Abstract
Following an operational framework derived from earlier research, our study research estimates the specific contribution of biophysical and socioeconomic factors to soil sensitivity to degradation at two-time points (Early-1990s and Early-2010s) in Italy, a Mediterranean hotspot for desertification risk. A total of 34 variables associated (directly or, at least, indirectly) with different processes of soil degradation (erosion, salinization, sealing, contamination, and compaction) and climate change were considered here, delineating the predominant (underlying) cause (i.e., biophysical or socioeconomic). This set of variables represented the largest (quantitative) information available from national and international data sources including official statistics at both national and European scale. Contribution of biophysical and socioeconomic dimensions to soil sensitivity to degradation was heterogeneous in Italy, with the level of soil sensitivity to biophysical factors being the highest in less accessible, natural areas mostly located in hilly and mountainous districts. The highest level of soil sensitivity to socioeconomic drivers was instead observed in more accessible locations around large cities and flat rural districts with crop intensification and low (but increasing) population density. All these factors delineated an enlarged divide in environmental quality between (i) flat and upland districts, and between (ii) Northern and Southern Italian regions. These findings suggest the appropriateness of policy strategies protecting soils with a strong place-specific knowledge, i.e., based on permanent monitoring of local (biophysical and socioeconomic) conditions.
1. Introduction
Soil is a particularly sensitive environmental matrix affected together by biophysical degradation and socioeconomic transformations [1,2,3]. While human activities shape territories to expand their limits and living places, an enlarged anthropogenic pressure is generating a planetary ecological crisis [4]. Undoubtedly, humans need to exploit natural resources; however, it is necessary to identify specific thresholds to avoid the activation of irreparable processes of soil degradation [5,6,7]. Therefore, defining and characterizing research dimensions such as soil sensitivity to degradation [8,9], in turn, associated with the notion of multi-hazard risk of desertification [10,11,12,13], is vital to perform integrated monitoring approaches. While soils are recognized as the most ignored part of the global ecosystem, they are likely the most affected by physical and economic deterioration [14,15,16].
During millennia, the connection between humans and soils became indispensable, allowing the ordered development of the most important advances to establish the current society, including agriculture and mining [17,18,19,20] among others. Soils represent a complex interface which interacts with multiple factors, natural and human ones, whose intensity is unevenly distributed in time and space [21,22]. When the soil surface is properly managed, conserved, and protected, it can be considered a renewable resource [23,24]. However, soil characteristics such as fertility, quality, or depth, are particularly expensive to maintain and associated with very slow (natural) renovation processes [25,26]. Scholars highlight several types of soil degradation processes affecting these above-mentioned characteristics such as erosion [27,28,29,30], organic carbon depletion [31,32,33], sealing [34,35], pollution due to trace or toxic elements [36,37], compaction [38,39], salinization [40,41], nutrient leaching [42,43], or the loss of biodiversity, e.g., because of climate change [44,45,46,47]. All of them could be also enhanced following the potential intensification of human activities [48,49] and global warming [50,51]. To date, the damage caused to the ecosystem services is becoming higher and soil functions are significantly reduced [52,53].
Soil degradation processes have been increasingly observed in both advanced economies and emerging countries. Europe, and especially the Northern Mediterranean region, is widely regarded as a hotspot of soil degradation driven by climate change and increasing human pressure [47,54]. Surpassing soil degradation thresholds may lead to an inevitable process characteristic of soils shifting from an initial (reversible) status of sensitivity to degradation to (strictly irreversible) conditions for desertification [7,55,56]. In these regards, the Mediterranean belt was defined as one of the most sensitive areas affected by soil degradation and early desertification processes [57,58]. Among them, Italy is considered a critical hotspot for many issues together, that include biodiversity loss, wildfires, habitat fragmentation, soil erosion, deforestation, water shortage, and reduction in soil organic matter content [59,60]. In this country, as likely everywhere in the Mediterranean basin, abuse or misuse of soil resources, but also the allocation of land for unsustainable uses have also caused regional disparities in many socio-environmental variables that may further enhance soil degradation intensity [8]. However, it is worthy to highlight that soil degradation is not distributed with the same intensity throughout the Italian territory. Earlier studies demonstrate that there is a spatial asymmetry in the level of soil sensitivity to degradation [61,62]. Together with the rather well-known issue of “territorial disparities” (namely, “socioeconomic inequalities” among regions in the same country), soil quality, and, more generally, “environmental divides” across space (considering both ecological and socioeconomic conditions) are getting increasing attention at both regional and national planning scales [63]. In Italy, soil sensitivity to degradation is recognized to have a strong connection with multiple socioeconomic dimensions, but detailed analyses at the regional scale are rather scarce. Investigating together socioeconomic and biophysical drivers of soil degradation at the appropriate spatial scale will consolidate empirical knowledge about the spatial distribution of soil degradation processes and the more effective policies required to combat them.
In these regards, soil degradation is defined here as a complex process impacting crop production and resulting in the decline of environmental quality and ecosystem services [54]. The distribution of soil quality is assumed to be spatially heterogeneous, depending on geological, climatic, vegetation, and human factors [64,65]. In recent years, however, climate and land-use changes, population increase, and differential economic growth were also assumed to exacerbate soil sensitivity to degradation. Taken together, the effect of such factors can be spatially “neutral” (stable or increasing level of sensitivity over a given area) or “asymmetric” (increasing sensitivity in areas with low or high soil quality), thus amplifying (or reducing) regional disparities in soil quality.
