]. Marrugo-Negrete et al. (2007) reported that the average T-Hg concentrations measured in sediments collected at the site where the Cauca River enters the Ayapel swamp during a sampling period were 0.8 ± 0.02 mg kg−1 [13]. Other recent investigations have revealed worrying concentrations of Hg in various environmental compartments in this region, with values up to 2.3 mg kg−1 in soils around the Ayapel swamp, high concentrations of T-Hg in fish such as Pseudoplatystoma fasciatun (0.43 ± 0.1 μg g−1, fresh weight [fw]), and mean values of 0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg in sediments [14,15,16,17], which greatly exceeds the limits established by international bodies for the protection of health and ecosystems [7,18]. This situation represents a persistent risk of chronic mercury poisoning in human populations, in addition to significant ecological impacts due to the bioaccumulation and biomagnification of the metal through the trophic chain.
Mercury, classified as a priority pollutant due to its toxicity, persistence, and mobility, is released into the environment during the gold amalgamation process, and its volatilization and leaching contribute to its distribution in soils, water bodies, and biota. Despite the various technologies evaluated at laboratory scale, such as the use of electrochemical treatment technologies and constructed wetlands, these strategies face technical and economic limitations that hinder their large-scale application in hard-to-reach rural areas. Soil remediation involves techniques aimed at restoring soil using biological, physical, and chemical processes. The goal is to reduce the impact on plants, animals, humans, and the environment as a whole [19]. Of this set of techniques, phytoremediation has been identified as one of the best alternatives to reduce the amounts of toxic elements in soils, where plants with the capacity to extract contaminants such as heavy metals are used, characterized by its low cost, simple operation, and greater acceptance compared with other more aggressive techniques [20]. Phytoremediation, a technique based on the use of plants to extract, stabilize, or transform contaminants, has positioned itself as a sustainable, low-cost, and environmentally compatible alternative for the management of soils contaminated with heavy metals. In Colombia, species such as Jatropha curcas, Cecropia peltate, and Paspalum fasciculatum have shown potential in Hg removal, although with variable yields depending on edaphoclimatic conditions [7,21].
In this context, the study of native species or those adapted to local conditions acquires special relevance. Piper marginatum Jacq., belonging to the Piperaceae family, is a neotropical aromatic species widely distributed in humid ecosystems of the Colombian Caribbean, traditionally used by indigenous communities for its medicinal properties [22,23,24]. Although it has not been extensively used in phytoremediation processes, a preliminary study identified its presence in contaminated soils in the El Alacrán Mine (Córdoba), reporting a bioconcentration factor (BCF) of 0.9 and a translocation factor (TF) of 0.58, suggesting a moderate capacity for Hg accumulation and transport [16].
For the reason stated previously, the present study aimed to evaluate the phytoremediation capacity of Piper marginatum in mercury-contaminated soils in an experimental plot located in the municipality of Ayapel, Colombia. This research aims not only to validate the potential of this species as a tool for ecological restoration, but also to contribute to the identification of solutions based on local biodiversity, thus contributing to the development of sustainable strategies for the management of environmental liabilities in areas impacted by gold mining.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted in a rural area of the municipality of Ayapel, located at the eastern end of the department of Córdoba, Colombia, surrounded by the San Jorge River and the Ayapel swamp. The site is specifically located at the geographical coordinates 8°10′27.14″ N and 75°9′5.87″ W, with an altitude of 28 m above sea level (Figure 1).
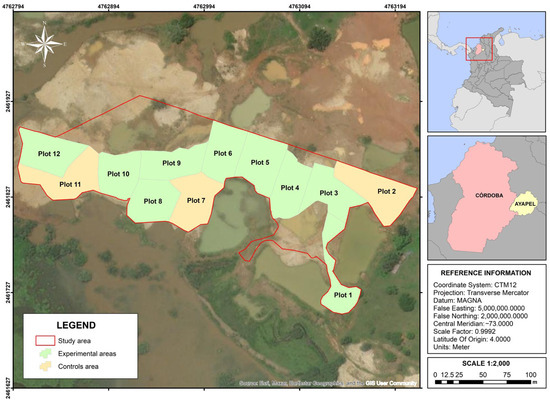
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area in Ayapel, Córdoba, Colombia. The experimental areas correspond to Plot 1, Plot 3, Plot 4, Plot 5, Plot 6, Plot 8, Plot 9, Plot 10, and Plot 12. The control areas correspond to Plot 2, Plot 7, and Plot 11.
2.2. Soil Sampling
The experiment was carried out in a 2.4 ha plot located in an area degraded by gold mining activities. The area was subdivided into 12 experimental plots of 2000 m2 each, following a completely randomized design with two treatments: nine plots planted with Piper marginatum and three plots without sowing, which acted as controls. Plot selection considered site homogeneity in terms of historical use, slope, soil texture, and environmental exposure, in order to reduce spatial variability and ensure comparable conditions between treatments.
Soil sampling was carried out at two points during the experiment: at the beginning, prior to planting, and at the end of the evaluation period. Each sampling period lasted one day, and five composite samples were collected per plot, each one consisting of five subsamples randomly distributed within the plot, with a depth of 30 cm, using a stainless steel trowel, following the methodological recommendations described by USEPA [25]. Each composite sample weighed approximately 1 kg. In this context, 60 samples were taken for each sampling time (45 treatments and 15 control).
Samples were placed in labeled polyethylene bags, stored under controlled conditions, and transported to the laboratory for processing. In the laboratory, samples were homogenized, dried at room temperature for seven days, and sieved to remove roots, stones, or other debris prior to chemical analysis.
The choice of establishing three plots as controls was based on technical criteria and methodological precedents widely used in phytoremediation studies in the field, where the emphasis is placed on the replication of the experimental treatment, and the control plays a referential role to compare the effects of the biotic process [26,27]. This configuration allows a statistical evaluation of the plant effect, provided that the assumptions of normality and homogeneity of variances are verified, which were tested in this study. The adopted methodological strategy offers an adequate balance between experimental control, ecological representativeness, and operational applicability in real environmental restoration scenarios [28,29].
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis of Soils
Physical and chemical parameters were determined for each sample; the texture was determined by measuring the proportions of clay, silt, and sand particles present in the soil using the Bouyoucos method, following that established by the IGAC (2006) [30]. The pH was determined at a soil–water ratio (w/v) 1:1 using the potentiometric quantification method [31].
The organic matter (OM) content was calculated by multiplying the Van Bemmelen correction factor equivalent to 1.7 by the organic carbon content, determined by the Walkley–Black extraction method. This factor is used assuming that, in soil organic matter, organic carbon (OC) participates with a value of 58% [32].
The available sulfur (S) content was determined by extraction with monocalcium phosphate and turbidimetric quantification; and available phosphorus (P) was determined through Bray II/Olsen extraction and colorimetric quantification [33,34]. The cation exchange capacity was calculated by the sum of extractable cations Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, and Al3+ + H+ in 1.0 M ammonium acetate at pH 7.0 and atomic absorption and atomic emission spectroscopy quantification methods. This method allows for the exchange of adsorbed bases with an ammonium acetate solution where the exchangeable bases were replaced with ammonium ions for subsequent quantification by measuring the light absorbed or emitted by excited-state atoms, using calibration curves with known standards [35].
2.4. Seedling Production
Piper marginatum seeds were collected from uncontaminated land not impacted by mining and propagated in a nursery. The development time in the nursery was three months and they were transferred to the study area for planting in the definitive site.
In each experimental plot, the plants were trained with distances of 2.2 m × 2.2 m between plants and rows, covering most of the land of the unit, using a grid spatial distribution.
