Summertime Soil-Atmosphere Ammonia Exchange in the Colorado Rocky Mountain Front Range Pine Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
KH∙[H+],
2. Materials and Methods
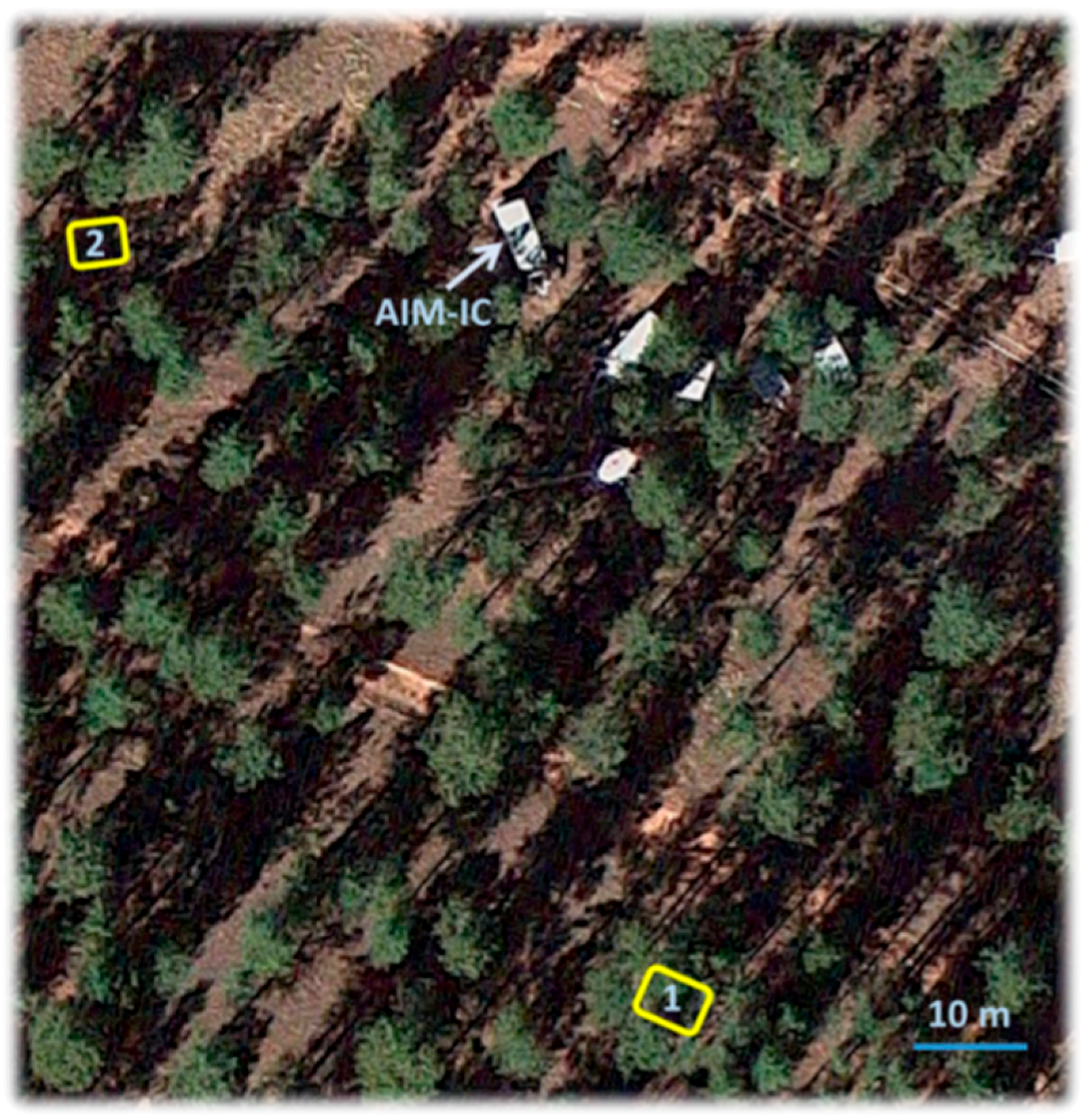
2.1. Site Description
2.2. In-Canopy Trace Gas and Particle Composition Measurements
2.3. Soil Measurements
2.4. Ponderosa Pine Measurements
2.5. Flux Calculations
3. Results
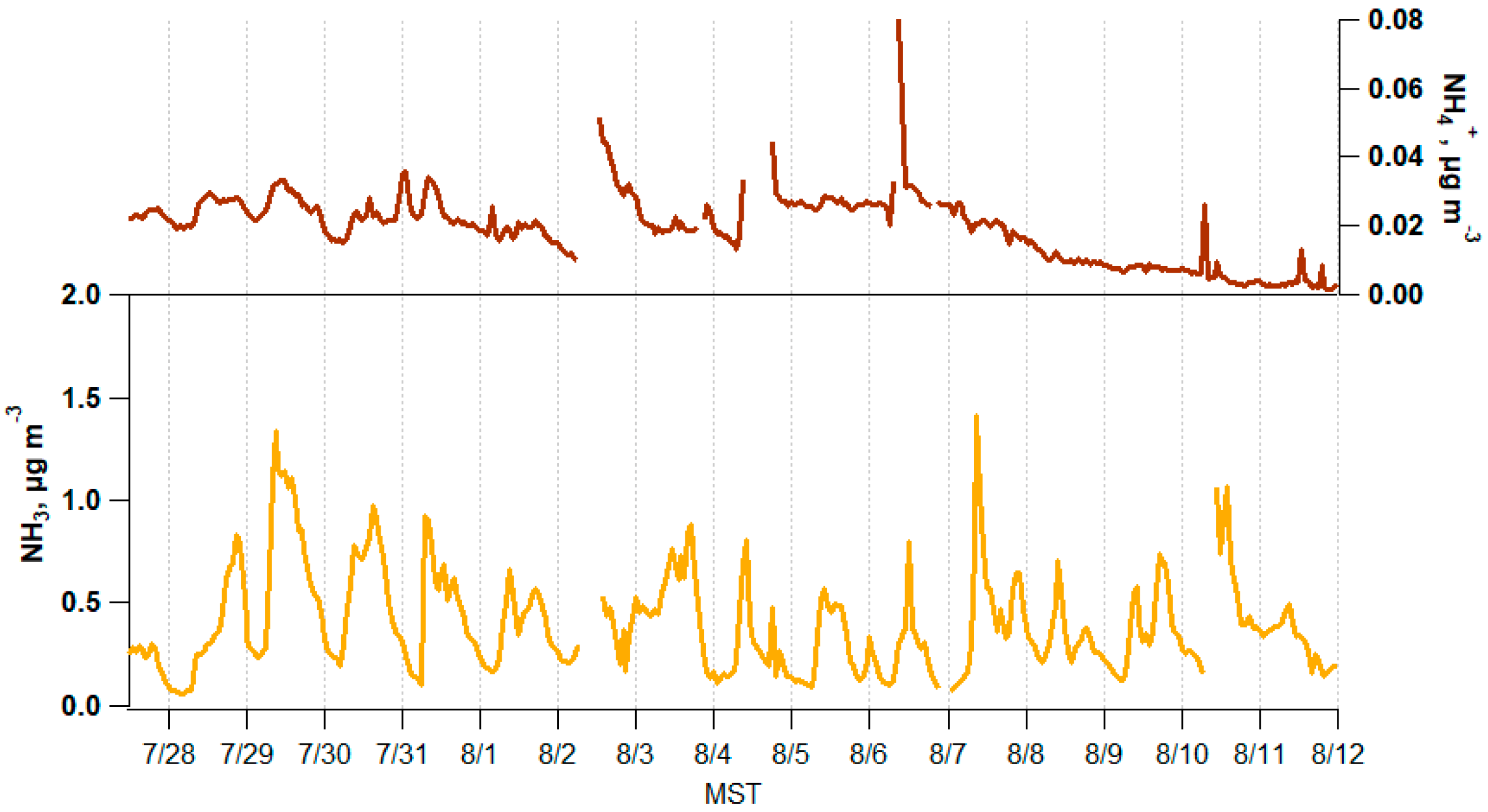
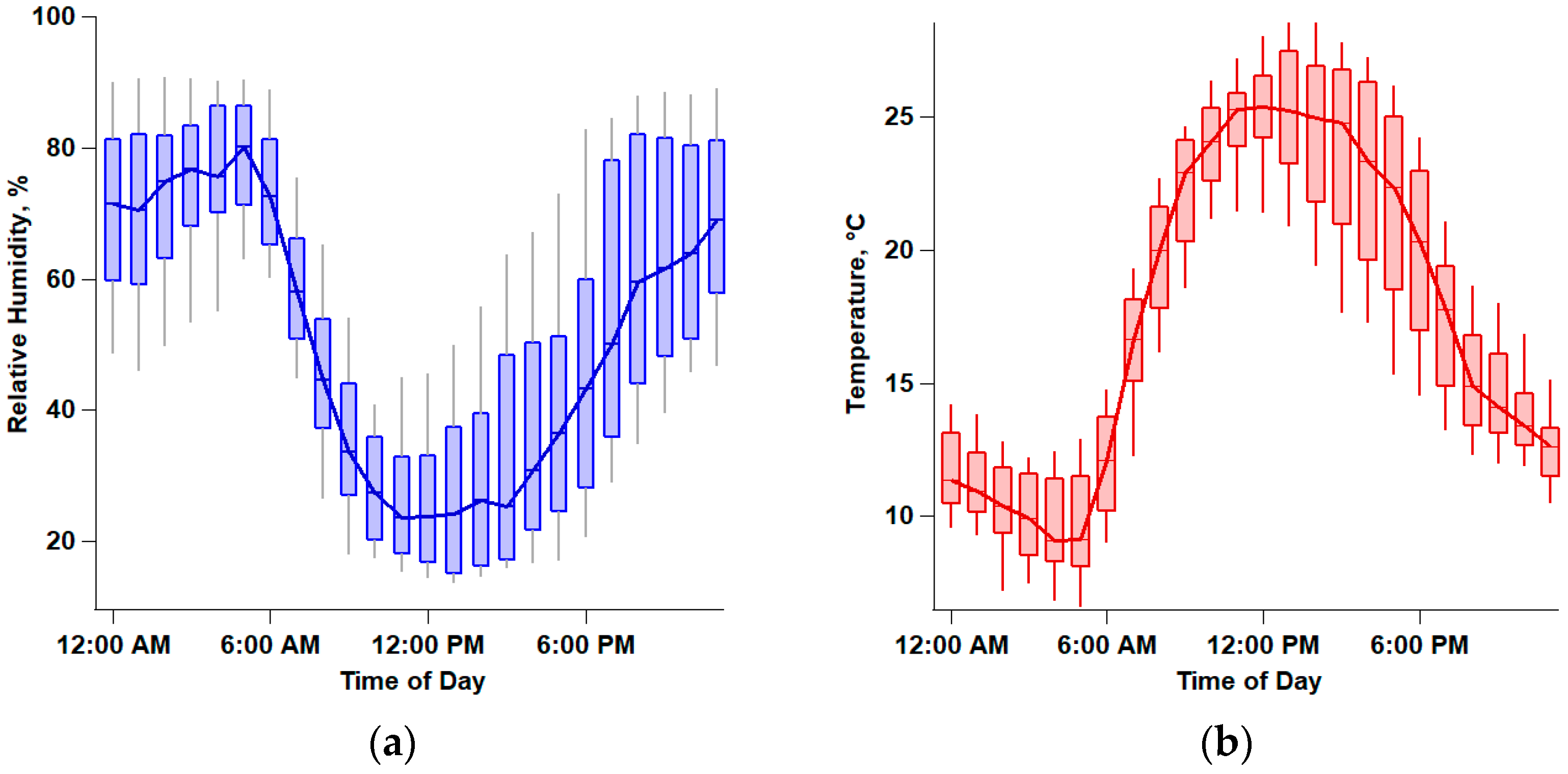
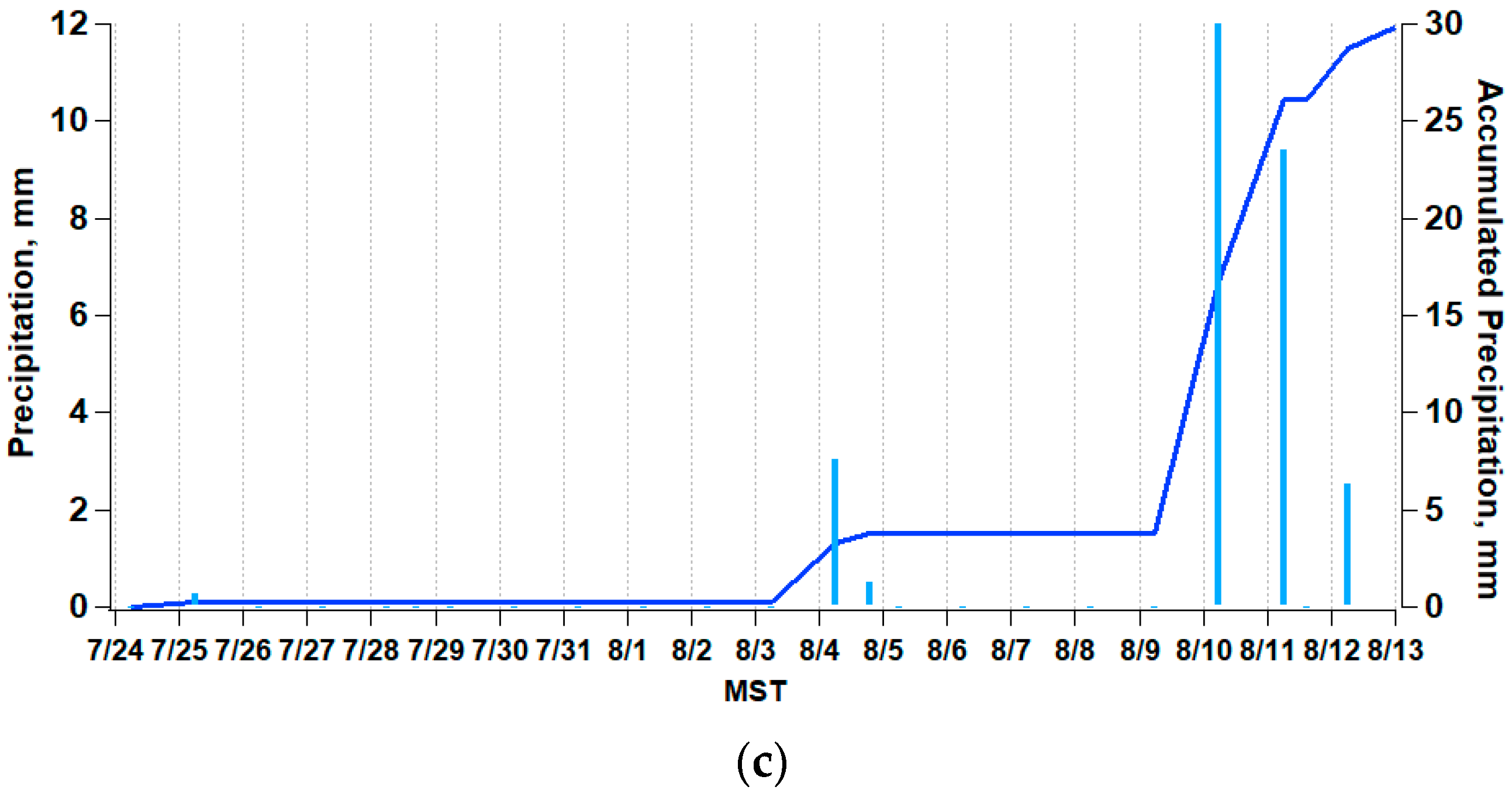
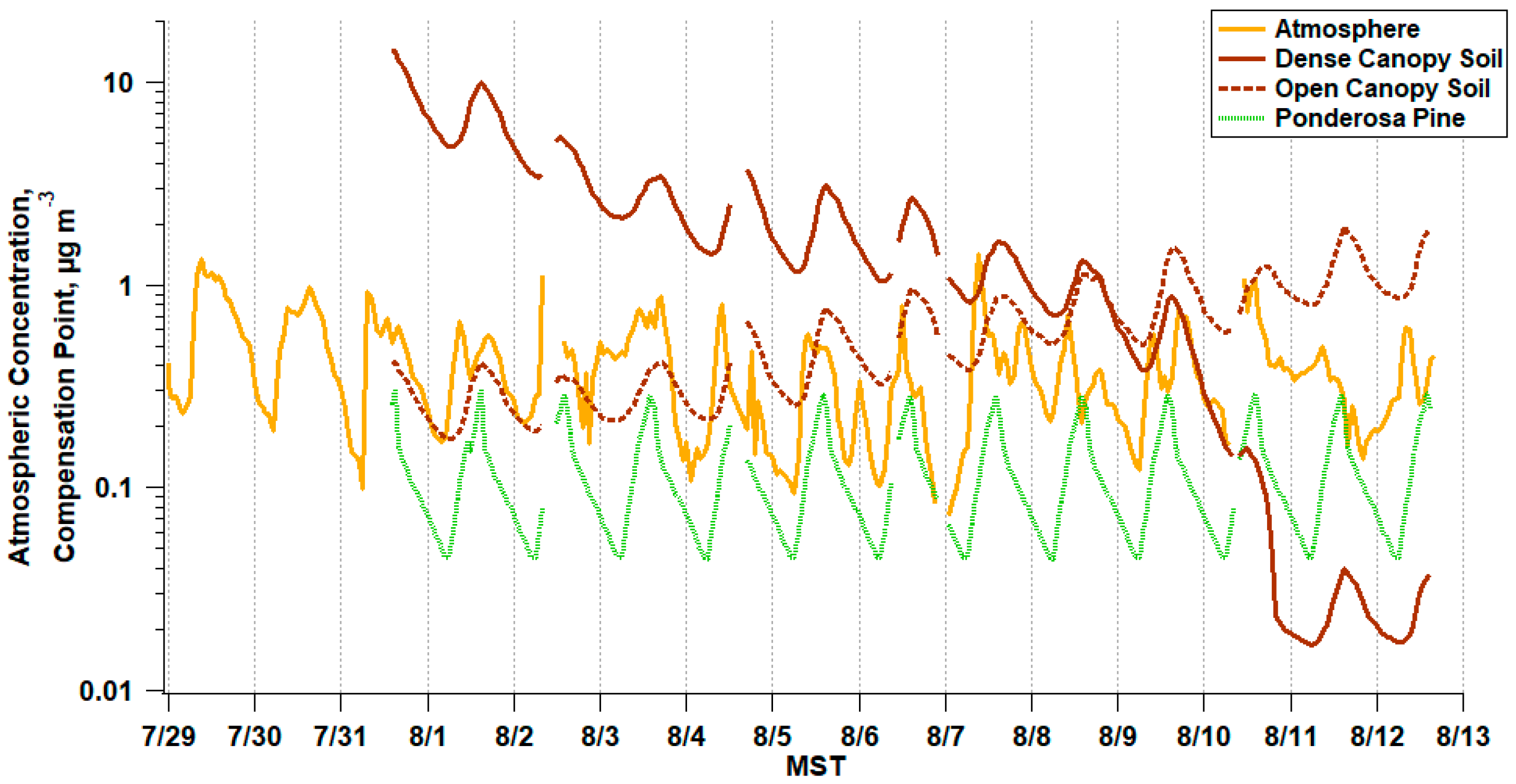
3.1. Atmospheric Trace Gas and PM2.5 Composition
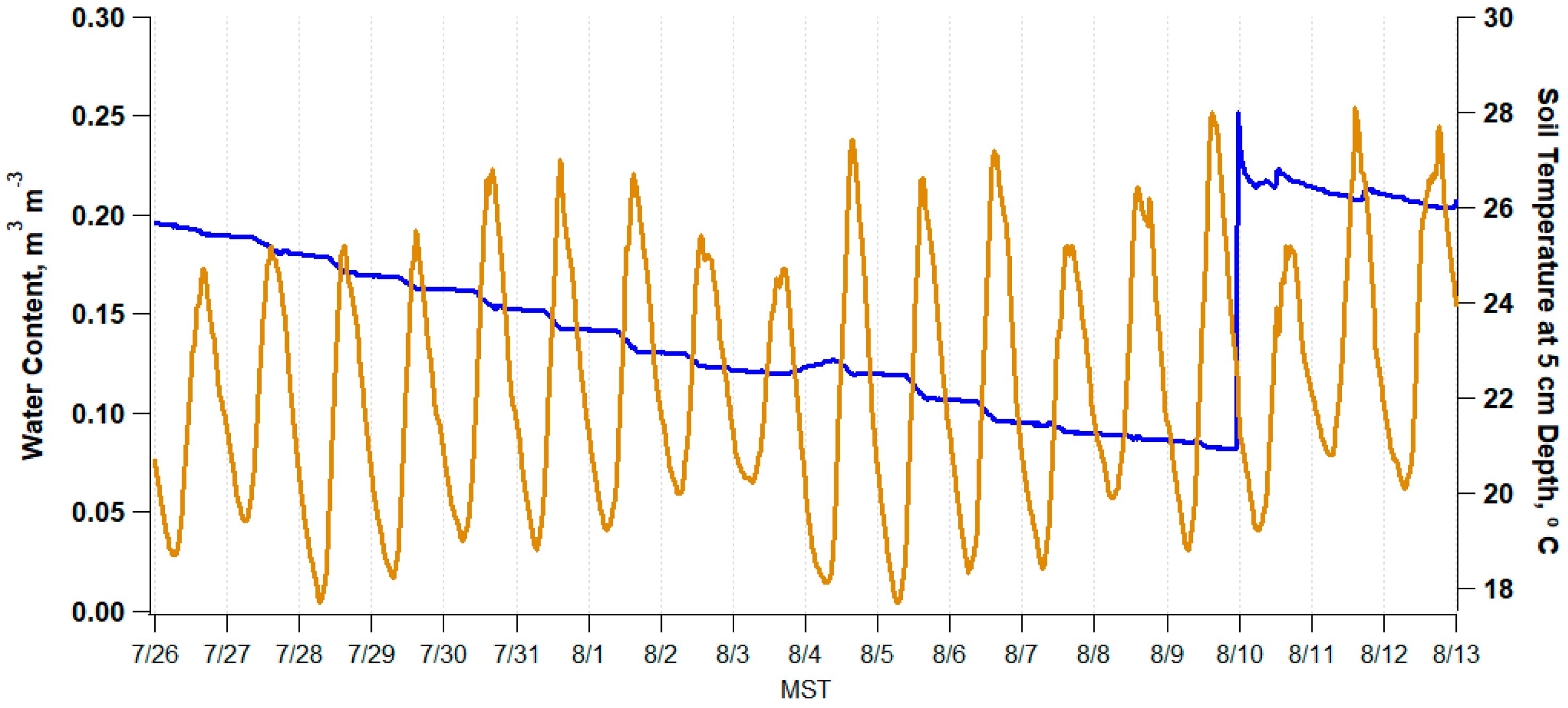
3.2. Physiochemical Soil Properties
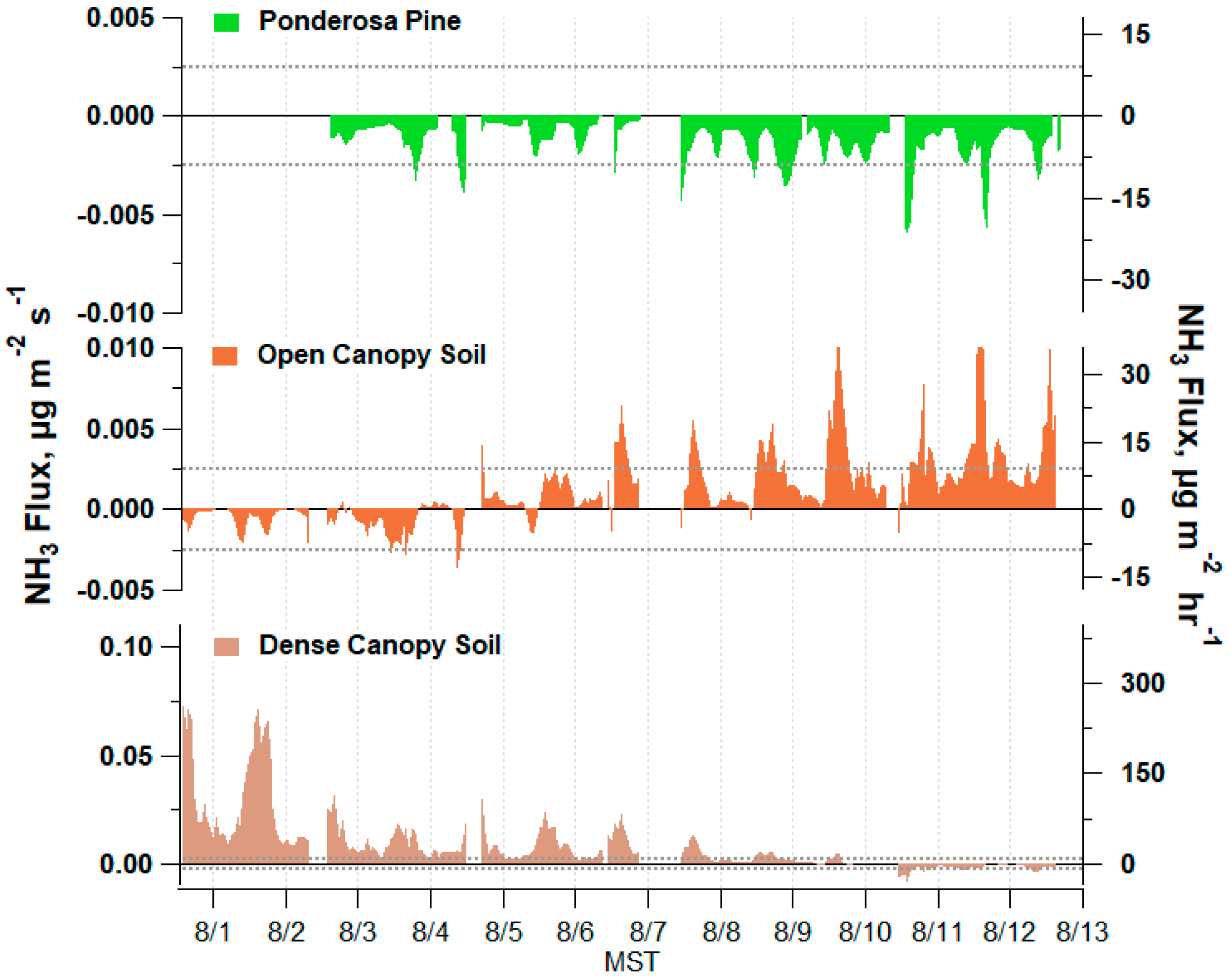
3.3. Measured Soil Emission Potentials
3.4. Measured Stomatal Emission Potentials
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges of Measuring NH3 in Ecosystem Compartments
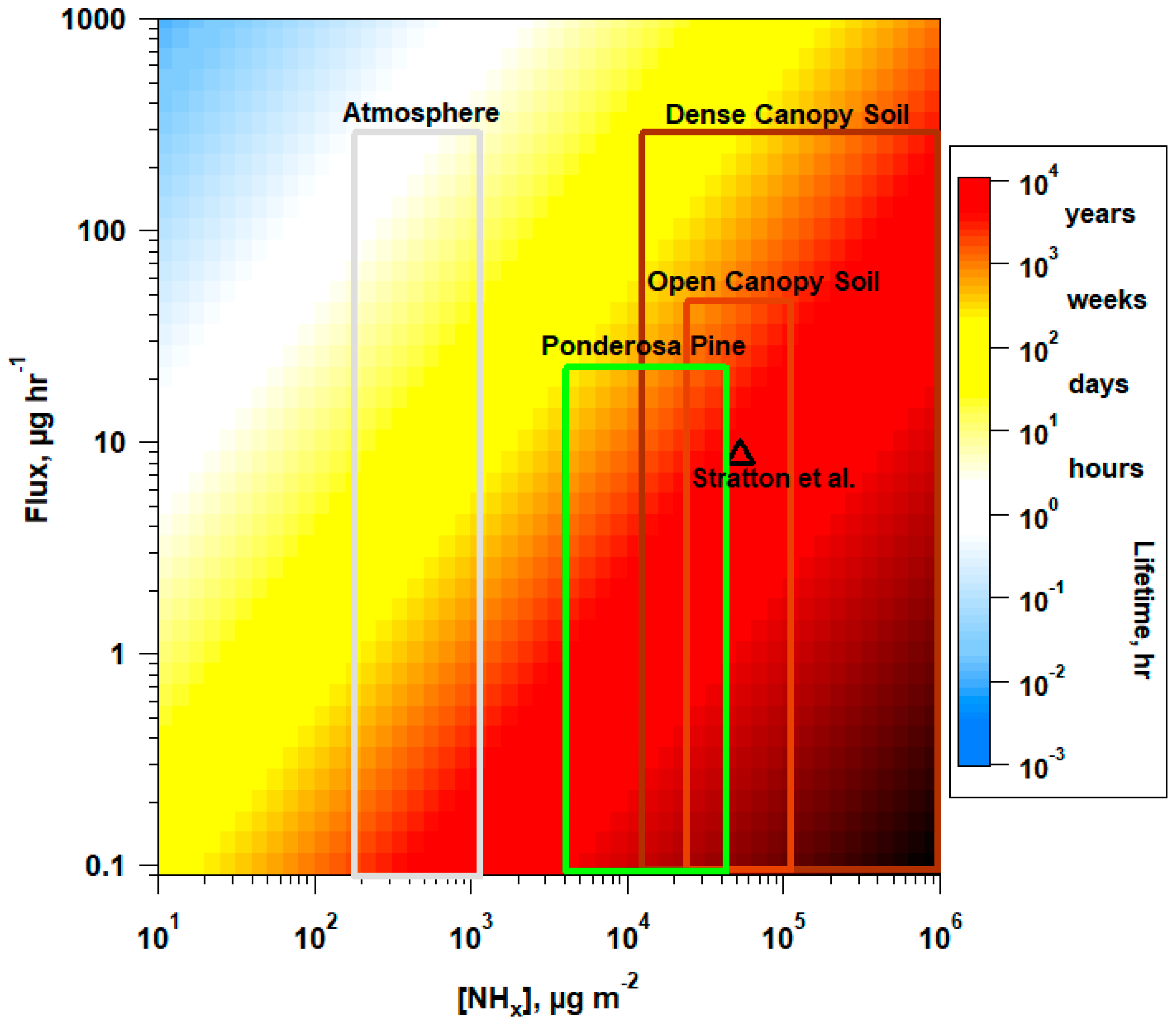
4.2. Implications of Γg Variability on NH3 Flux
4.3. Distribution of NH3 Pools in Forest Ecosystem
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Reis, S.; Riddick, S.N.; Dragosits, U.; Nemitz, E.; Theobald, M.R.; Tang, Y.S.; Braban, C.F.; Vieno, M.; Dore, A.J.; et al. Towards a climate-dependent paradigm of ammonia emission and deposition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Erisman, J.W.; Dentener, F.; Möller, D. Ammonia in the environment: From ancient times to the present. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilerman, S.J.; Peischl, J.; Neuman, J.A.; Ryerson, T.B.; Aikin, K.C.; Holloway, M.W.; Zondlo, M.A.; Golston, L.M.; Pan, D.; Floerchinger, C.; et al. Characterization of Ammonia, Methane, and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations in Northeastern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10885–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tao, L.; Miller, D.J.; Pan, D.; Golston, L.M.; Zondlo, M.A.; Griffin, R.J.; Wallace, H.W.; Leong, Y.J.; Yang, M.M.; et al. Vehicle Emissions as an Important Urban Ammonia Source in the United States and China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2472–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.A.; Stedman, D.H.; Burgard, D.A.; Atkinson, O. High-Mileage Light-Duty Fleet Vehicle Emissions: Their Potentially Overlooked Importance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5405–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.B.; Neuman, J.A.; Bahreini, R.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Holloway, J.S.; McKeen, S.A.; Parrish, D.D.; Ryerson, T.B.; Trainer, M. Ammonia sources in the California South Coast Air Basin and their impact on ammonium nitrate formation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Aneja, V.P.; Balasubramanian, R. Ammonia in the atmosphere: A review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8092–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; Wile-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780471720171. [Google Scholar]
- Malo, B.A.; Purvis, E.R. Soil absorption of atmospheric ammonia. Soil Sci. 1964, 97, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Talhelm, A.F.; Burton, A.J.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Campione, M.A. Forest Ecology and Management Chronic nitrogen deposition reduces the abundance of dominant forest understory and groundcover species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 293, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Asman, W.A.H.; Schjoerring, J.K. Dry deposition of reduced nitrogen. Tellus B 1994, 46, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, S.