To identify sensitive areas in Italy over a sufficiently long time interval, the present study applies a framework originally proposed by Salvati et al. [63] analyzing 34 variables that quantify the intensity of 6 processes of soil degradation and allow estimation of the overall contribution of biophysical and socioeconomic dimensions of change to the level of soil sensitivity to degradation at an appropriately detailed spatial scale (773 homogeneous agricultural districts) in Italy. Our study completes a traditional, mainstream research based on the Mediterranean Desertification and Land Use (MEDALUS) philosophy to the analysis of desertification risk [62]. The empirical results of this study are considered key to developing efficient decision-making tools informing country-scale and regional-scale measures of soil conservation, reducing spatial disparities in the level of land degradation [63,66]. Relatively few studies were aimed at estimating the specific contribution of biophysical and socioeconomic dimensions of soil degradation at a sufficiently detailed spatial scale over large areas with the final objective of designing more effective policy strategies targeting the causes underlying soil, landscape, and environmental processes of change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Italy extends a surface area of 301,330 km2 and its coastline extends for almost 7500 km. Marked variability in topography, latitude, and proximity to the sea accounts for a great variation in environments, landscapes, climates, and soils [67,68,69]. For instance, the average annual rainfall ranges from less than 400 mm in Sicily to 1500 mm in Northeastern Italy. The country is also socially divided into affluent regions (mainly in Northern Italy) and economically disadvantaged districts (primarily in Southern Italy) [70,71,72].
2.2. Data Sources and Variables
The present study estimates the specific contribution of biophysical and socioeconomic drivers to soil sensitivity to degradation in Italy by applying the operational framework proposed by Salvati et al. [63] and considering a total of 37 variables classified into 6 dimensions of soil degradation (Table 1). These dimensions were delineated following the EU Communication on soil conservation (231/2006) and include five processes of soil degradation (erosion, salinization, sealing, compaction, and (point and diffused) contamination) and an additional component of climate change, supposed to (indirectly) influence soil quality [73]. Variables (and general dimensions) of soil degradation were theoretically related with the proximal cause—either biophysical or socioeconomic—in order to estimate a composite indicator of biophysical (and socioeconomic) sensitivity of soils to degradation (see Table 1). Statistical redundancy when manipulating a high number of variables with the final aim at preparing indicators of soil sensitivity was reduced using multidimensional approaches (e.g., factor analysis). The empirical results of this procedure were finally validated through fieldwork [63].

Table 1.
List and number of variables used in the empirical approach presented in our study distinguishing the related process of soil degradation and the basic component of change (biophysical or socioeconomic).
The selected variables were derived from official statistics (Censuses of Agriculture, Population and Buildings, Industry and Services, whose results were disseminated by the Italian National Statistical Institute (Istat)), land-use and land cover databases (maps derived from the pan-European CORINE Land Cover project: See technical details below in the section), and additional country-specific sources like meteorological statistics and soil cartography. All variables refer to the Early-1990s (mainly 1990 or 1991) and the Early-2010s (mainly 2010 or 2011). All data were collected at a detailed spatial resolution (e.g., municipality or census track for socioeconomic variables, 1:250,000 (or lesser) scale for biophysical variables). Variables were selected according to their documented relationship with soil sensitivity to degradation [73,74,75,76,77,78] according to a previous work by Salvati et al. [63]. A comprehensive review of the rationale for use of most variables as indicators of soil sensitivity to degradation was given in Salvati et al. [63], together with methodological details and a complete description of the variables considered.
2.3. Biophysical and Socioeconomic Indicators of Soil Sensitivity to Degradation
The statistical procedure deriving composite indicators of soil sensitivity consisted of 3 steps: (i) standardization (into a 0–1 numerical scale) of each variable through the algorithm (xobs − xmin)/(xmax − xmin) at the selected spatial scale (773 homogeneous agricultural districts); (ii) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the standardized data matrix (34 variables by 773 locations); (iii) computation of two indicators—delineating the specific importance of “biophysical” and “socioeconomic” dimensions to soil sensitivity to degradation, as the weighted average of the selected variables appropriately associated with the relevant “biophysical” or “socioeconomic” dimension as illustrated in Table 1.
To objectively derive the weight for each indicator, standardized variables were converted to a regular grid covering the investigated area by way of ArcGIS software (ESRI Inc., Redwoods, CA, USA). A common grid size of 1 km was chosen according to the original resolution of the 34 layers considered in this study (1 km for climate, soils, and data derived from population census, 250 m for soil erosion, 100 m for land cover, land-use, and soil salinization variables). A 15 km point grid composed of 1346 nodes was, thus, extracted and the value of each variable estimated at each grid node, after transformation into a 0–1 range [79]. The PCA was then applied to the matrix composed of the 34 transformed variables. The number of significant axes (m) was chosen according to the components with eigenvalues higher than 1. A weight was attributed to each variable by multiplying its contribution to the i-th PCA axis by the proportion of explained variance. The sum of these products for all m-th axes corresponds to the weight assigned to each variable. Weights were expressed as a value ranging between 0 and 1. Composite “biophysical” and “socioeconomic” indicators were finally calculated as the weighted average of the respective variables [8]. The scores of the composite indicators therefore range between 0 and 1, respectively indicating the lowest and the highest contribution to the level of soil sensitivity to degradation at a given location.