During the time the plants were established in the field, they were provided with agronomic management, seeking to guarantee maximum survival. Composted bovine manure was used as fertilizer; in addition, hydrated hydrogel was used for moisture retention and plant development.
2.5. Sampling of Contaminated Plant Biomass
One hundred and twenty days after sowing, three samples of contaminated plant biomass were collected, composed of four plants from each experimental plot. The sampling of biomass contaminated with mercury was carried out in the nine plots established with Piper marginatum. Twelve plants were selected in each experimental plot to form three composite samples, made up of four plants, always spatially covering the field and choosing plants from the same sector as a subsample. The composite samples were divided into roots, stems, and leaves, obtaining 9 samples per plot; in the case of plot 12 it was not possible to obtain leaf samples, since the species did not develop properly, obtaining a total of 78 samples in the sampling.
The collection of plant biomass samples was performed using a stainless-steel paddle by collecting, in its entirety, the plant with as much of the root system as possible [16]. Subsequently, they were divided into roots, stems, and leaves using pruning shears and packed in paper bags for transport to the laboratory.
2.6. Processing and Analysis of Total Mercury in Soil Samples and Plant Biomass
The plant biomass samples were rinsed and weighed on a balance to guarantee a minimum delivery of 5 g to the laboratory; they were then dried in an oven at 30 °C for three days. After drying, they were processed in an electric mill, model Wiley TE-650/1, and packed in Ziploc bags duly labeled. The total mercury (THg) concentrations in soils and plants were determined using a Millestone DMA-80 direct mercury analyzer, according to EPA method 7473 (thermal decomposition, amalgamation, and atomic absorption spectrophotometry) [36]. For this, 10 mg of sample was weighed and subjected to controlled heating in an oxygenated decomposition furnace to liberate mercury from solid samples. The decomposition products were transported to an amalgamator that selectively trapped mercury; then, the amalgamator was heated, causing the release of mercury vapor, which was transported by the oxygen flow through absorbance cells located in the light path of a single-wavelength atomic absorption spectrophotometer. The absorbance (peak height or peak area) was measured at 253.7 nm as a function of the mercury concentration, allowing its value to be determined [36].
The analytical quality control of the methods used was evaluated in triplicate and certified reference materials were used for soil: SQC001—Metals in soils from Sigma Aldrich, and for plants: Trace and Minor Elements in Lichen IAEA-336 from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In soils, the coefficient of variation (CV) ranged from 4.2 to 8.5%; percent recovery ranged from 100 to 125% for doped samples and from 95 to 105% for Sigma Aldrich reference material SQC001—Metals in soils. For plants, the coefficient of variation (CV) ranged from 1.2 to 10%. The percent recovery ranged from 95 to 120% for doped samples and from 98 to 98.5% for the reference material Lichen IAEA-336 (with CV < 2%). The detection limit for Hg was 0.73 µg kg−1 in both plants and soil, calculated as three times the standard deviation of the blanks (n = 10).
2.7. Phytoremediation Indices in Plants and Mercury Removal in Soils
The bioconcentration factor (BCF) and translocation factor (TF) were calculated. The bioconcentration factor was calculated considering the mercury concentration in the plant roots and the total mercury concentration in the soil. The translocation factor was determined as the ratio between the mercury content in the leaves and the mercury concentration in the roots [37,38].
The phytoremediation capacity of Piper marginatum was established as a function of the difference between the initial and final average concentrations of T Hg in the soils of the planted plots, relative to the initial average concentration of Hg in the soil.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The experimental design was completely randomized with three plots without sowing and nine plots for sowing. The results were expressed as the median (minimum - maximum) or average ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 5). The data did not present a normal distribution when the Shapiro–Wilk test was applied; therefore, the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test and post hoc tests, such as the Conover and Bonferroni tests, were used to determine if there were statistically significant differences between mercury concentrations in soils and plants with a p-value of 0.05. The Wilcoxon non-parametric test for related samples was also used to compare the initial and final physicochemical properties of the soils. Relationships between soil physicochemical parameters and mercury concentrations were identified using Spearman’s correlation. The analyses were performed in STATGRAPHICS CENTURION XVI, SAS 9.4 (Statistical Analysis System) and supplemented in RStudio 1.4.1717.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Characterization
According to the results obtained in the initial characterization, the predominant textural class was sandy; however, in some samples, higher levels of clay and silt were found. The pH in both the control and experimental plots was acidic, varying from very strongly acidic (4.5–5.0) to strongly acidic (5.1–5.5).
The percentage of organic matter (OM) increased with time in all the experimental units, although not always significantly, except for plot 5, where there was a slight decrease. In general, before and after the process, the plots presented low values (<2%), with an average of 0.30%, which was to be expected as the soil was disturbed and washed during the gold extraction process. However, these results suggest an increase in %OM over time; this could probably be due to the release of exudates from plant roots and plant debris from the spontaneous vegetation cover growing in the plots.
The cation exchange capacity (CEC) values were low, with an average of 2.7 cmolc kg−1. Plot 2 registered the highest CEC value at 9.94 cmolc kg−1, probably due to the soil texture present in this unit, which reported the highest clay contents (44.4%), compared with the other plots. The S and P contents, on the other hand, registered low levels (<10 mg kg−1 and <15 mg kg−1), without significant differences, thus evidencing nutrient-poor soils.
Based on these characteristics, it can be inferred that soils in the study area have low retention of heavy metals such as Hg, which increases their mobility and bioavailability to plants because there is less retention of exchangeable ions as they are predominantly sandy, acidic soils with low CEC [39].
3.2. Total Mercury Content in Soils
There is evidence of Hg contamination in the soils, associated with the gold mining activity that is actively developed in the area. Mercury concentration showed statistically significant differences between experimental plots and controls (p < 0.05). Table 1 shows the total mercury concentrations obtained for each of the control and experimental plots.

Table 1.
Initial total mercury content in soils expressed as medians.
This confirms that mercury concentrations are not uniform, but irregular throughout the experimental plot, with peaks of concentration in some plots. As expected in a field-scale experiment, there was high variability in soil Hg concentrations throughout the site, observed among the different plots. This situation caused the results of the soil Hg analyses to show notable scatter in the data, which makes it difficult to represent statistically significant treatment effects for field-scale work. However, to reduce the problem of spatial variability, in this study, the division of the site into different plots and the mixing of soil by taking samples composed of several subsamples allowed us to obtain a more homogeneous matrix in each experimental plot, as shown by some significantly different values over time.
The highest concentration of T Hg was found in plot 4, with a record of 52,044.4 µg kg−1, being the highest value recorded in the study area and corresponding to the site where soil washing was carried out during mining activities. On the other hand, the plot with the lowest mean value of total mercury corresponded to experimental unit 12, with 60.8 µg kg−1. The results indicate peaks of mercury concentration in some areas of the experimental plot and high variability in the field, according to the high standard deviations found between the concentrations of the samples.
The mean T Hg value among all plots was 1680.6 µg kg−1, exceeding the Bn background value of 51 ± 3 µg kg−1, calculated from mercury concentrations in soils without agricultural use in other areas of Colombia [40]. Likewise, both the mean T Hg value in the area, as well as in the experimental plots and controls, exceeded the reference value of 28 ± 7 µg kg−1 calculated by Marrugo-Negrete et al. (2017), corresponding to non-contaminated Colombian soil [41], thus evidencing mercury contamination. The average value of 70 µg kg−1 for crust and soils in the world was exceeded [40,41].