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Nielsen, K.H.; Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A. Stomatal compensation points for ammonia in oilseed rape plants under field conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, A.O.; Fehsenfeld, F.C. Natural Vegetation as a Source or Sink for Atmospheric Ammonia: A Case Study. Science 1992, 255, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, J.J.; Ham, J.; Borch, T. Ammonia Emissions from Subalpine Forest and Mountain Grassland Soils in Rocky Mountain National Park. J. Environ. Qual. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.S.; Rueth, H.M.; Wolfe, A.M.; Nydick, K.R.; Allstott, E.J.; Minear, J.T.; Moraska, B. Ecosystem responses to nitrogen deposition in the Colorado Front Range. Ecosystems 2000, 3, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.A. The effects of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado and southern Wyoming, USA—A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad, R.S.; Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A. Review and parameterisation of bi-directional ammonia exchange between vegetation and the atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10359–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad, R.S.; Loubet, B. Review and Integration of Biosphere-Atmosphere Modelling of Reactive Trace Gases and Volatile Aerosols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9789401772853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wright, L.P.; Asman, W.A.H. Bi-directional air-surface exchange of atmospheric ammonia: A review of measurements and a development of a big-leaf model for applications in regional-scale air-quality models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemitz, E.; Milford, C.; Sutton, M. A two-layer canopy compensation point model for describing bi-directional biosphere-atmosphere exchange of ammonia. Q. J. R. Meterorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A.; Wyers, G.P.; Otjes, R.P.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Gallagher, M.W.; Parrington, J.; Fowler, D.; Choularton, T.W. Surface/atmosphere exchange and chemical interaction of gases and aerosols over oilseed rape. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.M.; House, E.; Thomas, R.; Whitehead, J.; Phillips, G.J.; Famulari, D.; Fowler, D.; Gallagher, M.W.; Cape, J.N.; Sutton, M.A.; et al. Surface/atmosphere exchange and chemical interactions of reactive nitrogen compounds above a manured grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1488–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, G.R.; Murphy, J.G.; Gregoire, P.K.; Cheyne, C.A.L.; Tevlin, A.G.; Hems, R. Soil-atmosphere exchange of ammonia in a non-fertilized grassland: Measured emission potentials and inferred fluxes. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 5675–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Husted, S.; Paul Wyers, G. Resistance modelling of ammonia exchange over oilseed rape. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Sørensen, L.L.; Hertel, O.; Geels, C.; Skjøth, C.A.; Jensen, B.; Boegh, E. Ammonia emissions from deciduous forest after leaf fall. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4577–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, C.H.; Makar, P.A.; Shephard, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Akingunola, A.; Wentworth, G.; Murphy, J.; Kharol, S.K.; Cady-Pereira, K.E. Contributions of natural and anthropogenic sources to ambient ammonia in the Athabasca Oil Sands and north-western Canada. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2011–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Spence, P.; Kimbrough, S.; Robarge, W. Inferential model estimates of ammonia dry deposition in the vicinity of a swine production facility. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3407–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, G.D.; Firth, P.M.; Wetselaar, R.; Weir, B. On the Gaseous Exchange of Ammonia between Leaves and the Environment: Determination of the Ammonia Compensation Point. Plant Physiol. 1980, 66, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmead, O.T.; Freney, J.R.; Dunin, F.X. Gas exchange between plant canopies and the atmosphere: Case-studies for ammonia. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3394–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmead, O.T.; Freney, J.R.; Simpson, J.R. A closed ammonia cycle within a plant canopy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1976, 8, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Pilegaard, K.; Sutton, M.A.; Ambus, P.; Raivonen, M.; Duyzer, J.; Simpson, D.; Fagerli, H.; Fuzzi, S.; Schjoerring, J.K.; et al. Atmospheric composition change: Ecosystems-Atmosphere interactions. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5193–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Turnipseed, A.; Guenther, A.B.; Karl, T.G.; Day, D.A.; Gochis, D.; Huffman, J.A.; Prenni, A.J.; Levin, E.J.T.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; et al. Overview of the Manitou experimental forest observatory: Site description and selected science results from 2008 to 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6345–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R. Soil