3. Results
The spatial distribution of two composites (“biophysical” and “socioeconomic”) indicators of soil sensitivity to degradation at two-time points (the Early-1990s and Early-2010s) in Italy was illustrated in Figure 1 and tabulated as average scores by latitude and elevation (Table 2), regarded as relevant geographical gradients in the analysis of soil degradation and desertification risk in Italy. The indicator of soil sensitivity due to biophysical factors illustrate a north-south gradient in the country: Sensitivity increases substantially from Northern Italy to Southern Italy, mainly because of the inherent drift of climate regimes (more arid moving from Northern to Southern regions). Considering a measurement scale that ranges between 0 (no sensitivity) and 1 (the highest level of soil sensitivity), scores higher than 0.5 were extensively observed along the sea coast all over Italy, both in the major islands (Sicily and Sardinia) and in the Adriatic coast in North-Eastern Italy. Relatively high scores (between 0.4 and 0.5) were also recorded in flat districts close to the sea coast in Southern and Central Italy. A large part of the Po Plain, the largest lowland in Northern Italy, was classified within the same score range. Biophysical conditions leading to soil sensitivity became worse during the study period, as documented in the 2010s map.
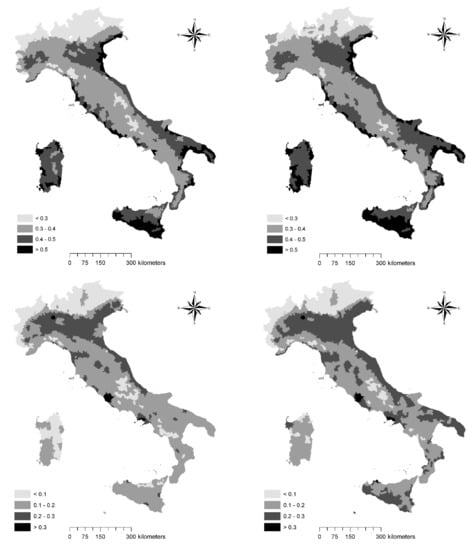
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of biophysical and socioeconomic components of soil sensitivity to degradation (upper left, biophysical indicator in the Early-1990s; upper right: Early-2010s; lower left: Socioeconomic indicator in the Early-1990s; and lower right: Early-2010s).

Table 2.
Average score of socioeconomic and biophysical dimensions of land sensitivity to degradation in Italy by macro-region and time point, and the absolute ratio of socioeconomic to biophysical indicator’s score.
Socioeconomic forces responsible for a high level of soil sensitivity in Italy showed a different spatial distribution centered on more specific territorial “hotspots” corresponding with urban areas, the surrounding peri-urban districts, and some additional flat and rural regions, irrespective of the latitude gradient. Representing the intimate geography of human pressure in Italy, the highest score was observed in the metropolitan areas of Milan, Rome, and Naples, the three major urban agglomerations in the country. A moderate anthropogenic pressure (scores ranging between 0.2 and 0.3) was also recorded in Northern Italy, along the Adriatic Sea coast in Central and Southern Italy and, more sparsely, in districts of South-Western Italy and the two major islands. As far as the role of human pressure shaping soil sensitivity, homogeneous regions were basically found in the Po plain, likely the most densely populated and affluent area of Italy, hosting a mix of intensive crop and livestock, industrial activities, traditional and advanced services, and infrastructures.
Considering average scores by geographical gradients, soil sensitivity to biophysical factors increased almost linearly from Northern regions to Southern regions and increased over time more in Central-Southern Italy than in Northern Italy. The average score in Southern Italy is the highest observed all over the country (0.44 over a 0–1 scale). Soil sensitivity was the highest in lowlands (0.45 over a 0–1 scale), decreasing moderately in uplands, and reaching the lowest level in mountainous districts. These findings delineate how impacts of biophysical drivers of land degradation are, on average, more intense in flat districts of Italy when ecological conditions are less favorable (e.g., drier climate regimes), despite a generally high level of soil fertility. The largest increase over time was found in the mountainous range, declining in both uplands and lowlands, revealing a sort of “spatial rebalance” in the distribution of biophysical drivers of land degradation all over Italy. However, statistical analysis demonstrates that the distribution of the “biophysical” indicator across districts was quite similar in the time points investigated here (Spearman rank correlation testing similarities between the 1990s and 2010s scores, rs = 0.98, p < 0.001, and n = 773).
Soil sensitivity to socioeconomic forces was less clearly distributed all over the country, being moderately higher in Central Italy than in Southern and Northern Italy. A latitude gradient was instead observed for the increase over time in the same indicator, being the largest in Southern Italy (an economically disadvantaged area) and declining in both Central and Northern Italy (including more affluent districts). As expected, lowlands had the highest sensitivity score, reflecting an intense anthropogenic pressure that grew rapidly over time. Scores decreased along the elevation gradient, reaching the lowest value in mountainous districts. Population density, urban concentration, infrastructural development, and industrial growth were likely the most effective forces of change determining, on average, a higher sensitivity of lowlands compared with uplands and mountain ranges. The largest increase over time in soil sensitivity to socioeconomic forces was observed in uplands, likely reflecting socioeconomic processes determining a particularly intense anthropogenic pressure that spreads from lowlands to the surrounding upland districts. The spatial distribution of the socioeconomic indicator remained mostly unaltered in both time periods (Spearman rank correlation testing similarity in the 1990s and 2010s scores, rs = 0.93, p < 0.001, and n = 773). Confirming earlier results, the biophysical indicator of soil sensitivity increased weakly with population density, a proxy of human pressure in Italy (rs = 0.31 and 0.26 for the Early-1990s and the Early-2010s, both at p < 0.05, and n = 773). As expected, the socioeconomic indicator showed the reverse pattern, rising significantly with density (rs = 0.58 and 0.61 for the Early-1990s and the Early-2010s, both at p < 0.001, and n = 773).