Compared with other reported values of mercury in soils from areas with gold mining activity, it was determined that the range of 40.8 to 52,044.4 µg kg−1 in the study area exceeds the maximum value obtained by Quintanilla-Villanueva et al. (2020) in a mining area in Mexico with concentrations of 340 to 41.8 µg kg−1 [42]. Likewise, the maximum value of this study exceeds that reported by Xiao et al. (2017), with a maximum concentration of 23,700 µg kg−1, and by Tomiyasu et al. (2013), with a value of 7000 µg kg−1, in areas impacted by artisanal and small-scale gold mining [43,44]. However, this value did not exceed the mean concentrations of 70,800 µg kg−1 at active mining sites reported by Gyamfi et al. (2021) in an artisanal gold community in Ghana [45].
The concentrations obtained in this study are above those reported by Martínez et al. (2017) in agricultural soils at a distance of 3 km from the El Alacrán Mine, with maximum concentrations of 260 µg kg−1, and Viña-Pico (2021) in two zones of a mining liability in the same area, with an average of 184.2 ± 7.8 µg kg−1 [46,47]. For this same area, Marrugo-Negrete (2016) reported low (230 to 500 µg kg−1) and high (3200 to 6320 µg kg−1) concentrations, indicating that only plot 4 with an average value of 10,894.2 µg kg−1 and a maximum value of 52,044.4 µg kg−1 exceeded the concentrations found in the El Alacrán mine [16].
3.3. Relationship Between Soil Parameters and Mercury Content
Table 2 shows the correlation between soil chemical parameters and total mercury content. There were significant positive and negative correlations (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Spearman’s correlation matrix.
The HgT concentration was significantly and positively correlated with OM, P, and CEC. The bioavailability of Hg in soil is strongly influenced by OM, since it is highly correlated with total organic carbon and can influence Hg methylation by altering the speciation and availability of this contaminant; an increase in soil carbon can stimulate microbial activity, resulting in an increase in the production of MeHg, the most toxic and bioaccumulative form of Hg [48,49,50]. The functional groups of OM can facilitate binding with Hg due to their high affinity, being an important property in the mobility and toxicity that Hg can present in the study area [49]. In turn, cation exchange capacity (CEC) is one of the soil chemical properties that provides conditions for HgT fixation and immobilization in soils [51].
Total mercury showed no significant correlation with S. However, according to Guedron et al. (2009), Hg is associated with sulfur-containing functional groups [52], since there is a high affinity of mercury for this element [53,54]. Similar results were obtained by Rojas et al. (2008), where a correlation was found between the mercury and sulfur contents in soils of a mining sector in Venezuela due to the high binding capacity of these two elements [54]. Sulfur is considered as a key soil component that can affect the behavior of mercury in contaminated sites, causing an increase or decrease in mercury methylation [55], even though HgS is considered as the least toxic form of Hg due to its stability in soil [56].
CEC was positively correlated with OM and S, while it was negatively correlated with pH. The cation exchange capacity is related to the OM due to the carboxyl groups, which generate deionized sites, H+ release, and a decrease in pH, hence resulting in the negative correlation of CEC with pH [57,58].
The correlation of pH with HgT was not significant; however, this parameter is one of the most influential in the mobility and bioavailability of Hg to plants [59].
3.4. Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Process
3.4.1. Chemical Parameters After the Phytoremediation Process
The chemical parameters before and after the phytoremediation process are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Initial and final chemical parameters in the phytoremediation process.
The pH decreased in all plots, varying from an average value of 5.0 to 4.7 mg kg−1, There were significant differences in six of the nine plots with sowing; plots 9, 10, and 12 were those without significant reductions, possibly associated with their own physicochemical characteristics, given the impact of mining activity on them. On the other hand, in the control plots (without sowing), there were significant differences in pH reduction in all of them.
OM increased from an average value of 0.3 to 0.5 mg kg−1, where control plot 2 obtained the maximum average value of 1%, while in the experimental plots, plot 3 obtained the maximum percentage of 0.94%. Significant differences were only found in plots 2 and 7 without sowing, possibly associated with the existence of more spontaneous vegetation in the area, where legumes, grasses, sedges, and dicotyledons were observed, generating a decrease in pH; likewise, the rainfall in the area possibly favored the decrease in pH due to the washing of basic cations (Ca, Mg, and K) [60,61].
Sulfur values showed an average increase from 3.7 to 5.7 mg kg−1, with significant positive differences only in plot 1. The resulting values after the phytoremediation process remained well below the ideal levels of sulfur in the soil, thus generating difficulties in plant development, with evidence of chlorosis and growth retardation, associated in turn with low soil fertility. Different letters before and after in each plot indicate significant statistical differences (p < 0.05) using the Wilcoxon nonparametric test for related samples.
Phosphorus showed an average decrease across the entire study area from 2.3 to 1.85 mg kg−1, which are very low values, considering that phosphorus, like sulfur, is an essential macronutrient for plants [62]. A positive significant difference was only found in plot 5, with negative significant differences in plots 1, 8, 2, and 7. The cation exchange capacity showed significant positive differences in plots 6, 2, and 7, and negative differences in plot 1.
Plots 9, 10, and 12 did not show significant variations in any of their physicochemical properties, a situation associated with their initial conditions and the difficulty in plant survival, due to their state of deterioration and the predominant sandy texture, low moisture retention, and low OM content.
In general terms, there were no representative changes in the physicochemical properties of the soils associated with the phytoremediation process, taking into account that it is a slow process that involves different stages and external factors that may interfere with its efficiency; in addition, the process should be evaluated over a longer period of time in which the plants achieve greater development and a possible greater effect of the phytoremediation process can be observed. However, the recovery of degraded mining soils, such as the one discussed in this study, requires effective interventions to improve their fertility, structure, and ecological functionality. Organic amendments, such as compost (ecological revitalizer), sewage sludge, and stabilized organic wastes, have proven to be promising strategies, as they increase the organic matter content, improve water retention and soil structure, and favor microbial activity. In addition, these materials act as heavy metal immobilizing agents through adsorption, precipitation, and complexation mechanisms, reducing their bioavailability and toxicity to plants [63]. Compost, in particular, is considered a multifunctional soil improver, with positive effects on soil physical, chemical, and biological properties, although its direct fertilizer function may be moderate. The addition of organic fertilizers such as poultry manure and the controlled use of nitrogen have also enhanced plant growth and phytoremediation efficiency in species such as Solanum nigrum and Pentas lanceolata by increasing aerial biomass and cadmium removal [64,65]. Also, the combination with rhizospheric bacteria can enhance contaminant uptake and energize the soil microbiome [66]. Phytoremediation is presented as an environmentally viable and socially acceptable solution, especially suitable for large post-industrial or mining areas with low levels of organic compounds and nutrients. In this context, organic amendments not only restore soil quality, but also allow for the recycling of residues and by-products, thus contributing to the sustainable management of disturbed ecosystems.
3.4.2. Total Mercury Content After Phytoremediation Process
According to the statistical analysis, there were statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between concentrations of total mercury in the soil before and after the phytoremediation process in some of the plots, both experimental and controls, as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Initial and final total mercury concentrations in the phytoremediation process expressed as medians.
From these results, considering the average global concentration before and after the process, a contaminant removal rate of 37.3% was achieved in the experimental plots (Table 5), with statistically significant differences between the percentages of removal between plots (p < 0.05). This constitutes a relevant finding in terms of phytoremediation efficacy. However, it is important to note that this study, due to its design and scope, does not allow us to quantitatively differentiate the specific mechanisms responsible for this decrease, such as plant uptake, direct volatilization, or leaching of the metal.

Table 5.
