Assessing the Global Sensitivity of RUSLE Factors: A Case Study of Southern Bahia, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
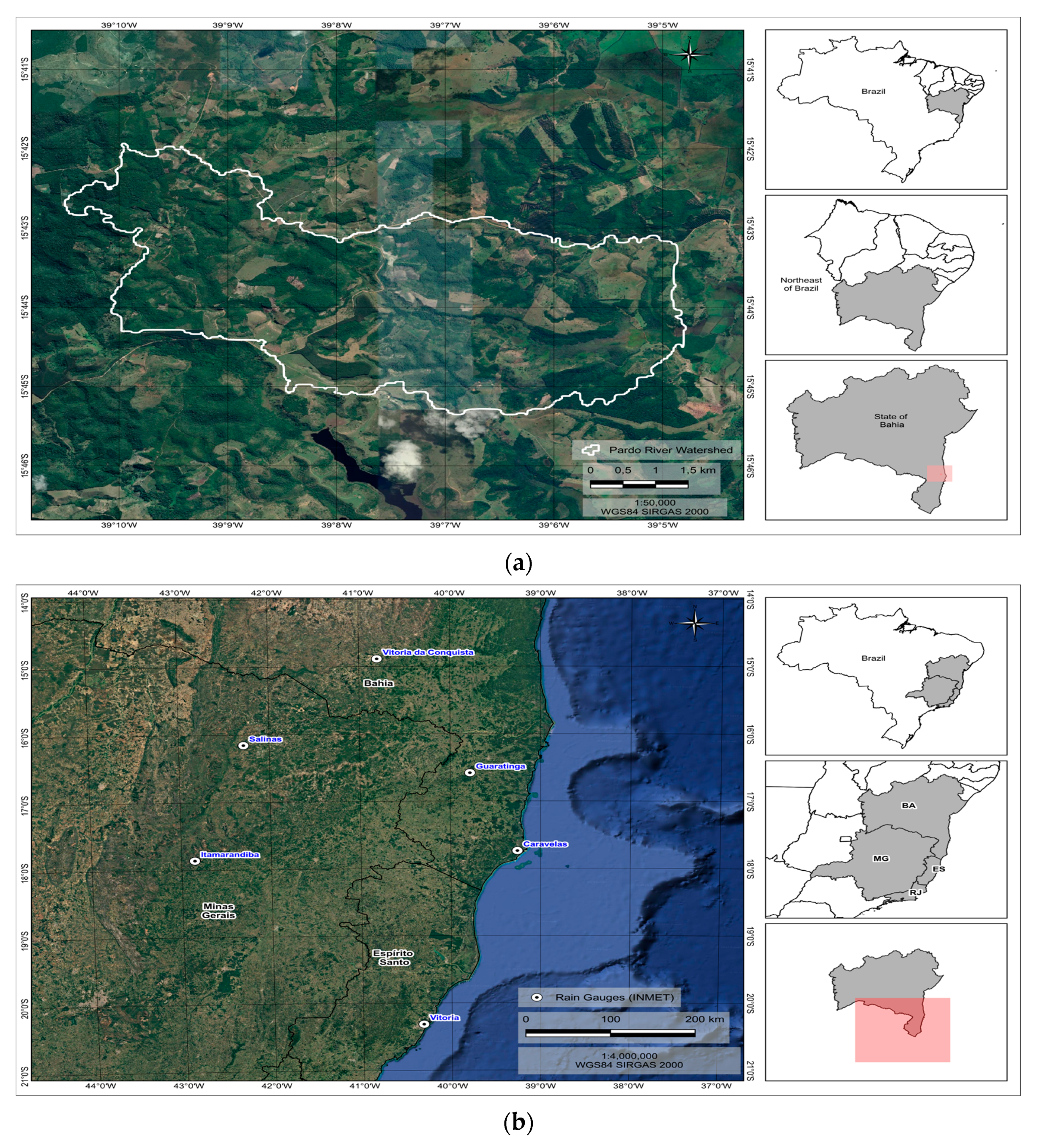
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Modeling
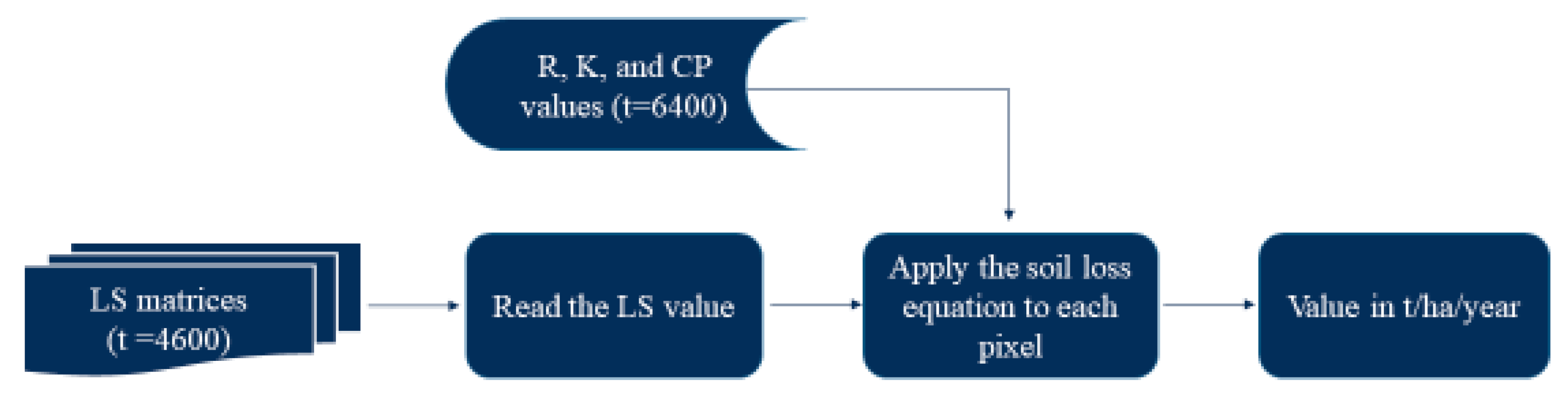
2.3. Calculation of Soil Loss
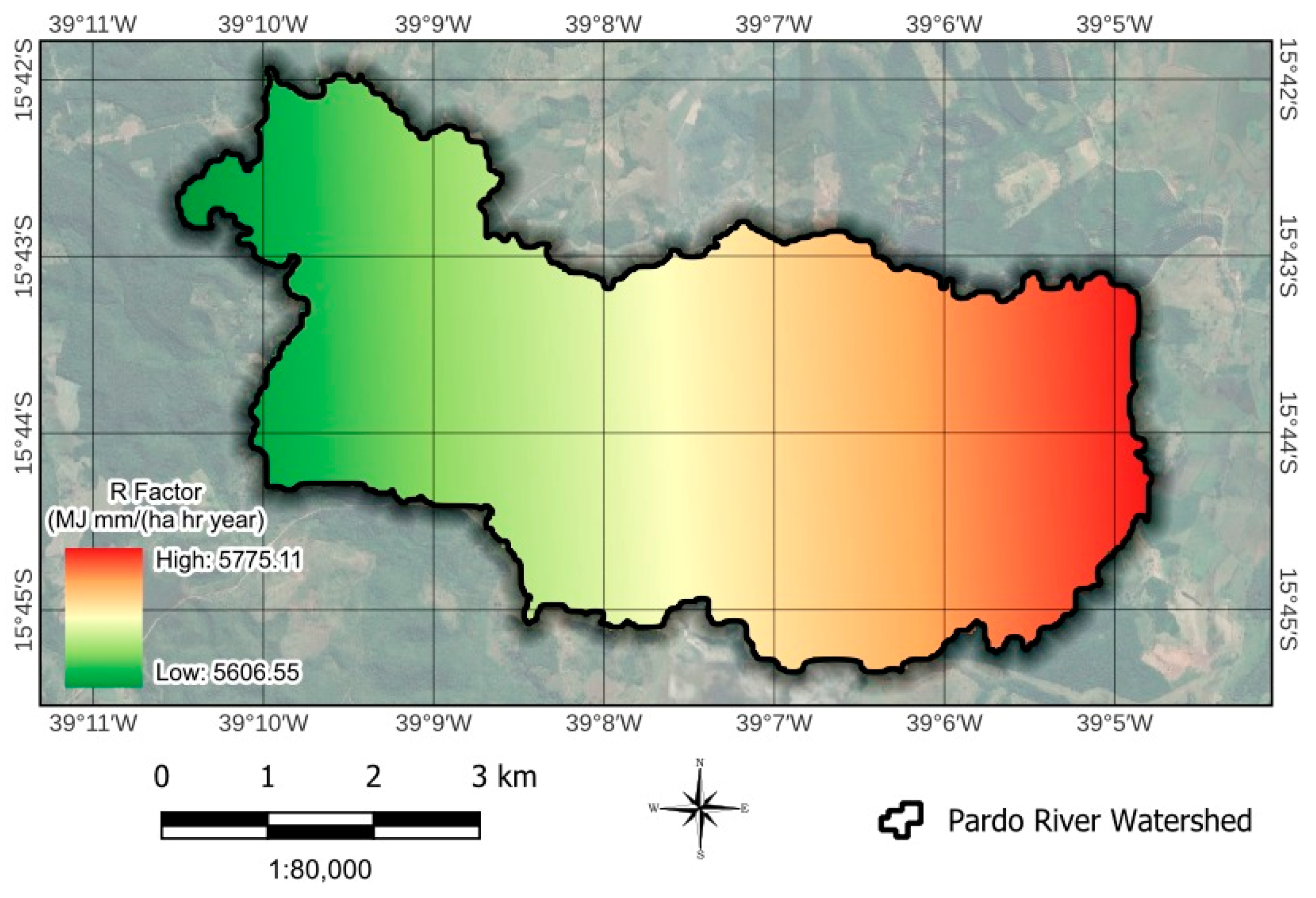
2.4. Rainfall Erosivity (R Factor)
2.5. Soil Erodibility (K Factor)
2.6. Topographical Factor (LS Factor)
2.7. Crop Management and Support Practice (CP Factor)
3. Sensitivity Associated with RUSLE Model
Soil Loss Calculations Based on VARS Sampling
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Nominal Soil Erosion Losses
4.1.1. R Factor
4.1.2. K Factor
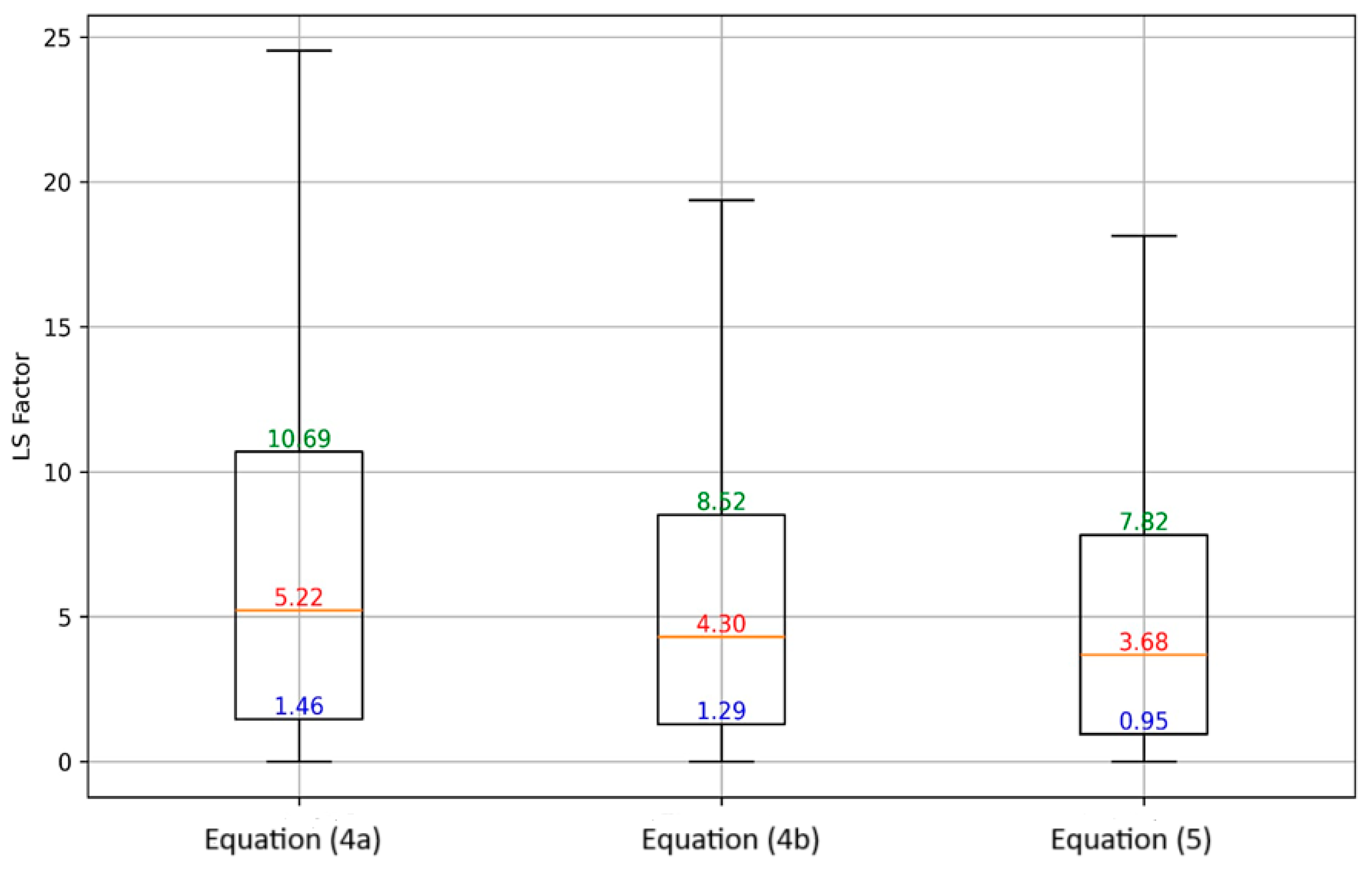
4.1.3. LS Factor
4.1.4. CP Factor
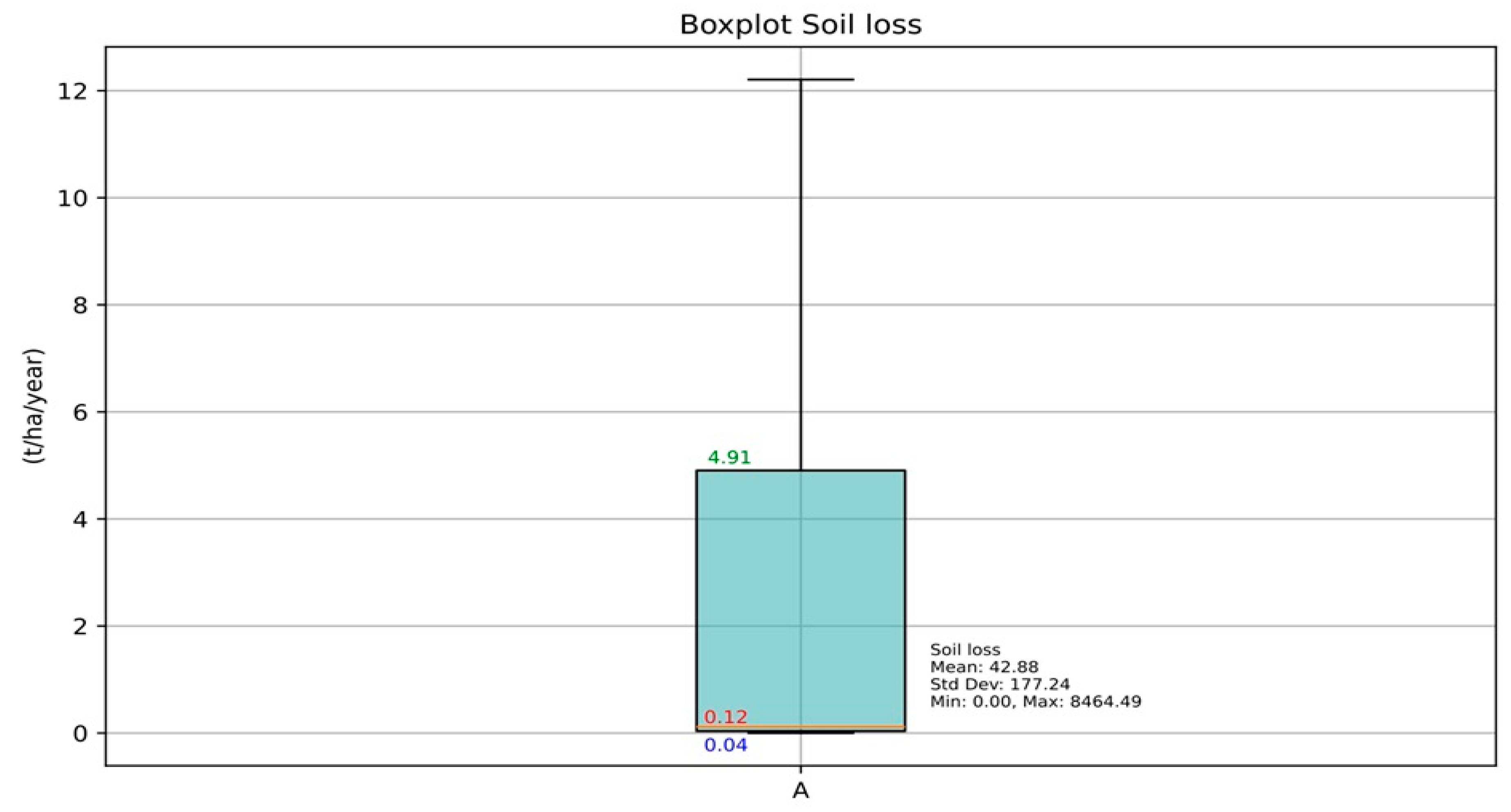
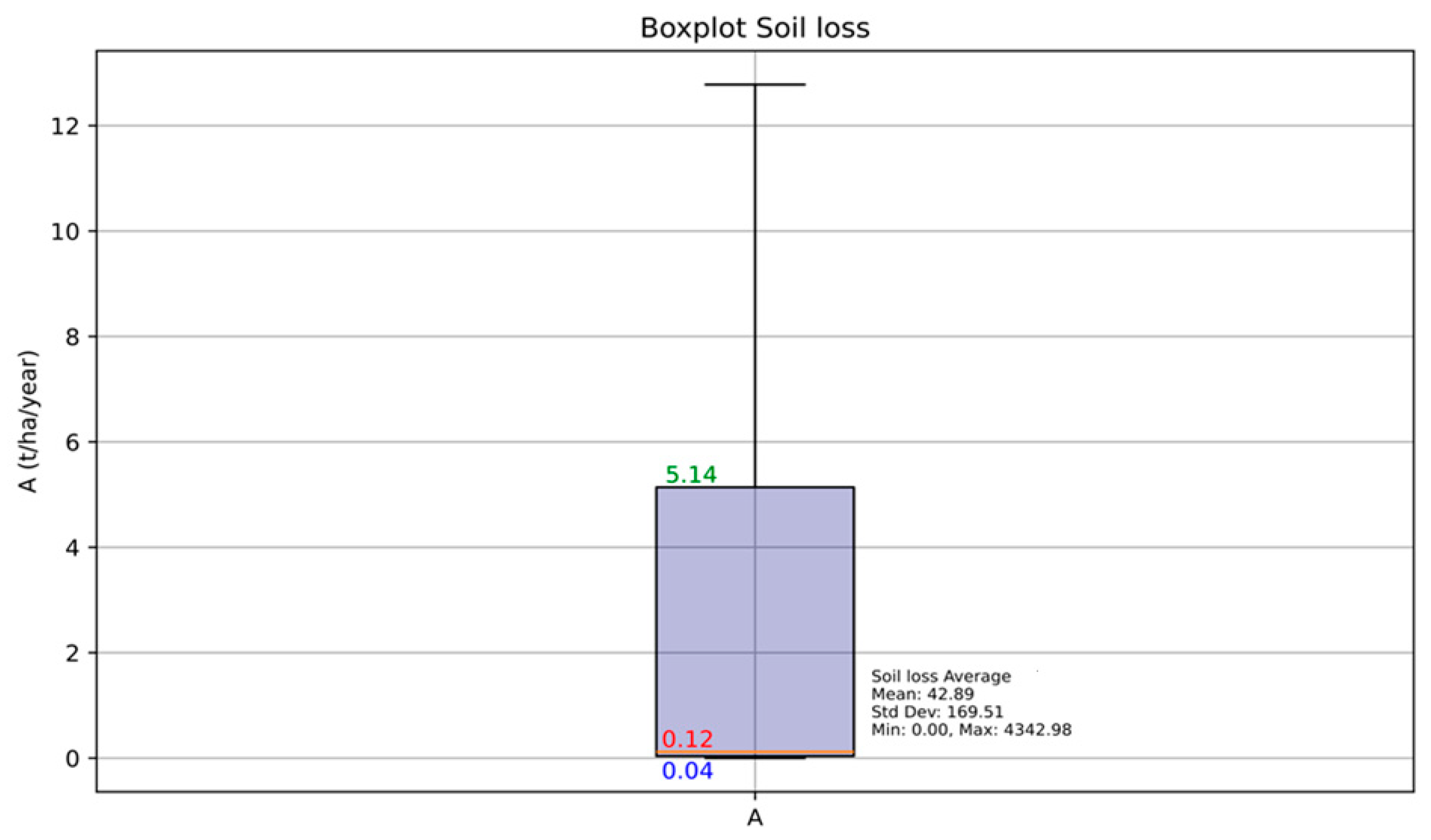
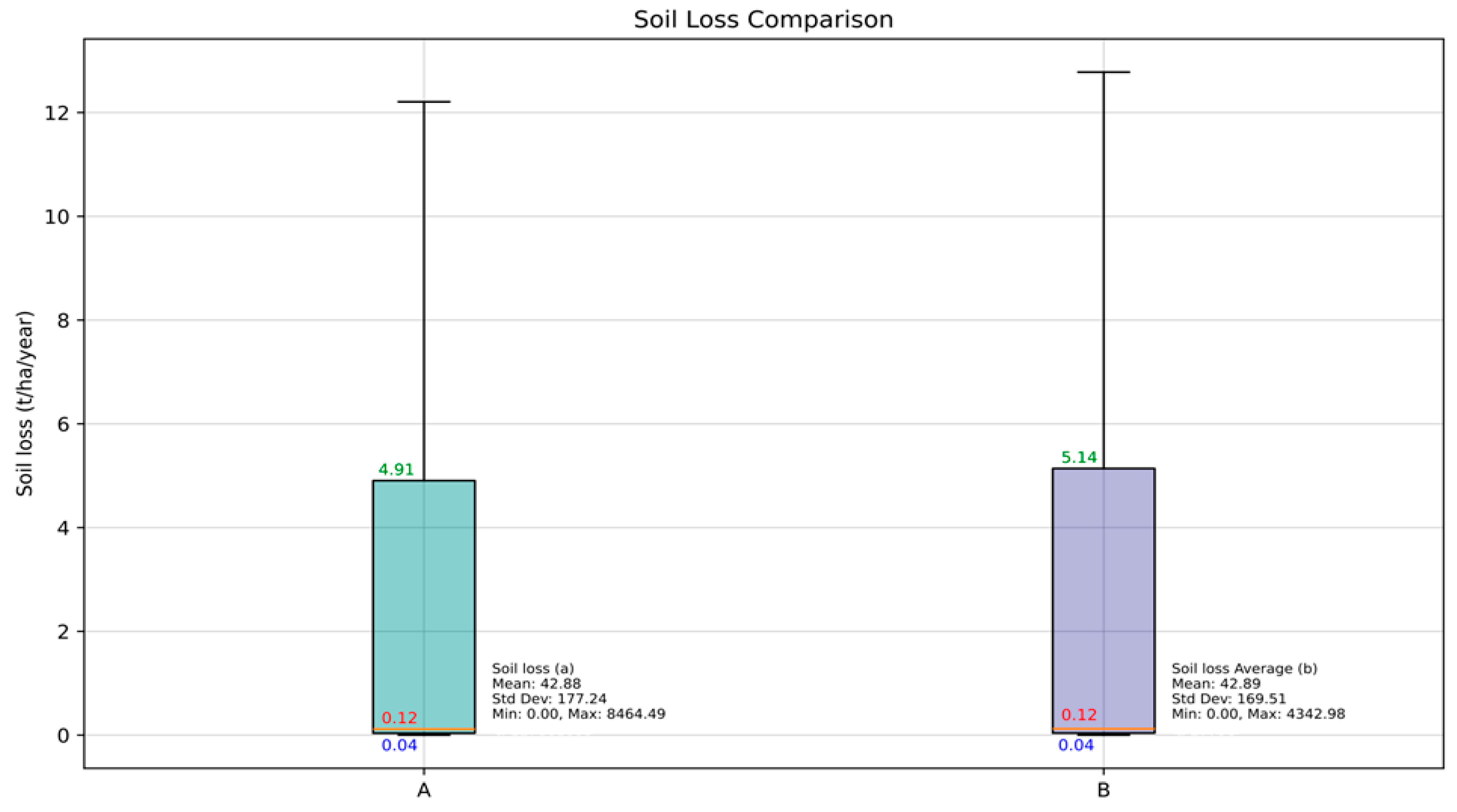
4.1.5. Potential Soil Loss
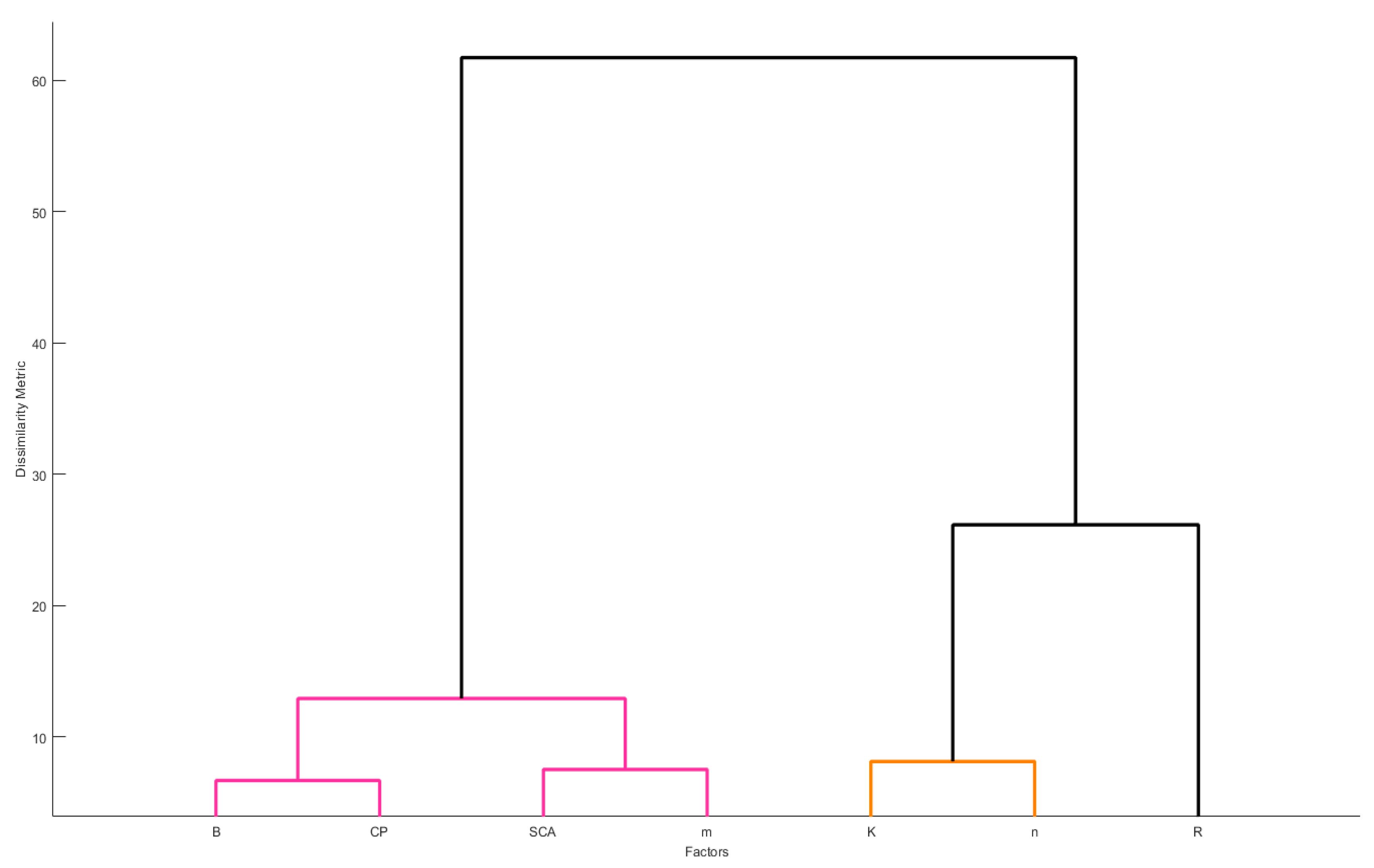
4.2. Uncertainty and Global Sensitivity of RUSLE Parameters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Palencia, C.; Keesstra, S.; Jordán, A.; Fraile, R.; Angulo-Martínez, M.; Cerdà, A. Splash erosion: A review with unanswered questions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajigholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.M.; Fuentes, H.R. Raindrop-induced erosion and sediment transport modeling in shallow waters: A review. J. Soil Water Sci. 2018, 1, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Restoring soil quality to mitigate soil degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárceles Rodríguez, B.; Durán-Zuazo, V.H.; Soriano Rodríguez, M.; García-Tejero, I.F.; Gálvez Ruiz, B.; Cuadros Tavira, S. Conservation Agriculture as a Sustainable System for Soil Health: A review. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidoro, J.C.; De Freitas, P.L.; Hernani, L.C.; Anjos, L.H.C.D.; Rodrigues, R.D.A.R.; Cesário, F.V.; Andrade, A.G.D.; Ribeiro, J.L. Potential impact of plans and policies based on the principles of conservation agriculture on the control of soil erosion in Brazil. Land Degrad Dev. 2021, 32, 3457–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskan, O.; Dengiz, O. Comparison of traditional and geostatistical methods to estimate soil erodibility factor. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2008, 22, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Biggelaar, C.; Lal, R.; Wiebe, K.; Breneman, V. Impact of Soil Erosion on Crop Yields in North America. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Telles, T.S.; Guimarães, M.D.F.; Dechen, S.C.F. The costs of soil erosion. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2011, 35, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.S. Land degradation and challenges of food security. Rev. Eur. Stud. 2019, 11, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarelli, M.; Pinto, L.P.; Silva, J.M.C.; Hirota, M.; Bedê, L. Challenges and Opportunities for Biodiversity Conservation in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.D.; DeBlasis, P.; Fish, S.K.; Fish, P.K. Sambaqui (shell mound) societies of coastal Brazil. In Handbook of South American Archaeology; Silverman, E., Isbell, W.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 319–338. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.P.; Faria, C.P. Conservation priorities for the bryophytes of Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. J. Biol. 2008, 30, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, F.R.; Ceotto, P. Brazilian Atlantic Forest: Impact, vulnerability, and adaptation to climate change. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.M.; Valero, C.; Muñoz, M.