Microbial Diversity and Heavy Metal Resistome in Slag-Contaminated Soils from an Abandoned Smelter in Chihuahua, Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Metagenomic Data Analysis
2.5. Analysis of MRGs
2.6. Metagenome-Assembled Genomes (MAGs)
3. Results
3.1. Soil Major Characteristics
3.2. Composition, Abundance, and α-Diversity of Microbial Communities
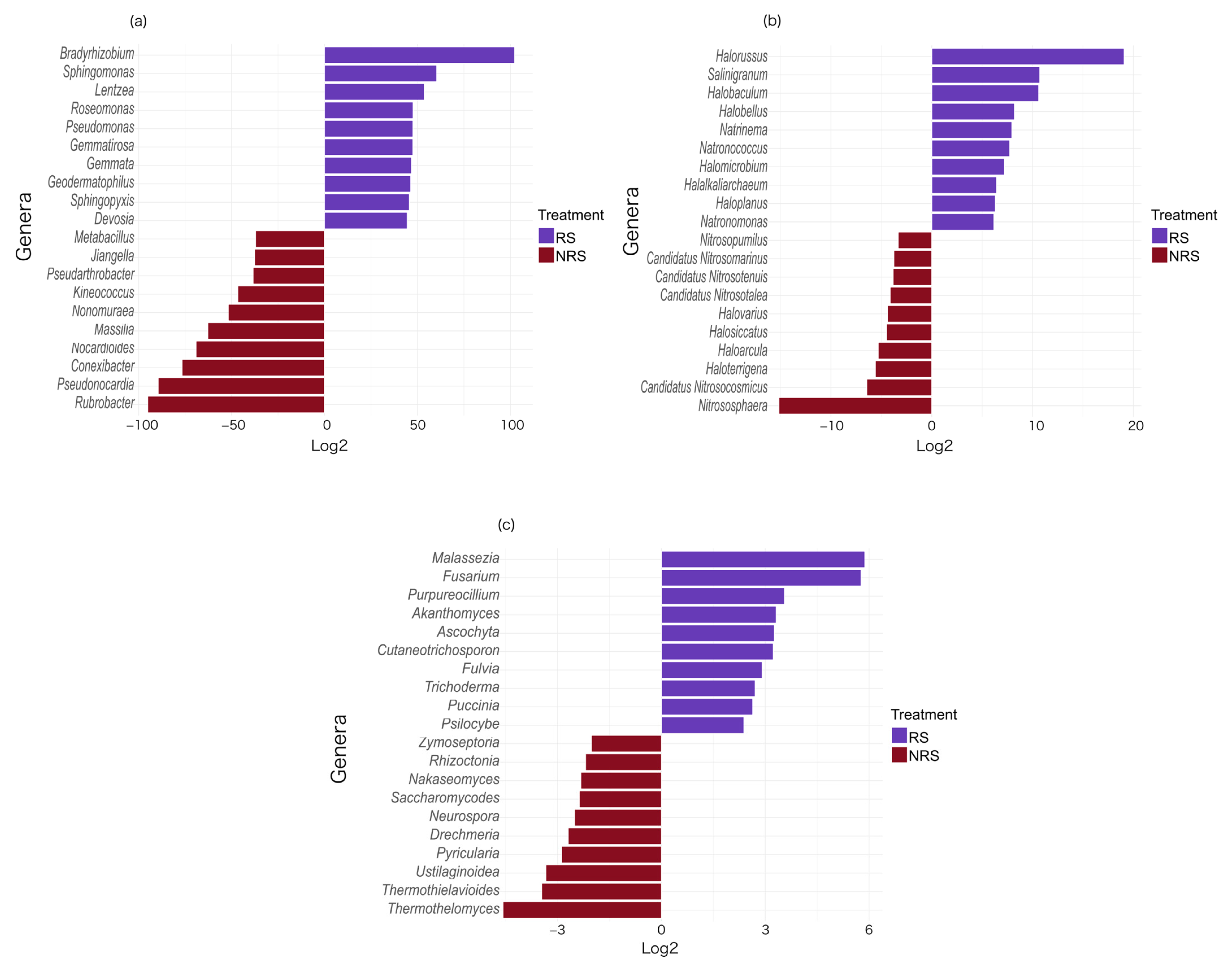
3.3. ALDEx2 Analysis
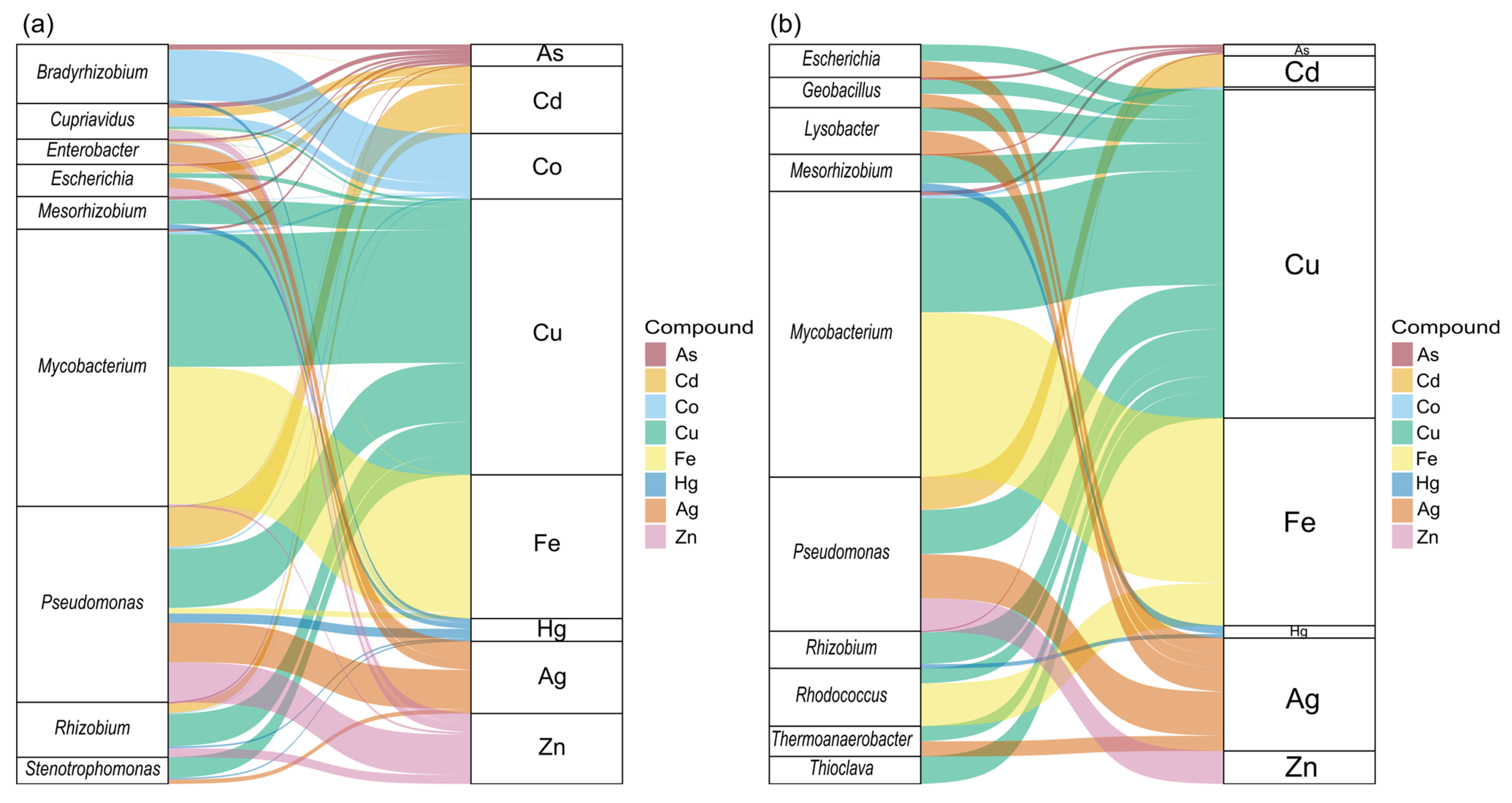
3.4. Identification and Abundance of MRGs
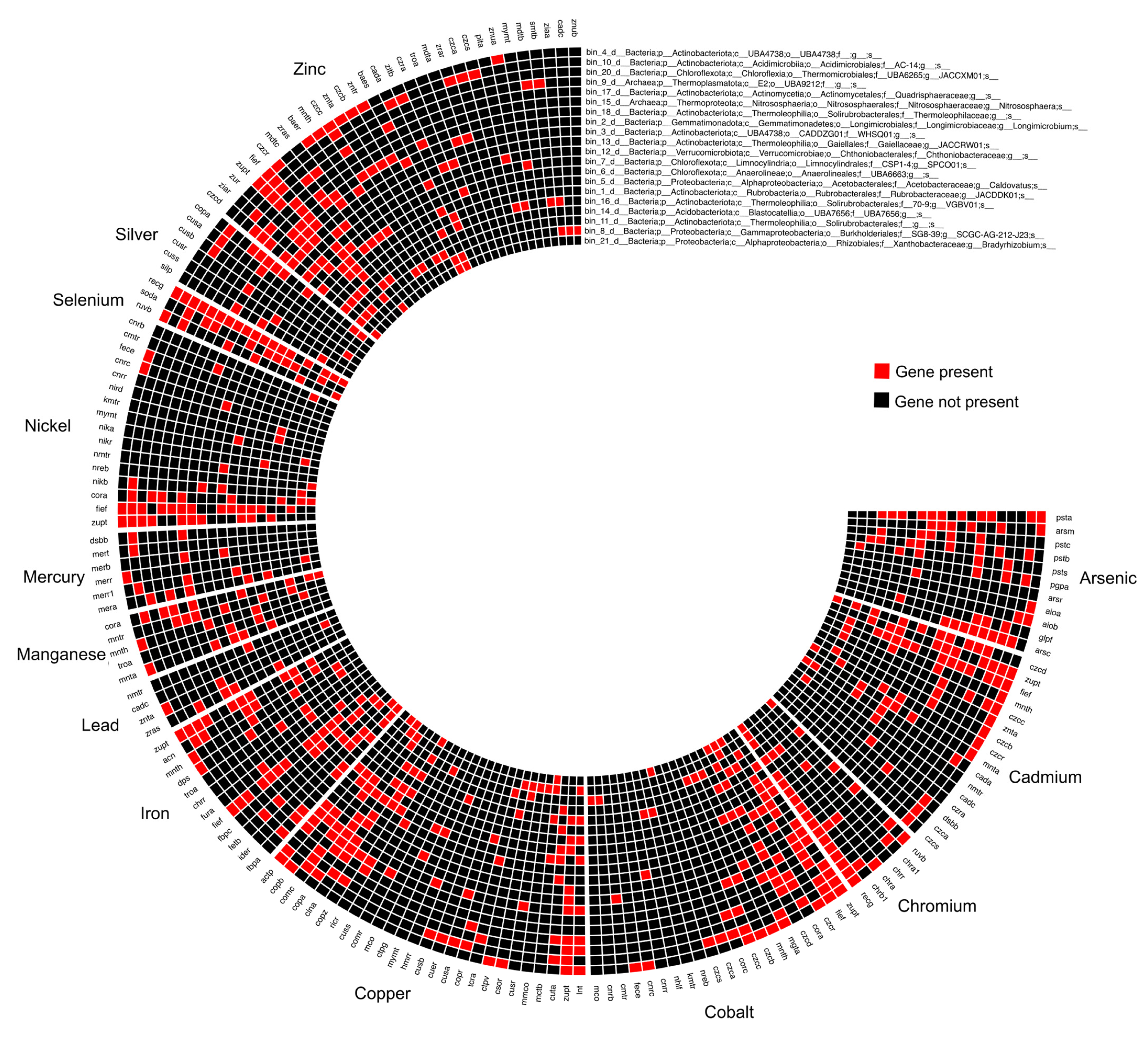
3.5. Characteristics of the Recovered MAGs and Identification of MRGs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adnan, M.; Xiao, B.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, P.; Li, R.; Bibi, S. Research Progress on Heavy Metals Pollution in the Soil of Smelting Sites in China. Toxics 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerizghi, T.; Guo, Q.; Tian, L.; Wei, R.; Zhao, C. An Integrated Approach to Quantify Ecological and Human Health Risks of Soil Heavy Metal Contamination around Coal Mining Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Jiang, K.; Wei, M.; Wang, S. Effects of Different Concentrations and Types of Cu and Pb on Soil N-Fixing Bacterial Communities in the Wheat Rhizosphere. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2019, 144, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zhu, J.; Rensing, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.R. Recent Advances in Exploring the Heavy Metal(Loid) Resistant Microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Saha, J.; Sarkar, M.; Mandal, P. Bacterial Survival Strategies and Responses under Heavy Metal Stress: A Comprehensive Overview. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, G.; Cernava, T. The Plant Microbiota Signature of the Anthropocene as a Challenge for Microbiome Research. Microbiome 2022, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Huang, M.; Fang, L. Biological Roles of Soil Microbial Consortium on Promoting Safe Crop Production in Heavy Metal(Loid) Contaminated Soil: A Systematic Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, L.B.; Obayori, O.S.; Ilori, M.O.; Amund, O.O. Chromium Contamination Accentuates Changes in the Microbiome and Heavy Metal Resistome of a Tropical Agricultural Soil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, G.