T Hg removal rates in experimental plots and controls (process efficiency).
The accumulation of mercury in plant tissues (estimated at 109.2 µg kg−1 in roots, 80.6 µg kg−1 in stems, and 122.6 µg kg−1 in leaves) confirms the existence of an active process of uptake and translocation of the metal by the species, which supports its direct contribution to the removal of the contaminant from the soil. However, the total magnitude of Hg removed by the plant biomass alone does not explain the reduction recorded in the substrate, suggesting the possible concurrence of other physicochemical processes.
Among them, the volatilization of elemental Hg (Hg0) could have partially contributed to the decrease, especially in an environment with high solar radiation and low surface cover, conditions that favor the emission of gaseous mercury from the soil, even in the absence of vegetation [67]. Likewise, although it is recognized that Hg leaching is limited in tropical soils with high adsorption capacity, it can increase in scenarios of acidification or intense rainfall [68]. No visible soil losses or significant runoff were evident in the present study, suggesting that leaching was probably a minor contributing mechanism.
Consequently, the decrease in Hg in the soil should be interpreted as the result of the joint action of biotic and abiotic processes, among which phytoextraction plays a central, but not exclusive, role. Future research should incorporate specific tools for monitoring gaseous fluxes and leaching losses in order to quantify the relative weight of each mechanism in the total removal of the contaminant.
The highest percentage of removal occurred in plot 4 with a value of 62%; decreases were also reported in plots 1, 5, and 9 with values of 35. 2 and 47%, respectively; increases in average T Hg concentrations were reported in plots 3, 6, 8, 10, and 12.
On the other hand, in the control plots, there was an average increase of 23.5% in T Hg concentrations due to increases in plot 7 (Table 5).
The increase in mercury (Hg) concentrations in several experimental plots (3, 6, 8, 10, and 12) and in the control plot (7) can be explained by a spatial redistribution of the contaminant, mainly driven by environmental factors such as topography and heavy rainfall in the study area. During the study period, rainfall events favored surface runoff, moving contaminated soil particles from higher elevations to lower areas. According to the rainfall record of the Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales (IDEAM. (n.d.)) [69], the precipitation records in Ayapel for the months of February, March, April, and May during the year 2022 (last 4 months in which this research was developed) were 98.2, 92.2, 359.8, and 205.5 mm, respectively, far exceeding the average historical record of the last 30 years for those same months in the region: February (19.8 mm), March (49.1 mm), April (162.9 mm), and May (293.5 mm) [70].
This rain caused runoff processes generating movement of soil particles between the different units, mainly in those whose elevations were lower compared with the rest, presenting different slopes that favored the natural movement of water and therefore the accumulation of mercury in certain areas, given that this element tends to move between the aquatic environment and the soil, mainly by runoff or flooding, as occurs with different heavy metals [71,72]. This mobilization is particularly important in soils such as those in the study area, characterized by a sandy texture, low organic matter content, acidic pH, and low cation exchange capacity, conditions that favor the mobility and bioavailability of Hg. It is important to note that the effect of precipitation on mercury mobility increases when it is in labile forms, such as methylmercury (MeHg) or soluble salts. Its transport in the soil is conditioned by the interaction between the physical–chemical properties of the substrate, water saturation, the presence of organic matter, and microbial processes, such as sulfate reduction, which favors Hg2+ methylation. In waterlogged soils or soils with low oxygenation, mercury can be partially immobilized by forming stable compounds such as mercury sulfide (HgS), but heavy rains can reverse this immobilization and increase its availability. Studies in the Reda River basin in the southern Baltic have confirmed this pattern of mobility induced by extreme hydrometeorological events [73,74]. These findings underline the complexity of the processes regulating the distribution of mercury in soils and its persistence as a contaminant in terrestrial environments.
The decrease in mercury concentration in the control plots (2 and 11) is possibly associated with the spontaneous vegetation existing in the area that was explored, where the presence of species of the families Malvaceae, Onagraceae, Poaceae, Fabaceae, Verbenaceae, Malpighiaceae, Melastomataceae, Lorantaceae, Solanaceae, Rubiaceae, Cyperaceae, Mimosaceae, Dilleniaceae, and Verbenaceae was identified; some of these plants have been identified as natives with presence in sites impacted by mining and have been studied as possible heavy metal accumulators [16,38,75]. On the other hand, these results suggest that vegetation could have increased the mobility and availability of the metal, through chemical changes in the rhizosphere and through chemical and microbial effects induced by the composition of the litter and root, generated in the process [76]. This change could represent the first step for Hg solubilization and subsequent plant uptake, which probably requires more time for evaluation. This finding, although not the central focus of the analysis, reveals active environmental processes affecting mercury dynamics in systems without vegetation cover, and indirectly highlights the stabilizing role of vegetation in contaminated soils.
One possible explanation for this increase is related to the atmospheric deposition of Hg, a phenomenon widely documented in areas with intense artisanal mining activity, such as the municipality of Ayapel. During gold amalgamation, volatile forms of mercury are released and can return to the soil through dry or wet deposition, especially in exposed areas without vegetation cover to act as an interception barrier [68]. This process may contribute to a net Hg input in the unvegetated plots during the experimental period.
In addition, it is likely that processes of surface erosion and local redeposition of contaminated particles have occurred, facilitated by the lack of vegetation cover and by rainfall events in a terrain with microseepage, although of moderate slope. This redistribution of Hg bound to fine soil particles could have generated a differential accumulation in certain control plots.
Another factor to consider is the possibility of cross-contamination, since the field work included agronomic activities in the treated plots. Although measures were put in place to avoid interference, the transfer of contaminated particles by wind, runoff, or handling of plant material cannot be completely ruled out.
Finally, seasonal variations in the edaphic dynamics of mercury may also have played a role. Factors such as soil moisture, temperature, and microbial activity have been documented to affect Hg speciation and mobility, which may result in the surface redistribution of the metal in soils without plant protection [68,77].
Despite the existence of mercury removal in the soil by Piper marginatum plants, they did not adapt adequately to the physicochemical conditions of the soil, mainly due to the low retention of moisture in the soil and the low amount of nutrients for their adequate development. This low adaptation and development of Piper marginatum plants in these plots significantly limited the absorption and extraction of mercury. Adverse soil conditions, especially low water retention and a shortage of essential nutrients, prevented the plants from achieving optimal development, which reduced their effectiveness in stabilizing or removing mercury from the soil. This explains why, in plots like plot 4, where significant reductions in mercury concentration were recorded, the result was opposite, likely due to improved conditions at certain sampling points that partially favored plant performance. Given that these soils were subjected to constant washing processes, the phytoremediation process is limited, because it prevents the plants from adequately completing their life cycle [78]. Likewise, the efficiency of the phytoremediation process depends on several influencing factors, such as the type of plant, the period used, the cultivation cycles, the climatic conditions of the area, and the physicochemical parameters of the soil, requiring months and even years for an effective process for a complete rehabilitation of the impact generated [79,80].
3.5. Hg Concentration in Plant Tissues of Piper marginatum and Phytoremediation Indexes
According to the results obtained, the plant tissues (roots, stems, and leaves) of Piper marginatum showed T Hg accumulation values, as shown in Figure 2. Statistically significant differences between the plots were only found for the concentrations in the stems (p < 0.05).
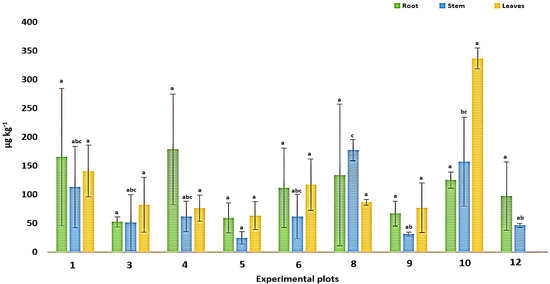
Figure 2.