Á.; Gil-Rodríguez, M.; Barreiro, P. Effect of reservoir tillage on rainwater harvesting and soil erosion control under a developed rainfall simulator. Catena 2014, 113, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, G.R.F.; Rasul, A.; Ali Hamid, A.; Ali, Z.F.; Dewana, A.A. Suitable site selection for rainwater harvesting and storage case study using Dohuk Governorate. Water 2019, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Junior, W.; Loireau, M.; Fargette, M.; Calderano Filho, B.; Wélé, A. Correlation between soil erodibility and satellite data on areas of current desertifcation: A case study in Senegal. Rev. Ciênc. Tróp. 2017, 41, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, I.P.; Williams, L. The effect of wildfire on runoff and erosion in native eucalyptus forest. Hydrol. Processes 1998, 12, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.J.Y.; Nascimento, R.Q. Efeitos das alterações no uso e ocupação do solo nas perdas de solo da bacia do rio de janeiro, oeste da Bahia: Effects of changes in soil use and occupation on soil losses in the Rio de Janeiro basin, West of Bahia. Bol. Goia. Geogr. 2021, 41, e65397. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadić, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalíková, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Greece. Catena 2016, 137, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquetti, N.B.; Mello, C.R.; Beskow, S.; Viola, M.R. Rainfall erosivity in South America: Current patterns and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N. The new assessment of soil erodibility in Greece. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M. Erosion risk assessment for prioritization of conservation measures in Geleda watershed, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, A.A.; Mersey, J.E. Adapting the RUSLE to model soil erosion potential in a mountainous tropical watershed. Catena 1999, 38, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.; Govers, G. A GIS-procedure for the automated calculation of the USLE LS-factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; He, X.; Nearing, M.A. Detachment of undisturbed soil by shallow flow. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A. A Single, Continuous function for slope steepness influence on soil loss. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle Júnior, R.F.D.; Galbiatti, J.A.; Martins Filho, M.V.; Pissarra, T.C.T. Potencial de erosão da bacia do Rio Uberaba. Eng. Agríc. 2010, 30, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitasova, H.; Hofierka, J.; Zlocha, M.; Iverson, L.R. Modelling topographic potential for erosion and deposition using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Modeling erosion and deposition: Topographic effects. Trans. ASAE. 1986, 29, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Shiny, R.; Geetha, N.; Vijith, H. Spatial prediction of soil erosion risk by remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE approach: A case study of Siruvani river watershed in Attapady valley, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, J.R.; Akomolafe, J.K.; Ajibade, F.O. Development of flood prone area map for Igbokoda Township using geospatial technique. J. Appl. Sci. Process Eng. 2017, 4, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Luukkanen, O.; Tokola, T.; Nieminen, J. Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena 2008, 75, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Ferreira, V.A. RUSLE model description and database sensitivity. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.P.R.; Lalitha, R.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Nagarajan, M. Assessment of Topographical Factor (LS-Factor) Estimation Procedures in a Gently Sloping Terrain. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanifar, J.; Khademalrasoul, A. Multiscale comparison of LS factor calculation methods based on different flow direction algorithms in Susa Ancient landscape. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Bora, P.K.; Das, R. Estimation of slope length gradient (LS) factor for the sub-watershed areas of Juri River in Tripura. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesemans, J.; Meivenne, M.V.; Gabriels, D. Extending the RUSLE with Monte Carlo error propagation technique to predict long-term average off-site sediment accumulation. J. Soil Water conserv. 2000, 55, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Aziz, S.; Steward, B.L.; Kaleita, A.; Karkee, M. Assessing the effects of DEM uncertainty on erosion rate estimation in an agricultural field. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.-M.; Liang, Y.; Sun, B. Research on sensitivity for soil erosion evaluation from DEM and remote sensing data source of different map scales and image resolutions. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Fang, S.; Shinkareva, S.; Gertner, G.Z.; Anderson, A.B. Spatial uncertainty in prediction of the topographical factor for the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, B.; Hu, Y.; Fu, S.; Cao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Huang, T. Soil erosion topographic factor (LS): Accuracy calculated from different data sources. Catena 2020, 187, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, J.; Huang, G. An evaluation of grid size uncertainty in empirical soil loss modeling with digital elevation models. Environ. Model. Assess. 2005, 10, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, M.; Ozcan, A.U.; Erpul, G.C.; Anga, M.R. Spatial variability of organic matter and some soil properties of mineral topsoil in Çankiri Indagi blackpine (Pinus nigra) plantation region. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Ozcan, A.U.; Erpul, G.; Basaran, M.; Erdogan, H.E. Use of USLE/GIS technology integrated with geostatistics to assess soil erosion risk in different land uses of Indagi Mountain Pass—Çankırı, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gertner, G.; Liu, X.; Anderson, A. Uncertainty assessment of soil erodibility factor for revised universal soil loss equation. Catena 2001, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, D.; Poesen, J.; Borselli, L. Predictability and uncertainty of the soil erodibility factor using a global dataset. Catena 1997, 31, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhraoui, F.; Hasbaia, M. Evaluation of the sensitivity of the RUSLE erosion model to rainfall erosivity: A case study of the Ksob watershed in central Algeria. Water Supply 2023, 23, 3262–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, D.A.; Deumlich, D.; Šarapatka, B.; Doktor, D. Quantifying the sensitivity of NDVI-Based C factor estimation and potential soil erosion prediction using spaceborne earth observation data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Chan, K.; Scott, E.M. Sensitivity Analysis. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 504. [Google Scholar]
- Saltelli, A.; Tarantola, S.; Campolongo, F.; Ratto, M. Sensitivity Analysis in Practice: A Guide to Assessing Scientific Models; John Wiley & Sons: New Delhi, India, 2004; pp. 1–219. [Google Scholar]
- Iooss, B.; Lemaître, P. A Review on Global Sensitivity Analysis Methods. In Uncertainty Management in Simulation-Optimization of Complex Systems; Operations Research/Computer Science Interfaces Series; Dellino, G., Meloni, C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 101–122. [Google Scholar]
- Saltelli, A. Global Sensitivity Analysis: An introduction. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sensitivity Analysis of Model Output (SAMO 2004), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 8–11 March 2005; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Homma, T.; Saltelli, A. Importance measures in global sensitivity analysis of nonlinear models. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1996, 52, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medauar, C.C.; Menezes, A.A.; Ramos, A.; Galvão, M.Í.; De Assis Silva, S. Climatic characterization and evaluation of the need for supplementary irrigation for cacao in southern Bahia, Brazil. Agron. Colomb. 2020, 38, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.S.; Carvalho, T.S.; Santos, R.B.; Maffei, E.M.D.; Soares, B.D.F. Potencial genotóxico em amostras de água do Rio Pardo (Itapetinga/Ba) pelo teste Allium cepa L. In VIII Seagrus. Os Desafios para a Agricultura no Seculo XXI; UESB: Vitória da Conquista, Brazil, 2017; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mapbiomas Brasil|Analise-de-Acuracia. Available online: https://brasil.mapbiomas.org/analise-de-acuracia/ (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Renard, K.G.; Forester, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Mccool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In Agriculturae Handbook, 703; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 404. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, A.F.; Oliveira, E.F.; Mioto, C.L.; Paranhos Filho, A.C. The application of the universal soil loss equation by using free and available softwares. Anu. Inst. Geocienc. 2015, 38, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, I.; Zregat, D.; Farhan, I. Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk using RUSLE approach, RS, and GIS techniques: A case study of Kufranja watershed, Northern Jordan. J. Water Resource Prot. 2013, 5, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM National Conference, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 August 1968; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, M.; Gonçalves Pontes, M.C.; De Vasconcelos, R.N.; De Oliveira, U.C.; Peixoto Da Silva, H.; Faria, D.; Mariano-Neto, E. Assessing soil erosion and its drivers in agricultural landscapes: A case study in southern Bahia, Brazil. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 3312–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassol, E.A.; Eltz, F.L.F.; Martins, D.; Lemos, A.M.; Lima, V.S.; Bueno, A.C. Erosividade, padrões hidrológicos, período de retorno e probabilidade de ocorrência das chuvas em São Borja, RS. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2008, 32, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.A.; Lima, J.S.S.; Souza, G.S.; Oliveira, R.B. Variabilidade espacial do potencial erosivo das chuvas para o estado do Espírito Santo, Brasil. Irriga, Botucatu 2010, 15, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi Neto, F.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Erosividade da chuva: Sua distribuicao e relacao com perdas de solo em Campinas-SP.Bragantia. Campinas 1992, 51, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, J.; Lombardi Neto, F. Conservação do Solo, 8th ed.; Ícone Editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meira, L.; Oliveira, E.; Silva, P.; Tomaz, A. Rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility and natural water erosion potential in the Huambo region, Angola. J. Agr. Rural Develop. Trop. Subtrop. 2021, 122, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.; Lima Neto, I.E.; Studart, T.M.; Campos, J.N.B. Influence of sediment distribution on the relationships among reservoir yield, spill, and evaporation losses. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2018, 23, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, L.; Torri, D.; Poesen, J.; Iaquinta, P. A robust algorithm for estimating soil erodibility in different climates. Catena 2012, 97, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskow, S.; Mello, C.R.; Norton, L.D.; Curi, N.; Viola, M.R.; Avanzi, J.C. Soil erosion prediction in the Grande River Basin, Brazil using distributed modeling. Catena 2009, 79, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannigel, A.R.; E Carvalho, M.D.P.; Moreti, D.; Medeiros, L.D.R. Fator erodibilidade e tolerância de perda dos solos do Estado de São Paulo. Acta Sci. Agron. 2008, 24, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, J.B.P.; Becegato, V.A.; Scopel, I.; Lopes, R.M. Uso de técnicas de geoprocessamento para mapear o potencial natural de erosão da chuva na bacia hidrográfica do reservatório de Cachoeira Dourada—GO/MG. R. RA’E GA 2005, 10, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belasri, A.; Lakhouili, A. Estimation of soil erosion risk using the universal soil loss equation (usle) and geo-information technology in Oued El Makhazine Watershed, Morocco. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting rainfall erosion losses: A guide to conservation planning. In Agriculture Handbook; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 537, p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Soil Erosion and Conservation, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley Longman: Edinburgh, UK, 1995; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Mitasova, H.; Barton, C.M.; Ullah, I.; Hofierka, J.; Harmon, R. GIS-Based Soil Erosion Modeling. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Remote Sensing and GIScience in Geomorphology; Volume 3, pp. 228–258. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, M.L.; Beasley, D.B.; Fletcher, J.J.; Foster, G.R. Estimating soil loss on topographically nonuniform field and farm units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1988, 43, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.D.; Wilson, J.P. Length-slope factors for the revised universal soil loss equation: Simplified method of estimation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1992, 47, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Marešová, J.; Gdulová, K.; Pracná, P.; Moravec, D.; Gábor, L.; Prošek, J.; Barták, V.; Moudrý, V. Applicability of data acquisition characteristics to the identification of local artefacts in global digital elevation models: Comparison of the Copernicus and TanDEM-X DEMs. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannadi, M.A.; Alebooye, S.; Izadi, M.; Ghanadi, A. Vertical accuracy assessment of copernicus dem (case study: Tehran and Jam cities). ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2023, X-4/W1-2022, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moradas, M.R.; Viveen, W.; Vidal-Villalobos, R.A.; Villegas-Lanza, J.C. A performance comparison of SRTM v. 3.0, AW3D30, ASTER GDEM3, Copernicus and TanDEM-X for tectonogeomorphic analysis in the South American Andes. Catena 2023, 228, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, G.; Xiao, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, S. The scaling method of specific catchment area from DEMs. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdan, O.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; Saby, N.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Gobin, A.; Vacca, A.; Quinton, J.; Auerswald, K.; Klik, A.; et al. Sheet and Rill Erosion. In Soil Erosion in Europe; Boardman, J., Poesen, J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 501–513. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2015, 8, 2271–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, K.M.R.; Carvalho Júnior, O.A.; Martins, E.S.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Guimarães, R.F. Vulnerabilidade natural: A perda de solo da bacia do rio Carinhanha (MG/BA) usando uma abordagem qualitativa da equação universal de perda de solos. Geographia 2013, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.B.R.; Pereira, G.; Fonseca, B.M.; Costa, J.C.; Cardozo, F.D.S. Estimativa de perda de solo no Oeste da Bahia (Brasil) a partir da alteração do uso e cobertura da terra. Caminhos Geogr. 2019, 20, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, U.C.; Cidral, W.R.S.; Silva, I.S.; Evangelista, J.P. Spatial distribution of soil loss in the Itacolomi river hydrographic basin, Ceará, Brazil. Ciênc. Geográfica 2023, 2, 977–989. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, D.P.; Donzeli, A.F.; Gimenez, A.F.; Ponçano, W.L.; Lombardi Neto, F. Potencial de erosão laminar, natural e antrópico na bacia do peixe paranapanema. Simpósio Nac. De Controle De Erosão São Paulo 1987, 4, 105–136. [Google Scholar]
- Pena, D.S. Influência da Expansão Agrícola Sobre a Perda de Solo no Estado de Goiás. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Goiás, Goiás, Brazil, 2020; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, A.; Awoye, H.; Stadnyk, T.; Asadzadeh, M. Time variant sensitivity analysis of hydrological model parameters in a cold region using flow signatures. Water 2020, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, s.; Sheikholeslami, R.; Gupta, H.V.; Haghnegahdar, A. VARS-TOOL: A toolbox for comprehensive, efficient, and robust sensitivity and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 112, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, I.M. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math. Comput. Simul. 2001, 55, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.D. Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments. Technometrics 1991, 33, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.A.; Foulon, E.; Rousseau, A.N. Deriving synthetic rating curves from a digital elevation model to delineate the inundated areas of small watersheds. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meles, M.B.; Goodrich, D.C.; Gupta, H.V.; Shea Burns, I.; Unkrich, C.L.; Razavi, S.; Guertin, D.P. Multi-criteria, time dependent sensitivity analysis of an event-oriented, physically-based, distributed sediment and runoff model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korgaonkar, Y.; Meles, M.B.; Guertin, D.P.; Goodrich, D.C.; Unkrich, C. Global sensitivity analysis of KINEROS2 hydrologic model parameters representing green infrastructure using the STAR-VARS framework. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 132, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Gupta, H.V. A new framework for comprehensive, robust, and efficient global sensitivity analysis: 1. Theory. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 8324, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Gupta, H.V. A new framework for comprehensive, robust, and efficient global sensitivity analysis: 2. Application. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, N.O. Hidrossedimentologia Prática; CPRM: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1994; p. 600. [Google Scholar]
- Fistarol, P.H.B.; Santos, J.Y.B.; Nakamura, T.C. Estimativa das perdas de solo na bacia do Rio de Ondas, estado da Bahia. In Proceedings of the XII Encontro Nacional de Engenharia de Sedimentos, Porto Velho, Brazil, 28 November–2 December 2016; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, R.Q.; Santos, J.Y.G. Análise das perdas de solo na bacia do Rio de Janeiro, Bahia. In Proceedings of the XXIII Simpósio Brasileiro de Recursos Hídricos, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 24–28 November 2019; p. 10, ISSN 2318-0358. [Google Scholar]
- Godoi, R.D.F.; Rodrigues, D.B.B.; Borrelli, P.; Oliveira, P.T.S. High-resolution soil erodibility map of Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Simões, S.J.C.; Forti, M.C.; Ometto, J.P.H.B.; Nora, E.L.D. Using Geotechnology to Estimate Annual Soil Loss Rate in the Brazilian Cerrado. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2017, 9, 420–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinasso, M.; Carvalho Júnior, O.A.D.; Guimarães, R.F.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Ramos, V.M. Avaliação Qualitativa do Potencial de Erosão Laminar em Grandes Áreas por Meio da EUPS Equação Universal de Perdas de Solos Utilizando Novas Metodologias em SIG para os Cálculos dos seus Fatores na Região do Alto Parnaíba PI-MA. Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2006, 7, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, G.D.O.R.; Giarolla, A.; Sampaio, G.; Marinho, M.D.A. Estimates of Annual Soil Loss Rates in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo. 2016, 40, e0150497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinne, A.; Rosseau, P. L’érodibilité des sols de moyenne et haute Belgique. Bull. Soc. Géogr. Liège 1978, 14, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Benito, E.; Varela, M.E.; Rodriquez-Alleres, M.; Garcia-Corona, R.; Santiago, J.L. Soil erodibility: Influencing factors and their importance in post-fire erosion. In The Environment in Galicia: A Book of Images; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 597–614. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Lin, L.; Ding, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, K.; Zhao, Y. Characteristics of soil erodibility k value and its influencing factors in the Changyan Watershed, Southwest Hubei, China. Land 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.U.; Shakir, M. Nexus of land use land cover dynamics and extent of soil loss in the Panjkora River Basin of eastern Hindu Kush. J. Water Clim Change 2023, 14, 4669–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Rahman, A.; Mahmood, S. Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk using RUSLE model in District Swat, Eastern Hindu Kush, Pakistan. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 1881–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymond, J.R. Soil erosion in New Zealand is a net sink of CO2. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2010, 35, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, W.C.D.S.; Guerra, A.J.T.; Valladares, G.S. Soil Erosion Modeling Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and a Geographic Information System in a Watershed in the Northeastern Brazilian Cerrado. Geosciences 2024, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, F.M.L.; De Araújo Filho, P.F.; Da Silva, R.M.; Silva, L.P.; Montenegro, S.M.G.L.; de Azevedo, J.R.G. Concentração de sedimentos em suspensão em uma pequena bacia rural no nordeste do Brasil. Simp. Recur. Hídr. Nordeste 2010, 1–15. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/40986856/CONCENTRA%C3%87%C3%83O_DE_SEDIMENTOS_EM_SUSPENS%C3%83O_EM_UMA_PEQUENA_BACIA_RURAL_NO_NORDESTE_DO_BRASIL (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Fistarol, P.H.B.; Santos, J.Y.G. Implicações das alterações no uso e ocupação do solo nas perdas de solo da Bacia do Rio de Ondas, estado da Bahia. Ver. OKARA Geogr. Debate. 2020, 14, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, L.D.S. Estimativa de perda de solos na bacia hidrográfica do rio da Dona—BA. Bachelors’ Thesis, Universidade Federal do Recôncavo da Bahia—UFRB, Cruz das Almas, Brazil, 2018; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulou, M.; Depountis, N.; Nikolakopoulos, K.; Boumpoulis, V. The significance of digital elevation models in the calculation of ls factor and soil erosion. Land 2022, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.R.; George, J.; Raghavendra, S.; Kumar, S.; Agrawal, S. Effect of DEM resolution on LS factor computation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII–5, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shan, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Cruse, R.M.; Liu, B.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Pang, G. Impacts of horizontal resolution and downscaling on the USLE LS factor for different terrains. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İrvem, A.; Topaloğlu, F.; Uygur, V. Estimating spatial distribution of soil loss over Seyhan River Basin in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gertner, G.; Parysow, P.; Anderson, A. Spatial prediction and uncertainty assessment of topographic factor for revised universal soil loss equation using digital elevation models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2001, 56, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, R.; Razavi, S.; Gupta, H.V.; Becker, W.; Haghnegahdar, A. Global sensitivity analysis for high-dimensional problems: How to objectively group factors and measure robustness and convergence while reducing computational cost. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2019, 111, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, E.R.; Bacani, V.M.; Panachuki, E. Modeling soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS in a watershed occupied by rural settlement in the Brazilian Cerrado. Nat Hazards. 2017, 85, 851–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchin, M.; Moura, M.M.D.; Nunes, M.C.M.; Tuchtenhagen, I.K.; Lima, C.L.R.D. Assessment of soil loss susceptibility in Santa Rita watershed in southern Brazil. Eng. Agríc. 2021, 41, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, W.S.; Martins, A.P.; Morais, W.A.; Pôssa, É.M.; Castro, R.M.; Borges de Moura, D.M. USLE modelling of soil loss in a Brazilian cerrado catchment. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 27, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



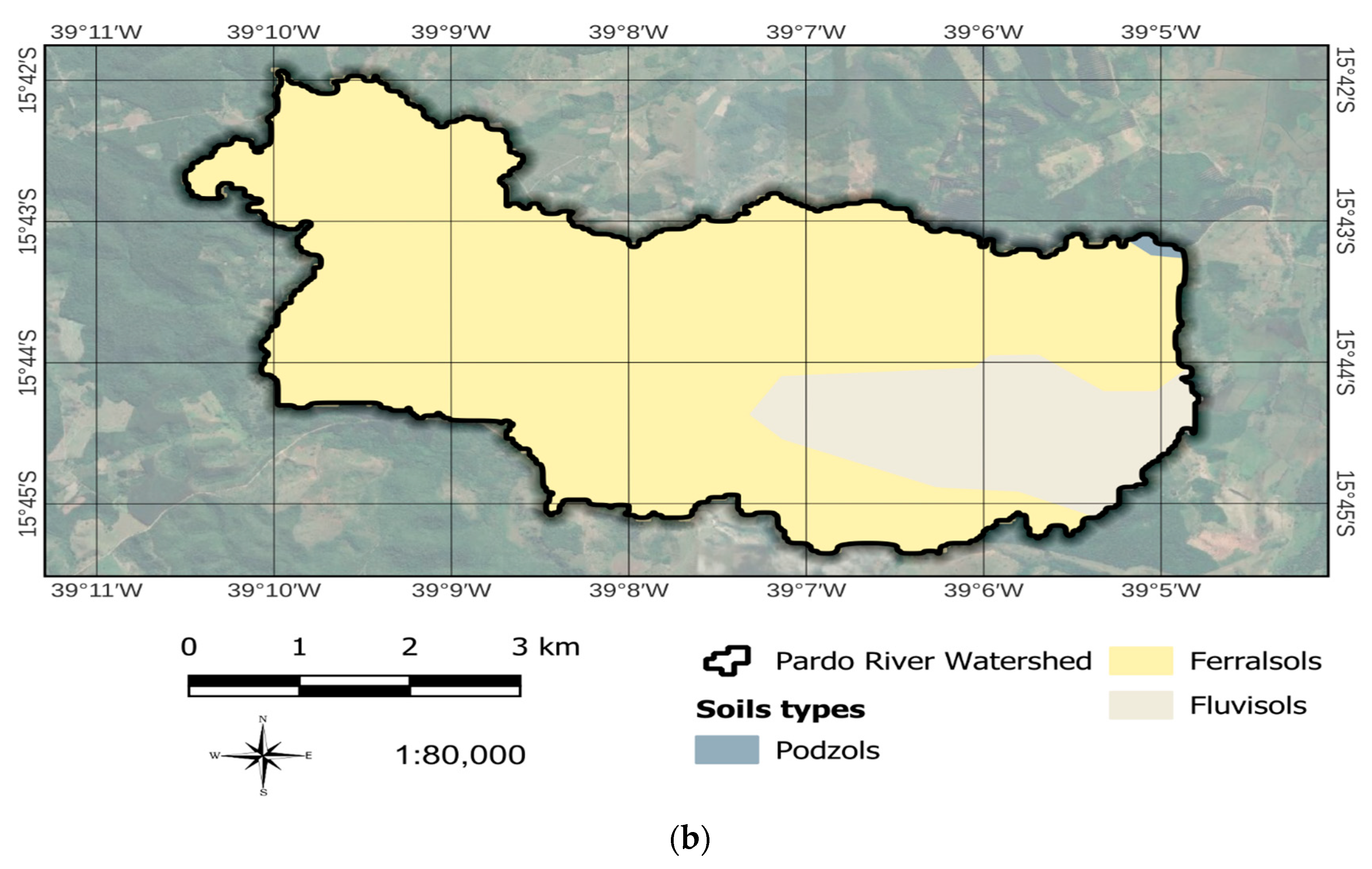
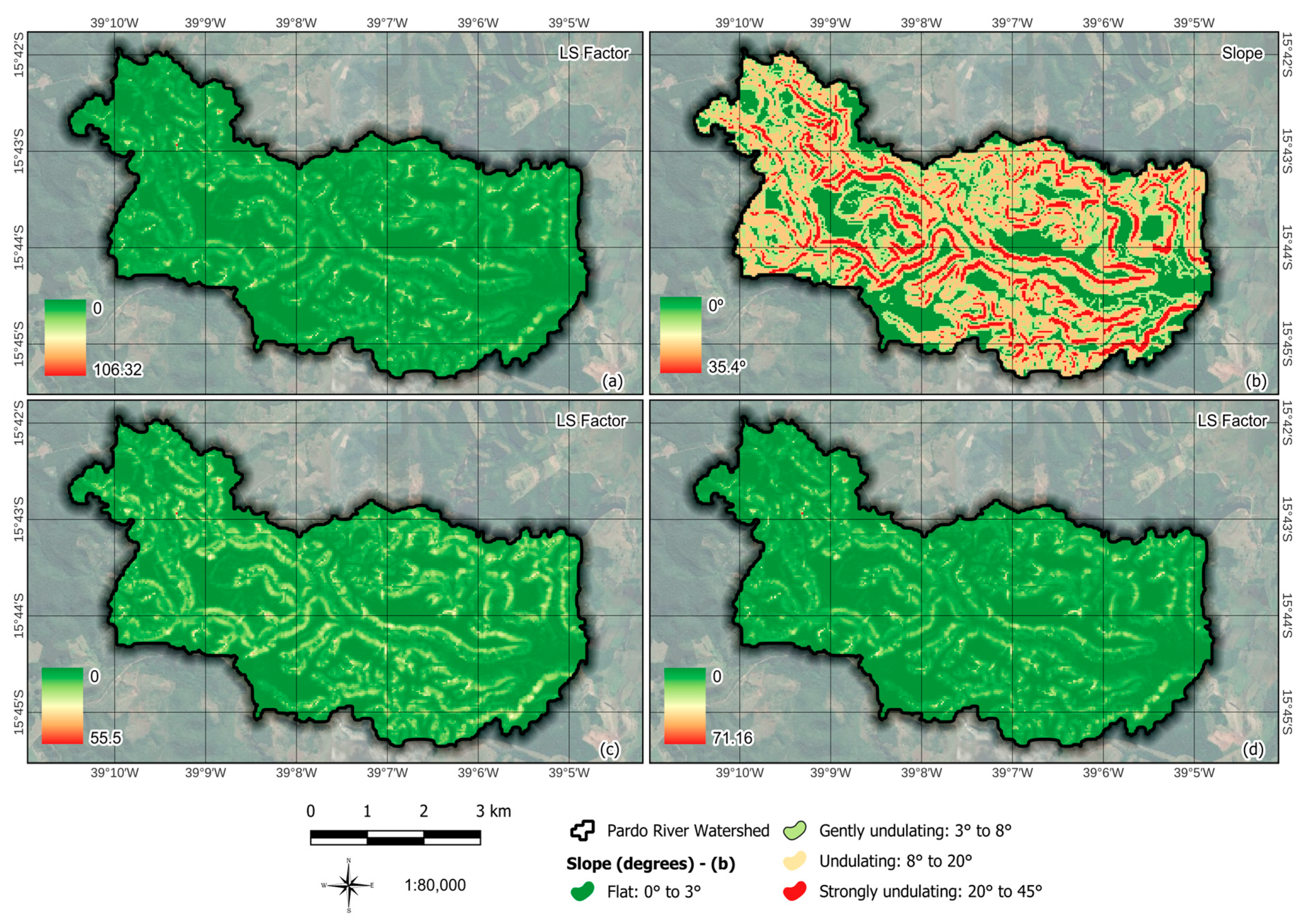
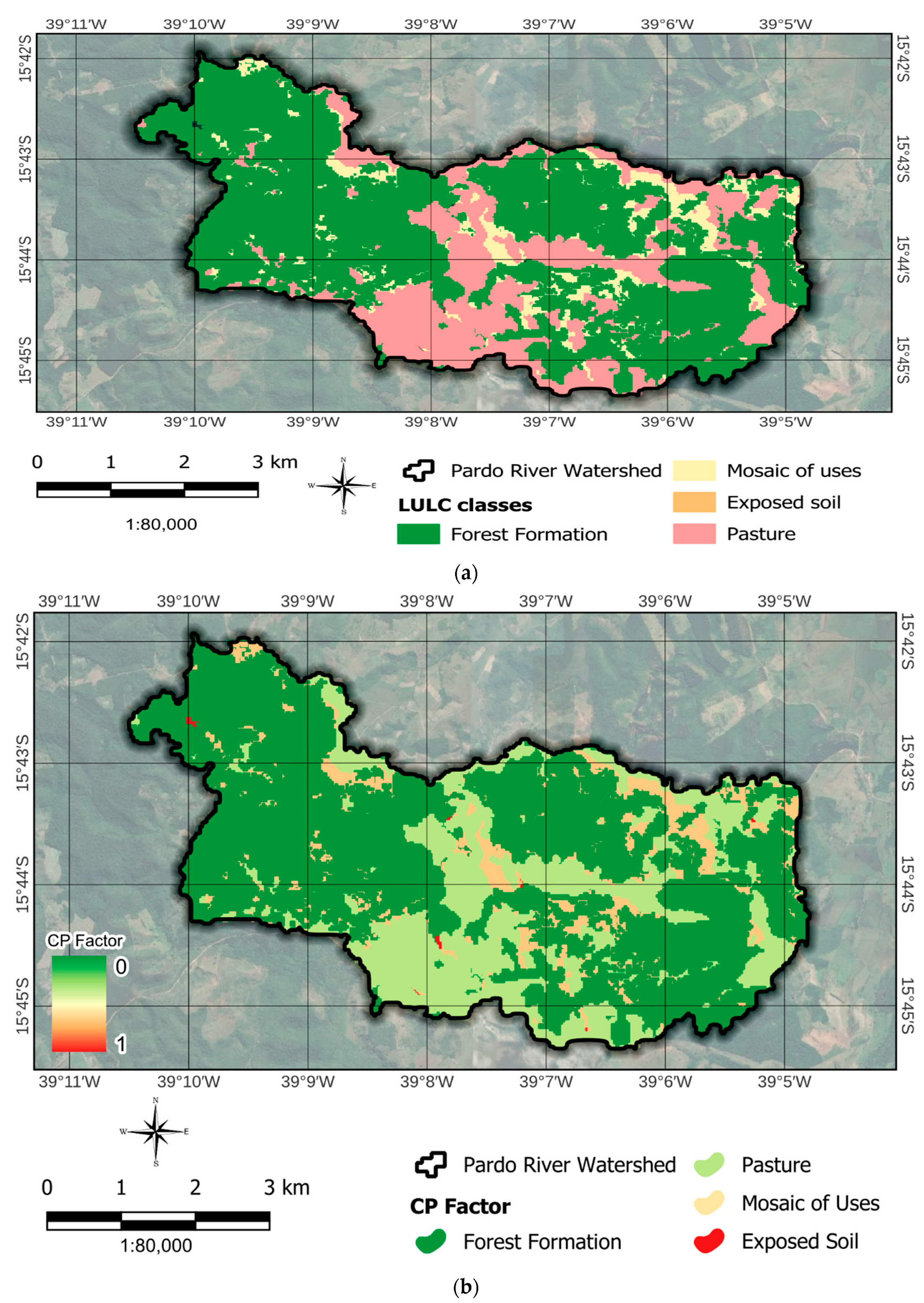




| Locations | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m) | Annual Mean (mm/year) | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caravelas | −17.73944444 | −39.25861111 | 6 | 1426.61 | 1992–2021 |
| Guaratinga | −16.58081 | −39.783182 | 199 | 872.4 | 1992–2021 |