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y. Chemical Fertilizers Promote Dissemination of ARGs in Maize Rhizosphere: An Overlooked Risk Revealed after 37-Year Traditional Agriculture Practice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Mi, H.; Xu, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Rensing, C.; Wang, Y. Prevalence of Antibiotic and Metal Resistance Genes in Phytoremediated Cadmium and Zinc Contaminated Soil Assisted by Chitosan and Trichoderma Harzianum. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xu, Z.; Fan, L. Response of Heavy Metal and Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Related Microorganisms to Different Heavy Metals in Activated Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.; Tong, H.; Zhang, X.; Jia, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, C. Heavy Metal Tolerance Genes Associated With Contaminated Sediments From an E-Waste Recycling River in Southern China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 665090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Cruz-Paredes, C.; Zhang, S.; Rousk, J. Can Heavy Metal Pollution Induce Bacterial Resistance to Heavy Metals and Antibiotics in Soils from an Ancient Land-Mine? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejel-García, D.; Espejel-García, V.V.; Villalobos-Aragón, A.; Espejel-García, D.; Espejel-García, V.V.; Villalobos-Aragón, A. Chemical Characterization of Slags from an Old Smelter in Chihuahua, Mexico. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2022, 10, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Escobedo, R.; Muñoz-Castellanos, L.N.; Muñoz-Ramirez, Z.Y.; Guigón-López, C.; Avila-Quezada, G.D. Rhizosphere Bacterial and Fungal Communities of Healthy and Wilted Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) in an Organic Farming System. Cienc. Rural. 2022, 53, 20220072. [Google Scholar]
- Crickard, P., III. Leaflet. Js Essentials; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2014; ISBN 1783554827. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas, C. Geovisualization: Integration and Visualization of Multiple Datasets Using Mapbox. Bachelor’s Thesis, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Reyna-Nájera, D.N.; Cortés-Palacios, L.; Sandino-Aquino de Los Ríos, G.; Martínez-Salvador, M.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, L.M. Estudio Del Comportamiento de Especies Vegetales En Un Proceso de Fitoestabilización Para Remediación de Suelo Contaminado Por Jal Minero Abandonado. Epistemus 2022, 16, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Ramírez, Z.Y.; González-Escobedo, R.; Avila-Quezada, G.D.; Ramírez-Sánchez, O.; Higareda-Alvear, V.M.; Zapata-Chávez, E.; Borrego-Loya, A.; Muñoz-Castellanos, L.N. Exploring Microbial