Conservation Service Soil Survey of Pike National Forest, Eastern Part, Colorado, Parts of Douglas, El Paso, Jefferson and Teller Counties; Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, M.Z.; VandenBoer, T.C.; Murphy, J.G. Characterization and optimization of an online system for the simultaneous measurement of atmospheric water-soluble constituents in the gas and particle phases. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1872–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Malhi, S.S. Comparison of Factors Affecting Soil Nitrate Nitrogen and Ammonium Nitrogen Extraction. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Pryor, S.C.; Boegh, E.; Hornsby, K.E.; Jensen, B.; Sørensen, L.L. Background concentrations and fluxes of atmospheric ammonia over a deciduous forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214–215, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, E.C.C.; Aita, C.; Rochette, P.; Chantigny, M.H.; Angers, D.A.; Bertrand, N.; Gasser, M.-O. Static Chamber Measurements of Ammonia Volatilization from Manured Soils: Impact of Deployment Duration and Manure Characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delon, C.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Serça, D.; Loubet, B.; Camara, N.; Gardrat, E.; Saneh, I.; Fensholt, R.; Tagesson, T.; Le Dantec, V.; et al. Soil and vegetation-atmosphere exchange of NO, NH3, and N2O from field measurements in a semi arid grazed ecosystem in Senegal. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 156, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.W.; Raven, J.A.; Loubet, B.; Fowler, D.; Sutton, M.A. Comparison of Gas Exchange and Bioassay Determinations of the Ammonia Compensation Point in Luzula sylvatica (Huds.) Gaud. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.; Pitcairn, C.; Whitfield, C. Bioindicator and Biomonitoring Methods for Assessing the Effects of Atmospheric Nitrogen on Statutory Nature Conservation Sites; Report No. 356; Joint Nature Conservation Committee: Peterborough, UK, 2004.
- Xiao, C.W.; Janssens, I.A.; Curiel Yuste, J.; Ceulemans, R. Variation of specific leaf area and upscaling to leaf area index in mature Scots pine. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2006, 20, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.M.; Hart, S.C. High rates of nitrification and nitrate turnover in undisturbed coniferous forests. Nature 1997, 385, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharko, N.K.; Schütte, U.M.E.; Berke, A.E.; Banina, L.; Peel, H.R.; Donaldson, M.A.; Hemmerich, C.; White, J.R.; Raff, J.D. Combined Flux Chamber and Genomics Approach Links Nitrous Acid Emissions to Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea in Urban and Agricultural Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13825–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, M.D.; Beese, F.O.; Brumme, R. Soil Nitrogen Cycle in High Nitrogen Deposition Forest: Changes under Nitrogen Saturation and Liming. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Menge, D.N.L.; Reed, S.C.; Cleveland, C.C. Biological nitrogen fixation: Rates, patterns and ecological controls in terrestrial ecosystems. Philisophical Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, T.H.; Zackrisson, O.; Nilsson, M.-C.; Sellstedt, A. Letters To Nature. Lett. Nat. 2002, 419, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Date | Dense Canopy Soil | Open Canopy Soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [NH4+] µg g−1 wet soil | pH | Γg | [NH4+] µg g−1 wet soil | pH | Γg | |