HgT concentrations in plant organs. Different letters between plots indicate significant statistical differences (p < 0.05) using Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test.
T Hg accumulation in the plots presented the following order: leaves > roots > stems, with a mean concentration of mercury in the leaves of 122.60 µg kg−1, identifying a maximum of 356.32 µg kg−1 in plot 10, followed by the roots, with a mean value of 109.22 µg kg−1, and the stems, with an average of 80.62 µg kg−1. There was a tendency of accumulation in the roots and its rapid diffusion to the leaves, where the greatest accumulation occurred, being transferred by the stems, since its main function is the transport of nutrients from the roots to the aerial parts (leaves) [38]; likewise, Hg could reach the leaves by volatilization and be captured by the stomata [81]. When herbaceous plants such as Piper marginatum are subjected to periods of stress by heavy metal contents in the soil, the highest accumulations occur in the roots and leaves, as observed in this study [37,82]. The pattern of accumulation observed in Piper marginatum (leaves > roots > stems) suggests the existence of physiological and biochemical mechanisms associated with differential translocation and compartmentalization of mercury within the plant. The higher concentration of the metal in leaves indicates a probable efficient translocation through the xylem, possibly in the form of complexes with organic acids or organometallic compounds, as has been described in species with phytoextraction capacity [26,29,83]. This strategy may represent a tolerance mechanism in which mercury is sequestered in less sensitive tissues, such as leaf cell vacuoles, thus minimizing its toxicity at the cytoplasmic level [77,84].
The low accumulation in stems could be related to a mainly structural function of this tissue, with a limited capacity to store heavy metals, while the intermediate concentration observed in roots could be due to processes of root exclusion, immobilization in the rhizosphere, or adsorption in the apoplast, phenomena described in plants native to contaminated environments [77]. In addition, it has been proposed that certain species of the genus Piper present metabolic adaptations that favor detoxification in photosynthetic tissues, associated with secondary metabolism pathways.
This pattern has been reported in other species with phytoremediation potential, such as Jatropha curcas, Cecropia peltata, Limnocharis flava, and macrophytes growing in tropical wetlands, in which aerial accumulation exceeds root accumulation under specific conditions of contaminant bioavailability [39,83,85,86,87]. These findings reinforce the potential of Piper marginatum as a native species suitable for mercury phytoextraction, while opening questions about the molecular mechanisms involved, which should be the subject of future studies.
Bioconcentration and translocation factors were calculated for each plot to determine the capacity of the Piper marginatum plant to retain Hg from the soil and move it to the leaves. An average BCF among all plots of 0.3 and an average TF of 1.4 was obtained. In plot 12, it was not possible to calculate the TF, since the plants had no leaves, showing that they were not adaptable to the soil conditions. There were statistically significant differences between the BCF values (p < 0.05), while for the TF, there were no significant differences (Figure 3). A single average value with BCF > 1 was obtained in plot 12 corresponding to 1.2, while TF > 1 was reported in 8 of the 9 experimental plots, with a maximum average value in plot 10 of 2.7. The data obtained indicate that the BCF of Piper marginatum in the present study is below that reported by Marrugo-Negrete et al. (2016), with a value of 0.9; meanwhile, the TF exceeds the reported 0.6 [16]. This factor represents a possible approximation to the level of bioavailability of mercury to plants, since it is influenced by the concentration of mercury in the soil, pH, organic matter, texture, cation exchange capacity, iron, and aluminum oxide and sulfate concentrations, which are highly interrelated, and it is difficult to identify individually their contribution to the process of the accumulation of this metal in plant organs [59,88].
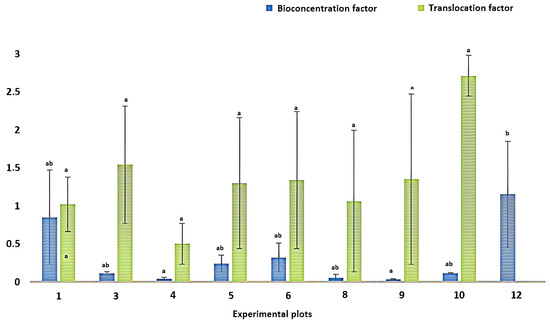
Figure 3.
Translocation and bioconcentration factors. Different letters between plots indicate significant statistical differences (p < 0.05) using Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test.
The evaluation of Piper marginatum in mercury-contaminated soils yielded an average bioconcentration factor (BCF) of 0.3, reflecting a low ability to absorb the metal from the substrate. However, the translocation factor (TF) was higher than 1, indicating an efficient mobilization of the absorbed Hg to aerial organs. This ratio of BCF < 1 and TF > 1 suggests that, although the plant has internal transport mechanisms that favor accumulation in harvestable tissues, the limited initial uptake restricts its usefulness as a phytoextractant. These results differ from those observed by Monteiro et al. (2024), who reported in Paspalum repens an average BCF of 1.3 in roots and only 0.41 in aerial tissues, accompanied by an average TF of 0.1, which indicates high subway accumulation and scarce translocation, favoring phytostabilization over phytoextraction [89]. For their part, Figueira et al. (2012) documented, in Juncus maritimus, BCF values between 2.4 and 5.8 in roots, with a consistently low TF (<0.05), confirming that root retention of Hg limits its effective removal, but contributes to the immobilization of the metal in sediments [90]. In the study by Noverita and Tjiong (2017), BCF > 1 was observed for Cu and Zn in Avicennia and Rhizophora roots, with TF > 1 for some metals, although not specifically for Hg, highlighting that only species with high efficiency in both factors can be considered phytoextractives [91]. Finally, Moreno-Jiménez et al. (2006) identified, in Rumex induratus and Marrubium vulgare, a bioaccumulation capacity (BAF) lower than 1 for available Hg, together with evidence of moderate translocation, mainly in Rumex induratus, which supported their classification as candidate species for phytoremediation, although with emphasis on tolerance and not on contaminant removal [92]. In this context, Piper marginatum, with its low capacity to extract mercury from the edaphic resource, does not constitute a viable alternative for the practical phytoextraction of Hg in highly contaminated soils.
The environmental conditions present during the experiment had a significant influence on the growth of Piper marginatum and, consequently, on its ability to absorb and translocate mercury.
The growth of plants in the genus Piper can be affected by environmental conditions, such as high solar radiation and intense rainfall. A study conducted by Pacheco et al. (2013) on Piper aduncum found that photosynthetic activity and the production of photosynthetic pigments varied significantly under different levels of irradiance, indicating that light intensity influences the metabolism and growth of these plants [93]. Additionally, research on related species, such as Piper auritum and Piper aequale, has shown that intense solar radiation can induce photooxidative stress, negatively affecting photosynthesis and growth [94]. Likewise, intense rainfall can alter nutrient and water availability, impacting plant development. The study site, characterized by soils impacted by gold mining, presented unfavorable edaphic conditions, such as low organic matter content, high surface temperature, low vegetation cover, and fluctuations in soil moisture. These adverse conditions generate abiotic stress that can limit both vegetative development and physiological mechanisms associated with heavy metal uptake.