Rhizosphere Communities in Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Apple Trees Using Amplicon Sequencing and Shotgun Metagenomics. Agronomy 2024, 14, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, F. Trim Galore!: A Wrapper Around Cutadapt and FastQC to Consistently Apply Adapter and Quality Trimming to FastQ Files, with Extra Functionality for RRBS Data; Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 700, p. 879. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; D’, L.; Mcgowan, A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Macklaim, J.M.; Linn, T.G.; Reid, G.; Gloor, G.B. ANOVA-Like Differential Expression (ALDEx) Analysis for Mixed Population RNA-Seq. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. MetaSPAdes: A New Versatile Metagenomic Assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Rensing, C.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. BacMet: Antibacterial Biocide and Metal Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D737–D743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and Sensitive Protein Alignment Using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2014, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennekes, M.; Ellis, P. R Package Treemap Visualization Version 2.4-2. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=treemap (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Uritskiy, G.V.; DiRuggiero, J.; Taylor, J. MetaWRAP—A Flexible Pipeline for Genome-Resolved Metagenomic Data Analysis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the Quality of Microbial Genomes Recovered from Isolates, Single Cells, and Metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A Toolkit to Classify Genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.Q. Heavy Metals and Pesticides Toxicity in Agricultural Soil and Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, D.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G. Rhizospheric Effects on the Microbial Community of E-Waste-Contaminated Soils Using Phospholipid Fatty Acid and Isoprenoid Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraether Analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9904–9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazykin, I.; Khmelevtsova, L.; Azhogina, T.; Sazykina, M. Heavy Metals Influence on the Bacterial Community of Soils: A Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Smalla, K. Plant Species and Soil Type Cooperatively Shape the Structure and Function of Microbial Communities in the Rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütze, E.; Kothe, E. Heavy Metal-Resistant Streptomycetes in Soil. In Bio-Geo Interactions in Metal-Contaminated Soils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Huqail, A.A.; El-Bondkly, A.M.A. Improvement of Zea mays L. Growth Parameters under Chromium and Arsenic Stress by the Heavy Metal-Resistant Streptomyces sp. NRC21696. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 5301–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thooppeng, P.; Junpradit, C.; Rongsayamanont, W.; Duangmal, K.; Prapagdee, B. Cadmium-Resistant Streptomyces Stimulates Phytoextraction Potential of Crotalaria juncea L. in Cadmium-Polluted Soil. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2023, 25, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timková, I.; Sedláková-Kaduková, J.; Pristaš, P. Biosorption and Bioaccumulation Abilities of Actinomycetes/Streptomycetes Isolated from Metal Contaminated Sites. Separations 2018, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska-Jaroszuk, M.; Jaszek, M.; Starosielec, M.; Sulej, J.; Matuszewska, A.; Janczarek, M.; Bancerz, R.; Wydrych, J.; Wiater, A.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides as a Modern Biotechnological Tool for Modification of Fungal Laccase Properties and Metal Ion Binding. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, A.; Boulila, F. Heavy Metals Multi-Tolerant Bradyrhizobium Isolated from Mercury Mining Region in Algeria. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baati, H.; Siala, M.; Azri, C.; Ammar, E.; Dunlap, C.; Trigui, M. Genomic Analysis of Heavy Metal-Resistant Halobacterium Salinarum Isolated from Sfax Solar Saltern Sediments. Extremophiles 2022, 26, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Dong, H.; Sheng, G.P. Haloarchaea, Excellent Candidates for Removing Pollutants from Hypersaline Wastewater. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarredona, L.; Zafrilla, B.; Camacho, M.; Bonete, M.J.; Esclapez, J. Understanding the Tolerance of Halophilic Archaea to Stress Landscapes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e70039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.-J.; Gwak, J.-H.; Choi, S.; Jung, M.-Y.; Lee, T.K.; Ryu, H.; Awala, S.I.; Wanek, W.; Wagner, M.; Quan, Z.