The spatial relationship between socioeconomic and biophysical indicators of soil sensitivity to degradation in Italy was illustrated in Figure 2 at the level of homogeneous agricultural districts. At both investigation times, the relationship was strongly positive (Early-1990s: Socioeconomic indicator = 0.733 * (biophysical indicator) + 0.266, R2 = 0.275; Early-2010s: Socioeconomic indicator = 0.757 * (biophysical indicator) + 0.269, R2 = 0.320). A non-parametric Spearman pair-wise rank correlation confirmed these results, indicating a significant correlation between the two indicators of soil sensitivity to degradation, both in the Early-1990s (rs = 0.56, p < 0.001, and n = 773), and in the Early-2010s (rs = 0.56, p < 0.001, and n = 773). Although the studied relationship was linear, a more evident heterogeneity was observed in agricultural districts showing the highest values of soil sensitivity to biophysical factors.

Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of the absolute ratio of socioeconomic-to-biophysical indicator of soil sensitivity to degradation in Italy (left, the Early-1990s; middle: The Early-2010s; and right: Change over time, where “<1” indicates a decreasing ratio, “>1” denotes an increasing ratio).
Taken together, these results indicate a partial substitution between biophysical and socioeconomic factors of soil sensitivity especially in agricultural districts with less critical background conditions (left side of Figure 2). In such contexts, the intrinsically linear relationship between the two drivers suggests the importance of (formal and informal) measures impacting both (“socioeconomic” and “biophysical”) dimensions of change, e.g., enhancing adaptation to climate change and mitigating human pressure at the same time. In more critical conditions (right side of Figure 2), the relationship between the two drivers was found less homogeneous and predictable, suggesting the key role of local forces (mostly “biophysical”) shaping particularly high levels of sensitivity to soil degradation.
The absolute ratio of socioeconomic to biophysical indicators’ scores provides a summary view of the intrinsic role of both drivers in soil sensitivity to degradation of Italy. Generally speaking, the importance of biophysical factors was dominant all over Italy, as far as soil sensitivity is concerned. However, spatial asymmetries were observed that may indicate differentiated conditions at both regional and local levels. According to basic statistics reported in Table 2, the ratio was higher (stronger role of socioeconomic forces) in Central and Northern Italy, reflecting a significantly higher human pressure than in the rest of Italy, increasing largely over time. Southern Italy totalized the lowest importance of socioeconomic forces and the lowest increase over time in the country. Socioeconomic forces were particularly intense in lowlands, reducing progressively in uplands and, especially, mountainous districts, as illustrated in Figure 3.
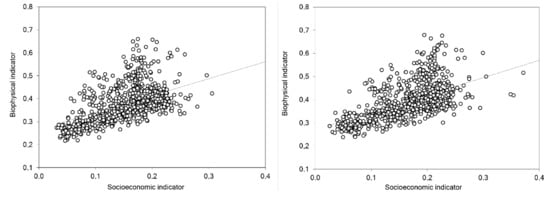
Figure 3.
The relationship between socioeconomic and biophysical indicators of soil sensitivity to degradation in Italy at the spatial level of agricultural homogeneous districts (left: Early-1990s and right: Early-2010s).
4. Discussion
With our study, emphasis has been placed on a detailed analysis’ scale of land degradation dynamics in the Mediterranean region, since earlier studies covering large areas were especially oriented to calibrate monitoring approaches addressing desertification risk [79,80,81]. On the contrary, diachronically quantifying spatial disparities in soil sensitivity to degradation in both affected and non-affected regions at country (or supra-national) scale, provides robust, key information for policies aimed at contrasting soil deterioration, land degradation, and, ultimately, desertification in the Mediterranean basin [82]. Results of our study suggest how soil degradation can be effectively managed only by a thorough understanding of the factors generating territorial disparities and influencing the quality of the environment [64]. By the contrary, environmental policies more frequently concentrated on specific soil degradation processes, such as soil erosion, e.g., by introducing agro-environmental schemes and measures within the Common Agricultural Policy framework. These measures have been demonstrated to be partially effective in the Mediterranean region [82], needing a broader action framework that encompasses multiple degradation processes with both biophysical and socioeconomic origin (from soil erosion to salinization, from soil sealing to contamination).
By considering six groups of factors related to soil degradation, this study showed how the affected land area increased throughout Italy during the investigated period. The highest increase was concentrated in the region’s most vulnerable to soil deterioration. This process seems to amplify the “environmental divide” observed in the Early-1990s between “structurally” sensitive lands (i.e., semi-arid or dryland districts, agriculture-oriented, and with rural poverty, mainly found in Southern Italy) and less sensitive lands (relatively wet climate, mainly service-oriented regions with high per capita income, mostly located in Central and Northern Italy). This gap may trigger a downward spiral of land degradation determining soil quality loss at the regional scale (e.g., [63]). More specifically, the empirical findings of our study indicate that: (i) in districts with most critical conditions (mainly located in Southern Italy), soil sensitivity to degradation mostly depends on the synergic action of biophysical factors. In such contexts, the additional impact of socioeconomic forces was spatially heterogeneous and quite moderate; (ii) in less critical contexts, the impact of biophysical and socioeconomic forces was more balanced and both drivers contribute substantially to determine the (increasing) level of soil sensitivity to degradation.