| July 31 | 44.8 ± 13.5 | 6.0 | 2122 ± 642 | 0.72 ± 0.36 | 6.2 | 61 ± 22 |
| Aug 2 | 51.5 ± 14.6 | 5.4 | 708 ± 200 | 1.44 ± 1.08 | 5.9 | 62 ± 46 |
| Aug 10 | 1.08 ± 1.44 | 5.4 | 5 ± 4 | 2.7 ± 0.54 | 6.2 | 220 ± 39 |
| Aug 17 1 | 0.72 | 5.4 | 8 | 3.6 | 6.4 | 466 |
| Sampling Time of Day | Tree Base (1 m) | Middle (3.6 m) | Near Top (7 m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [NH4+] µg g−1 needle | Γst | [NH4+] µg g−1 needle | Γst | [NH4+] µg g−1 needle | Γst | |
| Morning (5:00–7:00) | 12.9 ± 0.2 (2) | 37 | 11.3 ± 1.4 (2) | 54 | 8.3 ± 0.7 (2) | 30 |
| Midday (10:00–16:00) | 7.9 ± 1.3 (2) | 29 | 12.6 ± 5.6 (11) | 38 | 13.7 ± 7.6 (2) | 40 |
| Evening (17:00–19:00) | 12.8 1 | 37 | 12.1 1 | 35 | 10.8 1 | 33 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hrdina, A.; Moravek, A.; Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; Murphy, J. Summertime Soil-Atmosphere Ammonia Exchange in the Colorado Rocky Mountain Front Range Pine Forest. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3010015
Hrdina A, Moravek A, Schwartz-Narbonne H, Murphy J. Summertime Soil-Atmosphere Ammonia Exchange in the Colorado Rocky Mountain Front Range Pine Forest. Soil Systems. 2019; 3(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleHrdina, Amy, Alexander Moravek, Heather Schwartz-Narbonne, and Jennifer Murphy. 2019. "Summertime Soil-Atmosphere Ammonia Exchange in the Colorado Rocky Mountain Front Range Pine Forest" Soil Systems 3, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3010015
APA StyleHrdina, A., Moravek, A., Schwartz-Narbonne, H., & Murphy, J. (2019). Summertime Soil-Atmosphere Ammonia Exchange in the Colorado Rocky Mountain Front Range Pine Forest. Soil Systems, 3(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3010015