-X.; et al. “Ca. Nitrosocosmicus” Members Are the Dominant Archaea Associated with Plant Rhizospheres. mSphere 2024, 9, e00821-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, W.; Luo, J. Production and Excretion of Polyamines To Tolerate High Ammonia, a Case Study on Soil Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaeon “Candidatus Nitrosocosmicus Agrestis”. mSystems 2021, 6, e01003-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Q.; Reitz, T.; Schädler, M.; Hodgskiss, L.H.; Peng, J.; Schnabel, B.; Buscot, F.; Eisenhauer, N.; Schleper, C.; Heintz-Buschart, A. Metabolic Potential of Nitrososphaera-Associated Clades. ISME J. 2024, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, M.T.; El-Sayed, A.S.A. Tolerance and Mycoremediation of Silver Ions by Fusarium Solani. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, S.; Parveen, K.; Usman, J.; Nasir, K.; Akhtar, N.; Arouj, S.; Ahmad, I. Heavy Metal Tolerance of Filamentous Fungal Strains Isolated from Soil Irrigated with Industrial Wastewater. Biologija 2012, 58, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Harrasi, A. Sphingomonas: From Diversity and Genomics to Functional Role in Environmental Remediation and Plant Growth. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, M.; Sugita, T. Taxonomy of Pathogenic Yeasts Candida, Cryptococcus, Malassezia, and Trichosporon Current Status, Future Perspectives, and Proposal for Transfer of Six Candida Species to the Genus Nakaseomyces. Med. Mycol. J. 2022, 63, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renker, C.; Alphei, J.; Buscot, F. Soil Nematodes Associated with the Mammal Pathogenic Fungal Genus Malassezia (Basidiomycota: Ustilaginomycetes) in Central European Forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, R.M.; El Baidouri, F.; Mitchison-Field, L.M.Y.; Lim, F.Y.; Ekena, J.; Vogt, E.J.D.; Gladfelter, A.; Theberge, A.B.; Amend, A.S. Malassezia Is Widespread and Has Undescribed Diversity in the Marine Environment. Fungal Ecol. 2023, 65, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Chen, Q.; Du, W.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Cai, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Xu, N.; Wang, J. Deciphering the Dynamics of Metal and Antibiotic Resistome Profiles under Different Metal(Loid) Contamination Levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altimira, F.; Yãez, C.; Bravo, G.; González, M.; Rojas, L.A.; Seeger, M. Characterization of Copper-Resistant Bacteria and Bacterial Communities from Copper-Polluted Agricultural Soils of Central Chile. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmat-Jou, M.H.; Liu, S.; Liang, Y.; Chen, G.; Fang, L.; Li, F. Microbial Arsenic Methylation in Soil-Water Systems and Its Environmental Significance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, K.; Chandirika, J.U.; Vinothkanna, A.