These findings were graphically summarized in Figure 4 comparing the per cent rate of growth over time characteristic of both socioeconomic and biophysical indicators. The two rates of growth were significant and non-linearly correlated (rs = 0.13, p < 0.05, and n = 773), evidencing a moderate inverse U-shaped trend that denotes how the highest increase in the socioeconomic indicator of soil sensitivity was observed in agricultural districts experiencing an intermediate growth of the biophysical indicator of soil sensitivity. More importantly, the largest part (nearly nine out of ten) of critical districts (with a biophysical indicator score systematically above 0.5) experienced a positive increase of both indicators during the study period. Moreover, the intrinsic growth of the socioeconomic indicator was significantly higher in highly sensitive districts than in non-sensitive areas. Such evidence delineates a future scenario with worse conditions of soil sensitivity driven by an even stronger interplay of biophysical and socioeconomic forces. While the most critical districts remain associated with a profile of soil sensitivity to degradation basically dependent on biophysical factors, intermediate and moderately critical districts were increasingly characterized by the joint impact of both forces. Differentiated strategies targeting soil sensitivity to degradation should address critical and less critical areas, distinguishing the impact of specific drivers of sensitivity over a sufficiently long time interval and taking specific actions against the most relevant factors of land degradation.
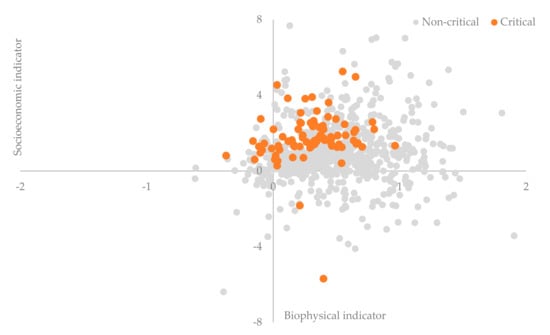
Figure 4.
Per cent rate of change over time (from the Early-1990s to the Early-2010) in two indicators of soil sensitivity to degradation in homogeneous agricultural districts of Italy, distinguishing between critical and non-critical districts (biophysical indicator >0.5 or <0.5 in the early 2010s).
Taken together, these results refine and corroborate the empirical findings presented in earlier studies [79], outlining the need for more careful identification of local “hot-spots” of soil degradation in non-affected regions. Furthermore, our study confirms that the increased sensitivity to soil degradation in Italy depends on the synergic impact of biophysical and socioeconomic factors [64,65,73]. Interestingly enough, the socioeconomic drivers of soil degradation, including changes in land management, crop intensification, population growth, and urban sprawl, explain the larger increase in the degree of land sensitivity especially in the less ecologically “fragile” areas, with definite implications for policies aimed at reducing socioeconomic disparities among regions [83,84,85]. In this perspective, a renewed effort should be made to deploy multi-scalar and multi-targeted policies for mitigation of soil degradation and, ultimately, desertification risk [78]. Fields of application should encompass agriculture, water, sustainable use of land, population dynamics, economic growth, and social change. Measures should go therefore towards an “integrated vision” of territorial processes and disparities related to soil degradation [86,87,88].
Following the commitment of the National Action Plans developed in Northern Mediterranean countries (e.g., Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece) [89], there is an evident need to coordinate regional, country and supra-national strategies for soil quality and sustainable development in order to reduce the “environmental divide” between critical and non-critical areas [90,91,92]. In these regards, coordinated policies should promote the economic growth of regions together with the conservation of their socio-environmental quality within a spatially balanced framework [93]. According to the European Strategy for Soil Protection, a comprehensive approach informing synergic, multi-target measures against soil degradation at country scale should parallel sector policies and single-target actions enforced at regional and local scales. Examples of single-target actions include measures reducing soil erosion by water or wind in affected areas, e.g., giving incentives (or economic subsidies) to farmers adopting less intensive mechanization (e.g., no-tillage and minimum tillage). This kind of measures should be better connected with broader policies promoting rural development, e.g., supporting farms that adopt organic cultivations protocols reducing the use of chemicals, with positive implications for soil contamination. Fine-tuning of actions addressing specific soil degradation targets will definitely improve the overall effectiveness of any national strategy of soil protection. Additionally, further studies should incorporate an explicit analysis of other dimensions of soil degradation—mainly based on the geological risk. Landslides, flooding, and the intrinsic contribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and tsunamis to soil degradation can be more effectively identified and quantified, being relevant phenomena in Mediterranean countries. The proposed analysis’ framework can easily incorporate these dimensions providing a truly “holistic” analysis of soil degradation.