In particular, high irradiance and soil surface temperatures can induce alterations in leaf physiology, decreasing photosynthetic efficiency, reducing the effective leaf area, and affecting biomass growth, which directly affects phytoextraction capacity [95]. On the other hand, edaphic humidity, presenting marked variations during the trial, could have influenced the solubility and mobility of mercury in the soil. Although low humidity can reduce Hg bioavailability, it has also been reported that certain wetting pulses transiently increase its availability, facilitating root uptake [77,96,97]. These dynamic interactions between plant, soil, and climatic environment conditions impact the effectiveness of the phytoremediation process, which must be understood as the result of multiple synergistic factors.
4. Conclusions
Artisanal gold mining activities in the evaluated region have resulted in significant mercury concentrations in soils, with values ranging from 40.80 to 52,044.4 µg kg−1 in the experimental plots and from 55.9 to 2587.4 µg kg−1 in the controls. In this scenario, the native species Piper marginatum contributed to an average reduction of 37.3% in the mercury concentration in the plots established with the plants, in contrast to an increase of 23.5% in the unplanted controls. Similarly, the average total mercury concentrations in root, stem and leaves were estimated to be 109.22 µg kg−1, 80.62 µg kg−1, and 122.60 µg kg−1, respectively. This accumulation pattern, together with bioconcentration factors (BCFs) lower than 1 and translocation factors (TFs) higher than 1, suggests an efficient transfer of the metal to the aerial part, a key mechanism in phytoextraction. Under the evaluated scenario, Piper marginatum presented an average bioconcentration factor (BCF) of 0.3 (<1), which shows low absorption of mercury from the soil. Although the translocation factor (TF) was greater than 1, a BCF < 1 suggests that, even though the plant was efficient in mobilizing mercury from the root system to the above-ground plant tissue, any real use for phytoextraction will be limited in terms of what the plant extracts from the soil, so the species did not demonstrate practical potential to remove Hg from the soil under the conditions of this study.
The remediation process was conditioned by the physicochemical parameters of the soil, characterized by a predominantly sandy texture, low moisture retention, acid pH, and low nutrient content, including organic matter below 2%. These limitations reduced the optimal biomass growth and thus the overall mercury removal efficiency in some plots. The heterogeneous behavior of contaminant level across plots also reveals the influence of processes such as runoff and metal redistribution inherent to soils disturbed by intensive mining practices.
Taken together, these findings indicate that, despite unfavorable soil conditions, Piper marginatum can be considered within a comprehensive environmental remediation strategy for mercury-contaminated sites. The implementation of organic amendments, pH correctors, and other practices that improve the substrate, together with the extension of the establishment period and the diversification of native species, could enhance the root and foliar development of this plant. All of this would ultimately increase the metal absorption and translocation capacity, contributing to a more effective ecological restoration of soils affected by gold mining.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.l.R.-M. and M.V.-P.; methodology, M.D.l.R.-M. and M.V.-P.; software, M.D.l.R.-M.; validation, M.D.l.R.-M., M.V.-P. and J.M.-N.; formal analysis, M.D.l.R.-M. and M.V.-P.; investigation, M.D.l.R.-M., M.V.-P. and J.M.-N.; resources, J.M.-N.; data curation, M.D.l.R.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.l.R.-M. and M.V.-P.; writing—review and editing, M.D.l.R.-M., M.V.-P. and J.M.-N.; visualization, M.D.l.R.-M. and M.V.-P.; supervision, J.M.-N.; project administration, J.M.-N.; funding acquisition, J.M.-N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded for the project “IMPLEMENTATION OF A SUSTAINABLE STRATEGY FOR THE RECOVERY OF DEGRADED AND CONTAMINATED ECOSYSTEMS WITH MERCURY GENERATED BY MINING IN THE DEPARTMENTS OF CÓRDOBA, SUCRE, CHOCÓ” with BPIN code: 2020000100055.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because they are part of an ongoing study. Requests for access to the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the University of Córdoba and the Laboratories of Toxicology and Environmental Management and Soils and Water, A special thanks for funding the research to the project “IMPLEMENTATION OF A SUSTAINABLE STRATEGY FOR THE RECOVERY OF DEGRADED AND CONTAMINATED ECOSYSTEMS WITH MERCURY GENERATED BY MINING IN THE DEPARTMENTS OF CÓRDOBA, SUCRE, CHOCÓ” with BPIN code: 2020000100055, and to all of the work team that participated in it.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BCF | Bioconcentration factor |
| TF | Translocation factor |
| CEC | Cation exchange capacity |
| OM | Organic matter |
| OC | Organic carbon |
References
- Yevugah, L.L.; Darko, G.; Bak, J. Does mercury emission from small-scale gold mining cause widespread soil pollution in Ghana? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 116945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansah, E.; Bak, J.L.; Sørensen, P.; Darko, G. Modelling mercury concentration in Ghanaian soil. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, G.; Yan, Z. Status and environmental management of soil mercury pollution in China: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MME/Unicor. Concentraciones de Mercurio en Aire y en Suelo, en las Zonas de Influencia Minera de los Diez Principales Departamentos productores de oro en Colombia; Convenio GGC 524. Informe Ejecutivo; Ministerio de Minas y Energía: Bogotá, Colombia, 2017; 33p. [Google Scholar]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Benitez, L.N.; Olivero-Verbel, J.; Lans, E.; Gutierrez, F.V. Spatial and seasonal mercury distribution in the Ayapel Marsh, Mojana region, Colombia. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2010, 20, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Díez, S. Speciation and bioavailability of mercury in sediments impacted by gold mining in Colombia. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Geochemistry of mercury in tropical swamps impacted by gold mining. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CVS/INGEOMINAS. Inventario y Diagnóstico Minero Ambiental del Departamento de Córdoba; Monografía municipio Ayapel; Convenio interadministrativo 029–2003; Ministerio De Minas y Energía: Bogotá, Colombia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- MME/UPME/Unicor. Estudio de la Cadena de Mercurio en Colombia con Énfasis en la Actividad Minera de Oro; Ministerio De Minas y Energía: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014; Volume 3, 253p. [Google Scholar]
- MME/UPME/Unicor. Incidencia Real de la Minería del Carbón, del oro y del Uso del Mercurio en la Calidad Ambiental con Énfasis Especial en el Recurso Hídrico—Diseño de Herramientas para la Planeación Sectorial; Ministerio De Minas y Energía: Bogotá, Colombia, 2015; 663p. [Google Scholar]
- Negrete, J.M.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Paternina–Uribe, R.; Quiroz-Aguas, L.; Pacheco-Florez, S. Distribución espacial y evaluación de la contaminación ambiental por mercurio en la región de la Mojana, Colombia. Rev. Mvz Cordoba 2018, 23, 7062–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, L.; Marrugo, J.L.; Alvis, E. Contaminación por mercurio en humanos y peces en el municipio de Ayapel, Córdoba, Colombia 2009. Rev. Fac. Nac. Salud Pública 2010, 28, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo, J.; Lans, E.; Benítez, L. Hallazgo de mercurio en peces de la Ciénaga de Ayapel, Córdoba, Colombia. Rev. MVZ Cordoba 2007, 12, 878–886. Available online: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=69312103 (accessed on 21 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.L.; Urango-Cardenas, I.D.; Núñez, S.M.B.; Díez, S. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in the mining area of the San Jorge river basin, Colombia. Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2014, 7, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Camacho, C.; Salas-Moreno, M.; Marrugo-Madrid, S.; Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Díez, S. Dietary human exposure to mercury in two artisanal small-scale gold mining communities of northwestern Colombia. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Marrugo-Madrid, S.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Durango-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Screening of native plant species for phytoremediation potential at a Hg-contaminated mining site. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 542, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, A.M.Z. Diagnóstico Ambiental de la Ciénaga de Ayapel a Través de la Variación Temporal de los Aspectos Morfo Funcionales del Fitoplancton y un Indicador de Calidad Ecológica. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Antioquia, Medellín, Columbia, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10495/9074 (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Guimaraes, J.R.; Meili, M.; Hylander, L.D.; de Castro e Silva, E.; Roulet, M.; Mauro, J.B.; de Lemos, R. Mercury net methylation in five tropical flood plain regions of Brazil: High in the root zone of floating macrophyte mats but low in surface sediments and flooded soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2000, 261, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Dai, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Tan, X.; Peng, C.; Ali, I.; Naz, I. A critical review on the phytoremediation of heavy metals from environment: Performance and challenges. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.-A.; Urbanovich, O.; Nagorskaya, L.; Li, X.; Tang, L. A review on phytoremediation of mercury contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Torres, Y.; Caballero-Gallardo, K.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Mercury pollution by gold mining in a global biodiversity hotspot, the Choco biogeographic region, Colombia. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brú, J.; Guzman, J.D. Folk medicine, phytochemistry and pharmacological application of Piper marginatum. Rev. Bras. de Farm. 2016, 26, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.d.O.; Santos, B.d.O. Constituents from Piper marginatum fruits. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant-Archibold, A.A.; Santana, A.I.; Gupta, M.P. Ethnomedical uses and pharmacological activities of most prevalent species of genus Piper in Panama: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 217, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, And Soils; Revision 2; Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macci, C.; Doni, S.; Peruzzi, E.; Bardella, S.; Filippis, G.; Ceccanti, B.; Masciandaro, G. A real-scale soil phytoremediation. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Metal uptake, transport and release by wetland plants: Implications for phytoremediation and restoration. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilon-Smits, E. Phytoremediation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Geográfico Agustín Codazzi. Métodos Analíticos del Laboratorio de Suelos, Sexta Edición; IGAC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- NTC 5264:2018; Calidad del Suelo. Determinación del pH. Segunda actualización, Numeral 5, Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación—ICONTEC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2018.