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, D. Bacterial Adaptive Strategies to Cope with Metal Toxicity in the Contaminated Environment—A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhar, A.; Gul, B.; Gurmani, A.R.; Khan, S.M.; Ali, S.; Sultan, T.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Rafique, M.; Rizwan, M. Heavy Metal Remediation and Resistance Mechanism of Aeromonas, Bacillus, and Pseudomonas: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 1868–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, U.; Nongkhlaw, M.; Joshi, S.R. Molecular Evidence for Occurrence of Heavy Metal and Antibiotic Resistance Genes Among Predominant Metal Tolerant Pseudomonas sp. and Serratia sp. Prevalent in the Teesta River. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Canchaya, C.; Tauch, A.; Chandra, G.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Chater, K.F.; van Sinderen, D. Genomics of Actinobacteria: Tracing the Evolutionary History of an Ancient Phylum. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 495–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Asiani, K.; Arya, S.; Rensing, C.; Stekel, D.J.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Hobman, J.L. Metal Resistance and Its Association With Antibiotic Resistance. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2017, 70, 261–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Quan, Q.; Gan, Y.; Dong, J.; Fang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Effects of Heavy Metals on Microbial Communities in Sediments and Establishment of Bioindicators Based on Microbial Taxa and Function for Environmental Monitoring and Management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Muñoz, D.; Burgos, W.D.; Sánchez-España, J.; Couradeau, E.; Falagán, C.; Macalady, J.L. Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Study of Microbial Metal Resistance in an Acidic Pit Lake. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Khan, I.U.; Hussain, F.; Zhou, E.M.; Xiao, M.; Ahmed, I.; Zhi, X.Y.; Li, W.J. Caldovatus sediminis Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Moderately Thermophilic Bacterium Isolated from a Hot Spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4716–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.J.; Xian, W.D.; Lv, Y.Q.; Peng, C.X.; Shan, R.X.; Cheng, Z.C.; Lv, Q.; Tian, Y.; Jiao, J.Y.; Tan, S.; et al. Caldovatus aquaticus Sp. Nov., a Moderately Thermophilic Bacterium Isolated from Hot Spring Microbial Mat. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, C.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. CaAl-Layered Double Hydroxides-Modified Biochar Composites Mitigate the Toxic Effects of Cu and Pb in Soil on Pea Seedlings. Materials 2024, 17, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Properties | RS | NRS |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Sandy loam | Silty |