5. Conclusions
Contribution of biophysical and socioeconomic dimensions to soil sensitivity to degradation was largely heterogeneous in Italy, with the level of soil sensitivity to biophysical factors being the largest in less accessible, natural areas mostly located in hilly and mountainous districts. The highest level of soil sensitivity to socioeconomic drivers was instead observed in more accessible locations around large cities and flat rural districts with crop intensification and low (but increasing) population density. All these factors delineate an enlarged “environmental divide” between (i) flat and upland districts and between (ii) Northern and Southern Italy, suggesting the appropriateness of dedicated, policy strategies protecting soils with a strong place-specific knowledge, i.e., based on permanent monitoring of local (biophysical and socioeconomic) conditions. These strategies should achieve a particularly ambitious objective improving environmental cohesion between more and less sensitive territories to soil degradation in light of a “spatial justice” vision.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S. and G.E.; methodology, F.G. and M.P.; software, A.G.-M.; validation, G.E.; formal analysis, N.M., A.G.-M. and F.G.; investigation, M.P. and N.M.; resources, F.G. and G.E.; data curation, G.E.; writing—original draft preparation, L.S. and A.C.; writing—review and editing, N.M. and J.R.-C.; visualization, M.P.; supervision, A.G.-M.; project administration, F.G.; funding acquisition, F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received no funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data in this study were derived from official statistics from Eurostat (www.eurostat.eu), European Environment Agency (www.eea.eu) and national sources such as the Italian National Institute of Statistics (www.istat.it), and the Italian High Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (www.isprambiente.it).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; López-Vicente, M.; Kumar, V.; Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Valkó, O.; Rojas, C.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Salvati, L.; Bakr, N.; Vaudour, E.; et al. Soil Science Challenges in a New Era: A Transdisciplinary Overview of Relevant Topics. Air Soil Water Res. 2020, 13, 1178622120977491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Mausbach, M.J.; Doran, J.W.; Cline, R.G.; Harris, R.F.; Schuman, G.E. Soil quality: A concept, definition, and framework for evaluation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1997, 61, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, M. Territory incognita. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2020, 44, 1019–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gutiérrez, Á.; Schnabel, S.; Lavado-Contador, J.F. Gully erosion, land use and topographical thresholds during the last 60 years in a small rangeland catchment in SW Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.A.; Dugmore, A.J.; Thomson, A. Vésteinsson Crossing the thresholds: Human ecology and historical patterns of landscape degradation. Catena 2001, 42, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, M.; Eitzinger, J.; Hlavinka, P.; Dubrovský, M.; Semerádová, D.; Štěpánek, P.; Thaler, S.; Žalud, Z.; Možný, M.; Formayer, H. Climate-driven changes of production regions in Central Europe. Plant Soil Environ. 2009, 10, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Mancini, A.; Bajocco, S.; Gemmiti, R.; Carluxcci, M. Socioeconomic development and vulnerability to land degradation in Italy. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Brungard, C.W.; Finke, P. Disaggregating and updating a legacy soil map using DSMART, fuzzy c-means and k-means clustering algorithms in Central Iran. Geoderma 2019, 340, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.C.; Malamud, B.D. Anthropogenic processes, natural hazards, and interactions in a multi-hazard framework. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 166, 246–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardoni, P.; LaFave, J.M. Multi-hazard approaches to civil infrastructure engineering: Mitigating risks and promoting resilence. In Multi-Hazard Approaches to Civil Infrastructure Engineering; Gardoni, P., LaFave, J.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizerland, 2016; pp. 3–12. ISBN 978-3-319-29713-2. [Google Scholar]
- Orlecka-Sikora, B.; Lasocki, S.; Kocot, J.; Szepieniec, T.; Grasso, J.R.; Garcia-Aristizabal, A.; Schaming, M.; Urban, P.; Jones, G.; Stimpson, I.; et al. An open data infrastructure for the study of anthropogenic hazards linked to georesource exploitation. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Kariminejad, N.; Amiri, M.; Edalat, M.; Zarafshar, M.; Blaschke, T.; Cerda, A. Assessing and mapping multi-hazard risk susceptibility using a machine learning technique. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, E.M.; Oldeman, L.R. Global Assessment of Human-Induced Soil Degradation. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 1999, 13, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaikie, P.; Brookfield, H. Land Degradation and Society; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-317-41194-9. [Google Scholar]
- Prager, K.; Schuler, J.; Helming, K.; Zander, P.; Ratinger, T.; Hagedorn, K. Soil degradation, farming practices, institutions and policy responses: An analytical framework. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J. Five decades of soil erosion research in “terroir”. The State-of-the-Art. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Stott, D.E. A framework for evaluating physical and chemical indicators of soil quality. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezdicek, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 53–72. ISBN 0-89118-930-0. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, R.W. Soil Geography and Factor Functionality: Interacting Concepts. Factors Soil Form. A Fiftieth Anniv. Retrosp. 1994, 33, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, E.C.; Slaughter, L.; Singh, B.R.; Steffan, J.J.; Collier, D.; Barnhart, P.; Pereira, P. Soil and Human Health: Current Status and Future Needs. Air Soil Water Res. 2020, 13, 1178622120934441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B. Subsystem studies: Geophysical factors, soils. Environmental Monograph—Institute for Environmental Studies. Univ. Tor. 1981, 2, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gomiero, T. Soil Degradation, Land Scarcity and Food Security: Reviewing a Complex Challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berazneva, J.; Conrad, J.M.; Güereña, D.T.; Lehmann, J.; Woolf, D. Agricultural Productivity and Soil Carbon Dynamics: A Bioeconomic Model. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2019, 101, 1021–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Barham, B.L.; Coxhead, I. Recovering soil productivity attributes from experimental data: A statistical method and an application to soil productivity dynamics. Geoderma 2000, 96, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Lavee, H.; Romero-Díaz, A.; Hooke, J.; Montanarella, L. Preface: Soil erosion and degradation in mediterranean type ecosystems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Katsoyiannis, A. Soil erosion modelling: The new challenges as the result of policy developments in Europe. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.A.; Rosa, I.M.D.; Valentini, E.; Wolf, F.; Filipponi, F.; Karger, D.N.; Nguyen Xuan, A.; Mathieu, J.; Lavelle, P.; Eisenhauer, N. Global vulnerability of soil ecosystems to erosion. Landsc. Ecol 2020, 35, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Alsafadi, K.; Talukdar, S.; Kiwan, S.; Hennawi, S.; Alshihabi, O.; Sharaf, M.; Harsanyie, E. Estimation of soil erosion risk in southern part of Syria by using RUSLE integrating geo informatics approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Schneider, C. Environmental characteristics, agricultural land use, and vulnerability to degradation in Malopolska Province (Poland). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, J.L.; Davies, Z.G.; McHugh, N.; Gaston, K.J.; Leake, J.R. Organic carbon hidden in urban ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledo, A.; Smith, P.; Zerihun, A.; Whitaker, J.; Vicente-Vicente, J.L.; Qin, Z.; McNamara, N.P.; Zinn, Y.L.; Llorente, M.; Liebig, M.; et al. Changes in soil organic carbon under perennial crops. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 4158–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Schillaci, C.; Laudicina, V.A.; La Mantia, T. Turnover and availability of soil organic carbon under different Mediterranean land-uses as estimated by \textlesssup\textgreater13\textless/sup\textgreaterC natural abundance. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, A.; Frangi, P.; Mori, J.; Donzelli, D.; Ferrini, F. Nature based solutions to mitigate soil sealing in urban areas: Results from a 4-year study comparing permeable, porous, and impermeable pavements. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, M.; Salvati, L.; Zitti, M. Estimating soil sealing rate at national level—Italy as a case study. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 26, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Arenas-Lago, D.; Lago-Vila, M.; Vega, F.A.; Andrade Couce, L. Limitations for revegetation in lead/zinc minesoils (NW Spain). J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, A.; Kumar, V. Ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metal contamination in agricultural soils of Northeastern Iran. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.; Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Bienes, R.; García-Díaz, A.; Sastre, B. Effects of a Permanent Soil Cover on Water Dynamics and Wine Characteristics in a Steep Vineyard in the Central Spain. Air Soil Water Res. 2020, 13, 1178622120948069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, M.; Schnabel, S.; Lavado Contador, J.F.; Lozano-Parra, J.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, Á.; Brevik, E.C.; Cerdà, A. Reduction of the frequency of herbaceous roots as an effect of soil compaction induced by heavy grazing in rangelands of SW Spain. Catena 2017, 158, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababou, A.; Chouieb, M.; Khader, M.; Mederbal, K.; Saidi, D. Using vegetation units as salinity predictors in the Lower Cheliff Algeria. Turk. J. Bot. 2010, 34, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, J.A.; Faz, A.; Jansen, B.; Kalbitz, K.; Martínez-Martínez, S. Assessment of salinity status in intensively cultivated soils under semiarid climate, Murcia, SE Spain. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arheimer, B.; Lidén, R. Nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations from agricultural catchments—Influence of spatial and temporal variables. J. Hydrol. 2000, 227, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, M.; Våje, P.I. Monitoring erosion and nutrient losses from small basins representative of Norwegian agriculture. Agricultural effects on ground and surface waters: Research at the edge of science and society. In Proceedings of the an international symposium, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 21 October 2002; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Baveye, P.C.; Berthelin, J.; Munch, J.-C. Too much or not enough: Reflection on two contrasting perspectives on soil biodiversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Trivedi, C.; Eldridge, D.J.; Abades, S.; Alfaro, F.D.; Bastida, F.; Berhe, A.A.; Cutler, N.A.; Gallardo, A.; et al. Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W. Patterns and uncertainties of species’ range shifts under climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S., III; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global Biodiversity Scenarios for the Year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, S.; Prasuhn, V.; Liniger, H.; Herweg, K.; Hurni, H.; Candinas, A.; Gujer, H.U. A high-resolution map of direct and indirect connectivity of erosion risk areas to surface waters in Switzerland—A risk assessment tool for planning and policy-making. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M. The effects of land uses on soil erosion in Spain: A review. CATENA 2010, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalov, S.; Golosov, V.; Collins, A.; Stone, M. Preface: Land use and climate change impacts on erosion and sediment transport. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2019, 381, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Pruski, F.F.; O’Neal, M.R. Expected climate change impacts on soil erosion rates: A review. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Baveye, P.C.; Baveye, J.; Gowdy, J. Soil “Ecosystem” Services and Natural Capital: Critical Appraisal of Research on Uncertain Ground. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsson, J.Ö.G.; Davíðsdóttir, B. Classification and valuation of soil ecosystem services. Agric. Syst. 2016, 145, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, D.; Cramer, W.; Leemans, R.; Prentice, I.C.; Araújo, M.B.; Arnell, N.W.; Bondeau, A.; Bugmann, H.; Carter, T.R.; Gracia, C.A.; et al. Ecosystem Service Supply and Vulnerability to Global Change in Europe. Science 2005, 310, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, N.; Weindorf, D.C.; Bahnassy, M.H.; El-Badawi, M.M. Multi-temporal assessment of land sensitivity to desertification in a fragile agro-ecosystem: Environmental indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Bao, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, L.; Long, C.; Kong, Z.; Peng, P.; Xiao, J.; Lu, Q. Desertification: China provides a solution to a global challenge. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2017, 4, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaez, J.; Lasanta, T.; Errea, M.P.; Ortigosa, L. Land abandonment, landscape evolution, and soil erosion in a Spanish Mediterranean mountain region: The case of Camero Viejo. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Stellmes, M.; Udelhoven, Th.; Röder, A.; Sommer, S. Mediterranean desertification and land degradation: Mapping related land use change syndromes based on satellite observations. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajocco, S.; de Angelis, A.; Salvati, L. A satellite-based green index as a proxy for vegetation cover quality in a Mediterranean region. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajocco, S.; Salvati, L.; Ricotta, C. Land degradation versus fire: A spiral process? Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2011, 35, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairis, O.; Karavitis, C.; Salvati, L.; Kounalaki, A.; Kosmas, K. Exploring the Impact of Overgrazing on Soil Erosion and Land Degradation in a Dry Mediterranean Agro-Forest Landscape (Crete, Greece). Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Karamesouti, M.; Kounalaki, K.; Detsis, V.; Vassiliou, P.; Salvati, L. Land degradation and long-term changes in agro-pastoral systems: An empirical analysis of ecological resilience in Asteroussia—Crete (Greece). Catena 2016, 147, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Bajocco, S.; Ceccarelli, T.; Zitti, M.; Perini, L. Towards a process-based evaluation of land vulnerability to soil degradation in Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoff, A.W.; Meri, J. (Eds.) Unravelling Desertification; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 978-90-76998-42-8. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, J.M.; Misana, S.; Campbell, D.; Mbonile, M.; Mugisha, S. Framework to Identify the Root Causes of Land Use Change Leading to Land Degradation and Changing Biodiversity. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Framework-to-Identify-the-Root-Causes-of-Land-Use-Olson-Misana/e195e5b0a2ad27fee15bfec7ca80aeabe082dc09 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Sommer, S.; Zucca, C.; Grainger, A.; Cherlet, M.; Zougmore, R.; Sokona, Y.; Hill, J.; Peruta, R.D.; Roehrig, J.; Wang, G. Application of indicator systems for monitoring and assessment of desertification from national to global scales. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarascia, M.E.V.; Battista, F.D.; Salvati, L. Water resources in Italy: Availability and agricultural uses. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incerti, G.; Feoli, E.; Salvati, L.; Brunetti, A.; Giovacchini, A. Analysis of bioclimatic time series and their neural network-based classification to characterise drought risk patterns in South Italy. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2007, 51, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Petitta, M.; Ceccarelli, T.; Perini, L.; Battista, F.D.; Scarascia, M.E.V. Italy’s renewable water resources as estimated on the basis of the monthly water balance. Irrig. Drain. 2008, 57, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelli, F.M.; Ciommi, M.; Emili, A.; Gigliarano, C.; Taralli, S. Assessing the Equitable and Sustainable Well-Being of the Italian Provinces. Int. J. Unc. Fuzz. Knowl. Based Syst. 2016, 24, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciommi, M.; Gigliarano, C.; Emili, A.; Taralli, S.; Chelli, F.M. A new class of composite indicators for measuring well-being at the local level: An application to the Equitable and Sustainable Well-being (BES) of the Italian Provinces. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciommi, M.; Gentili, A.; Ermini, B.; Gigliarano, C.; Chelli, F.M.; Gallegati, M. Have Your Cake and Eat it Too: The Well-Being of the Italians (1861–2011). Soc. Indic. Res. 2017, 134, 473–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L. Trends in land degradation in Europe. In Climate and Land Degradation; Sivakumar, M.V.K., Ndiang’ui, N., Eds.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 83–104. ISBN 978-3-540-72438-4. [Google Scholar]
- Salvati, L.; Zitti, M.; Ceccarelli, T. Integrating economic and environmental indicators in the assessment of desertification risk: A case study. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2007, 6, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado Contador, J.F. Adaptive management, monitoring, and the ecological sustainability of a thermal-polluted water ecosystem: A case in SW Spain. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 104, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavado Contador, J.F.; Schnabel, S.; Gómez Gutiérrez, Á; Pulido Fernández, M. Sensibilidad ambiental a la degradación en Extremadura (España). Boletín de la Asoc. de Geógrafos Españoles 2010, 53, 147–164. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, M.; Caccamo, G.; Laurenti, A.; Noce, S.; Valentini, R. A multi-component GIS framework for desertification risk assessment by an integrated index. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.L.; Recatalá, L. The relevance and consequences of Mediterranean desertification including security aspects. In Proceedings of the Desertification in the Mediterranean Region. A Security Issue; Kepner, W.G., Rubio, J.L., Mouat, D.A., Pedrazzini, F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 133–165. [Google Scholar]
- Salvati, L.; Zitti, M. Assessing the impact of ecological and economic factors on land degradation vulnerability through multiway analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado Contador, J.F.; Schnabel, S.; Gómez Gutiérrez, Á. An evaluation of the MEDALUS ESA Index (environmental sensitivity to land degradation), from regional to plot scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Desertification, Bari, Italy, 16–18 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, E.A.C.; Urbano, F.; Aramini, G.; Barbetti, R.; Bellino, F.; Bocci, M.; Bonati, G.; Fais, A.; L’Abate, G.; Loj, G.; et al. Rationale and methods for compiling an atlas of desertification in Italy. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, H. Governing desertification in Mediterranean Europe: The challenge of environmental policy integration in multi-level governance contexts. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosti, L.; Yamaguchi, C.; Castagnetti, C. Educational Performance as Signalling Device: Evidence from Italy. Econ. Bull. 2005, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rosti, L.; Chelli, F. Self-employment among Italian female graduates. Educ. Train. 2009, 51, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliarano, C.; Chelli, F.M. Measuring inter-temporal intragenerational mobility: An application to the Italian labour market. Qual. Quant. 2016, 50, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar-Schuster, M.; Stringer, L.C.; Erlewein, A.; Metternicht, G.; Minelli, S.; Safriel, U.; Sommer, S. Unpacking the concept of land degradation neutrality and addressing its operation through the Rio Conventions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Monitoring soil for sustainable development and land degradation neutrality. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; De Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; Molenaar, C.; de Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-Related Sustainable Development Goals: Four Concepts to Make Land Degradation Neutrality and Restoration Work. Land 2018, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, H. Combating land degradation and desertification: The land-use planning quandary. Land 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Benedetti, A.; Ferrara, C.; Salvati, L. Soil matters? A multivariate analysis of socioeconomic constraints to urban expansion in Mediterranean Europe. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 146, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamesouti, M.; Detsis, V.; Kounalaki, A.; Vasiliou, P.; Salvati, L.; Kosmas, C. Land-use and land degradation processes affecting soil resources: Evidence from a traditional Mediterranean cropland (Greece). Catena 2015, 132, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairis, O.; Karavitis, C.; Kounalaki, A.; Salvati, L.; Kosmas, C. The effect of land management practices on soil erosion and land desertification in an olive grove. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuindeau, B. Territorial Equity and Sustainable Development. Environ. Values 2007, 16, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).