- Barrezueta-Unda, S.; Cervantes-Alava, A.; Ullauri-Espinoza, M.; Barrera-Leon, J.; Condoy-Gorotiza, A. Evaluación del Método de Ignición para Determinar Materia Orgánica en Suelos de la Provincia El Oro-Ecuador. FAVE Sección Cienc. Agrar. 2020, 19, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTC 5402:2006; Calidad del Suelo, determinación del azufre disponible. 2 numeral 4.4.1. Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación—ICONTEC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2006.
- NTC 5350:2020; Calidad del suelo. Determinación de fósforo disponible. Segunda actualización Numerales 5.4. y 5.5; Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación—ICONTEC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020.
- NTC 5349:2016; Calidad de suelo. Determinación de las bases cambiables: Método del acetato de amonio 1M pH 7.0. Instituto Colombiano de Normas Técnicas y Certificación—ICONTEC: Bogotá, Colombia, 2016.
- SW-846Method 7473: Mercury in Solids and Solutions by Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry, Revision 0 ed; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 1–17. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-07/documents/epa-7473.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Qin, H. Bioconcentration and translocation of heavy metals in the soil-plants system in Machangqing copper mine, Yunnan Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 200, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Yánez, E.V.; Martínez-Macea, M.A.; Enamorado-Montes, G.; Caballero, E.C.; Marrugo-Negrete, J. Phytoremediation of Soils Contaminated with Heavy Metals from Gold Mining Activities Using Clidemia sericea D. Don. Plants 2022, 11, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Durango-Hernández, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Olivero-Verbel, J.; Díez, S. Phytoremediation of mercury-contaminated soils by Jatropha curcas. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Combatt, E.M.; Bravo, A.G.; Díez, S. Flood-induced metal contamination in the topsoil of floodplain agricultural soils: A case-study in Colombia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Villanueva, G.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, M.; Guzmán-Mar, J.; Torres-Gaytan, D.; Hernández-Ramírez, A.; Orozco-Rivera, G.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L. Mobility and speciation of mercury in soils from a mining zone in Villa Hidalgo, SLP, Mexico: A preliminary risk assessment. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyasu, T.; Kono, Y.; Kodamatani, H.; Hidayati, N.; Rahajoe, J.S. The distribution of mercury around the small-scale gold mining area along the Cikaniki river, Bogor, Indonesia. Environ. Res. 2013, 125, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Li, R.H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Z.Q. Soil heavy metal contamination and health risks associated with artisanal gold mining in Tongguan, Shaanxi, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyamfi, O.; Sørensen, P.B.; Darko, G.; Ansah, E.; Vorkamp, K.; Bak, J.L. Contamination, exposure and risk assessment of mercury in the soils of an artisanal gold mining community in Ghana. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, Z.; González, M.S.; Paternina, J.; Cantero, M. Contaminación de suelos agrícolas por metales pesados, zona minera El Alacrán, Colombia. Temas Agrar. 2017, 22, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, M.A.V. Recuperación de un Suelo Mediante Fitorremediación con Jatropha curcas L. como una Estrategia Para el Manejo de Pasivos Ambientales Mineros en el Norte de Colombia. 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.unicordoba.edu.co/entities/publication/c7b28f9b-d21e-49b8-8371-d9fe09218ed0/full (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Hu, H.; Gao, Y.; Tan, W.; Xi, B. Effects of dissolved organic matter on mercury speciation in rice rhizosphere amended with sulfur-rich biochar. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckley, C.S.; Luxton, T.P.; Stanfield, B.; Baldwin, A.; Holloway, J.; McKernan, J.; Johnson, M.G. Effect of organic matter concentration and characteristics on mercury mobilization and methylmercury production at an abandoned mine site. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 271, 116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.P. Influencia de las Variables Ambientales en la Estructura de las Comunidades Bentónicas y su Relación con el flujo de Mercurio en la Bahía de Buenaventura. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Palmira Valle, Colombia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Trinidad, S.; Hernández-Silva, G.; Heydrich, S.C. Metodología para establecer la relación del mercurio total con propiedades físicas y químicas del suelo en San Joaquín, Qro., México. Actas Del INAGEQ 2013, 19, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Guedron, S.; Grangeon, S.; Lanson, B.; Grimaldi, M. Mercury speciation in a tropical soil association; Consequence of gold mining on Hg distribution in French Guiana. Geoderma 2009, 153, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, X. El mercurio Como Contaminante global: Desarrollo de Metodologías Para su Determinación en Suelos Contaminados y Estrategias Para la Reducción de su Liberación al Medio Ambiente. 2004. Available online: https://www.tdx.cat/bitstream/handle/10803/3174/xgm1de1.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- De Astudillo, L.R.; Prin, J.L.; Noriega, J.; Albornoz, L.A.; Hidalgo-Prada, B.; Ramírez, A. Determinación de mercurio en suelos del sector minero las claritas, estado bolívar, mediante procesos analiticos de especiación y microscopía electrónica de barrido (Meb), Saber. Rev. Multidiscip. Del Cons. De Investig. De La Universidad de Oriente 2008, 20, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhu, N.; Chao, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, D.; et al. Mobilization and methylation of mercury with sulfur addition in paddy soil: Implications for integrated water-sulfur management in controlling Hg accumulation in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sysalová, J.; Kučera, J.; Drtinová, B.; Červenka, R.; Zvěřina, O.; Komárek, J.; Kameník, J. Mercury species in formerly contaminated soils and released soil gases. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 584-585, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaradat, A.A.; Johnson, J.M.; Weyers, S.L.; Barbour, N.W. Determinants and Prediction of Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio in Five Diverse Crop Plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 40, 2688–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Mora, E.; Hernández-Vázquez, M.; Luna-Zendejas, H.; Ortiz-Ortíz, E.; García-Gallegos, E. Evaluación del contenido de materia orgánica en suelos agrícolas y su relación carbono/nitrógeno. Rev. Iberoam. De Ciencias 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Yang, J.; Hussain, J.; Sattar, A.; Ullah, S.; Hussain, I.; Rahman, S.U.; Zandi, P.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Mercury fractionation, bioavailability, and the major factors predicting its transfer and accumulation in soil–wheat systems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 847, 157432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.L. Efectos del Biochar, Bokashi y Compost en las Dinámicas del Carbono y Nitrógeno en Suelos con pH Contrastados. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de Jaén, Jaén, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yerima, B.; Enang, R.; Kome, G.; Van Ranst, E. Exchangeable aluminium and acidity in Acrisols and Ferralsols of the north-west highlands of Cameroon. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 23, e00343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiling, M.; von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Factors influencing phosphorus placement and effects on yield and yield parameters: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 216, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelak, A. Organic soil amendments in the phytoremediation process. In Phytoremediation: Management of Environmental Contaminants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 21–39. ISBN 9783319418117. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Srivastava, M.; Chiu, S.; Zhan, J.; Wu, Z.; Sun, T. Effect of fertilizer amendments on phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil by a newly discovered hyperaccumulator JSolanum nigrum L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-T.; Lee, M.-C.; Wu, C.-W.; Lai, Y.-H. Nitrogen fertilization promotes the phytoremediation of cadmium in Pentas lanceolata. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2013, 85, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titah, H.S.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Mushrifah, I.; Anuar, N.; Basri, H.; Mukhlisin, M. Effect of applying rhizobacteria and fertilizer on the growth of Ludwigia octovalvis for arsenic uptake and accumulation in phytoremediation. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.S.; E Lindberg, S.; Austin, K.; Coolbaugh, M.; Vette, A.; Zhang, H. Assessing the contribution of natural sources to regional atmospheric mercury budgets. Sci. Total. Environ. 2000, 259, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skyllberg, U. Chemical speciation of mercury in soil and sediment. In Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology of Mercury; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 219–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible de Colombia, Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales (IDEAM). Datos Consultados de las Estaciones Meteorológicas del Catálogo Nacional de Estaciones: CECILIA [25020780], AYAPEL–AUT [25025030] y MARRALU–AUT [25027770]. Available online: http://dhime.ideam.gov.co/atencionciudadano/ (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Federación Nacional de Arroceros (FEDEARROZ). Histórico Región—Al día con el clima. Datos Consultados de las Estaciones meteorológicas del Catálogo Nacional de Estaciones: CECILIA [25020780], AYAPEL–AUT [25025030] y MARRALU–AUT [25027770]. Available online: https://clima.fedearroz.com.co/historico-region/ (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Ramírez-Morales, D.; Rodríguez-Artavia, B.; Sáenz-Vargas, W.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, R.; Villalobos-González, W.; Mora-Barrantes, J.C. Minerías artesanales para la extracción de oro mediante el uso de mercurio: Estado del arte del impacto ambiental en los medios agua, aire y suelo. Rev. Tecnol. En Marcha 2019, 32, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, J. Heavy metals and soil fertility at NChannelirrigation, Puno, Peru. Manglar 2021, 18, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Baczewska-Dąbrowska, A.H. Mercury in the terrestrial environment: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębka, K.; Saniewska, D.; Bełdowska, M. Mobility of mercury in soil and its transport into the sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8492–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Karwadiya, J.; Srivastava, S.; Patra, P.K.; Venugopalan, V. Potential of indigenous plant species for phytoremediation of arsenic contaminated water and soil. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 175, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowack, B.; Schulin, R.; Luster, J. Metal fractionation in a contaminated soil after reforestation: Temporal changes versus spatial variability. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3272–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Sharma, A. Mercury toxicity in plants. Bot. Rev. 2000, 66, 379–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, F.J.M. Physiological functions of mineral macronutrients. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Dumat, C. A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 182, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Daverey, A. Phytoremediation: A multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Durango-Hernández, J.; Díaz-Fernández, L.; Urango-Cárdenas, I.; Araméndiz-Tatis, H.; Vergara-Flórez, V.; Bravo, A.G.; Díez, S. Transfer and bioaccumulation of mercury from soil in cowpea in gold mining sites. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, S. Phytoextraction potential of heavy metals by native wetland plants growing on chlorolignin containing sludge of pulp and paper industry. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant science: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, N.; Hermans, C.; Schat, H. Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Enamorado-Montes, G.; Durango-Hernández, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Removal of mercury from gold mine effluents using Limnocharis flava in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, S.E.R.; Negrete, J.L.M.; Rios, J.E.A.; Hadad, H.R.; Maine, M.A. Hg, Cu, Pb, Cd, and Zn Accumulation in Macrophytes Growing in Tropical Wetlands. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 216, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durango, J.V.V.; Negrete, J.L.M.; Jaramillo, B.C.; Perez, L.M.C. Remediación de suelos contaminados con mercurio utilizando guarumo (Cecropia peltata). Ing. Y Desarro. 2010, 27, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Yang, J.; Hussain, J.; Hussain, I.; Kumar, M.; Ullah, S.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X.; Jia, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. Phytoavailability and transfer of mercury in soil-pepper system: Influencing factors, fate, and predictive approach for effective management of metal-impacted spiked soils. Environ. Res. 2021, 207, 112190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.C.; Vieira, L.C.G.; Bernardi, J.V.E.; Rodrigues, Y.O.S.; de Mesquita, L.P.B.; de Souza, J.P.R.; Sena, G.; Oliveira, I.A.d.S.; Cabral, C.d.S.; Júnior, J.F.G.; et al. Mercury Bioconcentration and Translocation in Rooted Macrophytes (Paspalum repens Berg.) from Floodplain Lakes in the Araguaia River Watershed, Brazilian Savanna. Water 2024, 16, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, E.; Freitas, R.; Pereira, E.; Duarte, A. Mercury uptake and allocation in Juncus maritimus: Implications for phytoremediation and restoration of a mercury contaminated salt marsh. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takarina, N.D.; Pin, T.G. Bioconcentration Factor (BCF) and Translocation Factor (TF) of Heavy Metals in Mangrove Trees of Blanakan Fish Farm. Makara J. Sci. 2017, 21, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Gamarra, R.G.; Carpena-Ruiz, R.O.; Millán, R.; Peñalosa, J.; Esteban, E. Mercury bioaccumulation and phytotoxicity in two wild plant species of Almadén area. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, F.V.; Silveira, H.R.d.O.; Alvarenga, A.A.; Alvarenga, I.C.A.; Pinto, J.E.B.P.; Lira, J.M.S. Gas Exchange and Production of Photosynthetic Pigments of Piper aduncum L. Grown at Different Irradiances. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 04, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco-Ojanguren, C.; Pearcy, R.W. Stomatal dynamics and its importance to carbon gain in two rainforest Piper species—I. VPD effects on the transient stomatal response to lightflecks. Oecologia 1993, 94, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Levizou, E.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Sebastian, A.; Baum, C.; Prasad, M.N.; Wenzel, W.W.; Rinklebe, J. Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: Phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation–A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasat, M.M. Phytoextraction of Metals from Contaminated Soil: A Review of Plant/Soil/Metal Interaction and Assessment of Pertinent Agronomic Issues. J. Hazard. Subst. Res. 1999, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumins, J.A.; Goodey, N.M.; Gallagher, F. Plant–soil interactions in metal contaminated soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).