| Itamarandiba | −17.85972222 | −42.85277777 | 920 | 1006.86 | 1992–2021 |
| Salinas | −16.154862 | −42.284921 | 477 | 833.65 | 1992–2021 |
| Salvador (Ondina) | −13.00583333 | −38.50583333 | 53 | 1847.89 | 1992–2021 |
| Vitoria | −20.31583333 | −40.31694443 | 32 | 1294.08 | 1992–2021 |
| Vitoria da Conquista | −14.88638888 | −40.80138888 | 880 | 709.94 | 1992–2021 |
| Input Factors | (F1) | (F2) | (F3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| CP | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| R | 5606.55 | 5775.11 | 5606.55 | 5775.11 | 5606.55 | 5775.11 |
| K | 0.028 | 0.0592 | 0.028 | 0.0592 | 0.028 | 0.0592 |
| m | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.56 |
| n | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.3 |
| β | 0 | 35.436 | 0 | 35.436 | 0 | 35.436 |
| SCA | 8.786 | 15,535.153 | 8.786 | 15,535.153 | 8.786 | 15,535.153 |
| Types of Soils | K (t h MJ−1 mm−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Ferralsols | 0.028 | [106] |
| Fluvisols | 0.046 | [107] |
| Podsols | 0.0592 | [108] |
| Equation No | LS Equations | [m, n] | Min | Max | STD-Dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (4a) | [0.5, 1.15] | 0.0 | 106.32 | 7.07 | |
| (4b) | [0.4, 1.15] | 0.0 | 55.50 | 5.03 | |
| (5) | [0.48, 1.25] | 0.0 | 71.16 | 5.05 |
| Classes | CP Factor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Forest formation | 0.00004 | [91] |
| Pasture | 0.01 | [91] |
| Mosaic of uses | 0.15 | [92] |
| Water | 0 | [61] |
| Exposed soil | 1.0 | [61,114] |
| LS | RUSLE | [m, n] | Min | Max | Mean | STD-Dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (4a) | [0.5, 1.15] | 0.0 | 2733.27 | 29.77 | 117.52 | |
| (4b) | [0.4, 1.15] | 0.0 | 2282.69 | 23.76 | 91.94 | |
| (5) | [0.48, 1.25] | 0.0 | 2103.27 | 21.52 | 85.67 |
| Severity Range t.(ha.year)−1 | Severity Classes | Using LS (4a) | Using LS (4b) | Using LS (5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Area (%) | Area (km2) | Area (%) | Area (km2) | Area (%) | ||
| <5 | Very low | 19.18 | 76.69 | 19.36 | 77.44 | 19.70 | 78.80 |
| 512 | Low | 1.36 | 5.44 | 1.59 | 6.36 | 1.58 | 6.32 |
| 1250 | Moderate | 2.22 | 8.88 | 1.90 | 7.6 | 1.67 | 6.68 |
| 50100 | High | 0.37 | 1.48 | 0.35 | 1.4 | 0.41 | 1.64 |
| 100200 | Very high | 0.56 | 2.24 | 0.66 | 2,64 | 0.69 | 2.76 |
| >200 | Severe | 1.32 | 5.27 | 1.14 | 4.56 | 0.96 | 3.84 |
| Severity Range t.(ha.year)−1 | Severity Classes | Using LS (4a) | Using LS (4b) | Using LS (5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Area (%) | Area (km2) | Area (%) | Area (km2) | Area (%) | ||
| <5 | Very low | 18.72 | 74.87 | 18.87 | 75.47 | 19.19 | 76.74 |
| 512 | Low | 1.15 | 4.58 | 1.23 | 4.93 | 1.31 | 5.25 |
| 1250 | Moderate | 2.62 | 10.46 | 2.57 | 10.27 | 2.30 | 9.19 |
| 50100 | High | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.32 | 1.27 | 0.32 | 1.27 |
| 100200 | Very high | 0.39 | 1.55 | 0.46 | 1.82 | 0.51 | 2.04 |
| >200 | Severe | 1.59 | 6.35 | 1.51 | 6.02 | 1.34 | 5.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
François, M.; Gordon, C.A.; Costa de Oliveira, U.; Rousseau, A.N.; Mariano-Neto, E. Assessing the Global Sensitivity of RUSLE Factors: A Case Study of Southern Bahia, Brazil. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040125
François M, Gordon CA, Costa de Oliveira U, Rousseau AN, Mariano-Neto E. Assessing the Global Sensitivity of RUSLE Factors: A Case Study of Southern Bahia, Brazil. Soil Systems. 2024; 8(4):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040125
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrançois, Mathurin, Camila A. Gordon, Ulisses Costa de Oliveira, Alain N. Rousseau, and Eduardo Mariano-Neto. 2024. "Assessing the Global Sensitivity of RUSLE Factors: A Case Study of Southern Bahia, Brazil" Soil Systems 8, no. 4: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040125
APA StyleFrançois, M., Gordon, C. A., Costa de Oliveira, U., Rousseau, A. N., & Mariano-Neto, E. (2024). Assessing the Global Sensitivity of RUSLE Factors: A Case Study of Southern Bahia, Brazil. Soil Systems, 8(4), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8040125