| EC (mS·cm−1) | 1.78 | 1.18 |
| OM (%) | 1.3 | 3.03 |
| pH | 7.14 | 7.32 |
| Cu | 1994.65 | 702.78 |
| Zn | 19,563.67 | 2179.42 |
| Fe | 54,817.13 | 15,233.6 |
| As | 172.92 | 314.61 * |
| Mg | 1900.13 | 2440.36 |
| Cd | 57.77 | 341.95 |
| Co | 37.29 | 31.81 |
| Cr | 67.92 | 49.2 |
| Pb | 1495.04 * | 7355.86 * |
| Ca | 14,716.06 | 2299.2 |
| Mn | 5171.52 | 605.86 |
| Ni | 16.92 | 29.32 |
| Mo | 118.4 | 104.87 |
| Be | 12.96 | 25.84 |
| Sb | 59 | 137.18 |
| Se | 16.06 | 86.98 |
| Sample | Community | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS | Bacteria | 2022.0 | 5.45 | 0.98 |
| Archaea | 148.0 | 3.87 | 0.97 | |
| Fungi | 52 | 1.16 | 0.52 | |
| NRS | Bacteria | 1697.6 | 5.01 | 0.97 |
| Archaea | 129.7 | 3.63 | 0.96 | |
| Fungi | 44 | 2.91 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montes-Montes, G.; Muñoz-Ramírez, Z.Y.; Cortes-Palacios, L.; Carrillo-Campos, J.; Ramírez-Sánchez, O.; Ortiz-Aguirre, I.; Muñoz-Castellanos, L.N.; González-Escobedo, R. Microbial Diversity and Heavy Metal Resistome in Slag-Contaminated Soils from an Abandoned Smelter in Chihuahua, Mexico. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020030
Montes-Montes G, Muñoz-Ramírez ZY, Cortes-Palacios L, Carrillo-Campos J, Ramírez-Sánchez O, Ortiz-Aguirre I, Muñoz-Castellanos LN, González-Escobedo R. Microbial Diversity and Heavy Metal Resistome in Slag-Contaminated Soils from an Abandoned Smelter in Chihuahua, Mexico. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontes-Montes, Gustavo, Zilia Y. Muñoz-Ramírez, Leonor Cortes-Palacios, Javier Carrillo-Campos, Obed Ramírez-Sánchez, Ismael Ortiz-Aguirre, Laila N. Muñoz-Castellanos, and Román González-Escobedo. 2025. "Microbial Diversity and Heavy Metal Resistome in Slag-Contaminated Soils from an Abandoned Smelter in Chihuahua, Mexico" Soil Systems 9, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020030
APA StyleMontes-Montes, G., Muñoz-Ramírez, Z. Y., Cortes-Palacios, L., Carrillo-Campos, J., Ramírez-Sánchez, O., Ortiz-Aguirre, I., Muñoz-Castellanos, L. N., & González-Escobedo, R. (2025). Microbial Diversity and Heavy Metal Resistome in Slag-Contaminated Soils from an Abandoned Smelter in Chihuahua, Mexico. Soil Systems, 9(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020030











